power steering FORD SIERRA 1985 1.G Routine Manintenance And Servicing Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1985, Model line: SIERRA, Model: FORD SIERRA 1985 1.GPages: 22, PDF Size: 1.26 MB
Page 2 of 22

Cooling system
Drivebelt tensions:
Air conditioning system compressor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10.0 mm (0.4 in) deflection at the midpoint of the belt’s longest run
under firm thumb pressure
Coolant pump/alternator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10.0 mm (0.4 in) deflection midway between coolant pump and
alternator (or power steering pump) pulleys under firm thumb pressure
Fuel system
Air filter element:
Carburettor type:
1.3 and 1.6 litre (SOHC - Ford carburettor) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion W110
1.6 litre (SOHC - Weber carburettor) and 1.8 litre SOHC . . . . . . . .Champion W118
1.6 litre (SOHC - 1984-on) and 2.0 litre SOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion W152
1.8 litre CVH . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion W219
2.0 litre DOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion W152
Fuel injection type:
2.0 litre SOHC and DOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion U507
1.6 and 1.8 litre (R6A type) CVH . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion W219
Fuel filter:
All fuel injection models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion L204
Ignition system
Spark plugs:
Make and type:
All except 1.8 CVH, CVH (R6A), 2.0 DOHC and P100 . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion RF7YCC or RF7YC
1.8 litre CVH . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion RC7YCC or RC7YC
P100 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion RF7YC or F7YC
1.6 and 1.8 litre (R6A type) CVH . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion RC7YCC
2.0 litre DOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion RC7YCC
Electrode gap*:
Champion F7YCC or RC7YCC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.8 mm (0.032 in)
Champion RF7YC, F7YC or RC7YC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.7 mm (0.028 in)
Ignition HT leads
Resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30 k ohms maximum per lead
Type:
All SOHC models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion LS-09 or LS-10 boxed set
1.8 litre CVH . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion LS-10 boxed set
1.6 and 1.8 litre (R6A type) CVH . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion LS-30 boxed set
2.0 litre DOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion LS-29 boxed set
*The spark plug gap quoted is that recommended by Champion for their specified plugs listed above. If spark plugs of any other type are to be
fitted, refer to their manufacturer’s recommendations.
Brakes
Brake pad friction material minimum thickness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.5 mm (0.06 in)
Brake shoe friction material minimum thickness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.0 mm (0.04 in)
Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Engine oil drain plug:
SOHC and DOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2816 to 21
CVH . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 3015 to 22
Engine block coolant drain plug (where fitted) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 25 16 to 18
Manual gearbox:
Oil filler/level plug:
A,B,C and N types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33 to 4124 to 30
MT75 type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29 to 4121 to 30
Oil drain plug:
MT75 type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29 to 4121 to 30
Final drive oil filler plug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35 to 4526 to 33
Roadwheel nuts:
Saloon, Hatchback and Estate models (steel and alloy wheels) . . . .70 to 10052 to 74
P100 models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .85 to 9063 to 66
Spark plugs:
SOHC models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2815 to 21
CVH models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18 to 3313 to 24
DOHC models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15 to 2111 to 15
Brake caliper guide bolts:
Front . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Rear . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31 to 3523 to 26
1•2Servicing specifications
Page 3 of 22
The maintenance intervals in this manual
are provided with the assumption that you will
be carrying out the work yourself. These are
the minimum maintenance intervals
recommended by the manufacturer for
vehicles driven daily. If you wish to keep your
vehicle in peak condition at all times, you maywish to perform some of these procedures
more often. We encourage frequent
maintenance, because it enhances the
efficiency, performance and resale value of
your vehicle.
If the vehicle is driven in dusty areas, used
to tow a trailer, or driven frequently at slowspeeds (idling in traffic) or on short journeys,
more frequent maintenance intervals are
recommended.
When the vehicle is new, it should be
serviced by a factory-authorised dealer
service department, in order to preserve the
factory warranty.
Capacities
Engine oil
SOHC engines:
With filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3.75 litres (6.6 pints)
Without filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3.25 litres (5.7 pints)
DOHC engine:
With filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4.5 litres (7.9 pints)
Without filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4.0 litres (7.0 pints)
1.6 litre CVH engine:
With filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3.5 litres (6.2 pints)
Without filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3.25 litres (5.7 pints)
1.8 CVH engines:
With filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4.0 litres (7.0 pints)
Without filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3.5 litres (6.2 pints)
Cooling system (including heater)
SOHC engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8.0 litres (14.1 pints)
DOHC engine:
Carburettor models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7.0 litres (12.3 pints)
Fuel injection models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7.3 litres (12.8 pints)
CVH engines:
1.6 and 1.8 litre (R2A) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9.5 litres (16.7 pints)
1.8 litre (R6A) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7.9 litres (13.9 pints)
Fuel tank
All models except P100 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60.0 litres (13.2 gals)
P100 models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66.0 litres (14.5 gals)
Manual gearbox
A1 and A2 types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.98 litre (1.72 pints)
B type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.46 litres (2.57 pints)
C type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.25 litres (2.20 pints)
N type up to 1987 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.90 litres (3.34 pints)
N type from 1987 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.25 litres (2.20 pints)
MT75 type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.2 litres (2.1 pints)
Automatic transmission
C3 type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6.3 litres (11.1 pints)
A4LD type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8.5 litres (15.0 pints)
Final drive (from dry)
All models except 1.3 and 1.6 litre Hatchback and P100 . . . . . . . . . . .0.9 litre (1.6 pints)
1.3 and 1.6 litre Hatchback models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.8 litre (1.4 pints)
P100 models (rear axle) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.14 litres (2.0 pints)
Power steering
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.65 litre (1.14 pints)
Servicing specifications 1•3
1
1Ford Sierra maintenance schedule
Page 4 of 22

1•4Maintenance schedule
Every 250 miles (400 km) or weekly
m mCheck the engine oil level (Section 3)
m mCheck the engine coolant level (Section 3)
m mCheck the brake fluid level (Section 3)
m mCheck the power steering fluid level (Section 3)
m mCheck the screen washer fluid level (Section 3)
m mVisually examine the tyres for tread depth, and wear
or damage (Section 4)
m mCheck and if necessary adjust the tyre pressures
(Section 4)
m mCheck and if necessary top-up the battery electrolyte
level - where applicable (Section 6)
m mCheck the operation of the horn, all lights, and the
wipers and washers (Sections 5 and 7)
Every 6000 miles (10 000 km) or
6 months - whichever comes sooner
m mRenew engine oil and filter (Section 8)
m mCheck brake pads or shoes for wear (front and rear)
(Section 9)
m mCheck operation of brake fluid level warning indicator
(Section 9)
m mInspect engine bay and underside of vehicle for fluid
leaks or other signs of damage (Section 10)
m mCheck function and condition of seat belts
(Section 11)
m mCheck condition and security of exhaust system
(Section 12)
m mCheck tightness of wheel nuts (Section 13)
m mClean oil filler cap (Section 14)
m mCheck idle speed (where applicable) (Section 15)
m mCheck mixture adjustment (where applicable)
(Section 16)
Every 12 000 miles (20 000 km) or
12 months - whichever comes sooner
m mCheck automatic transmission fluid level (engine hot)
(Section 17)
m mCheck manual gearbox oil level (Section 18)
m mCheck operation of latches, check straps and locks;
lubricate if necessary (Section 19)
m mRenew spark plugs (Section 20)
m mCheck condition and tension of auxiliary drivebelt(s);
adjust or renew as necessary (Section 21)
m mCheck tightness of battery terminals, clean and
neutralise corrosion if necessary (Section 22)
m mCheck engine valve clearances - SOHC only
(Section 23)
m mCheck handbrake mechanism (Section 24)
Every 24 000 miles (40 000 km) or
2 years - whichever comes sooner
m mCheck air cleaner inlet air temperature control
operation (carburettor models) (Section 36)
m mRenew pulse air filter element (1.6 litre CVH)
(Section 37)
m mRenew air cleaner element (Section 38)
m mClean and inspect distributor cap and HT leads
(Section 39)
m mCheck automatic transmission brake band
adjustment (Section 40)
m mRenew fuel filter (fuel-injection models only)
(Section 41)
m mRenew crankcase ventilation vent valve (SOHC and
DOHC) (Section 42)
m mClean radiator matrix and air conditioning condenser
fins (where applicable) (Section 25)
m mCheck air conditioning refrigerant charge (where
applicable) (Section 26)
m mCheck final drive oil level (Section 27)
m mLubricate automatic transmission selector/kickdown
linkage (Section 28)
m mCheck security and condition of steering and
suspension components, gaiters and boots
(Section 29)
m mCheck condition and security of driveshaft joints and
gaiters (Section 30)
m mInspect underbody and panels for corrosion or other
damage (Section 31)
m mInspect brake pipes and hoses (Section 32)
m mClean idle speed control linkage at throttle (where
applicable) (Section 33)
m mRoad test and check operation of ABS (Section 34)
m mCheck crankcase ventilation system (Section 35)
Every 36 000 miles (60 000 km) or
3 years - whichever comes sooner
m mRenew brake hydraulic system seals and hoses if
necessary (Section 43)
m mRenew brake hydraulic fluid (Section 44)
m mRenew camshaft drivebelt (optional on SOHC
models - compulsory on CVH) (Section 45)
m mRenew coolant (Section 46)
Every 12 000 miles (20 000 km) or
12 months - whichever comes sooner
(continued)
Page 6 of 22
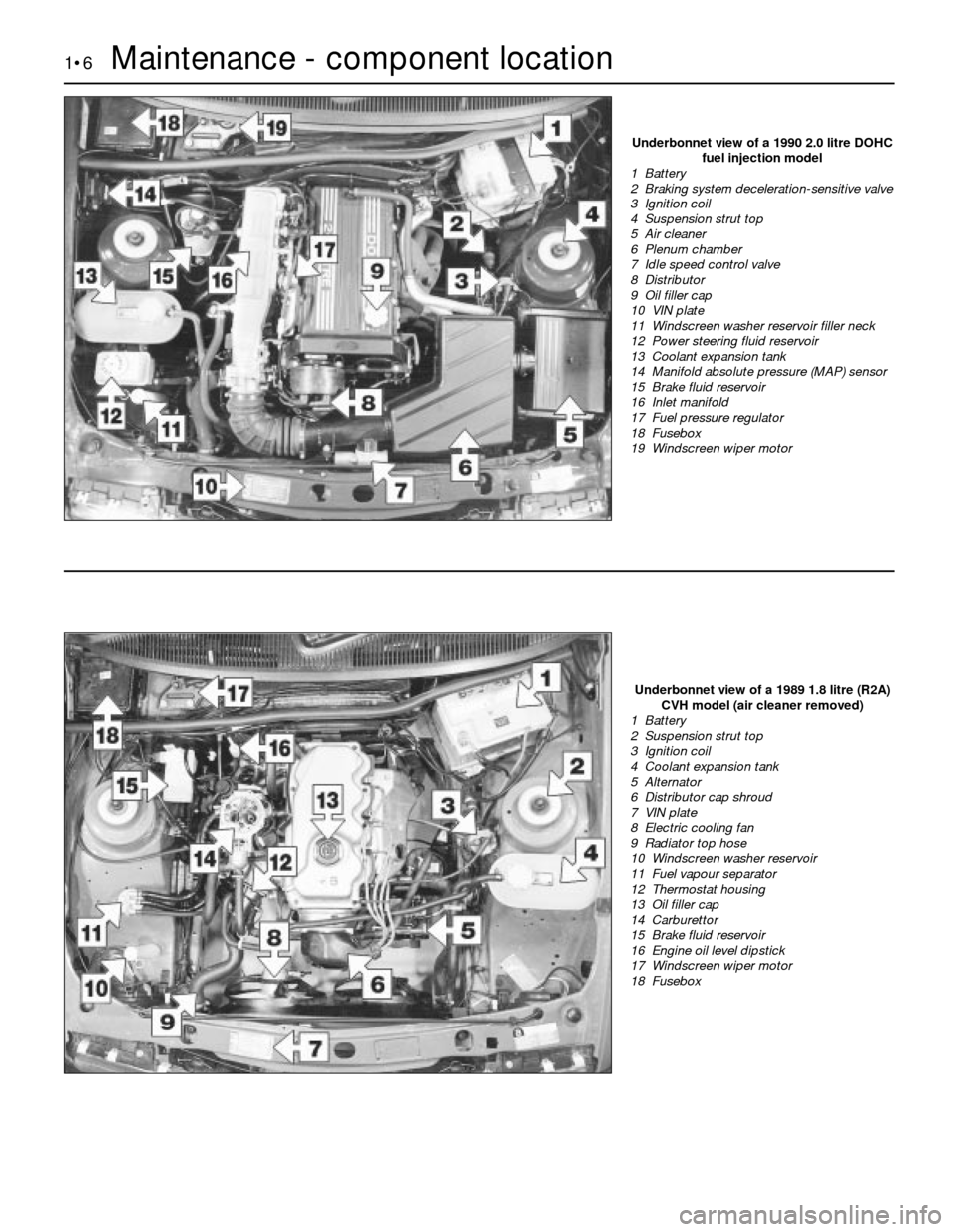
1•6Maintenance - component location
Underbonnet view of a 1990 2.0 litre DOHC
fuel injection model
1 Battery
2 Braking system deceleration-sensitive valve
3 Ignition coil
4 Suspension strut top
5 Air cleaner
6 Plenum chamber
7 Idle speed control valve
8 Distributor
9 Oil filler cap
10 VIN plate
11 Windscreen washer reservoir filler neck
12 Power steering fluid reservoir
13 Coolant expansion tank
14 Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
15 Brake fluid reservoir
16 Inlet manifold
17 Fuel pressure regulator
18 Fusebox
19 Windscreen wiper motor
Underbonnet view of a 1989 1.8 litre (R2A)
CVH model (air cleaner removed)
1 Battery
2 Suspension strut top
3 Ignition coil
4 Coolant expansion tank
5 Alternator
6 Distributor cap shroud
7 VIN plate
8 Electric cooling fan
9 Radiator top hose
10 Windscreen washer reservoir
11 Fuel vapour separator
12 Thermostat housing
13 Oil filler cap
14 Carburettor
15 Brake fluid reservoir
16 Engine oil level dipstick
17 Windscreen wiper motor
18 Fusebox
Page 7 of 22
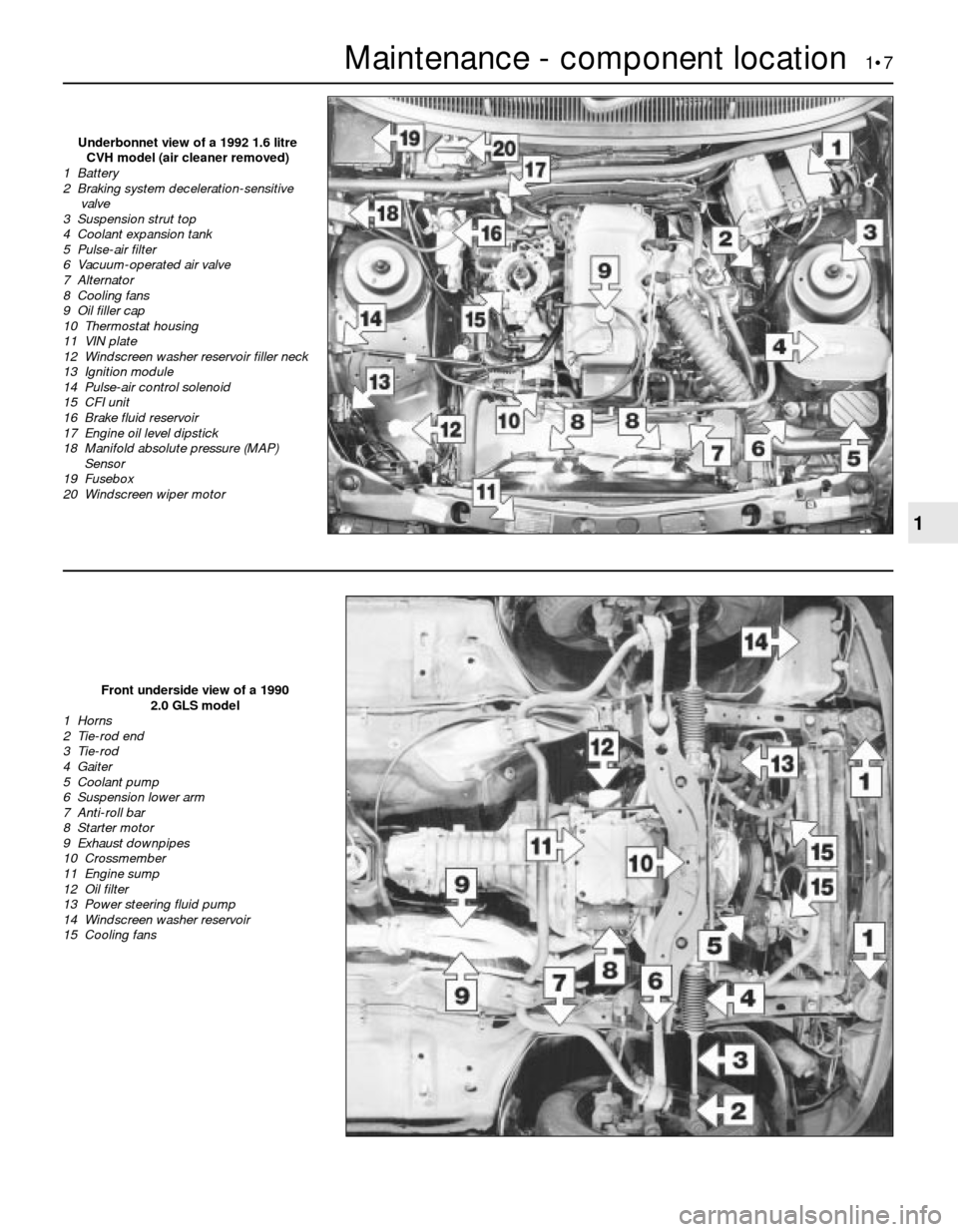
Maintenance - component location 1•7
1
Front underside view of a 1990
2.0 GLS model
1 Horns
2 Tie-rod end
3 Tie-rod
4 Gaiter
5 Coolant pump
6 Suspension lower arm
7 Anti-roll bar
8 Starter motor
9 Exhaust downpipes
10 Crossmember
11 Engine sump
12 Oil filter
13 Power steering fluid pump
14 Windscreen washer reservoir
15 Cooling fans
Underbonnet view of a 1992 1.6 litre
CVH model (air cleaner removed)
1 Battery
2 Braking system deceleration-sensitive
valve
3 Suspension strut top
4 Coolant expansion tank
5 Pulse-air filter
6 Vacuum-operated air valve
7 Alternator
8 Cooling fans
9 Oil filler cap
10 Thermostat housing
11 VIN plate
12 Windscreen washer reservoir filler neck
13 Ignition module
14 Pulse-air control solenoid
15 CFI unit
16 Brake fluid reservoir
17 Engine oil level dipstick
18 Manifold absolute pressure (MAP)
Sensor
19 Fusebox
20 Windscreen wiper motor
Page 11 of 22
4Carefully check the condition of all coolant,
fuel, power steering and brake hoses. Renew
any hose which is cracked, swollen or
deteriorated. Cracks will show up better if the
hose is squeezed. Pay close attention to the
hose clips that secure the hoses to the system
components. Hose clips can pinch and
puncture hoses, resulting in leaks. If wire type
hose clips are used, it may be a good idea to
replace them with screw-type clips.
5With the vehicle raised, inspect the fuel
tank and filler neck for punctures, cracks and
other damage. The connection between the
filler neck and tank is especially critical.
Sometimes a rubber filler neck or connecting
hose will leak due to loose retaining clamps or
deteriorated rubber.
6Similarly, inspect all brake hoses and metal
pipes. If any damage or deterioration is
discovered, do not drive the vehicle until the
necessary repair work has been carried out.
Renew any damaged sections of hose or pipe.
7Carefully check all rubber hoses and metal
fuel lines leading away from the petrol tank.
Check for loose connections, deteriorated
hoses, crimped lines and other damage. Pay
particular attention to the vent pipes and
hoses which often loop up around the filler
neck and can become blocked or crimped.
Follow the lines to the front of the vehicle
carefully inspecting them all the way. Renew
damaged sections as necessary.
8From within the engine compartment,
check the security of all fuel hose attachments
and pipe unions, and inspect the fuel hoses
and vacuum hoses for kinks, chafing and
deterioration.
9Where applicable, check the condition of
the oil cooler hoses and pipes.
10Check the condition of all exposed wiring
harnesses.
1Periodically check the belts for fraying or
other damage. If evident, renew the belt.
2If the belts become dirty, wipe them with a
damp cloth using a little detergent only.
3Check the tightness of the anchor bolts and
if they are ever disconnected, make quite sure
that the original sequence of fitting of
washers, bushes and anchor plates is
retained.
With the vehicle raised on a hoist or
supported on axle stands, check the exhaust
system for signs of leaks, corrosion or
damage and check the rubber mountings for
condition and security. Where damage or
corrosion are evident, renew the system
complete or in sections, as applicable, using
the information given in Chapter 4.With the wheels on the ground, slacken each
wheel nut by a quarter turn, then retighten it
immediately to the specified torque.
Remove and clean the oil filler cap of any
sludge build-up using paraffin.
Inspect the vent hose for blockage or
damage. A blocked hose can cause a build-
up of crankcase pressure, which in turn can
cause oil leaks.
Ford VV carburettor
1Ensure that the air cleaner is correctly fitted,
and that all vacuum hoses and pipes are
securely connected and free from restrictions,
then run the engine until it is at normal
operating temperature.
2Stop the engine, and connect a tachometer
and an exhaust gas analyser in accordance
with the manufacturer’s instructions.
3Start the engine and run it at 3000 rpm for
30 seconds, ensuring that all electrical loads
are switched off (headlamps, heater blower
etc), then allow the engine to idle and check
the idle speed and CO content. Note that the
CO reading will initially rise, then fall and finally
stabilise after between 5 and 25 seconds.4If necessary, adjust the idle speed screw to
give the specified idle speed (see
illustration).
5Checking and adjustment should be
completed within 30 seconds of the meter
readings stabilising. If this has not been
possible, repeat paragraphs 3 and 4, ignoring
the reference to starting the engine.
Weber 2V carburettor
Models without stepper motor
6Proceed as described for the Ford VV
carburettor but note the following:
7It is permissible to loosen the air cleaner
securing screws to allow easier access to the
carburettor adjustment screws but ensure
that all vacuum hoses and pipes are securely
connected. For adjustment screw location
(see illustrations).
Models with stepper motor (ESC II
system)
8The idle speed is controlled by the ESC II
module via the stepper motor. The only idle
speed adjustment possible is provided by the
“idle speed adjustment” wire, which can be
earthed to raise the idle speed by 75 rpm. No
other method of idle speed adjustment should
be attempted. If the idle speed is incorrect,
the problem should be referred to a Ford
dealer, as the problem probably lies in the
ESC II module for which special diagnostic
equipment is required.
15Engine idle speed check
14Oil filler cap check
13Roadwheel security check
12Exhaust system check
11Seat belt check
Every 6000 miles or 6 months 1•11
1
15.7b Weber 2V carburettor adjustment
screw locations - 1.6 litre models
A Idle mixture screwB Idle speed screw
15.7a Weber 2V carburettor adjustment
screw locations - 2.0 litre models up to 1985
A Idle speed screwB Idle mixture screw
15.4 Ford VV carburettor adjustment screw
locations
A Idle speed screwB Idle mixture screw
Caution: Refer to the
precautions in Section 1,
Chapter 4, Part A or B (as
applicable), before proceeding.
Before carrying out any carburettor
adjustments, ensure that the ignition
timing and spark plug gaps are set as
specified. To carry out the adjustments an
accurate tachometer and an exhaust gas
analyser (CO meter) will be required.
Page 14 of 22
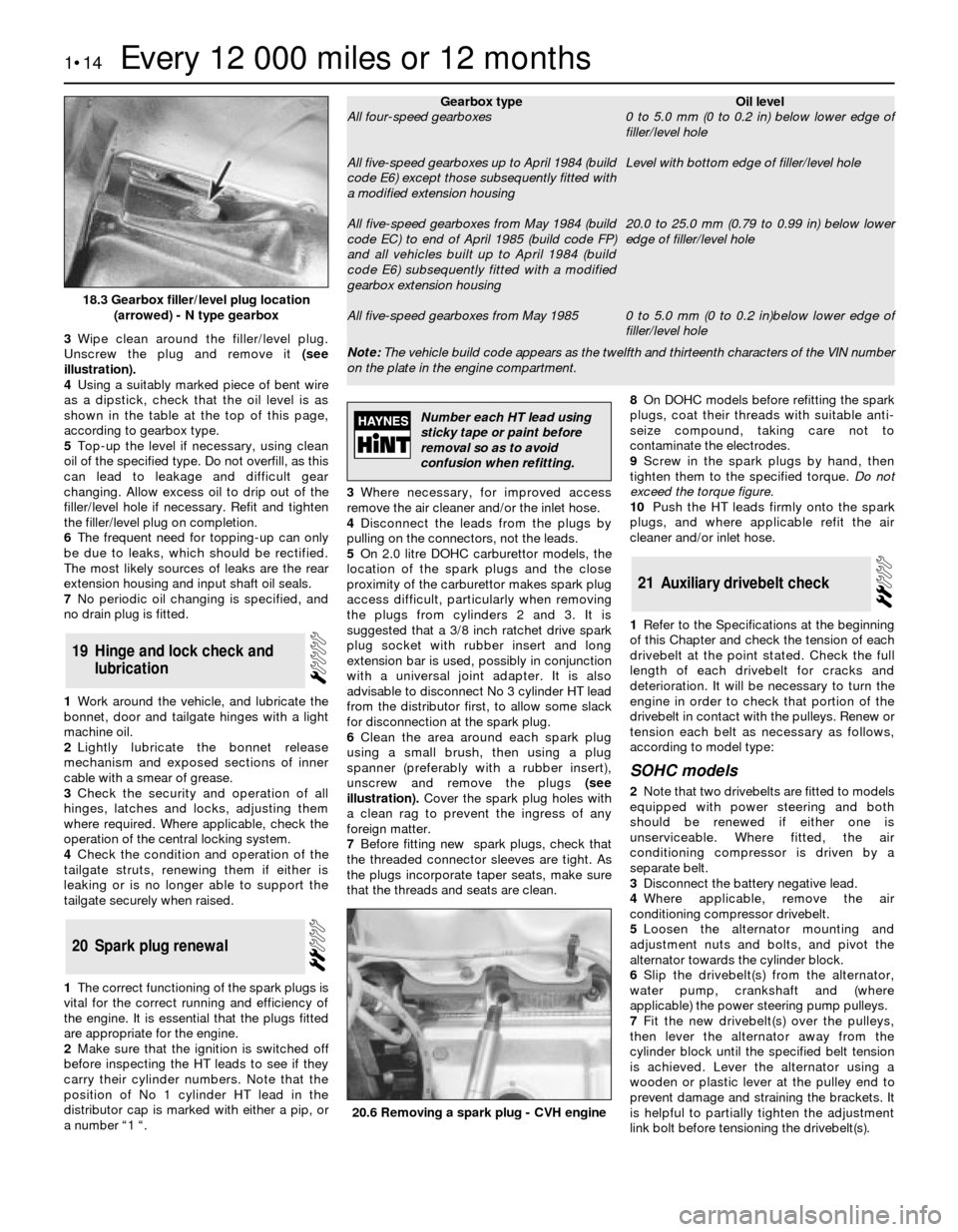
3Wipe clean around the filler/level plug.
Unscrew the plug and remove it(see
illustration).
4Using a suitably marked piece of bent wire
as a dipstick, check that the oil level is as
shown in the table at the top of this page,
according to gearbox type.
5Top-up the level if necessary, using clean
oil of the specified type. Do not overfill, as this
can lead to leakage and difficult gear
changing. Allow excess oil to drip out of the
filler/level hole if necessary. Refit and tighten
the filler/level plug on completion.
6The frequent need for topping-up can only
be due to leaks, which should be rectified.
The most likely sources of leaks are the rear
extension housing and input shaft oil seals.
7No periodic oil changing is specified, and
no drain plug is fitted.
1Work around the vehicle, and lubricate the
bonnet, door and tailgate hinges with a light
machine oil.
2Lightly lubricate the bonnet release
mechanism and exposed sections of inner
cable with a smear of grease.
3Check the security and operation of all
hinges, latches and locks, adjusting them
where required. Where applicable, check the
operation of the central locking system.
4Check the condition and operation of the
tailgate struts, renewing them if either is
leaking or is no longer able to support the
tailgate securely when raised.
1The correct functioning of the spark plugs is
vital for the correct running and efficiency of
the engine. It is essential that the plugs fitted
are appropriate for the engine.
2Make sure that the ignition is switched off
before inspecting the HT leads to see if they
carry their cylinder numbers. Note that the
position of No 1 cylinder HT lead in the
distributor cap is marked with either a pip, or
a number “1 “.3Where necessary, for improved access
remove the air cleaner and/or the inlet hose.
4Disconnect the leads from the plugs by
pulling on the connectors, not the leads.
5On 2.0 litre DOHC carburettor models, the
location of the spark plugs and the close
proximity of the carburettor makes spark plug
access difficult, particularly when removing
the plugs from cylinders 2 and 3. It is
suggested that a 3/8 inch ratchet drive spark
plug socket with rubber insert and long
extension bar is used, possibly in conjunction
with a universal joint adapter. It is also
advisable to disconnect No 3 cylinder HT lead
from the distributor first, to allow some slack
for disconnection at the spark plug.
6Clean the area around each spark plug
using a small brush, then using a plug
spanner (preferably with a rubber insert),
unscrew and remove the plugs(see
illustration).Cover the spark plug holes with
a clean rag to prevent the ingress of any
foreign matter.
7Before fitting new spark plugs, check that
the threaded connector sleeves are tight. As
the plugs incorporate taper seats, make sure
that the threads and seats are clean.8On DOHC models before refitting the spark
plugs, coat their threads with suitable anti-
seize compound, taking care not to
contaminate the electrodes.
9Screw in the spark plugs by hand, then
tighten them to the specified torque. Do not
exceed the torque figure.
10Push the HT leads firmly onto the spark
plugs, and where applicable refit the air
cleaner and/or inlet hose.
1Refer to the Specifications at the beginning
of this Chapter and check the tension of each
drivebelt at the point stated. Check the full
length of each drivebelt for cracks and
deterioration. It will be necessary to turn the
engine in order to check that portion of the
drivebelt in contact with the pulleys. Renew or
tension each belt as necessary as follows,
according to model type:
SOHC models
2Note that two drivebelts are fitted to models
equipped with power steering and both
should be renewed if either one is
unserviceable. Where fitted, the air
conditioning compressor is driven by a
separate belt.
3Disconnect the battery negative lead.
4Where applicable, remove the air
conditioning compressor drivebelt.
5Loosen the alternator mounting and
adjustment nuts and bolts, and pivot the
alternator towards the cylinder block.
6Slip the drivebelt(s) from the alternator,
water pump, crankshaft and (where
applicable) the power steering pump pulleys.
7Fit the new drivebelt(s) over the pulleys,
then lever the alternator away from the
cylinder block until the specified belt tension
is achieved. Lever the alternator using a
wooden or plastic lever at the pulley end to
prevent damage and straining the brackets. It
is helpful to partially tighten the adjustment
link bolt before tensioning the drivebelt(s).
21Auxiliary drivebelt check
20Spark plug renewal
19Hinge and lock check and
lubrication
1•14Every 12 000 miles or 12 months
18.3 Gearbox filler/level plug location
(arrowed) - N type gearbox
20.6 Removing a spark plug - CVH engine
Note: The vehicle build code appears as the twelfth and thirteenth characters of the VIN number
on the plate in the engine compartment.
Gearbox type
All four-speed gearboxes
All five-speed gearboxes up to April 1984 (build
code E6) except those subsequently fitted with
a modified extension housing
All five-speed gearboxes from May 1984 (build
code EC) to end of April 1985 (build code FP)
and all vehicles built up to April 1984 (build
code E6) subsequently fitted with a modified
gearbox extension housing
All five-speed gearboxes from May 1985Oil level
0 to 5.0 mm (0 to 0.2 in) below lower edge of
filler/level hole
Level with bottom edge of filler/level hole
20.0 to 25.0 mm (0.79 to 0.99 in) below lower
edge of filler/level hole
0 to 5.0 mm (0 to 0.2 in)below lower edge of
filler/level hole
Number each HT lead using
sticky tape or paint before
removal so as to avoid
confusion when refitting.
Page 15 of 22
8Tighten the alternator mounting and
adjustment nuts and bolts in the order shown
(see illustration).
9Where applicable, refit and tension the air
conditioning compressor drivebelt.
10Reconnect the battery negative lead.
11Drivebelt tension should be rechecked
and if necessary adjusted after the engine has
been run for a minimum of ten minutes.
DOHC models
12Three different types of drivebelt
arrangement are used, depending on model
(see illustrations).On models without powersteering, the drivebelt is tensioned by moving
the alternator. On models with power steering,
the power steering pump is also driven by the
coolant pump/alternator drivebelt and an
automatic belt tensioner is fitted (see
illustration).On models with air conditioning,
the drivebelt drives the alternator, coolant
pump, power steering pump and air
conditioning compressor, and an automatic
belt tensioner is fitted.
13On models without power steering, loosen
the alternator mounting and adjustment bolts,
and pivot the alternator towards the cylinder
block. Slip the drivebelt from the pulleys.
14On models with power steering, the
automatic tensioner can be released using a
17 mm socket and a wrench on the boss in
the centre of the pulley. Lever the tensioner
assembly clockwise, slide the belt from the
pulleys, then slowly release the tensioner.
15To fit a new belt on models without
power steering, slide the belt over the pulleys,
then lever the alternator away from the
cylinder block until the correct belt tension is
achieved. Lever the alternator using a plastic
or wooden lever at the pulley end to prevent
damage. It is helpful to partially tighten the
adjustment link bolt before tensioning the
drivebelt. When the correct tension is
achieved, tighten all the bolts.
16To fit a new belt on models with power
steering, lever the tensioner clockwise as
during removal, then slide the belt over the
pulleys, and slowly release the tensioner.
1The battery fitted as original equipment is
“maintenance-free”, and requires nomaintenance apart from having the case kept
clean, and the terminals clean and tight.
2To clean the battery terminals disconnect
them, after having first removed the cover
(later models) - negative earth first. Use a wire
brush or abrasive paper to clean the
terminals. Bad corrosion should be treated
with a solution of bicarbonate of soda, applied
with an old toothbrush. Do not let this solution
get inside the battery.
3Coat the battery terminals with petroleum
jelly or a proprietary anti-corrosive compound
before reconnecting them. Reconnect and
tighten the positive (live) lead first, followed by
the negative (earth) lead. Do not overtighten.
4Keep the top of the battery clean and dry.
Inspect the battery tray for corrosion, and
make good as necessary.
SOHC engines
1The valve clearances must be checked with
the engine cold. On carburettor models
remove the air cleaner.
2Disconnect the HT leads from the spark
plugs and release them from the clips on the
camshaft cover.
3On fuel injection models, unbolt and
remove the bracing strut securing the inlet
manifold to the right-hand side of the cylinder
head.
4Where applicable, unclip any hoses and
wires from the camshaft cover, then unscrew
the securing bolts and remove the camshaft
cover and gaskets. Take care not to lose the
spacer plates which fit under the bolt heads,
where applicable.
23Engine valve clearance
check
22Battery terminal check
Every 12 000 miles or 12 months 1•15
1
21.12b Coolant pump/alternator drivebelt
arrangement - 2.0 litre DOHC engine with
power steering
1 Alternator
2 Automatic belt
tension
3 Coolant pump4 Crankshaft pulley
5 Power steering
pump21.12d Alternator/coolant pump drivebelt
tensioner indicator position -
2.0 litre DOHC engine
Inset shows tensioner at maximum
adjustment
1 Alternator
2 Automatic belt
tensioner
3 Coolant pump4 Air conditioning
compressor
5 Crankshaft pulley
6 Power steering
pump
21.12c Coolant pump/alternator drivebelt
arrangement - 2.0 litre DOHC engine with
power steering and air conditioning
21.12a Coolant pump/alternator drivebelt
arrangement - 2.0 litre DOHC engine
without power steering
1 Alternator
2 Coolant pump3 Crankshaft
pulley
21.8 Alternator mounting tightening
sequence - SOHC engines
Caution: Before carrying out
any work on the vehicle battery,
read through the precautions
given in “Safety first!” at the
beginning of this manual.
It will be easier to turn the
engine by hand if the spark
plugs are removed but take
care not to allow dirt to enter
the spark plug holes.