check engine FORD SIERRA 1989 2.G Introduction Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1989, Model line: SIERRA, Model: FORD SIERRA 1989 2.GPages: 18, PDF Size: 0.5 MB
Page 2 of 18

LIVING WITH YOUR FORD SIERRAIntroduction to the Ford SierraPage0•4
AcknowledgementsPage0•4
Safety first!Page0•5
ROADSIDE REPAIRSJacking, vehicle support and wheel changingPage0•6
TowingPage0•7
Identifying leaksPage0•8
Jump startingPage0•9
Weekly Checks
IntroductionPage0•10
Underbonnet check pointsPage0•10
Engine Oil levelPage0•12
Coolant levelPage0•12
Screen washer fluid levelPage0•13
Brake fluid levelPage0•13
Power steering fluid levelPage0•14
Electrical systemsPage0•14
BatteryPage0•15
Wiper bladesPage0•15
Tyre condition and pressurePage0•16
Lubricants and fluidsPage0•17
Tyre pressuresPage0•18
MAINTENANCE
Routine Maintenance and ServicingPage1•1
Maintenance schedulePage1•4
Maintenance proceduresPage1•9
Contents
Page 3 of 18

REPAIRS AND OVERHAUL
Engine and Associated Systems
SOHC enginesPage2A•1
DOHC enginesPage2B•1
CVH enginesPage2C•1
Cooling, heating and air conditioning systemsPage3•1
Fuel/exhaust systems - carburettor modelsPage4A•1
Fuel/exhaust systems - fuel injection modelsPage4B•1
Engine electrical systemsPage5•1
TRANSMISSION
ClutchPage6•1
Manual gearboxPage7A•1
Automatic transmissionPage7B•1
Propellor shaftPage8•1
Final drive and driveshaftsPage9•1
BRAKES AND SUSPENSION
Braking systemPage10•1
Suspension and steeringPage11•1
BODY EQUIPMENT
Bodywork, trim and fittingsPage12•1
Body electrical systemsPage13•1
Wiring DiagramsPage13•22
Reference
General dimensions and weightsPageREF•1
Buying spare parts and vehicle identificationPageREF•3
General repair proceduresPageREF•4
Tools and working facilitiesPageREF•5
MOT test checks PageREF•7
Fault findingPageREF•11
Glossary of technical termsPageREF•18
IndexPageREF•23
Contents
Page 5 of 18

0•5Safety First!
Working on your car can be dangerous.
This page shows just some of the potential
risks and hazards, with the aim of creating a
safety-conscious attitude.
General hazards
Scalding
• Don’t remove the radiator or expansion
tank cap while the engine is hot.
• Engine oil, automatic transmission fluid or
power steering fluid may also be dangerously
hot if the engine has recently been running.
Burning
• Beware of burns from the exhaust system
and from any part of the engine. Brake discs
and drums can also be extremely hot
immediately after use.
Crushing
• When working under or near
a raised vehicle,
always
supplement the
jack with axle
stands, or use
drive-on
ramps.
Never
venture
under a car which
is only supported by a jack.
• Take care if loosening or tightening high-
torque nuts when the vehicle is on stands.
Initial loosening and final tightening should
be done with the wheels on the ground.
Fire
• Fuel is highly flammable; fuel vapour is
explosive.
• Don’t let fuel spill onto a hot engine.
• Do not smoke or allow naked lights
(including pilot lights) anywhere near a
vehicle being worked on. Also beware of
creating sparks
(electrically or by use of tools).
• Fuel vapour is heavier than air, so don’t
work on the fuel system with the vehicle over
an inspection pit.
• Another cause of fire is an electrical
overload or short-circuit. Take care when
repairing or modifying the vehicle wiring.
• Keep a fire extinguisher handy, of a type
suitable for use on fuel and electrical fires.
Electric shock
• Ignition HT
voltage can be
dangerous,
especially to
people with heart
problems or a
pacemaker. Don’t
work on or near the
ignition system with
the engine running or
the ignition switched on.• Mains voltage is also dangerous. Make
sure that any mains-operated equipment is
correctly earthed. Mains power points should
be protected by a residual current device
(RCD) circuit breaker.
Fume or gas intoxication
• Exhaust fumes are
poisonous; they often
contain carbon
monoxide, which is
rapidly fatal if inhaled.
Never run the
engine in a
confined space
such as a garage
with the doors shut.
• Fuel vapour is also
poisonous, as are the vapours from some
cleaning solvents and paint thinners.
Poisonous or irritant substances
• Avoid skin contact with battery acid and
with any fuel, fluid or lubricant, especially
antifreeze, brake hydraulic fluid and Diesel
fuel. Don’t syphon them by mouth. If such a
substance is swallowed or gets into the eyes,
seek medical advice.
• Prolonged contact with used engine oil can
cause skin cancer. Wear gloves or use a
barrier cream if necessary. Change out of oil-
soaked clothes and do not keep oily rags in
your pocket.
• Air conditioning refrigerant forms a
poisonous gas if exposed to a naked flame
(including a cigarette). It can also cause skin
burns on contact.
Asbestos
• Asbestos dust can cause cancer if inhaled
or swallowed. Asbestos may be found in
gaskets and in brake and clutch linings.
When dealing with such components it is
safest to assume that they contain asbestos.
Specia hazards
Hydrofluoric acid
• This extremely corrosive acid is formed
when certain types of synthetic rubber, found
in some O-rings, oil seals, fuel hoses etc, are
exposed to temperatures above 400
0C. The
rubber changes into a charred or sticky
substance containing the acid. Once formed,
the acid remains dangerous for years. If it
gets onto the skin, it may be necessary to
amputate the limb concerned.
• When dealing with a vehicle which has
suffered a fire, or with components salvaged
from such a vehicle, wear protective gloves
and discard them after use.
The battery
• Batteries contain sulphuric acid, which
attacks clothing, eyes and skin. Take care
when topping-up or carrying the battery.
• The hydrogen gas given off by the battery
is highly explosive. Never cause a spark or
allow a naked light nearby. Be careful when
connecting and disconnecting battery
chargers or jump leads.
Air bags
• Air bags can cause injury if they go off
accidentally. Take care when removing the
steering wheel and/or facia. Special storage
instructions may apply.
Diesel injection equipment
• Diesel injection pumps supply fuel at very
high pressure. Take care when working on
the fuel injectors and fuel pipes.
Warning: Never expose the hands,
face or any other part of the body
to injector spray; the fuel can
penetrate the skin with potentially fatal
results.
Remember...
DO
• Do use eye protection when using power
tools, and when working under the vehicle.
• Do wear gloves or use barrier cream to
protect your hands when necessary.
• Do get someone to check periodically
that all is well when working alone on the
vehicle.
• Do keep loose clothing and long hair well
out of the way of moving mechanical parts.
• Do remove rings, wristwatch etc, before
working on the vehicle – especially the
electrical system.
• Do ensure that any lifting or jacking
equipment has a safe working load rating
adequate for the job.
A few tips
DON’T
• Don’t attempt to lift a heavy component
which may be beyond your capability – get
assistance.
• Don’t rush to finish a job, or take
unverified short cuts.
• Don’t use ill-fitting tools which may slip
and cause injury.
• Don’t leave tools or parts lying around
where someone can trip over them. Mop
up oil and fuel spills at once.
• Don’t allow children or pets to play in or
near a vehicle being worked on.
Page 10 of 18

0•10
There are some very simple checks which
need only take a few minutes to carry out, but
which could save you a lot of inconvenience
and expense.
These "Weekly checks" require no great skill
or special tools, and the small amount of time
they take to perform could prove to be very
well spent, for example;MKeeping an eye on tyre condition and
pressures, will not only help to stop them
wearing out prematurely, but could also save
your life.
MMany breakdowns are caused by electrical
problems. Battery-related faults are
particularly common, and a quick check on a
regular basis will often prevent the majority of
these.MIf your car develops a brake fluid leak, the
first time you might know about it is when your
brakes don't work properly. Checking the level
regularly will give advance warning of this kind
of problem.
MIf the oil or coolant levels run low, the cost
of repairing any engine damage will be far
greater than fixing the leak, for example.
Underbonnet check points
§2.0 litre OHC
Carburettor model
(air cleaner removed for clarity)
ALocation of oil level dipstick
BEngine oil filler cap
CCoolant expansion tank
DBrake fluid reservoir
EWindscreen washer reservoir
FBattery
§2.0 litre OHC
Fuel injection model
AOil level dipstick
BEngine oil filler cap
CCoolant expansion tank
DBrake fluid reservoir
EWindscreen washer reservoir
FBattery
Introduction
Weekly checks
Page 11 of 18
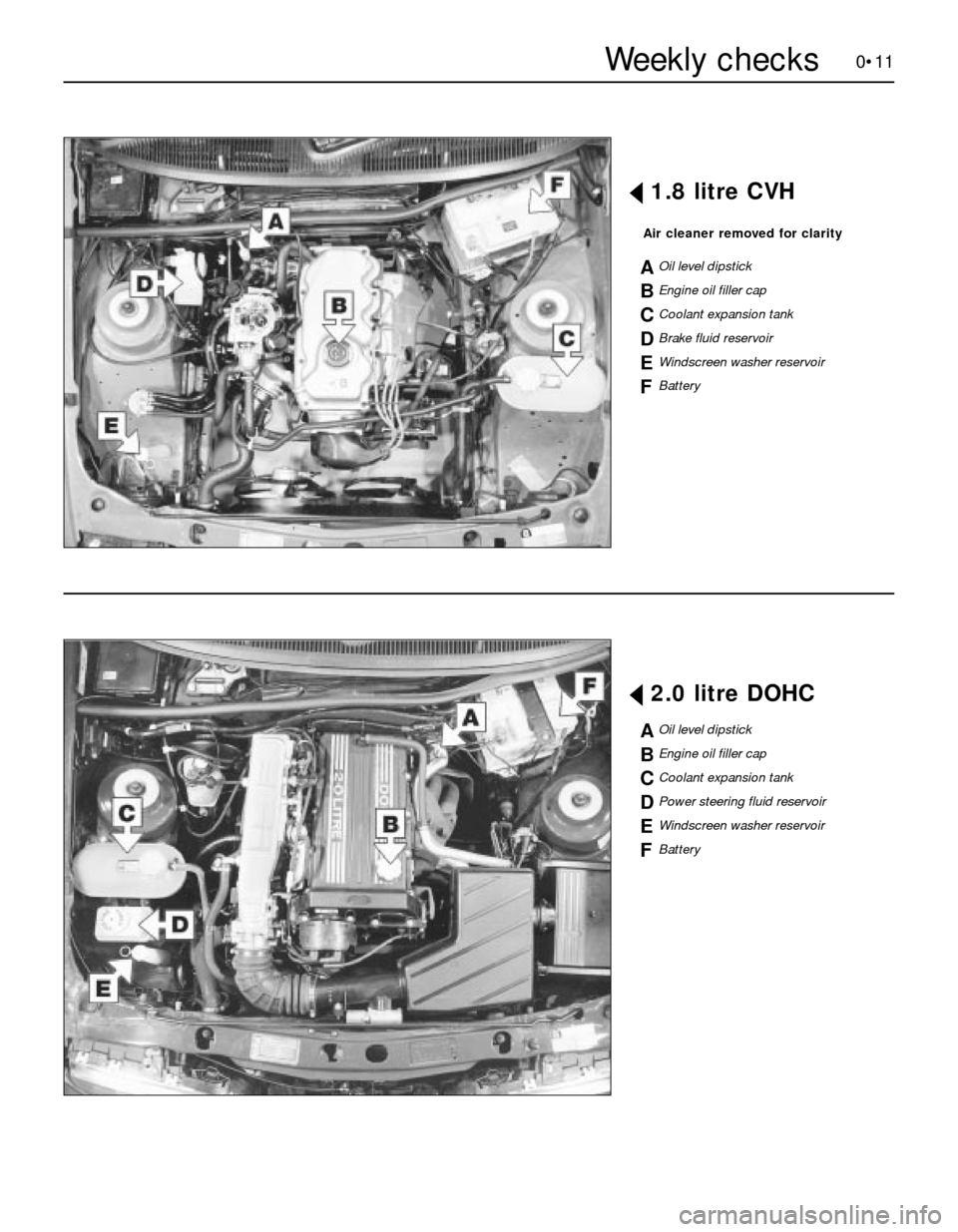
0•11
§1.8 litre CVH
Air cleaner removed for clarity
AOil level dipstick
BEngine oil filler cap
CCoolant expansion tank
DBrake fluid reservoir
EWindscreen washer reservoir
FBattery
§2.0 litre DOHC
AOil level dipstick
BEngine oil filler cap
CCoolant expansion tank
DPower steering fluid reservoir
EWindscreen washer reservoir
FBattery
Weekly checks
Page 12 of 18
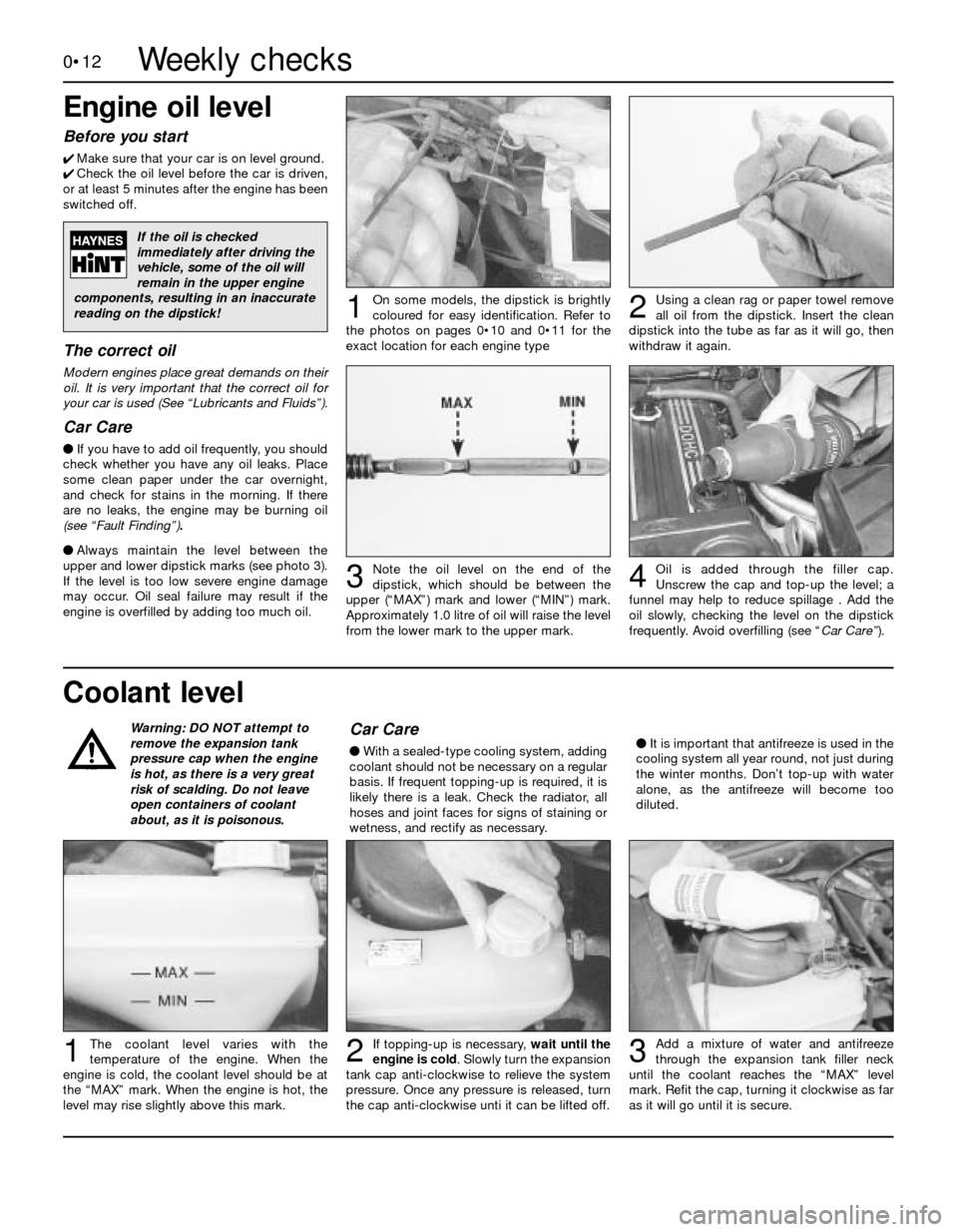
Coolant level Engine oil level
Before you start
4Make sure that your car is on level ground.
4Check the oil level before the car is driven,
or at least 5 minutes after the engine has been
switched off.
The correct oil
Modern engines place great demands on their
oil. It is very important that the correct oil for
your car is used (See “Lubricants and Fluids”).
Car Care
l If you have to add oil frequently, you should
check whether you have any oil leaks. Place
some clean paper under the car overnight,
and check for stains in the morning. If there
are no leaks, the engine may be burning oil
(see “Fault Finding”).
lAlways maintain the level between the
upper and lower dipstick marks (see photo 3).
If the level is too low severe engine damage
may occur. Oil seal failure may result if the
engine is overfilled by adding too much oil.
0•12
Using a clean rag or paper towel remove
all oil from the dipstick. Insert the clean
dipstick into the tube as far as it will go, then
withdraw it again.
Add a mixture of water and antifreeze
through the expansion tank filler neck
until the coolant reaches the “MAX” level
mark. Refit the cap, turning it clockwise as far
as it will go until it is secure.
If topping-up is necessary, wait until the
engine is cold. Slowly turn the expansion
tank cap anti-clockwise to relieve the system
pressure. Once any pressure is released, turn
the cap anti-clockwise unti it can be lifted off.The coolant level varies with the
temperature of the engine. When the
engine is cold, the coolant level should be at
the “MAX” mark. When the engine is hot, the
level may rise slightly above this mark.
Note the oil level on the end of the
dipstick, which should be between the
upper (“MAX”) mark and lower (“MIN”) mark.
Approximately 1.0 litre of oil will raise the level
from the lower mark to the upper mark.Oil is added through the filler cap.
Unscrew the cap and top-up the level; a
funnel may help to reduce spillage . Add the
oil slowly, checking the level on the dipstick
frequently. Avoid overfilling (see “Car Care”).
On some models, the dipstick is brightly
coloured for easy identification. Refer to
the photos on pages 0•10 and 0•11 for the
exact location for each engine type12
3
123
4
Warning: DO NOT attempt to
remove the expansion tank
pressure cap when the engine
is hot, as there is a very great
risk of scalding. Do not leave
open containers of coolant
about, as it is poisonous.Car Care
lWith a sealed-type cooling system, adding
coolant should not be necessary on a regular
basis. If frequent topping-up is required, it is
likely there is a leak. Check the radiator, all
hoses and joint faces for signs of staining or
wetness, and rectify as necessary.lIt is important that antifreeze is used in the
cooling system all year round, not just during
the winter months. Don’t top-up with water
alone, as the antifreeze will become too
diluted.
If the oil is checked
immediately after driving the
vehicle, some of the oil will
remain in the upper engine
components, resulting in an inaccurate
reading on the dipstick!
Weekly checks
Page 13 of 18
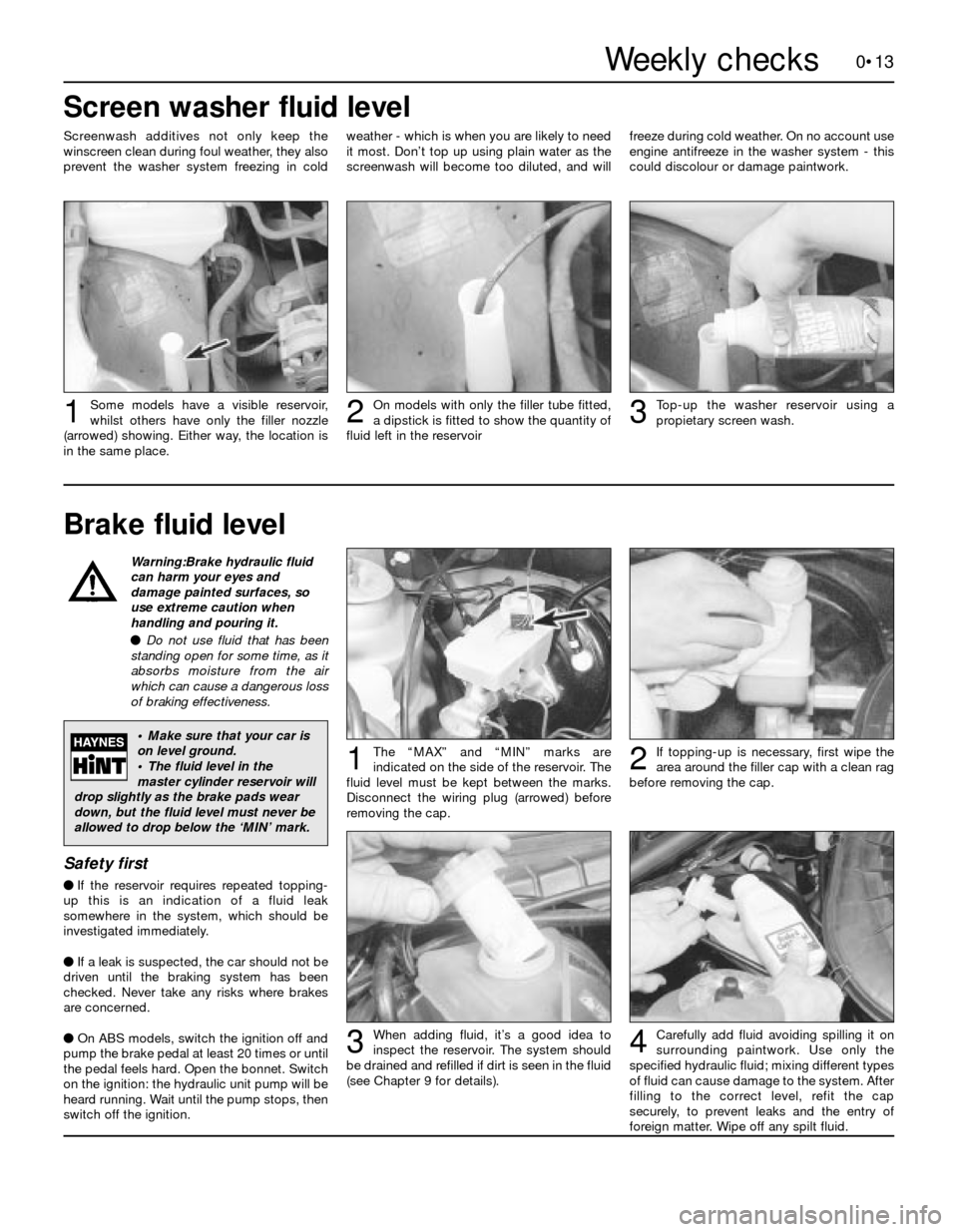
Warning:Brake hydraulic fluid
can harm your eyes and
damage painted surfaces, so
use extreme caution when
handling and pouring it.
l Do not use fluid that has been
standing open for some time, as it
absorbs moisture from the air
which can cause a dangerous loss
of braking effectiveness.
Safety first
lIf the reservoir requires repeated topping-
up this is an indication of a fluid leak
somewhere in the system, which should be
investigated immediately.
lIf a leak is suspected, the car should not be
driven until the braking system has been
checked. Never take any risks where brakes
are concerned.
lOn ABS models, switch the ignition off and
pump the brake pedal at least 20 times or until
the pedal feels hard. Open the bonnet. Switch
on the ignition: the hydraulic unit pump will be
heard running. Wait until the pump stops, then
switch off the ignition.
Brake fluid level
0•13
Carefully add fluid avoiding spilling it on
surrounding paintwork. Use only the
specified hydraulic fluid; mixing different types
of fluid can cause damage to the system. After
filling to the correct level, refit the cap
securely, to prevent leaks and the entry of
foreign matter. Wipe off any spilt fluid.When adding fluid, it’s a good idea to
inspect the reservoir. The system should
be drained and refilled if dirt is seen in the fluid
(see Chapter 9 for details).
The “MAX” and “MIN” marks are
indicated on the side of the reservoir. The
fluid level must be kept between the marks.
Disconnect the wiring plug (arrowed) before
removing the cap.1If topping-up is necessary, first wipe the
area around the filler cap with a clean rag
before removing the cap.2
34
Screen washer fluid level
Some models have a visible reservoir,
whilst others have only the filler nozzle
(arrowed) showing. Either way, the location is
in the same place.Top-up the washer reservoir using a
propietary screen wash.On models with only the filler tube fitted,
a dipstick is fitted to show the quantity of
fluid left in the reservoir
Screenwash additives not only keep the
winscreen clean during foul weather, they also
prevent the washer system freezing in coldweather - which is when you are likely to need
it most. Don’t top up using plain water as the
screenwash will become too diluted, and willfreeze during cold weather. On no account use
engine antifreeze in the washer system - this
could discolour or damage paintwork.
123
• Make sure that your car is
on level ground.
• The fluid level in the
master cylinder reservoir will
drop slightly as the brake pads wear
down, but the fluid level must never be
allowed to drop below the ‘MIN’ mark.
Weekly checks
Page 14 of 18
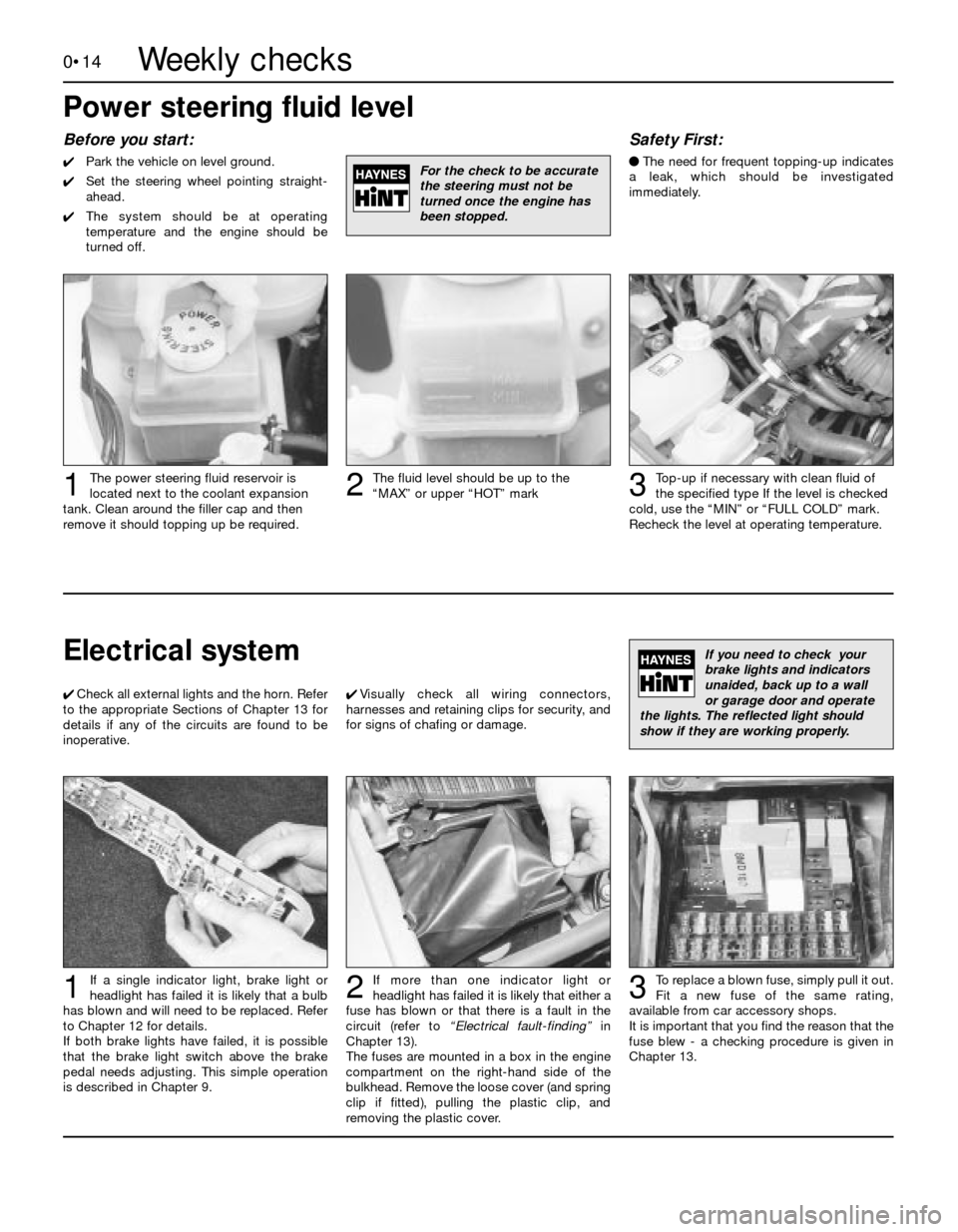
0•14
Before you start:
4Park the vehicle on level ground.
4Set the steering wheel pointing straight-
ahead.
4The system should be at operating
temperature and the engine should be
turned off.
Safety First:
lThe need for frequent topping-up indicates
a leak, which should be investigated
immediately.
Top-up if necessary with clean fluid of
the specified typeIf the level is checked
cold, use the “MIN” or “FULL COLD” mark.
Recheck the level at operating temperature.
The fluid level should be up to the
“MAX” or upper “HOT” markThe power steering fluid reservoir is
located next to the coolant expansion
tank. Clean around the filler cap and then
remove it should topping up be required.123
For the check to be accurate
the steering must not be
turned once the engine has
been stopped.
Power steering fluid level
Weekly checks
Electrical system
To replace a blown fuse, simply pull it out.
Fit a new fuse of the same rating,
available from car accessory shops.
It is important that you find the reason that the
fuse blew - a checking procedure is given in
Chapter 13.If more than one indicator light or
headlight has failed it is likely that either a
fuse has blown or that there is a fault in the
circuit (refer to“Electrical fault-finding”in
Chapter 13).
The fuses are mounted in a box in the engine
compartment on the right-hand side of the
bulkhead. Remove the loose cover (and spring
clip if fitted), pulling the plastic clip, and
removing the plastic cover.If a single indicator light, brake light or
headlight has failed it is likely that a bulb
has blown and will need to be replaced. Refer
to Chapter 12 for details.
If both brake lights have failed, it is possible
that the brake light switch above the brake
pedal needs adjusting. This simple operation
is described in Chapter 9.1
If you need to check your
brake lights and indicators
unaided, back up to a wall
or garage door and operate
the lights. The reflected light should
show if they are working properly.
4Check all external lights and the horn. Refer
to the appropriate Sections of Chapter 13 for
details if any of the circuits are found to be
inoperative.4Visually check all wiring connectors,
harnesses and retaining clips for security, and
for signs of chafing or damage.
23
Page 15 of 18
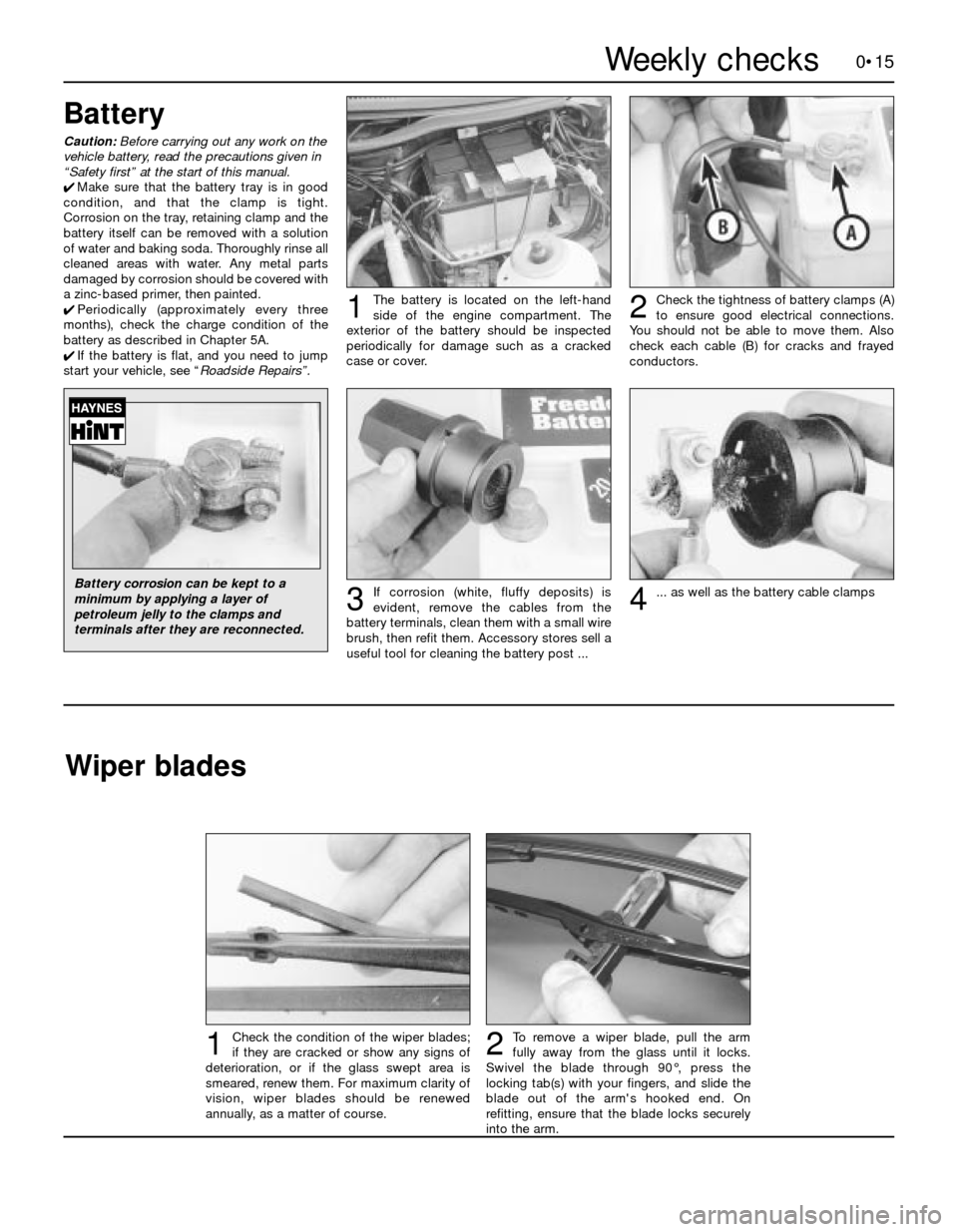
0•15
To remove a wiper blade, pull the arm
fully away from the glass until it locks.
Swivel the blade through 90°, press the
locking tab(s) with your fingers, and slide the
blade out of the arm's hooked end. On
refitting, ensure that the blade locks securely
into the arm.Check the condition of the wiper blades;
if they are cracked or show any signs of
deterioration, or if the glass swept area is
smeared, renew them. For maximum clarity of
vision, wiper blades should be renewed
annually, as a matter of course.21Weekly checks
Battery
Caution:Before carrying out any work on the
vehicle battery, read the precautions given in
“Safety first” at the start of this manual.
4Make sure that the battery tray is in good
condition, and that the clamp is tight.
Corrosion on the tray, retaining clamp and the
battery itself can be removed with a solution
of water and baking soda. Thoroughly rinse all
cleaned areas with water. Any metal parts
damaged by corrosion should be covered with
a zinc-based primer, then painted.
4Periodically (approximately every three
months), check the charge condition of the
battery as described in Chapter 5A.
4If the battery is flat, and you need to jump
start your vehicle, see “Roadside Repairs”.The battery is located on the left-hand
side of the engine compartment. The
exterior of the battery should be inspected
periodically for damage such as a cracked
case or cover.
Check the tightness of battery clamps (A)
to ensure good electrical connections.
You should not be able to move them. Also
check each cable (B) for cracks and frayed
conductors.
If corrosion (white, fluffy deposits) is
evident, remove the cables from the
battery terminals, clean them with a small wire
brush, then refit them. Accessory stores sell a
useful tool for cleaning the battery post ...
12
3... as well as the battery cable clamps4
Battery corrosion can be kept to a
minimum by applying a layer of
petroleum jelly to the clamps and
terminals after they are reconnected.
Wiper blades
Page 17 of 18
0•17Weekly checks
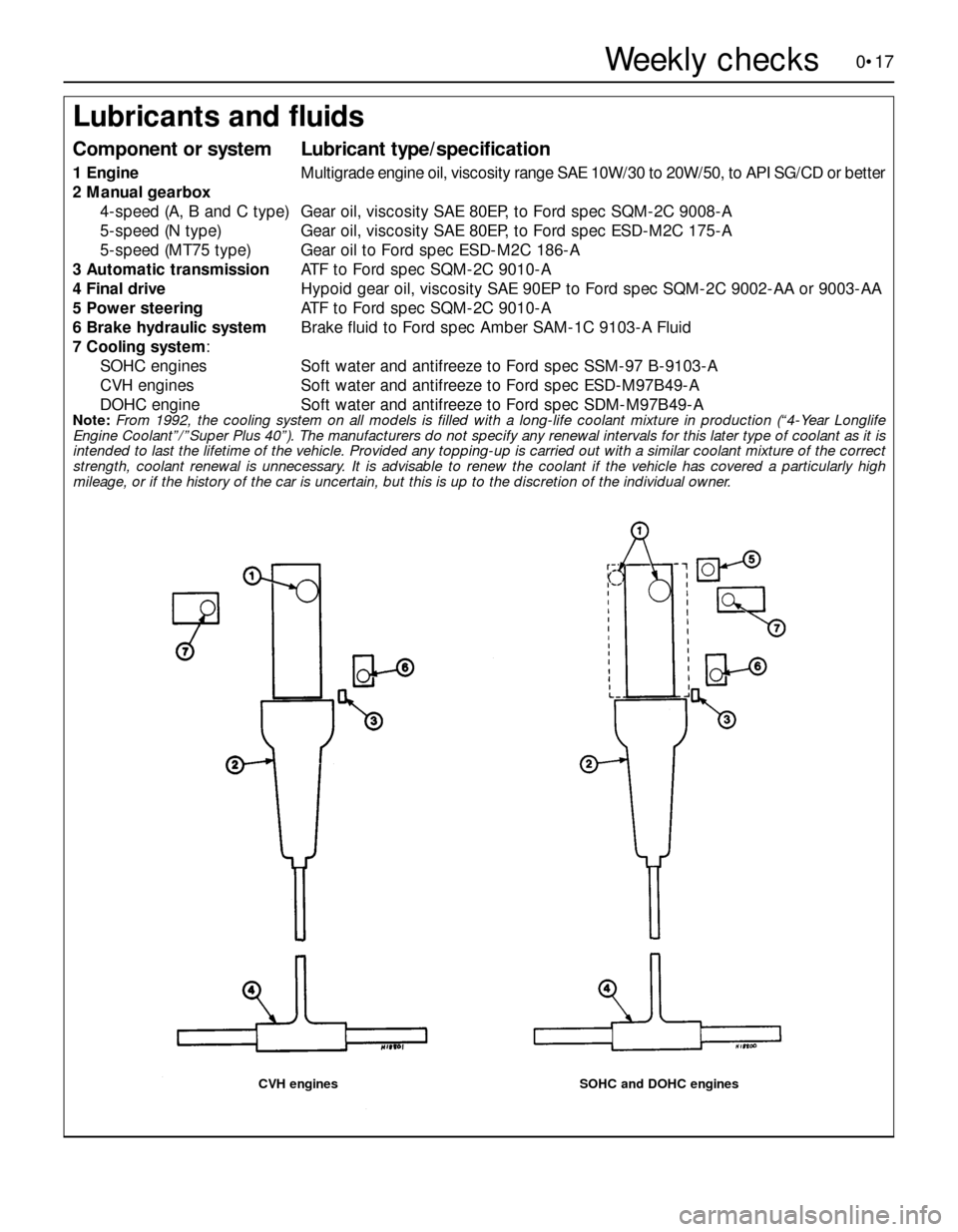
Lubricants and fluids
Component or systemLubricant type/specification
1EngineMultigrade engine oil, viscosity range SAE 10W/30 to 20W/50, to API SG/CD or better
2Manual gearbox
4-speed (A, B and C type)Gear oil, viscosity SAE 80EP, to Ford spec SQM-2C 9008-A
5-speed (N type)Gear oil, viscosity SAE 80EP, to Ford spec ESD-M2C 175-A
5-speed (MT75 type)Gear oil to Ford spec ESD-M2C 186-A
3Automatic transmissionATF to Ford spec SQM-2C 9010-A
4Final driveHypoid gear oil, viscosity SAE 90EP to Ford spec SQM-2C 9002-AA or 9003-AA
5Power steeringATF to Ford spec SQM-2C 9010-A
6Brake hydraulic systemBrake fluid to Ford spec Amber SAM-1C 9103-A Fluid
7Cooling system:
SOHC enginesSoft water and antifreeze to Ford spec SSM-97 B-9103-A
CVH enginesSoft water and antifreeze to Ford spec ESD-M97B49-A
DOHC engineSoft water and antifreeze to Ford spec SDM-M97B49-A
Note:From 1992, the cooling system on all models is filled with a long-life coolant mixture in production (“4-Year Longlife
Engine Coolant”/”Super Plus 40”). The manufacturers do not specify any renewal intervals for this later type of coolant as it is
intended to last the lifetime of the vehicle. Provided any topping-up is carried out with a similar coolant mixture of the correct
strength, coolant renewal is unnecessary. It is advisable to renew the coolant if the vehicle has covered a particularly high
mileage, or if the history of the car is uncertain, but this is up to the discretion of the individual owner.
CVH enginesSOHC and DOHC engines