brake light FORD TRANSIT 2006 7.G Body And Equipment Mounting Section Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 2006, Model line: TRANSIT, Model: FORD TRANSIT 2006 7.GPages: 234, PDF Size: 33.19 MB
Page 7 of 234

1.2 Commercial and Legal Aspects
1.2.1 Terminology
NOTE: Any modifications to the vehicle must
be noted in the owner's handbook or new
descriptive literature included with the owner's
documentation.
Vehicle Converter refers to any re-seller altering
the vehicle by converting the body and adding
or modifying any equipment not originally
specified and or supplied by Ford.
Unique component or similar wording refers to
non-Ford specified or after sale fitment not
covered by Ford warranty.
1.2.2 Warranty on Ford Vehicles
Please contact The National Sales Company in
the country where the vehicle will be registered
for details of the terms of any applicable Ford
warranty.
The Vehicle Converter should warrant its design,
materials and construction for a period at least
equal to any applicable Ford warranty
The Vehicle Converter must ensure that any
alteration made to a Ford vehicle or component
does not reduce the safety, function, or durability
of the vehicle or any component.
The Vehicle Converter shall be solely responsible
for any damage resulting from any alteration
made by the Vehicle Converter or any of its
agents to a Ford Vehicle Component.
The Vehicle Converter releases Ford from all
claims by any third party for any cost or loss
(including any consequential damages) arising
from work performed by a Vehicle Converter
unless Ford has given its prior written consent
to such liability.
1.2.3 Legal and Vehicle Type
Approval
•All components embodied on Ford vehicles
are approved to the applicable legal
requirements.
•Ford vehicles have Type Approval for the
intended marketing territories.
WARNING: Exception - Incomplete
vehicles require further approval
when completed by the Body
Builder.
•The Transit range has Type Approval for many
territories, although the full range of vehicles
shown in this manual are not necessarily
released in all territories. Check with your local
ford National Sales Company representative.
•Significant changes to the vehicle may affect
its legal compliance. Strict adherence to the
original design intent for brakes, weight
distribution, lighting, occupant safety and
hazardous materials compliance in particular
is mandatory.
1.2.4 Alternative Type Approval
If significant changes are made the Body Builder
must negotiate with the relevant authority. Any
changes to the vehicle operating conditions must
be advised to the customer.
1.2.5 Legal Obligations and
Liabilities
The Vehicle Converter should consult with its
legal advisor on any questions concerning its
legal obligations and liabilities.
1.2.6 General Product Safety
Requirement
The Vehicle Converter shall ensure that any
vehicle it places on the market complies with the
European General Product safety Directive
2001/95/EC (as amended periodically). The
Vehicle Converter shall also ensure that any
alteration it makes to a Ford vehicle or
component does not reduce its compliance with
the European General Product Safety Directive.
The Vehicle Converter shall release Ford from all
liability for damages resulting from:
•Failure to comply with these Body Equipment
Mounting directives, in particular warnings.
•Faulty design, production, installation,
assembly or alteration not originally specified
by Ford.
•Failure to comply with the basic fit for purpose
principles inherent in the original product.
WARNINGS:
Do not exceed the gross vehicle
mass, gross train mass, axle plates
and trailer plate
Do not change the tire size or load
rating
Do not modify the steering system.
Excessive heat can build up from
the exhaust system, in particular
from the catalytic converter. Ensure
adequate heat shields are
maintained. Maintain sufficient
clearance to hot parts
FordTransit 2006.5 (April 2006–)
Date of Publication: 12/2006
1 General Information
7
Page 33 of 234

1.13 Package and Ergonomics
1.13.1 General Component
Package Guidelines
WARNING: Do not modify, drill, cut
or weld any suspension
components, specifically the
steering gear system, subframe or
anti-roll bars, springs or shock
absorbers including mounting
brackets.
The Vehicle Converter has to ensure that
sufficient clearance is maintained under all drive
conditions to moving components such as axles,
fans, steering, brake system etc.
The Vehicle Converter is responsible for all
installed components during the conversion. The
durability has to be confirmed by appropriate test
procedures.
1.13.2 Driver Reach Zones
Controls and/or equipment required to be used
while driving should be located within easy reach
of the driver so as not to impair driver control
1.13.3 Driver Field of View
WARNING: Make sure that the
modified vehicle complies with all
relevant legal requirements.
1.13.4 Conversion Affects on
Parking Aids
WARNING: Ensure that monitors
mounted in the cabin meet the
interior package and safety
requirements
On conversions requiring a rear camera, the
reverse signal may be taken as described in the
electrical section, described in reversing lamps.
Refer to: 4.11 Exterior Lighting (page 116).
1.13.5 Aids for Vehicle Entry and
Exit
Steps
WARNINGS:
Make sure that the modified vehicle
complies with all relevant legal
requirements.
If this modification alters the
homologated dimensions, a new
approval may be necessary.
CAUTION: Make sure that
reinforcements are installed to
maintain the integrity of the original
body structure.
Steps can be ordered as an option on the base
vehicle. Please check for availability.
Where additional steps are installed the required
ground clearance line is to be maintained.
The Vehicle Converter must make sure that a
movable step is set in the stored position when
the vehicle is running. The step surface must be
non-slip.
Grab Handles
WARNING: Make sure that the
location of the no-drill zones are
checked before drilling.
CAUTION: Make sure that
reinforcements are installed to
maintain the integrity of the original
body structure.
Grab handles can be ordered as an option on
the base vehicle. Please check for availability.
NOTE: For further information please contact
your local National Sales Company
representative, or Local Ford Dealer. If they are
unable to help you then please contact the
Vehicle Converter Advisory Service at
[email protected].
FordTransit 2006.5 (April 2006–)
Date of Publication: 12/2006
1 General Information
33
Page 91 of 234
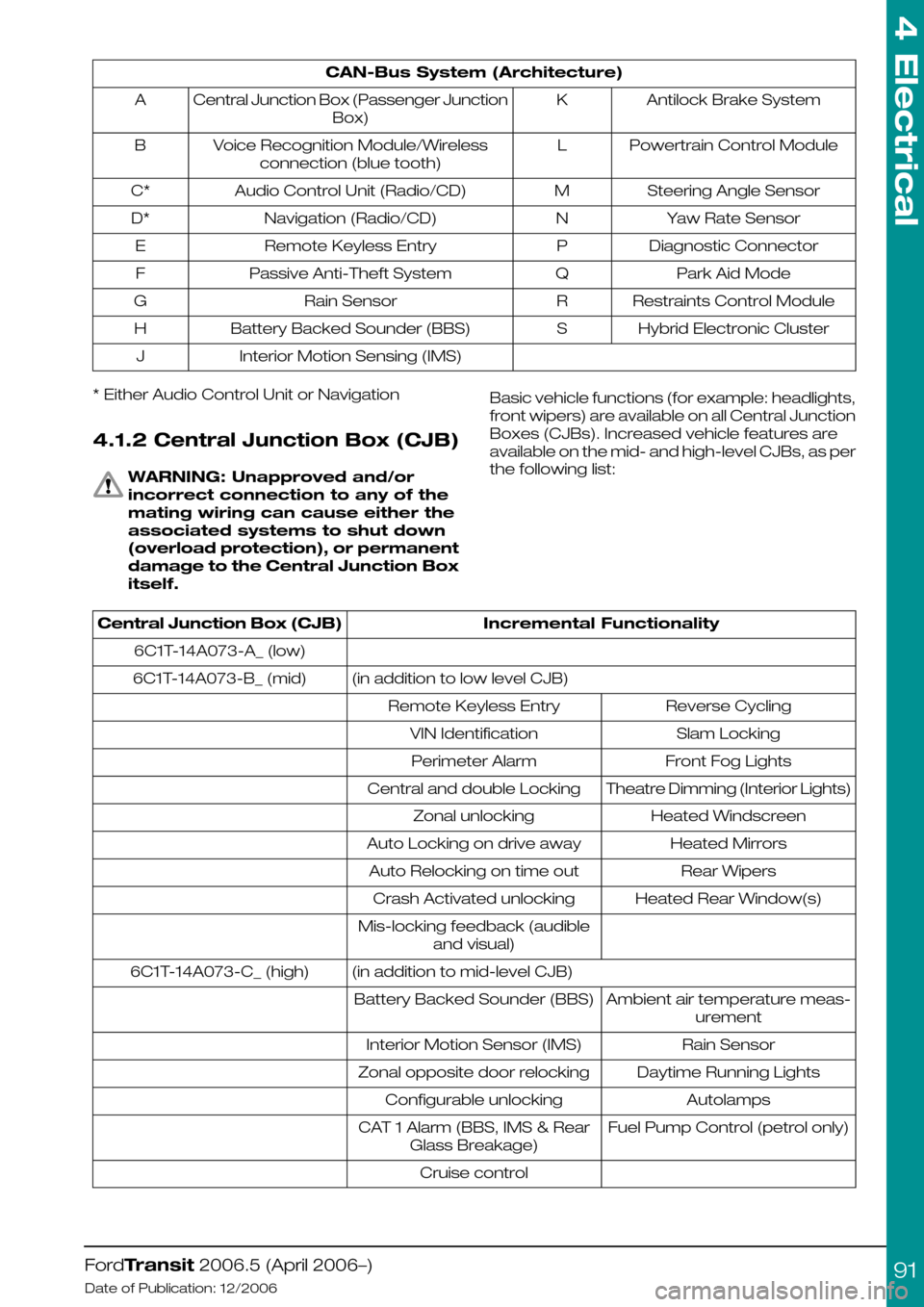
CAN-Bus System (Architecture)
Antilock Brake SystemKCentral Junction Box (Passenger Junction
Box)
A
Powertrain Control ModuleLVoice Recognition Module/Wireless
connection (blue tooth)
B
Steering Angle SensorMAudio Control Unit (Radio/CD)C*
Yaw Rate SensorNNavigation (Radio/CD)D*
Diagnostic ConnectorPRemote Keyless EntryE
Park Aid ModeQPassive Anti-Theft SystemF
Restraints Control ModuleRRain SensorG
Hybrid Electronic ClusterSBattery Backed Sounder (BBS)H
Interior Motion Sensing (IMS)J
* Either Audio Control Unit or Navigation
4.1.2 Central Junction Box (CJB)
WARNING: Unapproved and/or
incorrect connection to any of the
mating wiring can cause either the
associated systems to shut down
(overload protection), or permanent
damage to the Central Junction Box
itself.
Basic vehicle functions (for example: headlights,
front wipers) are available on all Central Junction
Boxes (CJBs). Increased vehicle features are
available on the mid- and high-level CJBs, as per
the following list:
Incremental FunctionalityCentral Junction Box (CJB)
6C1T-14A073-A_ (low)
(in addition to low level CJB)6C1T-14A073-B_ (mid)
Reverse CyclingRemote Keyless Entry
Slam LockingVIN Identification
Front Fog LightsPerimeter Alarm
Theatre Dimming (Interior Lights)Central and double Locking
Heated WindscreenZonal unlocking
Heated MirrorsAuto Locking on drive away
Rear WipersAuto Relocking on time out
Heated Rear Window(s)Crash Activated unlocking
Mis-locking feedback (audible
and visual)
(in addition to mid-level CJB)6C1T-14A073-C_ (high)
Ambient air temperature meas-
urement
Battery Backed Sounder (BBS)
Rain SensorInterior Motion Sensor (IMS)
Daytime Running LightsZonal opposite door relocking
AutolampsConfigurable unlocking
Fuel Pump Control (petrol only)CAT 1 Alarm (BBS, IMS & Rear
Glass Breakage)
Cruise control
FordTransit 2006.5 (April 2006–)
Date of Publication: 12/2006
4 Electrical
91
Page 95 of 234

4.3 Charging System
4.3.1 General Information and
Specific Warnings
The Transit electrical system is a 12-Volt supply
with a negative earth return. The alternator and
battery equipment used as standard are
designed for normal operations with the type of
engine fitted. Higher capacity batteries are
available as standard production options and
special vehicle options. Before installing additional
electrical equipment check that the battery
capacity, harness load capability, and alternator
output are suitable for the extra load.
The battery capacity and charge available from
the alternator must be adequate to ensure
engine cranking in unfavorable climatic conditions
but excessive battery capacity could damage
the starter motor.
The Transit utilizes multiplexed vehicle electronics
- it is recommended that the appropriate Ford
proprietary accessory systems are used.
Inappropriate or incorrect connection of
additional equipment could cause mis-operation,
or damage to the vehicle, and so invalidate any
warranty.
Additional connection points are provided
specifically for customer use (except M1 and M2
Bus), and are located on the outside of the
driver's seat base.
Do not jump-start the vehicle directly from the
battery. Use designated jump-start points. Refer
to the owners literature.
4.3.2 Power Management
Settings
There are four Power Management Settings
available:
•Factory
•Transport
•Normal
•Crash
Factory and Transport modes are only active
with ignition off; with ignition on, the vehicle
operates with full functionality. When in Transport
mode, the interior lights, clocks, and power
locking and alarms (where fitted) do not work.
It is possible to switch from Transport Mode to
Normal Mode without the use of any ancillary
equipment, but not vice versa. To change mode,
the brake pedal must be depressed five times,
and the hazard warning switch operated twice
(in any combination) within 10 seconds.
WARNING: It is not possible to return
the transport setting without using
the vehicle's diagnostics.
At the end of production, the vehicle is
configured to the transport setting to minimize
power consumption. As part of the Pre Delivery
Inspection process at the Ford dealership, the
vehicle is reconfigured to normal operation.
4.3.3 Electrical Conversions
Operator requirements for additional and
specialised electrical equipment varies. The
vehicle converter/modifier must, therefore,
consider the following points when designing the
installation:
•Legality and regulatory conformity of the base
vehicle.
•Drive-ability and serviceability of the base
vehicle.
•The effect of regulations governing the
proposed conversion including National
Legislation in the country of sale.
•The method of integrating the circuit into the
base vehicle.
•No additional circuits are to be run alongside
the electrical circuits (shown in blue in the
figure below) associated with the
Management System (shown in green in the
figure below), due to the possible Electro
Motive Force (EMF) effect on the circuits.
FordTransit 2006.5 (April 2006–)
Date of Publication: 12/2006
4 Electrical
95
Page 134 of 234
Where wires are required to be extended, break
in points should only be at existing connector
points and only Ford approved connectors should
be used.
Ford approved link harnesses should be used.
Unused Connectors
The harnesses may have a number of unused
connectors – these are dedicated to other
features and options, e.g. heated seats, but are
not always present depending on level of
harness fitted. Ford do not recommend the use
of these connectors for any other purpose than
that intended by design.
Power Outlet / Cigar Lighter
Both features adopt a 20A fusing strategy. With
a single battery system, continued loading of
these features will lead to battery drain, and risk
vehicle starting. If continuous power is required,
a second battery option should be installed and
the customer connection points, where fitted,
utilized.
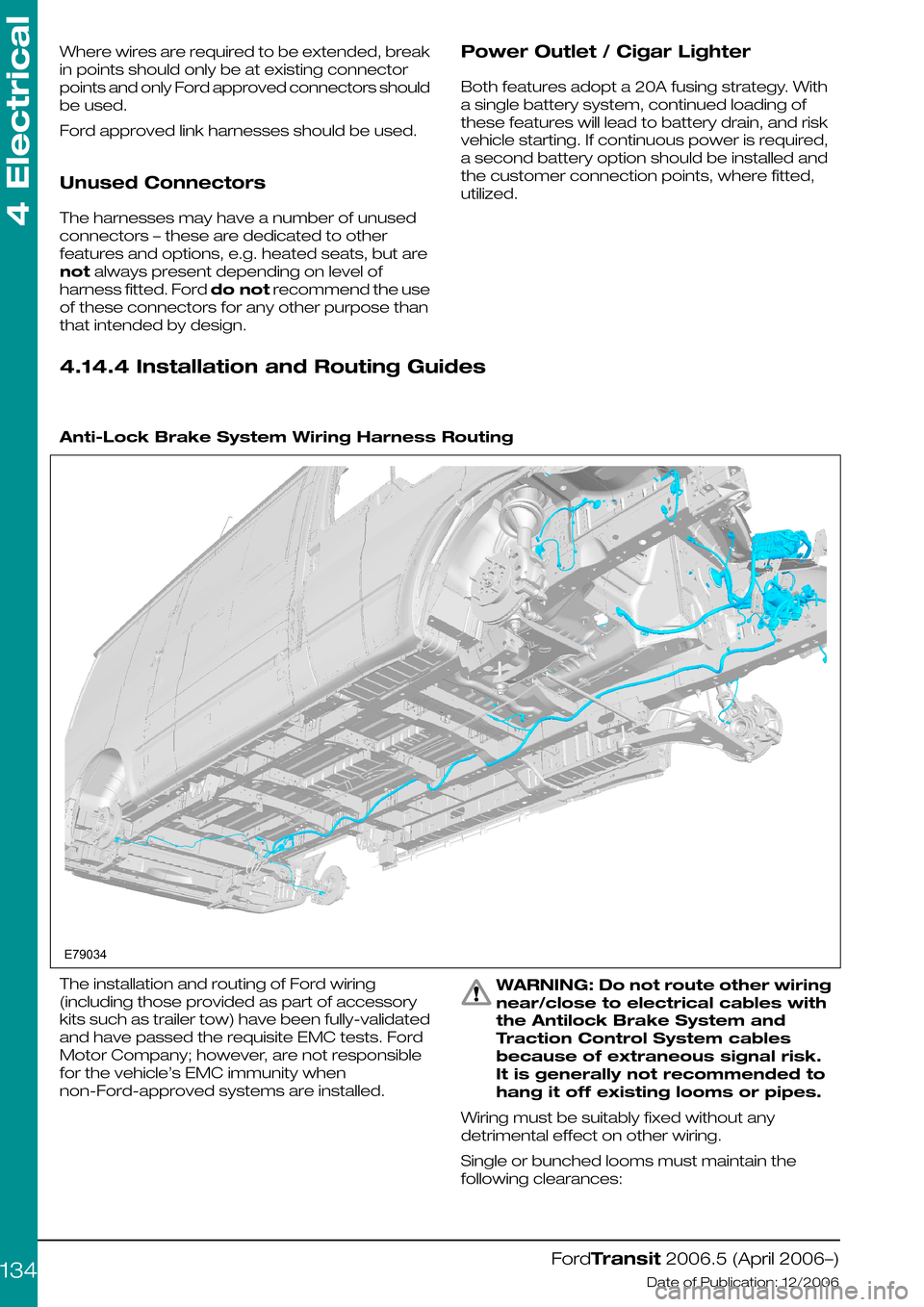
4.14.4 Installation and Routing Guides
Anti-Lock Brake System Wiring Harness Routing
The installation and routing of Ford wiring
(including those provided as part of accessory
kits such as trailer tow) have been fully-validated
and have passed the requisite EMC tests. Ford
Motor Company; however, are not responsible
for the vehicle’s EMC immunity when
non-Ford-approved systems are installed.
WARNING: Do not route other wiring
near/close to electrical cables with
the Antilock Brake System and
Traction Control System cables
because of extraneous signal risk.
It is generally not recommended to
hang it off existing looms or pipes.
Wiring must be suitably fixed without any
detrimental effect on other wiring.
Single or bunched looms must maintain the
following clearances:
FordTransit 2006.5 (April 2006–)
Date of Publication: 12/2006
4 Electrical
134E79034
Page 147 of 234
4.14.8 Additional Vehicle Signals
/ Features
Reverse Signal
A reverse signal is available on the tail light
connector. In order to avoid electrical issues due
to leakage, and to ensure connector
compatibility, a mating connector with
seals/plugs and pre-crimped wire & terminal
should be used. For Additional information refer
to Adding Connectors, Terminals and Wiring in
this manual.
NOTE: It is not recommended that signal is used
to drive auxiliary equipment directly – a relay (max
300mA) should be used. The existing reverse
light load is close to the threshold and is
hard-wired through the Central Junction Box for
current sensing to generate the appropriate CAN
message.
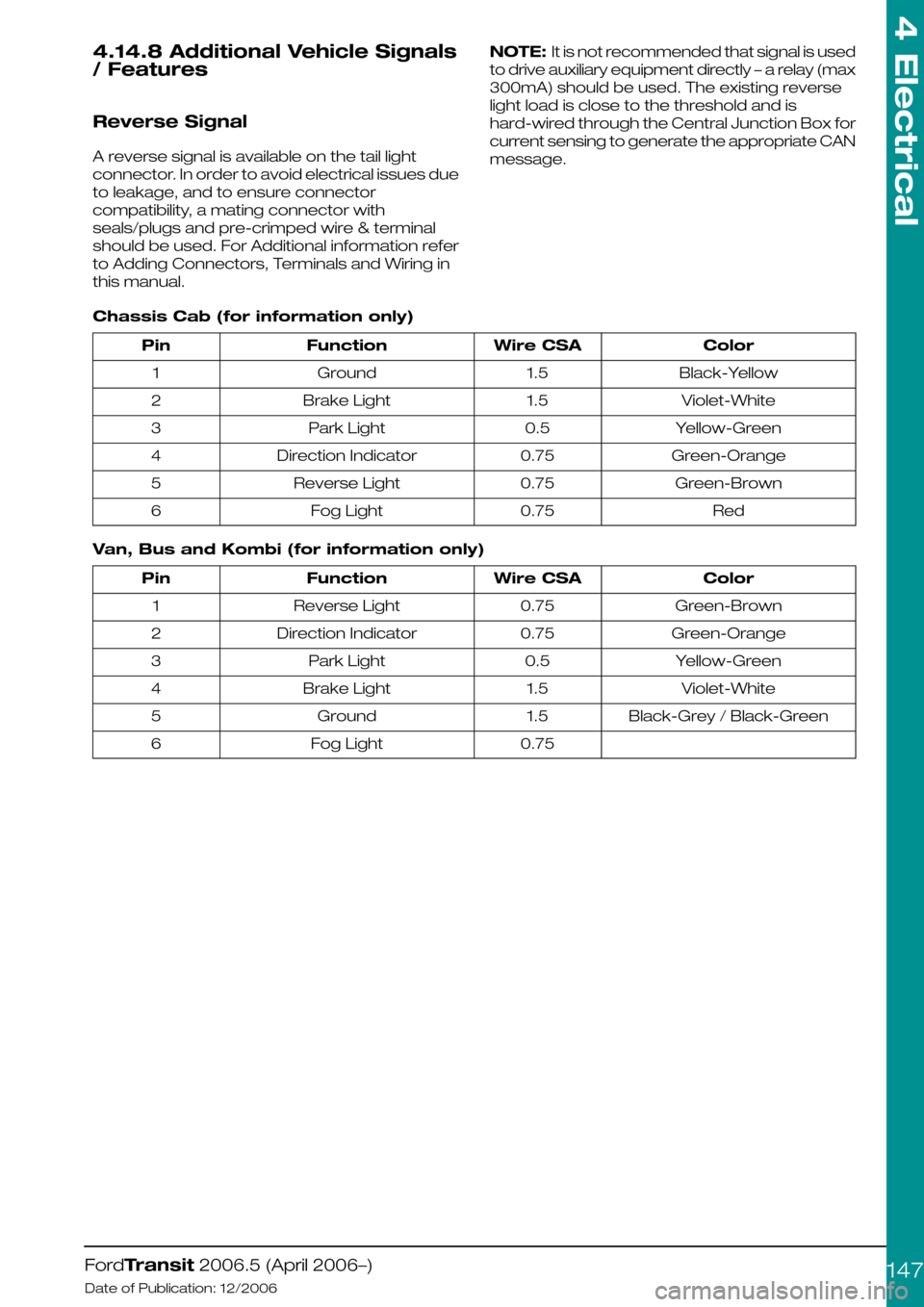
Chassis Cab (for information only)
ColorWire CSAFunctionPin
Black-Yellow1.5Ground1
Violet-White1.5Brake Light2
Yellow-Green0.5Park Light3
Green-Orange0.75Direction Indicator4
Green-Brown0.75Reverse Light5
Red0.75Fog Light6
Van, Bus and Kombi (for information only)
ColorWire CSAFunctionPin
Green-Brown0.75Reverse Light1
Green-Orange0.75Direction Indicator2
Yellow-Green0.5Park Light3
Violet-White1.5Brake Light4
Black-Grey / Black-Green1.5Ground5
0.75Fog Light6
FordTransit 2006.5 (April 2006–)
Date of Publication: 12/2006
4 Electrical
147
Page 149 of 234
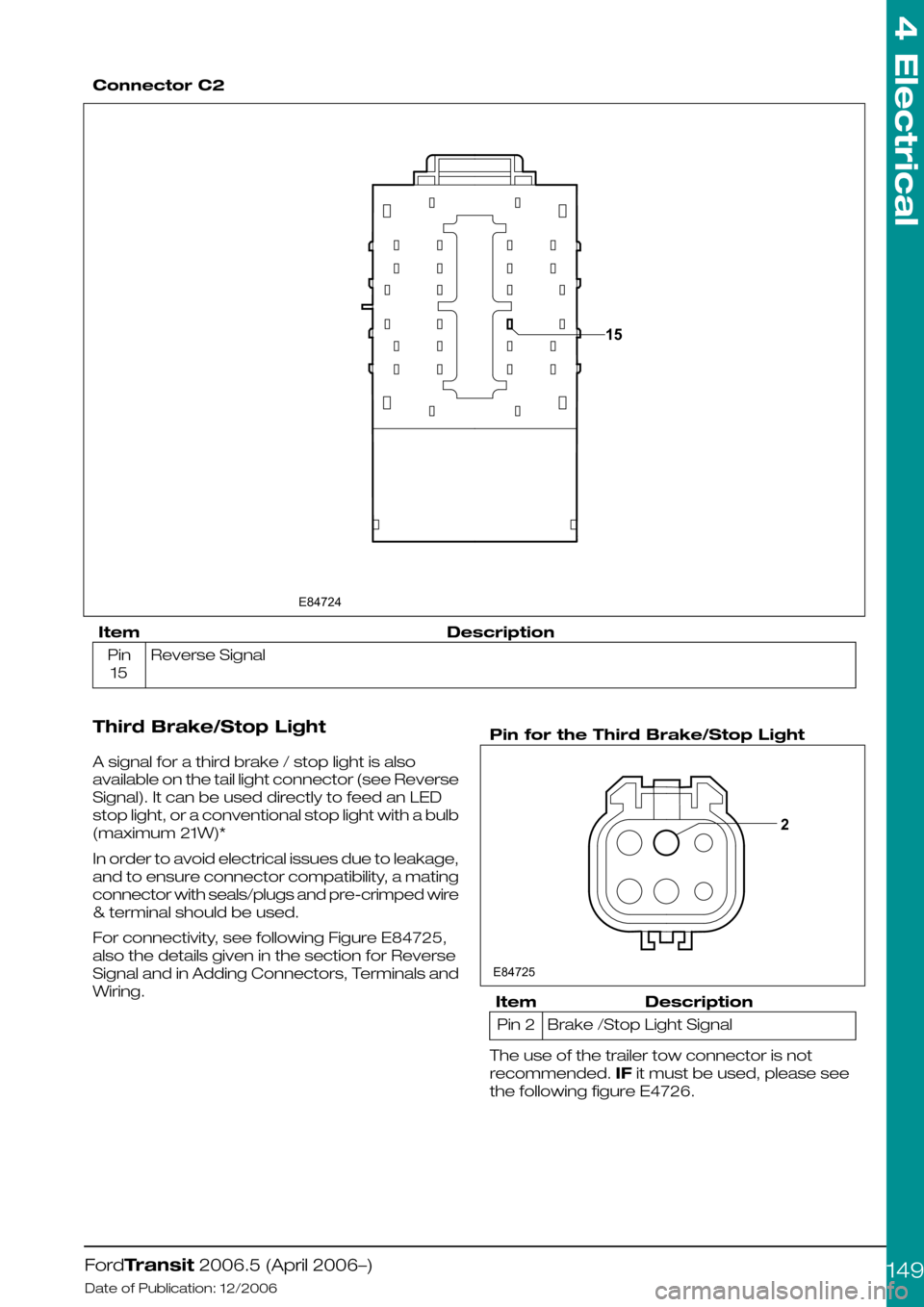
Connector C2
DescriptionItem
Reverse SignalPin
15
Third Brake/Stop Light
A signal for a third brake / stop light is also
available on the tail light connector (see Reverse
Signal). It can be used directly to feed an LED
stop light, or a conventional stop light with a bulb
(maximum 21W)*
In order to avoid electrical issues due to leakage,
and to ensure connector compatibility, a mating
connector with seals/plugs and pre-crimped wire
& terminal should be used.
For connectivity, see following Figure E84725,
also the details given in the section for Reverse
Signal and in Adding Connectors, Terminals and
Wiring.
Pin for the Third Brake/Stop Light
DescriptionItem
Brake /Stop Light SignalPin 2
The use of the trailer tow connector is not
recommended. IF it must be used, please see
the following figure E4726.
FordTransit 2006.5 (April 2006–)
Date of Publication: 12/2006
4 Electrical
14915E84724 2E84725
Page 150 of 234
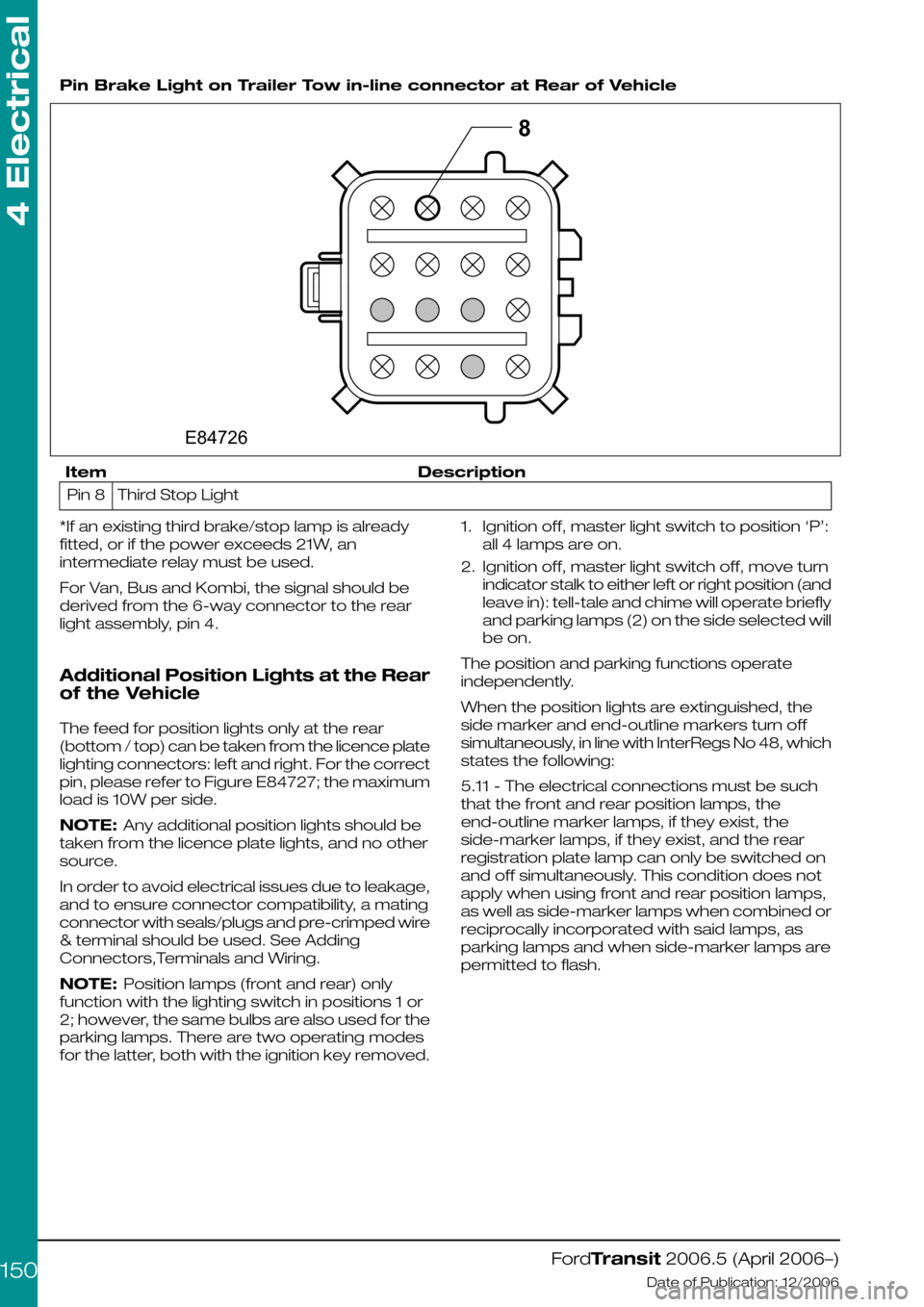
Pin Brake Light on Trailer Tow in-line connector at Rear of Vehicle
DescriptionItem
Third Stop LightPin 8
*If an existing third brake/stop lamp is already
fitted, or if the power exceeds 21W, an
intermediate relay must be used.
For Van, Bus and Kombi, the signal should be
derived from the 6-way connector to the rear
light assembly, pin 4.
Additional Position Lights at the Rear
of the Vehicle
The feed for position lights only at the rear
(bottom / top) can be taken from the licence plate
lighting connectors: left and right. For the correct
pin, please refer to Figure E84727; the maximum
load is 10W per side.
NOTE: Any additional position lights should be
taken from the licence plate lights, and no other
source.
In order to avoid electrical issues due to leakage,
and to ensure connector compatibility, a mating
connector with seals/plugs and pre-crimped wire
& terminal should be used. See Adding
Connectors,Terminals and Wiring.
NOTE: Position lamps (front and rear) only
function with the lighting switch in positions 1 or
2; however, the same bulbs are also used for the
parking lamps. There are two operating modes
for the latter, both with the ignition key removed.
1.Ignition off, master light switch to position ‘P’:
all 4 lamps are on.
2.Ignition off, master light switch off, move turn
indicator stalk to either left or right position (and
leave in): tell-tale and chime will operate briefly
and parking lamps (2) on the side selected will
be on.
The position and parking functions operate
independently.
When the position lights are extinguished, the
side marker and end-outline markers turn off
simultaneously, in line with InterRegs No 48, which
states the following:
5.11 - The electrical connections must be such
that the front and rear position lamps, the
end-outline marker lamps, if they exist, the
side-marker lamps, if they exist, and the rear
registration plate lamp can only be switched on
and off simultaneously. This condition does not
apply when using front and rear position lamps,
as well as side-marker lamps when combined or
reciprocally incorporated with said lamps, as
parking lamps and when side-marker lamps are
permitted to flash.
FordTransit 2006.5 (April 2006–)
Date of Publication: 12/2006
4 Electrical
1508E84726
Page 154 of 234

harness that provides roof-mounted rear turn
indicators, powered via relays. This should be
used in conjunction with SVO fusebox.
3.Chassis cab LED rear lamp cluster
replacement recommendations, especially
turn indicator relay implications – see lighting
load table. Generally the use of LED equivalent
lighting systems reduces the electrical load on
the vehicle; however, special care needs to
be taken with respect to any change to or
addition of turn indicator lights. Depending on
the current requirements of the LED(s)
compared to the bulb it is replacing, a ballast
resistor may be required, if not already
integrated into the LED lamp assembly.
Without this, bulb outage detection for turn
indicators will be affected, which is a legal
requirement.
Additional turn indicators must be powered
through relays (max 300mA), driven by existing
turn lights. The maximum load that the Central
Junction Box can drive is 3 x 21W per side (front,
rear and CAT 6 turn indicators); but even if the
vehicle is not fitted with the CAT 6 lights, the feeds
for these should not be used as the Central
Junction Box would need reconfiguring, which
could have safety as well as functional
implications.
4.Special Vehicle Option beacon switch: wiring
locations, circuit diagrams and max amperage
– see Special Vehicle Option fuse box
schematic (max current is 15A); there is
provision for the Special Vehicle Option beacon
switch in an empty switch location on the
instrument panel.
5.Rear loom connector detail location and supply
details for retro-fit loom extension for
example:- when extending a medium wheel
base, long wheel base or extended frame
overhang, what connectors do they use to
make a plug and play loom extension? – for
chassis cab vehicles, there is an Special
Vehicle Option extension loom for rear lamps
(part number 6C1V-14408-A*). There is not, at
present, a similar loom for Van, Bus and
Kombi's, although the appropriate mating
connector is now tooled, so this would be
possible.
Miscellaneous Systems
Handbrake on - Cluster Warning Light -
Unless the vehicle is specified with options that
drive the handbrake warning light (for example
ESP, Australia market), the components making
up this system are not fitted. We do not
recommend installation of this feature as an
aftermarket addition. There are several reasons
for this:
1.Not all circuits carry the requisite wire as a give
away:
•The wires might be part of the main vehicle
harness (14401) even if not used – for example
camper vehicles are normally ordered with
power mirrors, and the wires will be present
as a give-away.
•The seat pedestal harness (14K076), however,
is vehicle specific – if the handbrake is not part
of the specification, it will not be present or
give-away. This harness would need to be
changed to the compatible part that also
includes the handbrake warning light circuit.
2.The handbrake switch (part number
2F2T-15852-A*) together with its short jumper
harness (6C1T-15K857-A*) would need to be
obtained and fitted.
3.The handbrake warning light is in all clusters,
but unless the vehicle config. parameter
“parking brake switch” is set, the Central
Junction Box will not read this input, and hence
NO CAN message sent to the cluster.
Reconfiguration can only be done at a Ford
Dealer.
NOTE: If a vehicle already has a handbrake
warning light in the cluster, or one is installed as
per the Ford design, it is not possible to utilize the
wire from the handbrake switch as part of an
interlock circuit (this is a pull up resistor input that
provides a wetting current of 20mA – anything in
excess of this, for example through additional
circuitry, will almost certainly damage the Central
Junction Box). If there is no handbrake switch
installed, it would be possible to add one and
utilize this as part of a separate circuit, up to a
maximum current of 500mA through the switch.
Reverse Sensors (Rear Park Aid
Module)- The factory-fit option is a CAN-based
system, but for Van, Bus, and Kombi vehicles
only. Stand-alone systems can be installed (for
example for chassis cab conversions), but would
need to utilize the PTA line of the radio if muting
is required.
Fuel Fired Heater (FFH)- Add FFH: wiring is
only present (give-away) in certain harnesses.
There was an aftermarket kit available for this
system on current Transit, which could probably
be “updated” to suit V347/8.
Fuel Fired Heater (FFH) - Programmable
FFH: this utilizes a timer/control module mounted
to the Instrument Panel, which necessitates
having the correct Instrument Panel harness
fitted. Retrofit of this would be a difficult.
For both systems, the appropriate 6C1T-14K132
harness would be required (suffix -A* for
Programmable FFH, and suffix –B* for Add FFH).
Central Locking
Locking is controlled by the Central Junction Box
module. There is current sensing on certain
locking circuit pins as part of the security system
– if these are tampered with, locking cannot be
guaranteed.
FordTransit 2006.5 (April 2006–)
Date of Publication: 12/2006
4 Electrical
154
Page 161 of 234

The software in the PCM responds to the change
of state, so it is recommended that these 3
middle switches be non-latching push button
micro switches. When going from idle to an
elevated RPM the execution of the command
will occur as the button is released. When going
to idle the execution of the command occurs as
the button is pressed.
The final button (the one on the left in Fig. 4) acts
as an ‘emergency’ vehicle engine stop. It is
recommended that this be a red & oversize
non-latching micro switch button. The execution
of this command will occur as the button is
pressed.
All wiring connecting the PCM to the resistance
ladder control box should be shielded & twisted
(33 twists / m) to reduce EMC effects
All resistors should have a tolerance of +/- 5% or
better
Switch contact, connectors & loom (loom
between the green/white wires & the control
box) total resistance must be no greater than 5
ohm max.
The PCM to resister ladder control switch box
loom should not come within 100mm of any other
harness, especially any carrying heavy loads.
Designs which do not require all the button
switches must still have the complete resistor
network with the switches positioned correctly
within the network.
The resistance ladder is acting as a potential
divider
The 220 nF capacitor is used in the circuit to
reduce EMC effects on the system
A suitable two way quality connector should be
used to connect the control box to the two
green/white wires
How to change the default settings
By default, when the feature is first enabled
(either via factory order or via dealer IDS tools),
it will be set to the 3 speed mode of operation
with preset RPM values of 1100, 1600 & 2030rpm
for the 3 speeds.
There are two methods by which these defaults
can be modified:
1.via the IDS diagnostics system at a Ford dealer
(there may be a charge for this)
2.via an inbuilt vehicle ‘learn mode’
Via the IDS system the mode of operation can
freely be changed between any of the 3 modes
of operation, the feature can even be turn off
(disabled). The 3 default RPM speeds can also
be modified.
Via the vehicle ‘learn mode’ the 3 speed mode
& the variable speed mode can be freely
interchanged, however it is not possible to select
the idle up speed mode via the vehicle learn
mode. The 3 default RPM speeds can also be
modified via ‘learn mode’
It is not possible via either method above, to
change the step value of 25rpm per press or the
250 rpm per sec for a held down button, in the
variable rpm speed mode.
Via IDS The RPM Speed Controller menu is under
the tool box tab, then Powertrain, then service
functions, then PCM. The IDS on screen menus
will guide the dealer through the options & setup.
How to enter vehicle ‘Learn mode’
1.Make sure that the RPM Speed controller
switch box is connected but turned off (not
‘armed’)
2.Start the engine (vehicle out of gear & no foot
pedals being pressed, handbrake on)
3.Wait a couple of seconds for the instrument
panel start up diagnostic lights to extinguish
4.Press & release the clutch pedal
5.Press & release the brake pedal
6.Repeat steps 4) & 5) a further four times
(clutch & brake pressed a total of five times
sequentially each)
NOTE: Steps 4) to 6) have to be started within
10 seconds of the engine start
The vehicle should now be in ‘learn mode’
How to Select between modes
1.Enter ‘learn mode’ (see directions above)
2.Arm the RPM speed controller (turn the key
switch to ‘on’)
If the vehicle is already in 3 speed mode (the
initial default):
3.Press & release the brake pedal five times
The vehicle should now be in variable speed
mode. The new settings can be saved & learn
mode exited (see below)
Alternatively
4.Press & release the brake pedal once
The vehicle should now be in 3 speed mode.
The new settings can be saved & learn mode
exited (see below)
Using this method it is easy to change between
these two modes of operation for the RPM
speed controller
NOTE: If the engine stalls out at the initial brake
pedal input then the vehicle was not in, or has
dropped out of ‘learn mode’ & you will have to
restart the procedure.
FordTransit 2006.5 (April 2006–)
Date of Publication: 12/2006
4 Electrical
161