Valve HONDA CIVIC 1998 6.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HONDA, Model Year: 1998, Model line: CIVIC, Model: HONDA CIVIC 1998 6.GPages: 2189, PDF Size: 69.39 MB
Page 840 of 2189
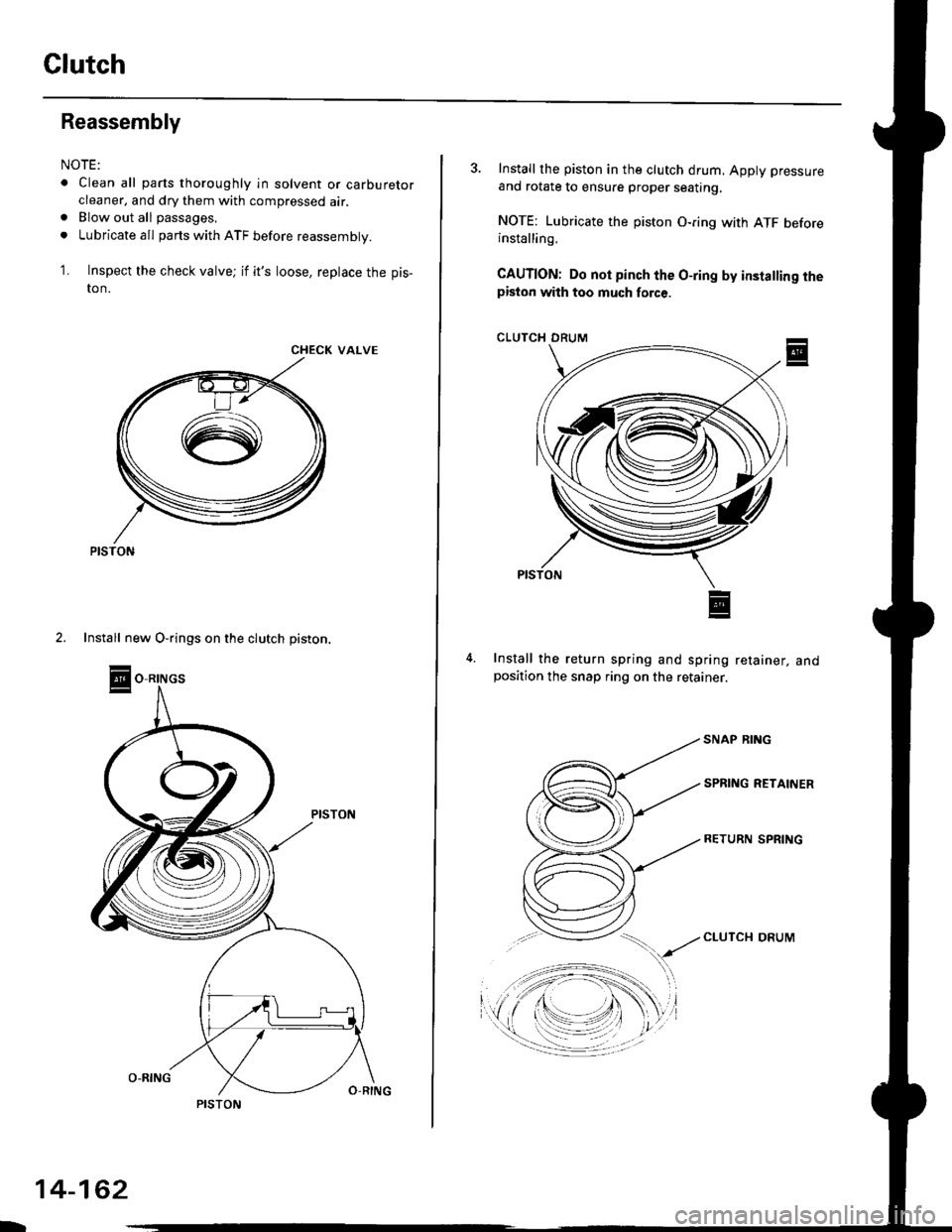
Clutch
Reassembly
NOTE:
. Clean all parts thoroughly in solvent or carburetor
a
cleaner, and dry them with compressed air.
Blow out all passages.
Lubricate all parts with ATF before reassembly.
Inspect the check valve; if it's loose, replace the pis-
to n.
1.
CHECK VALVE
2. Install new O-rings on the clutch piston.
O RINGS
PISTON
-
14-162
3. Install the piston in the clutch drum, Apply pressure
and rotate to ensure proper seating,
NOTE: Lubricate the piston O-ring with ATF beforeinstalling.
CAUTION: Do not pinch the O-ring by insta ing thepiston with too much force.
CLUTCII DRUM
Install the return spring and spring retainer, andposition the snap ring on the retainer.
CLUTCI{ DRUM
Page 854 of 2189
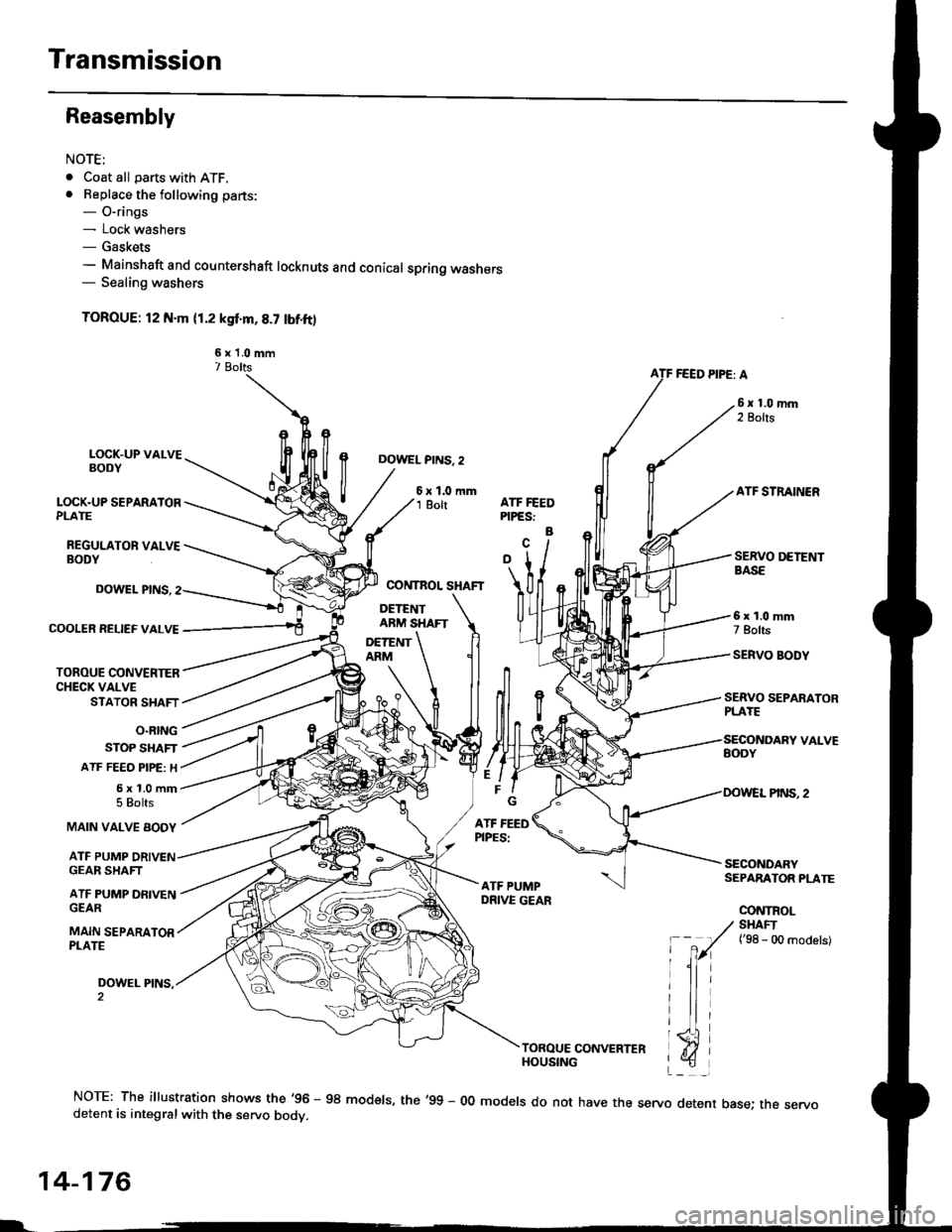
Transmission
Reasembly
NOTE;
. Coat all parts with ATF.. Beplace the following parts:- O-rings- Lock washers- Gaskets- Mainshaft and countershaft locknuts and conical spring washers- Sealing washers
TOROUE: l2 N.m (1.2 ksf'm,8.7 lbf.ft)
6 x 'l.0 mm7 BoltsFEED PIPE: A
LOCK.UP VALVEBODY
LOCK.UP SEPARATORPLATE
REGULATOR VALVEBODY
DOWEL PINS. 2
6xl.0mm1 BoltATF STRAINERATF FEEDPIPES:
a
COOIER RELIEF VALVE
TOROUE CONVENIERCHECK VALVESTATOR SHAFT
O.RING
STOP SHAFT
ATF FEEO PIPE: H
5x1.0mm5 Bolts
DOWEL PINS.
MAIN VALVE BODY
ATF PUMP
SERVO SEPARATORPLAYE
6x1.0mm7 Bolts
SERVO BODY
SECONOARYSEPARATOR PLATE
CONTROL
GEAR SHAFT
ATF PUMP DFIVENGEAR
MAIN SEPARATORPLATE
DOWEL PINS,
/ SHAFI
' -
7r(
t'se - oo ^od"t"t
lli
triTOROUE CONVERTERHOUSING
NOTE: The illustration shows the'96 - 98 modsls, the'99 - 00 models do not have the servo detent base; the servodetent is integralwith the servo bodv.
14-176
L-
Page 855 of 2189
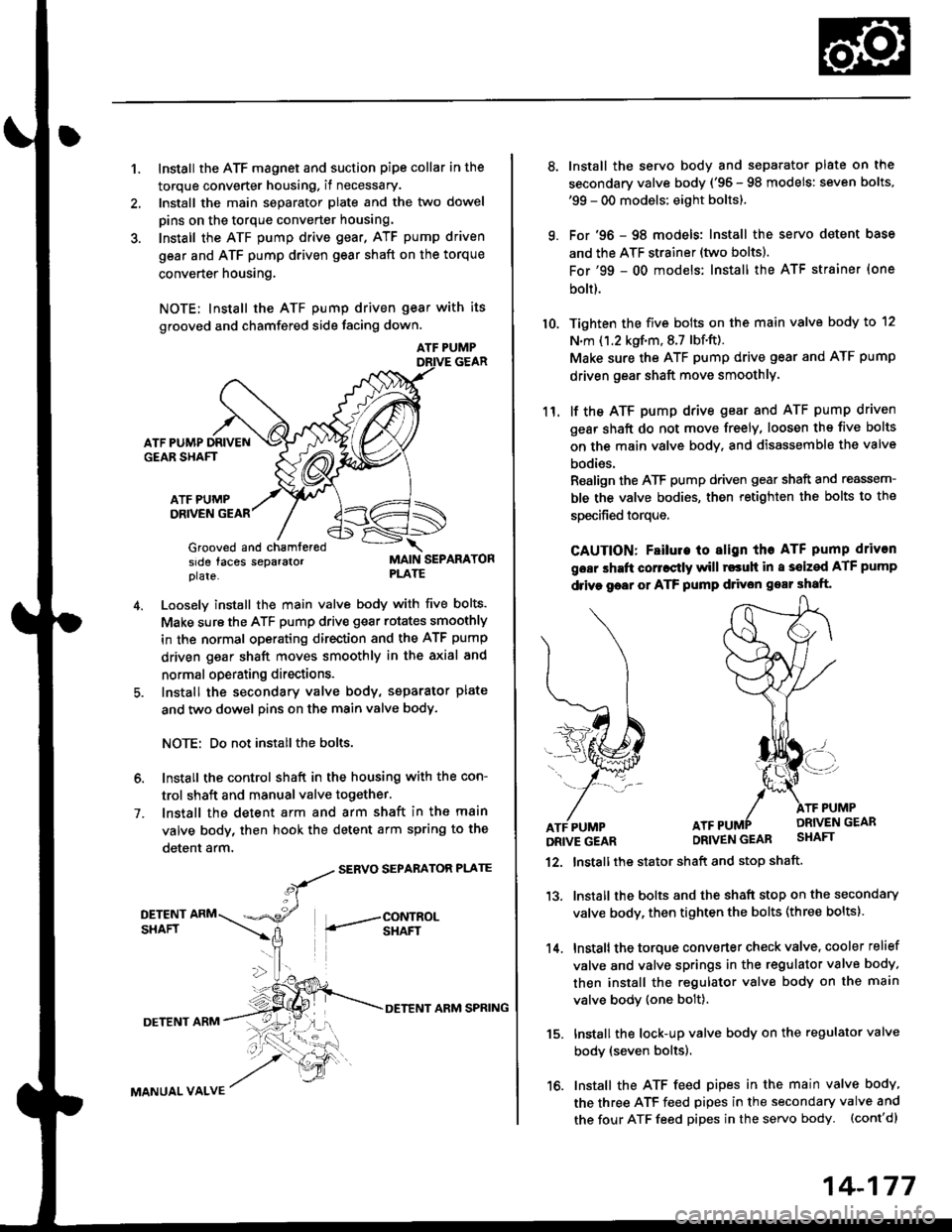
1.Install the ATF magnet and suction pipe collar in the
torque converter housing. if necessary.
lnstall the main seDarator plate and the two dowel
pins on the torque converter housang.
Install the ATF pump drive gear, ATF pump driven
gear and ATF pump driven gear shaft on the torque
converter housing.
NOTE; Install the ATF pump driven gear with its
grooved and chamfered side tacing down.
ATF PUMP
ATF PUMP DRIVENGEAR SHAFT
ATF PUMPDRIVEN GEAR
Grooved and chamferedside taces separalorplate.MAIN SEPARATORPLATE
4.Loosely install the main valve body with five bolts.
Make sure the ATF pump drive gear rotates smoothly
in the normal operating direction and the ATF pump
driven gear shaft moves smoothly in the axial and
normal operating directions.
Install the secondary valve body, separator plate
and two dowel pins on the main valve body.
NOTE: Do not installthe bolts.
6. Install the control shaft in the housing with the con-
trol shaft and manual valve together.
7. lnstall the detent arm and arm shaft in the main
valve body, then hook the detent arm spring to the
detent arm,
SERVO SEPARATOR PLATE
DETENT
MANUAL VALVE
DETENT ARM SPRING
15.
14-177
a
10.
11.
Install the servo body and separator plate on the
secondary valve body ('95 - 98 models: seven bolts.'99 - 00 models: eight boltsl.
For '96 - 98 models: Install the servo detent base
and the ATF strainer (two boltsl.
For'99 - 00 models: Install the ATF strainer (one
bolt).
Tighten the five bolts on the main valve body to 12
N.m ('1.2 kgf.m,8.7 lbf.ft).
Make sure the ATF pump drive gear and ATF pump
driven gear shaft move smoothlY'
lf the ATF pump drive gsar and ATF pump driven
gear shaft do not move freely, loosen ths five bolts
on the main valve body, and disassemble the valve
bodies.
Realign the ATF pump driven gear shaft and reassem-
ble the valve bodies, then retighten the bolts to the
specified torque,
CAUTION: Fsilule to align tho ATF pump driven
goar shaft corr.ctly will rscuh in a s€ized ATF pump
drive goar or ATF pump d ven gear shaft.
Install the stator shaft and stop shaft.
Install the bolts and the shaft stop on the secondary
valve body, then tighten the bolts (three boltsl.
Install the torque converter check valve, cooler relief
valve and valve springs in the regulator valve body.
then install the regulator valve body on the main
valve bodv (one bolt).
Install the lock-up valve body on the regulator valve
bodv (seven bolts).
Install the ATF feed pipes in the main valve bodY,
the three ATF feed pipes in the secondary valve and
the four ATF feed pipes in the servo body. (cont'dl
12.
't 3.
14.
PUMP
Page 865 of 2189
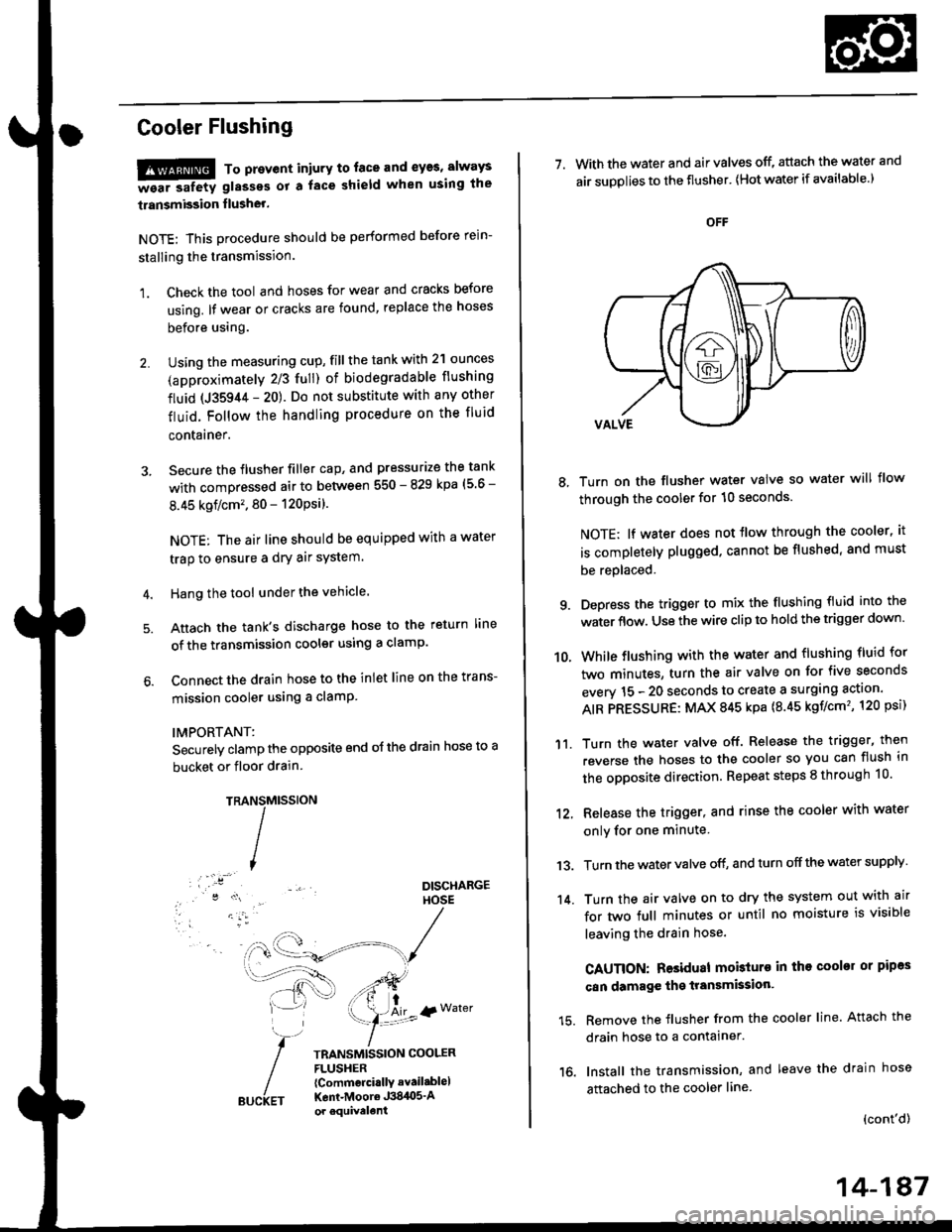
Cooler Flushing
!!!@ To prevent iniury to. face and eyas, always
-ea. safetv glasses ot a face shield when using the
transmission flusher.
NOTE: This procedure should be performed before rein-
stalling the transmission.
1. Check the tool and hoses for wear and cracks before
using. lf wear or cracks are found, replace the hoses
before using.
Using the measuring cup, fill the tank with 2'l ounces
(approximately 2/3 full) of biodegradable flushing
fluid (J35944 - 20). Do not substitute with any other
fluid. Follow the handling procedure on the fluid
contarner.
Secure the flusher filler cap, and pressurize the tank
with compressed air to between 550 - 829 kpa (5 6 -
8.45 kgflcm'�. 80 - 120Psi).
NOTE: The air line should be equipped with a water
trap to ensure a dry air system.
Hang the tool under the vehicle.
Attach the tank's discharge hose to the return line
of the transmission cooler using a clamp.
Connect the drain hose to the inlet line on the trans-
mission cooler using a clamP
IMPORTANT:
Securely clamp the opposite end oJ the drain hose to a
bucket or floor drain.
TRAMtssroN
TRANSMISSION COOLERFLUSHER{Commcrci.llY avail.blel
Kent-Moore J384O5'Aor equivelent
NS
I
{r Water
7. With the water and air valves off, attach the water and
air suDolies to the flusher' lHot water if available.)
8, Turn on the flusher water valve so water will flow
through the cooler for 10 seconds.
NOTE; lf water does not tlow through the cooler, it
is completely plugged. cannot be flushed, and must
be replaced.
9. Depress the trigger to mix the flushing fluid into the
water flow. Use the wire clip to hold the trigger down'
While flushing with the water and flushing fluid for
two minutes, turn the air valve on for five seconds
everv 15 - 20 seconds to create a surging action'
AIR PRESSURE: MAX 845 kpa {8.45 kgf/cm'�, 120 psi)
Turn the water valve off. Release the trigger, then
reverse the hoses to the cooler so you can flush in
the opposite direction. Repeat steps 8 through 10'
12, Release the trigger, and rinse the cooler with water
onlv for one minute
13. Turn the water valve off, and turn off the water supply
14. Turn the air valve on to dry the system out with air
for two full minutes or until no moisture is visible
leaving the drain hose.
CAUTION: Residual mobturo in tho cooler or pipas
can damage the transmksion'
15. Remove the flusher from the cooler line. Attach the
drain hose to a contalner.
16. Install the transmission, and leave the drain hose
attached to the cooler line
{cont'd)
10.
'11.
14-187
Page 871 of 2189

Continuously Variable Transmission (CVTI
Special Tools ................ 14-194
Description .................... 14-195
Clutches/Reverse Brake/Planetary
Gear/Pulleys .......... 14-198
power Flow ..............,..... 14-200
Electronic Control SYstem(,96 - 98 Modets) ......14-203
Electronic Control System
('99 - oo Models) " 14-205
Hydraulic Control '....... 14-208
Hydraulic Flow .'..-.....'... '14-212
Park Mechanism .....-...'.' 14-222
Eleqtrical Systom
Component Locations'96 - 98 Models """"""' 14-224,99 - 00 Modets ............. 14-225
TCM Circuit Diagram ('96 - 98 Models) ............. 14-226
TCM Terminal Voltage/Measuring Condiiions ('96 - 98 Models) '.... 14-228
PcM Circuit Oiaqram{A/T Control System: '99 - 00 Models} ...--.... 14-230
PCM Terminal Voltage/Measuring Conditions('99 - 00 Models)
A/4 Control System .'.'...14-232
Troubleshooting Procedures ... . .... .....',........."' '14-234
Symptom-to-ComPonent Chart
Electrical System - '96 - 98 Models ......'..... '14-234
Electrical System -'99 - 00 Models ..'....-..-. '11-210
Electrical Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Flowcharts('96 - 98 Models) """'11-242
Troubleshooting Flowchart
('99 - 0O Modets) ...... 14-265
Linear Solenoids/lnhibitor Solenoid
Test ......................... . ...... 14-29f
Drive Pulley/Driven Pulley/Secondary Gear
Shaft Speed Sensors
Replacement .........'...... .14-292
Start Clutch Control
Start Clutch Calibration Procedure ....... ....,. 14-293
Hydraulic SYstem
Symptom-to-ComPonent Chart
Hydraulic System '.'.......14-294
Road Test ............................ 14-296
Stall Speed
Test......................... ...... 14-294
Fluid Level
Checking/Changing ....... 14-299
Pressure Testing ................. 14-300
Lower Valve BodY AssemblY
Replacement ..........,... 14-302
ATF Filter
Removal/lnstallation ..... 14-303
Transmission
Transmission
Removal ........... . 14-304
lllustrated Index
Transmission/Lower Valve BodY
Assembly ................. 14-308
Transmission Housing/Flywheel Housing ... 14-310
End Cover/f ntermediate Housing ..........'.'.... 14-312
Transmission Housing/Lower Valve Body Assembly
Removal ..........'.... .. " 14-314
Transmission Housing/Flywhesl Housing
Removal ................. ........ 1+316
End Cover/lntermediate Housing
14-318Removal .........,...............
Manual Valve Body
Disassembly/lnspection/Reassemblv .'.'.'..... 1 4-320
Forward Clutch
lltustrated Index ........................................ 14-321
Disassemblv .................. 14-322
Reassemblv , ,, . ',','......14-324
Secondary Gear Shaft
25 x 35 mm Thrust Shim Selection ..'.'....-... 14-324
Differential
lllustrated lndex ...,.....................,.,...-.-.-...'... 14-329
Backlash Inspection .-....14-329
Bearing Replacement ......'........'....'... ....'... 14-330
Differential Carrier Replacement ........'........ 14-330
Oil Seal Removal ........... 14-331
Oil Seal Installation/Side Clearance ....... . . 14-331
Flywheel Housing Input Shaft Oil Seal
Replacement .....,.... ...'.'.. 14-333
Transmission Housing Bearings
Driven Pulley Shaft Bearing
Replacenient ...................'. . ...................'.. 14-334
Secondary Gear Shaft Bearing
Reolacbment ...................... . .......... . ........ 14-335
Flywheel Housing Beating
Secondary Gear Shaft BearingReo1acement..................,........................... 14-335
Ring Gear Bearing
Replacement......... ........ 14-336
Control Shaft Assembly
Removal/lnstallation ....................'........... 14-336
Transmission
Reassembly .................. 14-338
Flywheel/Drive Plate .. . ...... . ...... ... . ....-.....'.'...14-341
Transmission
lnstalation ..................... 14-348
Cooler Flushing .'......... 14-352
shift cable
Removal/lnstallation....'........." """ 14-354
Adjustment .......'........ 14-355
Shift Lever ........................,. 14'356
Shift Indicator Panel
Adjustment ................ 14-357
ATF Cooler/Hoses
lnsta llation ......,,...... .... 14-357
Page 873 of 2189

Description
The Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT) is an electronically controlled automatic transmission with drive and driv
en Oullevs, and a steel belt. The CVT provides non stage speeds forward and one reverse. The entire unit is positioned in
line with the engine.
Transmission
Around the outside of the flywheel is a ring gear which meshes with the starter pinion when the engine is being staned.
The transmission has four parallel shafts: the input shaft, the drive pulley shaft. the driven pulley shaft, and the secondary
gear shaft. The input shaft is in line with the engine crankshaft. The drive pulley shaft and the driven pulley shaft consist of
movable and fixed face pulleys. Both pulleys are linked by the steel belt.
The input shaft includes the sun gear. The drive pulley shaft includes the forward clutch which mounts the carrier assem-
bly on the forward clutch drum. The carrier assembly includes the pinion gears which mesh with the sun gear and the ring
gear. The ring gear has a hub-mounted reverse brake disc.
The driven pulley shaft includes the start clutch and the secondary drive gear which is integral with the park gear' The sec-
ondary gear shaft is positioned between the secondary drive gear and the final driven gear. The secondary gear shaft
includes the secondary driven gear which serves to change the rotation direction. because the drive pulley shaft and the
driven oullev shaft rotate the same direction. When certain combinations of planetary gears in the transmission are
engaged by the clutches and the reverse brake, power is transmitted from the drive pulley shaft to the driven pulley shaft
to provide E, E, E, and El.
Electronic Control'96 - 98 Models:
The electronic control system consists of the Transmission Control Module (TCM), sensors, three linear solenoids, and a
inhibitor solenoid. Shifting is electronically controlled under all conditions'
The TCM is located below the dashboard, behind the kick panel on the driver's side.'99 - 00 Models:
The electronic control svstem consists of a Powertrain Control Module (PCM), sensors, three linear solenoids and an
inhibitor solenoid. Shifting is electronically controlled under all conditions. A Grade Logic Control System to control shift-
ing in E position while the vehicle is ascending or descending a slope.
The PCM is located below the dashboard, under the kick panel on the passenger's side.
Hydraulic Control
The lower valve body assembly includes the main valve body, the Pressure Low (PL) reguiator valve body, the shift valve
body, the start clutch control valve body, and the secondary valve body. They are positioned on the lower part of the
transmission housing.
The main valve body contains the Pressure High (PH) control valve, the lubrication valve, and the pitot regulator valve.
The secondary valve body contains the PH regulator valve, the clutch reducing valve, the start clutch valve accumulator,
and the shift inhibitor valve. The PL regulator valve body contains the PL regulator valve and the PH-PL control valve
which is ioined to the PH,PL control linear solenoid. The inhibitor solenoid valve is bolted on the PL regulator valve body.
The shift valve body contains the shift valve and the shift control valve. which is joined to the shift control linear solenoid.
The start clutch control valve body contains the start clutch control valve, which is joined to the start clutch control linear
solenoid. The linear solenoids and the inhibitor solenoid are controlled by the TCM or PCM. The manual valve body which
contains the manual valve and the reverse inhibitor valve, is bolted on the intermediate housing.
The ATF pump assembly is located on the transmission housing, and is linked with the input shaft by the sprockets and
the sprocket chain. The pulleys and the clutch receive fluid from their respective feed pipes, and the reverse brake receives
fluid from internal hydraulic circuit.
Shift Control Mechanism
Input from various sensors located throughout the vehicle determines which linear solenoid the TCM or PCM will activate.
Activating the shift control linear solenoid changes the shift control valve pressure, causing the shift valve to move. This
pressurizes the drive pulley pressure to the drive pulley and the driven pulley pressure to the driven pulley and changes
their effective pulley ratio. Activating the start clutch control linear solenoid moves the start clutch control valve. The start
clutch control valve uncovers the port, providing pressure to the start clutch to engage it(cont'd)
14-195
,!
Page 886 of 2189
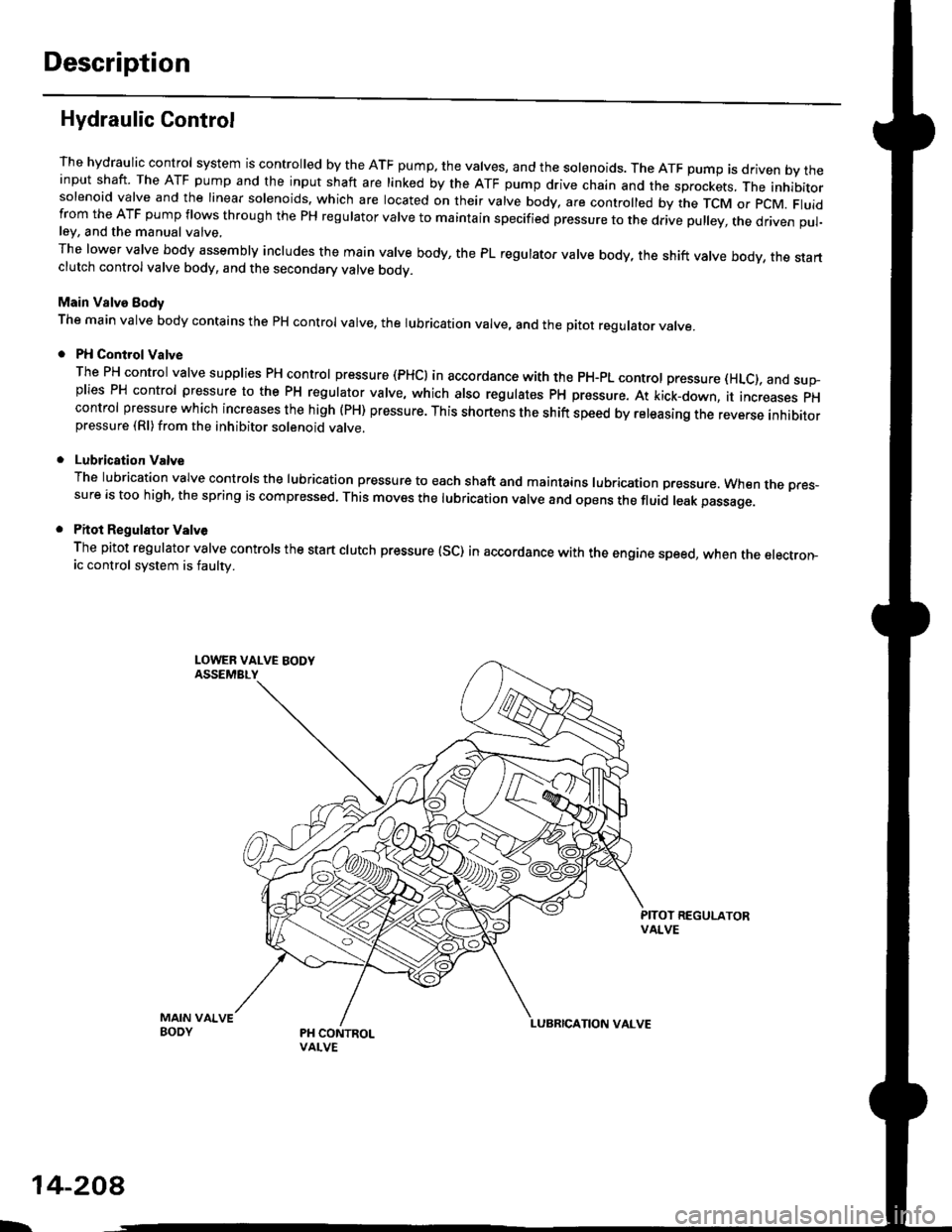
Description
Hydraulic Control
The hydraulic control system is controlled by the ATF pump. the valves, and the solenoids. The ATF pump is driven by theinput shaft. The ATF pump and the input shaft are linked by the ATF pump drive chain and the sprockets, The inhibitorsolenoid valve and the linear solenoids. which are located on their valve body, are controlled by the TCM or pcM. Fluidfrom the ATF pump flows through the PH regulator valve to maintain specified pressure to the drive pulley, the driven pul-ley, and the manual valve,
The lower valve body assembly includes the main valve body, the PL regulator valve body, the shift valve body, the startclutch control valve body, and the secondary valve bodv.
Main Valve Eody
The main valve body contains the pH control valve, the rubrication valve, and the pitot regulator valve.
PH Control Valve
The PH control valve supplies PH control pressure (PHCI in accordance with the pH-pL control pressure (HLc), and sup-plies PH control pressure to the PH regulator valve, which also regulatss PH pressure. At kick-down, it increases pHcontrol pressure which increases the high (PH) pressure. This shortens the shift speed by releasing the reverse inhibitorpressure (Rl)from the inhibitor solenoid valve.
Lubrication Valve
The lubrication valve controls the lubrication pressure to each shaft and maintains lubrication pressure. When rne pres-sure is too high, the spring is compressed. This moves the lubrication valve and opens the fluid leak passage.
Pitot Regulalor Valv6
The pitot regulator valve controls the start clutch pressure (SC) in accordance with the engine speed, when the electron-ic control system is faulw.
MAIN VAIVEBODY
L.
14-208
Page 887 of 2189
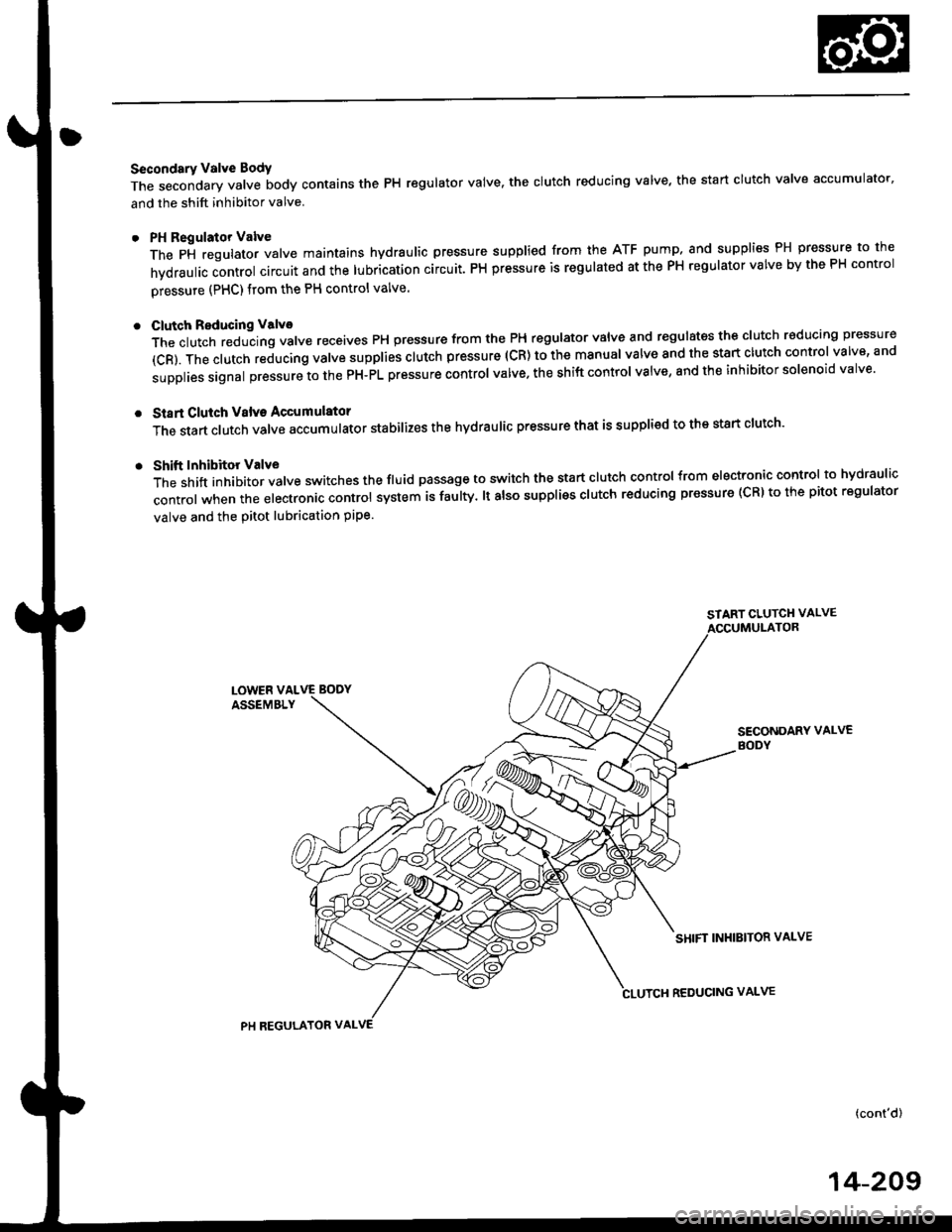
Secondary Valve Body
The secondary valve body contains the PH regulator valve. the clutch reducing valve' the start clutch valve accumulator'
and the shift inhibitor valve
PH Regulator Valve
The pi regulator valve maintains hydraulic pressure supplied from the ATF pump. and supplies PH pressure to the
hvdraulic control circuit and the lubrication circuit. PH pressure is regulated at the PH regulator valve by the PH control
pressure (PHC) from the PH control valve.
Cluteh Reducing Valvo
The clutch reducing valve receives PH pressure from the PH regulator valve and regulates the clutch reducing pressure
(cR). The clutch reducing valve supplies clutch pressure (cR) to the manual valve and the start clutch control valve' and
supplies signal pressure to the PH-PL pressure control valve. the shift control valve, and the inhibitor solenoid valve'
Start Clutch Valv€ Accumulator
The start clutch vatve accumutator stabilizes the hydraulic pressure that is supplied to the start clutch'
Shift Inhibitor Valve
The shift inhibitor valve switches the fluid passage to switch the start clutch control from electronic control to hydraulic
control when the electronic control system is faulty. lt also suppliss clutch reducing pressure (cR) to the pitot regulator
valve and the pitot lubrication pipe.
START CLUTCH VALVE
SECONDARY VALVEBODY
SHIFT INHIBITOE VALVE
(cont'd)
PH REGULATOR VAL
REDUCING VALVE
14-209
Page 888 of 2189

Description
Hydraulic Control {cont'dl
PL Regulator Valve Body
The PL regulator valve body contains the PL regulator valve and the PH-PL control valve. which is joined wirh the pH-pL
control linear solenoid. The inhibitor solenoid is bolted on the pL regulator valve body.
. PL Regulator Valve
The PL regulator valve supplies low p.essure (pL) to the pulley to eliminate steel belt slippage.The PL pressure is controlled by the pH-pL control pressure (HLC).
. PH-PL Control Valve
The PH-PL control valve controls the PL regulator valve according to engine torque. The PH-PL control valve suooliesPH-PL control pressure (HLC) to the PH control valve to regulate PH pressure higher than pL pressure. The pH-pL con-trol valve is controlled by the PH-PL control linear solenoid. which is controlled by the TcM or pcM,
. Inhibitor Solenoid
The inhibitor solenoid controls the reverse inhibitor valve by turning on and off. Also, the inhibitor solenoad controls pH
control pressure (PHC) by applying reverse inhibitor pressure (Rl) to the PH control valve. The inhibitor solenoid is con-trolled by the TCM or Pclvl.
Start Clutch Control Valv€ Body
The start clutch control valve body contains the start clutch control valve. Both are joined to the stan clutch control linearsolenoid.
. Start Clutch Control Valve
The start clutch control valve controls start clutch engagement according to the throttle opening. The start clutch con,trol valve is controlled by the stan clutch control linear solenoid, which is controlled bv the TCM o. pCM.
START CLUTCH CONTROLvAt-vE
LOWER VALVE BODYASSEMBI-Y
PH.PL CONTROLLINEAR SOLENOID
I.
14-210
Page 889 of 2189
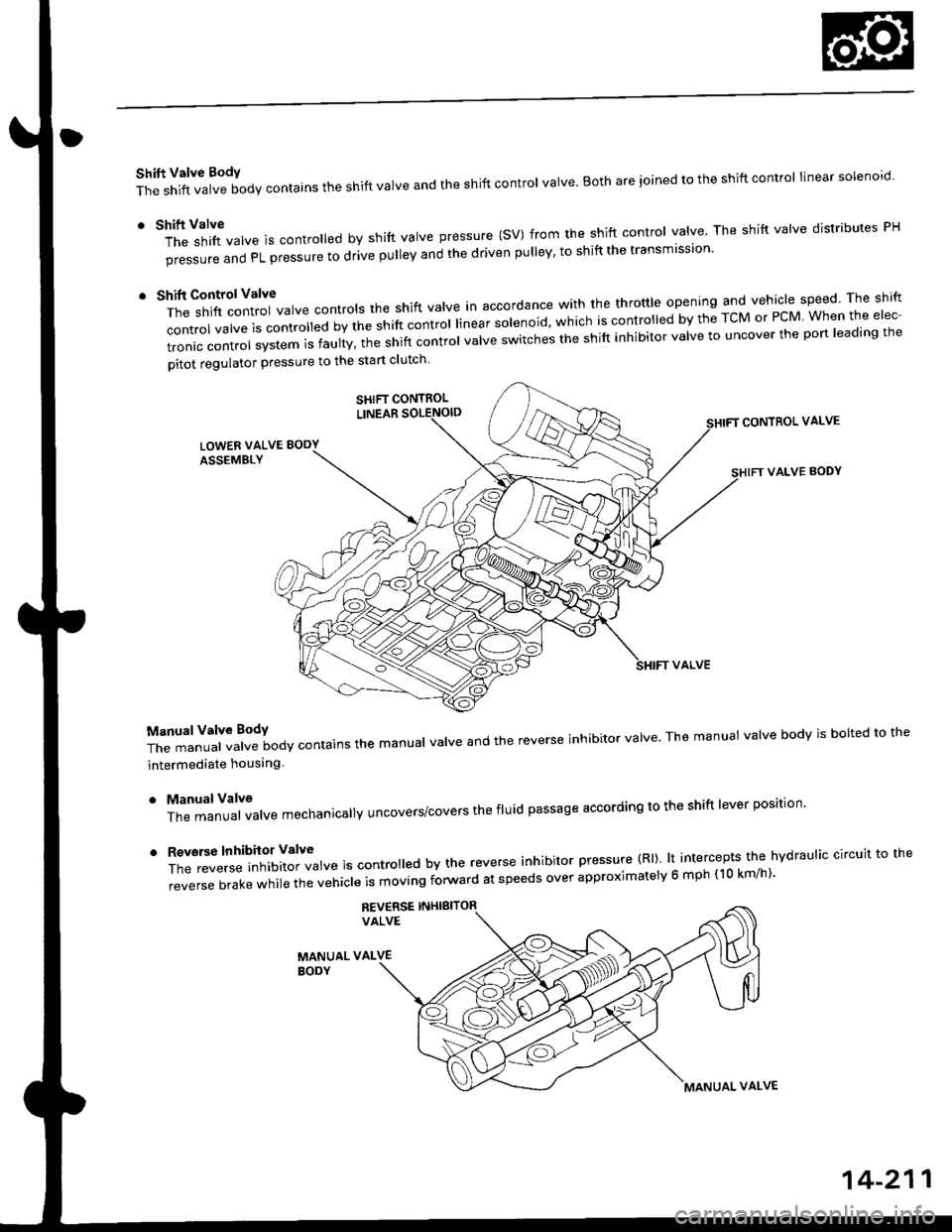
Shift Valve BodY
The shift valve body contains the shift valve and the shift control valve. Both are ioined to the shift control linear solenoro.
r tl'ft1il1rf"","" is controred by shift varve pressure (sV) from the shift contror varve. The shift varve distributes pH
pi""aur" "nO PL pressure to drive pulley and the driven pulley' to shift the transmission'
t t*"rilf:::lr';ivarve contrors the shift varve in accordance with the throttre opening and vehicle speed rhe shift
control valve is convorr"o uv ti" "iirt "ontrol linear solenoid, which is controlled by the TcM or PcM When the elec-
tronic control system is faulty, t;; snift controt uutue "witches the shift inhibitor valve to uncover the port leading the
pitot regulator pressure to the start clutch
CONTROL VALVE
VALVE BODY
T;J:"i"""1ff"t""ilody contains the manuar varve and the reverse inhibitor varve. The manuat varve bodv is borted to the
intermediate houslng
. ManualValve
The manual valve mechanicallY uncovers/covers the fluid passage according to the shift lever position'
'
ff:e;;;.'::'?Xftl::T",* is contro ed by the reverse inhibitor pressure (Rl). lt intercepts the hvdraulic circuit to the
reverse brake while the vehicle is moving forward at speeds over approximatelv 6 mph (10 km/h)'
REV€RSE INHIBITORVALVE
MANUAL VALVEBODY
SHIFT CONTROL
MANUAL VALVE
14-211