jacking FORD SIERRA 1991 2.G Introduction Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1991, Model line: SIERRA, Model: FORD SIERRA 1991 2.GPages: 18, PDF Size: 0.5 MB
Page 2 of 18

LIVING WITH YOUR FORD SIERRAIntroduction to the Ford SierraPage0•4
AcknowledgementsPage0•4
Safety first!Page0•5
ROADSIDE REPAIRSJacking, vehicle support and wheel changingPage0•6
TowingPage0•7
Identifying leaksPage0•8
Jump startingPage0•9
Weekly Checks
IntroductionPage0•10
Underbonnet check pointsPage0•10
Engine Oil levelPage0•12
Coolant levelPage0•12
Screen washer fluid levelPage0•13
Brake fluid levelPage0•13
Power steering fluid levelPage0•14
Electrical systemsPage0•14
BatteryPage0•15
Wiper bladesPage0•15
Tyre condition and pressurePage0•16
Lubricants and fluidsPage0•17
Tyre pressuresPage0•18
MAINTENANCE
Routine Maintenance and ServicingPage1•1
Maintenance schedulePage1•4
Maintenance proceduresPage1•9
Contents
Page 5 of 18

0•5Safety First!
Working on your car can be dangerous.
This page shows just some of the potential
risks and hazards, with the aim of creating a
safety-conscious attitude.
General hazards
Scalding
• Don’t remove the radiator or expansion
tank cap while the engine is hot.
• Engine oil, automatic transmission fluid or
power steering fluid may also be dangerously
hot if the engine has recently been running.
Burning
• Beware of burns from the exhaust system
and from any part of the engine. Brake discs
and drums can also be extremely hot
immediately after use.
Crushing
• When working under or near
a raised vehicle,
always
supplement the
jack with axle
stands, or use
drive-on
ramps.
Never
venture
under a car which
is only supported by a jack.
• Take care if loosening or tightening high-
torque nuts when the vehicle is on stands.
Initial loosening and final tightening should
be done with the wheels on the ground.
Fire
• Fuel is highly flammable; fuel vapour is
explosive.
• Don’t let fuel spill onto a hot engine.
• Do not smoke or allow naked lights
(including pilot lights) anywhere near a
vehicle being worked on. Also beware of
creating sparks
(electrically or by use of tools).
• Fuel vapour is heavier than air, so don’t
work on the fuel system with the vehicle over
an inspection pit.
• Another cause of fire is an electrical
overload or short-circuit. Take care when
repairing or modifying the vehicle wiring.
• Keep a fire extinguisher handy, of a type
suitable for use on fuel and electrical fires.
Electric shock
• Ignition HT
voltage can be
dangerous,
especially to
people with heart
problems or a
pacemaker. Don’t
work on or near the
ignition system with
the engine running or
the ignition switched on.• Mains voltage is also dangerous. Make
sure that any mains-operated equipment is
correctly earthed. Mains power points should
be protected by a residual current device
(RCD) circuit breaker.
Fume or gas intoxication
• Exhaust fumes are
poisonous; they often
contain carbon
monoxide, which is
rapidly fatal if inhaled.
Never run the
engine in a
confined space
such as a garage
with the doors shut.
• Fuel vapour is also
poisonous, as are the vapours from some
cleaning solvents and paint thinners.
Poisonous or irritant substances
• Avoid skin contact with battery acid and
with any fuel, fluid or lubricant, especially
antifreeze, brake hydraulic fluid and Diesel
fuel. Don’t syphon them by mouth. If such a
substance is swallowed or gets into the eyes,
seek medical advice.
• Prolonged contact with used engine oil can
cause skin cancer. Wear gloves or use a
barrier cream if necessary. Change out of oil-
soaked clothes and do not keep oily rags in
your pocket.
• Air conditioning refrigerant forms a
poisonous gas if exposed to a naked flame
(including a cigarette). It can also cause skin
burns on contact.
Asbestos
• Asbestos dust can cause cancer if inhaled
or swallowed. Asbestos may be found in
gaskets and in brake and clutch linings.
When dealing with such components it is
safest to assume that they contain asbestos.
Specia hazards
Hydrofluoric acid
• This extremely corrosive acid is formed
when certain types of synthetic rubber, found
in some O-rings, oil seals, fuel hoses etc, are
exposed to temperatures above 400
0C. The
rubber changes into a charred or sticky
substance containing the acid. Once formed,
the acid remains dangerous for years. If it
gets onto the skin, it may be necessary to
amputate the limb concerned.
• When dealing with a vehicle which has
suffered a fire, or with components salvaged
from such a vehicle, wear protective gloves
and discard them after use.
The battery
• Batteries contain sulphuric acid, which
attacks clothing, eyes and skin. Take care
when topping-up or carrying the battery.
• The hydrogen gas given off by the battery
is highly explosive. Never cause a spark or
allow a naked light nearby. Be careful when
connecting and disconnecting battery
chargers or jump leads.
Air bags
• Air bags can cause injury if they go off
accidentally. Take care when removing the
steering wheel and/or facia. Special storage
instructions may apply.
Diesel injection equipment
• Diesel injection pumps supply fuel at very
high pressure. Take care when working on
the fuel injectors and fuel pipes.
Warning: Never expose the hands,
face or any other part of the body
to injector spray; the fuel can
penetrate the skin with potentially fatal
results.
Remember...
DO
• Do use eye protection when using power
tools, and when working under the vehicle.
• Do wear gloves or use barrier cream to
protect your hands when necessary.
• Do get someone to check periodically
that all is well when working alone on the
vehicle.
• Do keep loose clothing and long hair well
out of the way of moving mechanical parts.
• Do remove rings, wristwatch etc, before
working on the vehicle – especially the
electrical system.
• Do ensure that any lifting or jacking
equipment has a safe working load rating
adequate for the job.
A few tips
DON’T
• Don’t attempt to lift a heavy component
which may be beyond your capability – get
assistance.
• Don’t rush to finish a job, or take
unverified short cuts.
• Don’t use ill-fitting tools which may slip
and cause injury.
• Don’t leave tools or parts lying around
where someone can trip over them. Mop
up oil and fuel spills at once.
• Don’t allow children or pets to play in or
near a vehicle being worked on.
Page 6 of 18
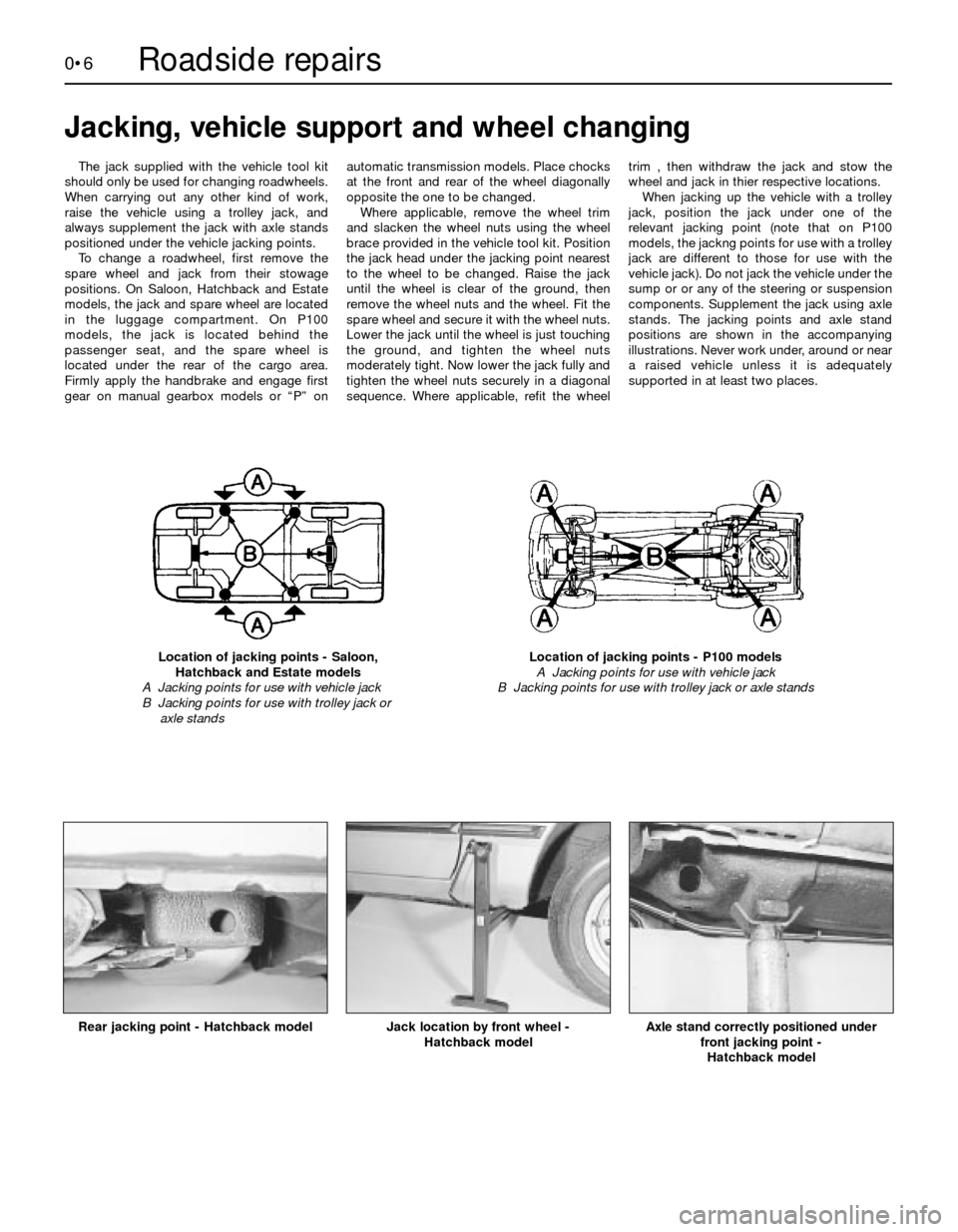
0•6
The jack supplied with the vehicle tool kit
should only be used for changing roadwheels.
When carrying out any other kind of work,
raise the vehicle using a trolley jack, and
always supplement the jack with axle stands
positioned under the vehicle jacking points.
To change a roadwheel, first remove the
spare wheel and jack from their stowage
positions. On Saloon, Hatchback and Estate
models, the jack and spare wheel are located
in the luggage compartment. On P100
models, the jack is located behind the
passenger seat, and the spare wheel is
located under the rear of the cargo area.
Firmly apply the handbrake and engage first
gear on manual gearbox models or “P” onautomatic transmission models. Place chocks
at the front and rear of the wheel diagonally
opposite the one to be changed.
Where applicable, remove the wheel trim
and slacken the wheel nuts using the wheel
brace provided in the vehicle tool kit. Position
the jack head under the jacking point nearest
to the wheel to be changed. Raise the jack
until the wheel is clear of the ground, then
remove the wheel nuts and the wheel. Fit the
spare wheel and secure it with the wheel nuts.
Lower the jack until the wheel is just touching
the ground, and tighten the wheel nuts
moderately tight. Now lower the jack fully and
tighten the wheel nuts securely in a diagonal
sequence. Where applicable, refit the wheeltrim , then withdraw the jack and stow the
wheel and jack in thier respective locations.
When jacking up the vehicle with a trolley
jack, position the jack under one of the
relevant jacking point (note that on P100
models, the jackng points for use with a trolley
jack are different to those for use with the
vehicle jack). Do not jack the vehicle under the
sump or or any of the steering or suspension
components. Supplement the jack using axle
stands. The jacking points and axle stand
positions are shown in the accompanying
illustrations. Never work under, around or near
a raised vehicle unless it is adequately
supported in at least two places.
Jacking, vehicle support and wheel changing
Location of jacking points - Saloon,
Hatchback and Estate models
A Jacking points for use with vehicle jack
B Jacking points for use with trolley jack or
axle standsLocation of jacking points - P100 models
A Jacking points for use with vehicle jack
B Jacking points for use with trolley jack or axle stands
Rear jacking point - Hatchback model
Jack location by front wheel -
Hatchback modelAxle stand correctly positioned under
front jacking point -
Hatchback model
Roadside repairs