fuel FORD SIERRA 1982 1.G Reference Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1982, Model line: SIERRA, Model: FORD SIERRA 1982 1.GPages: 26, PDF Size: 0.57 MB
Page 3 of 26
Buying spare parts
Spare parts are available from many
sources, including maker’s appointed
garages, accessory shops, and motor factors.
To be sure of obtaining the correct parts, it
will sometimes be necessary to quote the
vehicle identification number. If possible, it
can also be useful to take the old parts along
for positive identification. Items such as
starter motors and alternators may be
available under a service exchange scheme -
any parts returned should always be clean.
Our advice regarding spare part sources is
as follows.
Officially-appointed garages
This is the best source of parts which are
peculiar to your car, and which are not
otherwise generally available (eg badges,
interior trim, certain body panels, etc). It is
also the only place at which you should buy
parts if the vehicle is still under warranty.
Accessory shops
These are very good places to buy
materials and components needed for themaintenance of your car (oil, air and fuel
filters, spark plugs, light bulbs, drivebelts, oils
and greases, brake pads, touch-up paint, etc).
Components of this nature sold by a
reputable shop are of the same standard as
those used by the car manufacturer.
Besides components, these shops also sell
tools and general accessories, usually have
convenient opening hours, charge lower
prices, and can often be found not far from
home. Some accessory shops have parts
counters where the components needed for
almost any repair job can be purchased or
ordered.
Motor factors
Good factors will stock all the more
important components which wear out
comparatively quickly, and can sometimes
supply individual components needed for the
overhaul of a larger assembly (eg brake seals
and hydraulic parts, bearing shells, pistons,
valves, alternator brushes). They may also
handle work such as cylinder block reboring,
crankshaft regrinding and balancing, etc.
Tyre and exhaust specialists
These outlets may be independent, or
members of a local or national chain. They
frequently offer competitive prices when
compared with a main dealer or local garage,
but it will pay to obtain several quotes before
making a decision. When researching prices,
also ask what “extras” may be added - for
instance, fitting a new valve and balancing the
wheel are both commonly charged on top of
the price of a new tyre.
Other sources
Beware of parts or materials obtained from
market stalls, car boot sales or similar outlets.
Such items are not invariably sub-standard,
but there is little chance of compensation if
they do prove unsatisfactory. In the case of
safety-critical components such as brake
pads, there is the risk not only of financial loss
but also of an accident causing injury or death.
Second-hand components or assemblies
obtained from a car breaker can be a good
buy in some circumstances, but this sort of
purchase is best made by the experienced
DIY mechanic.
Vehicle identification numbers
Modifications are a continuing and
unpublicised process in vehicle manufacture,
quite apart from major model changes. Spareparts lists are compiled upon a numerical
basis, the individual vehicle identification
numbers being essential to correct
identification of the component concerned.
When ordering spare parts, always give as
much information as possible. Quote the car
model, year of manufacture, body and engine
numbers, as appropriate.
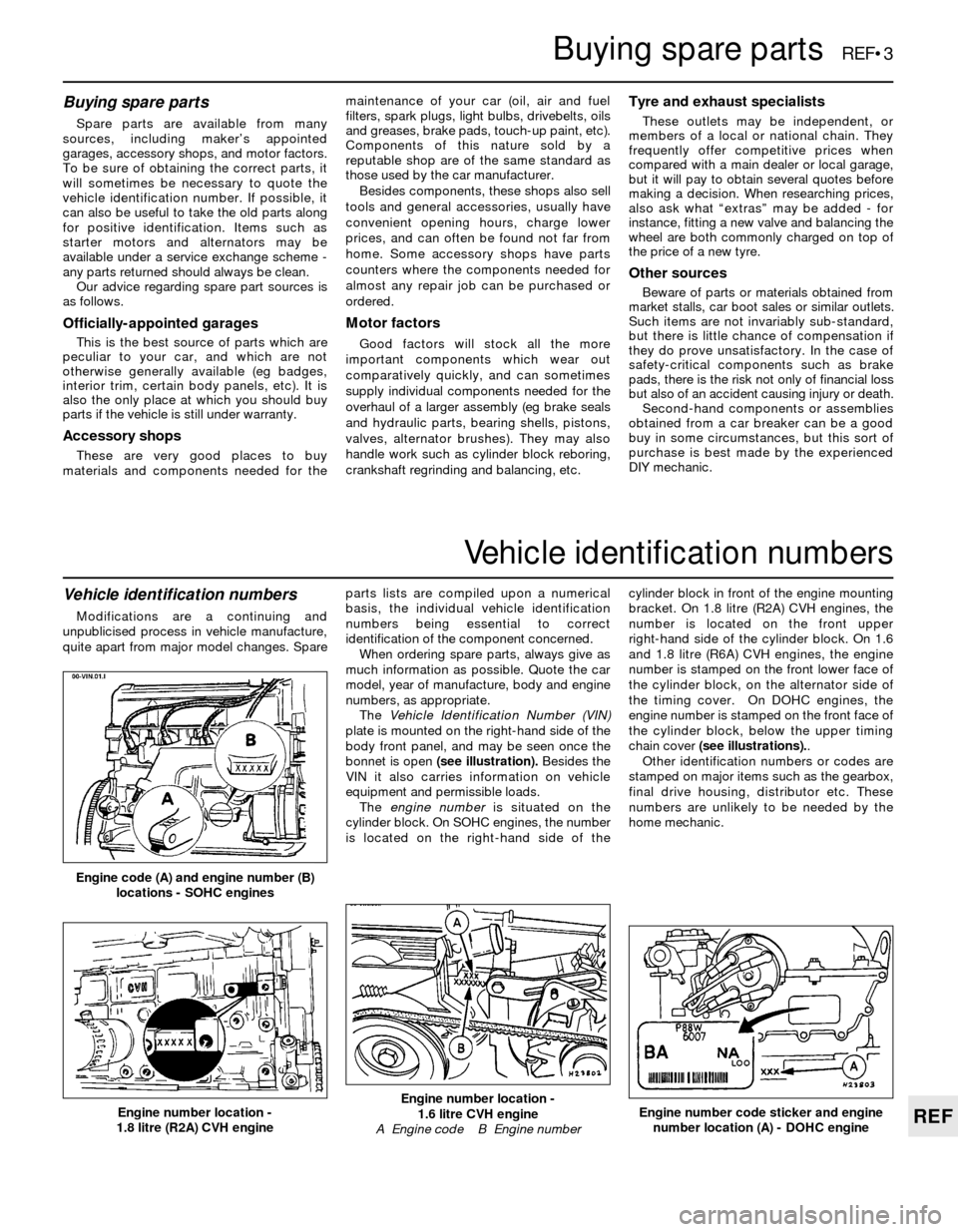
The Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
plate is mounted on the right-hand side of the
body front panel, and may be seen once the
bonnet is open (see illustration).Besides the
VIN it also carries information on vehicle
equipment and permissible loads.
The engine numberis situated on the
cylinder block. On SOHC engines, the number
is located on the right-hand side of thecylinder block in front of the engine mounting
bracket. On 1.8 litre (R2A) CVH engines, the
number is located on the front upper
right-hand side of the cylinder block. On 1.6
and 1.8 litre (R6A) CVH engines, the engine
number is stamped on the front lower face of
the cylinder block, on the alternator side of
the timing cover. On DOHC engines, the
engine number is stamped on the front face of
the cylinder block, below the upper timing
chain cover (see illustrations)..
Other identification numbers or codes are
stamped on major items such as the gearbox,
final drive housing, distributor etc. These
numbers are unlikely to be needed by the
home mechanic.
Buying spare parts REF•3
Engine code (A) and engine number (B)
locations - SOHC engines
Engine number location -
1.8 litre (R2A) CVH engineEngine number code sticker and engine
number location (A) - DOHC engineEngine number location -
1.6 litre CVH engine
A Engine code B Engine number
REF
Vehicle identification numbers
Page 4 of 26

Whenever servicing, repair or overhaul work
is carried out on the car or its components, it
is necessary to observe the following
procedures and instructions. This will assist in
carrying out the operation efficiently and to a
professional standard of workmanship.
Joint mating faces and gaskets
When separating components at their
mating faces, never insert screwdrivers or
similar implements into the joint between the
faces in order to prise them apart. This can
cause severe damage which results in oil
leaks, coolant leaks, etc upon reassembly.
Separation is usually achieved by tapping
along the joint with a soft-faced hammer in
order to break the seal. However, note that
this method may not be suitable where
dowels are used for component location.
Where a gasket is used between the mating
faces of two components, ensure that it is
renewed on reassembly, and fit it dry unless
otherwise stated in the repair procedure.
Make sure that the mating faces are clean and
dry, with all traces of old gasket removed.
When cleaning a joint face, use a tool which is
not likely to score or damage the face, and
remove any burrs or nicks with an oilstone or
fine file.
Make sure that tapped holes are cleaned
with a pipe cleaner, and keep them free of
jointing compound, if this is being used,
unless specifically instructed otherwise.
Ensure that all orifices, channels or pipes
are clear, and blow through them, preferably
using compressed air.
Oil seals
Oil seals can be removed by levering them
out with a wide flat-bladed screwdriver or
similar implement. Alternatively, a number of
self-tapping screws may be screwed into the
seal, and these used as a purchase for pliers or
some similar device in order to pull the seal free.
Whenever an oil seal is removed from its
working location, either individually or as part
of an assembly, it should be renewed.
The very fine sealing lip of the seal is easily
damaged, and will not seal if the surface it
contacts is not completely clean and free from
scratches, nicks or grooves. If the original
sealing surface of the component cannot be
restored, and the manufacturer has not made
provision for slight relocation of the seal
relative to the sealing surface, the component
should be renewed.
Protect the lips of the seal from any surface
which may damage them in the course of
fitting. Use tape or a conical sleeve where
possible. Lubricate the seal lips with oil before
fitting and, on dual-lipped seals, fill the space
between the lips with grease.
Unless otherwise stated, oil seals must be
fitted with their sealing lips toward the
lubricant to be sealed.
Use a tubular drift or block of wood of the
appropriate size to install the seal and, if the
seal housing is shouldered, drive the seal
down to the shoulder. If the seal housing is
unshouldered, the seal should be fitted withits face flush with the housing top face (unless
otherwise instructed).
Screw threads and fastenings
Seized nuts, bolts and screws are quite a
common occurrence where corrosion has set
in, and the use of penetrating oil or releasing
fluid will often overcome this problem if the
offending item is soaked for a while before
attempting to release it. The use of an impact
driver may also provide a means of releasing
such stubborn fastening devices, when used
in conjunction with the appropriate
screwdriver bit or socket. If none of these
methods works, it may be necessary to resort
to the careful application of heat, or the use of
a hacksaw or nut splitter device.
Studs are usually removed by locking two
nuts together on the threaded part, and then
using a spanner on the lower nut to unscrew the
stud. Studs or bolts which have broken off
below the surface of the component in which
they are mounted can sometimes be removed
using a proprietary stud extractor. Always
ensure that a blind tapped hole is completely
free from oil, grease, water or other fluid before
installing the bolt or stud. Failure to do this could
cause the housing to crack due to the hydraulic
action of the bolt or stud as it is screwed in.
When tightening a castellated nut to accept
a split pin, tighten the nut to the specified
torque, where applicable, and then tighten
further to the next split pin hole. Never
slacken the nut to align the split pin hole,
unless stated in the repair procedure.
When checking or retightening a nut or bolt
to a specified torque setting, slacken the nut
or bolt by a quarter of a turn, and then
retighten to the specified setting. However,
this should not be attempted where angular
tightening has been used.
For some screw fastenings, notably
cylinder head bolts or nuts, torque wrench
settings are no longer specified for the latter
stages of tightening, “angle-tightening” being
called up instead. Typically, a fairly low torque
wrench setting will be applied to the
bolts/nuts in the correct sequence, followed
by one or more stages of tightening through
specified angles.
Locknuts, locktabs and washers
Any fastening which will rotate against a
component or housing in the course of tightening
should always have a washer between it and the
relevant component or housing.
Spring or split washers should always be
renewed when they are used to lock a critical
component such as a big-end bearing
retaining bolt or nut. Locktabs which are
folded over to retain a nut or bolt should
always be renewed.
Self-locking nuts can be re-used in non-
critical areas, providing resistance can be felt
when the locking portion passes over the bolt or
stud thread. However, it should be noted that
self-locking stiffnuts tend to lose their
effectiveness after long periods of use, and insuch cases should be renewed as a matter of
course.
Split pins must always be replaced with
new ones of the correct size for the hole.
When thread-locking compound is found
on the threads of a fastener which is to be re-
used, it should be cleaned off with a wire
brush and solvent, and fresh compound
applied on reassembly.
Special tools
Some repair procedures in this manual
entail the use of special tools such as a press,
two or three-legged pullers, spring
compressors, etc. Wherever possible, suitable
readily-available alternatives to the
manufacturer’s special tools are described,
and are shown in use. In some instances,
where no alternative is possible, it has been
necessary to resort to the use of a
manufacturer’s tool, and this has been done
for reasons of safety as well as the efficient
completion of the repair operation. Unless you
are highly-skilled and have a thorough
understanding of the procedures described,
never attempt to bypass the use of any
special tool when the procedure described
specifies its use. Not only is there a very great
risk of personal injury, but expensive damage
could be caused to the components involved.
Environmental considerations
When disposing of used engine oil, brake
fluid, antifreeze, etc, give due consideration to
any detrimental environmental effects. Do not,
for instance, pour any of the above liquids
down drains into the general sewage system,
or onto the ground to soak away. Many local
council refuse tips provide a facility for waste
oil disposal, as do some garages. If none of
these facilities are available, consult your local
Environmental Health Department for further
advice.
With the universal tightening-up of
legislation regarding the emission of
environmentally-harmful substances from
motor vehicles, most current vehicles have
tamperproof devices fitted to the main
adjustment points of the fuel system. These
devices are primarily designed to prevent
unqualified persons from adjusting the fuel/air
mixture, with the chance of a consequent
increase in toxic emissions. If such devices
are encountered during servicing or overhaul,
they should, wherever possible, be renewed
or refitted in accordance with the vehicle
manufacturer’s requirements or current
legislation.
REF•4General Repair Procedures
Note: It is
antisocial and
illegal to dump oil
down the drain. To
find the location of
your local oil
recycling bank,
call this number
free.
Page 10 of 26

REF•10MOTtest checks
MExamine the handbrake mechanism,
checking for frayed or broken cables,
excessive corrosion, or wear or insecurity of
the linkage. Check that the mechanism works
on each relevant wheel, and releases fully,
without binding.
MIt is not possible to test brake efficiency
without special equipment, but a road test
can be carried out later to check that the
vehicle pulls up in a straight line.
Fuel and exhaust systems
MInspect the fuel tank (including the filler
cap), fuel pipes, hoses and unions. All
components must be secure and free from
leaks.
MExamine the exhaust system over its entire
length, checking for any damaged, broken or
missing mountings, security of the retaining
clamps and rust or corrosion.
Wheels and tyres
MExamine the sidewalls and tread area of
each tyre in turn. Check for cuts, tears, lumps,
bulges, separation of the tread, and exposure
of the ply or cord due to wear or damage.
Check that the tyre bead is correctly seated
on the wheel rim, that the valve is sound andproperly seated, and that the wheel is not
distorted or damaged.
MCheck that the tyres are of the correct size
for the vehicle, that they are of the same size
and type on each axle, and that the pressures
are correct.
MCheck the tyre tread depth. The legal
minimum at the time of writing is 1.6 mm over
at least three-quarters of the tread width.
Abnormal tread wear may indicate incorrect
front wheel alignment.
Body corrosion
MCheck the condition of the entire vehicle
structure for signs of corrosion in load-
bearing areas. (These include chassis box
sections, side sills, cross-members, pillars,
and all suspension, steering, braking system
and seat belt mountings and anchorages.)
Any corrosion which has seriously reduced
the thickness of a load-bearing area is likely to
cause the vehicle to fail. In this case
professional repairs are likely to be needed.
MDamage or corrosion which causes sharp
or otherwise dangerous edges to be exposed
will also cause the vehicle to fail.
Petrol models
MHave the engine at normal operating
temperature, and make sure that it is in good
tune (ignition system in good order, air filter
element clean, etc).
MBefore any measurements are carried out,
raise the engine speed to around 2500 rpm,
and hold it at this speed for 20 seconds. Allow
the engine speed to return to idle, and watchfor smoke emissions from the exhaust
tailpipe. If the idle speed is obviously much
too high, or if dense blue or clearly-visible
black smoke comes from the tailpipe for more
than 5 seconds, the vehicle will fail. As a rule
of thumb, blue smoke signifies oil being burnt
(engine wear) while black smoke signifies
unburnt fuel (dirty air cleaner element, or other
carburettor or fuel system fault).
MAn exhaust gas analyser capable of
measuring carbon monoxide (CO) and
hydrocarbons (HC) is now needed. If such an
instrument cannot be hired or borrowed, a
local garage may agree to perform the check
for a small fee.
CO emissions (mixture)
MAt the time of writing, the maximum CO
level at idle is 3.5% for vehicles first used after
August 1986 and 4.5% for older vehicles.
From January 1996 a much tighter limit
(around 0.5%) applies to catalyst-equipped
vehicles first used from August 1992. If the
CO level cannot be reduced far enough to
pass the test (and the fuel and ignition
systems are otherwise in good condition) then
the carburettor is badly worn, or there is some
problem in the fuel injection system or
catalytic converter (as applicable).
HC emissionsMWith the CO emissions within limits, HC
emissions must be no more than 1200 ppm
(parts per million). If the vehicle fails this test
at idle, it can be re-tested at around 2000
rpm; if the HC level is then 1200 ppm or less,
this counts as a pass.
MExcessive HC emissions can be caused by
oil being burnt, but they are more likely to be
due to unburnt fuel.
Diesel models
MThe only emission test applicable to Diesel
engines is the measuring of exhaust smoke
density. The test involves accelerating the
engine several times to its maximum
unloaded speed.
Note: It is of the utmost importance that the
engine timing belt is in good condition before
the test is carried out.
M
Excessive smoke can be caused by a dirty
air cleaner element. Otherwise, professional
advice may be needed to find the cause.
4Checks carried out on
YOUR VEHICLE’S EXHAUST
EMISSION SYSTEM
Page 11 of 26

The vehicle owner who does his or her own maintenance according
to the recommended service schedules should not have to use this
section of the manual very often. Modern component reliability is such
that, provided those items subject to wear or deterioration are
inspected or renewed at the specified intervals, sudden failure is
comparatively rare. Faults do not usually just happen as a result of
sudden failure, but develop over a period of time. Major mechanical
failures in particular are usually preceded by characteristic symptoms
over hundreds or even thousands of miles. Those components which
do occasionally fail without warning are often small and easily carried
in the vehicle.
With any fault-finding, the first step is to decide where to begin
investigations. Sometimes this is obvious, but on other occasions, alittle detective work will be necessary. The owner who makes half a
dozen haphazard adjustments or replacements may be successful in
curing a fault (or its symptoms), but will be none the wiser if the fault
recurs, and ultimately may have spent more time and money than was
necessary. A calm and logical approach will be found to be more
satisfactory in the long run. Always take into account any warning
signs or abnormalities that may have been noticed in the period
preceding the fault - power loss, high or low gauge readings, unusual
smells, etc - and remember that failure of components such as fuses or
spark plugs may only be pointers to some underlying fault.
The pages which follow provide an easy-reference guide to the more
common problems which may occur during the operation of the
vehicle. These problems and their possible causes are grouped under
Fault diagnosisREF•11
REF
Engine
MEngine fails to rotate when attempting to start
MStarter motor turns engine slowly
MEngine rotates, but will not start
MEngine difficult to start when cold
MEngine difficult to start when hot
MStarter motor noisy or excessively-rough in engagement
MEngine starts, but stops immediately
MEngine idles erratically
MEngine misfires at idle speed
MEngine misfires throughout the driving speed range
MEngine hesitates on acceleration
MEngine stalls
MEngine lacks power
MEngine backfires
MOil pressure warning light illuminated with engine running
MEngine runs-on after switching off
MEngine noises
Cooling system
MOverheating
MOvercooling
MExternal coolant leakage
MInternal coolant leakage
MCorrosion
Fuel and exhaust systems
MExcessive fuel consumption
MFuel leakage and/or fuel odour
MExcessive noise or fumes from exhaust system
Clutch
MPedal travels to floor - no pressure or very little resistance
MClutch fails to disengage (unable to select gears)
MClutch slips (engine speed increases; no increase in vehicle speed)
MJudder as clutch is engaged
MNoise when depressing or releasing clutch pedal
Manual gearbox
MNoisy in neutral with engine running
MNoisy in one particular gear
MDifficulty engaging gears
MJumps out of gear
MVibration
MLubricant leaks
Automatic transmission
MFluid leakage
MTransmission fluid brown, or has burned smellMGeneral gear selection problems
MTransmission will not downshift (kickdown) with acceleration
MEngine will not start in any gear, or starts in gears other than Park
or Neutral
MTransmission slips, shifts roughly, is noisy, or has no drive in forward
or reverse gears
Propeller shaft
MClunking or knocking noise when taking up drive
MVibration when accelerating or decelerating
Final drive and driveshafts
MExcessive final drive noise
MOil leakage from final drive
MGrating, knocking or vibration from driveshafts
Braking system
MVehicle pulls to one side under braking
MNoise (grinding or high-pitched squeal) when brakes applied
MExcessive brake pedal travel
MBrake pedal feels spongy when depressed
MExcessive brake pedal effort required to stop vehicle
MJudder felt through brake pedal or steering wheel when braking
MPedal pulsates when braking hard
MBrakes binding
MRear wheels locking under normal braking
Suspension and steering systems
MVehicle pulls to one side
MWheel wobble and vibration
MExcessive pitching and/or rolling around corners, or during braking
MWandering or general instability
MExcessively-stiff steering
MExcessive play in steering
MLack of power assistance
MTyre wear excessive
Electrical system
MBattery will not hold a charge for more than a few days
MIgnition/no-charge warning light remains on with engine running
MIgnition/no-charge warning light fails to come on
MLights inoperative
MInstrument readings inaccurate or erratic
MHorn inoperative, or unsatisfactory in operation
MWindscreen/tailgate wipers inoperative, or unsatisfactory in operation
MWindscreen/tailgate washers inoperative, or unsatisfactory in
operation
MElectric windows inoperative, or unsatisfactory in operation
MCentral locking system inoperative, or unsatisfactory in operation
Introduction
Page 12 of 26

headings denoting various components or systems, such as Engine,
Cooling system, etc. The Chapter and/or Section which deals with the
problem is also shown in brackets. Whatever the fault, certain basic
principles apply. These are as follows:
Verify the fault. This is simply a matter of being sure that you know
what the symptoms are before starting work. This is particularly
important if you are investigating a fault for someone else, who may
not have described it very accurately.
Don’t overlook the obvious. For example, if the vehicle won’t start, is
there fuel in the tank? (Don’t take anyone else’s word on this particular
point, and don’t trust the fuel gauge either!) If an electrical fault is
indicated, look for loose or broken wires before digging out the test
gear.Cure the disease, not the symptom. Substituting a flat battery with a
fully-charged one will get you off the hard shoulder, but if the
underlying cause is not attended to, the new battery will go the same
way. Similarly, changing oil-fouled spark plugs for a new set will get
you moving again, but remember that the reason for the fouling (if it
wasn’t simply an incorrect grade of plug) will have to be established
and corrected.
Don’t take anything for granted. Particularly, don’t forget that a
“new” component may itself be defective (especially if it’s been rattling
around in the boot for months), and don’t leave components out of a
fault diagnosis sequence just because they are new or recently-fitted.
When you do finally diagnose a difficult fault, you’ll probably realise
that all the evidence was there from the start.
Engine fails to rotate when attempting to start
MBattery terminal connections loose or corroded (Chapter 1).
MBattery discharged or faulty (Chapter 5).
MBroken, loose or disconnected wiring in the starting circuit (Chapter 5).
MDefective starter solenoid or switch (Chapter 5).
MDefective starter motor (Chapter 5).
MStarter pinion or flywheel/driveplate ring gear teeth loose or broken
(Chapters 2 or 5).
MEngine earth strap broken or disconnected.
Starter motor turns engine slowly
MPartially-discharged battery (recharge, use jump leads, or push start)
(Chapter 5).
MBattery terminals loose or corroded (Chapter 1).
MBattery earth to body defective (Chapter 5).
MEngine earth strap loose.
MStarter motor (or solenoid) wiring loose (Chapter 5).
MStarter motor internal fault (Chapter 5).
Engine rotates, but will not start
MFuel pump inertia switch tripped (electric pump) (Chapter 4).
MFuel tank empty.
MBattery discharged (engine rotates slowly) (Chapter 5).
MBattery terminal connections loose or corroded (Chapter 1).
MIgnition components damp or damaged (Chapters 1 and 5).
MBroken, loose or disconnected wiring in the ignition circuit (Chapters 1
and 5).
MWorn, faulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
MFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
MMajor mechanical failure (eg broken timing chain) (Chapter 2).
Engine difficult to start when cold
MBattery discharged (Chapter 5).
MBattery terminal connections loose or corroded (Chapter 1).
MWorn, faulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
MFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
MOther ignition system fault (Chapters 1 and 5).
MLow cylinder compressions (Chapter 2).
Engine difficult to start when hot
MAir filter element dirty or clogged (Chapter 1).
MFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
MLow cylinder compressions (Chapter 2).
Starter motor noisy or excessively-rough in
engagement
MStarter pinion or flywheel/driveplate ring gear teeth loose or broken
(Chapters 2 or 5).
MStarter motor mounting bolts loose or missing (Chapter 5).
MStarter motor internal components worn or damaged (Chapter 5).
Engine starts, but stops immediately
MLoose or faulty electrical connections in the ignition circuit
(Chapters 1 and 5).
MVacuum leak at the throttle body or inlet manifold (Chapter 4).
MFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
Engine idles erratically
MIncorrectly-adjusted idle speed (Chapter 4).
MAir filter element clogged (Chapter 1).
MVacuum leak at the throttle body, inlet manifold or associated
hoses (Chapter 4).
MWorn, faulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
MUneven or low cylinder compressions (Chapter 2).
MCamshaft lobes worn (Chapter 2).
MFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
Engine misfires at idle speed
MWorn, faulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
MFaulty spark plug HT leads (Chapter 5).
MVacuum leak at the throttle body, inlet manifold or associated
hoses (Chapter 4).
MFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
MDistributor cap cracked or tracking internally, where applicable
(Chapter 5).
MUneven or low cylinder compressions (Chapter 2).
MDisconnected, leaking, or perished crankcase ventilation hoses
(Chapter 4).
Engine misfires throughout the driving speed range
MFuel filter choked (Chapter 1).
MFuel pump faulty, or delivery pressure low (Chapter 4).
MFuel tank vent blocked, or fuel pipes restricted (Chapter 4).
MVacuum leak at the throttle body, inlet manifold or associated
hoses (Chapter 4).
MWorn, faulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
MFaulty spark plug HT leads (Chapter 5).
MDistributor cap cracked or tracking internally, where applicable
(Chapter 5).
MFaulty ignition coil (Chapter 5).
MUneven or low cylinder compressions (Chapter 2).
MFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
Engine hesitates on acceleration
MWorn, faulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
MVacuum leak at the throttle body, inlet manifold or associated
hoses (Chapter 4).
MFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
Engine stalls
MVacuum leak at the throttle body, inlet manifold or associated
hoses (Chapter 4).
REF•12Fault diagnosis
Engine
Page 13 of 26

MFuel filter choked (Chapter 1).
MFuel pump faulty, or delivery pressure low (Chapter 4).
MFuel tank vent blocked, or fuel pipes restricted (Chapter 4).
MFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
Engine lacks power
MFuel filter choked (Chapter 1).
MFuel pump faulty, or delivery pressure low (Chapter 4).
MUneven or low cylinder compressions (Chapter 2).
MWorn, faulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
MVacuum leak at the throttle body, inlet manifold or associated
hoses (Chapter 4).
MFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
MBrakes binding (Chapters 1 and 10).
MClutch slipping (Chapter 6).
Engine backfires
MVacuum leak at the throttle body, inlet manifold or associated
hoses (Chapter 4).
MFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
Oil pressure warning light illuminated with engine
running
MLow oil level, or incorrect oil grade (Chapter 1).
MFaulty oil pressure sensor (Chapter 2).
MWorn engine bearings and/or oil pump (Chapter 2).
MExcessively high engine operating temperature (Chapter 3).
MOil pressure relief valve defective (Chapter 2).
MOil pick-up strainer clogged (Chapter 2).
Note:Low oil pressure in a high-mileage engine at tickover is not
necessarily a cause for concern. Sudden pressure loss at speed is far
more significant. In any event, check the gauge or warning light sender
before condemning the engine.
Engine runs-on after switching off
MExcessive carbon build-up in engine (Chapter 2).
MExcessively high engine operating temperature (Chapter 3).
Engine noises
Pre-ignition (pinking) or knocking during acceleration or
under load
MIgnition timing incorrect/ignition system fault (Chapters 1 and 5).
MIncorrect grade of spark plug (Chapter 1).
MIncorrect grade of fuel (Chapter 1).
MVacuum leak at throttle body, inlet manifold or associated hoses
(Chapter 4).
MExcessive carbon build-up in engine (Chapter 2).
MFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
Whistling or wheezing noises
MLeaking inlet manifold or throttle body gasket (Chapter 4).
MLeaking exhaust manifold gasket (Chapter 4).
MLeaking vacuum hose (Chapters 4 and 10).
MBlowing cylinder head gasket (Chapter 2).
Tapping or rattling noises
MWorn valve gear, timing chain, camshaft or hydraulic tappets
(Chapter 2).
MAncillary component fault (water pump, alternator, etc) (Chapters 3, 5)
Knocking or thumping noises
MWorn big-end bearings (regular heavy knocking, perhaps less
under load) (Chapter 2).
MWorn main bearings (rumbling and knocking, perhaps worsening
under load) (Chapter 2).
MPiston slap (most noticeable when cold) (Chapter 2).
MAncillary component fault (water pump, alternator, etc) (Chapters 3, 5)
Overheating
MAuxiliary drivebelt broken or incorrectly adjusted (Chapter 1).
MInsufficient coolant in system (Chapter 1).
MThermostat faulty (Chapter 3).
MRadiator core blocked, or grille restricted (Chapter 3).
MElectric cooling fan or thermostatic switch faulty (Chapter 3).
MViscous-coupled fan faulty (Chapter 3).
MIgnition timing incorrect, or ignition system fault (Chapters 1 and 5).
MInaccurate temperature gauge sender unit (Chapter 3).
MAirlock in cooling system (Chapter 3).
Overcooling
MThermostat faulty (Chapter 3).
MInaccurate temperature gauge sender unit (Chapter 3).
External coolant leakage
MDeteriorated or damaged hoses or hose clips (Chapter 1).
MRadiator core or heater matrix leaking (Chapter 3).
MPressure cap faulty (Chapter 3).
MWater pump internal seal leaking (Chapter 3).
MWater pump-to-block seal leaking (Chapter 3).
MBoiling due to overheating (Chapter 3).
MCore plug leaking (Chapter 2).
Internal coolant leakage
MLeaking cylinder head gasket (Chapter 2).
MCracked cylinder head or cylinder block (Chapter 2).
Corrosion
MInfrequent draining and flushing (Chapter 1).
MIncorrect coolant mixture or inappropriate coolant type (Chapter 1).
Fault diagnosisREF•13
REF
Cooling system
Excessive fuel consumption
MAir filter element dirty or clogged (Chapter 1).
MFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
MIgnition timing incorrect or ignition system fault (Chapters 1 and 5).
MBrakes binding (Chapter 10).
MTyres under-inflated (Chapter 1).
Fuel leakage and/or fuel odour
MDamaged fuel tank, pipes or connections (Chapters 1 and 4).
Excessive noise or fumes from exhaust system
MLeaking exhaust system or manifold joints (Chapters 1 and 4).
MLeaking, corroded or damaged silencers or pipe (Chapters 1 and 4).
MBroken mountings causing body or suspension contact (Chapter 4).
Fuel and exhaust systems
Page 17 of 26

Ignition/no-charge warning light fails to come on
MWarning light bulb blown (Chapter 13).
MBroken, disconnected, or loose wiring in warning light circuit
(Chapter 13).
MAlternator faulty (Chapter 5).
Lights inoperative
MBulb blown (Chapter 13).
MCorrosion of bulb or bulbholder contacts (Chapter 13).
MBlown fuse (Chapter 13).
MFaulty relay (Chapter 13).
MBroken, loose, or disconnected wiring (Chapter 13).
MFaulty switch (Chapter 13).
Instrument readings inaccurate or erratic
Instrument readings increase with engine speed
MFaulty voltage regulator (Chapter 13).
Fuel or temperature gauges give no reading
MFaulty gauge sender unit (Chapters 4 and 5).
MWiring open-circuit (Chapter 13).
MFaulty gauge (Chapter 13).
Fuel or temperature gauges give continuous maximum
reading
MFaulty gauge sender unit (Chapters 4 and 5).
MWiring short-circuit (Chapter 13).
MFaulty gauge (Chapter 13).
Horn inoperative, or unsatisfactory in operation
Horn operates all the time
MHorn contacts permanently bridged or horn push stuck down
(Chapter 13).
Horn fails to operate
MBlown fuse (Chapter 13).
MCable or cable connections loose, broken or disconnected
(Chapter 13).
MFaulty horn (Chapter 13).
Horn emits intermittent or unsatisfactory sound
MCable connections loose (Chapter 13).
MHorn mountings loose (Chapter 13).
MFaulty horn (Chapter 13).
Windscreen/tailgate wipers inoperative, or
unsatisfactory in operation
Wipers fail to operate, or operate very slowly
MWiper blades stuck to screen, or linkage seized or binding
(Chapters 1 and 13).
MBlown fuse (Chapter 13).
MCable or cable connections loose, broken or disconnected
(Chapter 13).
MFaulty relay (Chapter 13).
MFaulty wiper motor (Chapter 13).
Wiper blades sweep over too large or too small an area of
the glass
MWiper arms incorrectly positioned on spindles (Chapter 1).
MExcessive wear of wiper linkage (Chapter 13).
MWiper motor or linkage mountings loose or insecure (Chapter 13).
Wiper blades fail to clean the glass effectively
MWiper blade rubbers worn or perished (Chapter 1).
MWiper arm tension springs broken, or arm pivots seized (Chapter 13).
MInsufficient windscreen washer additive to adequately remove road
film (Chapter 1).
Windscreen/tailgate washers inoperative, or
unsatisfactory in operation
One or more washer jets inoperative
MBlocked washer jet (Chapter 1).
MDisconnected, kinked or restricted fluid hose (Chapter 13).
MInsufficient fluid in washer reservoir (Chapter 1).
Washer pump fails to operate
MBroken or disconnected wiring or connections (Chapter 13).
MBlown fuse (Chapter 13).
MFaulty washer switch (Chapter 13).
MFaulty washer pump (Chapter 13).
Washer pump runs for some time before fluid is emitted
from jets
MFaulty one-way valve in fluid supply hose (Chapter 13).
Electric windows inoperative, or unsatisfactory in
operation
Window glass will only move in one direction
MFaulty switch (Chapter 13).
Window glass slow to move
MRegulator seized or damaged, or in need of lubrication (Chapter 12).
MDoor internal components or trim fouling regulator (Chapter 12).
MFaulty motor (Chapter 12).
Window glass fails to move
MBlown fuse (Chapter 13).
MFaulty relay (Chapter 13).
MBroken or disconnected wiring or connections (Chapter 13).
MFaulty motor (Chapter 13).
Central locking system inoperative, or unsatisfactory
in operation
Complete system failure
MBlown fuse (Chapter 13).
MFaulty relay (Chapter 13).
MBroken or disconnected wiring or connections (Chapter 13).
Latch locks but will not unlock, or unlocks but will not lock
MFaulty switch (Chapter 13).
MBroken or disconnected latch operating rods or levers (Chapter 12).
MFaulty relay (Chapter 13).
One solenoid/motor fails to operate
MBroken or disconnected wiring or connections (Chapter 13).
MFaulty solenoid/motor (Chapter 12).
MBroken, binding or disconnected latch operating rods or levers
(Chapter 12).
MFault in door latch (Chapter 12).
Fault diagnosisREF•17
REF
Page 19 of 26
Glossary of Technical termsREF•19
REF
CamshaftA rotating shaft on which a series
of cam lobes operate the valve mechanisms.
The camshaft may be driven by gears, by
sprockets and chain or by sprockets and a
belt.
CanisterA container in an evaporative
emission control system; contains activated
charcoal granules to trap vapours from the
fuel system.
CarburettorA device which mixes fuel with
air in the proper proportions to provide a
desired power output from a spark ignition
internal combustion engine.
CastellatedResembling the parapets along
the top of a castle wall. For example, a
castellated balljoint stud nut.
CastorIn wheel alignment, the backward or
forward tilt of the steering axis. Castor is
positive when the steering axis is inclined
rearward at the top.Catalytic converterA silencer-like device in
the exhaust system which converts certain
pollutants in the exhaust gases into less
harmful substances.
CirclipA ring-shaped clip used to prevent
endwise movement of cylindrical parts and
shafts. An internal circlip is installed in a
groove in a housing; an external circlip fits into
a groove on the outside of a cylindrical piece
such as a shaft.
ClearanceThe amount of space between
two parts. For example, between a piston and
a cylinder, between a bearing and a journal,
etc.
Coil springA spiral of elastic steel found in
various sizes throughout a vehicle, for
example as a springing medium in the
suspension and in the valve train.
CompressionReduction in volume, and
increase in pressure and temperature, of a
gas, caused by squeezing it into a smaller
space.
Compression ratioThe relationship between
cylinder volume when the piston is at top
dead centre and cylinder volume when the
piston is at bottom dead centre.
Constant velocity (CV) jointA type of
universal joint that cancels out vibrations
caused by driving power being transmitted
through an angle.
Core plugA disc or cup-shaped metal device
inserted in a hole in a casting through which
core was removed when the casting was
formed. Also known as a freeze plug or
expansion plug.
CrankcaseThe lower part of the engine
block in which the crankshaft rotates.
CrankshaftThe main rotating member, or
shaft, running the length of the crankcase,
with offset “throws” to which the connecting
rods are attached.Crocodile clipSee Alligator clip
DDiagnostic codeCode numbers obtained by
accessing the diagnostic mode of an engine
management computer. This code can be
used to determine the area in the system
where a malfunction may be located.
Disc brakeA brake design incorporating a
rotating disc onto which brake pads are
squeezed. The resulting friction converts the
energy of a moving vehicle into heat.
Double-overhead cam (DOHC)An engine
that uses two overhead camshafts, usually
one for the intake valves and one for the
exhaust valves.
Drivebelt(s)The belt(s) used to drive
accessories such as the alternator, water
pump, power steering pump, air conditioning
compressor, etc. off the crankshaft pulley.
DriveshaftAny shaft used to transmit
motion. Commonly used when referring to the
axleshafts on a front wheel drive vehicle.
Drum brakeA type of brake using a drum-
shaped metal cylinder attached to the inner
surface of the wheel. When the brake pedal is
pressed, curved brake shoes with friction
linings press against the inside of the drum to
slow or stop the vehicle.
Castellated nut
Catalytic converter
Crankshaft assembly
Carburettor
Canister
Drum brake assembly
Accessory drivebelts
Driveshaft
Page 20 of 26
REF•20Glossary of Technical terms
EEGR valveA valve used to introduce exhaust
gases into the intake air stream.
Electronic control unit (ECU)A computer
which controls (for instance) ignition and fuel
injection systems, or an anti-lock braking
system. For more information refer to the
Haynes Automotive Electrical and Electronic
Systems Manual.
Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI)A computer
controlled fuel system that distributes fuel
through an injector located in each intake port
of the engine.
Emergency brakeA braking system,
independent of the main hydraulic system,
that can be used to slow or stop the vehicle if
the primary brakes fail, or to hold the vehicle
stationary even though the brake pedal isn’t
depressed. It usually consists of a hand lever
that actuates either front or rear brakes
mechanically through a series of cables and
linkages. Also known as a handbrake or
parking brake.
EndfloatThe amount of lengthwise
movement between two parts. As applied to a
crankshaft, the distance that the crankshaft
can move forward and back in the cylinder
block.
Engine management system (EMS)A
computer controlled system which manages
the fuel injection and the ignition systems in
an integrated fashion.
Exhaust manifoldA part with several
passages through which exhaust gases leave
the engine combustion chambers and enter
the exhaust pipe.
FFan clutchA viscous (fluid) drive coupling
device which permits variable engine fan
speeds in relation to engine speeds.Feeler bladeA thin strip or blade of hardened
steel, ground to an exact thickness, used to
check or measure clearances between parts.
Firing orderThe order in which the engine
cylinders fire, or deliver their power strokes,
beginning with the number one cylinder.
Flywheel A heavy spinning wheel in which
energy is absorbed and stored by means of
momentum. On cars, the flywheel is attached
to the crankshaft to smooth out firing
impulses.
Free playThe amount of travel before any
action takes place. The “looseness” in a
linkage, or an assembly of parts, between the
initial application of force and actual
movement. For example, the distance the
brake pedal moves before the pistons in the
master cylinder are actuated.
FuseAn electrical device which protects a
circuit against accidental overload. The typical
fuse contains a soft piece of metal which is
calibrated to melt at a predetermined current
flow (expressed as amps) and break the
circuit.
Fusible linkA circuit protection device
consisting of a conductor surrounded by
heat-resistant insulation. The conductor is
smaller than the wire it protects, so it acts as
the weakest link in the circuit. Unlike a blown
fuse, a failed fusible link must frequently be
cut from the wire for replacement.
GGapThe distance the spark must travel in
jumping from the centre electrode to the sideelectrode in a spark plug. Also refers to the
spacing between the points in a contact
breaker assembly in a conventional points-
type ignition, or to the distance between the
reluctor or rotor and the pickup coil in an
electronic ignition.
GasketAny thin, soft material - usually cork,
cardboard, asbestos or soft metal - installed
between two metal surfaces to ensure a good
seal. For instance, the cylinder head gasket
seals the joint between the block and the
cylinder head.
GaugeAn instrument panel display used to
monitor engine conditions. A gauge with a
movable pointer on a dial or a fixed scale is an
analogue gauge. A gauge with a numerical
readout is called a digital gauge.
HHalfshaftA rotating shaft that transmits
power from the final drive unit to a drive
wheel, usually when referring to a live rear
axle.
Harmonic balancerA device designed to
reduce torsion or twisting vibration in the
crankshaft. May be incorporated in the
crankshaft pulley. Also known as a vibration
damper.
HoneAn abrasive tool for correcting small
irregularities or differences in diameter in an
engine cylinder, brake cylinder, etc.
Hydraulic tappetA tappet that utilises
hydraulic pressure from the engine’s
lubrication system to maintain zero clearance
(constant contact with both camshaft and
valve stem). Automatically adjusts to variation
in valve stem length. Hydraulic tappets also
reduce valve noise.
IIgnition timingThe moment at which the
spark plug fires, usually expressed in the
number of crankshaft degrees before the
piston reaches the top of its stroke.
Inlet manifoldA tube or housing with
passages through which flows the air-fuel
mixture (carburettor vehicles and vehicles with
throttle body injection) or air only (port fuel-
injected vehicles) to the port openings in the
cylinder head.
Exhaust manifold
Feeler blade
Adjusting spark plug gap
Gasket
EGR valve
Page 23 of 26

AAccelerator cable- 4A•8
Accelerator pedal- 4A•8
Acknowledgements- 0•4
Aerial- 13•20
Air cleaner- 1•18, 1•19, 4A•4, 4B•4
Air conditioning systems- 1•16, 3•1 et seq
Airflow meter- 4B•8
Alarm system- 13•19
Alternator- 5•6
Anti-roll bars- 11•6, 11•13
Anti-theft alarm- 13•19
Antifreeze- 0•17, 1•21, 3•3
ATF- 0•17, 1•3
Automatic transmission- 7B•1 et seq
extension housing oil seal - 7B•5
fault diagnosis - REF•11, REF•14
fluid - 0•17, 1•3
fluid checks - 1•13
gear selector mechanism - 7B•5
kickdown cable - 7B•3
removal and refitting - 7B•2
reversing lamp switch - 7B•6
selector rod - 7B•5
starter inhibitor switch - 7B•6
vacuum diaphragm unit - 7B•6
Auxiliary drivebelts- 1•14, 1•21
Auxiliary shaft- 2A•18
BBattery- 0•15, 1•15, 5•5
Bearings (engine) - 2A•23, 2B•17, 2C•23
Bleeding the power steering- 11•18
Bleeding the brakes- 10•2
Body damage- 12•2, 12•4
Body electrical systems - 13•1 et seq
Bodywork and fittings- 12•1 et seq
Bonnet release cable- 12•4
Bonnet lock- 12•4, 12•5
Boot lid lock- 12•5
Brake checks- 1•10
Brake fluid- 0•13, 0•1, 1•21
Braking system- 10•1 et seq
backplate - 10•12
bleeding the brakes - 10•2
brake caliper - 10•8, 10•10
brake disc - 10•3, 10•11
brake drum - 10•12
brake fluid pipes and hoses - 10•19
brake fluid reservoir - 10•15
brake lamp switch - 13•6
brake pads - 10•3
brake pedal - 10•22
brake shoes - 10•6
computer module (ABS) - 10•17
deceleration valve - 10•18
fault diagnosis - REF•11, REF•15
handbrake adjustment - 1•16, 10•20, 10•21
handbrake cables - 1•16, 10•20, 10•21
handbrake lever - 10•22
hoses brake - 10•19
hydraulic unit pressure switch - 10•17
hydraulic unit/pump/motor (ABS) - 10•15, 10•16
load apportioning valve - 10•19master cylinder (brake) - 10•13
pressure switch - 10•17
vacuum servo unit - 10•14
valve block (ABS) - 10•17
wheel cylinder - 10•12
wheel sensor - 10•18
Bulbs exterior- 13•16
Bulbs interior- 13•10
Bulbs ratings- 13•2
Bumpers- 12•13
Buying spare parts - REF•3
CCables:
accelerator - 4A•8
bonnet release - 12•4
clutch - 6•2
handbrake - 10•20, 10•21
kickdown - 7B•3
speedometer - 13•11
tailgate/boot lid/filler cap - 12•6
Caliper (brake) front/rear- 10•8, 10•10
Camshaft and followers- 2A•17, 2B•14, 2C•16
Capacities- 1•3
Carburettor:
Ford VV type - 1•12, 4A•8, 4A•13
Pierburg 2V type - 1•12, 4A•8, 4A•14
Weber 2V type - 1•12, 4A•8, 4A•14
Weber 2V TLD type - 1•12, 4A•8, 4A•15
Cargo area- 12•10
Carpets- 12•2
Catalytic converter- 4B•3, 4B•14
Central locking system- 13•18
Centre/overhead console- 12•18, 12•19
CFI unit- 4B•10
Charging system- 5•5
Cigarette lighter- 13•6
Clock- 13•6
Clutch- 6•1 et seq
assembly - 6•3
cable - 6•2
fault diagnosis - REF•11, REF•14
pedal - 6•2
release bearing - 6•5
Coil- 5•13
Coil spring (rear) - 11•10
Compression test- 2A•7
Computer module (ABS)- 10•17
Connecting rods- 2A•22, 2B•17, 2C•21
Contents- 0•2
Coolant- 0•12, 0•17, 1•21, 3•3
Coolant level- 0•12
Cooling, heating and air conditioning
systems- 3•1 et seq
antifreeze - 0•12, 0•17, 1•21, 3•3
coolant pump - 3•5
coolant temperature sender and sensor - 3•8
cooling fan - 3•7
draining - 1•21
drivebelt tensioner - 3•7
expansion tank/coolant sensor - 3•8
fan (radiator) - 3•7
fault diagnosis - REF•11, REF•13
filling - 1•21
flushing - 1•21heater - 3•9
radiator - 3•3
switches - 3•8
temperature gauge and sender unit - 3•8
thermostat - 3•4
Courtesy lamp switch- 13•5
Crankshaft oil seals- 2A•19, 2B•15, 2C•19
Crankshaft bearings- 2A•23, 2B•17, 2C•23
Cylinder bores- 2A•24
Cylinder head- 2A•14, 2B•10, 2C•13
DDents- 12•2
Depressurising fuel injection system- 4B•4
Dimensions and weights- REF•1
Disc brake - 10•3, 10•11
Distributor- 5•14, 5•15, 5•16
Door- 12•6
Door inner trim panel- 12•7
Door mirror switch- 13•5
Drivebelts check- 1•14, 1•21, 3•7
Driveplate- 2A•18, 2B•15, 2C•19
Driveshafts:
check - 1•17
fault diagnosis - REF•11, REF•15
overhaul - 9•5
removal and refitting - 9•4
Drum (brake)- 10•12
EEarth fault finding- 13•3
Electric windows- 13•18
Electrical fault finding- 13•2
Electrical system (body)- 13•1 et seq
Electrical system:
weekly checks - 0•14
fault diagnosis - REF•11, REF•16
Electronic vacuum regulator- 4B•11
Engine:
auxiliary shaft - 2A•18
bearings - 2A•23, 2B•17, 2C•23
bores - 2A•24
camshaft followers - 2A•17, 2B•14, 2C•16
codes - 2A•1, 2B•1, 2C•1
compartment views - 0•10, 1•5
compression test - 2A•7
connecting rods - 2A•22, 2B•17, 2C•21
crankshaft bearings - 2A•23, 2B•17, 2C•23
crankshaft oil seals - 2A•19, 2B•15, 2C•19
cylinder bores - 2A•24
cylinder head - 2A•14, 2B•10, 2C•13
dismantling - 2A•11, 2B•8, 2C•10
DOHC engines- 2B•1 et seq
driveplate - 2A•18, 2B•15, 2C•19
fault diagnosis - REF•11, REF•12
flywheel - 2A•18, 2B•15, 2C•19
main bearings - 2A•23, 2B•17, 2C•23
mountings - 2A•11, 2B•7, 2C•9
oils - 0•17, 1•3
oil and filter renewal - 1•9
oil level - 0•12
oil pump - 2A•21, 2B•16, 2C•20
oil seals crankshaft - 2A•19, 2B•15, 2C•19
piston - 2A•22, 2B•17, 2C•21
IndexREF•23
REF
Note: References throughout this index are in the form - “Chapter number” • “page number”