steering wheel FORD GRANADA 1985 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1985, Model line: GRANADA, Model: FORD GRANADA 1985Pages: 255, PDF Size: 14.98 MB
Page 2 of 255

Chapter 1
Routine maintenance and servicing
Air cleaner filter element renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
Air conditioner condenser check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Air conditioner refrigerant charge check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Automatic choke check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
Automatic transmission brake band adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
Automatic transmission fluid level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Automatic transmission selector lubrication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Auxiliary drivebelt check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Battery electrolyte level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Battery terminal check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Brake fluid renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
Brake pipe and hose check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Brake system seal and hose renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Camshaft drivebelt renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
Crankcase ventilation vent valve renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Driveshaft check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Electrical system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Engine coolant renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
Engine inlet manifold security check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Engine oil and filter renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Engine valve clearance check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Exhaust system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Final drive oil level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Fluid leak check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10Fluid level checks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Front and rear brake pad check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Fuel filter renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Hinge and lock check and lubrication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Hot starting check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
Idle mixture check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Idle speed check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Idle speed linkage clean . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Ignition system component check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
Intensive maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
Manual gearbox oil level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Oil filler cap check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Power steering fluid level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Road test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
Roadwheel security check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Seat belt check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Spark plug renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .See end of Chapter
Steering and suspension security check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Tyre checks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Underbody inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Wiper blade check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
The maintenance intervals in this manual are provided with the
assumption that you will be carrying out the work yourself. These are
the minimum maintenance intervals recommended by the manufacturer
for vehicles driven daily. If you wish to keep your vehicle in peak
condition at all times, you may wish to perform some of these
procedures more often. We encourage frequent maintenance, because
it enhances the efficiency, performance and resale value of your vehicle.
If the vehicle is driven in dusty areas, used to tow a trailer, or drivenfrequently at slow speeds (idling in traffic) or on short journeys, more
frequent maintenance intervals are recommended.
When the vehicle is new, it should be serviced by a factory-
authorised dealer service department, in order to preserve the factory
warranty.
1•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanicDifficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty Contents
1
Every 250 miles (400 km) or weekly
m mCheck the engine oil level (Section 3).
m mCheck the engine coolant level (Section 3).
m mCheck the brake fluid level (Section 3).
m mCheck the screen washer fluid level (Section 3).
m mVisually examine the tyres for tread depth, and wear or
damage (Section 4).
m mCheck and if necessary adjust the tyre pressures
(Section 4).
m mCheck and if necessary top-up the battery electrolyte
level - where applicable (Section 6).
m mCheck the operation of the horn, all lights, and the
wipers and washers (Sections 5 and 7).
Every 6000 miles (10 000 km) or
6 months – whichever comes sooner
m mRenew engine oil and filter (Section 8)
m mCheck brake pads for wear (front and rear) (Section 9)
m mCheck tightness of wheel nuts (Section 13)
m mCheck idle speed (1.8 litre only) (Section 15)
m mCheck idle mixture (not fuel-injection models) - at first
6000 miles only (Section 16)
m mClean oil filler cap (Section 14)
m mInspect engine bay and underside of vehicle for fluid
leaks or other signs of damage (Section 10)
m mCheck function and condition of seat belts (Section 11)
m mCheck operation of brake fluid level warning indicator
(Section 9)
m mCheck condition and security of exhaust system
(Section 12).
Ford Granada maintenance schedule
procarmanuals.com
Page 4 of 255

1•3
1
Maintenance Schedule
Engine oil
SOHC:
With filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3.75 litres (6.6 pints)
DOHC:
With filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4.5 litres (7.9 pints)
Without filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4.0 litres (7.0 pints)
V6:
With filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4.25 litres (7.5 pints)
Cooling system
OHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8.0 litres (14.1 pints)
V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8.5 litres (15.0 pints)
Fuel tank
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70 litres (15.4 gallons)
Manual gearbox
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.25 litres (2.2 pints)
Automatic transmission
All models (from dry) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8.5 litres (15.0 pints)
Final drive
7 inch crownwheel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.9 litres (1.6 pints)
7.5 inch crownwheel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.3 litres (2.3 pints)
Power steering
OHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.65 litres (1.1 pints)
V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.75 litres (1.3 pints)
Capacities
1 Battery
2 Engine oil dipstick
3 Inlet manifold
4 Throttle/kickdown cable
bracket
5 Suspension turrets
6 Ignition coil
7 Air cleaner cover
8 Fuel pressure regulator
9 Vane airflow meter
10 Headlight covers
11 Tune-up label
12 Idle speed control valve
13 Oil filler cap
14 Spark plug leads
15 VIN plate
16 Radiator hoses
17 Horn
18 Windscreen washer
pump19 Windscreen washer
reservoir
20 Alternator
21 Coolant expansion tank
cap
22 Engine mounting
23 Heater hose
24 Automatic transmission
fluid dipstick
25 Brake fluid reservoir
cap
26 Brake hydraulic unit
accumulator
27 Brake hydraulic unit
valve block
28 Main fuse/relay box
29 Wiper motor (behind
cover)
30 Heater blower cover
1 Windscreen wiper motor
2 Battery
3 Suspension strut top
mounting
4 Brake fluid reservoir
5 Ignition distributor
6 Coolant expansion tank
7 Washer fluid reservoir
8 Automatic transmission
fluid dipstick
9 Oil filler cap
10 Engine oil level dipstick
11 Air cleaner element
housing
12 Idle speed control valve
13 Ignition module
14 Manifold Absolute
Pressure (MAP) sensor15 Throttle position sensor
16 Power steering fluid
reservoir
17 Anti-theft alarm horn
18 Speed control system
diaphragm
19 Speed control system
vacuum pump
20 Vehicle identification
(VIN) plate
21 Fuel pressure regulator
22 Air charge temperature
sensor
23 Manifold absolute
pressure (MAP) sensor
vapour trap
24 Fuse/relay boxUnder-bonnet view of a 2.0 litre SOHC Granada with
fuel-injection
Under-bonnet view of a 2.0 litre DOHC Granada with
fuel-injection
procarmanuals.com
Page 9 of 255

6Over-inflation will cause rapid wear of the
centre part of the tyre tread, coupled with
reduced adhesion, harsher ride, and the
danger of shock damage occurring in the tyre
casing.
7Regularly check the tyres for damage in the
form of cuts or bulges, especially in the
sidewalls. Remove any nails or stones
embedded in the tread before they penetrate the
tyre to cause deflation. If removal of a nail does
reveal that the tyre has been punctured, refit the
nail so that its point of penetration is marked.
Then immediately change the wheel, and have
the tyre repaired by a tyre dealer. Do not drive on
a tyre in such a condition. If in any doubt as to
the possible consequences of any damage
found, consult your local tyre dealer for advice.
8Periodically remove the wheels, and clean
any dirt or mud from the inside and outside
surfaces. Examine the wheel rims for signs of
rusting, corrosion or other damage. Light alloy
wheels are easily damaged by “kerbing” whilst
parking, and similarly steel wheels may
become dented or buckled. Renewal of the
wheel is very often the only course of remedial
action possible.
9The balance of each wheel and tyre
assembly should be maintained to avoid
excessive wear, not only to the tyres but also
to the steering and suspension components.
Wheel imbalance is normally signified by
vibration through the vehicle’s bodyshell,
although in many cases it is particularly
noticeable through the steering wheel.
Conversely, it should be noted that wear ordamage in suspension or steering
components may cause excessive tyre wear.
Out-of-round or out-of-true tyres, damaged
wheels, and wheel bearing wear also fall into
this category. Balancing will not usually cure
vibration caused by such wear.
10Wheel balancing may be carried out with
the wheel either on or off the vehicle. If
balanced on the vehicle, ensure that the
wheel-to-hub relationship is marked in some
way prior to subsequent wheel removal, so
that it may be refitted in its original position.
11General tyre wear is influenced to a large
degree by driving style - harsh braking and
acceleration, or fast cornering, will all produce
more rapid tyre wear. Interchanging of tyres
may result in more even wear. However, if this
is completely effective, the added expense is
incurred of replacing all four tyres at once,
which may prove financially-restrictive for
many owners.
12Front tyres may wear unevenly as a result
of wheel misalignment. The front wheels
should always be correctly aligned according
to the settings specified by the vehicle
manufacturer.
13Legal restrictions apply to many aspects
of tyre fitting and usage, and in the UK this
information is contained in the Motor Vehicle
Construction and Use Regulations. It is
suggested that a copy of these regulations is
obtained from your local police, if in doubt as
to current legal requirements with regard to
tyre type and condition, minimum tread depth,
etc.Check the operation of all the electrical
equipment, ie. lights, direction indicators,
horn, washers, etc. Refer to the appropriate
Sections of Chapter 13 for details if any of the
circuits are found to be inoperative.
Visually check all accessible wiring
connectors, harnesses and retaining clips for
security, and for signs of chafing or damage.
Rectify any faults found.
Caution: Before carrying out any work on the
vehicle battery, read through the precautions
given in “Safety first!” at the beginning of this
manual.
1The battery fitted as original equipment is
“maintenance-free”, and requires no
maintenance apart from having the case kept
clean, and the terminals clean and tight.
2If a “traditional” type battery is fitted as a
replacement, remove the old cell covers and
check that the plate separators in each cell are
covered by approximately 6 mm (0.25 in) of
electrolyte. If the battery case is translucent,
the cell covers need not be removed to check
the level. Top-up if necessary with distilled or
de-ionized water; do not overfill, and mop up
any spillage at once(see illustration).
6Battery electrolyte level check
5Electrical system check
1•8Weekly checks
Tyre Tread Wear Patterns
Shoulder Wear
Underinflation
(wear on both sides)
Check and adjust pressures
Incorrect wheel camber
(wear on one side)
Repair or renew suspension
parts
Hard cornering
Reduce speed!
Centre Wear
Overinflation
Check and adjust pressures
If you sometimes have to inflate
your car’s tyres to the higher
pressures specified for maximum
load or sustained high speed,
don’t forget to reduce the
pressures to normal afterwards.
Toe Wear
Incorrect toe setting
Adjust front wheel alignment
Note: The feathered edge of
the tread which characterises
toe wear is best checked by
feel.
Uneven Wear
Incorrect camber or castor
Repair or renew suspension
parts
Malfunctioning suspension
Repair or renew suspension
parts
Unbalanced wheel
Balance tyres
Out-of-round brake disc/drum
Machine or renew
procarmanuals.com
Page 16 of 255

1Remove the radiator grille being careful not
to damage the condenser fins.
2Check the refrigerant charge as follows. The
engine should be cold and the ambient
temperature should be between 18°and 25°C
(64°and 77°F).
3Start the engine and allow it to idle. Observe
the refrigerant sight glass(see illustration)
and have an assistant switch on the air
conditioning to fan speed III. A few bubbles
should be seen in the sight glass as the
system starts up, but all bubbles should
disappear within 10 seconds. Persistent
bubbles, or no bubbles at all, mean that the
refrigerant charge is low. Switch off the
system immediately if the charge is low and do
not use it again until it has been recharged.
4Inspect the refrigerant pipes, hoses and
unions for security and good condition. Refit
the radiator grille.
5The air conditioning system will lose a
proportion of its charge through normal
seepage typically up to 100 g (4 oz) per year -
so it is as well to regard periodic recharging as
a maintenance operation.
1Check the final drive oil level as follows.
2Position the vehicle over a pit, or raise it at
front and rear on ramps or axle stands (see
“Jacking”). The vehicle must be level.
3Wipe clean around the final drive filler/level
plug (see illustration).Unscrew the plug with
a hexagon key. Using a piece of bent wire as
a dipstick, check that the oil is no more than
10 mm (0.4 in) below the plug hole.
4If topping-up is necessary, use clean gear
oil of the specified type. Do not overfill.
Frequent need for topping-up can only be due
to leaks, which should be rectified.
5When the level is correct, refit the filler/level
plug and tighten it.
6There is no requirement for periodic oil
changing, and no drain plug is provided. Lubricate the transmission selector and
kickdown linkages with engine oil or aerosol
lubricant.
1Examine all steering and suspension
components for wear and damage. Pay
particular attention to dust covers and gaiters,
which if renewed promptly when damaged can
save further damage to the component
protected.
2At the same intervals, check the front
suspension lower arm balljoints for wear by
levering up the arms(see illustration).
Balljoint free movement must not exceed
0.5 mm (0.02 in). The track rod end balljoints
can be checked in a similar manner, or by
observing them whilst an assistant rocks the
steering wheel back and forth. If the lower arm
balljoint is worn, the complete lower arm must
be renewed.
3Check the shock absorbers by bouncing the
vehicle up and down at each corner in turn.
When released, it should come to rest within
one complete oscillation. Continued
movement, or squeaking and groaning noises
from the shock absorber suggests that
renewal is required.Position the vehicle over a pit, or raise it at
front and rear on ramps or axle stands.
Examine the driveshaft joint rubber gaiters.
Flex the gaiters by hand and inspect the folds
and clips. Damaged or leaking gaiters must be
renewed without delay to avoid damage
occurring to the joint itself
Check the tightness of the final drive
mounting bolts and the driveshaft flange
screws.
1Except on vehicles with a wax-based
underbody protective coating, have the whole
of the underframe of the vehicle steam-
cleaned, engine compartment included, so
that a thorough inspection can be carried out
to see what minor repairs and renovations are
necessary.
2Steam-cleaning is available at many
garages, and is necessary for the removal of
the accumulation of oily grime, which
sometimes is allowed to become thick in
certain areas. If steam-cleaning facilities are
not available, there are some excellent grease
solvents available which can be brush-applied;
the dirt can then be simply hosed off.
3After cleaning, position the vehicle over a
pit, or raise it at front and rear on ramps or axle
stands.
4Using a strong light, work around the
underside of the vehicle, inspecting it for
corrosion or damage. If either is found, refer to
Chapter 12 for details of repair.
Periodically inspect the rigid brake pipes for
rust and other damage, and the flexible hoses
for cracks, splits or “ballooning”. Have an
assistant depress the brake pedal (ignition on)
and inspect the hose and pipe unions for
leaks. Renew any defective item without delay.
On 2.0 litre engines, good electrical contact
between the carburettor stepper motor
plunger and the adjusting screw is essential to
maintain a regular idle speed.
Clean the plunger and adjusting screw
contact faces with abrasive paper followed by
switch cleaning fluid. Switch cleaning fluid is
available from electronic component shops.
33Idle speed linkage clean
32Brake pipe and hose check
31Underbody inspection
30Driveshaft check
29Steering and suspension
security check
28Automatic transmission
selector linkage lubrication
27Final drive oil level check
26Air conditioner refrigerant
charge check
1•15
1
Every 12 000 miles or 12 months
27.3 Final drive oil filler/level plug (arrowed)
29.2 Checking a front suspension lower
arm balljoint
26.3 Refrigerant sight glass (arrowed)
procarmanuals.com
Page 17 of 255

Instruments and electrical
equipment
1Check the operation of all instruments and
electrical equipment.
2Make sure that all instruments read
correctly, and switch on all electrical
equipment in turn to check that it functions
properly.
Steering and suspension
3Check for any abnormalities in the steering,
suspension, handling or road “feel”.
4Drive the vehicle, and check that there are
no unusual vibrations or noises.
5Check that the steering feels positive, with
no excessive “sloppiness”, or roughness, and
check for any suspension noises when
cornering, or when driving over bumps.
Drivetrain
6Check the performance of the engine,
clutch, transmission and driveshafts.
7Listen for any unusual noises from the
engine, clutch and transmission.
8Make sure that the engine runs smoothly
when idling, and that there is no hesitation
when accelerating.
9Where applicable, check that the clutch
action is smooth and progressive, that the
drive is taken up smoothly, and that the pedal
travel is not excessive. Also listen for any
noises when the clutch pedal is depressed.
10Check that all gears can be engaged
smoothly, without noise, and that the gear
lever action is not abnormally vague or
“notchy”.
Check the operation and
performance of the braking system
11Make sure that the vehicle does not pull to
one side when braking, and that the wheels do
not lock prematurely when braking hard.
12Check that there is no vibration through
the steering when braking.
13Check that the handbrake operates
correctly, without excessive movement of the
lever, and that it holds the vehicle stationary
on a slope.
14Test the operation of the brake servo unit
as follows. With the engine off, depress the
footbrake four or five times to exhaust the
vacuum. Start the engine, holding the brake
pedal depressed. As the engine starts, there
should be a noticeable “give” in the brake
pedal as vacuum builds up. Allow the engine
to run for at least two minutes, and then
switch it off. If the brake pedal is depressed
now, it should be possible to detect a hiss
from the servo as the pedal is depressed. After
about four or five applications, no further
hissing should be heard, and the pedal should
feel considerably firmer.1The power steering fluid dipstick is
incorporated in the reservoir filler cap. The
reservoir is mounted on the pump. Observe
scrupulous cleanliness when checking the
level or topping-up.
2The system should be at operating
temperature and the engine switched off.
Wipe clean around the reservoir filler cap.
Unscrew the cap, withdraw the dipstick and
wipe it with a clean lint-free rag. Reinsert the
dipstick, screw the cap home, then unscrew it
again and read the level on the dipstick. It
should be up to the MAX or upper HOT mark
(depending on the dipstick markings) (see
illustration).
3Top-up if necessary with clean fluid of the
specified type. Check for leaks if topping-up is
frequently required.
4If the level is checked cold, use the MIN or
FULL COLD mark on the dipstick for reference.
Recheck the level at operating temperature.
On carburettor models, remove the air
cleaner cover and check that the automatic
choke is opening fully when the engine is hot.
Run the engine until it reaches normal
operating temperature. Stop the engine and
immediately restart it. If the engine fails to start
cleanly and immediately then refer to either
Chapters 4 or 5 and check fuel feed
adjustments.
37Hot starting check
36Automatic choke check
35Power steering fluid level
check34Road test
Carburettor models
SOHC engines
1Remove the screws from the air cleaner
cover(see illustration).
2Release the spring clips (when fitted), then
lift off the cover (see illustration).
3Lift out the air cleaner element(see
illustration). Wipe clean inside the air cleaner
housing, but be careful not to sweep dirt into
the carburettor throat.
4Where it is necessary to remove the air
cleaner body for cleaning or repair, first
disconnect the cold air inlet trunking from the
spout (see illustration). 5Disconnect the vacuum pipe from the inlet
manifold, and the hot air trunking from the
spout or exhaust manifold shroud(see
illustration). 6Remove the remaining screw which secures
the air cleaner to the valve cover, then lift off
the air cleaner.
7Refit by reversing the removal operations.
38Air cleaner filter element
renewal
1•16Every 24 000 miles or 2 years
35.2 Removing the power steering fluid
dipstick
38.2 Releasing an air cleaner cover clip
(carburettor model)38.1 Removing an air cleaner cover screw
(carburettor model)
Every 24 000 miles or 2 years
procarmanuals.com
Page 28 of 255

The cylinder head is of crossflow design
with the inlet manifold mounted on the left-
hand side and the exhaust manifold mounted
on the right-hand side.
Lubrication is by means of a bi-rotor pump
which draws oil through a strainer located
inside the sump, and forces it through a full-
flow filter into the engine oil galleries where it
is distributed to the crankshaft, camshaft and
auxiliary shaft. The big-end bearings are
supplied with oil via internal drillings in the
crankshaft.The undersides of the pistons are
supplied with oil from drillings in the big-ends.
The distributor shaft is intermittently supplied
with oil from the drilled auxiliary shaft. The
camshaft and cam followers are supplied with
oil via a drilled spray tube from the centre
camshaft bearing.
A semi-closed crankcase ventilation system
is employed whereby piston blow-by gases
are drawn into the inlet manifold via an oil
separator and on carburettor models a control
valve.
The following operations can be carried out
without removing the engine, although the
work may be easier and quicker with the
engine removed:
a)Removal and refitting of the cylinder head
b)Removal and refitting of the camshaft
(after removing the cylinder head)
c)Removal and refitting of the timing belt
and sprockets
d)Removal and refitting of the sump and oil
pump
e)Removal and refitting of the pistons,
connecting rods and big-end bearings
f)Renewal of the engine mountings
g)Renewal of the crankshaft oil seals
h)Removal and refitting of the auxiliary shaft
j)Removal and refitting of the flywheel
The engine must be removed from the
vehicle for the following operations:
a)Renewal of the crankshaft main bearings
b)Removal and refitting of the crankshaft
The engine may be lifted out either on its
own or together with the gearbox. Unless work
is also necessary on the gearbox it is
recommended that the engine is removed on
its own. Where automatic transmission is
fitted, the engine should be removed on its
own owing to the additional weight. If the
engine and gearbox are removed together,
they will have to be tilted at a very steep angle;
make sure that the range of the lifting tackle is
adequate.1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the bonnet.
3On carburettor models, remove the air
cleaner. On fuel-injection models, remove the
air cleaner cover, vane airflow meter and air
inlet trunking.
4If a splash guard is fitted, remove it.
5Release the securing clips and bolts and
remove the upper half of the fan shroud. On
carburettor models remove the lower half of
the shroud too.
6Drain the cooling system.
7Disconnect the radiator top and bottom
hoses from the thermostat housing and water
pump. Disconnect the top hose spur from the
expansion tank and unclip it.
8Disconnect the heater hoses from the water
pump and from the inlet manifold or automatic
choke housing. Unclip the hoses.
9On models with power steering, remove the
steering pump.
10Disconnect the vacuum pipe(s) from the
inlet manifold, labelling them if there is any
possibility of confusion.
11Disconnect the following wiring, as
applicable:
a)Alternator
b)Temperature gauge sender
c)Engine management temperature sensor
d)Distributor
e)Oil pressure switch
f)Automatic choke and thermo-switch
g)Carburettor stepper motor
h)Fuel-injection system sub-harness
j)Inlet manifold heater
12Disconnect the HT lead from the coil.
13If an oil level sensor is fitted, remove it
(see illustration).
14Unbolt the throttle cable bracket,
disconnect the inner cable and move the cable
and bracket aside. Also disconnect the
downshift cable on automatic transmission
models.
15On carburettor models, disconnect the
fuel lines from the fuel pump (mechanised
type) and from the carburettor. Be prepared
for fuel spillage.
16On fuel-injection models, disconnect the
fuel supply union from the injector rail, and the
fuel return pipe from the fuel pressureregulator. Be prepared for fuel spillage, and
for some spray if the supply side is still
under pressure.
17Unbolt the exhaust downpipe from the
manifold.
18On models with air conditioning, unbolt
the compressor and move it aside without
straining the flexible hoses.
19Remove the starter motor.
20Although not specified by the
manufacturers, the author advises that either
the radiator or the cooling fan be removed, to
reduce the risk of damage.
21Attach the lifting tackle to the two lifting
eyes on the engine, so that when suspended
the engine will be roughly horizontal. Take the
weight of the engine.
22Remove the single nut on each side which
secures each engine bearer to its mounting.
23Working under the vehicle, remove the
bracing strap which connects the engine and
transmission. Unbolt the adapter plate from
the bottom of the transmission bellhousing.
24On automatic transmission models, unbolt
the torque converter from the driveplate.
25Remove the engine-to-bellhousing bolts.
Note the location of the battery earth strap.
26Support the transmission, preferably with
a trolley jack.
27Check that nothing has been overlooked,
then raise the engine and draw it forwards
clear of the transmission input shaft. Do not
allow the weight of the engine to hang on the
shaft, and do not lift the transmission by it.
28On automatic transmission models, make
sure that the torque converter stays engaged
with the oil pump in the transmission as the
engine is withdrawn,
29Lift the engine out of the engine bay and
take it to the bench.
1Engine removal with automatic transmission
is not recommended.
2Proceed as in the previous Section,
paragraphs 1 to 18.
3Disconnect the wiring from the starter
motor, and release the battery earth cable
from its bellhousing bolt.
4Remove the radiator.
5Remove the propeller shaft.
6Disconnect and unclip the reversing light
switch and speedometer sender unit wiring.
7Disconnect the clutch cable.
8Unbolt the anti-roll bar mounting brackets
and lower the anti-roll bar as far as possible.
9From inside the vehicle remove the gear
lever.
10Drain the engine oil.
11Unhook the exhaust system from its
mounting on the gearbox crossmember. Either
support the system or remove it completely.
12Support the gearbox, preferably with a
trolley jack, then unbolt and remove the
gearbox crossmember. Note the earth strap (if
fitted) under one of the crossmember bolts.
13Attach lifting tackle to the two lifting eyes
on the engine so that when suspended it will
be at an angle of approximately 45°.
6Engine - removal with manual
gearbox
5Engine - removal leaving
gearbox/transmission in vehicle
4Methods of engine removal
3Major operations requiring
engine removal
2Major operations possible with
the engine in the vehicle
SOHCengines 2A•5
2A
5.13 Oil level sensor
procarmanuals.com
Page 32 of 255
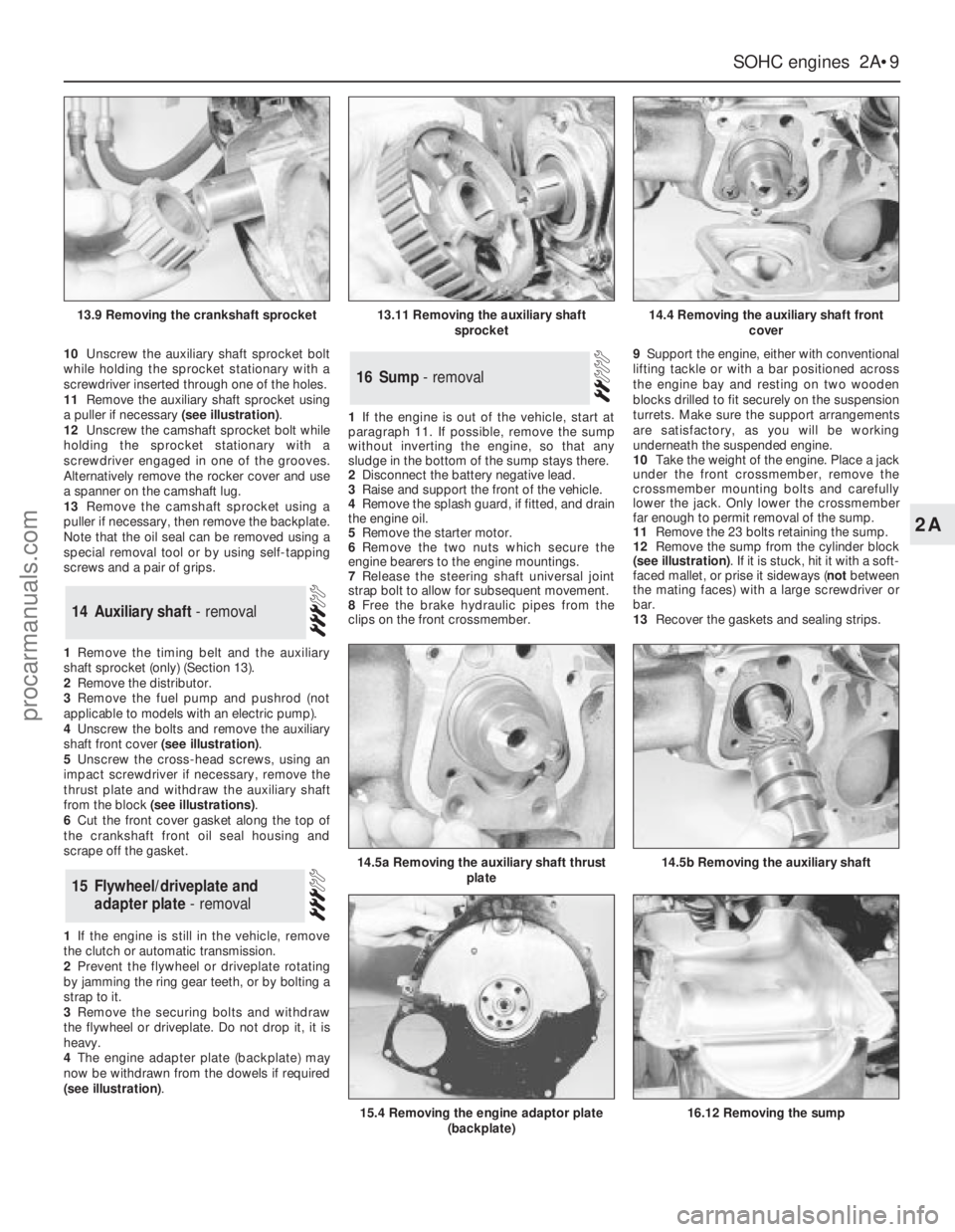
10Unscrew the auxiliary shaft sprocket bolt
while holding the sprocket stationary with a
screwdriver inserted through one of the holes.
11Remove the auxiliary shaft sprocket using
a puller if necessary (see illustration).
12Unscrew the camshaft sprocket bolt while
holding the sprocket stationary with a
screwdriver engaged in one of the grooves.
Alternatively remove the rocker cover and use
a spanner on the camshaft lug.
13Remove the camshaft sprocket using a
puller if necessary, then remove the backplate.
Note that the oil seal can be removed using a
special removal tool or by using self-tapping
screws and a pair of grips.
1Remove the timing belt and the auxiliary
shaft sprocket (only) (Section 13).
2Remove the distributor.
3Remove the fuel pump and pushrod (not
applicable to models with an electric pump).
4Unscrew the bolts and remove the auxiliary
shaft front cover (see illustration).
5Unscrew the cross-head screws, using an
impact screwdriver if necessary, remove the
thrust plate and withdraw the auxiliary shaft
from the block (see illustrations).
6Cut the front cover gasket along the top of
the crankshaft front oil seal housing and
scrape off the gasket.
1If the engine is still in the vehicle, remove
the clutch or automatic transmission.
2Prevent the flywheel or driveplate rotating
by jamming the ring gear teeth, or by bolting a
strap to it.
3Remove the securing bolts and withdraw
the flywheel or driveplate. Do not drop it, it is
heavy.
4The engine adapter plate (backplate) may
now be withdrawn from the dowels if required
(see illustration).1If the engine is out of the vehicle, start at
paragraph 11. If possible, remove the sump
without inverting the engine, so that any
sludge in the bottom of the sump stays there.
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Raise and support the front of the vehicle.
4Remove the splash guard, if fitted, and drain
the engine oil.
5Remove the starter motor.
6Remove the two nuts which secure the
engine bearers to the engine mountings.
7Release the steering shaft universal joint
strap bolt to allow for subsequent movement.
8Free the brake hydraulic pipes from the
clips on the front crossmember.9Support the engine, either with conventional
lifting tackle or with a bar positioned across
the engine bay and resting on two wooden
blocks drilled to fit securely on the suspension
turrets. Make sure the support arrangements
are satisfactory, as you will be working
underneath the suspended engine.
10Take the weight of the engine. Place a jack
under the front crossmember, remove the
crossmember mounting bolts and carefully
lower the jack. Only lower the crossmember
far enough to permit removal of the sump.
11Remove the 23 bolts retaining the sump.
12Remove the sump from the cylinder block
(see illustration). If it is stuck, hit it with a soft-
faced mallet, or prise it sideways (notbetween
the mating faces) with a large screwdriver or
bar.
13Recover the gaskets and sealing strips.
16Sump - removal
15Flywheel/driveplate and
adapter plate - removal
14Auxiliary shaft - removal
SOHCengines 2A•9
2A
13.9 Removing the crankshaft sprocket13.11 Removing the auxiliary shaft
sprocket14.4 Removing the auxiliary shaft front
cover
14.5b Removing the auxiliary shaft14.5a Removing the auxiliary shaft thrust
plate
15.4 Removing the engine adaptor plate
(backplate)16.12 Removing the sump
procarmanuals.com
Page 47 of 255

manifold. Piston blow-by gases are drawn
through the oil separator and the vent valve to
the inlet manifold. The blow-by gases are then
drawn into the engine together with the fuel/air
mixture. Refer to Chapter 1 for maintenance of
the system.
The following operations can be carried out
without removing the engine from the vehicle.
a)Removal of the camshafts.
b)Removal and servicing of the cylinder
head.
c)Removal of the timing chain and
sprockets.
d)Removal of the oil pump.
e)Removal of the sump.
f)Removal of the pistons and connecting
rods.
g)Removal of the big-end bearings.
h)Removal of the engine mountings.
i)Removal of the clutch and flywheel.
j)Removal of the crankshaft front and rear
oil seals.
The following operations can only be carried
out after removing the engine from the vehicle.
a)Removal of the crankshaft main bearings.
b)Removal of the crankshaft.
Note: A hoist and lifting tackle will be required
to lift the engine out of the vehicle.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the bonnet.
3On carburettor models, remove the air cleaner.
4On fuel-injection models, remove the air
inlet hose, plenum chamber and air cleaner lid
as an assembly.
5Disconnect the breather hose from the
camshaft cover, and unscrew the bolt
securing the hose support bracket to the left-
hand side of the cylinder head (see
illustration).
6Drain the cooling system.
7To provide additional working space,
remove the radiator.8Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
water pump housing on the left-hand side of
the engine and the cylinder head (see
illustration).
9Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
thermostat housing.
10Disconnect the heater coolant hose from
the inlet manifold.
11Where applicable, release the coolant
hose from the bracket under the carburettor
automatic choke housing.
12Disconnect the throttle cable and (where
necessary) speed control cable from the
throttle linkage.
13On carburettor models, disconnect the
vacuum pipe from the engine management
module.
14Disconnect the brake servo vacuum hose
(where necessary) from the inlet manifold.
15On fuel-injection models, disconnect the
vacuum pipes from the MAP sensor (located
on the suspension turret on the right-hand
side of the engine compartment) and, where
applicable, the air conditioning system.
16On carburettor models, disconnect the
fuel supply and return hoses at the
carburettor, and plug the ends of the hoses to
minimise petrol spillage. Take adequate fire
precautions.
17On fuel-injection models, slowly loosen
the fuel feed union at the fuel rail to relieve the
pressure in the fuel system before
disconnecting the union. Be prepared for
petrol spillage and take adequate fire
precautions. Disconnect the fuel feed hose,and disconnect the fuel return hose from the
fuel pressure regulator. Plug the ends of the
hoses to minimise petrol spillage.
18Disconnect the HT lead from the ignition
coil, and unclip it from the timing chain cover.
19Disconnect the wiring from the following
components as applicable, depending on
model. Then free the wiring loom from any
necessary retaining clips or ties and position it
clear of the engine.
a)Alternator.
b)Starter motor.
c)Oil pressure warning lamp switch.
d)Temperature gauge sender.
e)Cooling fan switch.
f)Anti-dieselling valve (carburettor models).
g)Automatic choke heater (carburettor
models).
h)Engine coolant temperature sensor.
i)Crankshaft speed/position sensor.
j)Air charge temperature sensor.
k)Throttle position sensor.
l)Fuel temperature sensor.
m)Fuel injectors.
20Remove the water pump/alternator
drivebelt, then unbolt the power steering
pump from the mounting bracket and move it
clear of the engine. Note that there is no need
to disconnect the fluid hoses, but make sure
that the pump is adequately supported to
avoid straining them.
21On models fitted with air conditioning,
unbolt the air conditioning compressor from the
mounting bracket, and move it clear of the
engine (see illustration). Do notdisconnect the
hoses, but make sure that the compressor is
adequately supported to avoid straining them.
22Unscrew and remove the top engine-to-
gearbox bolts which are accessible from the
engine compartment. Note the location of the
bolts, and the positions of the earth strap and
any wiring clips attached to the bolts.
23Unscrew the securing bolt, and
disconnect the earth lead from the rear left-
hand side of the cylinder head.
24Unscrew the nuts securing the engine
mountings to the engine mounting brackets.
25Apply the handbrake, jack up the front of
the vehicle and support it securely on axle
stands (see “Jacking”).
26Drain the engine oil into a container.
5Engine - removal leaving manual
gearbox in vehicle
4Major operations requiring
engine removal
3Major operations possible with
the engine in the vehicle
2B•4DOHCengine
5.5 Removing the hose support bracket
bolt from the cylinder head5.8 Water pump coolant hoses (viewed
from above)
5.21 Air conditioning compressor mounting
bolts (arrowed) (viewed from underneath)
Warning: Vehicles equipped with
air conditioning: Components of
the air conditioning system may
obstruct work being undertaken
on the engine, and it is not always possible
to unbolt and move them aside sufficiently,
within the limits of their flexible pipes. In
such a case, the system should be
discharged by a Ford dealer or air
conditioning specialist. Refer also to the
precautions given in Chapter 3.
procarmanuals.com
Page 48 of 255

27Remove the starter motor.
28Remove the exhaust downpipe.
29Ensure that the steering wheel is
positioned in the straight-ahead position then,
using a dab of paint or a suitable marker pen,
make alignment marks between the
intermediate shaft lower clamp and steering
gear pinion. Slacken and remove the lower
clamp bolt then disconnect the intermediate
shaft from the steering gear (see illustration).
30Working inside the vehicle, place a
wooden block under the clutch pedal to raise
it fully against the stop, so holding the
automatic adjuster pawl clear of the toothed
quadrant.
31Disconnect the clutch cable from the
clutch release arm, and pass the cable
through the bellhousing.
32Support the gearbox with a trolley jack,
using a block of wood between the jack and
the gearbox to spread the load.
33Unscrew and remove the remaining
engine-to-gearbox bolts, and remove the bolt
from the engine adapter plate (see
illustration). Recover any shims fitted
between the sump and the gearbox when
removing the lower engine-to-gearbox bolts.
34Make a final check to ensure that all
relevant wires, pipes and hoses have been
disconnected and positioned clear of the
engine to facilitate engine removal.
35Attach a suitable hoist to the engine lifting
brackets located at the front and rear of the
cylinder head, and carefully take the weight of
the engine.
36To improve clearance in the engine
compartment when lifting the engine, unbolt
the engine mounting brackets from the
cylinder block, and remove them (see
illustration).
37Detach the brake lines from the front
suspension crossmember (see illustration).
38Support the crossmember with a jack (do
not remove the jack from under the gearbox),
then loosen the bolts securing the
crossmember to the underbody. Remove the
bolts from one side, and carefully lower the
crossmember to allow sufficient room for the
sump to clear the steering rack and
crossmember when pulling the engine
forwards from the gearbox (see illustration).39Gently raise the engine, then pull it
forwards to disconnect it from the gearbox.
Ensure that the gearbox is adequately
supported, and take care not to strain the
gearbox input shaft.
40Once clear of the gearbox, lift the engine
from the vehicle, taking care not to damage
the components in the engine compartment.
Note:Refer to Part A, Section 4 of this
Chapter and to the warning that appears at the
start of Section 5 before proceeding. A
suitable hoist and lifting tackle will be required
for this operation.
1Proceed as described in paragraphs 1 to 21
of Section 5.
2Unscrew and remove the top engine-to-
transmission bolts which are accessible from
the engine compartment. Note the location of
the earth strap, vacuum pipe bracket, and
transmission dipstick tube bracket, as
applicable.
3Proceed as described in paragraphs 23 to 29
of Section 5.4Where applicable, remove the bolt securing
the transmission fluid dipstick tube to the left-
hand side of the cylinder block.
5Working through the starter motor aperture,
unscrew the four torque converter-to-
driveplate nuts. It will be necessary to turn the
crankshaft, using a suitable spanner on the
crankshaft pulley bolt, in order to gain access
to each bolt in turn through the aperture.
6Support the transmission with a trolley jack,
using a block of wood between the jack and
the transmission to spread the load.
7Unscrew and remove the remaining engine-
to-transmission bolts, and remove the bolt
from the engine adapter plate. Recover any
shims fitted between the sump and the
transmission when removing the lower engine-
to-transmission bolts. Where applicable, pull
the blanking plug from the adapter plate.
8Proceed as described in paragraphs 34 to 38
of Section 5.
9Gently raise the engine, then pull the engine
forwards to disconnect it from the
transmission. Ensure that the torque converter
is held firmly in place in the transmission
housing, otherwise it could fall out resulting in
fluid spillage and possible damage. It may be
necessary to rock the engine a little to release
it from the transmission.
10Once clear of the transmission, lift the
engine from the vehicle, taking care not to
damage the components in the engine
compartment.
6Engine - removal leaving
automatic transmission in vehicle
DOHCengine 2B•5
2B
5.29 Intermediate shaft lower clamp bolt
(arrowed)5.33 Engine adaptor plate bolt (arrowed)5.36 Remove the engine mounting brackets
to improve clearance
5.37 Removing a brake line securing clip
from the suspension crossmember5.38 Removing a suspension crossmember
securing bolt
It may be necessary to rock
the engine a little to release it
from the gearbox.
procarmanuals.com
Page 49 of 255

Note: Refer to Part A, Section 4 of this Chapter
and to the warning that appears at the start of
Section 5 before proceeding. A hoist and lifting
tackle will be required for this operation.
1Proceed as described in paragraphs 1 to 21
of Section 5.
2Unscrew the securing bolt, and disconnect
the earth lead from the rear left-hand side of
the cylinder head.
3Unscrew the nuts securing the engine
mountings to the engine mounting brackets.
4Jack up the vehicle and support it securely
on axle stands (see “Jacking”). Ensure that
there is enough working room beneath the
vehicle.
5To improve access, disconnect the exhaust
downpipe from the manifold and remove the
exhaust system.
6Drain the engine oil into a suitable container.
7On models fitted with a catalytic converter,
release the securing clips and withdraw the
exhaust heat shield from under the vehicle for
access to the propeller shaft.
8Remove the propeller shaft.
9Where applicable, bend back the locktabs,
then unscrew the two bolts in each case
securing the two anti-roll bar mounting clamps
to the vehicle underbody. Lower the anti-roll
bar as far as possible.
10Proceed as described in paragraphs 30
and 31 of Section 5.
11Support the gearbox with a trolley jack,
using a block of wood between the jack and
the gearbox to spread the load.
12Unscrew the four nuts securing the
gearbox crossmember to the vehicle
underbody. Unscrew the central bolt securing
the crossmember to the gearbox, and remove
the crossmember. Note the position of the
earth strap, where applicable. Recover the
mounting cup, and the exhaust mounting
bracket and heat shield (as applicable).
13Lower the gearbox slightly on the jack,
then remove the circlip, and disconnect the
speedometer drive cable from the gearbox.
14Disconnect the wiring from the reversing
lamp switch, and on models with fuel-injection,
disconnect the wiring from the vehicle speed
sensor mounted in the side of the gearbox.
15Slacken and remove the two bolts and
washers (one either side) securing the gear
linkage support bracket to the gearbox.
16Using a pin punch, drive out the roll pin
securing the gearchange rod to the gear linkage.
17Attach a hoist to the engine lifting brackets
located at the front and rear of the cylinder head,
and slowly take the weight of the engine. Arrange
the lifting tackle so that the engine/gearbox
assembly will assume a steep angle of
approximately 40°to 45°as it is being removed.
18To improve clearance in the engine
compartment when lifting the engine, unboltthe engine mounting brackets from the
cylinder block, and remove them.
19Ensure that the steering wheel is positioned
in the straight-ahead position then, using a dab
of paint or a marker pen, make alignment marks
between the intermediate shaft lower clamp
and steering gear pinion. Slacken and remove
the lower clamp bolt then disconnect the
intermediate shaft from the steering gear.
20Detach the brake lines from the front
suspension crossmember.
21Support the crossmember with a jack (do not
remove the jack from under the gearbox), then
loosen the bolts securing the crossmember to the
underbody. Remove the crossmember securing
bolts, and carefully lower the crossmember to
allow sufficient room for the engine sump to clear
the steering rack and crossmember as the
engine/gearbox assembly is removed.
22Make a final check to ensure that all
relevant wires, pipes and hoses have been
disconnected to facilitate removal of the
engine/gearbox assembly.
23Raise the engine/gearbox, at the same
time lowering the trolley jack which is
supporting the gearbox.
24Place a suitable rod across the vehicle
underbody to support the gear linkage support
bracket whilst the gearbox is removed.
25Tilt the engine/gearbox assembly using
the hoist and the trolley jack, until the
assembly can be lifted from the vehicle. Take
care not to damage surrounding components.
26If the vehicle is to be moved, with the
engine/gearbox assembly removed, temporarily
refit the suspension crossmember and the anti-
roll bar to the underbody, and reconnect the
steering column to the intermediate shaft.
27To separate the engine from the gearbox,
proceed as follows.
28Remove the starter motor.
29Support the engine and gearbox
horizontally on blocks of wood.
30Unscrew the engine-to-gearbox bolts,
noting the locations of the bolts, and the
positions of the earth strap and any wiring clips
attached to the bolts. Recover any shims fitted
between the sump and the gearbox when
removing the lower engine-to-gearbox bolts.
31Unscrew the bolt from the engine adapter
plate.
32Pull the engine and gearbox apart, taking
care not to strain the gearbox input shaft. It
may be necessary to rock the units slightly to
separate them.
Note: Refer to Part A, Section 4 of this
Chapter and to the warning that appears at the
start of Section 5 before proceeding. A
suitable hoist and lifting tackle will be required
for this operation. Any suspected faults in the
automatic transmission should be referred to a
Ford dealer or automatic transmissionspecialist before removal of unit, as the
specialist fault diagnosis equipment is
designed to operate with the transmission in
the vehicle.
1Proceed as described in paragraphs 1 to 21
of Section 5.
2Unscrew the securing bolt, and disconnect
the earth lead from the rear left-hand side of
the cylinder head.
3Unscrew the nuts securing the engine
mountings to the engine mounting brackets.
4Jack up the vehicle and support it securely
on axle stands (see “Jacking”). Ensure that
there is enough working room beneath the
vehicle.
5To improve access, disconnect the exhaust
downpipe from the manifold and remove the
exhaust system .
6Drain the engine oil into a suitable container.
7On models fitted with a catalytic converter,
release the securing clips and withdraw the
exhaust heat shield from under the vehicle for
access to the propeller shaft.
8Remove the propeller shaft.
9Where applicable, bend back the locktabs,
then unscrew the two bolts in each case
securing the two anti-roll bar mounting clamps
to the vehicle underbody. Lower the anti-roll
bar as far as possible.
10Support the transmission with a trolley
jack, using a block of wood between the jack
and the transmission to spread the load.
11Unscrew the four bolts securing the
transmission crossmember to the vehicle
underbody. Unscrew the central bolt securing
the crossmember to the transmission, and
remove the crossmember. Note the position of
the earth strap, where applicable. Recover the
mounting cup, and the exhaust mounting
bracket and heat shield (as applicable).
12Lower the transmission slightly on the jack.
13Unscrew the unions and disconnect the
fluid cooler pipes from the transmission. Plug
the open ends of the pipes and the
transmission to prevent dirt ingress and fluid
leakage. Where applicable, detach the fluid
cooler pipe bracket from the engine mounting
bracket, and move it to one side.
14Remove the two clips securing the
selector rod, and detach the selector rod from
the manual selector lever, and the selector
lever on the transmission.
15Disconnect the wiring from the starter
inhibitor switch, downshift solenoid, lock-up
clutch, reversing lamp switch, and where
applicable, the 3rd/4th gearchange solenoid.
16Remove the securing screw, and
disconnect the speedometer cable (where
fitted) from the transmission extension
housing. Plug the opening in the transmission
to prevent dirt ingress.
17Proceed as described in paragraphs 17 to 26
of Section 7, substituting transmission for
gearbox and ignoring paragraph 24.
18To separate the engine from the
transmission, proceed as follows.
19Remove the starter motor.
20Support the engine and transmission
horizontally on blocks of wood.
8Engine/automatic
transmission assembly -
removal and separation
7Engine/manual gearbox
assembly - removal and
separation
2B•6DOHCengine
procarmanuals.com