fuel cap GMC SAVANA PASSENGER 2008 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: GMC, Model Year: 2008, Model line: SAVANA PASSENGER, Model: GMC SAVANA PASSENGER 2008Pages: 402, PDF Size: 2.34 MB
Page 268 of 402

Cooling System
If your vehicle has a diesel engine, see “Van Models”
under “Cooling System” in the DURAMAX®Diesel
Supplement.
When you decide it is safe to lift the hood, here is what
you will see:
A. Radiator Pressure Cap
B. Coolant Recovery Tank
C. Engine Cooling Fan(s)If the coolant inside the coolant recovery tank is boiling,
do not do anything else until it cools down.
When the engine is cold, the coolant level should be at
or above the COLD FILL mark. If it is not, you may have
a leak at the pressure cap or in the radiator hoses, heater
hoses, radiator, water pump, or somewhere else in the
cooling system.
{CAUTION:
Heater, fuel operated heater (FOH), radiator
hoses, and other engine parts, can be very hot.
Do not touch them. If you do, you can be
burned.
CAUTION: (Continued)
5-28
Page 274 of 402

Engine Fan Noise
Your vehicle has a clutched engine cooling fan. When
the clutch is engaged, the fan spins faster to provide
more air to cool the engine. In most everyday driving
conditions, the fan is spinning slower and the clutch is
not fully engaged. This improves fuel economy and
reduces fan noise. Under heavy vehicle loading, trailer
towing, and/or high outside temperatures, the fan speed
increases as the clutch more fully engages, so you may
hear an increase in fan noise. This is normal and should
not be mistaken as the transmission slipping or making
extra shifts. It is merely the cooling system functioning
properly. The fan will slow down when additional cooling
is not required and the clutch partially disengages.
You may also hear this fan noise when you start the
engine. It will go away as the fan clutch partially
disengages.
Power Steering Fluid
The power steering fluid
reservoir is located in the
engine compartment on the
driver’s side of the vehicle.
SeeEngine Compartment
Overview on page 5-14for
reservoir location.
When to Check Power Steering Fluid
It is not necessary to regularly check power steering fluid
unless you suspect there is a leak in the system or you
hear an unusual noise. A fluid loss in this system could
indicate a problem. Have the system inspected and
repaired.
How to Check Power Steering Fluid
To check the power steering fluid, do the following:
1. Turn the key off and let the engine compartment
cool down.
2. Wipe the cap and the top of the reservoir clean.
3. Unscrew the cap and wipe the dipstick with a
clean rag.
5-34
Page 297 of 402

(E) Rim Diameter:Diameter of the wheel in
inches.
(F) Service Description
:The service description
indicates the load range and speed rating of a
tire. The load index can range from 1 to 279.
Speed ratings range from A to Z.
Tire Terminology and De�nitions
Air Pressure:The amount of air inside the tire
pressing outward on each square inch of the tire.
Air pressure is expressed in pounds per square
inch (psi) or kilopascal (kPa).
Accessory Weight
:This means the combined
weight of optional accessories. Some examples of
optional accessories are, automatic transmission,
power steering, power brakes, power windows,
power seats, and air conditioning.
Aspect Ratio
:The relationship of a tire’s height
to its width.
Belt
:A rubber coated layer of cords that is
located between the plies and the tread. Cords
may be made from steel or other reinforcing
materials.
Bead
:The tire bead contains steel wires wrapped
by steel cords that hold the tire onto the rim.Bias Ply Tire
:A pneumatic tire in which the plies
are laid at alternate angles less than 90 degrees
to the centerline of the tread.
Cold Tire Pressure
:The amount of air pressure
in a tire, measured in pounds per square inch (psi)
or kilopascals (kPa) before a tire has built up heat
from driving. SeeInflation - Tire Pressure on
page 5-60.
Curb Weight
:The weight of a motor vehicle with
standard and optional equipment including the
maximum capacity of fuel, oil, and coolant, but
without passengers and cargo.
DOT Markings
:A code molded into the sidewall
of a tire signifying that the tire is in compliance
with the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT)
motor vehicle safety standards. The DOT code
includes the Tire Identification Number (TIN),
an alphanumeric designator which can also identify
the tire manufacturer, production plant, brand, and
date of production.
GVWR
:Gross Vehicle Weight Rating. See
Loading Your Vehicle on page 4-20.
GAWR FRT
:Gross Axle Weight Rating for the
front axle. SeeLoading Your Vehicle
on page 4-20.
5-57
Page 300 of 402

In�ation - Tire Pressure
Tires need the correct amount of air pressure to
operate effectively.
Notice:Do not let anyone tell you that
under-in�ation or over-in�ation is all right. It is
not. If your tires do not have enough air
(under-in�ation), you can get the following:
Too much �exing
Too much heat
Tire overloading
Premature or irregular wear
Poor handling
Reduced fuel economy
If your tires have too much air (over-in�ation),
you can get the following:
Unusual wear
Poor handling
Rough ride
Needless damage from road hazardsA vehicle specific Tire and Loading Information
label is attached to your vehicle. This label shows
your vehicle’s original equipment tires and the
correct inflation pressures for your tires when they
are cold. The recommended cold tire inflation
pressure, shown on the label, is the minimum
amount of air pressure needed to support your
vehicle’s maximum load carrying capacity.
For additional information regarding how much
weight your vehicle can carry, and an example of
the Tire and Loading Information label, see
Loading Your Vehicle on page 4-20. How you load
your vehicle affects vehicle handling and ride
comfort. Never load your vehicle with more weight
than it was designed to carry.
When to Check
Check your tires once a month or more.
Do not forget to check the pressure of the spare
tire. SeeSpare Tire on page 5-94for additional
information.
5-60
Page 351 of 402
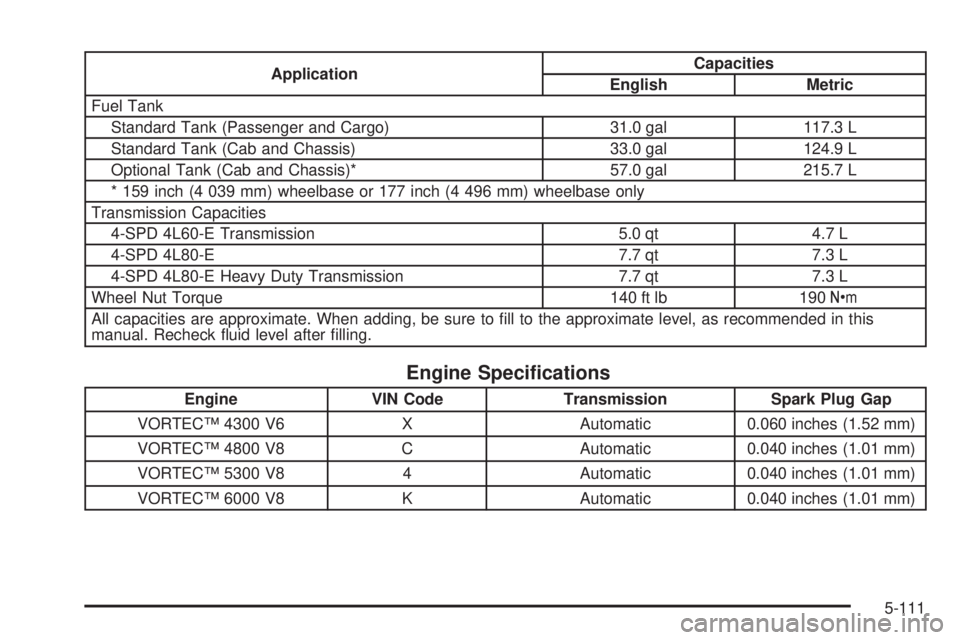
ApplicationCapacities
English Metric
Fuel Tank
Standard Tank (Passenger and Cargo) 31.0 gal 117.3 L
Standard Tank (Cab and Chassis) 33.0 gal 124.9 L
Optional Tank (Cab and Chassis)* 57.0 gal 215.7 L
* 159 inch (4 039 mm) wheelbase or 177 inch (4 496 mm) wheelbase only
Transmission Capacities
4-SPD 4L60-E Transmission 5.0 qt 4.7 L
4-SPD 4L80-E 7.7 qt 7.3 L
4-SPD 4L80-E Heavy Duty Transmission 7.7 qt 7.3 L
Wheel Nut Torque 140 ft lb 190Y
All capacities are approximate. When adding, be sure to fill to the approximate level, as recommended in this
manual. Recheck fluid level after filling.
Engine Speci�cations
Engine VIN Code Transmission Spark Plug Gap
VORTEC™ 4300 V6 X Automatic 0.060 inches (1.52 mm)
VORTEC™ 4800 V8 C Automatic 0.040 inches (1.01 mm)
VORTEC™ 5300 V8 4 Automatic 0.040 inches (1.01 mm)
VORTEC™ 6000 V8 K Automatic 0.040 inches (1.01 mm)
5-111
Page 361 of 402

(f)Lubricate all key lock cylinders, hood hinges, hood
prop rod pivot, hood latch assembly, secondary latch,
pivots, spring anchor, release pawl, rear compartment
hinges, latches, locks, fuel door hinge, and any moving
seat hardware. More frequent lubrication may be required
when exposed to a corrosive environment. Applying
silicone grease on weatherstrips with a clean cloth will
make them last longer, seal better, and not stick or
squeak.
(g)Vehicles with Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR)
above 10,000 lbs (4 536 kg) only: Inspect shields for
damage or looseness. Adjust or replace as required.
This is a Noise Emission Control Service. Applicable to
vehicles sold in the United States and recommended
for vehicles sold in Canada.
(h)Change automatic transmission fluid and filter if the
vehicle is mainly driven under one or more of these
conditions:
-In heavy city traffic where the outside temperature
regularly reaches 90°F (32°C) or higher.
-In hilly or mountainous terrain.
-When doing frequent trailer towing.
-Uses such as found in taxi, police, or delivery
service.(i)Drain, flush, and refill cooling system. This service can
be complex; you should have your dealer/retailer perform
this service. See Engine Coolant on page 5-23 for what to
use. Inspect hoses. Clean radiator, condenser, pressure
cap, and filler neck. Pressure test the cooling system and
pressure cap.
(j)A fluid loss in any vehicle system could indicate a
problem. Have the system inspected and repaired and
the fluid level checked. Add fluid if needed.
(k)Inspect system. Check all fuel and vapor lines and
hoses for proper hook-up, routing, and condition. Check
that the purge valve works properly, if equipped.
Replace as needed.
(l)If you drive regularly under dusty conditions, inspect
the filter at each engine oil change.
(m)Check system for interference or binding and for
damaged or missing parts. Replace parts as needed.
Replace any components that have high effort or
excessive wear. Do not lubricate accelerator or cruise
control cables.
(n)Visually inspect belt for fraying, excessive cracks, or
obvious damage. Replace belt if necessary.
6-9
Page 362 of 402

Owner Checks and Services
These owner checks and services should be performed
at the intervals specified to help ensure the safety,
dependability, and emission control performance of your
vehicle. Your dealer/retailer can assist you with these
checks and services.
Be sure any necessary repairs are completed at once.
Whenever any fluids or lubricants are added to your
vehicle, make sure they are the proper ones, as shown
inRecommended Fluids and Lubricants on page 6-14.
At the First 100, 1,000 and
6,000 Miles (160, 1 600 and
10 000 km)
For vehicles with dual wheels, check dual wheel nut
torque. For proper torque, seeCapacities and
Specifications on page 5-110.
At Each Fuel Fill
It is important to perform these underhood checks at
each fuel fill.
Engine Oil Level Check
Notice:It is important to check the engine oil
regularly and keep it at the proper level. Failure to
keep the engine oil at the proper level can cause
damage to the engine not covered by your warranty.
Check the engine oil level and add the proper oil if
necessary. SeeEngine Oil (Gasoline Engine) on
page 5-15.
Engine Coolant Level Check
Check the engine coolant level and add DEX-COOL®
coolant mixture if necessary. SeeEngine Coolant
on page 5-23.
Windshield Washer Fluid Level Check
Check the windshield washer fluid level in the windshield
washer fluid reservoir and add the proper fluid if
necessary.
6-10
Page 392 of 402

Automatic Transmission
Fluid..........................................................5-20
Operation...................................................2-22
B
Battery..........................................................5-39
Electric Power Management..........................3-17
Run-Down Protection...................................3-17
Brake
Emergencies................................................ 4-5
Brakes..........................................................5-36
System Warning Light..................................3-33
Braking........................................................... 4-3
Braking in Emergencies..................................... 4-5
Break-In, New Vehicle.....................................2-18
Bulb Replacement...........................................5-48
Center High-Mounted Stoplamp (CHMSL)........5-50
Front Turn Signal, Sidemarker and
Parking Lamps.........................................5-50
Halogen Bulbs............................................5-48
Headlamps.................................................5-48
Replacement Bulbs......................................5-52
Taillamps....................................................5-51
Buying New Tires...........................................5-70
C
Calibration.....................................................3-47
California Fuel.................................................. 5-6
California Perchlorate Materials Requirements....... 5-4
California Proposition 65 Warning....................... 5-3
Canadian Owners................................................ ii
Capacities and Specifications..........................5-110
Carbon Monoxide...........................2-30, 4-16, 4-28
Care of
Safety Belts................................................5-97
Cargo Door Relocking....................................... 2-7
CD, MP3 .......................................................3-77
Center High-Mounted Stoplamp (CHMSL)...........5-50
Chains, Tire...................................................5-76
Charging System Light....................................3-32
Check
Engine Light...............................................3-36
Checking Things Under the Hood......................5-12
Chemical Paint Spotting.................................5-101
Child Restraints
Child Restraint Systems...............................1-35
Infants and Young Children...........................1-32
Lower Anchors and Tethers for
Children..................................................1-39
Older Children.............................................1-29
2