Coolant temperature sensor FORD KUGA 2011 1.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 2011, Model line: KUGA, Model: FORD KUGA 2011 1.GPages: 2057
Page 1784 of 2057

If one of the two APP sensors fails, then only a
proportion of the engine's power will be available
when accelerating. Top speed can nevertheless
be achieved.
If both of the APP sensors fail, the engine is
regulated to a defined speed following a plausibility
check after the BPP (brake pedal position) switch
and brake light switch have been actuated once.
The vehicle can then only be accelerated to a
defined speed.
In either case, a fault is saved in the error memory
of the PCM.
Throttle control unit
E74167
1
2
Description
Item
TP (throttle position) sensor
1
Electric motor
2
CAUTION: The throttle control unit must
not be repaired or adjusted. The stop of
the throttle valve must on no account be
adjusted.
After disconnecting the battery or replacing the
throttle control unit or the PCM, initialization is
necessary. • engine off
• Accelerator pedal not pressed
• Battery voltage 11 ... 14 V
• Ignition key in ON position
• Wait approximately 30 seconds until initialization
is complete.
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT)
sensor
E94804
The ECT (engine coolant temperature) sensor is
designed as an NTC (negative temperature
coefficient) resistor.
If the signal from the ECT sensor fails, the cooling
fan is on all the time and the A/C (air conditioning)
is turned off. When the ignition is switched on, the
value from the IAT (intake air temperature) sensor
is read. When the engine is running, the
temperature is calculated using a temperature map
stored in the PCM according to how long the
engine has been running. This substitute value is
then used as the basis for calculating the injected
fuel quantity and the ignition timing.
Ignition coil-on-plug
E73540
G1021907en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 10
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
10
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1793 of 2057

Description
Item
CKP sensor
1
Tooth pitch
2
Flywheel ring gear
3
Reference mark
4
Voltage (sinusoidal-like signal curve)
5Description
Item
60-2 pulses per revolution of the
crankshaft
6
Tooth center
7
Reference mark
8
Tooth pitch
9
The acceleration of the flywheel at each power
stroke results in a change in the CKP signal.
During the power stroke, the combustion pressure
acting on the piston causes an acceleration of the
crankshaft and thus also of the flywheel. This is
apparent in the voltage curve from slightly higher
frequencies and amplitudes of the CKP signal.
Calculation of the ignition angle
Since propagation of the flame front in the air/fuel
mixture always takes the same amount of time, the
ignition of the air/fuel mixture has to take place
earlier or later depending on the engine speed.
The higher the speed, the earlier ignition must
occur. This ensures that maximum combustion
pressure is achieved immediately after Top Dead
Center and that maximum combustion pressure
acts on the piston.
When starting the engine, ignition timing is
determined by the CMP purely from the ignition
map and information on camshaft position (CKP
sensors) and crankshaft position (PCM sensor).
As soon as the engine is running, the following
data are used as a basis for calculating the ignition
angle:
• the engine speed,
• the engine load,
• the coolant temperature and
• the KS signal.
The ignition angle has a major impact on engine
operation. It affects
• engine performance
• exhaust emissions
• fuel consumption,
• combustion knock behavior and
• engine temperature.
The higher the engine load, i.e. the torque demand,
the richer the air/fuel mixture, the longer the
combustion period and the earlier the ignition. The PCM calculates engine load using the MAF
sensor signal, the throttle position and engine
speed. This is done using ignition maps that are
stored in the PCM. The ignition timing is adjusted
according to the operating condition of the engine,
for cold starting for example.
Ignition map
2
E96319
1
3
Description
Item
Engine load.
1
Engine speed
2
Ignition angle
3
The ignition maps were calculated in a series of
tests. Particular attention is paid to the emission
behaviour, power and fuel consumption of the
engine. The ignition map is stored in the data
memory of the PCM.
By adjusting the ignition timing it is also possible
to influence the engine speed to some extent
without having to change the throttle valve position.
This has advantages for idling stabilization, as the
engine speed and hence the engine torque respond
far more quickly to a change in the ignition timing
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 19
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
19
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1796 of 2057

current value is reached. The PCM then
permanently connects the heating element to earth.
The catalyst monitor sensor is used by the PCM
to measure the oxygen content in the exhaust gas
in the TWC. If all the conditions for catalyst
diagnostics are met, based on this information the
PCM can check that the TWC is working
satisfactorily. The information is also used to
improve the air/fuel mixture adjustment.
The catalyst monitor sensor is similar in function
to an HO2S. The signal transmitted by the catalyst
monitor sensor changes sharply if the oxygen
content in the exhaust gas changes. For this
reason, catalyst monitor sensors are also called
"jump lambda sensors".
Fuel tank purging
The EVAP purge valve is only actuated by the PCM
if the coolant temperature is at least 60°C.
Actuation is done ground side by means of a PWM
signal. This makes it possible to have the full range
of opening widths, from fully closed to fully open.
The PCM determines from the operating conditions
when and how wide to open the EVAP tank purge
valve. If the EVAP purge valve is opened, the
engine sucks in ambient air through the activated
charcoal in the evaporative emission canister as
a result of the vacuum in the intake manifold. In
this way the adsorbed hydrocarbons are led to the
combustion chamber of the engine.
The EVAP tank purge valve is not actuated and
system cleaning is interrupted if the engine
switches to idle and/or a closed-loop control
process is initiated.
Power (battery voltage) is supplied via the
Powertrain Control Module relay in the BJB. The
solenoid coil resistance is between 17 and 24 ohms
at 20°C.
Engine speed control
The APP sensor provides the PCM with information
about the driver's request for acceleration.
The throttle control unit receives a corresponding
input signal from the PCM. An electric motor then
moves the throttle valve shaft by means of a set
of gears. The position of the throttle is continuously
recorded by the TP sensor. Information on throttle
position is processed and monitored by the PCM.
The TP sensor comprises two potentiometers.
These work in opposite ways to each other. In one
potentiometer, the resistance increases when the
throttle is opened, in the other it decreases. Thisallows the operation of the potentiometers to be
checked. The signal from the TP sensor is
amplified in the lower range (idle to a quarter open)
by the PCM to enable more precise control of the
throttle in this range. This is necessary because
the engine is very sensitive to changes in throttle
angle in this throttle opening range.
With the throttle valve position kept constant, the
ignition angle and the injected fuel quantity are
then varied to meet the torque demands.
Depending on the operating state of the engine, a
change in the position of the throttle flap may not
be necessary when the APP sensor changes.
If a fault develops in the throttle control unit, a
standby function is executed. This standby function
allows a slight opening of the throttle flap, so that
enough air passes through to allow limited engine
operation. For this purpose, there is a throttle flap
adjustment screw on the throttle housing. The
return spring closes the throttle flap until the stop
of the toothed segment touches the stop screw. In
this way a defined throttle flap gap is formed for
limp home mode.
The stop screw has a spring loaded pin, which
holds the throttle flap open for limp home mode.
In normal operating mode, this spring loaded pin
is pushed in by the force of the electric motor when
the throttle flap must be closed past the limp home
position (e.g. for idle speed control or overrun
shutoff).
Oil monitoring
The engine does not have an oil pressure
switch.
The oil level and oil quality are calculated.
Calculating the engine oil level
The oil level is determined by continuous
measurement of the capacitance (i.e. the ability to
store an electrical charge) between the two
capacitive elements of the engine oil
level/temperature/quality sensor. The different oil
levels cause the capacitance between the elements
to change. The data are recorded by the PCM and
converted into an oil level value. Temporary
fluctuations in oil level are automatically filtered out
by the PCM.
Calculating oil quality
The PCM calculates the oil quality from the oil level
measurement and the oil temperature measured
by the sensor, plus the engine speed and the
average fuel consumption. The driver is informed
about when an oil change is due.
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 22
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
22
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1805 of 2057
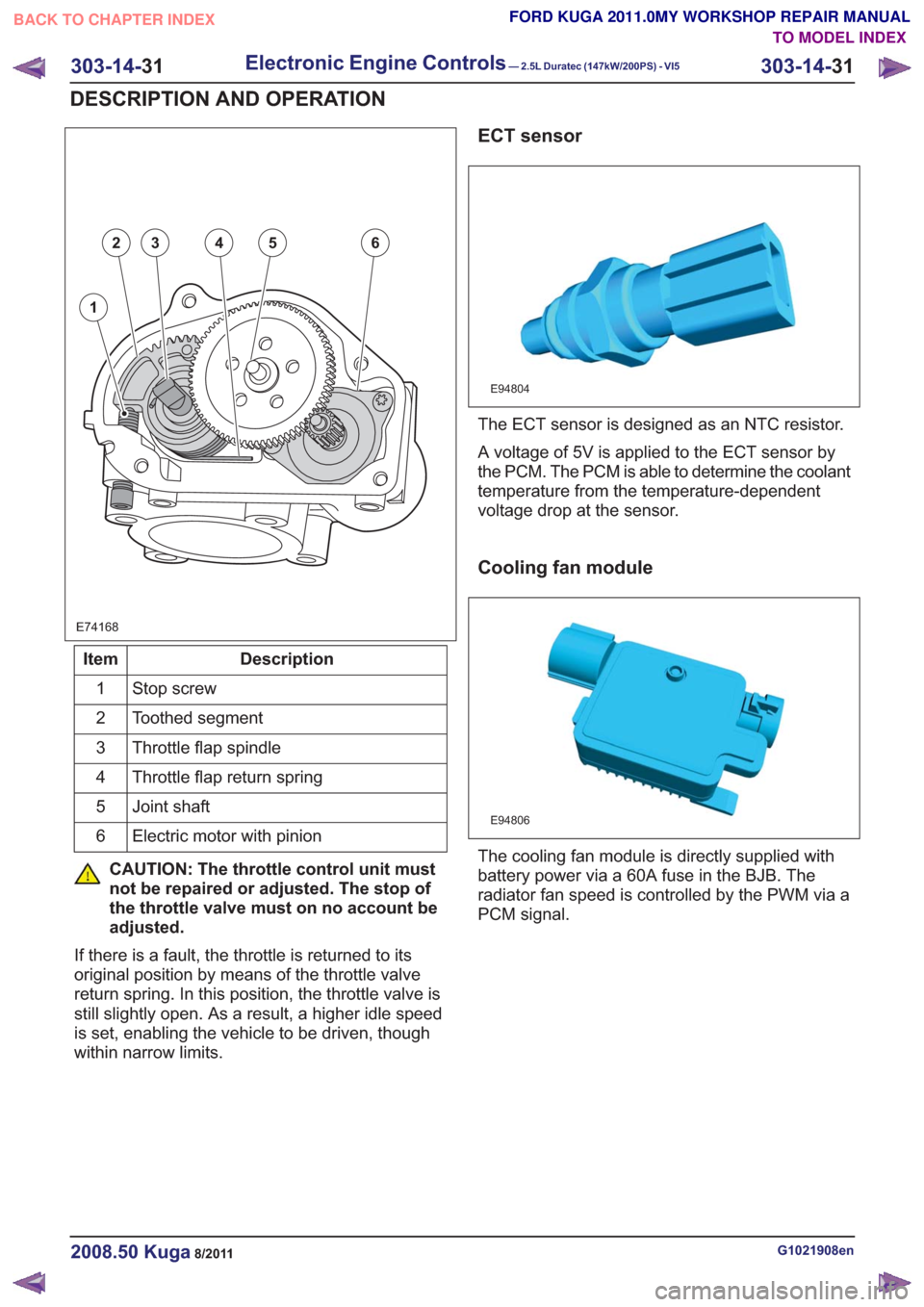
E74168
1
23456
Description
Item
Stop screw
1
Toothed segment
2
Throttle flap spindle
3
Throttle flap return spring
4
Joint shaft
5
Electric motor with pinion
6
CAUTION: The throttle control unit must
not be repaired or adjusted. The stop of
the throttle valve must on no account be
adjusted.
If there is a fault, the throttle is returned to its
original position by means of the throttle valve
return spring. In this position, the throttle valve is
still slightly open. As a result, a higher idle speed
is set, enabling the vehicle to be driven, though
within narrow limits.
ECT sensor
E94804
The ECT sensor is designed as an NTC resistor.
A voltage of 5V is applied to the ECT sensor by
the PCM. The PCM is able to determine the coolant
temperature from the temperature-dependent
voltage drop at the sensor.
Cooling fan module
E94806
The cooling fan module is directly supplied with
battery power via a 60A fuse in the BJB. The
radiator fan speed is controlled by the PWM via a
PCM signal.
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 31
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
31
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1847 of 2057
E112322
The TCM adapts the gear changing to ensure that
the correct gear is selected for the style of driving,
the engine load, driver requirements, vehicle speed
etc. This leads to lower fuel consumption together
with improved comfort through smoother gear
changes and lower noise levels.
The TCM receives information on the driver's
desired transmission range and type of driving
mode. In contrast to a transmission which is only
controlled hydraulically, the control module can
calculate the best times to shift gear and activate
torque converter lockup by using the signals from
the sensors in the transmission and the engine
management system.
The control module enables small changes in the
operating conditions to be made and adapts thevarious transmission functions to ensure that the
correct gear is always selected in relation to the
type of driving mode.
The TCM has adaptive capabilities. This ensures
smooth gear changes throughout the whole service
life of the transmission.
To exactly determine the activation points of the
gear shifts and torque converter lockup on the
basis of the type of driving mode chosen, the TCM
receives the following information:
• Transmission range chosen (TR sensor).
• Type of driving mode chosen
(normal/sport/select-shift).
• Transmission input shaft speed (TSS sensor).
• Transmission output shaft speed (OSS sensor).
• Transmission fluid temperature (TFT sensor).
• The engine speed and the torque as well as the throttle plate opening - from the PCM via the
CAN data bus.
• Actuation of the accelerator pedal - from the PCM via the CAN data bus.
• Coolant temperature - from the PCM via the CAN data bus.
• Vehicle speed - from the ABS via the CAN data bus.
• Actuation of the brake pedal - from the ABS via the CAN data bus.
Pin assignment for TCM connector 'A' (connection to vehicle)
11
E125669
Description
Item
Battery (+)
1
not assigned
2Description
Item
not assigned
3
not assigned
4
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 26
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 26
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1850 of 2057

To exactly determine the activation points of the
gear shifts and torque converter lockup on the
basis of the type of driving mode chosen, the TCM
receives the following information:
• Selected transmission range (TR sensor)
• Selected driving mode (normal/sport/select-shift)
• Transmission input shaft speed (TSS sensor)
• Transmission output shaft speed (OSS sensor)
• Transmission fluid temperature (TFT sensor)
• The engine speed and the torque as well as thethrottle plate opening - from the PCM via the
CAN databus
• Actuation of accelerator – from the PCM via the CAN databus
• The coolant temperature – from the PCM via the CAN databus
• Road speed – from the ABS module via the CAN databus
• Actuation of brake pedal – from the PCM via the CAN databus
Gearshift control
Adaptation
The TCM monitors every shift operation in all
driving conditions to make even and smooth gear
shifts possible. This is done by the control module,
which either lowers or increases the hydraulic line
pressure during gearshifts.
The changed pressure values are stored in the
control module memory after the engine is switched
off and retrieved during engine starting. This
improves the shift comfort and extends the service
life.
Full adaptability occurs when the following criteria
are met:
• Throttle plate opening is constant.
• Transmission fluid temperature between 65 °Cand 110 °C.
Shifting from 'P' to another transmission
range
To be able to move the selector lever from 'P' into
another transmission range, the ignition must be
switched on and the brake pedal pressed (stoplamp
switch on). The TCM detects the position of the
brake pedal via the CAN data bus and the engaged
transmission range from the TR sensor. Based on this information, the TCM transmits a
signal to the select-shift switch module. This
activates the brake shift interlock actuator in the
selector lever assembly.
When the brake shift interlock actuator is activated,
the locking pin is retracted so that another
transmission range can be selected.
The brake shift interlock actuator is deactivated
when the ignition is switched off. It is mechanically
locked when the gear selector lever is in 'P'.
Automatic transmission, selector lever in
position "D".
The TCM adapts the shift points to match the
driving conditions. Normally the TCM is in adaptive
mode and gear changes take place adapted to the
driving conditions. If special driving conditions are
detected, the TCM switches to predefined
characteristics.
When driving with normal acceleration, the TCM
uses a preset shift program which is optimized for
economical driving.
This shift program is suitable for "normal" driving
and delivers early upward changes and torque
converter lockup. Furthermore, the transmission
fluid pressure is adapted to make smooth
engagement of the gears possible.
Sport mode, selector lever in position "S"
The transmission switches from automatic
operation into sport mode. In this mode the TCM
switches to another set of characteristic curves.
These characteristic curves for control of the gear
changes are adapted to sporting calculations (e.g.
gear change at higher engine speed).
In the sport mode shift program the shift points are
set so that good performance is offered. Changing
down occurs at lower engine speeds.
Manual gear changes (select-shift mode) can be
made in sport mode by moving the selector lever
in the (+) or (-) direction.
Changing gear in select-shift mode
If you move the selector lever to 'S', the automatic
transaxle remains hydraulically in 'D' position. If
you move the gear selector lever forwards (-), the
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01-
29
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 29
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1865 of 2057

Description
Item
ABS5
Cruise control
6
Select-shift switch module
7
PCM
8
Selector lever lock
9
PWM solenoid valve – shift pressure (SLS)
10
PWM solenoid valve for main line pressure
(SLT)
11
PWM- solenoid valve – TCC (SLU)
12Description
Item
Shift solenoid S1 (open when dormant)
13
Shift solenoid S2 (closed when dormant)
14
Shift solenoid S3 (closed when dormant)
15
Shift solenoid S4 (open when dormant)
16
Shift solenoid S5 (closed when dormant)
17
The TSS sensor
18
The OSS sensor
19
The TFT sensor
20
TR sensor in TCM
21
Input signals
Hard wired
• Item 18: ISS (input shaft speed) sensor
– Supplies information on the transmissioninput shaft speed. Used for calculations, for
instance the shift process, checking the
torque converter lockup and for diagnosis of
the hydraulic/mechanical operations in the
transmission.
• Item 19: OSS sensor – Supplies information on the transmissionoutput shaft speed. Used for calculations, for
instance the vehicle speed and for diagnosis
of the hydraulic/mechanical operations in the
transmission.
• Item 20: TFT sensor – Supplies information on the transmission fluidtemperature. This information is used to
adjust the shift times and the fluid pressure.
• Item 21: TR sensor – Supplies the TCM with the information on thechosen transmission range. Starting is only
possible when the selector lever is in the P
or N position. The sensor is a permanent
magnet which creates a magnetic field over
the different Hall sensors and in this way
creates a specific voltage for each shift
operation.
Via the LIN data bus
• Item 7: Selector lever module (select-shift module)
– Indicates that the selector lever is locked inposition P and supplies information on the
sport mode status. Also transmits a control
signal during select-shift gear changes and
supplies information on the fault status in the selector lever module, so that the fault codes
in the module can be stored as required.
Via the CAN data bus
• Item 4: PCM – Stop light switch ON/OFF, is used by theTCC.
– Coolant temperature, used for diagnosis of the transmission temperature sensor and for
activating the catalytic converter.
– Engine speed >400 rpm = engine running. Used for starting the transmission fluid
pressure and diagnosis functions.
– Engine rpm. Used for checking the torque converter slip and the pressure build-up,
which have an effect on the shift comfort.
– Kickdown. If the accelerator pedal is pressed down and the throttle plate is wide open, the
PCM transmits a kickdown signal to the TCM.
– Current engine speed, used to check the line pressure of the transmission.
– Throttle plate opening, used to calculate the gear changes. During sport mode and
kickdown.
– Accelerator pedal position, used to calculate the shift threshold timings.
• Item 5: ABS module – Supplies information on the vehicle speedand also on the difference in speed between
the left-hand and right-hand wheels. Prevents
changing up if the speed difference is greater
than 40 km/h, to protect the differential in the
transmission.
• Item 6: Vehicle speed control system – Is used to calculate the acceleration,depending on the position of the resume and
set buttons.
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 44
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 44
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL