lock FORD SIERRA 1992 2.G Introduction Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1992, Model line: SIERRA, Model: FORD SIERRA 1992 2.GPages: 18, PDF Size: 0.5 MB
Page 4 of 18

0•4
The Ford Sierra was first introduced in late 1982 with the option of
seven different engines and four different trim levels. This manual
covers the four cylinder in-line petrol engines, but other models in the
range are fitted with V6 or diesel engines.
The Sierra was introduced by Ford as the successor to the Cortina
and initially received a mixed reception as it was one of the first
vehicles to make use of the “aeroback” body style designed to reduce
the air drag coefficient to a minimum in the interests of fuel economy.
Mechanically the Sierra is similar to the Cortina with the exception of
all-round independent suspension.
Initially, 1.3, 1.6 and 2.0 litre SOHC carburettor engines were
available, with Hatchback and Estate body styles. In late 1984, a 1.8
litre SOHC engine became available and in 1985, a performance
orientated 2.0 litre SOHC fuel injection engine was introduced.Towards the end of 1986, the 1.3 litre engine was phased out. In order
to fill a gap in the range, a Saloon body style, designated the Sapphire,
was introduced in early 1987 and shortly afterwards, a 1.8 litre CVH
engine replaced the previously used 1.8 litre SOHC engine throughout
the model range.
A 1.6 litre CVH engine was introduced in September 1991 to replace
the 1.6 litre SOHC engine used previously, this engine being broadly
similar to the original 1.8 litre CVH engine which was in turn uprated in
March, 1992.
A 2.0 litre DOHC (Double OverHead Camshaft) engine was in-
troduced in August 1989 to replace the 2.0 litre SOHC engine.
In early 1988, a Sierra-based P100 pick-up model became available
to replace the previous Cortina-based design. The P100 consists of a
Sierra-type “cab” and front suspension, and a Ford Transit-type rear
suspension and 2.0 litre engine.
A wide range of standard and optional
equipment is available within the Sierra
range to suit most tastes, including an
anti-lock braking system.
For the home mechanic, the Sierra is a
straightforward vehicle to maintain and
repair since design features have been
incorporated to reduce the actual cost of
ownership to a minimum, and most of the
items requiring frequent attention are
easily accessible.
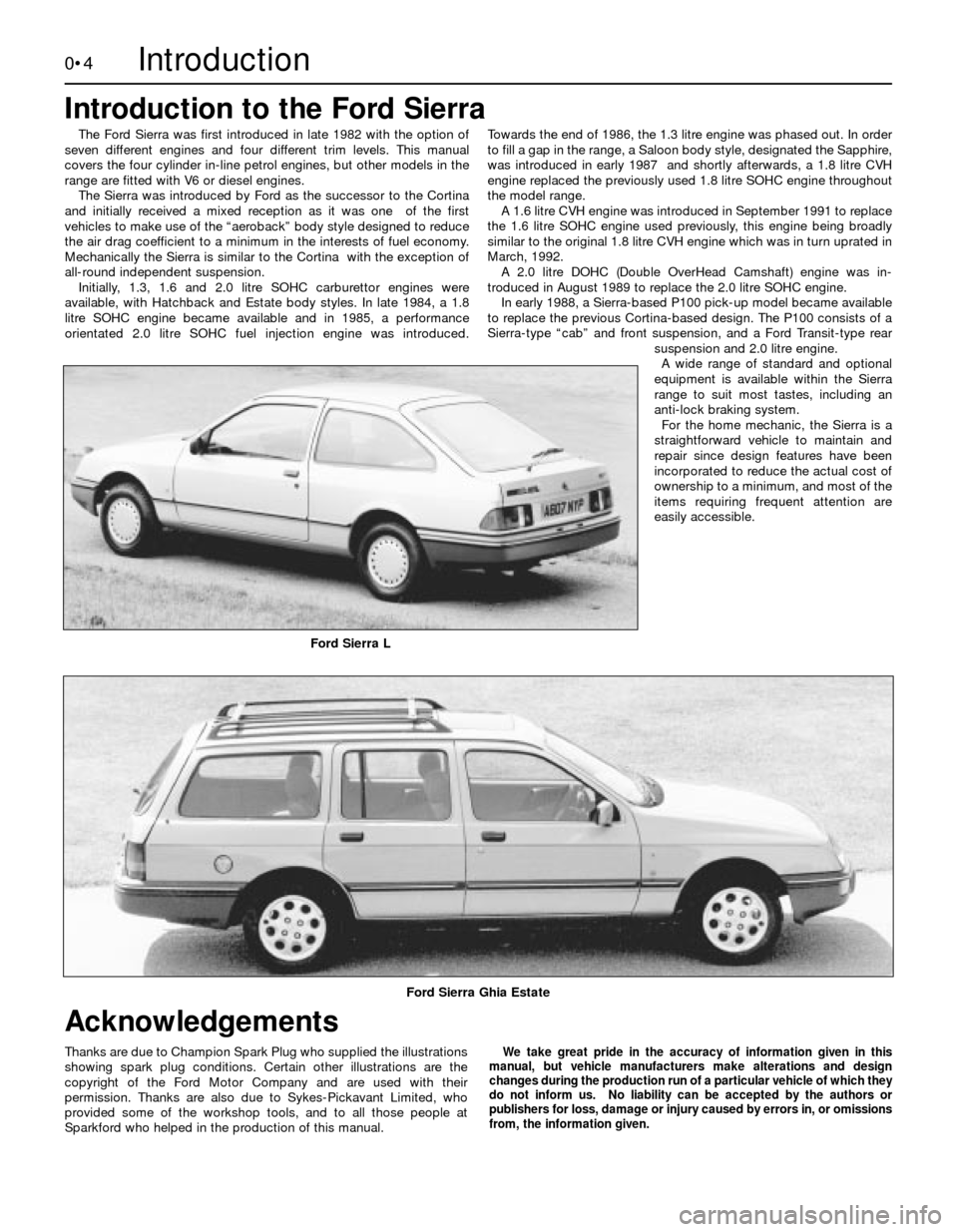
Ford Sierra L
Ford Sierra Ghia Estate
Introduction
We take great pride in the accuracy of information given in this
manual, but vehicle manufacturers make alterations and design
changes during the production run of a particular vehicle of which they
do not inform us. No liability can be accepted by the authors or
publishers for loss, damage or injury caused by errors in, or omissions
from, the information given.Thanks are due to Champion Spark Plug who supplied the illustrations
showing spark plug conditions. Certain other illustrations are the
copyright of the Ford Motor Company and are used with their
permission. Thanks are also due to Sykes-Pickavant Limited, who
provided some of the workshop tools, and to all those people at
Sparkford who helped in the production of this manual.
Introduction to the Ford Sierra
Acknowledgements
Page 7 of 18
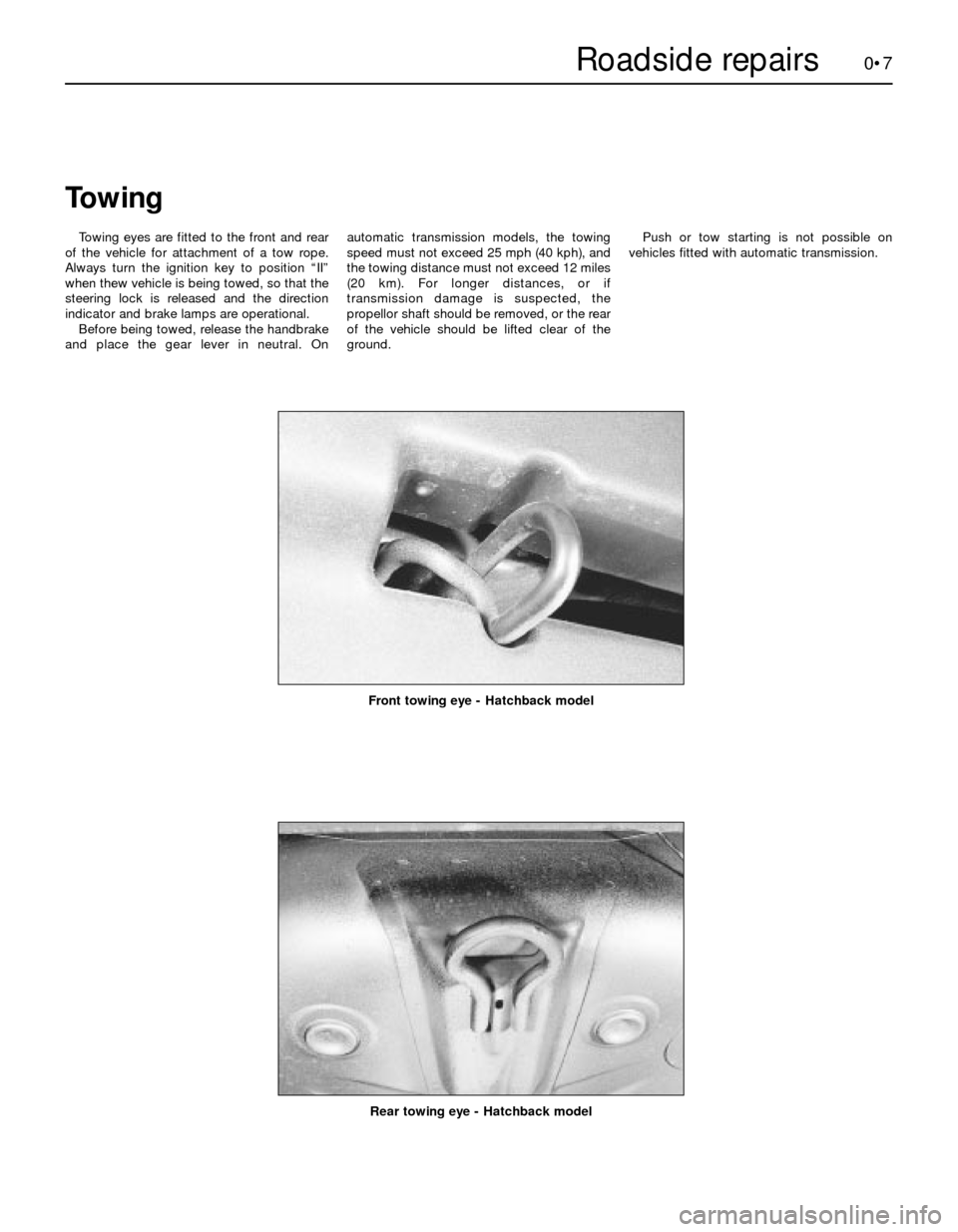
0•7
Rear towing eye - Hatchback model
Front towing eye - Hatchback model
Towing
Towing eyes are fitted to the front and rear
of the vehicle for attachment of a tow rope.
Always turn the ignition key to position “II”
when thew vehicle is being towed, so that the
steering lock is released and the direction
indicator and brake lamps are operational.
Before being towed, release the handbrake
and place the gear lever in neutral. Onautomatic transmission models, the towing
speed must not exceed 25 mph (40 kph), and
the towing distance must not exceed 12 miles
(20 km). For longer distances, or if
transmission damage is suspected, the
propellor shaft should be removed, or the rear
of the vehicle should be lifted clear of the
ground.Push or tow starting is not possible on
vehicles fitted with automatic transmission.
Roadside repairs
Page 9 of 18
0•9Roadside repairs
When jump-starting a car using a
booster battery, observe the following
precautions:
4Before connecting the booster
battery, make sure that the ignition is
switched off.
4Ensure that all electrical equipment
(lights, heater, wipers, etc) is
switched off.
4Make sure that the booster battery is
the same voltage as the discharged
one in the vehicle.
4If the battery is being jump-started
from the battery in another vehicle,
the two vehcles MUST NOT TOUCH
each other.
4Make sure that the transmission is in
neutral (or PARK, in the case of
automatic transmission).
Jump starting will get you out
of trouble, but you must correct
whatever made the battery go
flat in the first place. There are
three possibilities:
1The battery has been drained by
repeated attempts to start, or by
leaving the lights on.
2The charging system is not working
properly (alternator drivebelt slack
or broken, alternator wiring fault or
alternator itself faulty).
3The battery itself is at fault
(electrolyte low, or battery worn out).
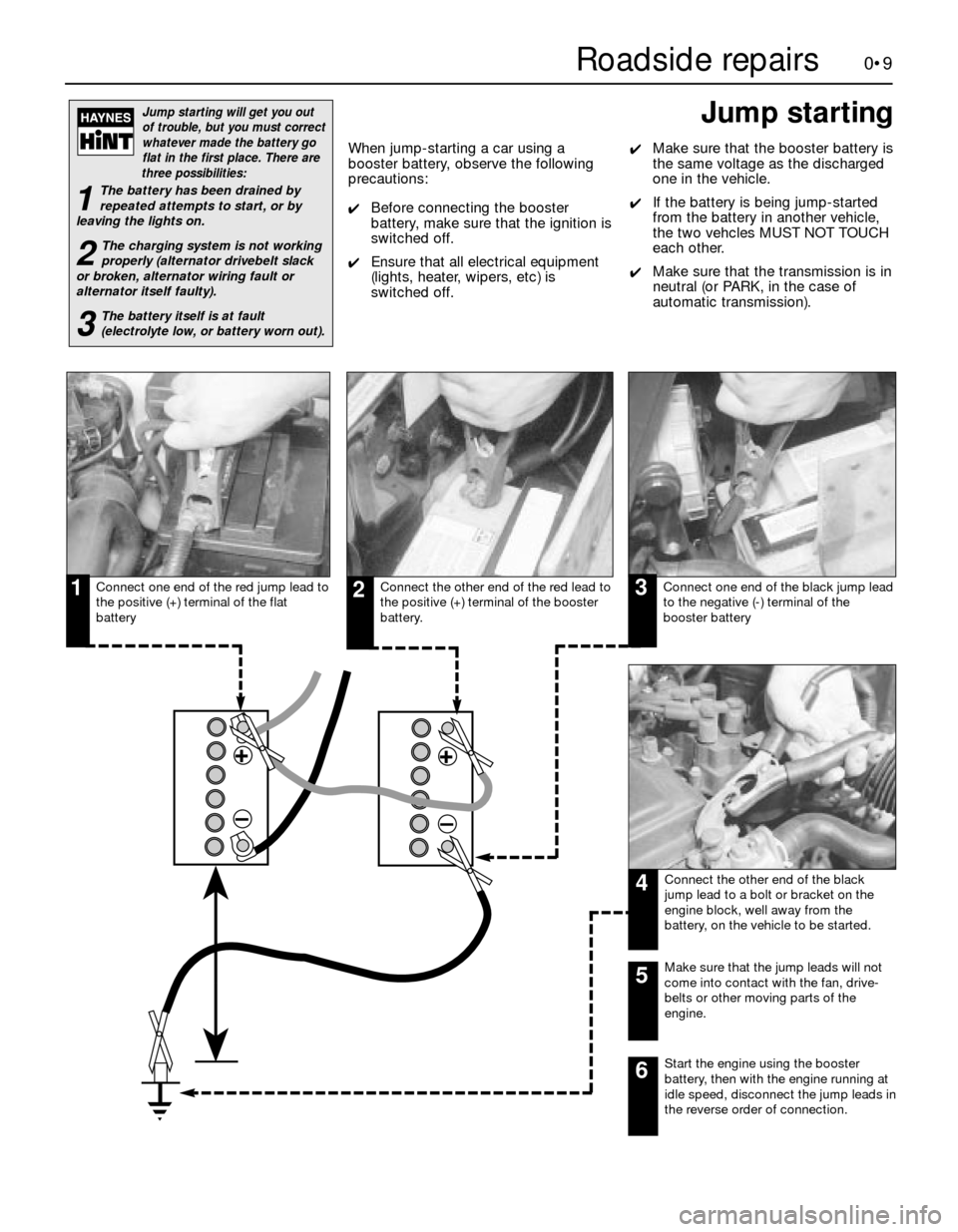
Connect one end of the red jump lead to
the positive (+) terminal of the flat
batteryConnect the other end of the red lead to
the positive (+) terminal of the booster
battery.Connect one end of the black jump lead
to the negative (-) terminal of the
booster battery
Connect the other end of the black
jump lead to a bolt or bracket on the
engine block, well away from the
battery, on the vehicle to be started.
123
4
Make sure that the jump leads will not
come into contact with the fan, drive-
belts or other moving parts of the
engine.5
Start the engine using the booster
battery, then with the engine running at
idle speed, disconnect the jump leads in
the reverse order of connection.6
Jump starting
Page 12 of 18
Coolant level Engine oil level
Before you start
4Make sure that your car is on level ground.
4Check the oil level before the car is driven,
or at least 5 minutes after the engine has been
switched off.
The correct oil
Modern engines place great demands on their
oil. It is very important that the correct oil for
your car is used (See “Lubricants and Fluids”).
Car Care
l If you have to add oil frequently, you should
check whether you have any oil leaks. Place
some clean paper under the car overnight,
and check for stains in the morning. If there
are no leaks, the engine may be burning oil
(see “Fault Finding”).
lAlways maintain the level between the
upper and lower dipstick marks (see photo 3).
If the level is too low severe engine damage
may occur. Oil seal failure may result if the
engine is overfilled by adding too much oil.
0•12
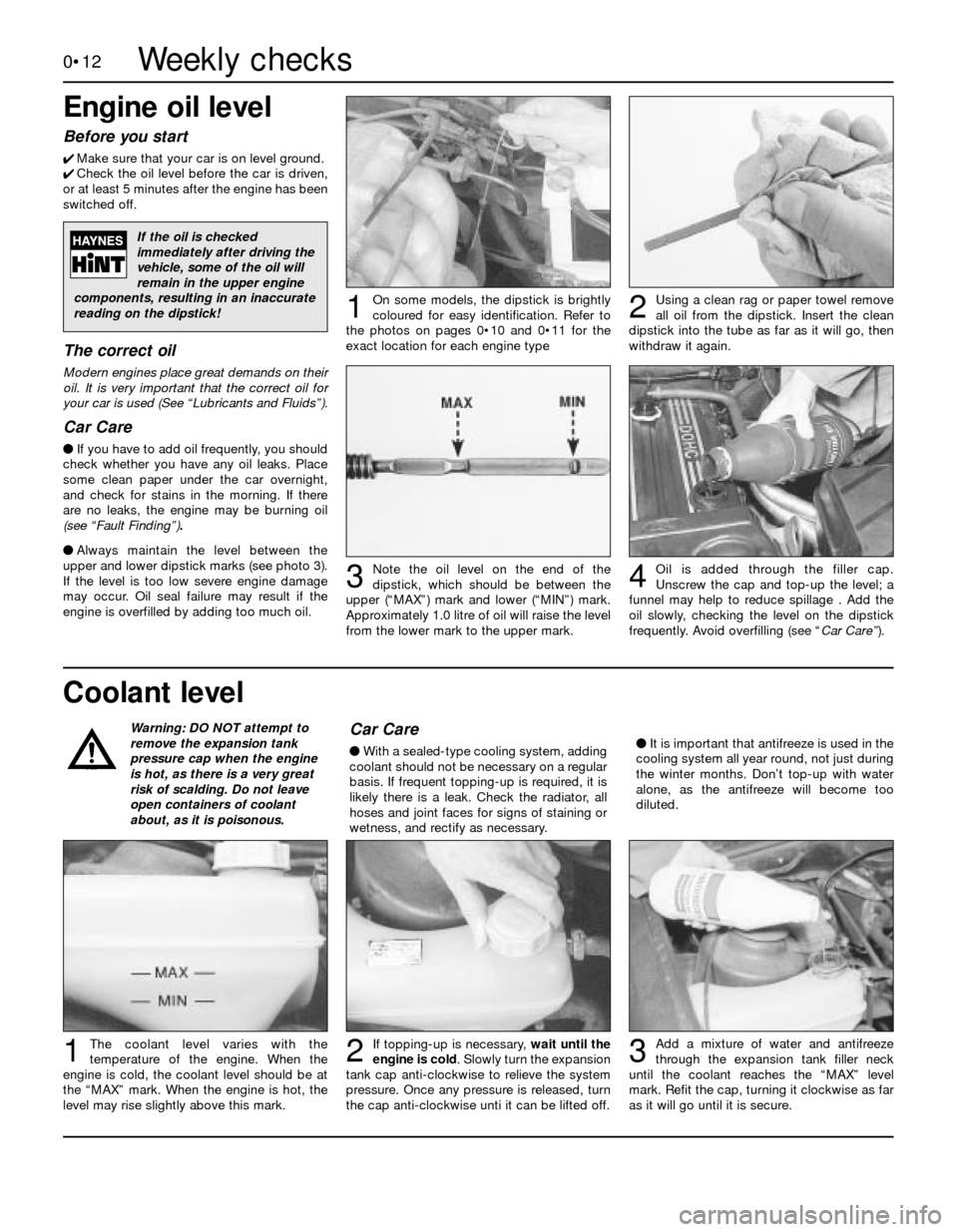
Using a clean rag or paper towel remove
all oil from the dipstick. Insert the clean
dipstick into the tube as far as it will go, then
withdraw it again.
Add a mixture of water and antifreeze
through the expansion tank filler neck
until the coolant reaches the “MAX” level
mark. Refit the cap, turning it clockwise as far
as it will go until it is secure.
If topping-up is necessary, wait until the
engine is cold. Slowly turn the expansion
tank cap anti-clockwise to relieve the system
pressure. Once any pressure is released, turn
the cap anti-clockwise unti it can be lifted off.The coolant level varies with the
temperature of the engine. When the
engine is cold, the coolant level should be at
the “MAX” mark. When the engine is hot, the
level may rise slightly above this mark.
Note the oil level on the end of the
dipstick, which should be between the
upper (“MAX”) mark and lower (“MIN”) mark.
Approximately 1.0 litre of oil will raise the level
from the lower mark to the upper mark.Oil is added through the filler cap.
Unscrew the cap and top-up the level; a
funnel may help to reduce spillage . Add the
oil slowly, checking the level on the dipstick
frequently. Avoid overfilling (see “Car Care”).
On some models, the dipstick is brightly
coloured for easy identification. Refer to
the photos on pages 0•10 and 0•11 for the
exact location for each engine type12
3
123
4
Warning: DO NOT attempt to
remove the expansion tank
pressure cap when the engine
is hot, as there is a very great
risk of scalding. Do not leave
open containers of coolant
about, as it is poisonous.Car Care
lWith a sealed-type cooling system, adding
coolant should not be necessary on a regular
basis. If frequent topping-up is required, it is
likely there is a leak. Check the radiator, all
hoses and joint faces for signs of staining or
wetness, and rectify as necessary.lIt is important that antifreeze is used in the
cooling system all year round, not just during
the winter months. Don’t top-up with water
alone, as the antifreeze will become too
diluted.
If the oil is checked
immediately after driving the
vehicle, some of the oil will
remain in the upper engine
components, resulting in an inaccurate
reading on the dipstick!
Weekly checks
Page 15 of 18
0•15
To remove a wiper blade, pull the arm
fully away from the glass until it locks.
Swivel the blade through 90°, press the
locking tab(s) with your fingers, and slide the
blade out of the arm's hooked end. On
refitting, ensure that the blade locks securely
into the arm.Check the condition of the wiper blades;
if they are cracked or show any signs of
deterioration, or if the glass swept area is
smeared, renew them. For maximum clarity of
vision, wiper blades should be renewed
annually, as a matter of course.21Weekly checks
Battery
Caution:Before carrying out any work on the
vehicle battery, read the precautions given in
“Safety first” at the start of this manual.
4Make sure that the battery tray is in good
condition, and that the clamp is tight.
Corrosion on the tray, retaining clamp and the
battery itself can be removed with a solution
of water and baking soda. Thoroughly rinse all
cleaned areas with water. Any metal parts
damaged by corrosion should be covered with
a zinc-based primer, then painted.
4Periodically (approximately every three
months), check the charge condition of the
battery as described in Chapter 5A.
4If the battery is flat, and you need to jump
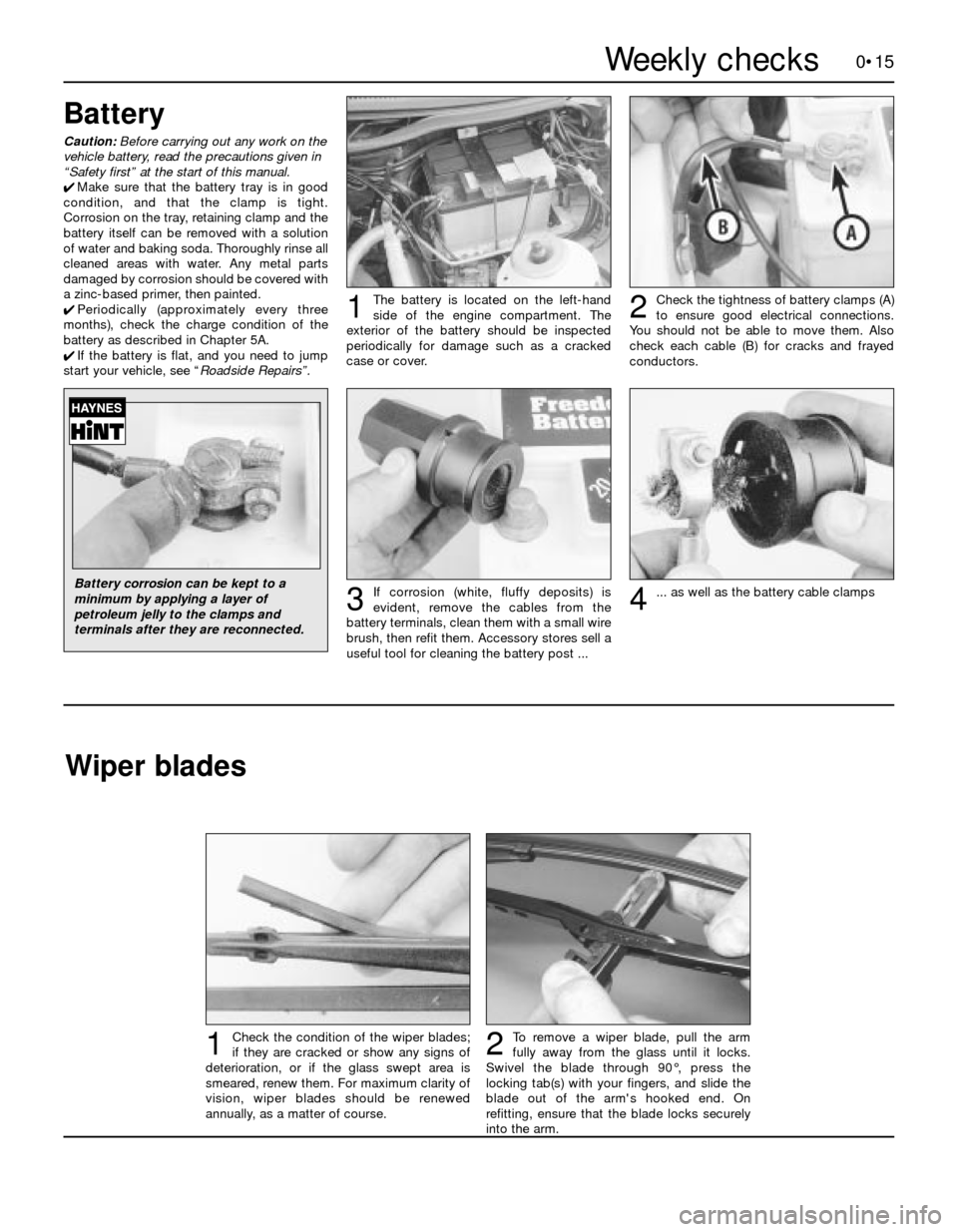
start your vehicle, see “Roadside Repairs”.The battery is located on the left-hand
side of the engine compartment. The
exterior of the battery should be inspected
periodically for damage such as a cracked
case or cover.
Check the tightness of battery clamps (A)
to ensure good electrical connections.
You should not be able to move them. Also
check each cable (B) for cracks and frayed
conductors.
If corrosion (white, fluffy deposits) is
evident, remove the cables from the
battery terminals, clean them with a small wire
brush, then refit them. Accessory stores sell a
useful tool for cleaning the battery post ...
12
3... as well as the battery cable clamps4
Battery corrosion can be kept to a
minimum by applying a layer of
petroleum jelly to the clamps and
terminals after they are reconnected.
Wiper blades