torque FORD SIERRA 1984 1.G Engine Electrical Systems Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1984, Model line: SIERRA, Model: FORD SIERRA 1984 1.GPages: 24, PDF Size: 0.93 MB
Page 2 of 24

Ignition timingLeaded petrolUnleaded petrol
(at idle with vacuum pipe disconnected)(4-star, 97 RON)(Premium, 95 RON)
Early “Economy” models (800 rpm - vacuum pipe connected) . . . . . . .16º BTDC12º BTDC
1.3 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12º BTDC8º BTDC*
1.6 litre models with VV carburettor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12º BTDC8º BTDC*
1.6 litre models with 2V carburettor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10º BTDC6º BTDC†
1.8 litre SOHC models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10º BTDC6º BTDC†
1.8 litre CVH models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .ESC Hybrid controlled, no adjustment possible
2.0 litre carburettor models up to 1985 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8º BTDC4º BTDC*
2.0 litre carburettor models from 1985 (except P100) . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10º BTDC6º BTDC†
P100 models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6º BTDC2º BTDC†
2.0 litre fuel injection models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12º BTDC8º BTDC†
*Fill with leaded petrol (4-star, 97 RON) every 4th tankful
†Not all vehicles are suitable for continuous operation on unleaded petrol.
Spark plugs
Make and type:
All models except 1.8 CVH, CVH (R6A), 2.0 DOHC and P100 . . . . . . . .Champion RF7YCC or RF7YC
1.8 CVH engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion RC7YCC or RC7YC
P100 model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion RF7YC or F7YC
1.6 and 1.8 CVH (R6A type) and 2.0 DOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion RC7YCC
Electrode gap:
Champion F7YCC or RC7YCC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.8 mm (0.032 in)
Champion RF7YC, F7YC or RC7YC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.7 mm (0.028 in)
Note: The electrode gap above is the figure quoted by Champion for use with their recommended spark plugs. If plugs of any other type are fitted,
refer to their manufacturer’s gap recommendations.
HT leads
All SOHC models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion LS-09 or LS-10 boxed set
1.8 CVH . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion LS-10 boxed set
1.6 and 1.8 CVH (R6A type) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion LS-30 boxed set
2.0 DOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion LS-29 boxed set
Maximum resistance per lead . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30 000 ohms
Alternator
Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Bosch, Lucas, Motorola, or Mitsubishi
Regulated output voltage at 4000 rpm (3 to 7 amp load) . . . . . . . . . . . .13.7 to 14.6 volts
Minimum brush length:
All alternator types except Motorola . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5.0 mm (0.20 in)
Motorola type alternators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4.0 mm (0.16 in)
Starter motor
Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Pre-engaged; Bosch, Cajavec, Lucas, or Nippondenso
Minimum brush length:
All except Bosch long frame 1.1 kW and JF, and Nippondenso . . . .8.0 mm (0.32 in)
Bosch long frame 1.1 kW and JF, Nippondenso starter motors . . . .10.0 mm (0.40 in)
Battery charge condition:
Poor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12.5 volts
Normal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12.6 volts
Good . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12.7 volts
Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Spark plugs:
SOHC models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2815 to 21
CVH models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18 to 3313 to 24
DOHC models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15 to 2111 to 15
Crankshaft speed/position sensor clamp bolt (ESC Hybrid system) . . .4 to 73 to 5
Crankshaft speed/position sensor screw (DOHC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3 to 52 to 4
Camshaft sprocket bolt (CVH models) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .95 to 11570 to 85
Air charge temperature sensor (CVH-R6A and DOHC) . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Engine coolant temperature sensor (CVH-R6A and DOHC) . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Fuel temperature sensor (DOHC injection) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 116 to 8
Alternator adjustment bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2815 to 20
Alternator mounting bolts:
With coloured patch on threads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41 to 5130 to 38
Without coloured patch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
5•2Engine electrical systems
Page 13 of 24
10The distributor cap (except on 1.6 and 1.8
litre CVH (R6A type) engines) and the HT
leads should be cleaned and checked at the
specified intervals. To test the HT leads,
remove them together with the distributor
cap, then connect an ohmmeter to the end of
each lead and its appropriate terminal within
the cap in turn (see illustration). If the
resistance of any lead is greater than the
maximum given in the Specifications, check
that the lead connection in the cap is good
before renewing the lead.
Refitting
11Before fitting the spark plugs, check that
the threaded connector sleeves are tight and
that the plug exterior surfaces are clean. As
the plugs incorporate taper seats also make
sure that the threads and seats are clean.
12On DOHC models before refitting thespark plugs, coat their threads with suitable
antiseize compound, taking care not to
contaminate the electrodes.
13Screw in the spark plugs by hand, then
tighten them to the specified torque. Do not
exceed the torque figure.
14Push the HT leads firmly onto the spark
plugs, and where applicable refit the air
cleaner and/or inlet hose.Testing
All models except 1.6 and 1.8 litre
CVH (R6A type)
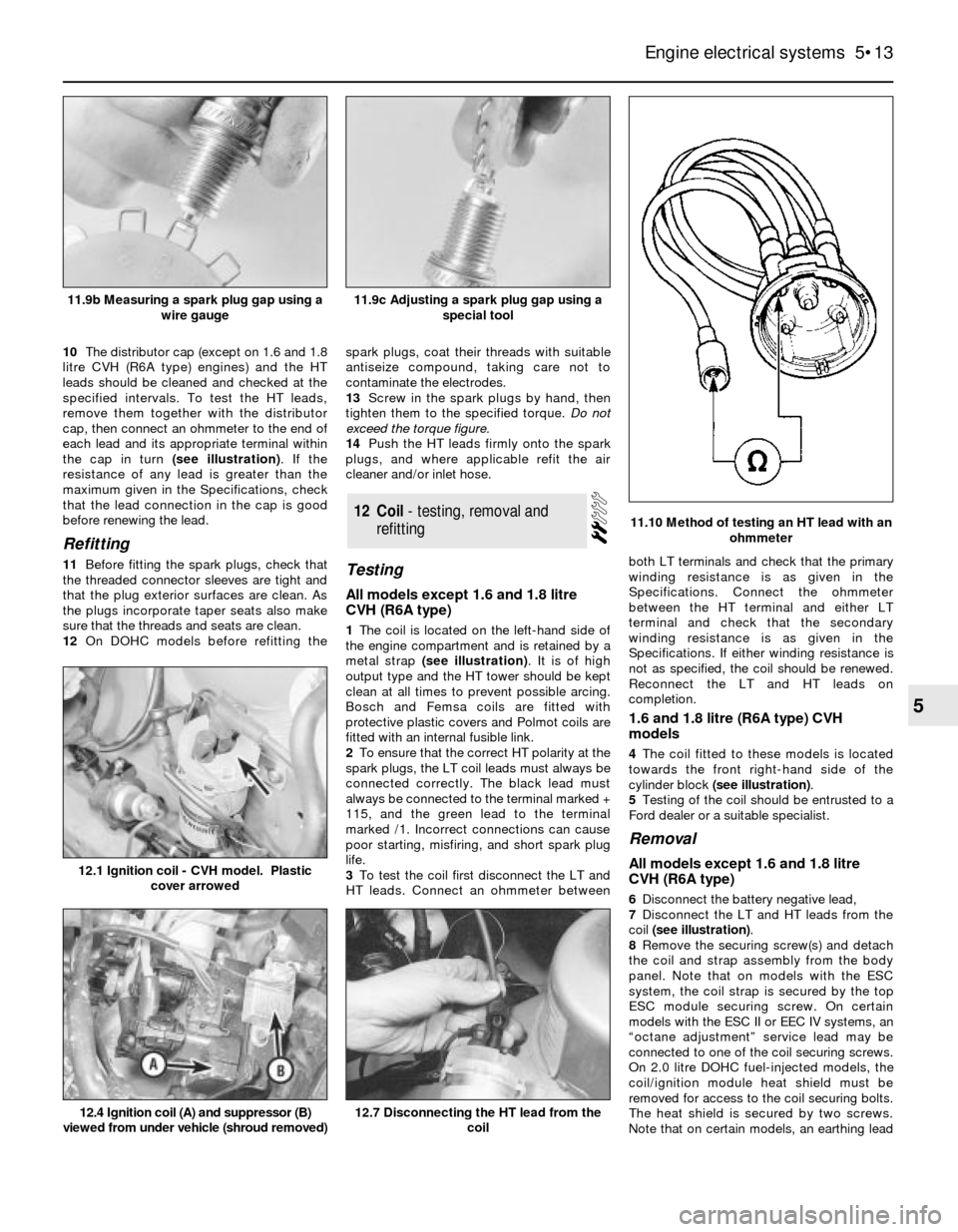
1The coil is located on the left-hand side of
the engine compartment and is retained by a
metal strap (see illustration). It is of high
output type and the HT tower should be kept
clean at all times to prevent possible arcing.
Bosch and Femsa coils are fitted with
protective plastic covers and Polmot coils are
fitted with an internal fusible link.
2To ensure that the correct HT polarity at the
spark plugs, the LT coil leads must always be
connected correctly. The black lead must
always be connected to the terminal marked +
115, and the green lead to the terminal
marked /1. Incorrect connections can cause
poor starting, misfiring, and short spark plug
life.
3To test the coil first disconnect the LT and
HT leads. Connect an ohmmeter betweenboth LT terminals and check that the primary
winding resistance is as given in the
Specifications. Connect the ohmmeter
between the HT terminal and either LT
terminal and check that the secondary
winding resistance is as given in the
Specifications. If either winding resistance is
not as specified, the coil should be renewed.
Reconnect the LT and HT leads on
completion.
1.6 and 1.8 litre (R6A type) CVH
models
4The coil fitted to these models is located
towards the front right-hand side of the
cylinder block (see illustration).
5Testing of the coil should be entrusted to a
Ford dealer or a suitable specialist.
Removal
All models except 1.6 and 1.8 litre
CVH (R6A type)
6Disconnect the battery negative lead,
7Disconnect the LT and HT leads from the
coil (see illustration).
8Remove the securing screw(s) and detach
the coil and strap assembly from the body
panel. Note that on models with the ESC
system, the coil strap is secured by the top
ESC module securing screw. On certain
models with the ESC II or EEC IV systems, an
“octane adjustment” service lead may be
connected to one of the coil securing screws.
On 2.0 litre DOHC fuel-injected models, the
coil/ignition module heat shield must be
removed for access to the coil securing bolts.
The heat shield is secured by two screws.
Note that on certain models, an earthing lead
12Coil - testing, removal and
refitting
Engine electrical systems 5•13
5
11.10 Method of testing an HT lead with an
ohmmeter
12.4 Ignition coil (A) and suppressor (B)
viewed from under vehicle (shroud removed)12.7 Disconnecting the HT lead from the
coil
12.1 Ignition coil - CVH model. Plastic
cover arrowed
11.9c Adjusting a spark plug gap using a
special tool11.9b Measuring a spark plug gap using a
wire gauge
Page 22 of 24
38Before refitting the sensor, examine the
O-ring, and renew it if damaged or worn.
39Refitting is a reversal of removal, noting
the torque setting for the sensor screw.
Note: Procedures for removal and refitting of
the ignition system components and
electronic module are given elsewhere in the
relevant Sections of this Chapter.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
Crankshaft speed/position sensor
2The sensor is mounted in a bracket on the
timing cover.
3Disconnect the sensor wiring plug by
pulling on the plug, not the wiring (see
illustration).
4Slacken the sensor clamping screw and
slide the sensor from its bracket.
5Refitting is a reversal of removal, but the
clearance between the sensor and the
toothed wheel on the crankshaft must be set
at 1.0 mm (0.04 in). This can be achieved by
inserting a suitable length of wire or rod with a
diameter of 1.0 mm (0.04 in) between the
sensor and the toothed wheel (see
illustration). Do not overtighten the clamping
screw, as damage to the sensor may result.
Engine coolant temperature
sensor
6The sensor is located in the side of the inlet
manifold(see illustration).
7Partially drain the cooling system.
8Disconnect the sensor wiring plug by
pulling on the plug, not the wiring.
9Unscrew the sensor from the inlet manifold
and remove it.
10Refitting is a reversal of removal. Fill the
cooling system.
Air charge temperature sensor
11The sensor is located in the base of the air
cleaner.
12Remove the air cleaner.
13Disconnect the sensor wiring plug by
pulling on the plug, not the wiring (see
illustration).14Unscrew the sensor from the air cleaner
using a suitable spanner.
15Refitting is a reversal of removal. Refit the
air cleaner. Ensure that the vacuum hose is
securely connected.
Electric choke heater
16The electric choke heater is an integral
part of the automatic choke housing on the
carburettor. Removal and refitting of the
choke housing is covered in Chapter 4.
17The operation of the electric choke heater
relay can be checked by starting the engine
from cold, and placing a finger on the relay
(see illustration). It should be possible to feel
the relay switching on and off. If this is not the
case, renew the relay.
Throttle damper control solenoid
18The solenoid is on the right-hand side of
the engine compartment (see illustration). 19Disconnect the solenoid wiring plug by
pulling on the plug, not the wiring.
20Disconnect the two vacuum pipes from
the solenoid, noting their locations for use
when refitting.
21Remove the securing screw and withdraw
the solenoid from the body panel.
22Refitting is a reversal of removal, but note
that the locating lug on the solenoid bracket
should engage with the body panel, and make
sure that the vacuum pipes are correctly
connected.
Throttle damper
23Remove the air cleaner.
24Disconnect the vacuum pipe from the
throttle damper.
20ESC Hybrid system
components - removal and
refitting
5•22Engine electrical systems
20.3 Disconnecting crankshaft
speed/position sensor wiring plug - ESC
Hybrid system
20.6 Engine coolant temperature sensor
location - ESC Hybrid system
20.25 Throttle damper assembly - ESC
Hybrid system
A Securing screws
B Adjusting screwC Throttle lever20.18 Throttle damper control solenoid -
ESC Hybrid system20.17 Electric choke heater relay location
(arrowed) in main fusebox - ESC Hybrid
system
20.13 Disconnecting air charge
temperature sensor wiring plug - ESC
Hybrid system
20.5 Setting the gap between the crankshaft
speed/position sensor and the crankshaft
toothed wheel - ESC Hybrid system
Page 23 of 24

25Remove the two securing screws and
detach the throttle damper and bracket
assembly from the carburettor (see
illustration).
26Commence refitting by securing the
throttle damper and bracket assembly to the
carburettor with the two screws. Ensure that
the throttle lever is correctly positioned in the
slot in the throttle damper actuating arm.
27Reconnect the vacuum pipe to the throttle
damper.
28Reconnect the air cleaner vacuum hose to
the inlet manifold, and reconnect the air
change temperature sensor wiring plug, then
place the air cleaner to one side to allow
access to the throttle damper.
29Reconnect the battery negative lead.
30Connect a tachometer to the engine in
accordance with the manufacturer’s
instructions.
31Start the engine, then check and if
necessary adjust the idle speed and mixture.
32Earth the “service adjustment” lead,
located in the battery negative wiring loom
(see illustration), for a minimum of 10
seconds. The throttle damper actuating arm
should move to the fully retracted position,
raising the engine speed.
33The engine speed should stabilise at 1700
±100 rpm. If adjustment is necessary, turn
the adjusting screw on the end of the throttle
damper actuating arm to give the correct
speed. Turn the screw clockwise to increase
the engine speed, or anti-clockwise to reduce
the engine speed.34On completion of adjustment, stop the
engine and disconnect the tachometer.
35Where necessary, ensure that any
tamperproof seals are refitted, then refit the
air cleaner, ensuring that the vacuum hose is
securely connected. Isolate the “service
adjustment” lead.
36Start the engine and check that normal
idle speed is resumed, then stop the engine.
Note:Procedures for removal and refitting of
the ignition system components and
electronic module are given elsewhere in the
relevant Sections of this Chapter.
Engine coolant temperature
sensor
2.0 litre SOHC fuel injection models
1For details of engine coolant temperature
sensor removal and refitting, refer to the
Section appertaining to the ESC II system.
1.6 and 1.8 litre (R6A type) CVH models
2The sensor is located in the side of the inlet
manifold.
3Disconnect the battery negative lead.
4Partially drain the cooling system.
5Disconnect the sensor wiring plug by
pulling on the plug, not the wiring (see
illustration).
6Unscrew the sensor from the inlet manifold
and remove it.
7Refitting is a reversal of removal. Refill the
cooling system.
2.0 litre DOHC fuel injection models
8The sensor is located in the side of the inlet
manifold, behind the throttle body. The
removal and refitting procedure is as
described for the 1.6 and 1.8 litre (R6A type)
CVH models above.
Crankshaft speed/position sensor
1.6 and 1.8 litre (R6A type) CVH
models
1.6 litre
9The sensor is located at the left-hand rear
of the cylinder block, above the starter motor
(see illustration).10Disconnect the battery negative lead.
11Remove the securing screw, and
withdraw the sensor shroud.
12Disconnect the sensor wiring plug.
13Remove the Torx securing screw, and
withdraw the sensor.
14Refitting is a reversal of removal.
1.8 litre
15Proceed as described for the ESC Hybrid
module. If a new sensor (not the original unit)
is being fitted, position it in the mounting
bracket so that it is in actual contact with one
of the teeth of the toothed wheel on the
crankshaft. Hold the sensor in this position,
and tighten the clamping screw. New sensors
have projections on their base, which will
wear away when the engine is cranking, and
automatically set the specified clearance.
2.0 litre DOHC fuel injection models
16This procedure is as described for the 2.0
litre DOHC carburettor models (ESC II
module).
Air charge temperature sensor
1.6 and 1.8 litre (R6A type) CVH
models
17The sensor is located in the side of the
CFI unit on 1.6 litre engines (see illustration),
and on the inlet manifold on 1.8 litre engines.
18Disconnect the battery negative lead.
19Disconnect the sensor wiring plug by
pulling on the plug, not the wiring.
20Unscrew the sensor from its location, and
remove it.
21Refitting is a reversal of removal, but coat
the threads of the sensor with suitable sealant
before fitting.
2.0 litre DOHC fuel injection models
22The sensor is located in the upper section
of the inlet manifold.
23Disconnect the battery negative lead.
24Disconnect the sensor wiring plug by
pulling on the plug, not the wiring (see
illustration).
25Unscrew the sensor from the inlet
manifold, and remove it.
26Refitting is a reversal of removal, noting
the torque setting for the sensor.
21EEC IV system components -
removaland refitting
Engine electrical systems 5•23
5
21.9 Crankshaft speed/position sensor
(arrowed) viewed from front of engine with
shroud removed21.17 Air charge temperature sensor
location on 1.6 litre engines (arrowed)
21.5 Disconnecting the engine coolant
temperature sensor wiring plug20.32 Service adjustment lead location
(arrowed) - ESC Hybrid system
Page 24 of 24
Vehicle speed sensor
1.6 and 1.8 litre CVH (R6A type) and
2.0 litre DOHC fuel injection models
27The sensor is located in the left-hand side
of the gearbox/transmission.
28Disconnect the battery negative lead.
29Jack up the vehicle and support it
securely on axle stands (see “Jacking and
Vehicle Support”).
30Detach the sensor wiring connector from
its bracket, and separate the two halves of the
connector.
31Unscrew the securing bolt, and withdraw
the wiring connector bracket, noting its
orientation.
32Withdraw the sensor from the
gearbox/transmission casing (see
illustration).
33Before refitting the sensor, examine the
O-ring, and renew if damaged or worn.
34Refitting is a reversal of removal, ensuring
that the wiring connector bracket is correctly
located.
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP)
sensor
1.6 and 1.8 litre CVH (R6A type) and
2.0 litre DOHC fuel injection models
35The sensor is located at the rear right-
hand side of the engine compartment (see
illustration).
36Disconnect the battery negative lead.
37Remove the two screws securing the
sensor to the body panel, and carefully
withdraw the sensor, taking care not to strainthe wiring.
38Disconnect the wiring plug from the
sensor, pulling on the plug, not the wiring,
then disconnect the vacuum hose and remove
the sensor.
39Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Fuel temperature sensor -
removal and refitting
2.0 litre DOHC fuel injection models
40The sensor is located in the top of the fuel
rail.
41Disconnect the battery negative lead, and
to improve access, disconnect the wiring plug
from the air charge temperature sensor (in the
inlet manifold). Disconnect the sensor wiring
plug by pulling on the plug, not the wiring.
42Disconnect the fuel temperature sensor
wiring plug, again pulling on the plug (see
illustration).
43Unscrew the sensor from the fuel rail, and
remove it.
44Refitting is a reversal of removal, noting
the torque setting for the sensor.
Spark delay and sustain valves
1Disconnect the vacuum pipes at the valve
and withdraw the valve.
2When refitting a spark delay valve, the valve
must be positioned with the black end
(marked “CARB”) towards the carburettor and
the coloured end (marked “DIST”) towards the
distributor or electronic module (as
applicable).
3When refitting a spark sustain valve, the
valve must be positioned with the end marked
“VAC” towards the carburettor and the side
marked “DIST” towards the distributor or
electronic module (as applicable).
Ported vacuum switch
4Where fitted, the switch(es) may be located
in the inlet manifold and/or in an adapter fitted
in one of the coolant hoses.
5To remove a switch, partially drain the
cooling system. Note that there is no need to
remove the cylinder block drain plug.
6Mark the vacuum pipes for location so that
they can be refitted in their correct positions,
then disconnect the pipes from the switch.
7Unscrew the valve from its location.
8Refitting is a reversal of removal, ensuring
that the vacuum pipes are correctly
connected. Refill the cooling system.
Fuel trap
9Disconnect the vacuum pipes at the fuel
trap and withdraw the fuel trap.
10When refitting, the fuel trap must be
positioned with the black end (marked
“CARB”) towards the carburettor, and the
white side (marked “DIST”) towards the
distributor, electronic module, or ported
vacuum switch (as applicable) (see
illustration).
Spark control system additional
components
11According to model, engine and
equipment, additional components such as
one-way valves or solenoids may also be
fitted as part of the spark control system.
12The removal and refitting procedures for
these components are basically as described
previously, and provided that all attachments
are marked for position prior to removal, no
problems should be encountered.
22Spark control system
components (carburettor
models) - removal and refitting
5•24Engine electrical systems
21.24 Disconnecting the air charge
temperature sensor wiring plug21.35 Manifold absolute pressure (MAP)
sensor location
22.10 Fuel trap vacuum connection
markings21.42 Disconnecting the fuel temperature
sensor wiring plug
21.32 Withdrawing the vehicle speed
sensor from the gearbox casing