Brake HONDA CIVIC 1999 6.G Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HONDA, Model Year: 1999, Model line: CIVIC, Model: HONDA CIVIC 1999 6.GPages: 2189, PDF Size: 69.39 MB
Page 874 of 2189
Description
(cont'd)
Gear Sel€stion
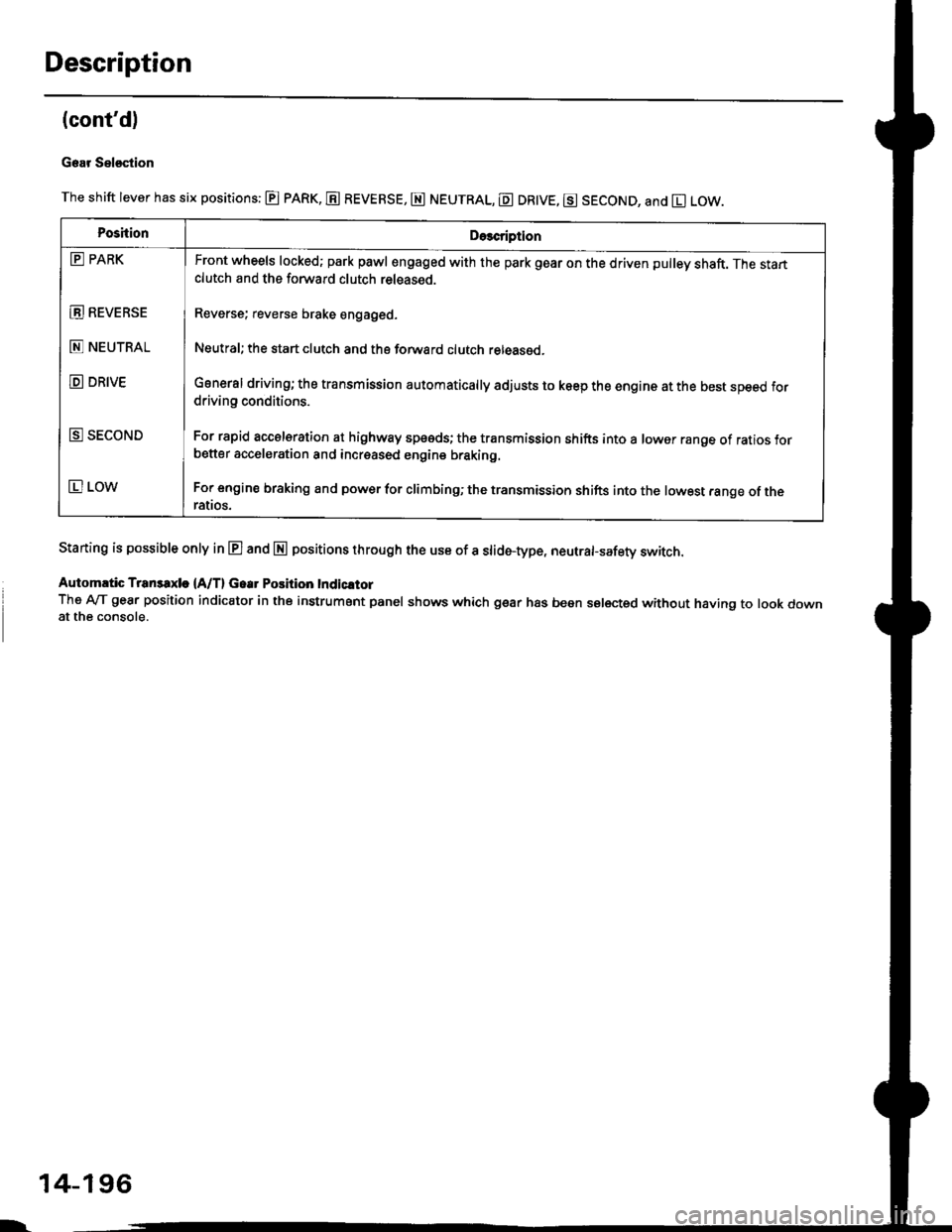
The shift lever has six positions: @ pARK, E REVERSE, E NEUTRAL, E DR|VE, g SECOND, and El LOW.
Staning is possible only in E and E positions through the use of a slid6-type, neutrafsafety switch.
Automrtic Transaxle {A/T} Gear Position Indicltor
The A-lT gear position indicator in the instrument panel shows which gear has been selected without having to look downat the console.
PoshionDe3cription
E PARK
E REVEBSE
E NEUTRAL
D DRIVE
E SECOND
E LOW
Front wheels locked; park pawl engaged with the park gear on the driven pulley shaft. The startclutch and the forward clutch released.
Reverse; reverse brake engaged.
Neutral; the start clutch and the forward clutch released.
General driving; the transmission automatically adjusts to keep the engine at the best speed fordriving conditions.
For rapid accelsration at highway speeds; the transmission shifts into a lower range of ratios forbetter acceleration and increased engine braking.
For engine braking and power for climbinO; the transmission shifts into the lowest range of theralros.
l-
14-196
Page 876 of 2189

Description
Clutches/Reverse Brake/Planetary Gear/Pulleys
Clulches/Reverse Brake
The CVT uses the hydraulically-actuated clutches and brake to engage or disengage the transmission gears. When
hydraulic pressure is introduced into the clutch drum and the reverse brake piston cavity, the clutch piston and the reverse
brake piston move. This presses the friction djscs and the steel plates together, locking them so they don't slip. Power is
then transmitted through the engaged clutch pack to its hub-mounted gear. and through engaged ring gear to pinion
gears.
Likewise, when the hydraulic pressure is bled from the clutch pack and the reverse brake piston cavity, the piston releases
the friction discs and the steel plates, and they are free to slide past each. This allows the gear to spin independently on its
shaft, transmitting no power.
Start Clutch
The start clutch, which is located at the end of the driven pulley shaft, engages/disengages the secondary drive gear.
The start clutch is supplied hydraulic pressure by its ATF feed pipes within the driven pulley shaft.
Forward Clutch
The forward clutch, which is located at the end of the drive pulley shaft, engages/disengages the sun gear.
The forward clutch is supplied hydraulic pressure by its ATF feed pipe within the drive pulley shaft.
Reverse Brake
The reverse brake, which is located inside the inte.mediate housing around the ring gear, locks the ring gear in E posi-
tion. The reverse brake discs are mounted to the ring gear and the reverse brake plates are mounted to the intermediate
housing. The reverse brake is supplied hydraulic pressure by a circuit connected to the internal hydraulic circuit.
Planetary Gear
The planetary gear consists of a sun gear, a carrier assembly, and a ring gear. The sun gear is connected to the input shaft
with splines. The pinion gears are mounted to the carrier which is mounted to the fo.ward clutch drum. The sun gear
inputs the engine power via the input shaft to the planetary gear, and the carrier outputs the engine power. The ring gear
is only used for switching the rotation direction of the pullev shafts,
In E. E, and E positions (forward range), the pinion gears don't rotate and revolve with the sun gear, so the carrier
rotates. In E] positjon {reverse range), the reverse brake locks the ring gear and the sun gear drives the pinion gears to
rotate. The pinion gears rotate and revolve in the opposite direction from the rotation direction of the sun gear, and the
carrier rotates with pinion gear revolution.
Pulleys
Each pulley consists of a movable face and a fixed face, and the effective pulley .atio changes with engine speed. The
drive pulley and the driven pulley are linked by the steel belt.
To achieve a low pulley ratio, high hydraulic pressure works on the movable face of the driven pulley and reduces the
effective diameter of the drive pulley. and a lower hydraulic pressure works on the movable face of the drive pulley to
eliminate the steel belt slippage. To achieve a high pulley ratio, high hydraulic pressure works on the movable face of the
drive pulley and reduces the eifective diameter of the driven pulley, and a lower hydraulic pressure works on the movable
face of the driven pulley to eliminate the steel belt slippage.
b
14-198
Page 877 of 2189
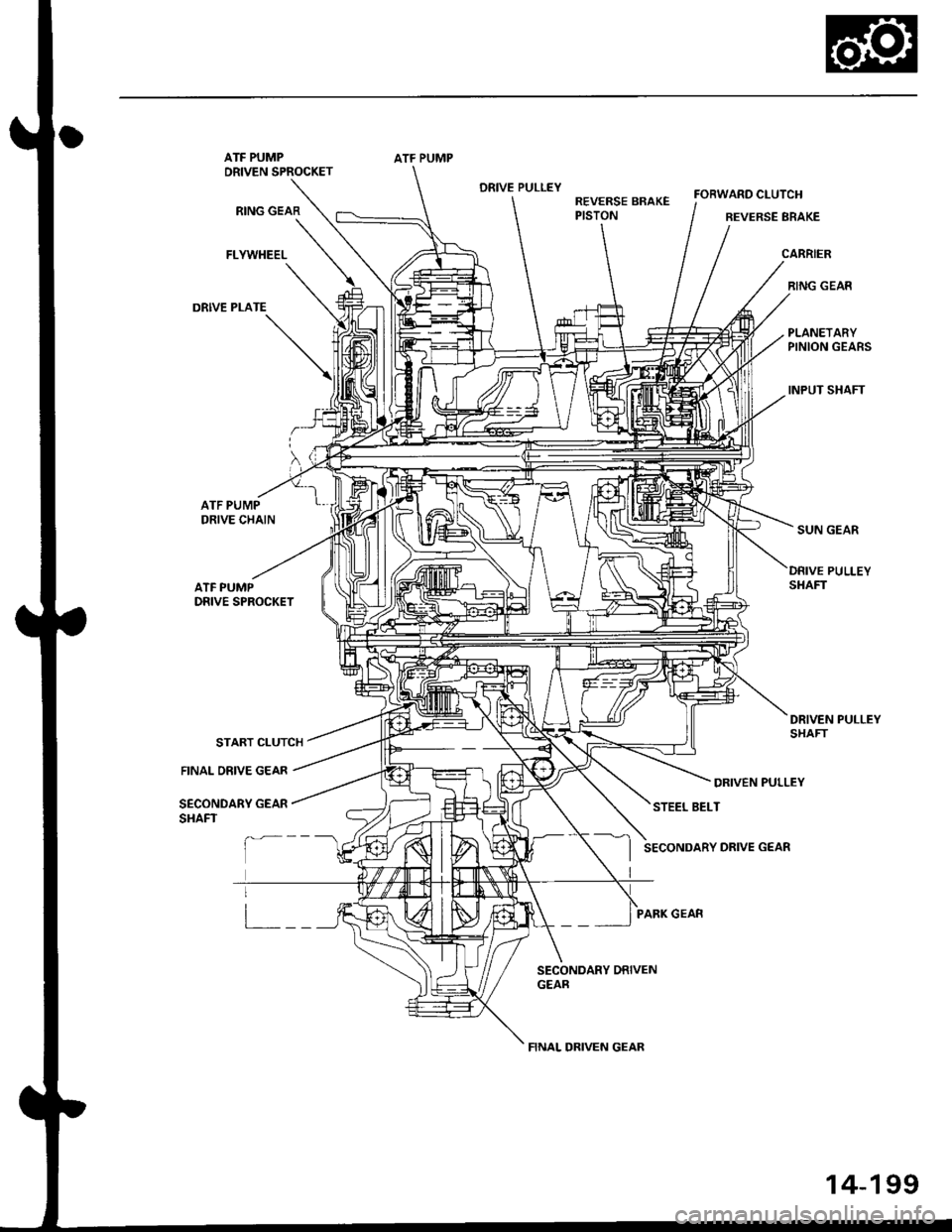
ATF PUMPDRIVEN SPROCKET
RING GEAR
FLYWHEEL
DRIVE PLATE
ATF PUMP
DRIVE PULLEYREVERSE BRAKEPISTON
FORWARD CLUTCH
BEVERSE BRAKE
CARRIER
RING GEAR
PLANETARYPINION GEARS
INPUT SHAFT
ATF PUMPDRIVE CHAIN
ATF PUMPDRIVE SPROCKET
START CLUTCH
DRIVEN PULLEY
STEEL BELT
SECONDARY DRIVE GEAR
PARK GEAR
DRIVEN PULLEYSHAFT
FINAL DRIVE GEAR
SECONDARY GEARSHAFT
a--
i___
il
14-199
Page 878 of 2189
Description
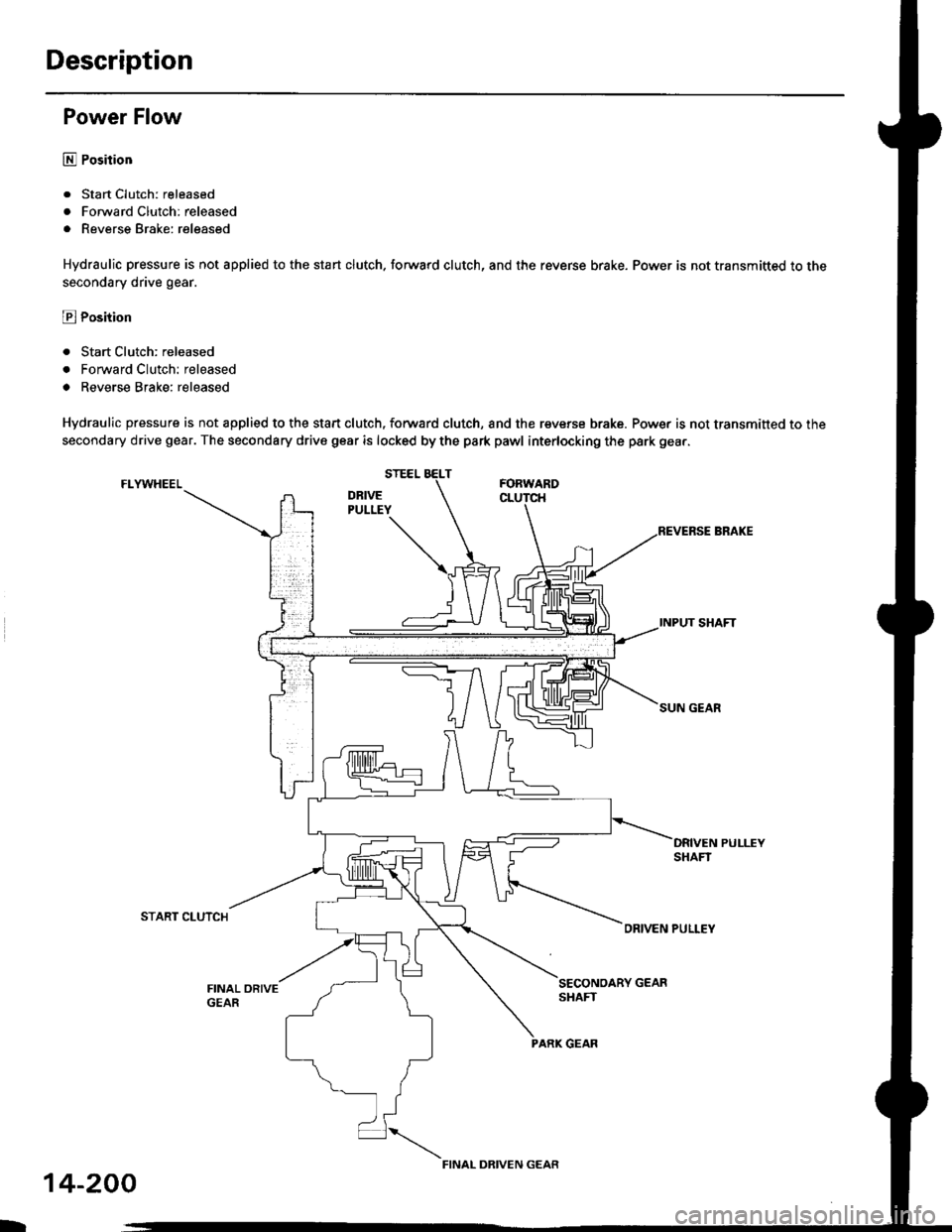
Power Flow
E Position
. Start Clutch: released
. Forward Clutch: released
. Reverse Brake: released
Hydraulic pressure is not applied to the start clutch. forward clutch, and the reverse brake. Power is not transmitted to the
secondary drive gear.
E Position
. Start Clutch: released
. Forward Clutch: released
a Reverse Brake; released
Hydraulic pressure is not applied to the start clutch, forward clutch, and the reverse brake. Power is not transmitted to the
secondary drive gear. The secondary drive gear is locked by the park pawl interlocking the park gea..
FI-YWHEELFORWARD
INPUT SHAFT
SUN GEAR
START CLUTCHORIVEN PULLEY
FINAL ORIVEGEAR
PARK GEAR
FINAL DRIVEN GEAR
D
14-200
Page 879 of 2189
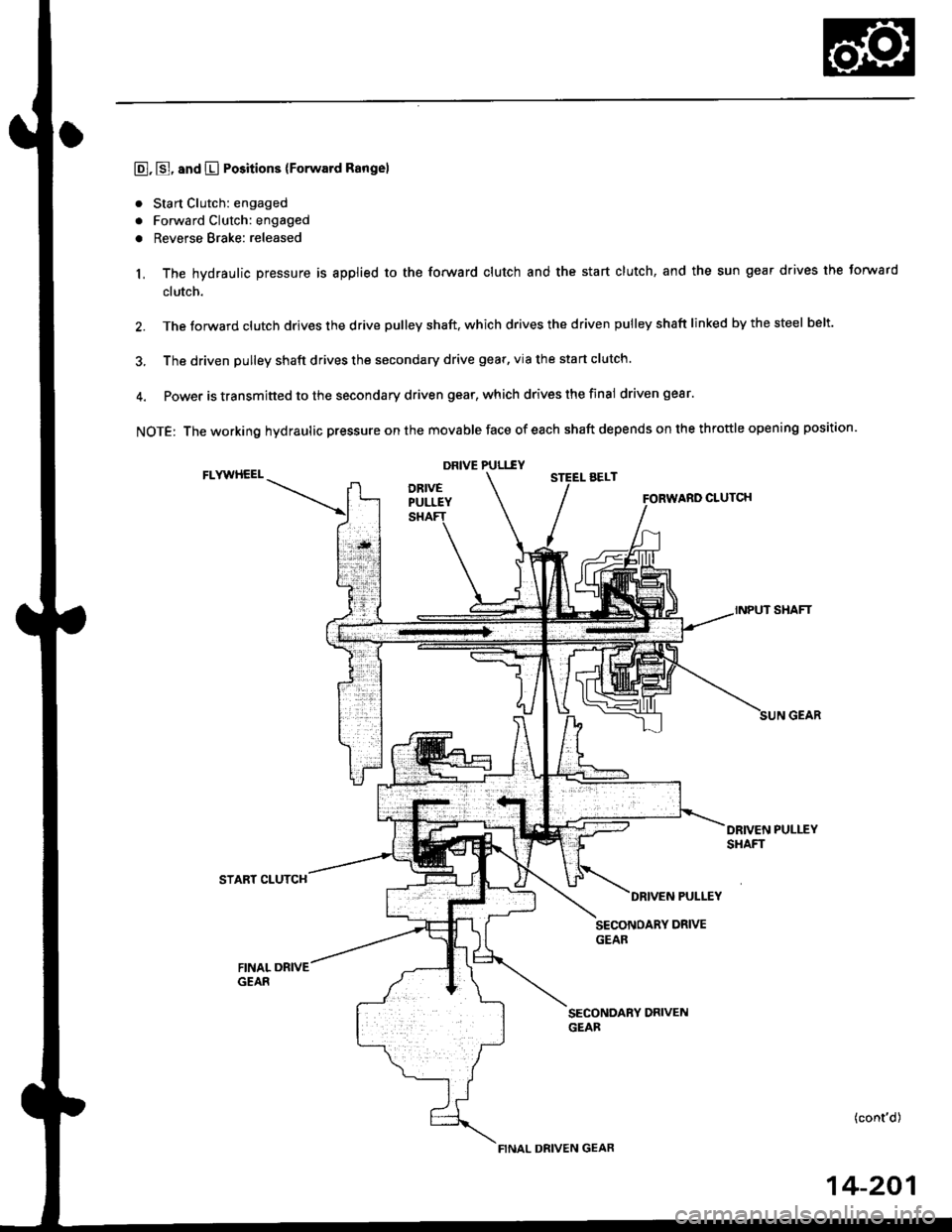
E, E, and E Positions {Forward Rangel
. Sta rt Clutch: engaged
. Forward Clutch: engaged
o Reverse Brake: released
1, The hydraulic pressure is applied to the forward clutch and the start clutch, and the sun gear drives the torward
clutch.
2. The torward clutch drives the drive pulleV shaft. which drives the driven pulley shaft linked by the steel belt.
3, The driven pulley shaft drives the secondary drive gear, via the start clutch.
4. Power is transmitted to the secondary driven gear, which drives the final driven gear.
NOTE: The working hydraulic pressure on the movable face of each shaft depends on the throttle opening position.
DRIVE PULI.f YFLYWHEELSTEEL AELT
CLUTCH
INPUT SHAFT
START CLUTCH
SECONDARY DRIVENGEAR
(cont'd)
FINAL DRIVEN GEAR
14-201
Page 880 of 2189
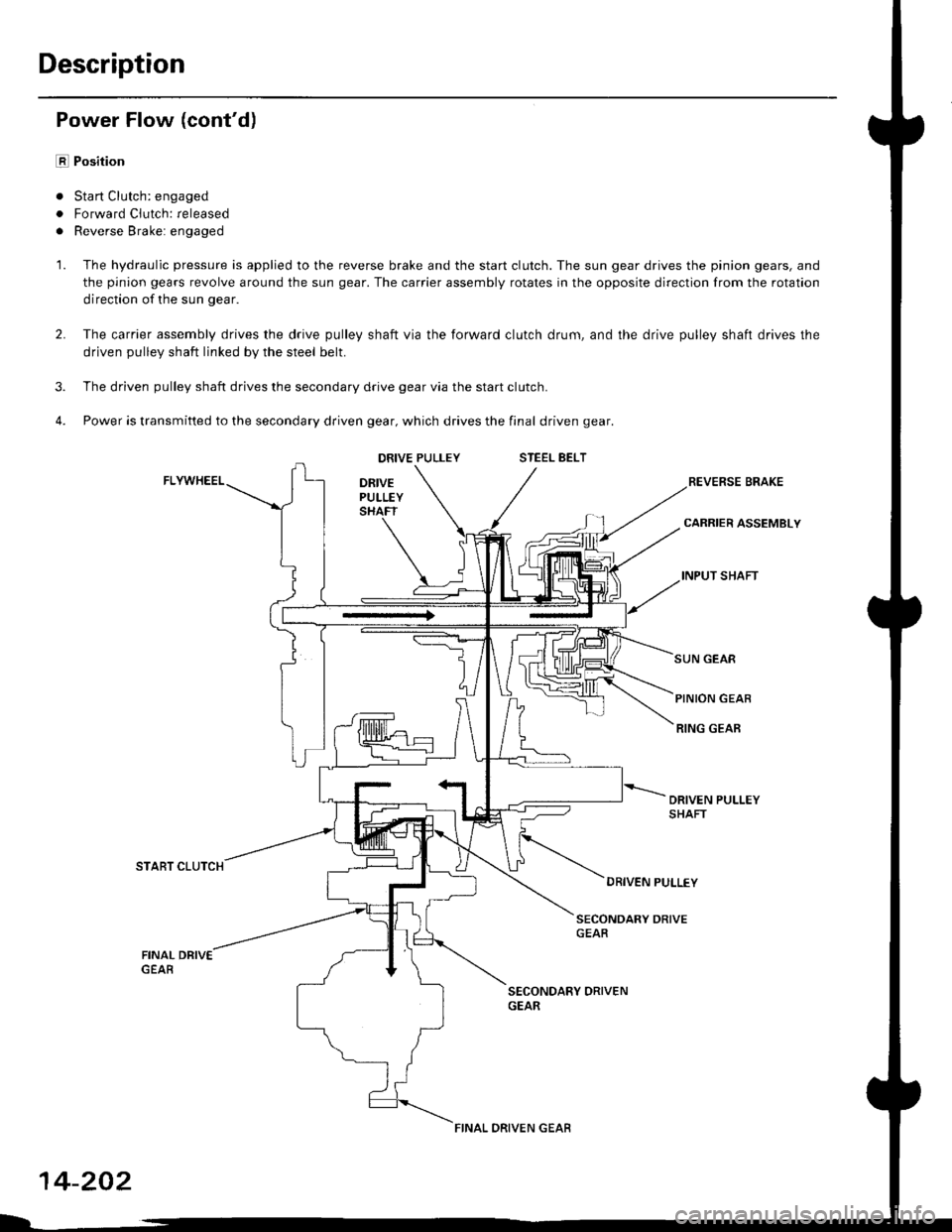
Description
Power Flow (cont'd)
E Position
. Sta rt Clutch: engaged
. Forward Clutch: released
. Reverse Brake: engaged
1. The hydraulic pressure is applied to the reverse brake and the start clutch. The sun gear drives the pinion gears, and
the pinion gears revolve around the sun gear. The carrier assembly rotates in the opposite direction from the rotation
direction of the sun gear.
The carrier assembly drives the drive pulley shaft via the forward clutch drum, and the drive pulley shaft drives the
driven pulley shaft linked by the steel belt.
The driven pulley shaft drives the secondary drive gear via the start clutch.
Power is transmitted to the secondary driven gear, which drives the final driven gear.
3.
4.
2.
DRIVE PULLEYSTEEL EELT
DRIVEPULLEYREVERSE BRAKE
CARRIER ASSEMBLY
INPUT SHAFT
SUN GEAR
PINION GEAB
RING GEAB
STABT CLUTCHDRIVEN PULLEY
SECONDARY DRIVEGEAR
FINALGEAB
SECONDARY ORIVENGEAR
FINAL ORIVEN GEAR
14-202
Page 884 of 2189

Description
Electronic Control System ('99 - 00 Modelsl (cont'dl
Grade Logic Control System
How it works:
The PcM compares actual driving conditions with memorized driving conditions. based on the input from the vehiclespeed sensor, the throttle position sensor, the manifold absolute pressure sensor, the engine coolant temperature sensor,the brake switch signal, and the shift lever position signal, to control shifting while the vehicle is ascending or descendinga slope.
Ascending Control
When the PCM determines that the vehicle is climbing a hill in E position, the system selects the most suitable shiftschedule (pulley ratio) according to the magnitude of a gradient. so the vehicle can run smooth and have more powerwhen needed. There are three ascending modes with different shift schedules according to the magnitude ot a gradient inthe PCM.
Descending Control
when the PCM determines that the vehicle is going down a hill in E position. the system selects the most suitable shiftschedule (pulley ratio) according to the magnitude of a gradient. This, in combinstion with engine braking, achievessmooth driving when the vehicle is descending, There are three descending modes with different shift schedules accord-ing to the magnitude of a gradient in the PCM.
L
14-206
Page 889 of 2189
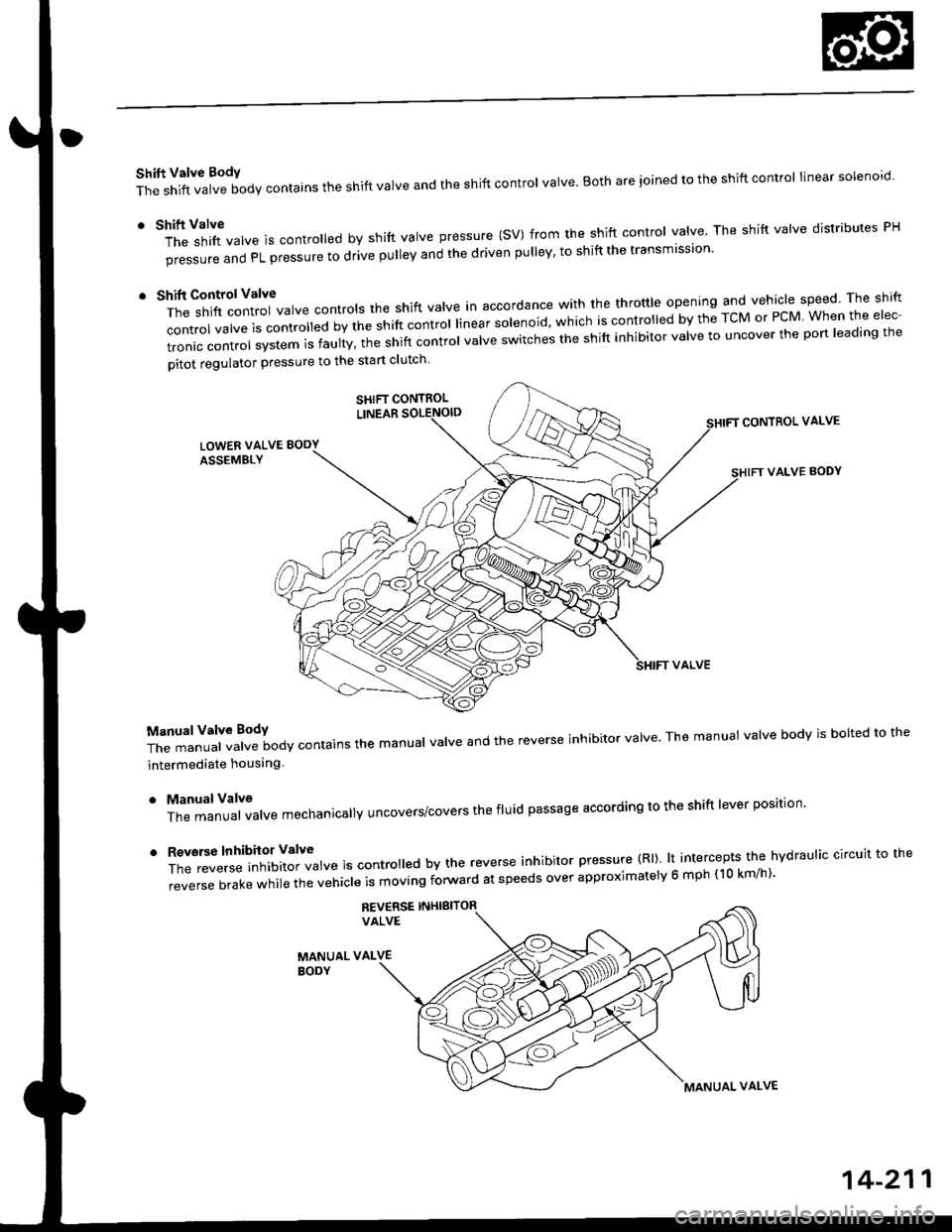
Shift Valve BodY
The shift valve body contains the shift valve and the shift control valve. Both are ioined to the shift control linear solenoro.
r tl'ft1il1rf"","" is controred by shift varve pressure (sV) from the shift contror varve. The shift varve distributes pH
pi""aur" "nO PL pressure to drive pulley and the driven pulley' to shift the transmission'
t t*"rilf:::lr';ivarve contrors the shift varve in accordance with the throttre opening and vehicle speed rhe shift
control valve is convorr"o uv ti" "iirt "ontrol linear solenoid, which is controlled by the TcM or PcM When the elec-
tronic control system is faulty, t;; snift controt uutue "witches the shift inhibitor valve to uncover the port leading the
pitot regulator pressure to the start clutch
CONTROL VALVE
VALVE BODY
T;J:"i"""1ff"t""ilody contains the manuar varve and the reverse inhibitor varve. The manuat varve bodv is borted to the
intermediate houslng
. ManualValve
The manual valve mechanicallY uncovers/covers the fluid passage according to the shift lever position'
'
ff:e;;;.'::'?Xftl::T",* is contro ed by the reverse inhibitor pressure (Rl). lt intercepts the hvdraulic circuit to the
reverse brake while the vehicle is moving forward at speeds over approximatelv 6 mph (10 km/h)'
REV€RSE INHIBITORVALVE
MANUAL VALVEBODY
SHIFT CONTROL
MANUAL VALVE
14-211
Page 890 of 2189
Description
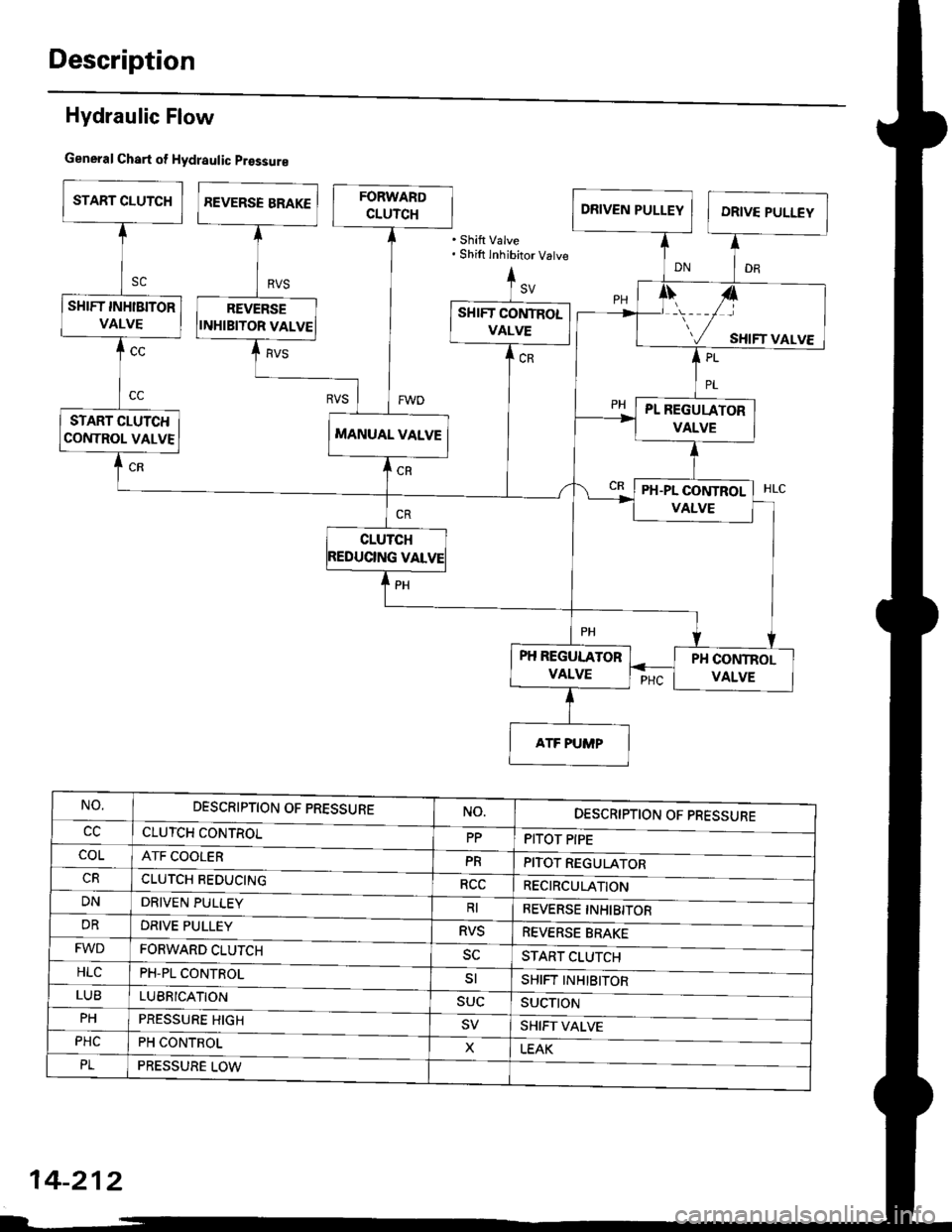
Hydraulic Flow
General Chart of Hydraulic prossure
'Shift Valve. Shift inhibitor Vatve
PH REGULATOR
VALVE
NO.DESCRIPTION OF PRESSURE
CLUTCH CONTROL
ATF COOLER
CLUTCH REDUCING
NO.DESCRIPTION OF PRESSURE
PITOT PIPEccPP
coLPRPITOT REGULATOR
RECIRCULATIONRCC
DNDRIVEN PULLEYRIREVERSE INHIBITOR
REVERSE BRAKE
START CLUTCH
SHIFT II"IHlBITOR
SUCTII'N
SHIFT VALVE
LEAK
DRDRIVE PULLEYRVS
FWDFORWARD CLUTCH
PH-PL CONTROL
sc
HLCsl
LUBLUBBICATION
PRESSURE HIGH
SUC
PH
PHCPH CONTROLX
PLPRESSURE LOW
14-212
Page 891 of 2189
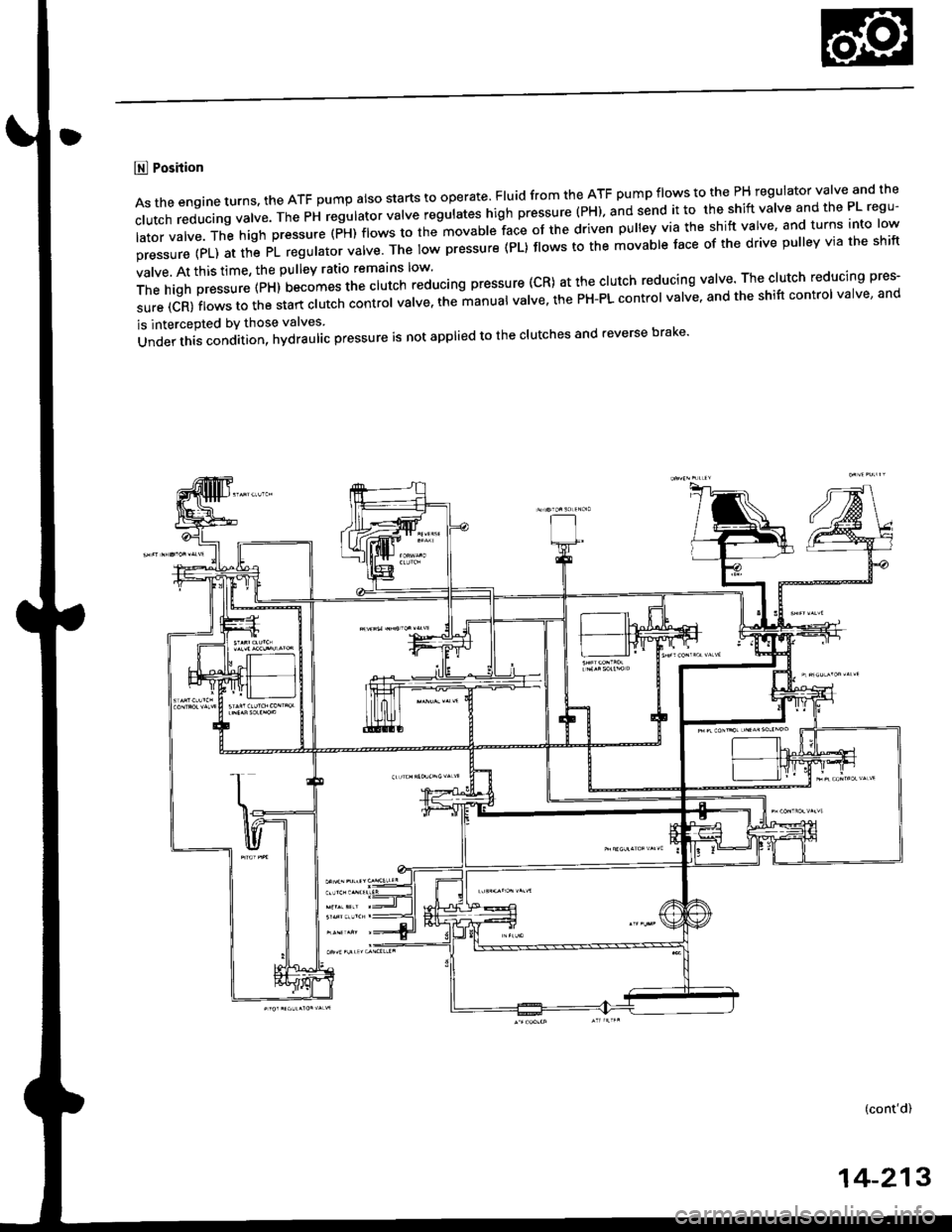
E Position
Astheengineturns.theATFpumpa|sostartstooperate.F|uidfromtheATFpumpf|owstothePHregu|atorva|veandthe
c|Utchreducingva|ve.ThePHregu|atorva|veregu|ateshighpressure(PH).andsendittotheshiftVa|veandthePLregU'
latorvalve.Thehighpressure(PH)flowstothemovablefaceofthedrivenpulleyviatheshiftvalve'andturnsintolow
pressure(PL)atthePLregu|atorva|ve.Thelowpressure(PL}f|owstothemovab|e'aceofthedrivepu||eYviatheshift
valve. At this time, the pulley ratio remarns low'
Thehighpressure(px)uecomesttrectutchreducingpressure(CR)atthec|utchreducingva|Ve.Thec|utchreducingpres.
sure (CR) flows to the start clutch cont'oi uatt". tn"lt"n'al valve' the PH-PL control valve' and the shift control valve' and
is intercepted bY those valves
Under this condition, hydraulac pressure is not applied to the clutches and reverse brake'
(cont'd)
14-213