remove seats FORD SIERRA 1983 1.G SOHC Engines Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1983, Model line: SIERRA, Model: FORD SIERRA 1983 1.GPages: 24, PDF Size: 1.03 MB
Page 12 of 24
Examination and renovation
11With the engine completely stripped,
clean all the components and examine them
for wear. Each part should be checked, and
where necessary renewed or renovated as
described in the relevant Sections. Renew
main and big end shell bearings as a matter of
course, unless it is known that they have had
little wear and are in perfect condition.
12If in doubt as to whether to renew a
component which is still just serviceable,
consider the time and effort which will be
incurred should it fail at an early date.
Obviously the age and expected life of the
vehicle must influence the standards applied.
13Gaskets, oil seals and O-rings must all be
renewed as a matter of routine. Flywheel and
Torx type cylinder head bolts must be
renewed because of the high stresses to
which they are subjected.
14Take the opportunity to renew the engine
core plugs while they are easily accessible.
Knock out the old plugs with a hammer and
chisel or punch. Clean the plug seats, smear
the new plugs with sealant and tap them
squarely into position.
Reassembly
15To ensure maximum life with minimum
trouble from a rebuilt engine, not only must
everything be correctly assembled, but it must
also be spotlessly clean. All oilways must be
clear, and locking washers and spring
washers must be fitted where indicated. Oil all
bearings and other working surfaces
thoroughly with clean engine oil during
assembly.
16Before assembly begins, renew any bolts
or studs with damaged threads.
17Gather together a torque wrench, oil can,
clean rag, and a set of engine gaskets and oil
seals, together with a new oil filter.
18If they have been removed, new Torx type
cylinder head bolts and new flywheel bolts will
be required.
19After reassembling the main engine
components, refit the ancillary components
listed, referring to the appropriate Chapters
where necessary. Delicate items such as the
alternator and distributor may be left until after
the engine has been refitted if preferred.20If the crankcase ventilation oil separator
was removed, apply a liquid sealing agent to
its tube before pressing it into the cylinder
block.
Note: Refer to the warning in Section 8 before
proceeding. On models from mid-1985
(without a timing belt tensioner spring) the belt
tension should be checked using Ford special
tool No 21-113 after refitting. On models up to
mid-1985 (with a tensioner spring), a suitable
splined socket will be required for the
tensioner spring bolt. A suitable puller may be
required to remove the sprockets.
Removal
1If the engine is in the vehicle, carry out the
following operations:
a)Disconnect the battery negative lead
b)Remove the thermo-viscous cooling fan
c)Remove the coolant
pump/alternator/power-steering pump
drivebelt(s)
d)For improved access, remove the radiator
and disconnect the radiator top hose from
the thermostat housing
2Unscrew the three securing bolts and
washers and withdraw the timing cover. Note
the position of the fourth bolt above the
crankshaft pulley which can be left in place.
3Using a socket on the crankshaft pulley
bolt, turn the engine clockwise until the TDC
(top dead centre) mark on the crankshaft
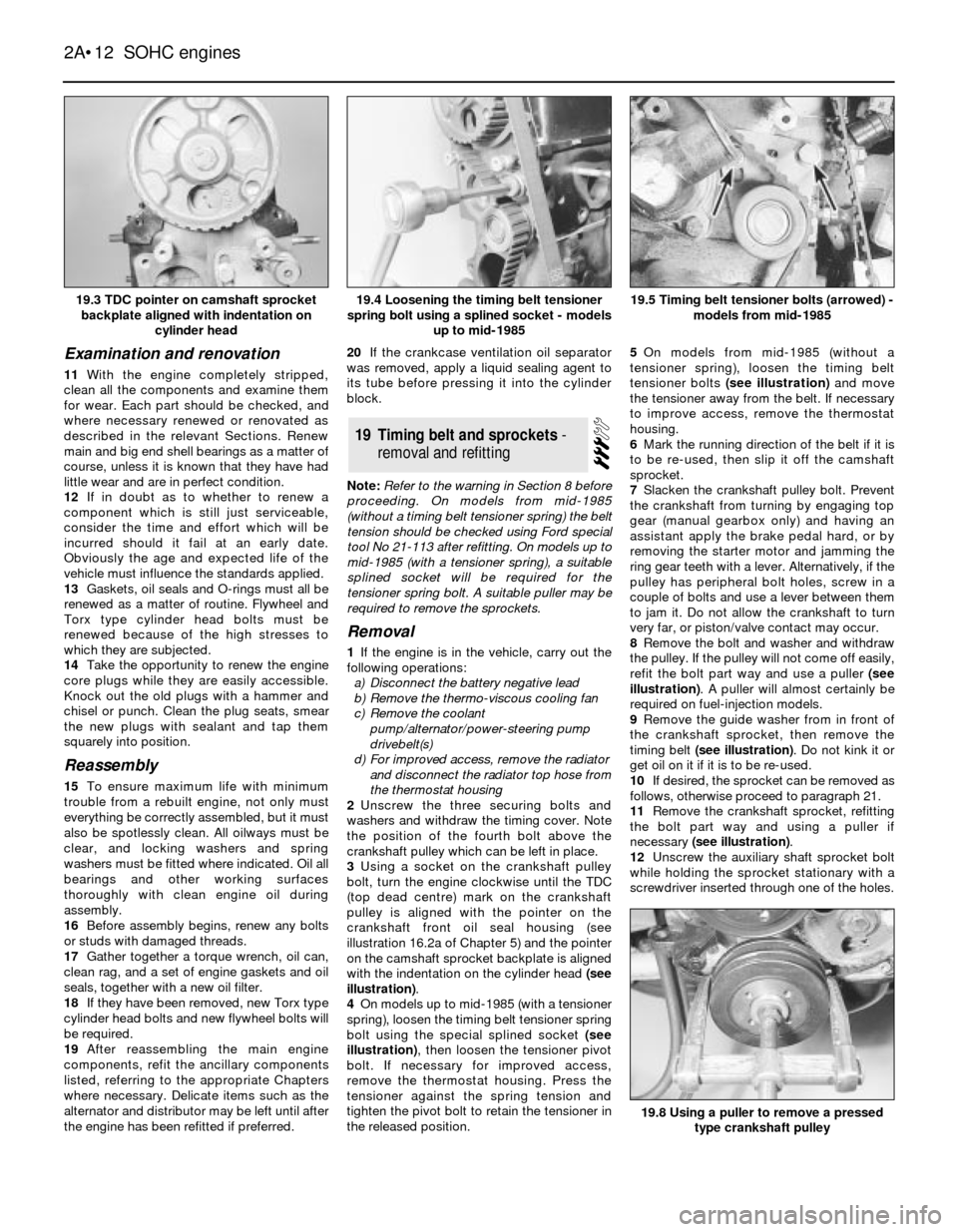
pulley is aligned with the pointer on the
crankshaft front oil seal housing (see
illustration 16.2a of Chapter 5) and the pointer
on the camshaft sprocket backplate is aligned
with the indentation on the cylinder head (see
illustration).
4On models up to mid-1985 (with a tensioner
spring), loosen the timing belt tensioner spring
bolt using the special splined socket (see
illustration), then loosen the tensioner pivot
bolt. If necessary for improved access,
remove the thermostat housing. Press the
tensioner against the spring tension and
tighten the pivot bolt to retain the tensioner in
the released position.5On models from mid-1985 (without a
tensioner spring), loosen the timing belt
tensioner bolts (see illustration)and move
the tensioner away from the belt. If necessary
to improve access, remove the thermostat
housing.
6Mark the running direction of the belt if it is
to be re-used, then slip it off the camshaft
sprocket.
7Slacken the crankshaft pulley bolt. Prevent
the crankshaft from turning by engaging top
gear (manual gearbox only) and having an
assistant apply the brake pedal hard, or by
removing the starter motor and jamming the
ring gear teeth with a lever. Alternatively, if the
pulley has peripheral bolt holes, screw in a
couple of bolts and use a lever between them
to jam it. Do not allow the crankshaft to turn
very far, or piston/valve contact may occur.
8Remove the bolt and washer and withdraw
the pulley. If the pulley will not come off easily,
refit the bolt part way and use a puller (see
illustration). A puller will almost certainly be
required on fuel-injection models.
9Remove the guide washer from in front of
the crankshaft sprocket, then remove the
timing belt (see illustration). Do not kink it or
get oil on it if it is to be re-used.
10If desired, the sprocket can be removed as
follows, otherwise proceed to paragraph 21.
11Remove the crankshaft sprocket, refitting
the bolt part way and using a puller if
necessary (see illustration).
12Unscrew the auxiliary shaft sprocket bolt
while holding the sprocket stationary with a
screwdriver inserted through one of the holes.
19Timing belt and sprockets -
removal and refitting
2A¥12SOHC engines
19.3 TDC pointer on camshaft sprocket
backplate aligned with indentation on
cylinder head19.5 Timing belt tensioner bolts (arrowed) -
models from mid-1985
19.8 Using a puller to remove a pressed
type crankshaft pulley
19.4 Loosening the timing belt tensioner
spring bolt using a splined socket - models
up to mid-1985
Page 16 of 24
Note: A valve spring compressor will be
required during this procedure. New valve
stem oil seals should be used on reassembly.
Dismantling
1With the cylinder head removed, remove
the camshaft.
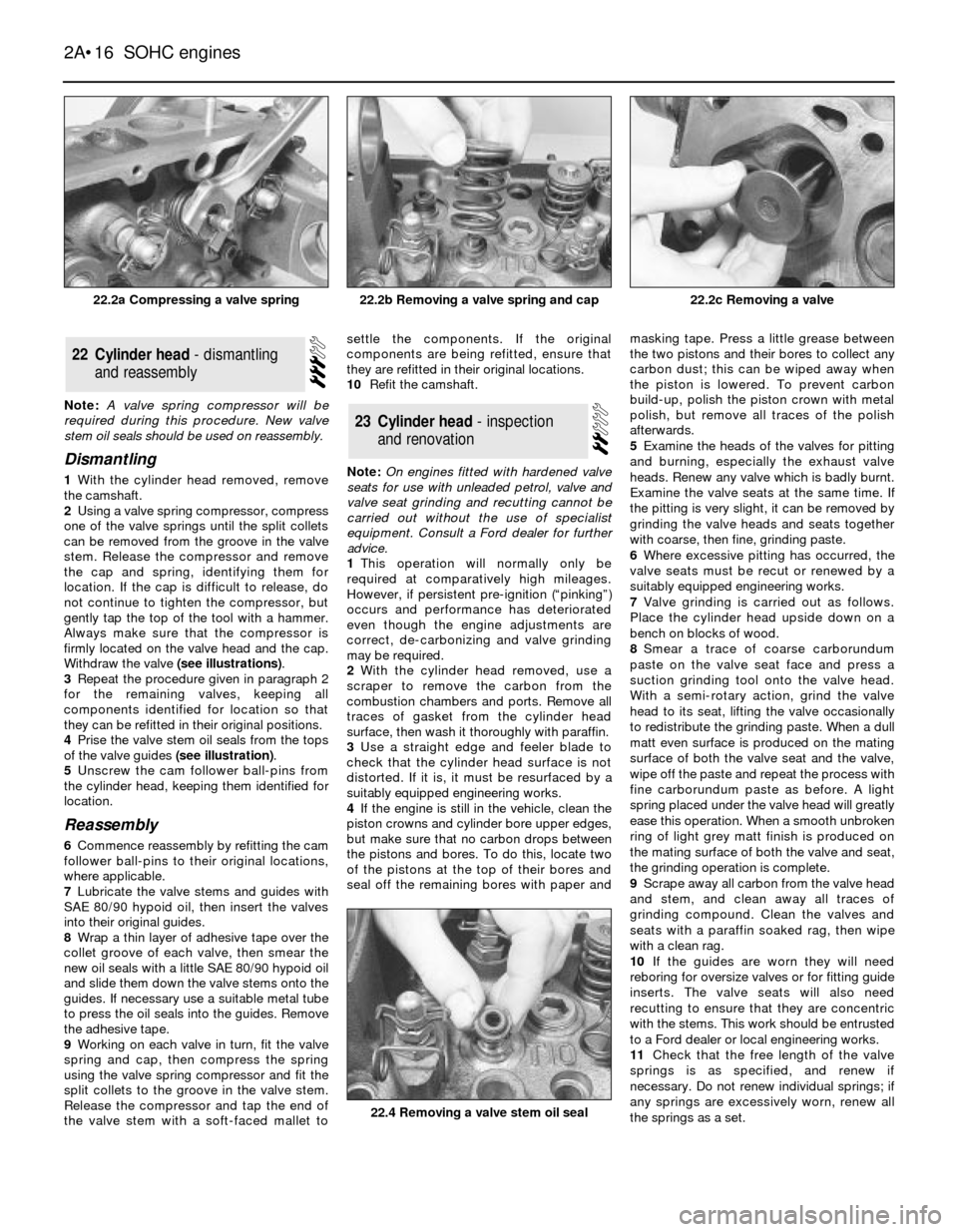
2Using a valve spring compressor, compress
one of the valve springs until the split collets
can be removed from the groove in the valve
stem. Release the compressor and remove
the cap and spring, identifying them for
location. If the cap is difficult to release, do
not continue to tighten the compressor, but
gently tap the top of the tool with a hammer.
Always make sure that the compressor is
firmly located on the valve head and the cap.
Withdraw the valve (see illustrations).
3Repeat the procedure given in paragraph 2
for the remaining valves, keeping all
components identified for location so that
they can be refitted in their original positions.
4Prise the valve stem oil seals from the tops
of the valve guides (see illustration).
5Unscrew the cam follower ball-pins from
the cylinder head, keeping them identified for
location.
Reassembly
6Commence reassembly by refitting the cam
follower ball-pins to their original locations,
where applicable.
7Lubricate the valve stems and guides with
SAE 80/90 hypoid oil, then insert the valves
into their original guides.
8Wrap a thin layer of adhesive tape over the
collet groove of each valve, then smear the
new oil seals with a little SAE 80/90 hypoid oil
and slide them down the valve stems onto the
guides. If necessary use a suitable metal tube
to press the oil seals into the guides. Remove
the adhesive tape.
9Working on each valve in turn, fit the valve
spring and cap, then compress the spring
using the valve spring compressor and fit the
split collets to the groove in the valve stem.
Release the compressor and tap the end of
the valve stem with a soft-faced mallet tosettle the components. If the original
components are being refitted, ensure that
they are refitted in their original locations.
10Refit the camshaft.
Note: On engines fitted with hardened valve
seats for use with unleaded petrol, valve and
valve seat grinding and recutting cannot be
carried out without the use of specialist
equipment. Consult a Ford dealer for further
advice.
1This operation will normally only be
required at comparatively high mileages.
However, if persistent pre-ignition (ÒpinkingÓ)
occurs and performance has deteriorated
even though the engine adjustments are
correct, de-carbonizing and valve grinding
may be required.
2With the cylinder head removed, use a
scraper to remove the carbon from the
combustion chambers and ports. Remove all
traces of gasket from the cylinder head
surface, then wash it thoroughly with paraffin.
3Use a straight edge and feeler blade to
check that the cylinder head surface is not
distorted. If it is, it must be resurfaced by a
suitably equipped engineering works.
4If the engine is still in the vehicle, clean the
piston crowns and cylinder bore upper edges,
but make sure that no carbon drops between
the pistons and bores. To do this, locate two
of the pistons at the top of their bores and
seal off the remaining bores with paper andmasking tape. Press a little grease between
the two pistons and their bores to collect any
carbon dust; this can be wiped away when
the piston is lowered. To prevent carbon
build-up, polish the piston crown with metal
polish, but remove all traces of the polish
afterwards.
5Examine the heads of the valves for pitting
and burning, especially the exhaust valve
heads. Renew any valve which is badly burnt.
Examine the valve seats at the same time. If
the pitting is very slight, it can be removed by
grinding the valve heads and seats together
with coarse, then fine, grinding paste.
6Where excessive pitting has occurred, the
valve seats must be recut or renewed by a
suitably equipped engineering works.
7Valve grinding is carried out as follows.
Place the cylinder head upside down on a
bench on blocks of wood.
8Smear a trace of coarse carborundum
paste on the valve seat face and press a
suction grinding tool onto the valve head.
With a semi-rotary action, grind the valve
head to its seat, lifting the valve occasionally
to redistribute the grinding paste. When a dull
matt even surface is produced on the mating
surface of both the valve seat and the valve,
wipe off the paste and repeat the process with
fine carborundum paste as before. A light
spring placed under the valve head will greatly
ease this operation. When a smooth unbroken
ring of light grey matt finish is produced on
the mating surface of both the valve and seat,
the grinding operation is complete.
9Scrape away all carbon from the valve head
and stem, and clean away all traces of
grinding compound. Clean the valves and
seats with a paraffin soaked rag, then wipe
with a clean rag.
10If the guides are worn they will need
reboring for oversize valves or for fitting guide
inserts. The valve seats will also need
recutting to ensure that they are concentric
with the stems. This work should be entrusted
to a Ford dealer or local engineering works.
11Check that the free length of the valve
springs is as specified, and renew if
necessary. Do not renew individual springs; if
any springs are excessively worn, renew all
the springs as a set.
23Cylinder head - inspection
and renovation
22Cylinder head - dismantling
and reassembly
2A¥16SOHC engines
22.2a Compressing a valve spring22.2c Removing a valve
22.4 Removing a valve stem oil seal
22.2b Removing a valve spring and cap