child restraint GMC SIERRA DENALI 2003 Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: GMC, Model Year: 2003, Model line: SIERRA DENALI, Model: GMC SIERRA DENALI 2003Pages: 428, PDF Size: 20.35 MB
Page 2 of 428
The 2003 GMC Sierra Denali Owner Manual a
Seats and Restraint Systems ........................... 1-1
Front Seats ............................................... 1-2
Rear Seats
............................................... 1-7
Safety Belts
.............................................. 1-8
Child Restraints
....................................... 1-30
Air Bag Systems
...................................... 1-57
Restraint System Check
............................ 1-73
Features and Controls
..................................... 2-1
Keys
........................................................ 2-2
Doors and Locks
....................................... 2-6
Windows
................................................. 2-1 0
Theft-Deterrent Systems ............................ 2-1 3
Starting and Operating Your Vehicle ........... 2-15
Mirrors
.................................................... 2-28
Onstar@ System
...................................... 2-33
HomeLink@ Transmitter
............................. 2-35
Storage Areas
......................................... 2-39
Instrument Panel
............................................. 3-1
Vehicle
Personalization
............................. 2-42
Instrument Panel Overview
.......................... 3-2
Climate Controls
...................................... 3-1 8
Warning Lights, Gages and Indicators
......... 3-24
Driver Information Center (DIC)
.................. 3-43
Audio System(s)
....................................... 3-61 Driving Your Vehicle
....................................... 4-1
Your
Driving, the Road, and Your Vehicle ..... 4-2
Towing
................................................... 4-45
Service and Appearance Care
.......................... 5-1
Service
..................................................... 5-3
Fuel
......................................................... 5-5
Checking Things Under the Hood
............................................. 5-10
All-Wheel Drive
........................................ 5-49
Rear Axle
............................................... 5-50
Front Axle
............................................... 5-51
Bulb Replacement
.................................... 5-52
Windshield Wiper Blade Replacement
......... 5-60
Tires
...................................................... 5-61
Appearance Care
..................................... 5-86
Vehicle Identification
................................. 5-94
Electrical System
...................................... 5-95
Capacities and Specifications
................... 5-1 04
Normal Maintenance Replacement Parts
.... 5-1 05
Maintenance Schedule
..................................... 6-1
Maintenance Schedule
................................ 6-2
Customer Assistance Information
.................... 7-1
Customer Assistance Information
.................. 7-2
Reporting Safety Defects
............................ 7-9
Index
................................................................. 1
Page 6 of 428
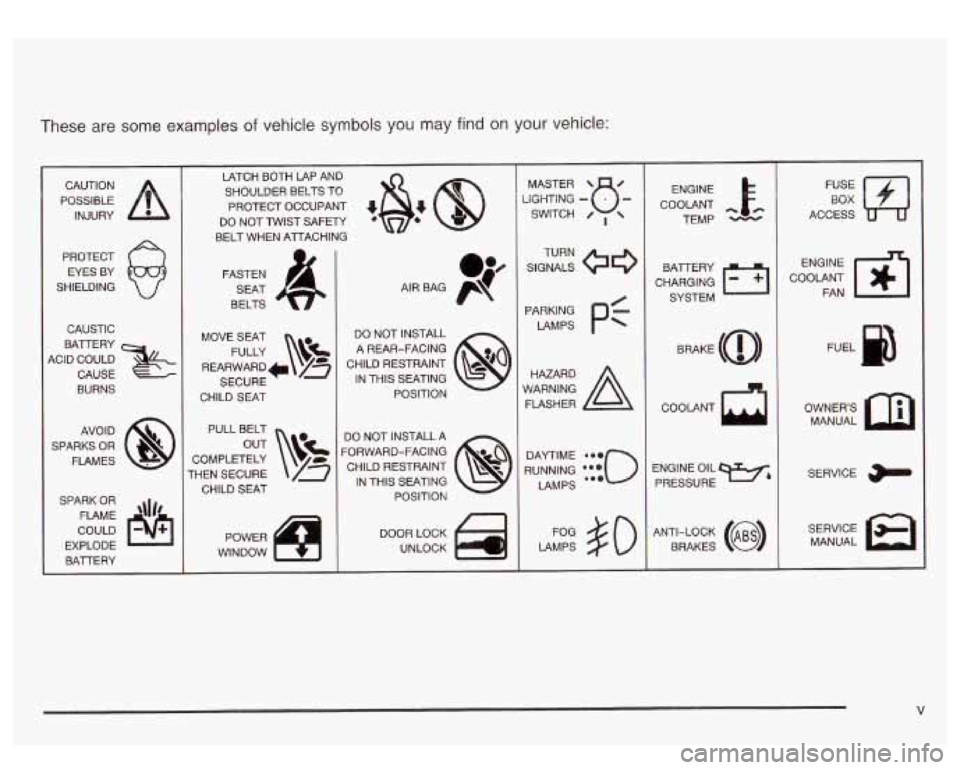
These are some examples of vehicle symbols you may find on your vehicle:
POSSIBLE /r
CAUTION
INJURY
PROTECT EYES BY
SHIELDING
CAUSTIC
ACID COULD BATTERY
CAUSE
BURNS
AVOID
SPARKS
OR
FLAMES
SPARK
OR
COULD FLAME
'\Ir8
EXPLODE
BAlTERY LATCH BOTH LAP AND
SHOULDER BELTS TO
PROTECT OCCUPANT
48: @
DO NOT TWIST SAFm
BELT WHEN AlTACHING
FASTEN SEAT
BELTS
MOVE SEAT FULLY
\v!
REARWARD* /g
SECURE
CHILD SEAT
PULL BELT
COMPLETELY
THEN SECURE CHILD
SEAT
DO NOT INSTALL
A REAR-FACING
CHILD RESTRAINT
@o
POSITION 8
IN THIS SEATING
DO NOT INSTALL
A
CHILD RESTRAINT p?
FORWARD-FACING IN THIS SEATING POSITION
8
DOOR LOCK
UNLOCK SGHTING
- MASTER SWITCH B- / ,
SIGNALS @e
TURN
PARKING
PC
LAMPS
RUNNING
*:{io
DAYTIME LAMPS
LAMPS
#O
ENGINE
COOLANT
cc.
TEMP
CHARGING BAlTERY
SYSTEM
COOLANT
ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
W&
ANTI-LOCK (@)
BRAKES
FE E]
ACCESS
COOLANT
m-1
ENGINE FAN
OWNERS MANUAL
SERVICE
MANUAL
V
Page 8 of 428
Section Seats and Restraint Systems
Front Seats ..................................................... .l -2
Power Seats ............................. .............. 1-2
Power Lumbar ............................................... 1-3
Heated Seats
................................................. 1-3
Reclining Seatbacks
........................................ 1-4
Head Restraints
............................................. 1-6
Rear Seats
....................................................... 1 -7
Rear Seat Operation
....................................... 1-7
Safety Belts
..................................................... 1-8
Questions and Answers About Safety Belts
...... 1-1 2
How to Wear Safety Belts Properly
................. 1-13
Driver Position
.............................................. 1.1 3
Safety Belt Use During Pregnancy
.................. 1-21
Right Front Passenger Position
....................... 1-22
Safety Belts: They
Are for Everyone
................. 1-8
Center Passenger Position
............. ..... 1-22
Rear Seat Passengers
...................... ..... 1-24
Rear Safety Belt Comfort Guides for Children and Small Adults
.......................... 1-27
Safety Belt Extender
......................... ..... 1-29
Child Restraints
............................. ..... 1-30
Older Children
.............................................. 1-30
Infants and Young Children ............................ 1-32
Child Restraint Systems
................................ -1-36
Where to Put the Restraint
............................. 1-38
Top Strap
................................................... .l -40
Top Strap Anchor Location ............................. 1.41
Children (LATCH System)
....................... 1-43
for the LATCH System
............................... 1-46
Outside Seat Position
................................ 1-46
Rear Seat Position
.................................... 1-48
Front Seat Position
.................................... 1-50
Air Bag Systems ....................... .............. 1-57
Where Are the Air Bags?
............................ 1-59
When Should an Air Bag Inflate? .................... 1-61
What Makes an Air Bag Inflate?
..................... 1-61
Lower Anchorages and Top
Tethers for
Securing a Child Restraint Designed
Securing a Child Restraint in a Rear
Securing a Child Restraint in a Center
Securing a Child Restraint
in the Right
How Does an Air Bag Restrain?
..................... 1-62
What Will You See After an Air Bag Inflates?
... 1-62
Air Bag
Off Switch ........................................ 1-64
Passenger Sensing System
............................ 1-68
Servicing Your Air Bag-Equipped Vehicle
......... 1-72
Adding Equipment to Your Air Bag-Equipped
Vehicle
.................................................... 1-72
Restraint System Check
.................................. 1-73
Checking Your Restraint Systems ................... 1-73
Replacing Restraint System Parts
After a Crash
.............................. ...... .l -73
1-1
Page 20 of 428

Q:
A:
If I’m a good driver, and I never drive far from
home, why should
I wear safety belts?
You may be an excellent driver, but
if you’re in an
accident
- even one that isn’t your fault - you and
your passengers can be hurt. Being a good
driver doesn’t protect you from things beyond your
control, such as bad drivers.
Most accidents occur within
25 miles (40 km) of
home. And the greatest number of serious injuries
and deaths occur at speeds of less than
40 mph
(65 km/h).
Safety belts are for everyone.
How to Wear Safety Belts Properly
This part is only for people of adult size.
Be aware that there are special things to know about
safety belts and children. And there are different
rules for smaller children and babies. If a child will be
riding in your vehicle, see
Older Children on page 1-30
or lnfants and Young Children on page 1-32. Follow
those rules for everyone’s protection.
First, you’ll want to know which restraint systems your
vehicle has.
Driver Position
This part describes the driver’s restraint system.
Lap-Shoulder Belt
The driver has a lap-shoulder belt. Here’s how to wear it
properly.
1. Close and lock the door.
2. Adjust the seat so you can sit up straight. To see
how, see “Seats’’ in the Index.
We’ll start with the driver position.
1-13
Page 29 of 428
The best way to protect the fetus is to protect the
mother. When a safety belt is worn properly, it’s more
likely that the fetus won’t be hurt in a crash. For
pregnant women, as for anyone, the key to making
safety belts effective is wearing them properly.
Right Front Passenger Position
To learn how to wear the right front passenger’s safety
belt properly, see
Driver Position on page 1-13.
The right front passenger’s safety belt works the same
way as the driver’s safety belt-except for one thing.
If you ever pull the shoulder portion of the belt out all the
way, you will engage the child restraint locking feature
which may turn
off the passenger’s frontal air bag. If this
happens unintentionally, just let the belt go back all
the way and start again.
Center Passenger Position
1-22
Page 37 of 428

Accident statistics show that children are safer if they
are restrained in the rear seat.
In a crash, children who are not buckled up can strike
other people who are buckled up, or can be thrown
out of the vehicle. Older children need to use safety
belts properly.
Child Restraints
Older Children
Q:
A:
Older children who have outgrown booster seats should
wear the vehicle’s safety belts. What
is the proper
way to wear safety belts?
If possible, an older child should wear a
lap-shoulder belt and get the additional restraint a
shoulder belt can provide. The shoulder belt
should not cross the face or neck. The lap belt
should
fit snugly below the hips, just touching the
top of the thighs.
It should never be worn over
the abdomen, which could cause severe or even
fatal internal injuries in
a crash.
If you have the choice, a child should sit in a seat that
has a lap-shoulder belt to get the additional restraint
a shoulder belt can provide.
1-30
Page 38 of 428

-
!ver do this.
Here two children are wearing the same belt.
The belt can’t properly spread the impact
forces.
In a crash, the two children can be
crushed together and seriously injured.
A belt
must be used by only one person at a time.
Q: What if a child is wearing a lap-shoulder belt,
but the child is
so small that the shoulder belt
is very close to the child’s face or neck?
be sure that the shoulder belt stili is on the child’s
shoulder,
so that in a crash the child’s upper
body would have the restraint the belts provide.
If the child is sitting in a rear seat outside position,
see
Rear Safety Belt Comfort Guides for Children
and Small Adults
on page 1-27.
If the child is so small that the shoulder belt is still
very close to the child’s face or neck, you might
want to place the child in a seat that has a lap belt,
if your vehicle has one.
A: Move the child toward the center of the vehicle, but
1-31
Page 39 of 428

1
Never do this.
Here a child is sitting in a seat that has a
lap-shoulder belt, but the shoulder part is
behind the child.
If the child wears the belt in
CAUTION: (Continued) way,
in a cra-..
2 c .... d mig--- slide under
the belt. The belt’s force would then be applied
right on the child’s abdomen. That could cause
serious
or fatal injuries.
Wherever the child sits, the lap portion
of the belt
should be worn low and snug on the hips, just touching
the child’s thighs. This applies belt force to the child’s
pelvic bones in a crash.
Infants and Young Children
Everyone in a vehicle needs protection! This includes
infants and all other children. Neither the distance
traveled nor the age and size of the traveler changes
the need, for everyone,
to use safety restraints. In fact,
the law in every state in the United States and in
every Canadian province says children up
to some age
must be restrained while
in a vehicle.
Every time infants
and young children ride in vehicles,
theyshould have the protection provided by appropriate
restraints. Young children should not use the vehicle’s
adult safety belts alone, unless there is no other choice.
Instead, they need to use a child restraint.
1-32
Page 41 of 428

Children who are up against, or v - lose to,
any air bag when
it inflates can be seriously
injured or killed. Air bags plus lap-shoulder
belts offer outstanding protection for adults and
older children, but not for young children and infants. Neither the vehicle’s safety belt system
nor
its air bag system is designed for them.
Young children and infants need the protection
that a child restraint system can provide.
Q: What are the different types of add-on child
restraints?
A: Add-on child restraints, which are purchased by the
vehicle’s owner, are available in four basic types.
Selection of a particular restraint should take into
consideration not only the child’s weight, height and
age but also whether or not the restraint will be
compatible with the motor vehicle in which it will
be used.
For most basic types of child restraints, there are
many different models available. When purchasing a
child restraint, be sure it is designed
to be used
in a motor vehicle. If it is, the restraint will have a
label saying that it meets federal motor vehicle
safety standards.
The restraint manufacturer’s instructions that come
with the restraint state the weight and height
limitations for a particular child restraint. In addition,
there are many kinds of restraints available for
children with special needs.
1-34
Page 42 of 428
Newborn infants need complete support,
including support for the head and neck. This
is
necessary because a newborn infant’s neck is
weak and its head weighs so much compared
with the rest of
its body. In a crash, an infant in a
rear-facing seat settles into the restraint, so the
crash forces can be distributed across the
strongest part of an infant’s body, the back and
shoulders. Infants always should be secured in
appropriate infant restraints. The body structure of a young child
is quite
unlike that of an adult or older child, for whom
the safety belts are designed.
A young child’s
hip bones are
still so small that the vehicle’s
regular safety belt may not remain
low on the
hip bones, as it should. Instead, it may settle
up around the child’s abdomen. In a crash, the
belt would apply force on a body area that’s
unprotected by any bony structure. This alone
could cause serious or fatal injuries. Young
children always should be secured in
appropriate child restraints.
1-35