Pulse HONDA CIVIC 1996 6.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HONDA, Model Year: 1996, Model line: CIVIC, Model: HONDA CIVIC 1996 6.GPages: 2189, PDF Size: 69.39 MB
Page 1701 of 2189
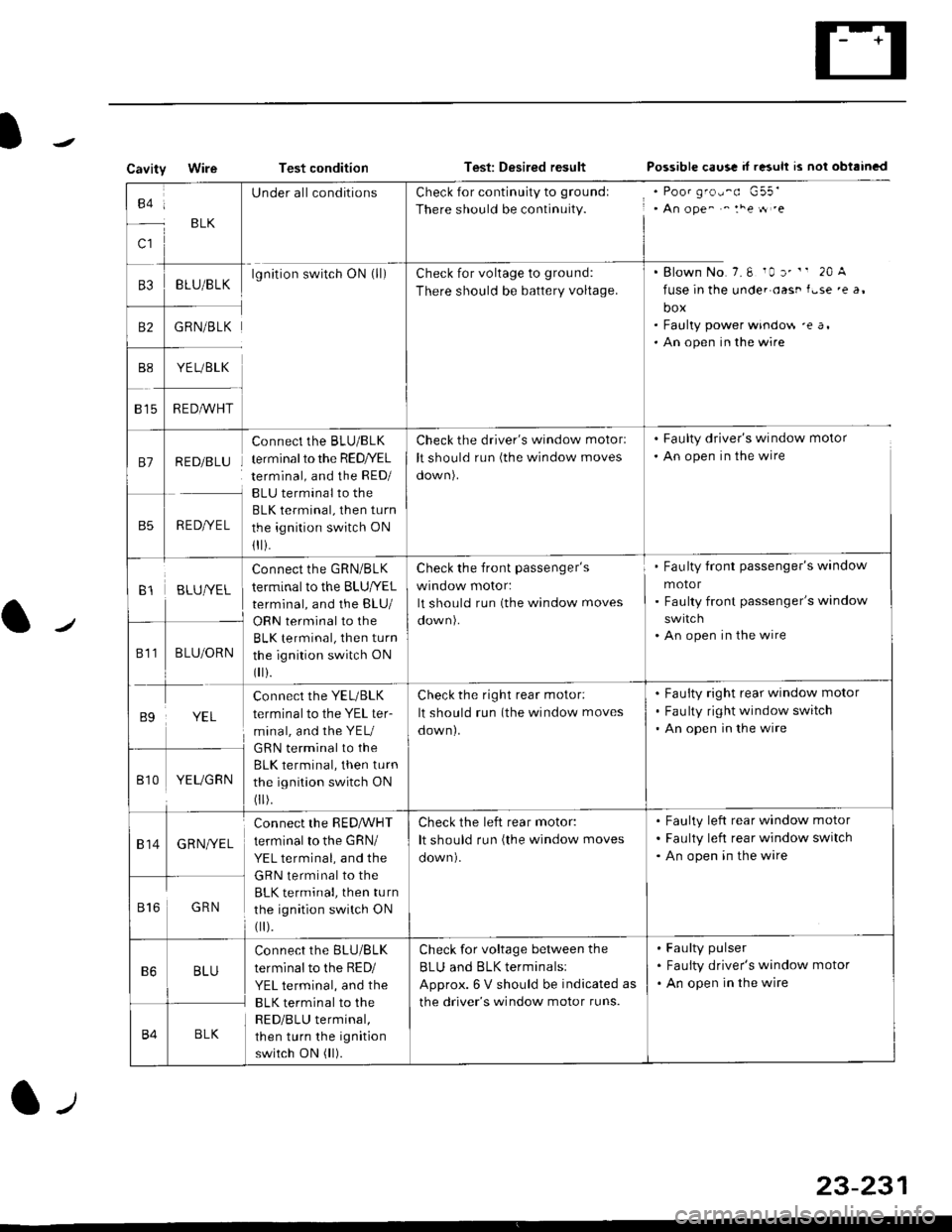
CavityWireTest conditionTest: Desired resultPossible caus! d r"suh rs nol obtrincd
to:
c1
BLK
UnderallconditionsCheck for continuity to groundl
There should be continuity., An ope^ ^ :he tt .e
. Blown No.7.6 10 r' " 20 A
fuse in the unde. oast f.se 'e a,
box. Faulty power windo$ 'e a,. An open in the wire
B3BLU/BLKlgnition switch ON (ll)Check for voltage to grou nd:
There should be battery voltage.
B2GRN/BLK
YE L/BLK
R EDA/VHT815
81RED/BLU
RED/YEL
Connect the BLU/BLK
terminal to the RED/YEL
terminal, and the RED/
BLU terminal to the
BLK terminal, then turn
the ignition switch ON
1I i.
Check the driver's window motorl
It should run (the window moves
oown).
. Faulty driver's window motor
. An open in the wire
B1BLUIVEL
Connect the GRN/BLK
terminal to the BLU|YEL
terminal, and the BLU/
Check the front passenger's
wrnoow motor:
It should run (the window moves
Fau lty front passenger's window
motor
Faulty front passenger's window
An open in the wire
811BLU/ORNBLK terminal, then turn
the ignition switch ON
0 r).
B9YEL
connect the YEL/BLK
terminal to the YEL ter-
minal, and the YEU
GRN terminal to the
BLK terminal, then turn
the ignition switch ON
0 r).
Check the right rear motor:
It should run (the window moves
down).
Fauity right rear window motor
Fau lty right window switch
An open in the wire
Bt0YEUGRN
814GRNI/EL
connect the RED,ryVHT
terminal to the GRN/
YEL terminal, and the
GRN terminal to the
BLK terminal, then turn
the ignition switch ON
0 r).
Check the left rear motor:
It should run (the window moves
Faulty left rear window motor
Faulty left rear window switch
An open in the wire
816GRN
B6BLU
Connect the BLU/BLK
terminal to the RED/
YEL terminal, and the
BLK terminal to the
RED/BLU terminal,
then turn the ignition
switch ON (ll).
Check for voltage between the
BLU and BLK terminalsl
Approx. 6 V should be indicated as
the driver's window motor runs.
Faulty pulser
Faulty driver's window motor
An open in the wire
B4BLK
23-231
Page 1833 of 2189

How To Use This Manual
Troubleshooting Tests (cont'd)
4. Turn on the short finder. This creates a
pulsing magnetic field around the wiring
between the fuse box and the short.
5. Beginning at the fuse box, slowly move
the short finder along the circuit wiring.
The meter will show current Dulses
through sheet metal and body trim. As
long as the meter is between the fuse and
lhe short, the needle will move with each
current pulse. Once you move the meter
past the point of the short, the needle will
stop moving. Check the wiring and
connectors in this area to locate the cause
of the short.
co
Page 1917 of 2189

- How the Gircuit Works
With the ignition switch in ON (ll) or START (lll),
battery voltage is supplied through fuse 15 and
the BLI(WHT and BLK/YEL wire to the vehicle
speed sensor (VSS). The sensor is grounded by
the BLK wire to G1 01 . The speedometer and
other control units in the circuit supply about 5
volts to the BLU/WHT wire. The vehicle soeed
sensor (VSS) intermittently grounds the
BLUMHT wire which generates a pulsed signal
in it. The number of pulses per minute
increases/decreasos with the soeed of the car.
Reter to th€ Service Manual (Section 23, Electrical)
tor specific tosts or troubleshooting procedures.
33-1
Page 1980 of 2189

Gauges (cont'd)
- How the Gircuit Works
When the ignition switch is in ON (ll) or START (lll),
battery voltage is supplied through fuse 25 to the
gauges in the gauge assembly.
Speedometer and Odometer
The odometer and soeedometer drive circuits
receive pulses from the vehicle speed sensor
(VSS). The pulse rate increases as the car
accelerates. The frequency and duration of these
input pulses are measured and displayed by the
speedometer, odometer and tripmeter.
Tachometer
The tachometer drive circuit receives pulses from
the ignition control module (lCM) in the distributor
assembly or the ECM/PCM. The solid-state
lachometer then displays these pulses as engine
speed. For each 200 pulses per minute from the
ignition control modul€ (lCM) or the ECM/PCM, the
tachometer displays 100 RPM.
Engine Coolant Temperature Gauge
The engine coolant temperature gauge has two
intersecting coils wound around a permanent
magnet rotor. Voltage applied to the coils, through
fuse 25, generates a magnetic lield. The magnetic
field, controlled by the coolant temperature sending
unit, causes the rotor to rotate and the gauge
needle to move. As the resistance in the sending
unit varies, current through the gauge coils
changes. The gauge needle moves toward the coil
with the strongest magnetic field.
The 6ngine coolant temperature sending unit's
resistance varies from about 137 ohms at low
engine temperature to between 3H6 ohms at high
temperature (radiator fan running).
Refer to the Service Manual (Section 23, Electrical)
for specific tests or troubleshooting procedures.
81-2
(
Fuel Gauge (All except cX)
The fuel gauge has two intersecting coils wound
around a permanent magnet rotor. Voltage applied
to the coils, through tuse 25, generates a magnetic
field. The magnetic field, controlled by the fuel
gauge sending unit, causes the rotor to rotate and
the gauge needle to move. As the resislance in the
sending unit varies, current through the gauge coils
changes. The gauge needle moves toward the coil
with the strongest magnetic field.
The fuel gauge sending unit's resistance varies
from about 2-5 ohms at full, to about 110 ohms at
empty. When you turn the ignition switch off, the
gauge remains at the last reading until you turn the
ignition switch to ON (ll) or START (lll) again,
Refer to the Service Manual (Section 23, Electrical)
for specific tests or troubleshooting procedures.
Fuel Gauge (GX)
The fuel gauge has two intersecting coils wound
around a permanent magnet rotor. Voltage applied
to the coils, through fuse 25, generates a magnetic
field. The magnetic field, controlled by the PCM,
causes the rotor to rotate and the gauge needle to
move. The PCM calculates the gas quantity in the
fuel tank by using the fuel pressure value detected
by the tuel tank pressure sensor and the fuel
temperature value detected by the fuel tank
temperalure sensor, and outputs the signal to the
gauge assembly. The gauge needle moves toward
the coil with the strongest magnetic field.
When you turn the ignition switch off , the gauge
remains at the last reading until you turn the ignition
switch to ON (ll) or START (lll) again. When the
PCM detects a malfunction with the fuel pressure or
temperature, or detects a gas leak, the PCM
reduces the fuel meter to 0.
Refer to the Service Manual GX Supplement
(Section 11 , Fuel and Emissions) for specific tests
or troubleshooting procedures.
a
a
Page 2018 of 2189

Power Windows (contd)
- How the Circuit Works
CAUTION: You could iniure your arms, hands, or
fingers if you unintentionally switch the driver's
window to "automatic down" while working in
that door with the power on. Disconnect the
window switch conneclot or the battery when
working in the driver's door.
System Description
The operation of the power windows is controlled by
the main switch in the power window master switch.
When the main switch is in OFF, only the driver's door
window can be opened or closed. With the main
switch ON, all windows can be ooened or closed
either by swtches in the master panel, or swttches in
the doors. The driver's window switch also has an
automatic down mode which is tumed on by pushing
the switch down to its second oosition.
The power windows are driven by reversible motors.
Each motor is protect€d by a built-in circuit breaker.
lf the window switch is held on too long (with the
window obstructed, or after the window is fully up or
down), the circuit breaker opens the circuit. The
circuit breaker resets automaticallv as it cools.
Driver's Window
With the ignition switch in ON, voltage is provided to
the coil of the power window relay through fus€ 24.
The contacts of the power window relay close, and
voltage is applied to the driver's switch. When you
push the power window master switch to UP, voltage
is applied to the driver's window motor. (The motor's
ground path is back through the master power
window switch.) The driver's window motor then
drives the window up. When you push the switch to
DOWN, voltage is applied in the opposite direction
and the motor drives the window down.
Automatic Down (Driver's Window)
With the ignition switch in ON or START, voltage is
applied to the coil of the power window relay. The
contacts of the power window relay close and
voltage is applied lo the power window master
switch. When you push the driveas switch to the
AUTO DOWN position, voltage is applied through
the driver's switch to the driver's window motor. The
control unit receives pulses at the pulser input while
the motor is running. When the window is fully
down, the motor stops, and pulses are no longer
generated by the pulser. This is sensed by the
control unit at the pulser input, and voltage is no
longer applied to the driver's window motor.
Passenger Windows
With the ignition switch in ON, voltage is applied to
the coil of the power window relay through fuse 24.
The contacts of the power window relay then close,
applying voltage to the individual window switches
and the power window master switch. With the
master panel main switch ON, the passenger
windows can be ooerated from the individual
window switches or from tho master panel switches.
When you push the front passengsr's window
switch to UP, voltage is applied to the f ront
passenger's window motor. (The motor is grounded
through the contacts in the front passenger's
window switch and the oower window master
switch.) The window moves up as long as you hold
the switch in the UP position. lf you push the switch
to DOWN, voltage is applied in th€ opposite
direction to the front passenger's window motor, and
the window movss down as long as you hold the
switch in the DOWN Dosition. The window switches
in the other doors operate similarly.
When you push the front passenger's switch in the
master panel to UP, voltage is applied through the
front passenger's window switch contacts to the
front passengefs window motor. (The motor is
grounded through the contacts in the front
passenger's window switch and the power window
master switch.) The window moves up as long as
you hold the switch in the UP position. lf you push
the switch to DOWN, voltage is applied in the
opposite direction to lhe front passenger's window
motor, and the window moves down as long as you
hold the switch in the DOWN position. The other
passenger window switches in the master panel
operate similarly.
Refer to the Service Manual (Section 23, Electrical)
for specific tests or troubleshooting procedures.
120-4