fuel line FORD KUGA 2011 1.G Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 2011, Model line: KUGA, Model: FORD KUGA 2011 1.GPages: 2057
Page 1849 of 2057
21
22 20 19
15 14 13
161718 12
876
9
10
11 5
3
42121
22 20 19
15 14 13
161718 12
876
9
10
11 5
3
421
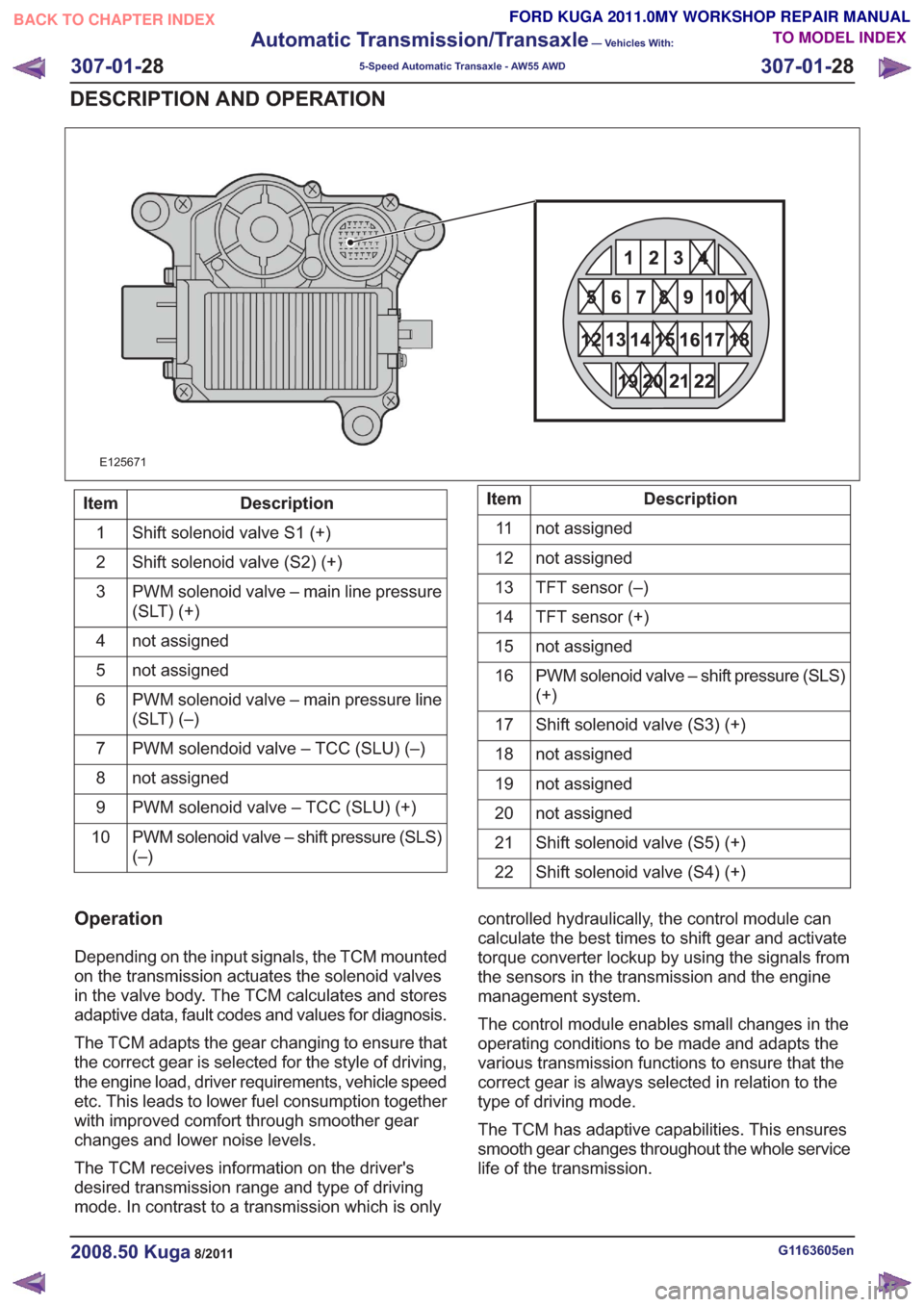
E125671
Description
Item
Shift solenoid valve S1 (+)
1
Shift solenoid valve (S2) (+)
2
PWM solenoid valve – main line pressure
(SLT) (+)
3
not assigned
4
not assigned
5
PWM solenoid valve – main pressure line
(SLT) (–)
6
PWM solendoid valve – TCC (SLU) (–)
7
not assigned
8
PWM solenoid valve – TCC (SLU) (+)
9
PWM solenoid valve – shift pressure (SLS)
(–)
10Description
Item
not assigned
11
not assigned
12
TFT sensor (–)
13
TFT sensor (+)
14
not assigned
15
PWM solenoid valve – shift pressure (SLS)
(+)
16
Shift solenoid valve (S3) (+)
17
not assigned
18
not assigned
19
not assigned
20
Shift solenoid valve (S5) (+)
21
Shift solenoid valve (S4) (+)
22
Operation
Depending on the input signals, the TCM mounted
on the transmission actuates the solenoid valves
in the valve body. The TCM calculates and stores
adaptive data, fault codes and values for diagnosis.
The TCM adapts the gear changing to ensure that
the correct gear is selected for the style of driving,
the engine load, driver requirements, vehicle speed
etc. This leads to lower fuel consumption together
with improved comfort through smoother gear
changes and lower noise levels.
The TCM receives information on the driver's
desired transmission range and type of driving
mode. In contrast to a transmission which is only controlled hydraulically, the control module can
calculate the best times to shift gear and activate
torque converter lockup by using the signals from
the sensors in the transmission and the engine
management system.
The control module enables small changes in the
operating conditions to be made and adapts the
various transmission functions to ensure that the
correct gear is always selected in relation to the
type of driving mode.
The TCM has adaptive capabilities. This ensures
smooth gear changes throughout the whole service
life of the transmission.
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01-
28
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 28
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1867 of 2057
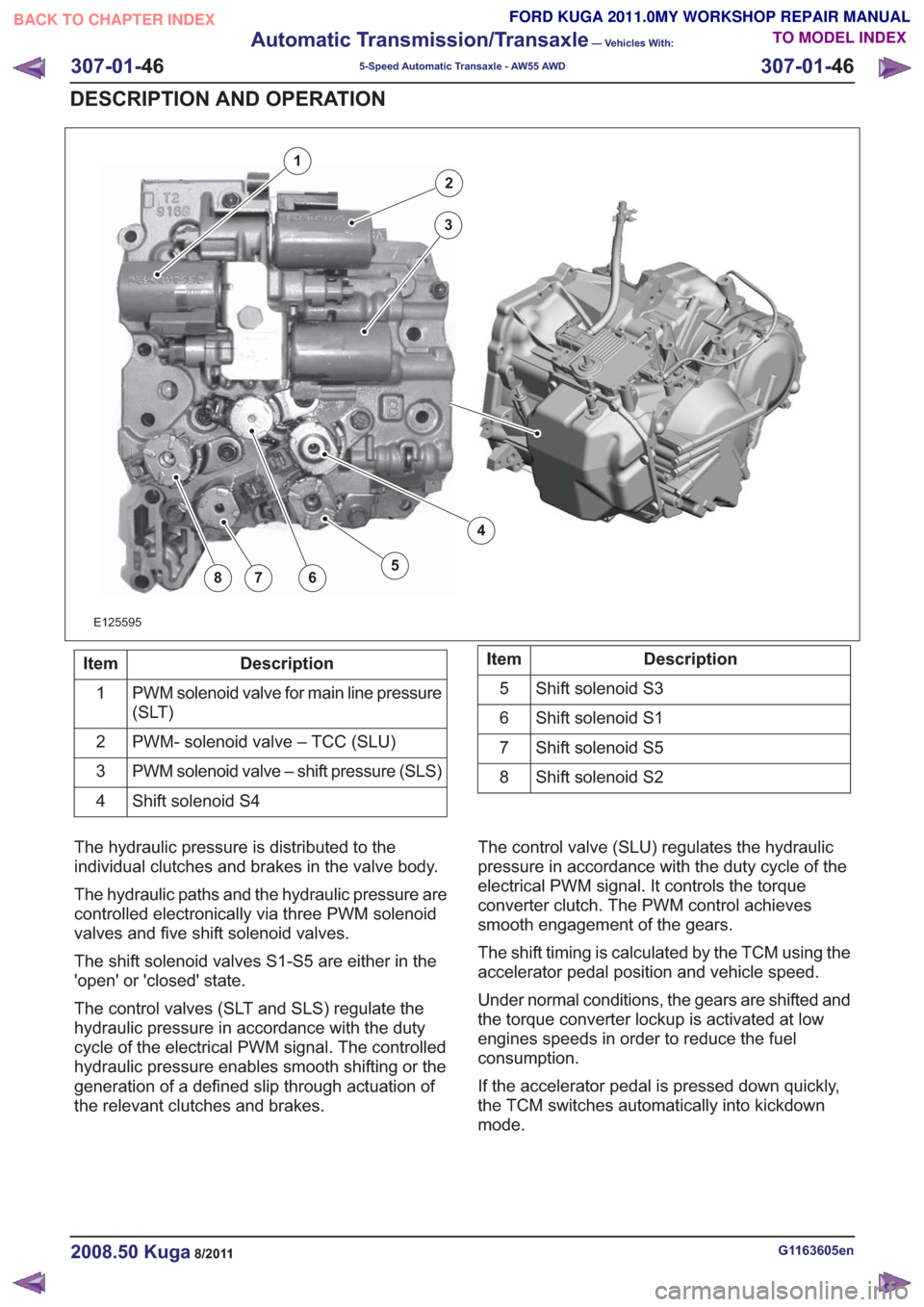
E125595
2
3
4
5678
1
Description
Item
PWM solenoid valve for main line pressure
(SLT)
1
PWM- solenoid valve – TCC (SLU)
2
PWM solenoid valve – shift pressure (SLS)
3
Shift solenoid S4
4Description
Item
Shift solenoid S3
5
Shift solenoid S1
6
Shift solenoid S5
7
Shift solenoid S2
8
The hydraulic pressure is distributed to the
individual clutches and brakes in the valve body.
The hydraulic paths and the hydraulic pressure are
controlled electronically via three PWM solenoid
valves and five shift solenoid valves.
The shift solenoid valves S1-S5 are either in the
'open' or 'closed' state.
The control valves (SLT and SLS) regulate the
hydraulic pressure in accordance with the duty
cycle of the electrical PWM signal. The controlled
hydraulic pressure enables smooth shifting or the
generation of a defined slip through actuation of
the relevant clutches and brakes. The control valve (SLU) regulates the hydraulic
pressure in accordance with the duty cycle of the
electrical PWM signal. It controls the torque
converter clutch. The PWM control achieves
smooth engagement of the gears.
The shift timing is calculated by the TCM using the
accelerator pedal position and vehicle speed.
Under normal conditions, the gears are shifted and
the torque converter lockup is activated at low
engines speeds in order to reduce the fuel
consumption.
If the accelerator pedal is pressed down quickly,
the TCM switches automatically into kickdown
mode.
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01-
46
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 46
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1870 of 2057
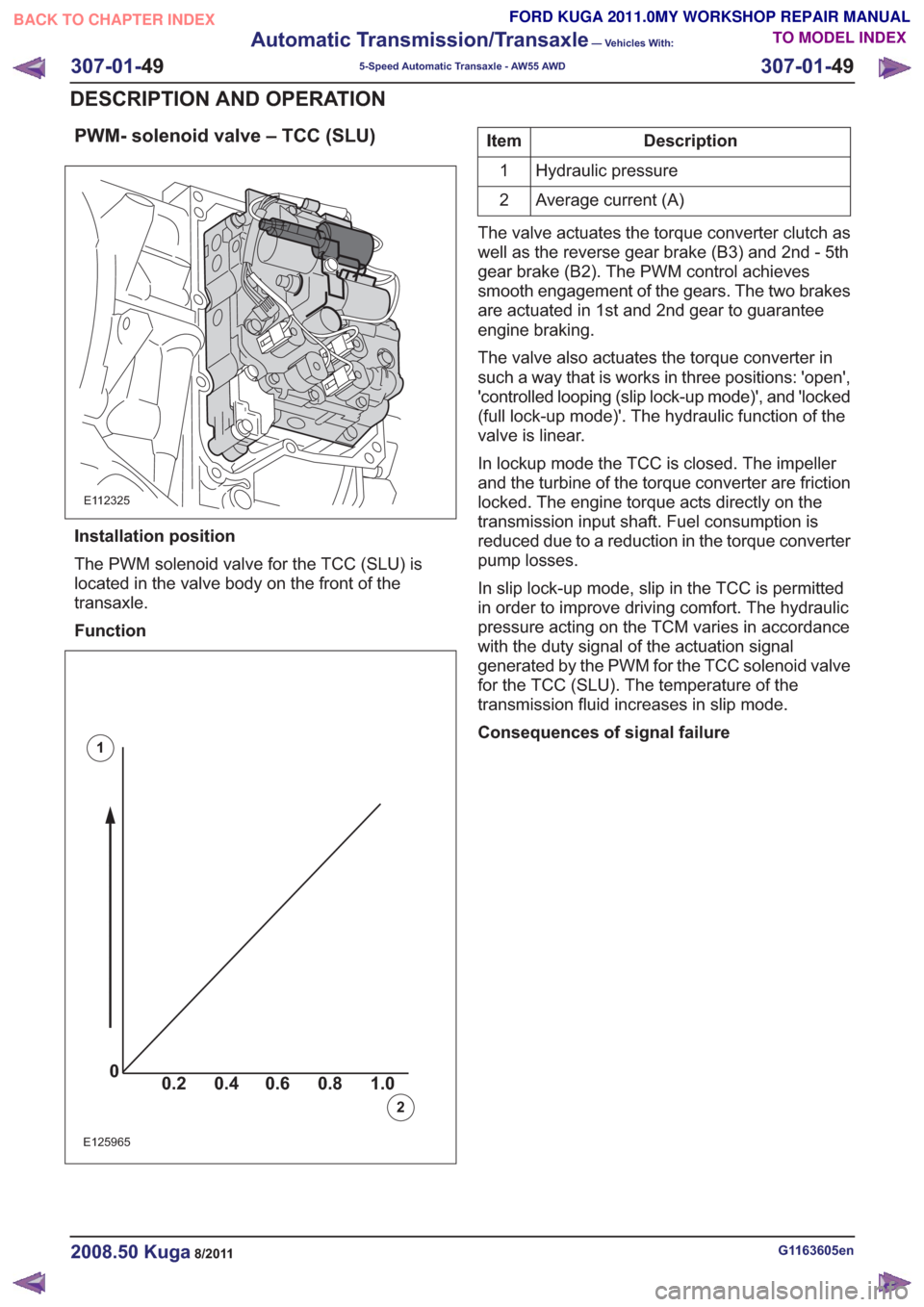
PWM- solenoid valve – TCC (SLU)
E112325
Installation position
The PWM solenoid valve for the TCC (SLU) is
located in the valve body on the front of the
transaxle.
Function
00.2 1.0 0.80.60.4
0
0.2 1.0
0.80.60.4
0
0.2 1.0
0.80.60.40
0.2 1.0 0.80.60.4
E125965
1
2
Description
Item
Hydraulic pressure
1
Average current (A)
2
The valve actuates the torque converter clutch as
well as the reverse gear brake (B3) and 2nd - 5th
gear brake (B2). The PWM control achieves
smooth engagement of the gears. The two brakes
are actuated in 1st and 2nd gear to guarantee
engine braking.
The valve also actuates the torque converter in
such a way that is works in three positions: 'open',
'controlled looping (slip lock-up mode)', and 'locked
(full lock-up mode)'. The hydraulic function of the
valve is linear.
In lockup mode the TCC is closed. The impeller
and the turbine of the torque converter are friction
locked. The engine torque acts directly on the
transmission input shaft. Fuel consumption is
reduced due to a reduction in the torque converter
pump losses.
In slip lock-up mode, slip in the TCC is permitted
in order to improve driving comfort. The hydraulic
pressure acting on the TCM varies in accordance
with the duty signal of the actuation signal
generated by the PWM for the TCC solenoid valve
for the TCC (SLU). The temperature of the
transmission fluid increases in slip mode.
Consequences of signal failure
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 49
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 49
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1876 of 2057
Description
Item
Drive
3
Intake side
4
Delivery side
5
The fluid pump operates on the principle of a
G-rotor fluid pump.
The fluid pump draws transmission fluid from the
fluid pan, builds up fluid pressure and then supplies
it to the valve body.
The fluid pump is driven by the crankshaft via the
torque converter housing.
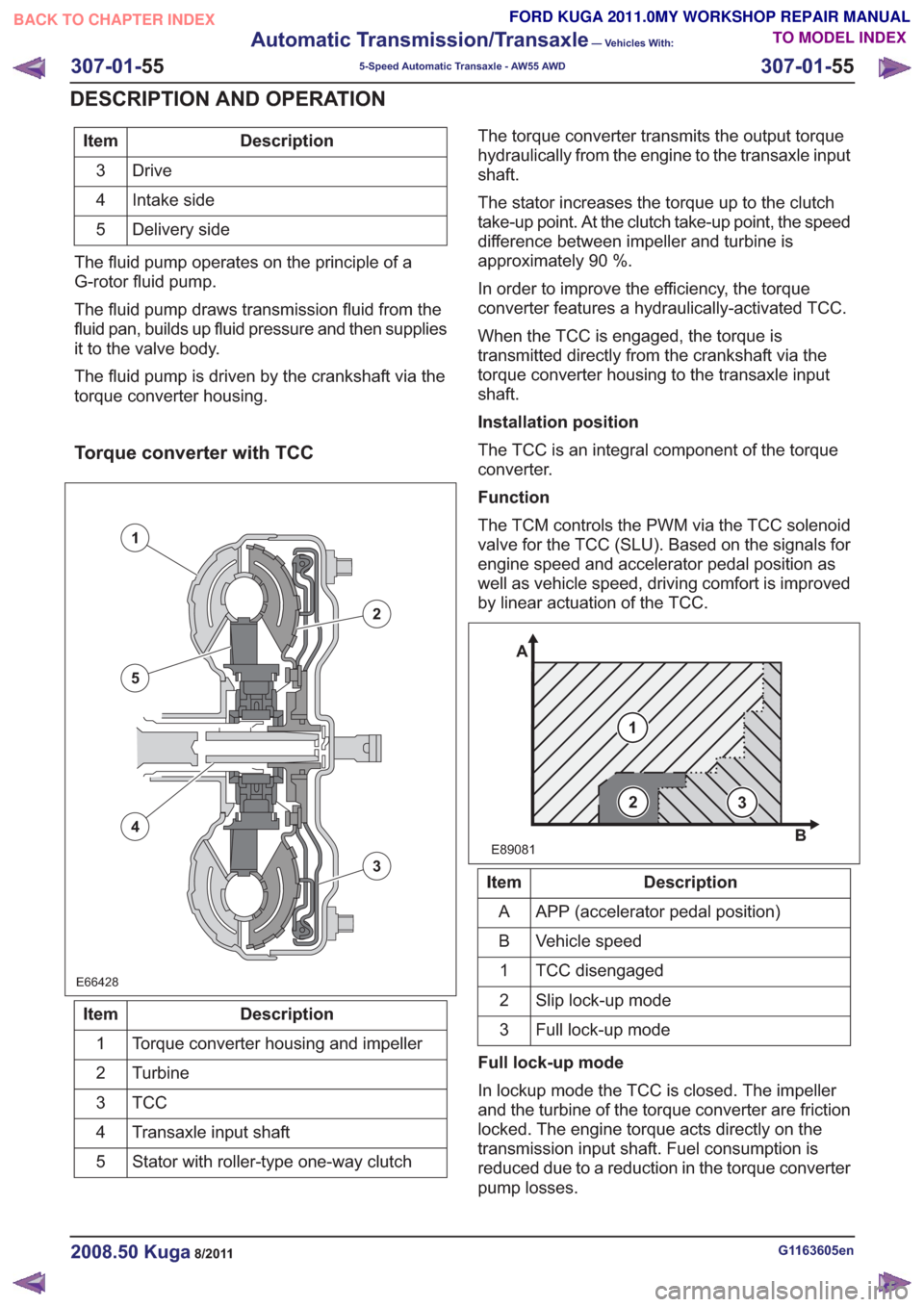
Torque converter with TCC
E66428E66428
1
2
3
5
4
Description
Item
Torque converter housing and impeller
1
Turbine
2
TCC3
Transaxle input shaft
4
Stator with roller-type one-way clutch
5 The torque converter transmits the output torque
hydraulically from the engine to the transaxle input
shaft.
The stator increases the torque up to the clutch
take-up point. At the clutch take-up point, the speed
difference between impeller and turbine is
approximately 90 %.
In order to improve the efficiency, the torque
converter features a hydraulically-activated TCC.
When the TCC is engaged, the torque is
transmitted directly from the crankshaft via the
torque converter housing to the transaxle input
shaft.
Installation position
The TCC is an integral component of the torque
converter.
Function
The TCM controls the PWM via the TCC solenoid
valve for the TCC (SLU). Based on the signals for
engine speed and accelerator pedal position as
well as vehicle speed, driving comfort is improved
by linear actuation of the TCC.
E89081
1
A
B
23
Description
Item
APP (accelerator pedal position)
A
Vehicle speed
B
TCC disengaged
1
Slip lock-up mode
2
Full lock-up mode
3
Full lock-up mode
In lockup mode the TCC is closed. The impeller
and the turbine of the torque converter are friction
locked. The engine torque acts directly on the
transmission input shaft. Fuel consumption is
reduced due to a reduction in the torque converter
pump losses.
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 55
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 55
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1970 of 2057

Fuel System — Vehicles With: Fuel Additive Tank
General EquipmentFord diagnostic equipment
Principles of Operation
WARNINGS:
This procedure involves fuel additive
handling. Be prepared for fuel additive
spillage at all times and always observe
fuel handling precautions. Failure to follow
these instructions may result in personal
injury.
Eye, hand, ear protection and protective
clothing are required to be worn during
any general service or removal and
installation service procedure of fuel
additive system components. Failure to
follow this instruction may result in
personal injury.
In case of fuel additive fluid contact with
the skin or the eyes, flush immediately with
water for a minimum of 15 minutes and
seek prompt medical attention. Failure to
follow these instructions may result in
personal injury.
If fuel additive fluid is swallowed, call a
physician immediately. Rinse mouth
immediately with water, do not induce
vomiting. Failure to follow these
instructions may result in personal injury.
Always provide adequate ventilation when
working on the fuel additive fluid system
or related components. Failure to follow
these instructions may result in personal
injury.
Do not smoke or carry lighted tobacco or
open flame of any type when working on
or near any fuel related components.
Highly flammable vapors are always
present and may ignite. Failure to follow
these instructions may result in personal
injury.
CAUTION: Make sure the workshop area
in which the vehicle is being worked on is
as clean and as dust free as possible.
Foreign matter from working on clutches,
brakes or from machining or welding
operations can contaminate the fuel
system and may result in later malfunction. The fuel additive system is an on-board system
that allows the injection of an additive at each
refueling operation by the customer. The additive
quantity is proportional to the fuel quantity that has
been added. The fuel additive system module
controls the amount of additive fluid entering the
fuel tank at each refueling, A switch mounted on
the fuel filler flap is used to detect the start of the
refueling event and the fuel gauge that is mounted
within the fuel tank informs the fuel additive tank
module the quantity of actual fuel added.
Inspection and Verification
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of leakage
and mechanical or electrical damage.
Visual Inspection Chart
Electrical
Mechanical
– Fuse(s)
– Fuel filler switch andmagnet
– Wiring harness(s)
– Electrical connector(s)
– Fuel additive system module
– Fuel additive tank module
– Instrument cluster
– Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
– Fuel level sensor
– Fuel additive tank
– Fuel additive tank
line(s)
– Fuel additive tank pipe(s)
– Fuel additive tank connector(s)
– Fuel tank filler cap
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible)
before proceeding to the next step
4. If the cause is not visually evident, REFER to the Ford diagnostic equipment.
G1080718en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
310-00- 2
Fuel System - General Information
310-00- 2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1971 of 2057

Spring Lock Couplings
Special Tool(s)310-040
Disconnect Tool, Fuel Line
(5/16")
23041
310-137
Disconnect Tool, Fuel Line
E51255
310-D004
Disconnect Tool, Spring Lock
Coupling (3/8" yellow)
23039
310-D005
Disconnect Tool, Spring Lock
Coupling (1/2" green)
23-040
412-038
Disconnect Tool, Spring Lock
Coupling (5/8" black)
34003
412-069
Disconnect Tool, Spring Lock
Coupling (3/4" white)
34002
Materials
Specification
Name
WSS-M2C153-G
Engine Oil - 5W-30
Disconnect
WARNINGS:
Refer to: Petrol and Petrol-Ethanol Fuel
Systems Health and Safety Precautions
(100-00 General Information, Description
and Operation).
NOTE: Fuel supply line connectors are color coded
white. Fuel return line connectors are color coded
red.
1. Release the fuel system pressure
Refer to: Fuel System Pressure Release
(310-00 Fuel System - General Information,
General Procedures).
2. Special Tool(s): 310-137
E77752
G544275en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
310-00- 3
Fuel System - General Information
310-00- 3
GENERAL PROCEDURES
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1974 of 2057
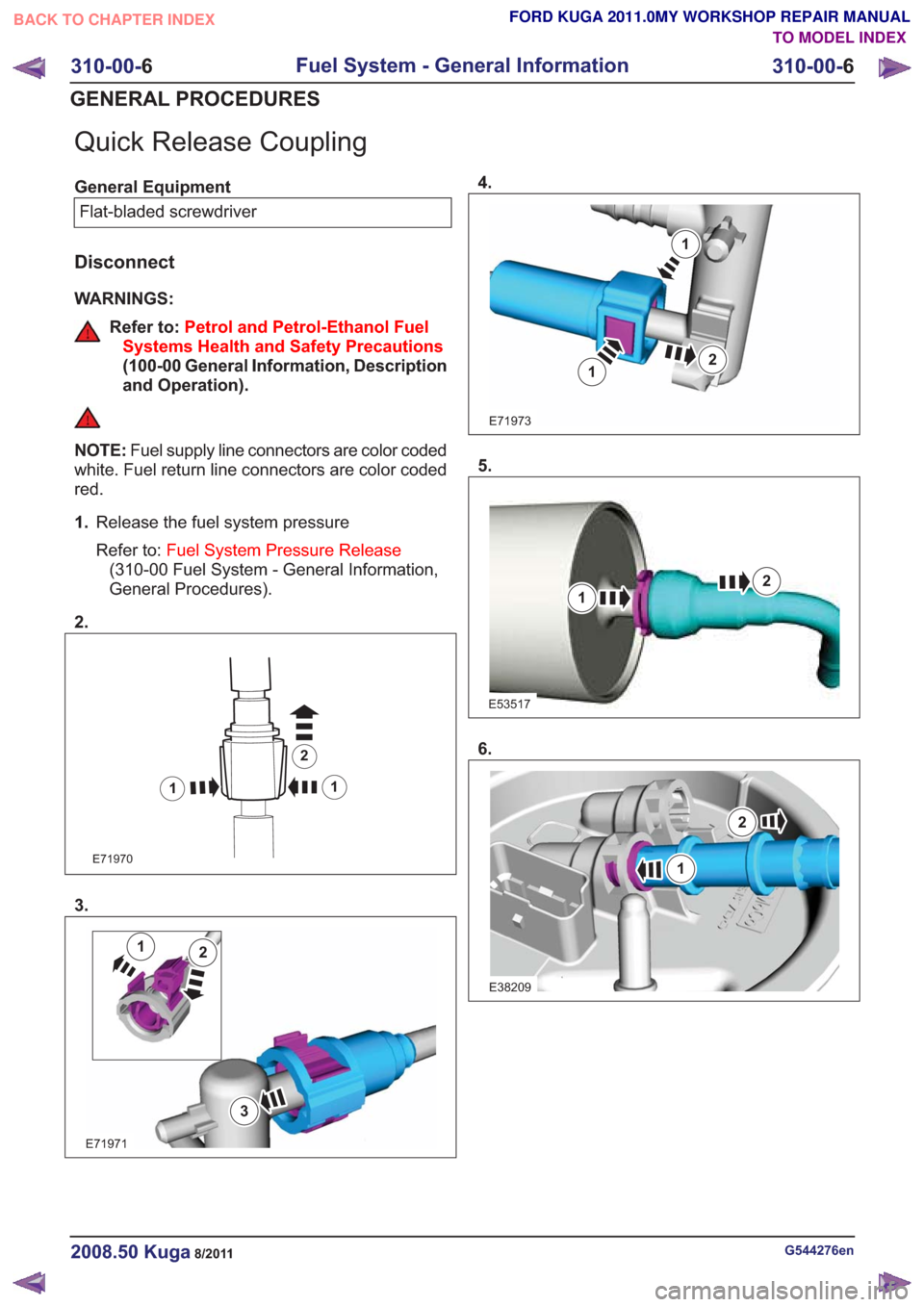
Quick Release Coupling
General EquipmentFlat-bladed screwdriver
Disconnect
WARNINGS:
Refer to: Petrol and Petrol-Ethanol Fuel
Systems Health and Safety Precautions
(100-00 General Information, Description
and Operation).
NOTE: Fuel supply line connectors are color coded
white. Fuel return line connectors are color coded
red.
1. Release the fuel system pressure
Refer to: Fuel System Pressure Release
(310-00 Fuel System - General Information,
General Procedures).
2.
E71970
1 2
1
3.
E71971
3
12
4.
E71973
21
1
5.
E53517
1
2
6.
E38209
2
1
G544276en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
310-00- 6
Fuel System - General Information
310-00- 6
GENERAL PROCEDURES
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1979 of 2057

Fuel Tank Draining
General EquipmentFluid Container
Fuel Tank Draining Equipment
Hose Clamp Remover/Installer
Activation
CAUTION: If the fuel tank has been filled
with the wrong type of fuel, the engine
must not be started.
NOTE: Removal steps in this procedure may
contain installation details.
6. Refer to: Petrol and Petrol-Ethanol Fuel
Systems Health and Safety Precautions
(100-00 General Information, Description and
Operation).
7. Refer to: Lifting(100-02 Jacking and Lifting,
Description and Operation).
8. WARNINGS:
Fuel may still be present in the fuel tank
after draining.
Be prepared to collect escaping fluids.
CAUTION: Use suitable paper to absorb
any escaping fluid. NOTE:
Make sure that a new component is
installed.
• General Equipment: Hose Clamp Remover/Installer
1. Make sure, that the fuel filler pipe is above the fuel level .
2. Drain the reservoir.
General Equipment: Fuel Tank DrainingEquipment
General Equipment: Fluid Container12
E116177
9. Refer to: Fuel Pump and Sender Unit - 2.5L
Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5 (310-01 Fuel
Tank and Lines, Removal and Installation).
10. WARNING: Be prepared to collect escaping fluids.
CAUTION: Use suitable paper to absorb
any escaping fluid.
G1165328en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
310-00- 11
Fuel System - General Information
310-00- 11
GENERAL PROCEDURES
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1981 of 2057

SECTION 310-01 Fuel Tank and Lines
VEHICLE APPLICATION:2008.50 Kuga
PA G E
CONTENTS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
310-01-2
Fuel Tank and Lines — 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5 (Component Location) .........
310-01-5
Fuel Tank and Lines — 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5 (Overview) ............................
310-01-5
Fuel tank ........................................................................\
.....................................................
310-01-5
Fuel pump and sender unit ........................................................................\
.........................
310-01-6
Fuel filler pipe and tank cap........................................................................\
........................
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION 310-01-8
Fuel Tank — 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5 ...............................................................
310-01-11
Fuel Level Sensor — 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5 .................................................
310-01-12
Fuel Tank Filler Pipe ........................................................................\
...................................
310-01-14
Fuel Filler Nozzle Inhibitor ........................................................................\
..........................
310-01-18
Fuel Pump and Sender Unit — 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5 ..................................
310-01-1
Fuel Tank and Lines
310-01- 1
.
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1982 of 2057
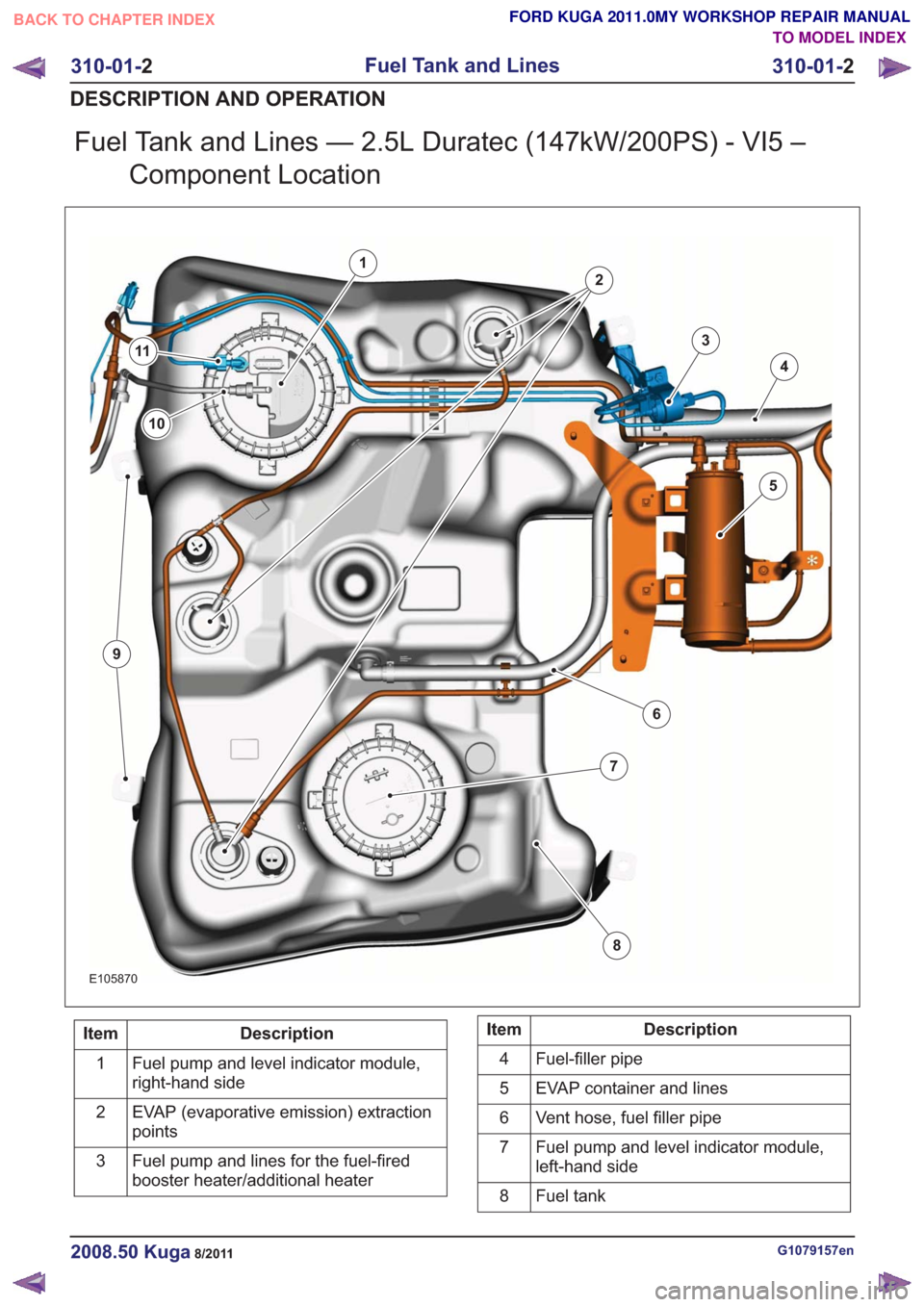
Fuel Tank and Lines — 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5 –Component Location
E105870
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
10
9
11
Description
Item
Fuel pump and level indicator module,
right-hand side
1
EVAP (evaporative emission) extraction
points
2
Fuel pump and lines for the fuel-fired
booster heater/additional heater
3Description
Item
Fuel-filler pipe
4
EVAP container and lines
5
Vent hose, fuel filler pipe
6
Fuel pump and level indicator module,
left-hand side
7
Fuel tank
8
G1079157en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
310-01- 2
Fuel Tank and Lines
310-01- 2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL