check engine FORD SIERRA 1988 2.G Routine Manintenance And Servicing User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1988, Model line: SIERRA, Model: FORD SIERRA 1988 2.GPages: 22, PDF Size: 1.26 MB
Page 17 of 22

system immediately if the charge is low and
do not use it again until it has been recharged.
4Inspect the refrigerant pipes, hoses and
unions for security and good condition. Refit
the radiator grille.
5The air conditioning system will lose a
proportion of its charge through normal
seepage typically up to 100 g (4 oz) per year -
so it is as well to regard periodic recharging
as a maintenance operation.
1Check the final drive oil level as follows.
2Position the vehicle over a pit, or raise it at
front and rear on ramps or axle stands. The
vehicle must be level.
3Wipe clean around the final drive filler/level
plug (see illustrations) and unscrew the
plug. Using a piece of bent wire as a dipstick,
check that the oil is no more than 10 mm (0.4
in) below the plug hole.
4If topping-up is necessary, use clean gear
oil of the specified type. Do not overfill.
Frequent need for topping-up can only be due
to leaks, which should be rectified.
5When the level is correct, refit the filler/level
plug and tighten it to the specified torque
loading.
6There is no requirement for periodic oil
changing, and no drain plug is provided.
Lubricate the transmission selector and
kickdown linkages with engine oil or aerosol
lubricant.
1Check the shock absorbers by bouncing
the vehicle up and down at each corner in
turn. When released, it should come to rest
within one complete oscillation. Continued
movement, or squeaking and groaning noises
from the shock absorber suggests that
renewal is required .
2Raise and support the vehicle. Examine all
steering and suspension components for
wear and damage. Pay particular attention to
dust covers and gaiters, which if renewed
promptly when damaged can save further
damage to the component protected.
3At the same intervals, check the front
suspension lower arm balljoints for wear by
levering up the arms(see illustration).
Balljoint free movement must not exceed 0.5
mm (0.02 in). The track rod end balljoints can
be checked in a similar manner, or by
observing them whilst an assistant rocks the
steering wheel back and forth. If the lower arm
balljoint is worn, the complete lower arm must
be renewed .4Wheel bearings can be checked for wear by
spinning the relevant roadwheel. Any
roughness or excessive noise indicates worn
bearings, which must be renewed, as no
adjustment is possible. It is unlikely that any
wear will be evident unless the vehicle has
covered a very high mileage. It should be
noted that it is normal for the bearings to
exhibit slight endfloat, which is perceptible as
wheel rock at the wheel rim.
1Position the vehicle over a pit, or raise it at
front and rear on ramps or axle stands (see
“Jacking and vehicle support”).
2Examine the driveshaft joint rubber gaiters.
Flex the gaiters by hand and inspect the folds
and clips. Damaged or leaking gaiters must
be renewed without delay to avoid damage
occurring to the joint itself
3Check the tightness of the final drive
mounting bolts and the driveshaft flange screws.
1Except on vehicles with a wax-based
underbody protective coating, have the whole
of the underframe of the vehicle steam-
cleaned, engine compartment included, so
that a thorough inspection can be carried out
to see what minor repairs and renovations are
necessary. 2Steam-cleaning is available at many
garages and is necessary for the removal of
the accumulation of oily grime which
sometimes is allowed to become thick in
certain areas. If steam-cleaning facilities are
not available, there are some excellent grease
solvents available which can be brush-
applied; the dirt can then be simply hosed off.
3After cleaning, position the vehicle over a
pit, or raise it at front and rear on ramps or axle
stands (see “Jacking and vehicle support”).
4Using a strong light, work around the
underside of the vehicle, inspecting it for
corrosion or damage. If either is found, refer
to Chapter 12 for details of repair.
Periodically inspect the rigid brake pipes for
rust and other damage, and the flexible hoses
for cracks, splits or “ballooning”. Have an
assistant depress the brake pedal (ignition on)
and inspect the hose and pipe unions for leaks.
Renew any defective item without delay.
On carburettor models which incorporate a
stepper motor (ie. Weber 2V from 1985), good
electrical contact between the motor plunger
and the adjusting screw is essential to
maintain a regular idle speed.
Clean the plunger and adjusting screw
contact faces with abrasive paper followed by
switch cleaning fluid. Switch cleaning fluid is
available from electronic component shops.
Instruments and electrical
equipment
1Check the operation of all instruments and
electrical equipment.
2Make sure that all instruments read
correctly, and switch on all electrical
equipment in turn to check that it functions
properly.
34Road test
33Idle speed linkage clean
32Brake pipe and hose check
31Underbody inspection
30Driveshaft check
29Steering and suspension
security check
28Automatic transmission
selector linkage lubrication
27Final drive oil level check
Every 12 000 miles or 12 months 1•17
1
29.3 Levering up lower arm to check
balljoint for wear
27.3b Rear axle filler plug location -
P100 models27.3a Final drive unit filler plug location
(arrowed) -
Saloon, Hatchback and Estate models
Page 18 of 22
Steering and suspension
3Check for any abnormalities in the steering,
suspension, handling or road “feel”.
4Drive the vehicle, and check that there are
no unusual vibrations or noises.
5Check that the steering feels positive, with
no excessive “sloppiness”, or roughness, and
check for any suspension noises when
cornering, or when driving over bumps.
Drivetrain
6Check the performance of the engine,
clutch, transmission and driveshafts.
7Listen for any unusual noises from the
engine, clutch and transmission.
8Make sure that the engine runs smoothly
when idling, and that there is no hesitation
when accelerating.9Where applicable, check that the clutch
action is smooth and progressive, that the
drive is taken up smoothly, and that the pedal
travel is not excessive. Also listen for any
noises when the clutch pedal is depressed.
10Check that all gears can be engaged
smoothly, without noise, and that the gear lever
action is not abnormally vague or “notchy”.
Check the operation and
performance of the braking
system
11Make sure that the vehicle does not pull to
one side when braking, and that the wheels
do not lock prematurely when braking hard.
12Check that there is no vibration through
the steering when braking.
13Check that the handbrake operates
correctly, without excessive movement of thelever, and that it holds the vehicle stationary
on a slope.
14Test the operation of the brake servo unit
as follows. With the engine off, depress the
footbrake four or five times to exhaust the
vacuum. Start the engine, holding the brake
pedal depressed. As the engine starts, there
should be a noticeable “give” in the brake
pedal as vacuum builds up. Allow the engine
to run for at least two minutes, and then
switch it off. If the brake pedal is depressed
now, it should be possible to detect a hiss
from the servo as the pedal is depressed.
After about four or five applications, no further
hissing should be heard, and the pedal should
feel considerably firmer.
1Inspect the crankcase ventilation system
for blockage or damage. A blocked hose can
cause a build-up of crankcase pressure,
which in turn can cause oil leaks (see
illustration).
2On carburettor model SOHC engines, clean
the oil filler cap with paraffin and check that
the vent valve is not blocked by pulling it from
the oil separator and loosening the hose clip
(Section 42).
3On CVH engines, check that the oil
separator and mushroom valve are not
blocked, and clean if necessary (see
illustration).
35Crankcase ventilation system
check
SOHC and DOHC carburettor
models
1A vacuum pump will be required to test the
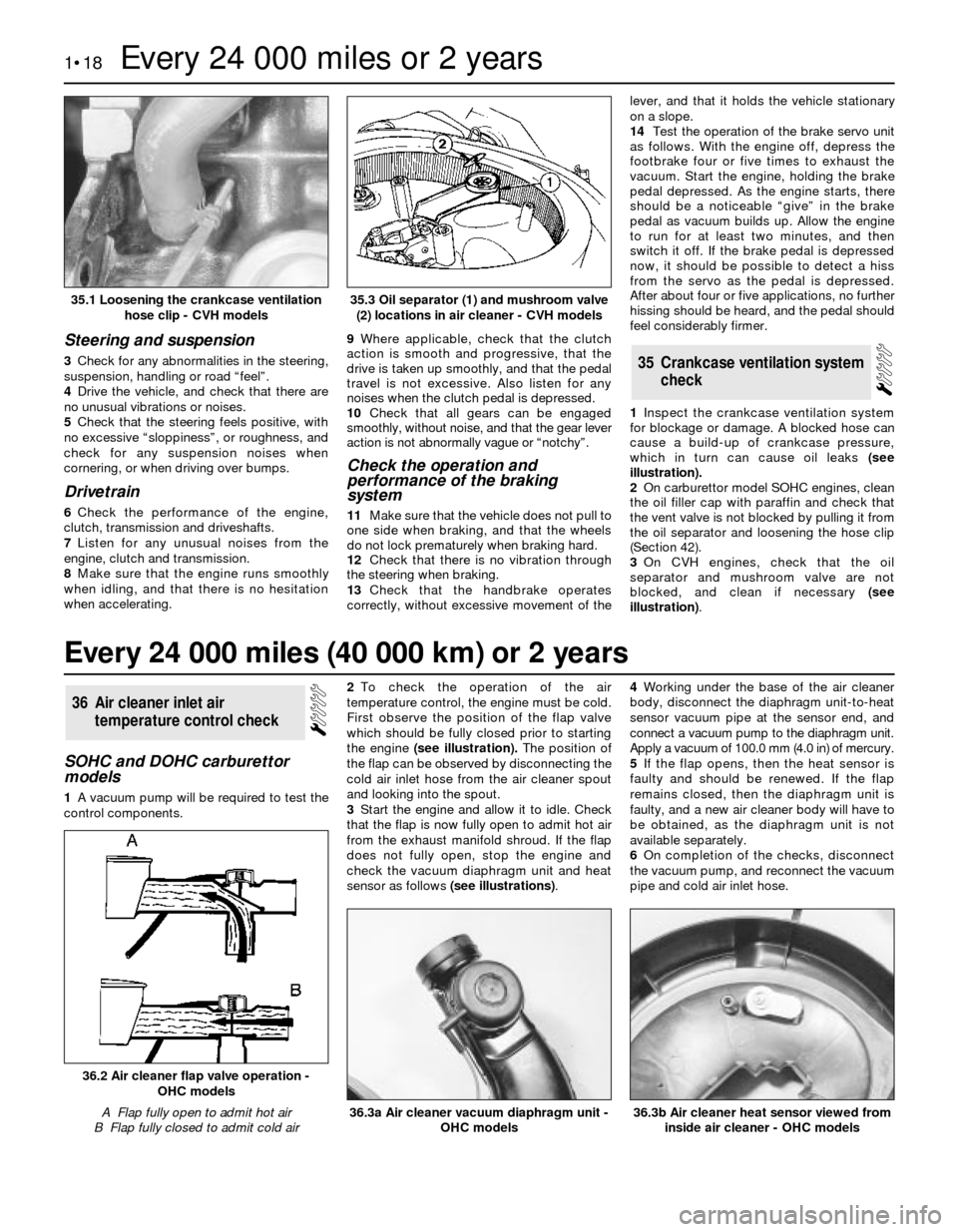
control components.2To check the operation of the air
temperature control, the engine must be cold.
First observe the position of the flap valve
which should be fully closed prior to starting
the engine(see illustration).The position of
the flap can be observed by disconnecting the
cold air inlet hose from the air cleaner spout
and looking into the spout.
3Start the engine and allow it to idle. Check
that the flap is now fully open to admit hot air
from the exhaust manifold shroud. If the flap
does not fully open, stop the engine and
check the vacuum diaphragm unit and heat
sensor as follows (see illustrations).4Working under the base of the air cleaner
body, disconnect the diaphragm unit-to-heat
sensor vacuum pipe at the sensor end, and
connect a vacuum pump to the diaphragm unit.
Apply a vacuum of 100.0 mm (4.0 in) of mercury.
5If the flap opens, then the heat sensor is
faulty and should be renewed. If the flap
remains closed, then the diaphragm unit is
faulty, and a new air cleaner body will have to
be obtained, as the diaphragm unit is not
available separately.
6On completion of the checks, disconnect
the vacuum pump, and reconnect the vacuum
pipe and cold air inlet hose.
36Air cleaner inlet air
temperature control check
1•18Every 24 000 miles or 2 years
35.1 Loosening the crankcase ventilation
hose clip - CVH models
36.3b Air cleaner heat sensor viewed from
inside air cleaner - OHC models36.3a Air cleaner vacuum diaphragm unit -
OHC models
36.2 Air cleaner flap valve operation -
OHC models
A Flap fully open to admit hot air
B Flap fully closed to admit cold air
35.3 Oil separator (1) and mushroom valve
(2) locations in air cleaner - CVH models
Every 24 000 miles (40 000 km) or 2 years
Page 19 of 22
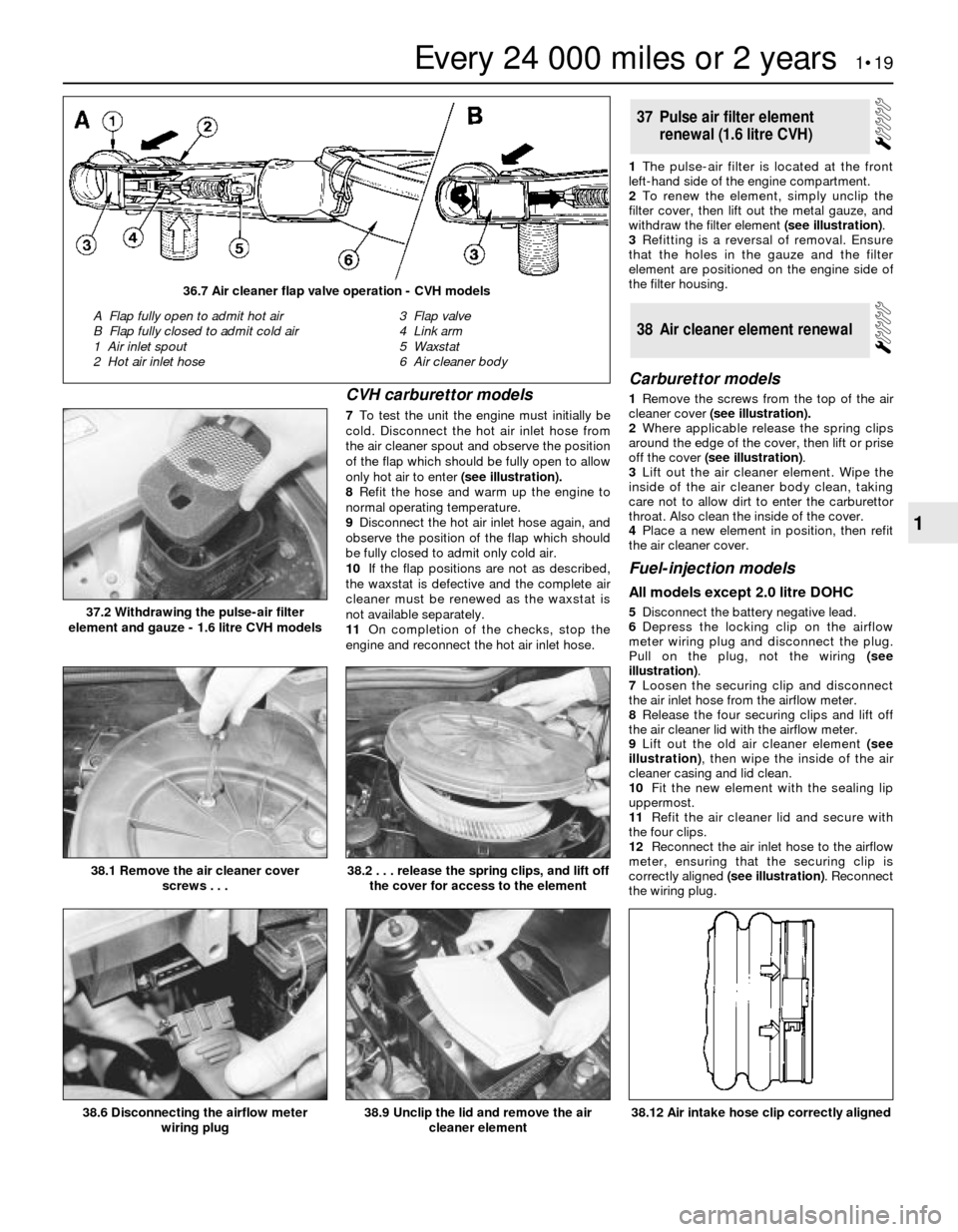
CVH carburettor models
7To test the unit the engine must initially be
cold. Disconnect the hot air inlet hose from
the air cleaner spout and observe the position
of the flap which should be fully open to allow
only hot air to enter (see illustration).
8Refit the hose and warm up the engine to
normal operating temperature.
9Disconnect the hot air inlet hose again, and
observe the position of the flap which should
be fully closed to admit only cold air.
10If the flap positions are not as described,
the waxstat is defective and the complete air
cleaner must be renewed as the waxstat is
not available separately.
11On completion of the checks, stop the
engine and reconnect the hot air inlet hose.1The pulse-air filter is located at the front
left-hand side of the engine compartment.
2To renew the element, simply unclip the
filter cover, then lift out the metal gauze, and
withdraw the filter element (see illustration).
3Refitting is a reversal of removal. Ensure
that the holes in the gauze and the filter
element are positioned on the engine side of
the filter housing.
Carburettor models
1Remove the screws from the top of the air
cleaner cover (see illustration).
2Where applicable release the spring clips
around the edge of the cover, then lift or prise
off the cover (see illustration).
3Lift out the air cleaner element. Wipe the
inside of the air cleaner body clean, taking
care not to allow dirt to enter the carburettor
throat. Also clean the inside of the cover.
4Place a new element in position, then refit
the air cleaner cover.
Fuel-injection models
All models except 2.0 litre DOHC
5Disconnect the battery negative lead.
6Depress the locking clip on the airflow
meter wiring plug and disconnect the plug.
Pull on the plug, not the wiring (see
illustration).
7Loosen the securing clip and disconnect
the air inlet hose from the airflow meter.
8Release the four securing clips and lift off
the air cleaner lid with the airflow meter.
9Lift out the old air cleaner element (see
illustration), then wipe the inside of the air
cleaner casing and lid clean.
10Fit the new element with the sealing lip
uppermost.
11Refit the air cleaner lid and secure with
the four clips.
12Reconnect the air inlet hose to the airflow
meter, ensuring that the securing clip is
correctly aligned (see illustration). Reconnect
the wiring plug.
38Air cleaner element renewal
37Pulse air filter element
renewal (1.6 litre CVH)
Every 24 000 miles or 2 years 1•19
1
37.2 Withdrawing the pulse-air filter
element and gauze - 1.6 litre CVH models
38.12 Air intake hose clip correctly aligned38.9 Unclip the lid and remove the air
cleaner element38.6 Disconnecting the airflow meter
wiring plug
38.2 . . . release the spring clips, and lift off
the cover for access to the element38.1 Remove the air cleaner cover
screws . . .
36.7 Air cleaner flap valve operation - CVH models
A Flap fully open to admit hot air
B Flap fully closed to admit cold air
1 Air inlet spout
2 Hot air inlet hose3 Flap valve
4 Link arm
5 Waxstat
6 Air cleaner body
Page 20 of 22
13Reconnect the battery negative lead.
2.0 litre DOHC models
14Disconnect the battery negative lead.
15Disconnect the wiring plug from the idle
speed control valve at the front of the plenum
chamber.
16Loosen the clamp, and detach the air inlet
hose from the air inlet tubing.
17Unscrew the securing nut, and release the
air inlet tube from the bracket on the engine
compartment front panel (see illustration).
18Release the air cleaner lid securing clips,
then lift away the air inlet tube, plenum
chamber and air cleaner lid as an assembly,
disconnecting the breather hose from the air
inlet tube.
19Lift out the air cleaner element (see
illustration), then wipe the inside of the air
cleaner lid and casing clean.
20Fit the new element with the sealing lip
uppermost.
21Further refitting is a reversal of removal.
1Before disturbing any part of the ignition
system, disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Identify and clearly mark all HT leads before
disconnecting them from the spark plugs.
3Refer to the appropriate Section in Chapter
5 and, where applicable, remove the
distributor cap and rotor arm.
4Clean the HT leads and distributor cap with
a dry cloth. Scrape any corrosion or otherdeposits from the connectors and terminals.
Also clean the coil tower.
5Renew the HT leads if they are cracked,
burnt or otherwise damaged. If a multi-meter
is available, measure the resistance of the
leads. The desired value is given in the
Specifications of Chapter 5.
6Renew the distributor cap if it is cracked or
badly burnt inside, or if there is evidence of
“tracking” (black lines marking the path of HT
leakage). If there is a carbon brush at the
centre of the cap, make sure that it moves
freely, and is not excessively worn (see
illustration).
7Clean the metal track of the rotor arm with
fine abrasive paper. Renew the arm if it is
cracked or badly burnt.
8Refit the rotor arm and distributor cap.
9Reconnect the HT leads to the spark plugs
and coil.
10Reconnect the battery and run the engine.
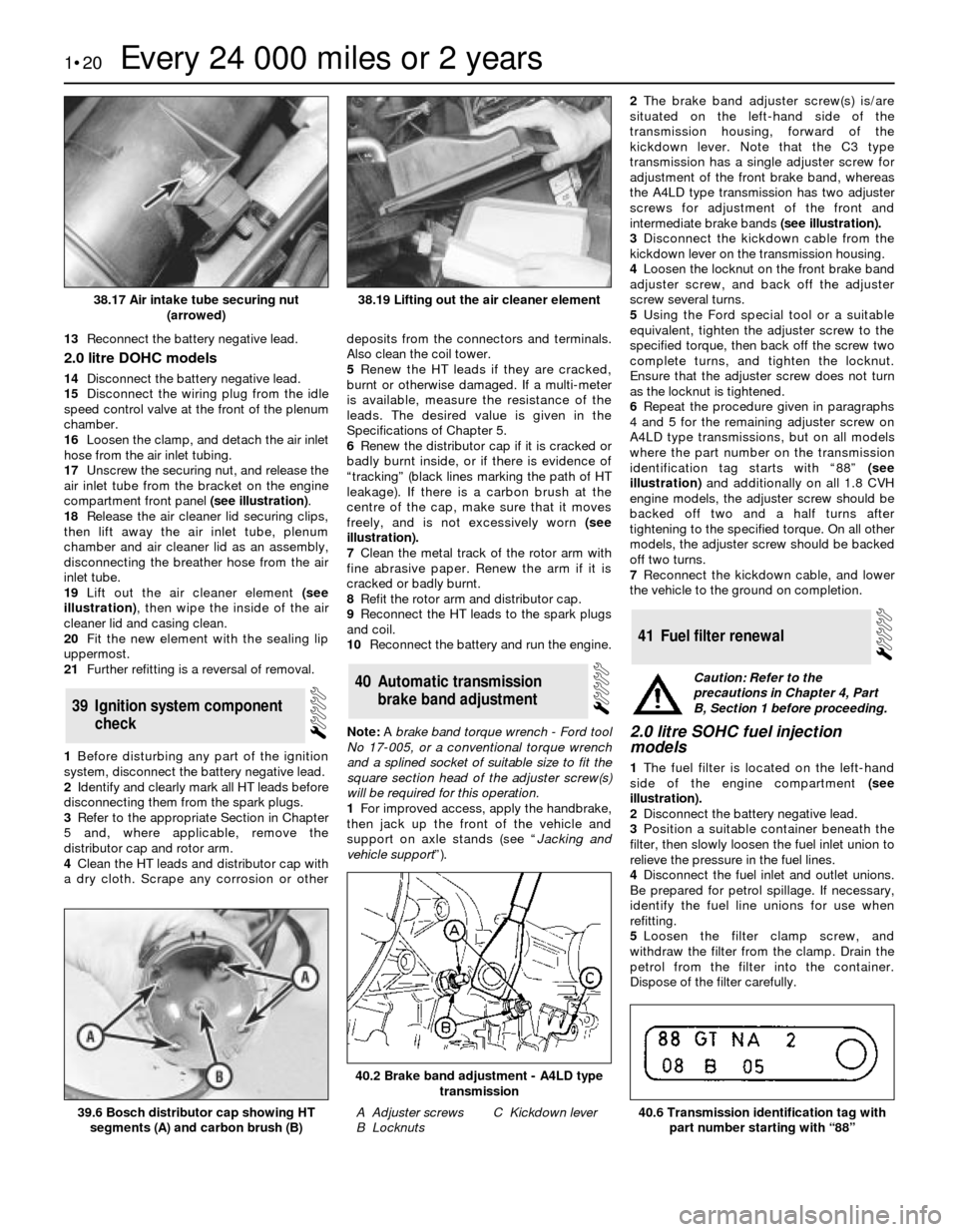
Note: A brake band torque wrench - Ford tool
No 17-005, or a conventional torque wrench
and a splined socket of suitable size to fit the
square section head of the adjuster screw(s)
will be required for this operation.
1For improved access, apply the handbrake,
then jack up the front of the vehicle and
support on axle stands (see “Jacking and
vehicle support”).2The brake band adjuster screw(s) is/are
situated on the left-hand side of the
transmission housing, forward of the
kickdown lever. Note that the C3 type
transmission has a single adjuster screw for
adjustment of the front brake band, whereas
the A4LD type transmission has two adjuster
screws for adjustment of the front and
intermediate brake bands(see illustration).
3Disconnect the kickdown cable from the
kickdown lever on the transmission housing.
4Loosen the locknut on the front brake band
adjuster screw, and back off the adjuster
screw several turns.
5Using the Ford special tool or a suitable
equivalent, tighten the adjuster screw to the
specified torque, then back off the screw two
complete turns, and tighten the locknut.
Ensure that the adjuster screw does not turn
as the locknut is tightened.
6Repeat the procedure given in paragraphs
4 and 5 for the remaining adjuster screw on
A4LD type transmissions, but on all models
where the part number on the transmission
identification tag starts with “88”(see
illustration)and additionally on all 1.8 CVH
engine models, the adjuster screw should be
backed off two and a half turns after
tightening to the specified torque. On all other
models, the adjuster screw should be backed
off two turns.
7Reconnect the kickdown cable, and lower
the vehicle to the ground on completion.
2.0 litre SOHC fuel injection
models
1The fuel filter is located on the left-hand
side of the engine compartment(see
illustration).
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Position a suitable container beneath the
filter, then slowly loosen the fuel inlet union to
relieve the pressure in the fuel lines.
4Disconnect the fuel inlet and outlet unions.
Be prepared for petrol spillage. If necessary,
identify the fuel line unions for use when
refitting.
5Loosen the filter clamp screw, and
withdraw the filter from the clamp. Drain the
petrol from the filter into the container.
Dispose of the filter carefully.
41Fuel filter renewal
40Automatic transmission
brake band adjustment
39Ignition system component
check
1•20Every 24 000 miles or 2 years
38.17 Air intake tube securing nut
(arrowed)
39.6 Bosch distributor cap showing HT
segments (A) and carbon brush (B)40.6 Transmission identification tag with
part number starting with “88”
40.2 Brake band adjustment - A4LD type
transmission
A Adjuster screws
B LocknutsC Kickdown lever
38.19 Lifting out the air cleaner element
Caution: Refer to the
precautions in Chapter 4, Part
B, Section 1 before proceeding.
Page 21 of 22
6Fit the new filter, ensuring that the arrows on
the filter body point in the direction of fuel flow.
7Tighten the clamp screw, and reconnect
the fuel inlet and outlet unions. Ensure that the
unions are correctly connected.
8Reconnect the battery negative lead, and
check the fuel line unions for leaks,
pressurising the system by switching the
ignition on and off several times.
All models except 2.0 litre SOHC
9Proceed as described for the 2.0 litre SOHCmodels, noting the following points.
10The fuel filter is located under the rear of
the vehicle, above the driveshaft (see
illustration). For access to the filter, chock
the front wheels, then jack up the rear of the
vehicle and support it on axle stands.
11To remove the filter, the mounting bracket
must first be removed from the floor, after
unscrewing the securing bolt. The filter can
then be removed from the bracket after
unscrewing the clamp bolt.On carburettor model SOHC engines,
renew the crankcase ventilation vent valve by
pulling it from the oil separator and loosening
the hose clip (see illustration). Fit the new
valve, tighten the clip, and insert it into the oil
separator grommet.
42Crankcase ventilation vent
valve renewal
If in doubt as to the condition of any of the
brake system seals and hoses, then renew
defective items whilst referring to the relevant
Sections of Chapter 10.
1An assistant and bleeding equipment will
be needed. A considerable quantity of
hydraulic fluid will be required - probably
about 2 litres (nearly half a gallon).
2Slacken the front wheel nuts. Raise and
support the front of the vehicle and remove
the front wheels.
3Remove the hydraulic fluid reservoir cap.
4Open both front bleed screws one full turn.
Attach one bleed tube to each screw, placing
the free end of each tube in a jar.
5Pump the brake pedal to expel fluid from
the bleed screws. Pause after each upstroke
to allow the master cylinder to refill.
6When air emerges from both bleed screws,
stop pumping. Detach the left-hand caliper
without disconnecting it and remove the
inboard brake pad.
7Depress the caliper piston, using a
purpose-made tool or a blunt item such as a
tyre lever, to force more fluid out of the
caliper. Hold the piston depressed and have
the assistant pump the pedal until air emerges
from the bleed screw again.8Tighten the bleed screw on the left-hand
caliper. Loosely refit the caliper and pad so
that the piston is not accidentally ejected.
9Repeat the purging operation on the right-
hand caliper, but do not refit it or tighten the
bleed screw yet.
10Fill the reservoir with fresh hydraulic fluid.
Position the bleed jar for the right-hand
caliper at least 300 mm (1 foot) above the
level of the bleed screw.
11Have the assistant pump the brake pedal
until fluid free of bubbles emerges from the
bleed screw. Tighten the bleed screw at the
end of a downstroke.
12Place a piece of wood in the caliper jaws
to limit piston travel. Keep your fingers clear
of the piston. Have the assistant depress the
brake pedal gentlyin order to move the
caliper piston out.
13With the pedal held depressed, slacken
the bleed screw on the right-hand caliper and
again depress the piston. Tighten the bleed
screw when the piston is retracted. The pedal
can now be released.
14Disconnect the bleed tube. Refit the right-
hand brake pad and caliper.
15Remove the left-hand caliper and inboard
pad again. Carry out the operations described
in paragraphs 10 to 14 on the left-hand
caliper.
16Bleed the rear brakes (Chapter 10).
17Refit the front wheels, lower the vehicle
and tighten the wheel nuts.
18Pump the brake pedal to bring the pads
up to the discs, then make a final check of the
hydraulic fluid level. Top-up and refit the
reservoir cap.Camshaft drivebelt renewal is
recommended as a precautionary measure for
SOHC engines but is compulsory for CVH
engines. Refer to Chapter 2 for the
appropriate renewal procedure.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2It is preferable to drain the cooling system
with the engine cold. If this is not possible,
take precautions against scalding when
removing the expansion tank cap. Place a
thick rag over the cap and slacken the cap a
little to release any pressure. When all
pressure has been released, carry on
unscrewing the cap and remove it.
3Early models have no radiator drain plug, so
the radiator must be drained by detaching the
bottom coolant hose from the outlet on the
right-hand side of the radiator. Later SOHC
models have a drain plug located in the base
of the left-hand radiator end tank, whilst all
CVH models have a drain plug in the
right-hand radiator end tank and DOHC
models have a plug to the bottom right-hand
side of the radiator.
46Engine coolant renewal
45Camshaft drivebelt renewal
44Brake hydraulic fluid renewal
43Brake hydraulic system seal
and hose renewal
Every 36 000 miles or 3 years 1•21
1
42.1 Removing the crankcase vent valve
from the oil separator41.10 Fuel filter location (arrowed) under
rear of vehicle41.1 Fuel filter location - outlet union
arrowed
Caution: Before proceeding,
note the precautions given in
Chapter 3, Section 1.
Every 36 000 miles (60 000 km) or 3 years
Page 22 of 22
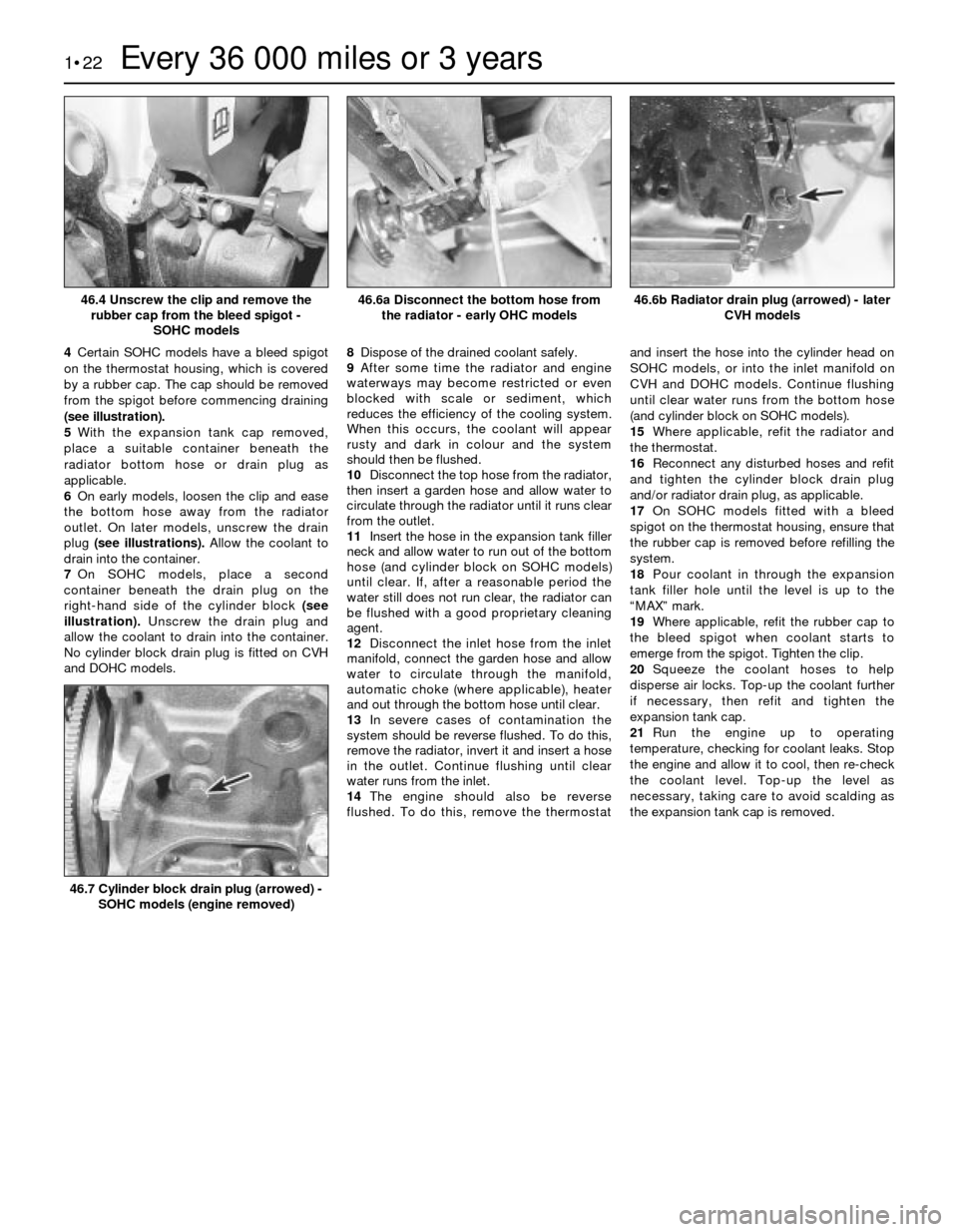
4Certain SOHC models have a bleed spigot
on the thermostat housing, which is covered
by a rubber cap. The cap should be removed
from the spigot before commencing draining
(see illustration).
5With the expansion tank cap removed,
place a suitable container beneath the
radiator bottom hose or drain plug as
applicable.
6On early models, loosen the clip and ease
the bottom hose away from the radiator
outlet. On later models, unscrew the drain
plug (see illustrations).Allow the coolant to
drain into the container.
7On SOHC models, place a second
container beneath the drain plug on the
right-hand side of the cylinder block (see
illustration).Unscrew the drain plug and
allow the coolant to drain into the container.
No cylinder block drain plug is fitted on CVH
and DOHC models.8Dispose of the drained coolant safely.
9After some time the radiator and engine
waterways may become restricted or even
blocked with scale or sediment, which
reduces the efficiency of the cooling system.
When this occurs, the coolant will appear
rusty and dark in colour and the system
should then be flushed.
10Disconnect the top hose from the radiator,
then insert a garden hose and allow water to
circulate through the radiator until it runs clear
from the outlet.
11Insert the hose in the expansion tank filler
neck and allow water to run out of the bottom
hose (and cylinder block on SOHC models)
until clear. If, after a reasonable period the
water still does not run clear, the radiator can
be flushed with a good proprietary cleaning
agent.
12Disconnect the inlet hose from the inlet
manifold, connect the garden hose and allow
water to circulate through the manifold,
automatic choke (where applicable), heater
and out through the bottom hose until clear.
13In severe cases of contamination the
system should be reverse flushed. To do this,
remove the radiator, invert it and insert a hose
in the outlet. Continue flushing until clear
water runs from the inlet.
14The engine should also be reverse
flushed. To do this, remove the thermostatand insert the hose into the cylinder head on
SOHC models, or into the inlet manifold on
CVH and DOHC models. Continue flushing
until clear water runs from the bottom hose
(and cylinder block on SOHC models).
15Where applicable, refit the radiator and
the thermostat.
16Reconnect any disturbed hoses and refit
and tighten the cylinder block drain plug
and/or radiator drain plug, as applicable.
17On SOHC models fitted with a bleed
spigot on the thermostat housing, ensure that
the rubber cap is removed before refilling the
system.
18Pour coolant in through the expansion
tank filler hole until the level is up to the
“MAX” mark.
19Where applicable, refit the rubber cap to
the bleed spigot when coolant starts to
emerge from the spigot. Tighten the clip.
20Squeeze the coolant hoses to help
disperse air locks. Top-up the coolant further
if necessary, then refit and tighten the
expansion tank cap.
21Run the engine up to operating
temperature, checking for coolant leaks. Stop
the engine and allow it to cool, then re-check
the coolant level. Top-up the level as
necessary, taking care to avoid scalding as
the expansion tank cap is removed.
1•22Every 36 000 miles or 3 years
46.4 Unscrew the clip and remove the
rubber cap from the bleed spigot -
SOHC models46.6b Radiator drain plug (arrowed) - later
CVH models
46.7 Cylinder block drain plug (arrowed) -
SOHC models (engine removed)
46.6a Disconnect the bottom hose from
the radiator - early OHC models