service FORD GRANADA 1985 Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1985, Model line: GRANADA, Model: FORD GRANADA 1985Pages: 255, PDF Size: 14.98 MB
Page 151 of 255
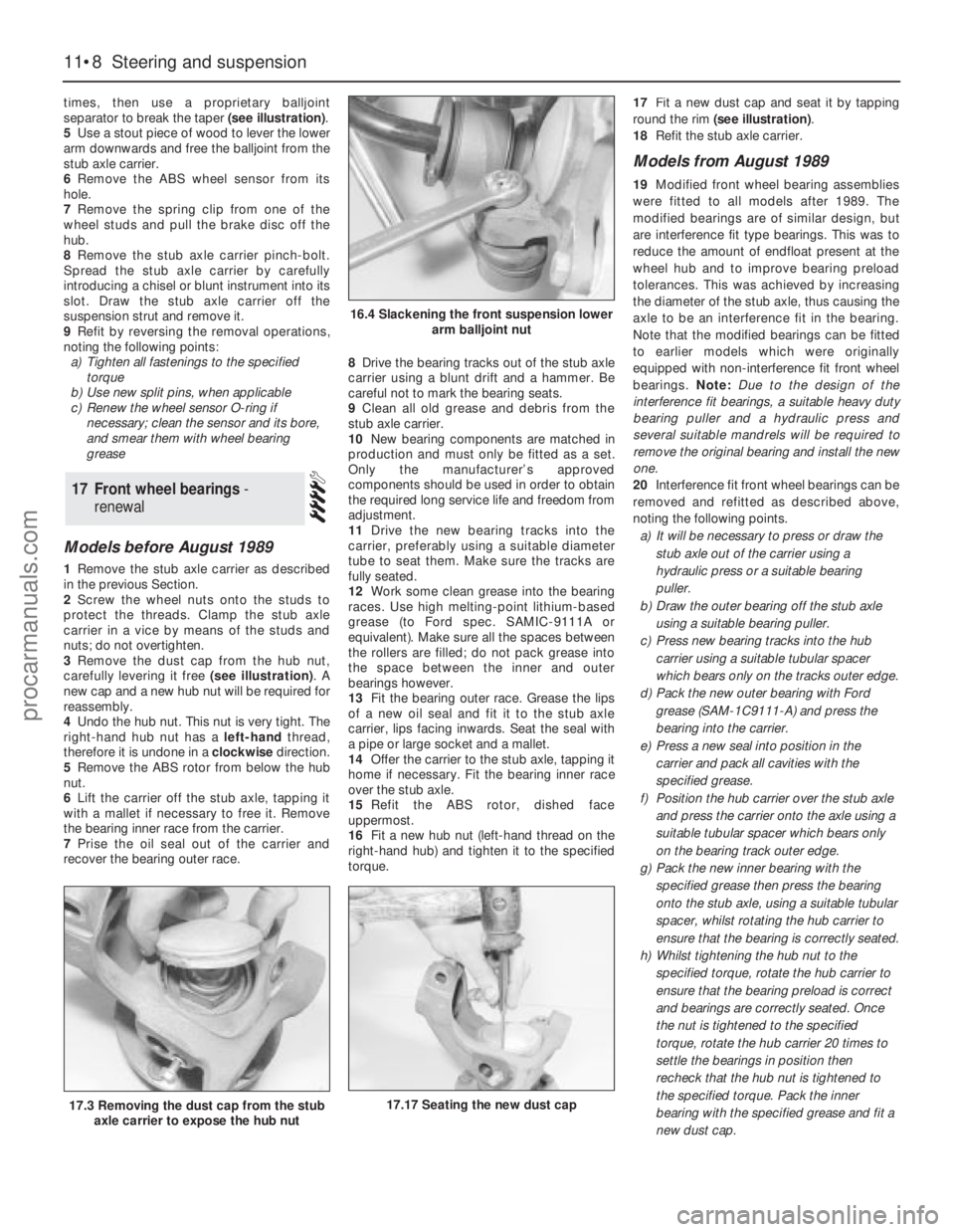
times, then use a proprietary balljoint
separator to break the taper (see illustration).
5Use a stout piece of wood to lever the lower
arm downwards and free the balljoint from the
stub axle carrier.
6Remove the ABS wheel sensor from its
hole.
7Remove the spring clip from one of the
wheel studs and pull the brake disc off the
hub.
8Remove the stub axle carrier pinch-bolt.
Spread the stub axle carrier by carefully
introducing a chisel or blunt instrument into its
slot. Draw the stub axle carrier off the
suspension strut and remove it.
9Refit by reversing the removal operations,
noting the following points:
a)Tighten all fastenings to the specified
torque
b)Use new split pins, when applicable
c)Renew the wheel sensor O-ring if
necessary; clean the sensor and its bore,
and smear them with wheel bearing
grease
Models before August 1989
1Remove the stub axle carrier as described
in the previous Section.
2Screw the wheel nuts onto the studs to
protect the threads. Clamp the stub axle
carrier in a vice by means of the studs and
nuts; do not overtighten.
3Remove the dust cap from the hub nut,
carefully levering it free (see illustration). A
new cap and a new hub nut will be required for
reassembly.
4Undo the hub nut. This nut is very tight. The
right-hand hub nut has a left-handthread,
therefore it is undone in a clockwisedirection.
5Remove the ABS rotor from below the hub
nut.
6Lift the carrier off the stub axle, tapping it
with a mallet if necessary to free it. Remove
the bearing inner race from the carrier.
7Prise the oil seal out of the carrier and
recover the bearing outer race.8Drive the bearing tracks out of the stub axle
carrier using a blunt drift and a hammer. Be
careful not to mark the bearing seats.
9Clean all old grease and debris from the
stub axle carrier.
10New bearing components are matched in
production and must only be fitted as a set.
Only the manufacturer’s approved
components should be used in order to obtain
the required long service life and freedom from
adjustment.
11Drive the new bearing tracks into the
carrier, preferably using a suitable diameter
tube to seat them. Make sure the tracks are
fully seated.
12Work some clean grease into the bearing
races. Use high melting-point lithium-based
grease (to Ford spec. SAMIC-9111A or
equivalent). Make sure all the spaces between
the rollers are filled; do not pack grease into
the space between the inner and outer
bearings however.
13Fit the bearing outer race. Grease the lips
of a new oil seal and fit it to the stub axle
carrier, lips facing inwards. Seat the seal with
a pipe or large socket and a mallet.
14Offer the carrier to the stub axle, tapping it
home if necessary. Fit the bearing inner race
over the stub axle.
15Refit the ABS rotor, dished face
uppermost.
16Fit a new hub nut (left-hand thread on the
right-hand hub) and tighten it to the specified
torque.17Fit a new dust cap and seat it by tapping
round the rim (see illustration).
18Refit the stub axle carrier.
Models from August 1989
19Modified front wheel bearing assemblies
were fitted to all models after 1989. The
modified bearings are of similar design, but
are interference fit type bearings. This was to
reduce the amount of endfloat present at the
wheel hub and to improve bearing preload
tolerances. This was achieved by increasing
the diameter of the stub axle, thus causing the
axle to be an interference fit in the bearing.
Note that the modified bearings can be fitted
to earlier models which were originally
equipped with non-interference fit front wheel
bearings. Note: Due to the design of the
interference fit bearings, a suitable heavy duty
bearing puller and a hydraulic press and
several suitable mandrels will be required to
remove the originalbearing and install the new
one.
20Interference fit front wheel bearings can be
removed and refitted as described above,
noting the following points.
a)It will be necessary to press or draw the
stub axle out of the carrier using a
hydraulic press or a suitable bearing
puller.
b)Draw the outer bearing off the stub axle
using a suitable bearing puller.
c)Press new bearing tracks into the hub
carrier using a suitable tubular spacer
which bears only on the tracks outer edge.
d)Pack the new outer bearing with Ford
grease (SAM-1C9111-A) and press the
bearing into the carrier.
e)Press a new seal into position in the
carrier and pack all cavities with the
specified grease.
f)Position the hub carrier over the stub axle
and press the carrier onto the axle using a
suitable tubular spacer which bears only
on the bearing track outer edge.
g)Pack the new inner bearing with the
specified grease then press the bearing
onto the stub axle, using a suitable tubular
spacer, whilst rotating the hub carrier to
ensure that the bearing is correctly seated.
h)Whilst tightening the hub nut to the
specified torque, rotate the hub carrier to
ensure that the bearing preload is correct
and bearings are correctly seated. Once
the nut is tightened to the specified
torque, rotate the hub carrier 20 times to
settle the bearings in position then
recheck that the hub nut is tightened to
the specified torque. Pack the inner
bearing with the specified grease and fit a
new dust cap.
17Front wheel bearings -
renewal
11•8Steering and suspension
16.4 Slackening the front suspension lower
arm balljoint nut
17.17 Seating the new dust cap17.3 Removing the dust cap from the stub
axle carrier to expose the hub nut
procarmanuals.com
Page 161 of 255

Where serious damage has occurred or
large areas need renewal due to neglect, it
means certainly that completely new sections
or panels will need welding in and this is best
left to professionals. If the damage is due to
impact, it will also be necessary to completely
check the alignment of the bodyshell
structure. Due to the principle of construction,
the strength and shape of the whole car can
be affected by damage to one part. In such
instances the services of a Ford agent with
specialist checking jigs are essential. If a body
is left misaligned, it is first of all dangerous as
the car will not handle properly, and secondly
uneven stresses will be imposed on the
steering, engine and transmission, causing
abnormal wear or complete failure. Tyre wear
may also be excessive.
1Open and prop the bonnet.
2Mark around the bonnet hinge bolts, using
soft pencil or a washable marker pen, to
provide a guide when refitting (see
illustration).
3Disconnect the windscreen washer hose atthe non-return valve or washer pump. Be
prepared for fluid spillage.
4Disconnect the under-bonnet light (when
fitted).
5Free the insulation from around the left-
hand hinge bolts. With the help of an assistant,
support the bonnet and remove the hinge
bolts. Unhook the bonnet from the pump and
remove it.
6Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Make sure that the gap between the bonnet
and the wings is equal on both sides when the
bonnet is shut; adjust if necessary at the hinge
bolts.
7Adjust the bump stops and bonnet lock
striker if necessary to obtain satisfactory
opening and closing of the bonnet (see
illustration).
Later models
8The operation for later models is essentially
as described above, noting thatit will be
necessary to unclip the insulation panel from
the underside of the bonnet to gain access to
the windscreen washer hose and washer
nozzle heater wiring plugs (see illustration).
9Disconnect the wiring plugs and hose and
free them from the retaining clips on the right-
hand side of the bonnet before removal.
10On refitting ensure that the hose and
wiring are correctly routed and retained by all
the necessary clips before refitting the
insulation panel (see illustrations).1Open the door and disconnect the wiring
multi-plug from the door pillar (see
illustration).
2Unbolt the door check strap.
3Slacken, but do not remove, the hinge
cotter pin nuts (see illustration).
4Open the door to approximately 60°from
the vehicle body and lift it off the hinges. If the
door is reluctant to move, make sure that it is
opened to the correct angle and that the cotter
pin nuts are adequately slackened.
5Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Adjust the door striker plate if necessary as
described in Section 12.
6If a new door is to be fitted, new hinges will
have to be welded to it after trial fitting.
Consult a Ford dealer for details.
Hatchback models
1Open the tailgate and remove the interior
trim panel, which is retained by eleven screws.
2Disconnect the wiring from the heated rear
window, aerial pre-amplifier and lock solenoid.
3Repeat paragraph 2 for the rear wiper motor
and the rear washer tube, and any other
electrical equipment.
8Tailgate - removal and refitting
7Door - removal and refitting
6Bonnet - removal and refitting
5Major body damage - repair
12•4Bodywork and fittings
6.2 Left-hand hinge bolts (arrowed) are
obscured by insulation
6.10 On refitting ensure the wiring and
hoses are correctly routed and secured by
all necessary retaining clips
7.1 Door wiring multi-plug7.3 One of the hinge cotter pins (arrowed)
6.7 Bonnet lock striker and safety catch6.8 On later models disconnect the washer
nozzle heater wiring plugs before removing
the bonnet
procarmanuals.com
Page 169 of 255
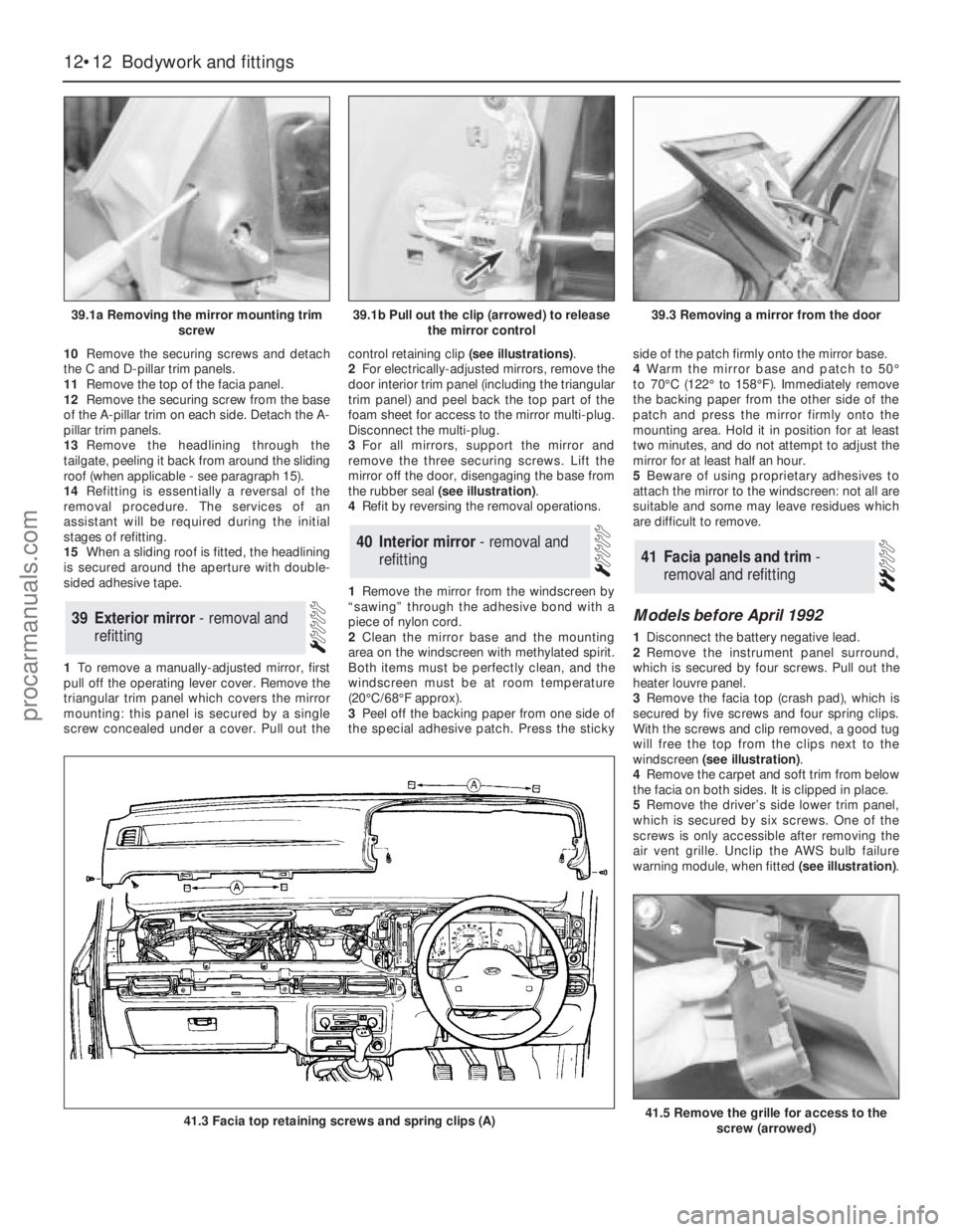
10Remove the securing screws and detach
the C and D-pillar trim panels.
11Remove the top of the facia panel.
12Remove the securing screw from the base
of the A-pillar trim on each side. Detach the A-
pillar trim panels.
13Remove the headlining through the
tailgate, peeling it back from around the sliding
roof (when applicable - see paragraph 15).
14Refitting is essentially a reversal of the
removal procedure. The services of an
assistant will be required during the initial
stages of refitting.
15When a sliding roof is fitted, the headlining
is secured around the aperture with double-
sided adhesive tape.
1To remove a manually-adjusted mirror, first
pull off the operating lever cover. Remove the
triangular trim panel which covers the mirror
mounting: this panel is secured by a single
screw concealed under a cover. Pull out thecontrol retaining clip (see illustrations).
2For electrically-adjusted mirrors, remove the
door interior trim panel (including the triangular
trim panel) and peel back the top part of the
foam sheet for access to the mirror multi-plug.
Disconnect the multi-plug.
3For all mirrors, support the mirror and
remove the three securing screws. Lift the
mirror off the door, disengaging the base from
the rubber seal (see illustration).
4Refit by reversing the removal operations.
1Remove the mirror from the windscreen by
“sawing” through the adhesive bond with a
piece of nylon cord.
2Clean the mirror base and the mounting
area on the windscreen with methylated spirit.
Both items must be perfectly clean, and the
windscreen must be at room temperature
(20°C/68°F approx).
3Peel off the backing paper from one side of
the special adhesive patch. Press the stickyside of the patch firmly onto the mirror base.
4Warm the mirror base and patch to 50°
to 70°C (122°to 158°F). Immediately remove
the backing paper from the other side of the
patch and press the mirror firmly onto the
mounting area. Hold it in position for at least
two minutes, and do not attempt to adjust the
mirror for at least half an hour.
5Beware of using proprietary adhesives to
attach the mirror to the windscreen: not all are
suitable and some may leave residues which
are difficult to remove.
Models before April 1992
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the instrument panel surround,
which is secured by four screws. Pull out the
heater louvre panel.
3Remove the facia top (crash pad), which is
secured by five screws and four spring clips.
With the screws and clip removed, a good tug
will free the top from the clips next to the
windscreen (see illustration).
4Remove the carpet and soft trim from below
the facia on both sides. It is clipped in place.
5Remove the driver’s side lower trim panel,
which is secured by six screws. One of the
screws is only accessible after removing the
air vent grille. Unclip the AWS bulb failure
warning module, when fitted (see illustration).
41Facia panels and trim -
removal and refitting40Interior mirror - removal and
refitting
39Exterior mirror - removal and
refitting
12•12Bodywork and fittings
39.1a Removing the mirror mounting trim
screw
41.3 Facia top retaining screws and spring clips (A)41.5 Remove the grille for access to the
screw (arrowed)
39.1b Pull out the clip (arrowed) to release
the mirror control39.3 Removing a mirror from the door
procarmanuals.com
Page 197 of 255

Speed control module
Models before April 1992
9Refer to Section 27. The speed control
module shares the same mountings as the
AWS module; the AWS module is larger.
Models from April 1992
10The speed control module fitted to these
models is situated behind the glovebox on the
left-hand side of the facia. To gain access to
the module remove the left-hand facia
undercover panel. The speed control module
is vertically mounted just to the right of the
engine management module. Push the module
upwards to release the retaining clips then
lower it out from under the facia and
disconnect the wiring connector (see
illustration).
11Refitting is a reverse of the removal
procedure ensuring that the module is
securely retained by the retaining clips.
Vacuum pump
12The vacuum pump is located behind the
left-hand headlight on carburettor models, and
behind the right-hand headlight on fue-
injection models. Start by removing the
appropriate headlight unit.
13Disconnect the multi-plug and the vacuum
hose from the pump. The multi-plug is
released by squeezing and pulling it at the
same time.
14Prise out the three mountings and remove
the pump.
15When refitting, pull the pump mountings
into position with pliers. 16Reconnect the vacuum hose and the
multi-plug, then refit the headlight unit.
Vacuum servo
17Disconnect the servo-to-throttle linkage
cable at one end.
18Disconnect the vacuum hose from the
servo.
19Undo the servo retaining nut and remove
the servo from its bracket.
20Refit by reversing the removal operations.
On all but 2.0 litre carburettor models, adjust
the cable so that it is slightly slack when the
throttle linkage is in the idle position (pedal
released).
21On 2.0 litre carburettor models, the
stepper motor plunger must be withdrawn
before the cable is adjusted. Proceed as
follows.
22Observe the stepper motor plunger. Have
an assistant switch on the ignition for a few
seconds, then switch it off again. When the
ignition is switched off, the stepper motor
plunger will retract fully (“vent manifold”
position). Disconnect the battery negative lead
while the stepper motor plunger is retracted.
23Adjust the servo cable so that it is slightly
slack, then reconnect the battery negative
lead.
Printed circuit board
24The printed circuit board is located in the
steering wheel. It can be removed after
detaching the horn contact plate and
disconnecting the switch spade terminals as
described at the beginning of this Section.1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Pull off the rubber sealing strip from the top
of the plenum chamber (see illustration).
3Pull the two wiring harness clips from the
front of the plenum chamber (see illustration).
4Remove the two screws and two clips
which secure the plenum chamber cover (see
illustration). Lift out the cover.
5Disconnect the multi-plug from the blower
motor resistor. Also disconnect the motor
earth cable (see illustration).
6Remove the two nuts which secure the
motor assembly. Lift out the motor, casing and
resistor together.
7The casing halves and the resistor can be
separated from the motor after prising open
the clamp which holds the casing halves
together.
8Refit by reversing the removal operations.
1Two DIN standard extraction tools will be
needed to remove the radio/cassette unit.
These tools are available from vehicle audio
equipment specialists.
Radio (only)
2Pull off the control knobs, remove the
spindle nuts and washers and remove the
radio face plate.
3Push the two securing lugs inwards, at the
same time pulling the radio from its location.
The services of an assistant may be required.
4Withdraw the radio and disconnect the
aerial cable and the other wiring plugs from it.
5If a new radio is to be fitted, transfer the
support brackets and locating plate from the
old unit to the new one.
6Refit by reconnecting the wiring to the radio,
then sliding it into its aperture. Press it in until
the securing lugs click into position.
7Refit the face plate, spindle nuts and washers
and control knobs. The top of the face plate is
marked on the side which faces the radio.
30Radio or radio/cassette
player (original equipment) -
removal and refitting
29Heater blower motor -
removal and refitting
13•20Body electrical system
28.10 Removing the speed control module
29.4 One of the plenum chamber cover
clips29.5 Blower motor showing wiring
connections
29.2 Pulling off the rubber sealing strip29.3 Pulling out a wiring harness clip
procarmanuals.com
Page 200 of 255

The components of the alarm system are a
control module, tripping switches, activating
switches, an alarm horn and a signal buzzer.
The control module is located behind the
facia. It determines whether the alarm is set or
not, monitors the tripping switches and the
ignition circuit, and limits the duration of the
alarm to 30 seconds. This last item is a legal
requirement. The control module also
operates the signal buzzer to tell the driver
that the alarm is set, and controls the activator
delay.
The tripping switches on the doors and
tailgate are the same as those used for “open
door” warnings in the AWS. The bonnet switch
is peculiar to the alarm system.
The activating switches are fitted to the
front door lock barrels, where they are
activated by a lug on the end of the barrel.
They only make contact momentarily as the
lock is operated.
The alarm horn is mounted next to the
battery. Both the horn and its leads are
claimed to be inaccessible without opening
the bonnet. The signal buzzer is also mounted
under the bonnet.
No service, repair or component renewal
procedures have been published for the alarmsystem components on earlier models. Any
problems arising which cannot be dealt with
by component substitution should therefore
be referred to a Ford dealer.
Ultrasonic sensor
1Disconnect the battery negative terminal.
2Prise out the retaining screw trim cap from
the centre of the sensor then slacken and
remove the retaining screws and lower the
sensor away from the headlining,
disconnecting the wiring plug as it becomes
accessible.
3Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure.
Anti-theft alarm module (models
from April 1992)
4On these models the alarm module is located
behind the righthand lower facia panel.
5To remove the module, remove the right-
hand facia undercover and lower facia panel.
6The anti-theft alarm module is the left-hand
of the two modules situated directly above the
control pedals. Release the module retaining
clips then disconnect the wiring connector and
remove the module from the vehicle (see
illustration).7Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure.
Alarm signal buzzer (models from
April 1992)
8The alarm signal buzzer is situated under
the bonnet where it is mounted on the upper
right-hand side of the engine compartment
bulkhead.
9To remove the buzzer, open the bonnet then
unclip the buzzer from the bulkhead and
disconnect the wiring connector (see
illustration).
10Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure.
Alarm system horn (models from
April 1992)
11On these models the alarm system horn is
mounted in the front right-hand corner of the
engine compartment (see illustration).
12To remove the horn, undo the two horn
mounting bracket retaining screws then
disconnect the wiring connectors and remove
the horn from the engine compartment.
13Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure.
Body electrical system 13•23
13
36.6 Removing the anti-theft alarm control
module36.9 Removing the alarm system warning
buzzer36.11 Alarm horn location
procarmanuals.com
Page 238 of 255

REF•3
The following list contains only those tools and
instruments freely available to the public, and not
those special tools produced by the vehicle
manufacturer specifically for its dealer network.
You will find occasional references to these
manufacturer’s special tools in the text of this
manual. Generally, an alternative method of doing
the job without the vehicle manufacturer’s special
tool is given. However, sometimes there is no
alternative to using them. Where this is the case
and the relevant tool cannot be bought or
borrowed, you will have to entrust the work to a
franchised garage.
MValve spring compressor (see illustration)
MValve grinding tool
MPiston ring compressor (see illustration)
MPiston ring removal/installation tool (see
illustration)
MCylinder bore hone (see illustration)
MBalljoint separator
MCoil spring compressors (where applicable)
MTwo/three-legged hub and bearing puller
(see illustration)
MImpact screwdriver
MMicrometer and/or vernier calipers (see
illustrations)
MDial gauge (see illustration)
MStroboscopic timing light (see illustration)
MDwell angle meter/tachometer
MUniversal electrical multi-meter
MCylinder compression gauge (see
illustration)
MHand-operated vacuum pump and gauge
(see illustration)
MClutch plate alignment set (see
illustration)
MBrake shoe steady spring cup removal tool
(see illustration)
MBush and bearing removal/installation set
(see illustration)
MStud extractors (see illustration)
MTap and die set (see illustration)
MLifting tackle
MTrolley jackBuying tools
For practically all tools, a tool factor is the
best source, since he will have a very
comprehensive range compared with the
average garage or accessory shop. Having
said that, accessory shops often offer
excellent quality tools at discount prices, so it
pays to shop around.
Remember, you don’t have to buy the most
expensive items on the shelf, but it is always
advisable to steer clear of the very cheap
tools. There are plenty of good tools around at
reasonable prices, but always aim to purchase
items which meet the relevant national safety
standards. If in doubt, ask the proprietor or
manager of the shop for advice before making
a purchase.
Care and maintenance of tools
Having purchased a reasonable tool kit, it is
necessary to keep the tools in a clean and
serviceable condition. After use, always wipe
off any dirt, grease and metal particles using a
clean, dry cloth, before putting the tools away.
Never leave them lying around after they have
been used. A simple tool rack on the garage or
workshop wall, for items such as screwdrivers
and pliers, is a good idea. Store all normal
spanners and sockets in a metal box. Any
measuring instruments, gauges, meters, etc,
must be carefully stored where they cannot be
damaged or become rusty.
Take a little care when tools are used.
Hammer heads inevitably become marked,
and screwdrivers lose the keen edge on their
blades from time to time. A little timely
attention with emery cloth or a file will soon
restore items like this to a good serviceable
finish.
Working facilities
Not to be forgotten when discussing tools is
the workshop itself. If anything more than
routine maintenance is to be carried out, some
form of suitable working area becomes
essential.
It is appreciated that many an owner-
mechanic is forced by circumstances to
remove an engine or similar item without the
benefit of a garage or workshop. Having done
this, any repairs should always be done under
the cover of a roof.
Wherever possible, any dismantling should
be done on a clean, flat workbench or table at
a suitable working height.
Any workbench needs a vice; one with a jaw
opening of 100 mm is suitable for most jobs.
As mentioned previously, some clean dry
storage space is also required for tools, as well
as for any lubricants, cleaning fluids, touch-up
paints and so on, which become necessary.
Another item which may be required, and
which has a much more general usage, is an
electric drill with a chuck capacity of at least 8
mm. This, together with a good range of twist
drills, is virtually essential for fitting
accessories.
Lastly, always keep a supply of old
newspapers and clean, lint-free rags available,
and try to keep any working area as clean as
possible.
Bush and bearing removal/installation setStud extractor setTap and die set
Tools and Working Facilities
procarmanuals.com
Page 240 of 255

The vehicle owner who does his or her own maintenance according
to the recommended service schedules should not have to use this
section of the manual very often. Modern component reliability is such
that, provided those items subject to wear or deterioration are
inspected or renewed at the specified intervals, sudden failure is
comparatively rare. Faults do not usually just happen as a result of
sudden failure, but develop over a period of time. Major mechanical
failures in particular are usually preceded by characteristic symptoms
over hundreds or even thousands of miles. Those components which
do occasionally fail without warning are often small and easily carried
in the vehicle.With any fault-finding, the first step is to decide where to begin
investigations. Sometimes this is obvious, but on other occasions, a
little detective work will be necessary. The owner who makes half a
dozen haphazard adjustments or replacements may be successful in
curing a fault (or its symptoms), but will be none the wiser if the fault
recurs, and ultimately may have spent more time and money than was
necessary. A calm and logical approach will be found to be more
satisfactory in the long run. Always take into account any warning
signs or abnormalities that may have been noticed in the period
preceding the fault - power loss, high or low gauge readings, unusual
smells, etc - and remember that failure of components such as fuses or
REF•5Fault Finding
Engine1
m mEngine fails to rotate when attempting to start
m mStarter motor turns engine slowly
m mEngine rotates, but will not start
m mEngine difficult to start when cold
m mEngine difficult to start when hot
m mStarter motor noisy or excessively-rough in engagement
m mEngine starts, but stops immediately
m mEngine idles erratically
m mEngine misfires at idle speed
m mEngine misfires throughout the driving speed range
m mEngine hesitates on acceleration
m mEngine stalls
m mEngine lacks power
m mEngine backfires
m mOil pressure warning light illuminated with engine running
m mEngine runs-on after switching off
m mEngine noises
Cooling system2
m
mOverheating
m mOvercooling
m mExternal coolant leakage
m mInternal coolant leakage
m mCorrosion
Fuel and exhaust systems3
m
mExcessive fuel consumption
m mFuel leakage and/or fuel odour
m mExcessive noise or fumes from exhaust system
Clutch4
m
mPedal travels to floor - no pressure or very little resistance
m mClutch fails to disengage (unable to select gears)
m mClutch slips (engine speed increases, with no increase in vehicle
speed)
m mJudder as clutch is engaged
m mNoise when depressing or releasing clutch pedal
Manual gearbox5
m
mNoisy in neutral with engine running
m mNoisy in one particular gear
m mDifficulty engaging gears
m mJumps out of gear
m mVibration
m mLubricant leaks
Automatic transmission6
m
mFluid leakage
m mTransmission fluid brown, or has burned smellm mGeneral gear selection problems
m mTransmission will not downshift (kickdown) with accelerator fully
depressed
m mEngine will not start in any gear, or starts in gears other than Park
or Neutral
m mTransmission slips, shifts roughly, is noisy, or has no drive in
forward or reverse gears
Propeller shaft7
m
mClicking or knocking noise on turns (at slow speed on full-lock)
m mVibration when accelerating or decelerating
Final drive and driveshafts8
m
mExcessive final drive noise
m mOil leakage from final drive
m mGrating, knocking or vibration from driveshafts
Braking system9
m
mVehicle pulls to one side under braking
m mNoise (grinding or high-pitched squeal) when brakes applied
m mExcessive brake pedal travel
m mBrake pedal feels spongy when depressed
m mExcessive brake pedal effort required to stop vehicle
m mJudder felt through brake pedal or steering wheel when braking
m mPedal pulsates when braking hard
m mBrakes binding
m mRear wheels locking under normal braking
Suspension and steering systems10
m
mVehicle pulls to one side
m mWheel wobble and vibration
m mExcessive pitching and/or rolling around corners, or during braking
m mWandering or general instability
m mExcessively-stiff steering
m mExcessive play in steering
m mLack of power assistance
m mTyre wear excessive
Electrical system11
m
mLights inoperative
m mIgnition/no-charge warning light remains illuminated with engine
running
m mIgnition/no-charge warning light fails to come on
m mBattery will not hold a charge for more than a few days
m mInstrument readings inaccurate or erratic
m mHorn inoperative, or unsatisfactory in operation
m mWindscreen/tailgate wipers inoperative, or unsatisfactory in
operation
m mWindscreen/tailgate washers inoperative, or unsatisfactory in
operation
m mElectric windows inoperative, or unsatisfactory in operation
m mCentral locking system inoperative, or unsatisfactory in operation
Introduction
procarmanuals.com
Page 243 of 255

REF•8
Pedal travels to floor - no pressure or very little
resistance
m m
Badly stretched or broken cable (Chapter 6).m
mStripped pawl on pedal (Chapter 6).m
mBroken clutch release bearing or arm (Chapter 6).m
mBroken diaphragm spring in clutch pressure plate (Chapter 6).
Clutch fails to disengage (unable to select gears)
m m
Cable free play excessive (Chapter 6).m
mClutch driven plate sticking on gearbox input shaft splines (Chapter 6).m
mClutch driven plate sticking to flywheel or pressure plate (Chapter 6).m
mFaulty pressure plate assembly (Chapter 6).m
mClutch release mechanism worn or incorrectly assembled (Chapter 6).
Clutch slips (engine speed increases, with no
increase in vehicle speed)
m m
Clutch driven plate linings excessively worn (Chapter 6).m
mClutch driven plate linings contaminated with oil or grease (Chapter 6).m
mFaulty pressure plate or weak diaphragm spring (Chapter 6).
Judder as clutch is engaged
m m
Clutch driven plate linings contaminated with oil or grease (Chapter 6).m
mClutch driven plate linings excessively worn (Chapter 6).m
mFaulty or distorted pressure plate or diaphragm spring (Chapter 6).m
mWorn or loose engine or gearbox mountings (Chapter 2).m
mClutch driven plate hub or gearbox input shaft splines worn
(Chapter 6).
Noise when depressing or releasing clutch pedal
m m
Worn clutch release bearing (Chapter 6).m
mWorn or dry clutch pedal pivot (Chapter 6).m
mFaulty pressure plate assembly (Chapter 6).m
mPressure plate diaphragm spring broken (Chapter 6).m
mBroken clutch driven plate cushioning springs (Chapter 6).
Excessive fuel consumption
m
mAir filter element dirty or clogged (Chapter 1).
m mFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
m mIgnition timing incorrect or ignition system fault (Chapters 1 and 5).
m mBrakes binding (Chapter 10).
m mTyres under-inflated (Chapter 1).
Fuel leakage and/or fuel odour
m
mDamaged fuel tank, pipes or connections (Chapters 1 and 4).
Excessive noise or fumes from exhaust system
m
mLeaking exhaust system or manifold joints (Chapters 1 and 4).
m mLeaking, corroded or damaged silencers or pipe (Chapters 1 and 4).
m mBroken mountings causing body or suspension contact (Chapter 4).
Fault Finding
4Clutch
5Manual gearbox
Noisy in neutral with engine running
m m
Input shaft bearings worn (noise apparent with clutch pedal
released, but not when depressed) (Chapter 7A).*
m mClutch release bearing worn (noise apparent with clutch pedal
depressed, possibly less when released) (Chapter 6).
Noisy in one particular gear
m m
Worn, damaged or chipped gear teeth (Chapter 7A).*
Difficulty engaging gears
m m
Clutch fault (Chapter 6).m
mWorn or damaged gear linkage (Chapter 7A).m
mWorn synchroniser units (Chapter 7A).*
Jumps out of gear
m m
Worn or damaged gear linkage (Chapter 7A).m
mWorn synchroniser units (Chapter 7A).*m
mWorn selector forks (Chapter 7A).*
Vibration
m m
Lack of oil (Chapter 1).m
mWorn bearings (Chapter 7A).*
Lubricant leaks
m m
Leaking oil seal (Chapter 7A).m
mLeaking housing joint (Chapter 7A).*
*Although the corrective action necessary to remedy the symptoms
described is beyond the scope of the home mechanic, the above
information should be helpful in isolating the cause of the condition, so
that the owner can communicate clearly with a professional mechanic.
6Automatic transmission
Note:Due to the complexity of the automatic transmission, it is difficult
for the home mechanic to properly diagnose and service this unit. For
problems other than the following, the vehicle should be taken to a
dealer service department or automatic transmission specialist.
Fluid leakage
m m
Automatic transmission fluid is usually deep red in colour. Fluid
leaks should not be confused with engine oil, which can easily be
blown onto the transmission by air flow.
m mTo determine the source of a leak, first remove all built-up dirt and
grime from the transmission housing and surrounding areas, using a
degreasing agent or by steam-cleaning. Drive the vehicle at low speed,
so that air flow will not blow the leak far from its source. Raise and
support the vehicle, and determine where the leak is coming from. The
following are common areas of leakage:
a)Fluid pan ( transmission “sump”).
b)Dipstick tube (Chapter 1).
c)Transmission-to-fluid cooler fluid pipes/unions (Chapter 7B).
3Fuel and exhaust systems
procarmanuals.com
Page 250 of 255

REF•15Glossary of Technical Terms
RotorIn a distributor, the rotating device
inside the cap that connects the centre
electrode and the outer terminals as it turns,
distributing the high voltage from the coil
secondary winding to the proper spark plug.
Also, that part of an alternator which rotates
inside the stator. Also, the rotating assembly
of a turbocharger, including the compressor
wheel, shaft and turbine wheel.
RunoutThe amount of wobble (in-and-out
movement) of a gear or wheel as it’s rotated.
The amount a shaft rotates “out-of-true.” The
out-of-round condition of a rotating part.
SSealantA liquid or paste used to prevent
leakage at a joint. Sometimes used in
conjunction with a gasket.
Sealed beam lampAn older headlight design
which integrates the reflector, lens and
filaments into a hermetically-sealed one-piece
unit. When a filament burns out or the lens
cracks, the entire unit is simply replaced.
Serpentine drivebeltA single, long, wide
accessory drivebelt that’s used on some
newer vehicles to drive all the accessories,
instead of a series of smaller, shorter belts.
Serpentine drivebelts are usually tensioned by
an automatic tensioner.
ShimThin spacer, commonly used to adjust
the clearance or relative positions between
two parts. For example, shims inserted into or
under bucket tappets control valve
clearances. Clearance is adjusted by
changing the thickness of the shim.
Slide hammerA special puller that screws
into or hooks onto a component such as a
shaft or bearing; a heavy sliding handle on the
shaft bottoms against the end of the shaft to
knock the component free.SprocketA tooth or projection on the
periphery of a wheel, shaped to engage with a
chain or drivebelt. Commonly used to refer to
the sprocket wheel itself.
Starter inhibitor switchOn vehicles with an
automatic transmission, a switch that
prevents starting if the vehicle is not in Neutral
or Park.
StrutSee MacPherson strut.
TTappetA cylindrical component which
transmits motion from the cam to the valve
stem, either directly or via a pushrod and
rocker arm. Also called a cam follower.
ThermostatA heat-controlled valve that
regulates the flow of coolant between the
cylinder block and the radiator, so maintaining
optimum engine operating temperature. A
thermostat is also used in some air cleaners in
which the temperature is regulated.
Thrust bearingThe bearing in the clutch
assembly that is moved in to the release
levers by clutch pedal action to disengage the
clutch. Also referred to as a release bearing.
Timing beltA toothed belt which drives the
camshaft. Serious engine damage may result
if it breaks in service.
Timing chainA chain which drives the
camshaft.
Toe-inThe amount the front wheels are
closer together at the front than at the rear. On
rear wheel drive vehicles, a slight amount of
toe-in is usually specified to keep the front
wheels running parallel on the road by
offsetting other forces that tend to spread the
wheels apart.
Toe-outThe amount the front wheels are
closer together at the rear than at the front. On
front wheel drive vehicles, a slight amount of
toe-out is usually specified.
ToolsFor full information on choosing and
using tools, refer to the Haynes Automotive
Tools Manual.
TracerA stripe of a second colour applied to
a wire insulator to distinguish that wire from
another one with the same colour insulator.
Tune-upA process of accurate and careful
adjustments and parts replacement to obtain
the best possible engine performance.TurbochargerA centrifugal device, driven by
exhaust gases, that pressurises the intake air.
Normally used to increase the power output
from a given engine displacement, but can
also be used primarily to reduce exhaust
emissions (as on VW’s “Umwelt” Diesel
engine).
UUniversal joint or U-jointA double-pivoted
connection for transmitting power from a
driving to a driven shaft through an angle. A
U-joint consists of two Y-shaped yokes and a
cross-shaped member called the spider.
VValveA device through which the flow of
liquid, gas, vacuum, or loose material in bulk
may be started, stopped, or regulated by a
movable part that opens, shuts, or partially
obstructs one or more ports or passageways.
A valve is also the movable part of such a
device.
Valve clearanceThe clearance between the
valve tip (the end of the valve stem) and the
rocker arm or tappet. The valve clearance is
measured when the valve is closed.
Vernier caliperA precision measuring
instrument that measures inside and outside
dimensions. Not quite as accurate as a
micrometer, but more convenient.
ViscosityThe thickness of a liquid or its
resistance to flow.
VoltA unit for expressing electrical
“pressure” in a circuit. One volt that will
produce a current of one ampere through a
resistance of one ohm.
WWeldingVarious processes used to join metal
items by heating the areas to be joined to a
molten state and fusing them together. For
more information refer to the Haynes
Automotive Welding Manual.
Wiring diagramA drawing portraying the
components and wires in a vehicle’s electrical
system, using standardised symbols. For
more information refer to the Haynes
Automotive Electrical and Electronic Systems
Manual.
Serpentine drivebelt
procarmanuals.com