Index FORD KUGA 2011 1.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 2011, Model line: KUGA, Model: FORD KUGA 2011 1.GPages: 2057
Page 382 of 2057
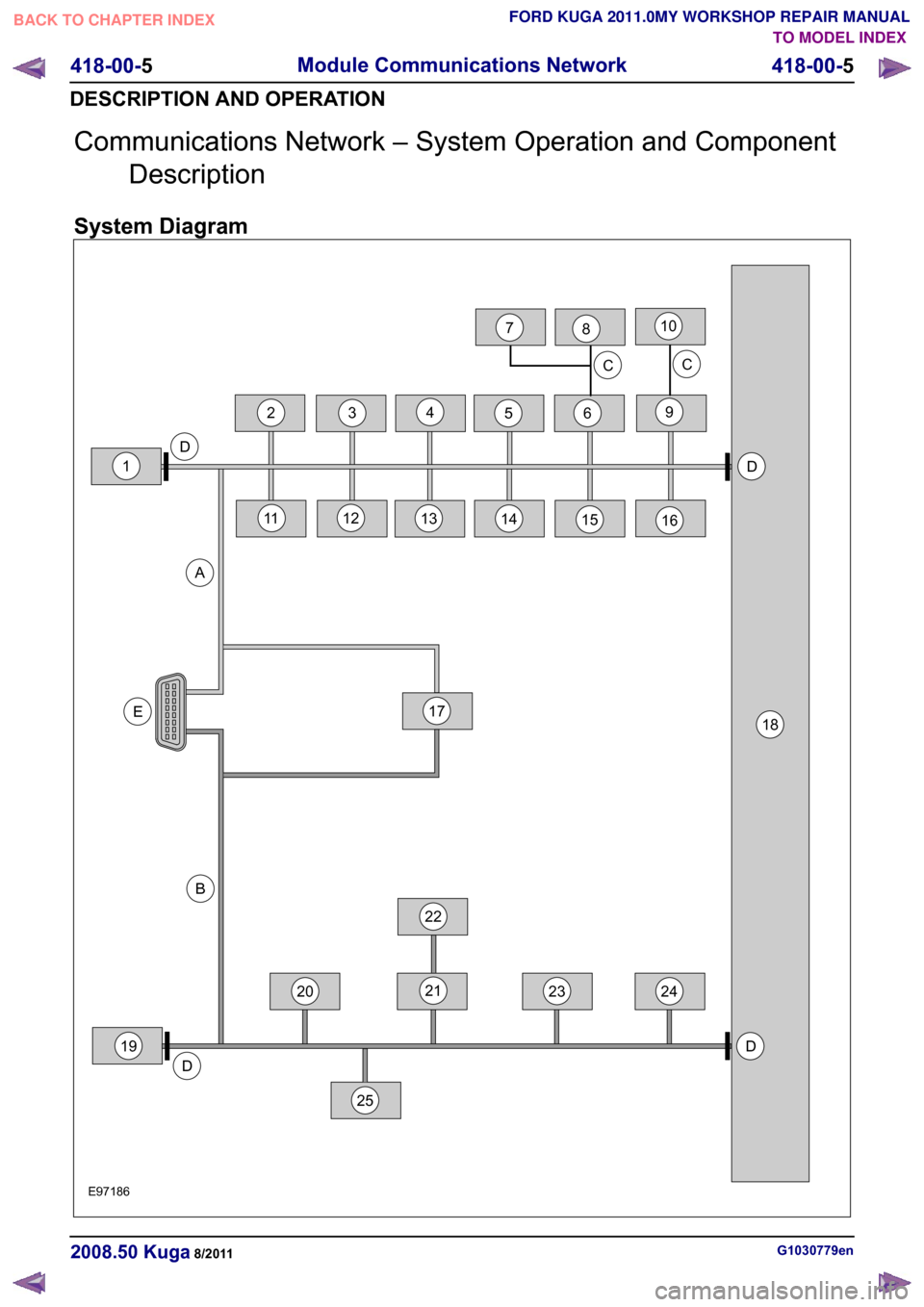
Communications Network – System Operation and Component
Description
System Diagram G1030779en
2008.50 Kuga 8/2011 418-00-5
Module Communications Network
418-00-5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATIONTO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUALE971864522DD18E20212319DAB3242513141516D1917C1011126C782
Page 383 of 2057
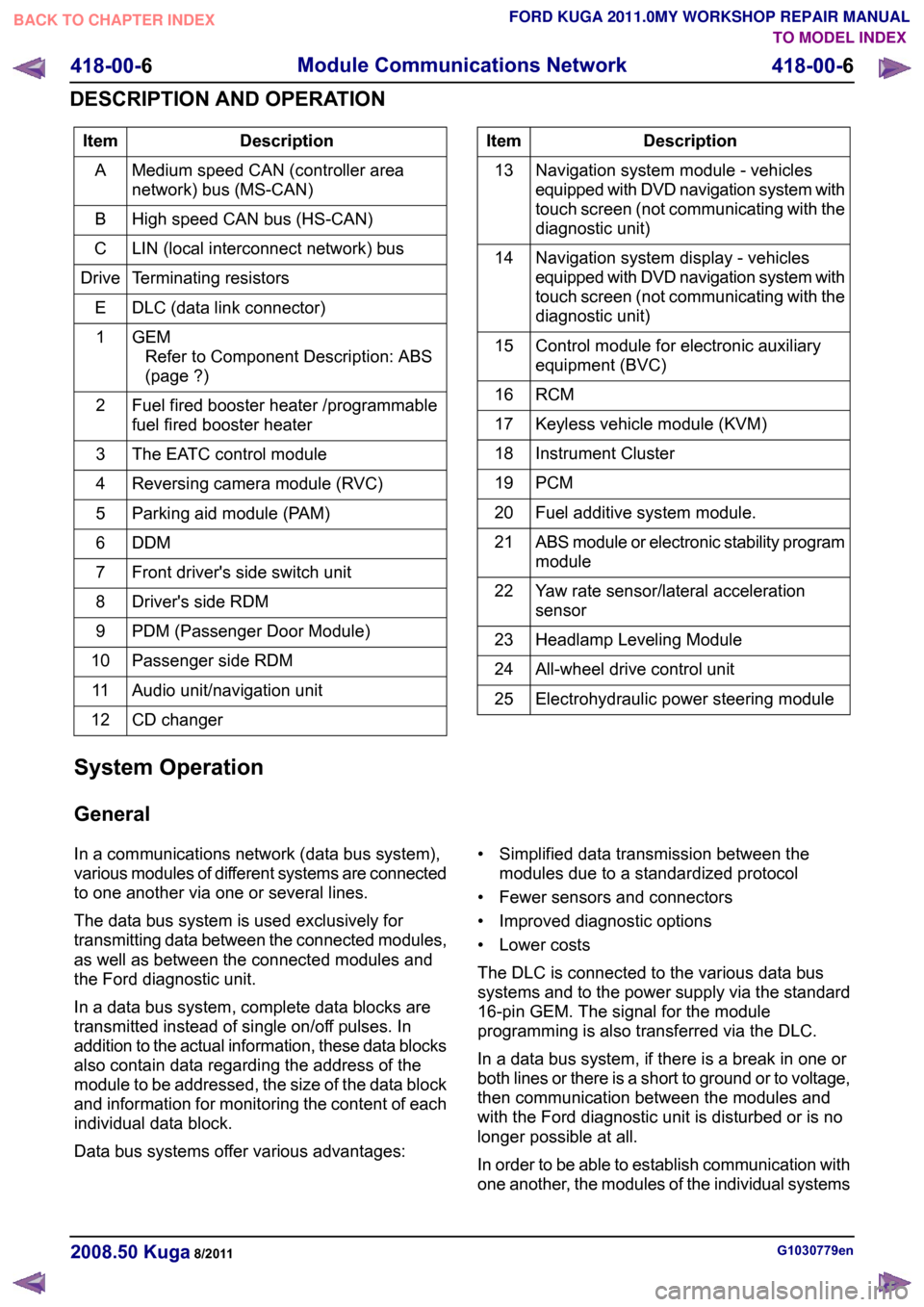
Description
Item
Medium speed CAN (controller area
network) bus (MS-CAN)
A
High speed CAN bus (HS-CAN)
B
LIN (local interconnect network) bus
C
Terminating resistors
Drive
DLC (data link connector)
E
GEMRefer to Component Description: ABS
(page ?)
1
Fuel fired booster heater /programmable
fuel fired booster heater
2
The EATC control module
3
Reversing camera module (RVC)
4
Parking aid module (PAM)
5
DDM6
Front driver's side switch unit
7
Driver's side RDM
8
PDM (Passenger Door Module)
9
Passenger side RDM
10
Audio unit/navigation unit
11
CD changer
12 Description
Item
Navigation system module - vehicles
equipped with DVD navigation system with
touch screen (not communicating with the
diagnostic unit)
13
Navigation system display - vehicles
equipped with DVD navigation system with
touch screen (not communicating with the
diagnostic unit)
14
Control module for electronic auxiliary
equipment (BVC)
15
RCM16
Keyless vehicle module (KVM)
17
Instrument Cluster
18
PCM19
Fuel additive system module.
20
ABS module or electronic stability program
module
21
Yaw rate sensor/lateral acceleration
sensor
22
Headlamp Leveling Module
23
All-wheel drive control unit
24
Electrohydraulic power steering module
25
System Operation
General
In a communications network (data bus system),
various modules of different systems are connected
to one another via one or several lines.
The data bus system is used exclusively for
transmitting data between the connected modules,
as well as between the connected modules and
the Ford diagnostic unit.
In a data bus system, complete data blocks are
transmitted instead of single on/off pulses. In
addition to the actual information, these data blocks
also contain data regarding the address of the
module to be addressed, the size of the data block
and information for monitoring the content of each
individual data block.
Data bus systems offer various advantages: • Simplified data transmission between the
modules due to a standardized protocol
• Fewer sensors and connectors
• Improved diagnostic options
• Lower costs
The DLC is connected to the various data bus
systems and to the power supply via the standard
16-pin GEM. The signal for the module
programming is also transferred via the DLC.
In a data bus system, if there is a break in one or
both lines or there is a short to ground or to voltage,
then communication between the modules and
with the Ford diagnostic unit is disturbed or is no
longer possible at all.
In order to be able to establish communication with
one another, the modules of the individual systems G1030779en
2008.50 Kuga 8/2011 418-00-6
Module Communications Network
418-00-6
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATIONTO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 384 of 2057

must use the same language. This language is
called a protocol.
At present, Ford uses three different data bus
systems. Depending upon model and equipment
level, all three data bus systems are used. Each
of these data bus systems has its own protocol.
Data bus systems
ISO 9141 bus
The International Organisation for Standardisation
ISO 9141 bus. This consists of a single wire and
is used exclusively for communication between the
modules and the Ford diagnostic unit. The fault
memories of the various modules are read out via
the ISO 9141 bus.
Local Interconnect Network (LIN) bus
The LIN bus is a standard specifically designed for
cost-effective communication between intelligent
sensors and actuators in vehicles. The LIN control
unit subnet is used in every situation where the
bandwidth and versatility of CAN is not needed.
The LIN specification comprises the LIN protocol,
a standard format for describing a complete LIN
and the interface between an LIN and the
application. An LIN comprises a LIN master and
one or more LIN slaves. The LIN utilizes the
master/slave principle for the purpose of bus
access control. This has the significant advantage
that few resources (CPU performance, ROM, RAM)
are required for bus management in the slave
module. The master is implemented in a control
module or a gateway which has the necessary
resources. All communication is initiated by the
master. Consequently, a message always consists
of a header, which is generated by the master, and
a response from the slave. The data transfer rate
is in the region of up to 20 Kbit/s. The LIN master
knows the time sequence of all data which are to
be transmitted. These data are transmitted by the
corresponding LIN slaves (e.g. ultrasonic sensors)
if they are requested to do so by the LIN master.
LIN is a single-wire bus, i.e. the data are
transmitted in the cable via one wire. Usually the
same cable is also used to provide the supply
voltage. The ground connection of the supply
voltage also acts as the ground connection of the
data transmission. An LIN does not use a
terminating resistor.
Controller Area Network (CAN) bus
This consists of two twisted wires and operates
serially (data is transmitted sequentially). It is used
for communication between the modules
themselves and between the modules and the Ford
diagnostic unit. The modules are connected to the
data bus in parallel. New modules can be
incorporated easily, without modifying the other
wiring or modules. The transmitted data is received
by every module connected to the control unit
network (CAN). As each data packet has an
identifier (label), in which the priority of the
message is determined as well as the content
identification, each module can detect whether or
not the data is relevant for its own information
processing. This enables several modules to be
addressed with a particular data packet and
supplied with data simultaneously. For this
purpose, it is ensured that important data (for
example from the ABS) is transmitted first. The
other modules are only able to submit their data to
the data bus after the high-priority messages have
been received.
The advantages of the CAN bus are:
• Minimization of wiring requirements
•
High degree of error protection (fault / fail-proof)
• Robustness
• Good extendibility
• Prioritization of messages
• Inexpensive
• Automatic repetition of faulty messages
• Independent system monitoring and the ability to disconnect faulty modules from the data bus
automatically
Due to the increased number of modules and the
resulting continued increase in data transfer, two
different CAN bus systems are used. Essentially,
they only differ in terms of their data transmission
rates and application areas.
To be able to distinguish between the individual
CAN bus systems, the CAN bus system with the
high transfer speed is called the high speed CAN
bus (HS-CAN). The data are transmitted at a baud
rate of 500 kB/s.
The CAN bus system with the medium transfer
speed is called the medium speed CAN bus
(MS-CAN) and is mainly used for communication
in the comfort electronics or the multimedia system.
The data are transmitted at a baud rate of 125 kB/s.
An interface (gateway) is used to exchange data
between the HS-CAN and the MS-CAN. This
provides the connection between the three CAN
databus systems and is installed in the GEM and
in the electronic instrument cluster. The number of
modules which are connected to the three databus G1030779en
2008.50 Kuga 8/2011 418-00-7
Module Communications Network
418-00-7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATIONTO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 385 of 2057

systems depends on the equipment level of the
vehicle.
In order to guarantee a high degree of error
protection, two 120 Ohm terminating resistors are
installed in the CAN. These are integrated in the
first module connected to the CAN and in the last
module connected to the CAN respectively and
are used for suppression as well as the elimination
of voltage peaks. In order to ensure correct
functioning of the data bus system, the modules
must always be connected with an integral
terminating resistor. In order to enable
communication between the modules on the
HS-CAN and the modules on the MS-CAN, one
module is connected to both data bus systems.
The connection of both data bus systems is
designated as a gateway. In this gateway, the
received data is converted to the transmission rate
required for the relevant data bus and is
transmitted. This ensures an optimal distribution
of information between both data bus systems.
Component Description
ABS
The GEM is integrated in the CJB (central junction
box) and cannot be replaced as a separate unit.
G1030779en
2008.50 Kuga 8/2011 418-00-8
Module Communications Network
418-00-8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATIONTO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 386 of 2057
Communications Network
Special Tool(s) / General Equipment
Terminal Probe Kit
418-S035Digital multimeter
The Ford approved diagnostic tool
Inspection and Checking
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of mechanical
or electrical damage.
NOTE: Ensure correct locking of wiring harness
connectors.
Visual Inspection Chart Electrical
- Fuse(s)
- Wiring harness - Connector
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible)
before proceeding to the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the diagnostic tab within
the Ford approved diagnostic tool. G1055035en
2008.50 Kuga 8/2011 418-00-9
Module Communications Network
418-00-9
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGTO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL29011A
Page 387 of 2057

SECTION 418-01 Module Configuration
VEHICLE APPLICATION:
2008.50 Kuga
PAGE
CONTENTS
GENERAL PROCEDURES
418-01-2
Module Configuration ..........................................................................................................
418-01-3
Programmable Module Installation ..................................................................................... 418-01-1
Module Configuration
418-01-1
.TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 388 of 2057

Module Configuration
Activation
1.
Install the most up-to-date software version in
the integrated diagnostic system (IDS).
2. In IDS, select the "Module reprogramming"
submenu in the "Module programming" menu
tool box and then follow the instructions.
3. Transfer a new software version (if available)
to the powertrain control module (PCM) using
IDS, if a module-reprogramming of the PCM
may be required in the case of engine running
concerns.
4. Following installation of a wheel/tire
combination, for which the tire-tread
circumference does not correspond to that of
standard tires, the tire size must be changed in
the PCM using IDS. Therefore select the
"Programmable parameters" submenu and enter
the corresponding tire size under the "tire size"
menu item. G1158256en
2008.50 Kuga 8/2011 418-01-2
Module Configuration
418-01-2
GENERAL PROCEDURESTO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 389 of 2057

Programmable Module Installation
Activation
5.
Install the most up-to-date software version in
IDS.
6. If, before replacing a module, it was not possible
to read out the vehicle-specific data using the
integrated diagnostic system (IDS) (the module
to be replaced does not respond) then, during
programming of the new module, the
vehicle-specific data must be entered manually
via a selection list in IDS or via a code which
can be obtained from the Technical Hotline.
7. In order to program, select the "Install
programmable module" submenu in the "Module
programming" menu tool box and then follow
the instructions.
8. The following modules must be programmed
after replacement:
•
• Anti-lock braking system module (ABS)
• Audio system module (ACM)
• CD player (CDP)
• Driver's door control unit (D-DCU)
• Passenger's door control unit (P-DCU)
• Rear left door control unit (RL-DCU)
• Rear right door control unit (RR-DCU)
• Electrical power steering (EPS)
• Generic Display Module (GDM) (vehicles
with DVD navigation system with
touchscreen)
• Generic electronic module (GEM)
• Headlamp control module (HCM) (vehicles with gas discharge headlamps)
• Instrument cluster (IC)
• Navigation system (NAV) (vehicles with navigation system)
• Parking aid module(PAM)
• Powertrain control module (PCM)
• Restraint control module (RCM)
• Rear entertainment system module (RETM) (vehicles with rear seat entertainment
system)
9. In order to configure the PCM, select the
"Programmable parameters" submenu in the
"Module programming" menu tool box and then
follow the instructions.
10. For vehicles with anti-lock braking system and
electronic stability program, these must also be configured using IDS following replacement of
the lateral acceleration sensor, yaw rate sensor
or pressure sensor. Configuration is performed
in the "Programmable parameters" menu tool
box.
G1158258en
2008.50 Kuga 8/2011 418-01-3
Module Configuration
418-01-3
GENERAL PROCEDURESTO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 390 of 2057

SECTION 418-02 Wiring Harnesses
VEHICLE APPLICATION:
2008.50 Kuga
PAGE
CONTENTS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
418-02-2
Wiring Harness...................................................................................................................
418-02-2
Inspection and Verification..................................................................................................
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION 418-02-4
Passenger Compartment Wiring Harness..........................................................................
418-02-24
Instrument Panel Wiring Harness.......................................................................................
418-02-37
Engine Compartment Wiring Harness................................................................................ 418-02-1
Wiring Harnesses
418-02-1
.TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 391 of 2057

Wiring Harness
General Equipment
Ford approved diagnostic tool
Inspection and Verification
1. Verify the customer concern. 2. Check the electrical connectors for security,
damage and incorrect connection. If the
electrical connectors are broken, damaged or
incorrectly connected, repair or replace the
components as required. TEST the system for
normal operation before proceeding to the next
step. 3. Disconnect the electrical connectors and check
for the following:
• Moisture in the connector due to misaligned, damaged or missing seals.
• Contamination from leaking fluids in the region of the connector. • Damaged or oxidised connector pins.
•
Disengaged connector pins (this can be checked
by carefully pressing on the individual pins).
4. If any of the conditions listed are present, repair or replace the components as required. TEST
the system for normal operation before
proceeding to the next step. G1021921en
2008.50 Kuga 8/2011 418-02-2
Wiring Harnesses
418-02-2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGTO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUALE61215