air conditioning FORD SIERRA 1992 2.G Reference Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1992, Model line: SIERRA, Model: FORD SIERRA 1992 2.GPages: 26, PDF Size: 0.57 MB
Page 19 of 26
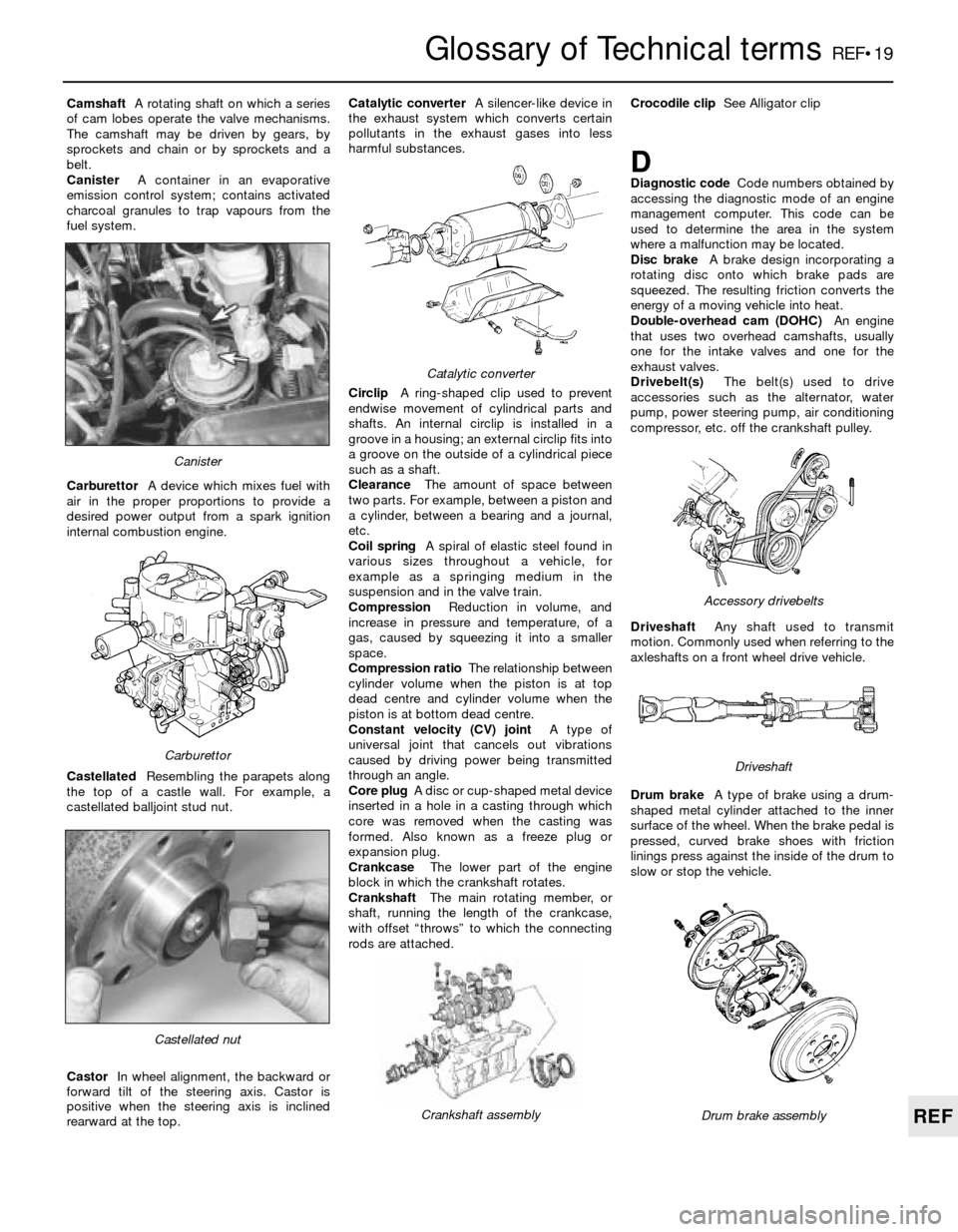
Glossary of Technical termsREF•19
REF
CamshaftA rotating shaft on which a series
of cam lobes operate the valve mechanisms.
The camshaft may be driven by gears, by
sprockets and chain or by sprockets and a
belt.
CanisterA container in an evaporative
emission control system; contains activated
charcoal granules to trap vapours from the
fuel system.
CarburettorA device which mixes fuel with
air in the proper proportions to provide a
desired power output from a spark ignition
internal combustion engine.
CastellatedResembling the parapets along
the top of a castle wall. For example, a
castellated balljoint stud nut.
CastorIn wheel alignment, the backward or
forward tilt of the steering axis. Castor is
positive when the steering axis is inclined
rearward at the top.Catalytic converterA silencer-like device in
the exhaust system which converts certain
pollutants in the exhaust gases into less
harmful substances.
CirclipA ring-shaped clip used to prevent
endwise movement of cylindrical parts and
shafts. An internal circlip is installed in a
groove in a housing; an external circlip fits into
a groove on the outside of a cylindrical piece
such as a shaft.
ClearanceThe amount of space between
two parts. For example, between a piston and
a cylinder, between a bearing and a journal,
etc.
Coil springA spiral of elastic steel found in
various sizes throughout a vehicle, for
example as a springing medium in the
suspension and in the valve train.
CompressionReduction in volume, and
increase in pressure and temperature, of a
gas, caused by squeezing it into a smaller
space.
Compression ratioThe relationship between
cylinder volume when the piston is at top
dead centre and cylinder volume when the
piston is at bottom dead centre.
Constant velocity (CV) jointA type of
universal joint that cancels out vibrations
caused by driving power being transmitted
through an angle.
Core plugA disc or cup-shaped metal device
inserted in a hole in a casting through which
core was removed when the casting was
formed. Also known as a freeze plug or
expansion plug.
CrankcaseThe lower part of the engine
block in which the crankshaft rotates.
CrankshaftThe main rotating member, or
shaft, running the length of the crankcase,
with offset “throws” to which the connecting
rods are attached.Crocodile clipSee Alligator clip
DDiagnostic codeCode numbers obtained by
accessing the diagnostic mode of an engine
management computer. This code can be
used to determine the area in the system
where a malfunction may be located.
Disc brakeA brake design incorporating a
rotating disc onto which brake pads are
squeezed. The resulting friction converts the
energy of a moving vehicle into heat.
Double-overhead cam (DOHC)An engine
that uses two overhead camshafts, usually
one for the intake valves and one for the
exhaust valves.
Drivebelt(s)The belt(s) used to drive
accessories such as the alternator, water
pump, power steering pump, air conditioning
compressor, etc. off the crankshaft pulley.
DriveshaftAny shaft used to transmit
motion. Commonly used when referring to the
axleshafts on a front wheel drive vehicle.
Drum brakeA type of brake using a drum-
shaped metal cylinder attached to the inner
surface of the wheel. When the brake pedal is
pressed, curved brake shoes with friction
linings press against the inside of the drum to
slow or stop the vehicle.
Castellated nut
Catalytic converter
Crankshaft assembly
Carburettor
Canister
Drum brake assembly
Accessory drivebelts
Driveshaft
Page 21 of 26

Glossary of Technical termsREF•21
REF
JJump startStarting the engine of a vehicle
with a discharged or weak battery by
attaching jump leads from the weak battery to
a charged or helper battery.
LLoad Sensing Proportioning Valve (LSPV)A
brake hydraulic system control valve that
works like a proportioning valve, but also
takes into consideration the amount of weight
carried by the rear axle.
LocknutA nut used to lock an adjustment
nut, or other threaded component, in place.
For example, a locknut is employed to keep
the adjusting nut on the rocker arm in
position.
LockwasherA form of washer designed to
prevent an attaching nut from working loose.
MMacPherson strutA type of front
suspension system devised by Earle
MacPherson at Ford of England. In its original
form, a simple lateral link with the anti-roll bar
creates the lower control arm. A long strut - an
integral coil spring and shock absorber - is
mounted between the body and the steering
knuckle. Many modern so-called MacPherson
strut systems use a conventional lower A-arm
and don’t rely on the anti-roll bar for location.
MultimeterAn electrical test instrument with
the capability to measure voltage, current and
resistance.
NNOxOxides of Nitrogen. A common toxic
pollutant emitted by petrol and diesel engines
at higher temperatures.
OOhmThe unit of electrical resistance. One
volt applied to a resistance of one ohm will
produce a current of one amp.
OhmmeterAn instrument for measuring
electrical resistance.
O-ringA type of sealing ring made of a
special rubber-like material; in use, the O-ring
is compressed into a groove to provide the
sealing action.Overhead cam (ohc) engineAn engine with
the camshaft(s) located on top of the cylinder
head(s).
Overhead valve (ohv) engineAn engine with
the valves located in the cylinder head, but
with the camshaft located in the engine block.
Oxygen sensorA device installed in the
engine exhaust manifold, which senses the
oxygen content in the exhaust and converts
this information into an electric current. Also
called a Lambda sensor.
PPhillips screwA type of screw head having a
cross instead of a slot for a corresponding
type of screwdriver.
PlastigageA thin strip of plastic thread,
available in different sizes, used for measuring
clearances. For example, a strip of Plastigage
is laid across a bearing journal. The parts are
assembled and dismantled; the width of the
crushed strip indicates the clearance between
journal and bearing.
Propeller shaftThe long hollow tube with
universal joints at both ends that carries
power from the transmission to the differential
on front-engined rear wheel drive vehicles.
Proportioning valveA hydraulic control
valve which limits the amount of pressure to
the rear brakes during panic stops to prevent
wheel lock-up.
RRack-and-pinion steeringA steering system
with a pinion gear on the end of the steering
shaft that mates with a rack (think of a geared
wheel opened up and laid flat). When the
steering wheel is turned, the pinion turns,
moving the rack to the left or right. This
movement is transmitted through the track
rods to the steering arms at the wheels.
RadiatorA liquid-to-air heat transfer device
designed to reduce the temperature of the
coolant in an internal combustion engine
cooling system.
RefrigerantAny substance used as a heat
transfer agent in an air-conditioning system.
R-12 has been the principle refrigerant for
many years; recently, however, manufacturers
have begun using R-134a, a non-CFC
substance that is considered less harmful tothe ozone in the upper atmosphere.
Rocker armA lever arm that rocks on a shaft
or pivots on a stud. In an overhead valve
engine, the rocker arm converts the upward
movement of the pushrod into a downward
movement to open a valve.
RotorIn a distributor, the rotating device
inside the cap that connects the centre
electrode and the outer terminals as it turns,
distributing the high voltage from the coil
secondary winding to the proper spark plug.
Also, that part of an alternator which rotates
inside the stator. Also, the rotating assembly
of a turbocharger, including the compressor
wheel, shaft and turbine wheel.
RunoutThe amount of wobble (in-and-out
movement) of a gear or wheel as it’s rotated.
The amount a shaft rotates “out-of-true.” The
out-of-round condition of a rotating part.
SSealantA liquid or paste used to prevent
leakage at a joint. Sometimes used in
conjunction with a gasket.
Sealed beam lampAn older headlight design
which integrates the reflector, lens and
filaments into a hermetically-sealed one-piece
unit. When a filament burns out or the lens
cracks, the entire unit is simply replaced.
Serpentine drivebeltA single, long, wide
accessory drivebelt that’s used on some
newer vehicles to drive all the accessories,
instead of a series of smaller, shorter belts.
Serpentine drivebelts are usually tensioned by
an automatic tensioner.
ShimThin spacer, commonly used to adjust
the clearance or relative positions between
two parts. For example, shims inserted into or
under bucket tappets control valve
clearances. Clearance is adjusted by
changing the thickness of the shim.
Slide hammerA special puller that screws
into or hooks onto a component such as a
shaft or bearing; a heavy sliding handle on the
shaft bottoms against the end of the shaft to
knock the component free.
SprocketA tooth or projection on the
periphery of a wheel, shaped to engage with a
chain or drivebelt. Commonly used to refer to
the sprocket wheel itself.
Starter inhibitor switchOn vehicles with an
O-ring
Serpentine drivebelt
Plastigage
Page 23 of 26

AAccelerator cable- 4A•8
Accelerator pedal- 4A•8
Acknowledgements- 0•4
Aerial- 13•20
Air cleaner- 1•18, 1•19, 4A•4, 4B•4
Air conditioning systems- 1•16, 3•1 et seq
Airflow meter- 4B•8
Alarm system- 13•19
Alternator- 5•6
Anti-roll bars- 11•6, 11•13
Anti-theft alarm- 13•19
Antifreeze- 0•17, 1•21, 3•3
ATF- 0•17, 1•3
Automatic transmission- 7B•1 et seq
extension housing oil seal - 7B•5
fault diagnosis - REF•11, REF•14
fluid - 0•17, 1•3
fluid checks - 1•13
gear selector mechanism - 7B•5
kickdown cable - 7B•3
removal and refitting - 7B•2
reversing lamp switch - 7B•6
selector rod - 7B•5
starter inhibitor switch - 7B•6
vacuum diaphragm unit - 7B•6
Auxiliary drivebelts- 1•14, 1•21
Auxiliary shaft- 2A•18
BBattery- 0•15, 1•15, 5•5
Bearings (engine) - 2A•23, 2B•17, 2C•23
Bleeding the power steering- 11•18
Bleeding the brakes- 10•2
Body damage- 12•2, 12•4
Body electrical systems - 13•1 et seq
Bodywork and fittings- 12•1 et seq
Bonnet release cable- 12•4
Bonnet lock- 12•4, 12•5
Boot lid lock- 12•5
Brake checks- 1•10
Brake fluid- 0•13, 0•1, 1•21
Braking system- 10•1 et seq
backplate - 10•12
bleeding the brakes - 10•2
brake caliper - 10•8, 10•10
brake disc - 10•3, 10•11
brake drum - 10•12
brake fluid pipes and hoses - 10•19
brake fluid reservoir - 10•15
brake lamp switch - 13•6
brake pads - 10•3
brake pedal - 10•22
brake shoes - 10•6
computer module (ABS) - 10•17
deceleration valve - 10•18
fault diagnosis - REF•11, REF•15
handbrake adjustment - 1•16, 10•20, 10•21
handbrake cables - 1•16, 10•20, 10•21
handbrake lever - 10•22
hoses brake - 10•19
hydraulic unit pressure switch - 10•17
hydraulic unit/pump/motor (ABS) - 10•15, 10•16
load apportioning valve - 10•19master cylinder (brake) - 10•13
pressure switch - 10•17
vacuum servo unit - 10•14
valve block (ABS) - 10•17
wheel cylinder - 10•12
wheel sensor - 10•18
Bulbs exterior- 13•16
Bulbs interior- 13•10
Bulbs ratings- 13•2
Bumpers- 12•13
Buying spare parts - REF•3
CCables:
accelerator - 4A•8
bonnet release - 12•4
clutch - 6•2
handbrake - 10•20, 10•21
kickdown - 7B•3
speedometer - 13•11
tailgate/boot lid/filler cap - 12•6
Caliper (brake) front/rear- 10•8, 10•10
Camshaft and followers- 2A•17, 2B•14, 2C•16
Capacities- 1•3
Carburettor:
Ford VV type - 1•12, 4A•8, 4A•13
Pierburg 2V type - 1•12, 4A•8, 4A•14
Weber 2V type - 1•12, 4A•8, 4A•14
Weber 2V TLD type - 1•12, 4A•8, 4A•15
Cargo area- 12•10
Carpets- 12•2
Catalytic converter- 4B•3, 4B•14
Central locking system- 13•18
Centre/overhead console- 12•18, 12•19
CFI unit- 4B•10
Charging system- 5•5
Cigarette lighter- 13•6
Clock- 13•6
Clutch- 6•1 et seq
assembly - 6•3
cable - 6•2
fault diagnosis - REF•11, REF•14
pedal - 6•2
release bearing - 6•5
Coil- 5•13
Coil spring (rear) - 11•10
Compression test- 2A•7
Computer module (ABS)- 10•17
Connecting rods- 2A•22, 2B•17, 2C•21
Contents- 0•2
Coolant- 0•12, 0•17, 1•21, 3•3
Coolant level- 0•12
Cooling, heating and air conditioning
systems- 3•1 et seq
antifreeze - 0•12, 0•17, 1•21, 3•3
coolant pump - 3•5
coolant temperature sender and sensor - 3•8
cooling fan - 3•7
draining - 1•21
drivebelt tensioner - 3•7
expansion tank/coolant sensor - 3•8
fan (radiator) - 3•7
fault diagnosis - REF•11, REF•13
filling - 1•21
flushing - 1•21heater - 3•9
radiator - 3•3
switches - 3•8
temperature gauge and sender unit - 3•8
thermostat - 3•4
Courtesy lamp switch- 13•5
Crankshaft oil seals- 2A•19, 2B•15, 2C•19
Crankshaft bearings- 2A•23, 2B•17, 2C•23
Cylinder bores- 2A•24
Cylinder head- 2A•14, 2B•10, 2C•13
DDents- 12•2
Depressurising fuel injection system- 4B•4
Dimensions and weights- REF•1
Disc brake - 10•3, 10•11
Distributor- 5•14, 5•15, 5•16
Door- 12•6
Door inner trim panel- 12•7
Door mirror switch- 13•5
Drivebelts check- 1•14, 1•21, 3•7
Driveplate- 2A•18, 2B•15, 2C•19
Driveshafts:
check - 1•17
fault diagnosis - REF•11, REF•15
overhaul - 9•5
removal and refitting - 9•4
Drum (brake)- 10•12
EEarth fault finding- 13•3
Electric windows- 13•18
Electrical fault finding- 13•2
Electrical system (body)- 13•1 et seq
Electrical system:
weekly checks - 0•14
fault diagnosis - REF•11, REF•16
Electronic vacuum regulator- 4B•11
Engine:
auxiliary shaft - 2A•18
bearings - 2A•23, 2B•17, 2C•23
bores - 2A•24
camshaft followers - 2A•17, 2B•14, 2C•16
codes - 2A•1, 2B•1, 2C•1
compartment views - 0•10, 1•5
compression test - 2A•7
connecting rods - 2A•22, 2B•17, 2C•21
crankshaft bearings - 2A•23, 2B•17, 2C•23
crankshaft oil seals - 2A•19, 2B•15, 2C•19
cylinder bores - 2A•24
cylinder head - 2A•14, 2B•10, 2C•13
dismantling - 2A•11, 2B•8, 2C•10
DOHC engines- 2B•1 et seq
driveplate - 2A•18, 2B•15, 2C•19
fault diagnosis - REF•11, REF•12
flywheel - 2A•18, 2B•15, 2C•19
main bearings - 2A•23, 2B•17, 2C•23
mountings - 2A•11, 2B•7, 2C•9
oils - 0•17, 1•3
oil and filter renewal - 1•9
oil level - 0•12
oil pump - 2A•21, 2B•16, 2C•20
oil seals crankshaft - 2A•19, 2B•15, 2C•19
piston - 2A•22, 2B•17, 2C•21
IndexREF•23
REF
Note: References throughout this index are in the form - “Chapter number” • “page number”