INTAKE HONDA CIVIC 2003 7.G Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HONDA, Model Year: 2003, Model line: CIVIC, Model: HONDA CIVIC 2003 7.GPages: 1139, PDF Size: 28.19 MB
Page 217 of 1139
Fuel and Emissions Systems
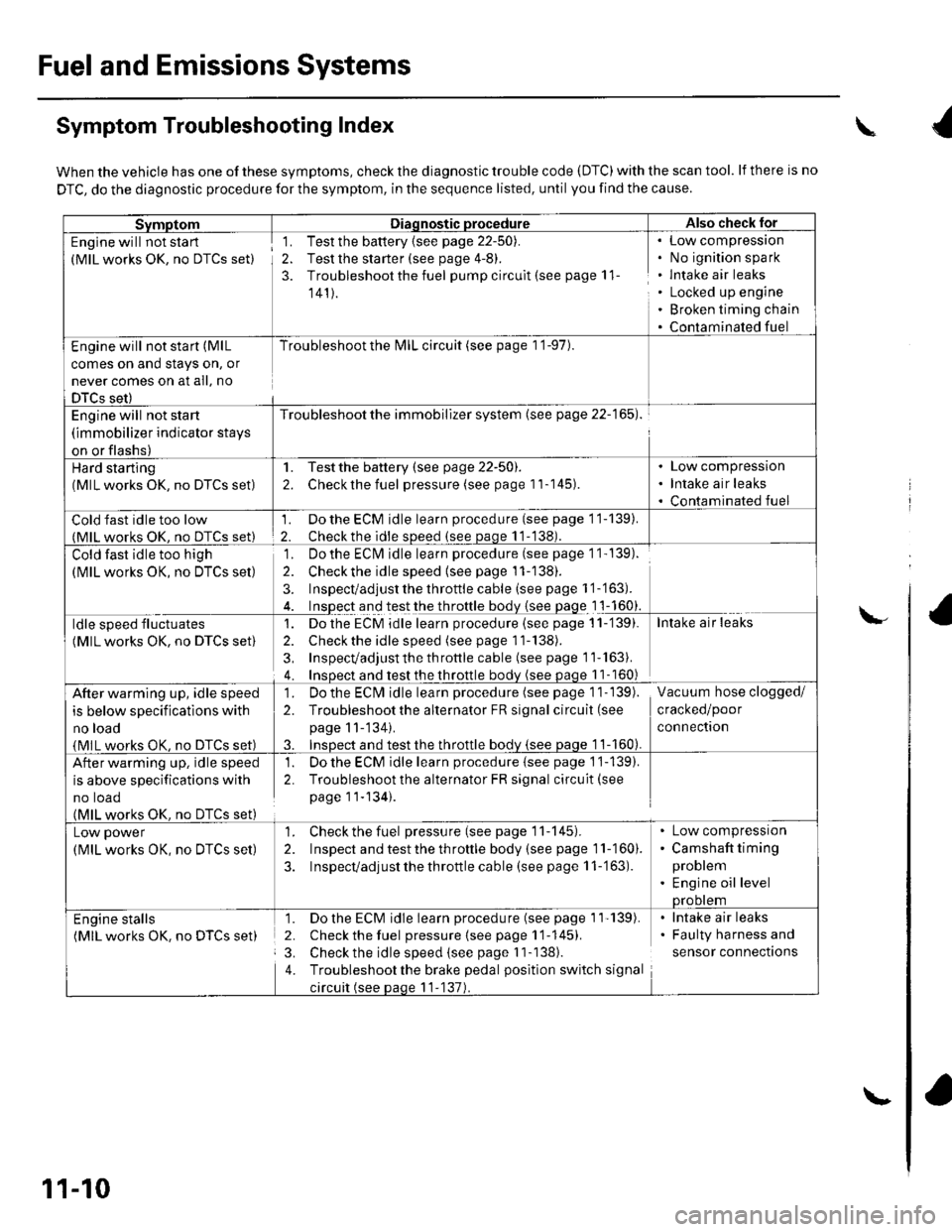
Symptom Troubleshooting Index
When the vehicle has one of these symptoms, check the diagnostic trouble code (DTC) with the scan tool. lf there is no
DTC, do the diagnostic procedure for the symptom, in the sequence listed, until you find the cause.
SvmotomDiaqnostic procedureAlso check lor
Engine will not sta rt
(MlL works OK, no DTCS set)
1. Test the battery {see page 22-50).
2. Test the starter (see page 4-8).
3. Troubleshoot the fuel pump circult (see page 11
141).
Low compressron
No ignition spark
lntake air leaks
Locked up engine
Broken timing chain
Contaminated fuel
Engine will not start (MlL
comes on and stays on, or
never comes on at all, no
DTCS set)
Troubleshoot the l\4lL circuit (see page 1 '1-97).
Engine will not start
(immobilizer indicator stays
on or flashs)
Troubleshoot the immobilizer system (see page 22-165).
Hard starting(MlL works OK, no DTCS set)
1. Testthe battery (see page 22-50).
2. Checkthe fuel pressure (see page 11-145).
Low compression
Intake air leaks
Contaminated fuel
Cold fast idle too low(MlL works OK. no DTCS set)
1. Do the ECM idle learn procedure (see page 11-139).
2. Checkthe idle sDeed (see paqe 11-138).
Cold fast idle too high
(MlL works OK, no DTCS set)
Do the ECI\4 idle learn procedure (see page 1 1- 139).
Checkthe idle speed {see page 11-138).
Inspect/adjust the throttle cable (see page 1 '1-'163).
Inspect and test the throttle body {see page 1 1-160}.
']�
2.
3.
ldle speed fluctuates
(MlL works OK, no DTCS set)
1. Dothe ECM idle learn procedure (see page 11-'139).
2. Check the idle speed (see page 11-138).
3, Inspecvadjust th e throttle cable (see page 11''163).
4. Insoect and test the throttle bodv (see paqe 11- 160)
Intake air leaks
After warming up, idle speed
is below specifications with
no load
{MlL works OK, no DTCS set)
1. Do the ECIVI idle learn procedure (see page 1 1- 139).
2. Troubleshootthe alternator FR signal circuit (see
page 11-'134).
3. InsDect and test the throttle bodv {see paqe 1 1-160).
Vacuum hose clogged/
cracked/poor
connectron
After warming up, idle speed
is above specifications with
no toao(MlL works OK. no DTCS set)
1. Do the ECM idle learn procedure {see page 1'j-139).
2. Troubleshoot the alternator FR signal circuit(see
page 11-134).
Low power
(MlL works OK, no DTCS set)
1. Check the fuel pressure(seepagell-145).
2. Inspect and test the th roftle body (see page 11-160).
3. Inspecvadjust the throttle cable (see page 11-'163).
Low compressron
Camshaft timing
problem
Engine oil levelprootem
Engine stalls(MlL works OK. no DTCS set)
1. Do the ECM idle learn procedure (see page 1'l'139).
2. Check the fuel pressure{seepagell-145).
3. Check the idle speed (see page I 1-138).
4. Troubleshootthe brake pedal position switch signal
circuit (see paqe 11-137).
lntake air leaks
Faulty harness and
sensor connections
\
\-
11-10
\-
Page 220 of 1139
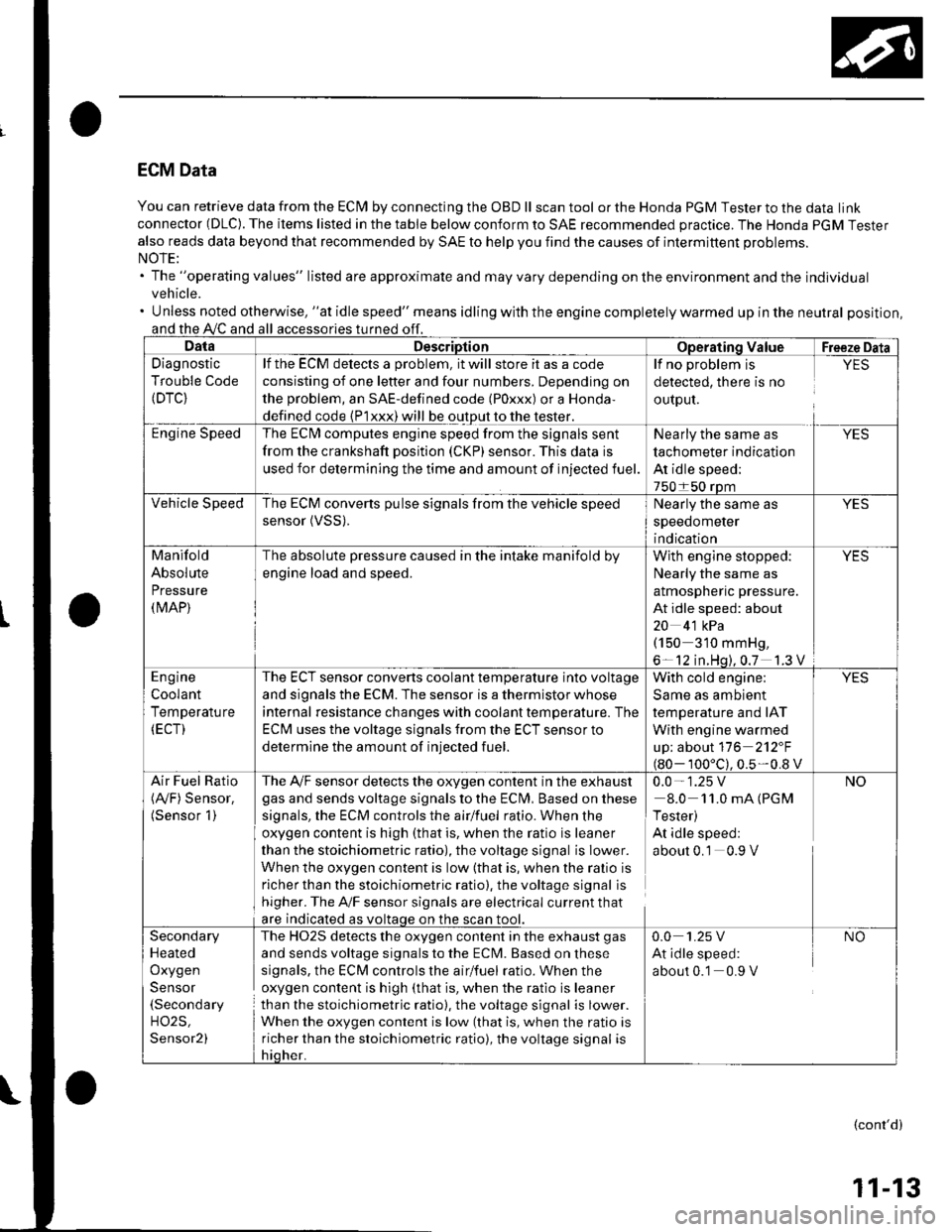
ECM Data
You can retrieve data from the ECI\4 by connecting the OBD ll scan tool or the Honda PGM Tester to the data link
connector (DLC). The items listed in the table below conform to SAE recommended practice. The Honda PGM Tester
also reads data beyond that recommended by SAE to help you find the causes of intermittent problems.
The "operating values" listed are approximate and may vary depending on the environment and the individual
vehicle.
Unless noted otherwise, "at idle speed" means idling with the engine completely warmed up in the neutral position,
and the A,/C and all
Diagnostic
Trouble Code(DTC}
lf the ECM delects a problem, it will store it as a code
consisting of one letter and four numbers. Depending on
the problem, an SAE-defined code (Poxxx) or a Honda,
defined code {P1xxx) will be output to the tester.
The ECI\4 computes engine speed from the signals sent
from the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor. This data is
used for determining the time and amount of injected fuel.
detected, there is no
ourpul.
lf no problem is YES
Nearly the same as
tachometer indication
At idle speed;
The ECM converts pulse signals from the vehicle speed
sensor (VSS).Nearly the same as
speedometer
indication
Manifold
Absolute
Pressure(MAP)
The absolute pressure caused in the intake manifold by
engine load and speed.
With engine stopped: YES
Nearly the same as
almospnenc pressure.
At idle speed: about
20 4'1 kPa(150 310 mmHg,
6- 12 in.Hq).0.7 1.3 V
The ECT sensor converts coolant temperature into voltage
and signals the ECM. The sensor is a thermistor whose
internal resistance changes with coolant tempetature. The
ECM uses the voltage signals from the ECT sensor to
determine the amount of injected fuel.
With cold engine:
Same as ambient
temperature and IAT
With engine warmed
up; about 116 2'12"F
100'c).0.5-0.8 v
Air Fuel Ratio The A,/F sensor detects the oxygen content in the exha ust 0.0 - 1 .25 V(Ay'F) Sensor. gas and sends voltage signals to the Eclvl, Basedonthese 8.0 11.0mA(PGM(Sensor 1) signals, the ECM controls the airlfuel ratio. When the I Tester)
oxygen content is high (that is, when the ratio is leaner At idle speed:
than the stoichiometric ratio), the voltage signal is Iower. about 0.1 0.9 V
When the oxygen content is low (that is, when the ralio is
richer than the stoichiometric ratio). the voltage signal is
higher. The A'lF sensor signals are electrical current that
are indicated as voltaqe on the
The HO2S detects the oxygen content in the exhaust gas
and sends voltage signals to the ECM. Based on these
signals, the ECM controls the airlfuel ratio. When the
oxygen content is high (that is, when the ratio is leaner
than the stoichiometric ratio), the voltage signal is lower.
When the oxygen content is low (that is, when the ratio is
richer than the stoichiometric ratio), the voltage signal is
Secondary
Heated
Oxygen
Sensor(Secondary
H02S,
Sensor2)
0.0 1.25 V NO
At idle speed:
about 0.1 0.9 V
(cont'd)
11-13
Page 221 of 1139
Fuel and Emissions Systems
System Descriptions (cont'd)
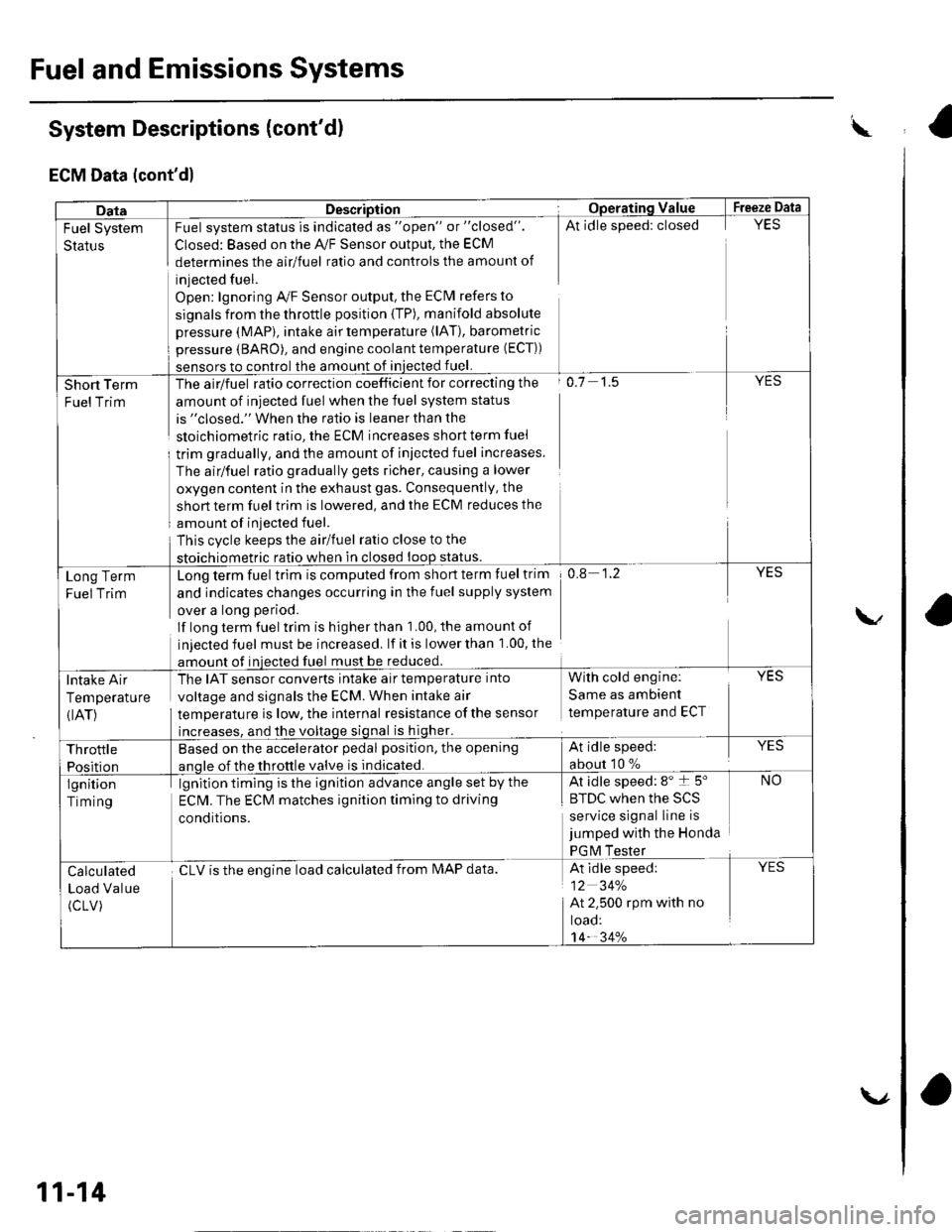
ECM Data (cont'd)
w
DataDescriptionOpera'ting ValueFreeze Data
Fuel System
Status
Fuel system status is indicated as "open" or "closed".
Closed: Based on the A,/F Sensor output, the ECM
determines the airlfuel ratio and controls the amount of
injected fuel.
Open: lgnoring Ay'F Sensor output, the ECM refers to
signals from the throttle position {TP), manifold absolute
pressure (MAP), intake air temperature (lAT), barometric
pressure (BARO), and engine coolant temperature (ECT))
sensors to control the amount of iniected fuel.
At idle speed: closedYES
Short Term
FuelTrim
The airlfuel ratio correction coefficient for correcting the
amount of injected fuel when the fuel system status
is "closed." When the ratio is leaner than the
sloichiometric ratio, the ECM increases short term fuel
trim gradually, and the amount of iniected fuel increases.
The airlfuel ratio gradually gets richer, causing a lower
oxygen content in the exhaust gas. Consequently, the
short term fuel trim is lowered, and the ECM reduces the
amount of injected fuel.
This cvcle keeps the airlfuel ratio close to the
stoichiometric ratio when in closed loop status.
o.7 1.5YES
Long Term
Fuel Trim
Long term fuel trim is computed from short term fuel trim
and indicates changes occurring in the fuel supply system
over a long period.
lf long term fuel trlm is higher than 1.00, the amounl of
injected fuel must be increased. lf it is lower than 1.00, the
amount of injected fuel must be reduced.
0.8 1.2YES
Intake Air
Temperature
{IAT)
The IAT sensor converts intake air temperature into
voltage and signals the ECM. When intake air
temperature is low, the internal resistance ofthe sensor
increases, and the voltage signal is higher.
With cold engine:
Same as ambient
temperature and ECT
YES
Throttle
Position
Based on the accelerator pedal position, the opening
anole of the throttle valve is indicated.
At idle speed:
about 10 %
YES
lgnition
Timing
lgnition timing is the ignition advance angle set by the
ECM. The ECM matches ignition timing to driving
conditions.
At idle speed: 8" t 5"
|' tuL wnen rne >L)
service signal line is
jumped with the Honda
PGM Tester
NO
Calculated
Load Value
(cLV)
cLV is the enoine load calculated from IMAP data.At idle speed:
12 34%
At 2.500 rpm with no
toao:'t4- 34%
YES
11-14
\.,
ra
Page 228 of 1139
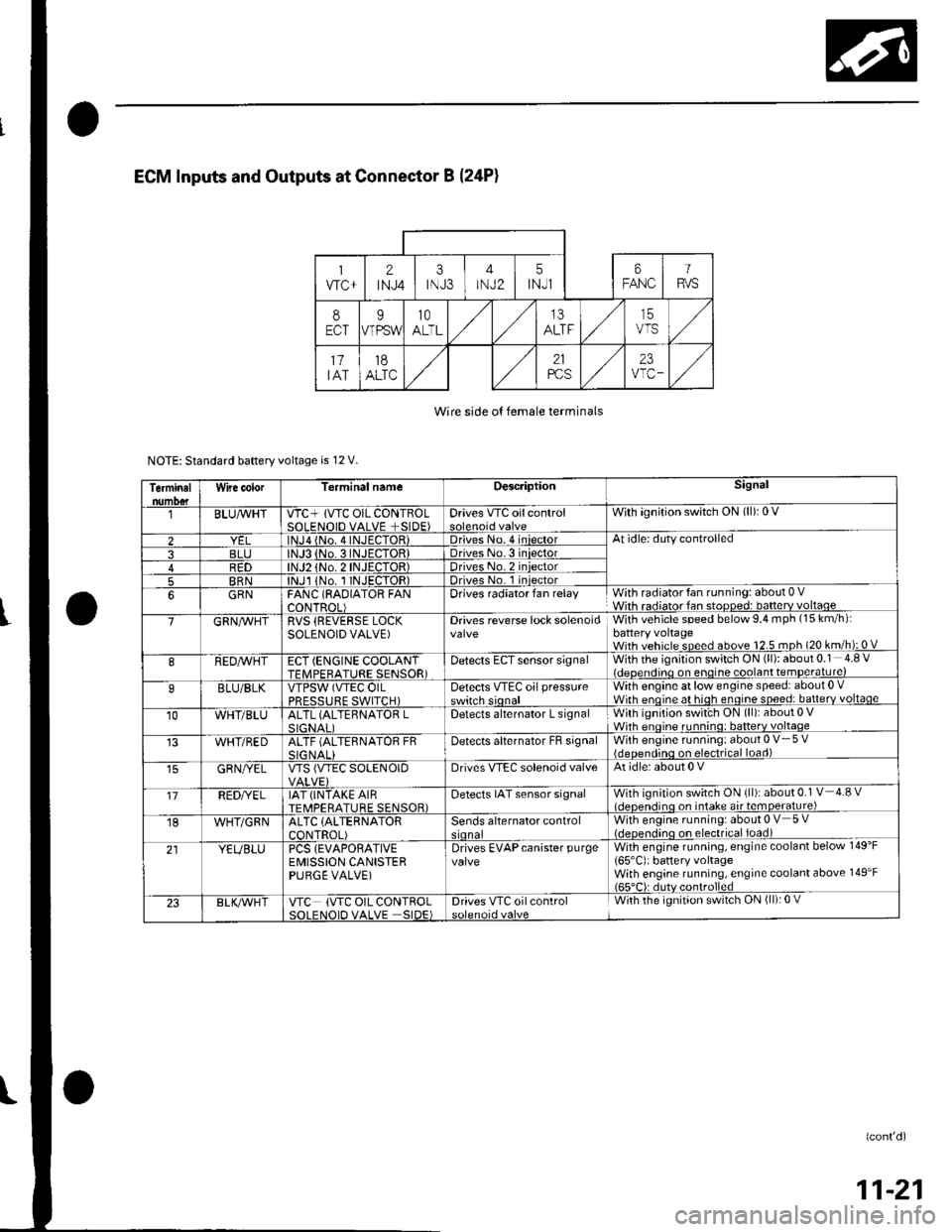
Wire side o{ female terminals
NOTE: Standard baftery voltage is 12 V.
Terminalnumo€tWire color[erminal nameDescriptionSignal
BLUAvHTVTC+ lVTC OIL CONTBOLSOLENOID VALVE +SIDE)Drives VTC oilcontrolWith ignition switch ON (ll): 0 V
2lNJa {No. 4INJECTOR)Driveso. 4 iniectorAt idle: duty controlled
3BLJo.3INJECTORIDriveso.3 iniector4R1)TOR)Driveso.2 iniector
5BRNlNJl 1No. I INJECTOR)Drives No. 1 iniector
6GRNFANC (RAOIATOR FANCONTROL)Drives radiator fan relayWith radiator fan running: about 0 VWith radiator fan stopped: batterv voltaoe
7GRN/vVHTRVS (REVERSE LOCKSOLENOID VALVE)Drives reverse lock solenoidWith vehicle speed below 9.4 mph (15 km/h):battery voltageWith vehicle speed above 12.5 mph (20 km/h): 0 V
8REDAVHTECT (ENGINE COOLANTTFMPFRATURE SENSOR)Detects ECT sensor signalWith the ignition switch ON (ll): about 0.1 4.8 Videoendino on enoine coolant temDerature)
9BLU/BLKVTPSW (VTEC OILPRFSSTIRF SWITCH)Detects VTEc oil pressureswitch sionalWith engine at low engine speed: about 0 .Wirh enoine at hioh enoine soeed: batterv voltaqe
10WHT/BLUALTL (ALTEBNATOR LSIGNAI IDetects alternator L signalWith ignition swit'ch ON (ll): about 0 VWhh enoine runnino: batterv voltaqe
WHT/REDALTF (ALTERNATOR FRSIG NALIDetecls alternator FB signalWith engine running: about 0 V- 5 V{deoendinq on electrical load)
GRN/YELVTS {VTEC SOLENOIDDrives VIEC solenoid valveAt idle: about 0 V
'17REDI/ELIAT (INTAKE AIRTEMPERATURE SENSOR)Detects IAT sensor signalWith ignition switch ON {ll): about 0.1 V 4.8 vl.lcnen.iino on intake air temoerature)
18WHT/GRNALTC (ALTERNATOR
CONTROL)Sends alternator controlWith engine running: about 0 V 5 V(.lcocn.lino on electrical ioad)
21YEUBLUPCS {EVAPORATIVEEMISSION CANISTERPURGE VALVE)
Drives EVAPcanister purgevalveWith engine running, engine coolant below 149'F
165'C): battery voltageWith engine running, engine coolant above 149'F165"C): dutv controlled
23BLK/Vr'HTVTC (VTC OIL CONTROLSOI FNOID VALVE SIDE)Drives VTC oilcontrolWith the ignition switch ON (ll): 0 V
(confd)
11-21
Page 231 of 1139
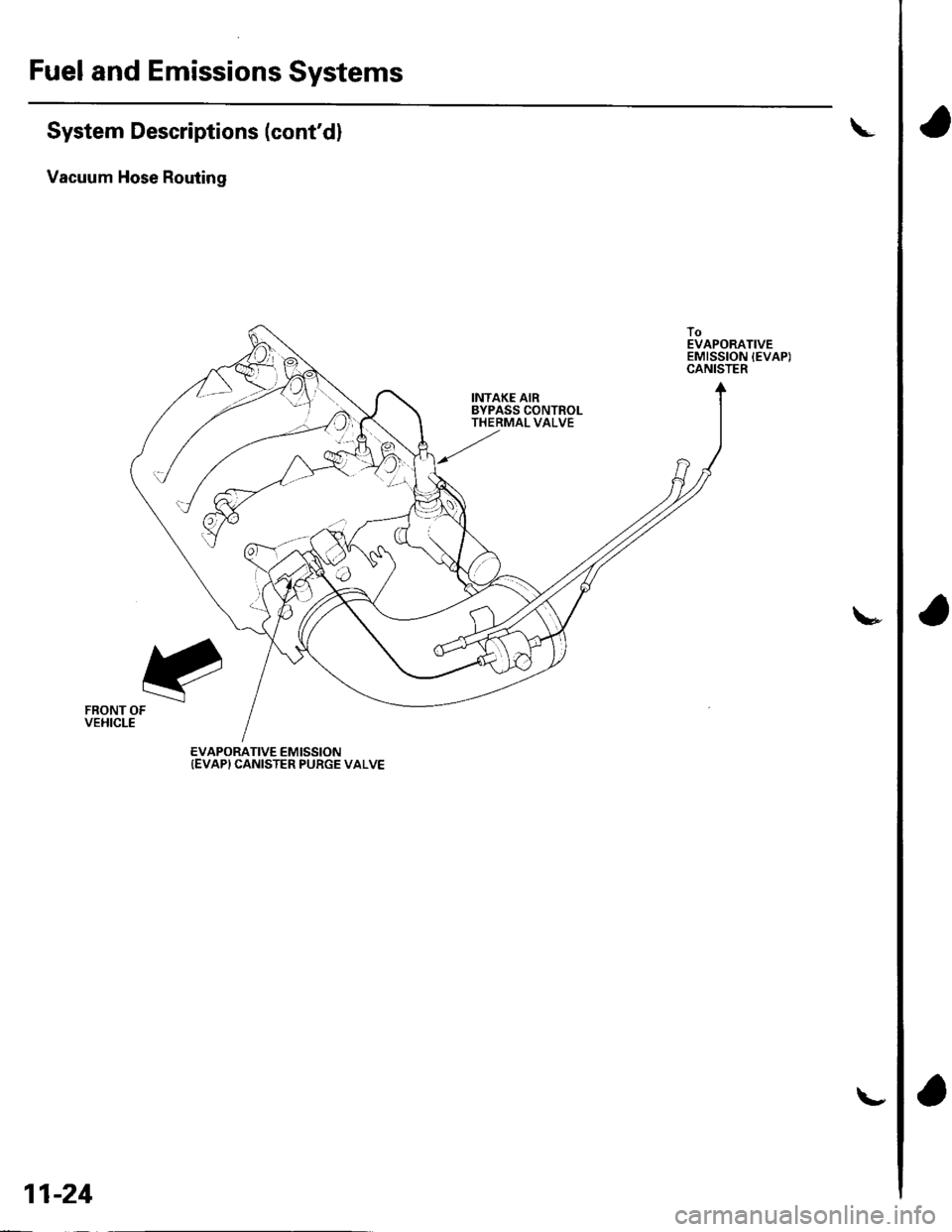
Fuel and Emissions Systems
System Descriptions (cont'dl
Vacuum Hose Routing
!
INTAKE AIRBYPASS CONTROLTHERMAL VALVE
\*
FRONT OFVEHICLE
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION{EVAP} CANISTER PURGE VALVE
11-24
\,
Page 232 of 1139
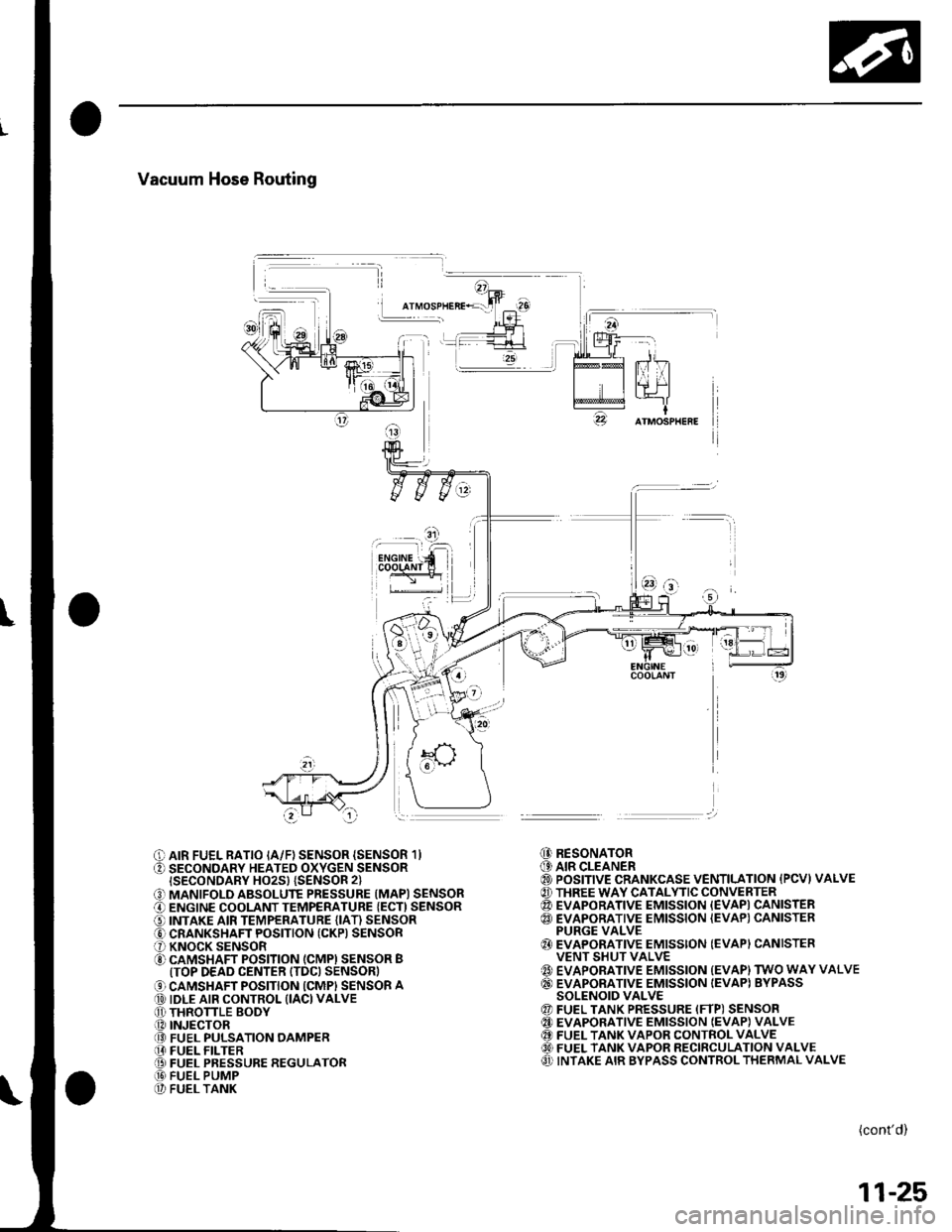
Vacuum Hose Routing
I
O AIR FUEL RATIO IA/F) SENSOR {SENSOR 1}O SECONDARY HEATED OXYGEN SENSORISECONDARY HO2S} {SENSOR 2}
O MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAPI SENSORO ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE {ECT) SENSORO INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE (IAT) SENSORO CRANKSHAFT POSITION (CKP) SENSORO KNOCK SENSORO CAMSHAFT POSITION (CMPI SENSOR BITOP DEAD CENTER ITDC) SENSOR)
O CAMSHAFT POSITION ICMPI SENSOR A@ IDLE AIR CONTROL (IACI VALVEO THRONLE BODY.O INJECTOR@ FUEL PULSATION OAMPER[I FUEL FILTER@ FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR@ FUEL PUMP@ FUEL TANK
@ RESONATOR(9 AIR CLEANER@ POSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILATION {PCVI VALVE@ THREE WAY CATALYTIC CONVERTER@ EVAPORATIVE EMISSION {EVAPI CANISTER@ EVAPORATIVE EMISSION {EVAP) CANISTERPURGE VALVE{} EVAPORATIVE EMISSION (EVAPI CANISTERVENT SHUT VALVE{' EVAPORATIVE EMISSION {EVAP) TWO WAY VALVE@ EVAPORATIVE EMISSION IEVAPI BYPASSSOLENOID VALVE@ FUEL TANK PRESSURE (FTP) SENSOR@ EVAPORATIVE EMISSION IEVAP} VALVE@ FUEL TANK VAPOR CONTROL VALVE60) FUEL TANK VAPOR RECIRCULATION VALVEO INTAKE AIR BYPASS CONTROL THERMAL VALVE
(cont'd)
11-25
Page 234 of 1139
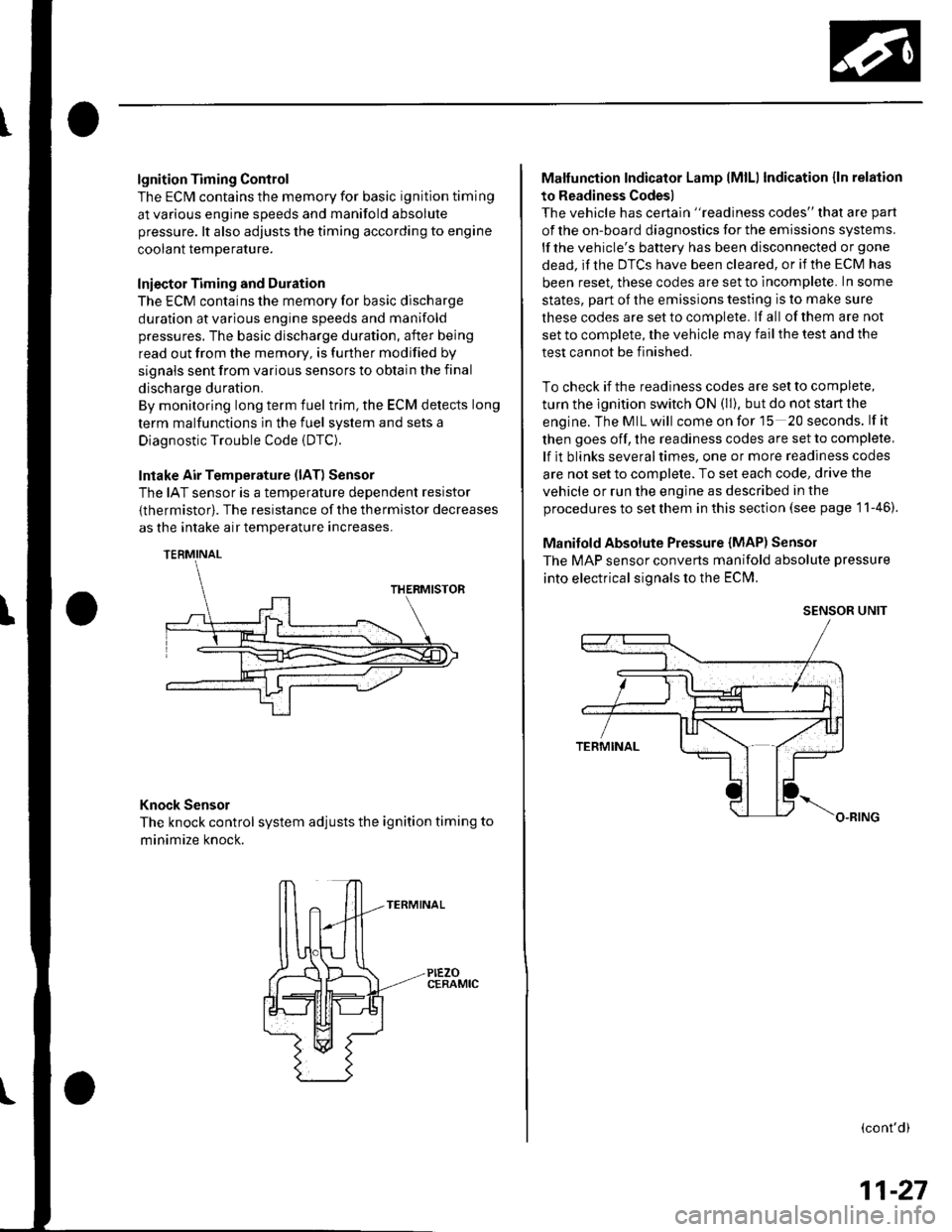
lgnition Timing Control
The ECM contains the memory for basic ignition timing
at various engine speeds and manifold absolute
pressure. lt also adjusts the timing according to engine
coolant temperature.
Iniector Timing and Duration
The ECM contains the memory for basic discharge
duration at various engine speeds and manifold
pressures. The basic discharge duration, after being
read out from the memory, is further modified by
signals sent from various sensors to obtain the final
discharge duration.
By monitoring long term fuel trim, the ECM detects long
term malfunctions in the fuel system and sets a
Diagnostic Trouble Code {DTC).
Intake Air Temperature (lAT) Sensor
The IAT sensor is a temperature dependent resistor
{thermistor). The resistance of the thermistor decreases
as the intake air temDerature increases.
Knock Sensor
The knock control system adjusts the ignition timing to
minimize knock.
PIEZOCERAMIC
Malfunction Indicator Lamp lMlLl Indication {ln relation
to Readiness Codes)
The vehicle has certain "readiness codes" that are part
of the on-board diagnostics for the emissions systems.
lf the vehicle's baftery has been disconnected or gone
dead. if the DTCS have been cleared, or if the ECM has
been reset. these codes are set to incomplete. In some
states, part of the emissions testing is to make sure
these codes are set to comDlete. lf all of them are not
set to complete, the vehicle may fail the test and the
test cannot be finished.
To check if the readiness codes are set to complete,
turn the ignition switch ON (ll). but do not start the
engine.TheMILwill comeonforlS 20seconds. lf it
then goes off, the readiness codes are set to complete,
lf it blinks severaltimes, one or more readiness codes
are not set to comolete. To set each code, drive the
vehicle or run the engine as described in the
procedures to set them in this section (see page 1 1-46).
Manifold Absolute Pressure {MAP) Senso]
The MAP sensor converts manifold absolute pressure
into electrical signals to the ECM.
SENSOR UNIT
(cont'd)
11-27
Page 236 of 1139
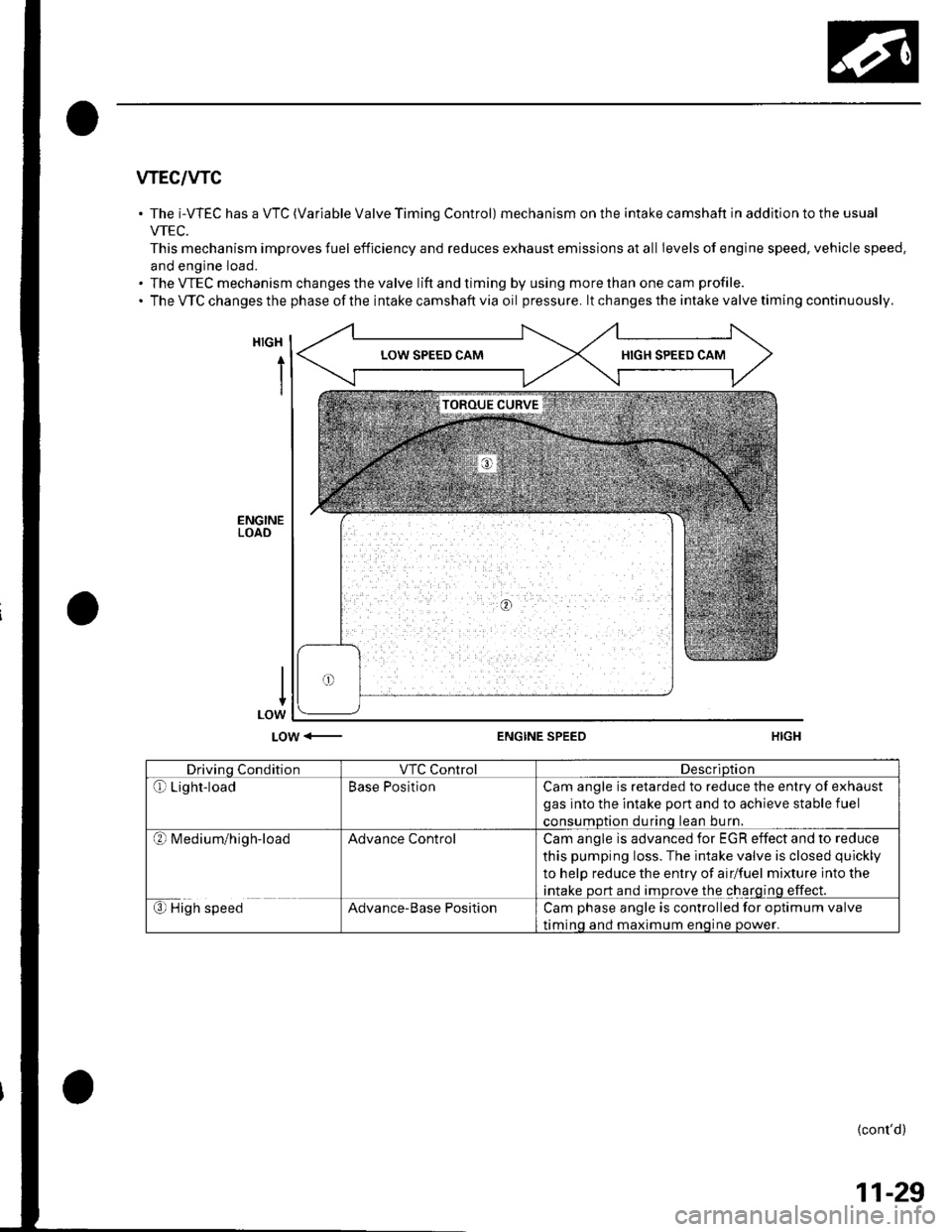
wEc/wc
The i-WEC has a VTC (Variable Valve Timing Control) mechanism on the intake camshaft in addition to the usual
VTEC.
This mechanism improves fuel efficiency and reduces exhaust emissions at all Ievels of engine speed, vehicle speed.
and engine load.
The VTEC mechanism changes the valve lift and timing by using more than one cam profile.
The VTC changes the phase of the intake camshaft via oil pressure. lt changes the intake valve timing continuously.
HIGH
i
LOW <-ENGINE SPEED
Drivino ConditionVTC ControlDescriDtion
Qr Light-loadBase PositionCam angle is retarded to reduce the entry of exhaust
gas into the intake port and to achieve stable fuel
consumDtion durinq lean bu rn.
?l M ed iu m/h ig h-loadAdvance ControlCam angle is advanced for EGR effect and to reduce
this pumping loss. The intake valve is closed quickly
to help reduce the entry of airlfuel mixture into the
intake port and improve the charging effect.
€) High speedAdvance-Base PositionCam phase angle is controlled for optimum valve
timinq and maximum enoine oower.
{cont'd)
11-29
Page 237 of 1139
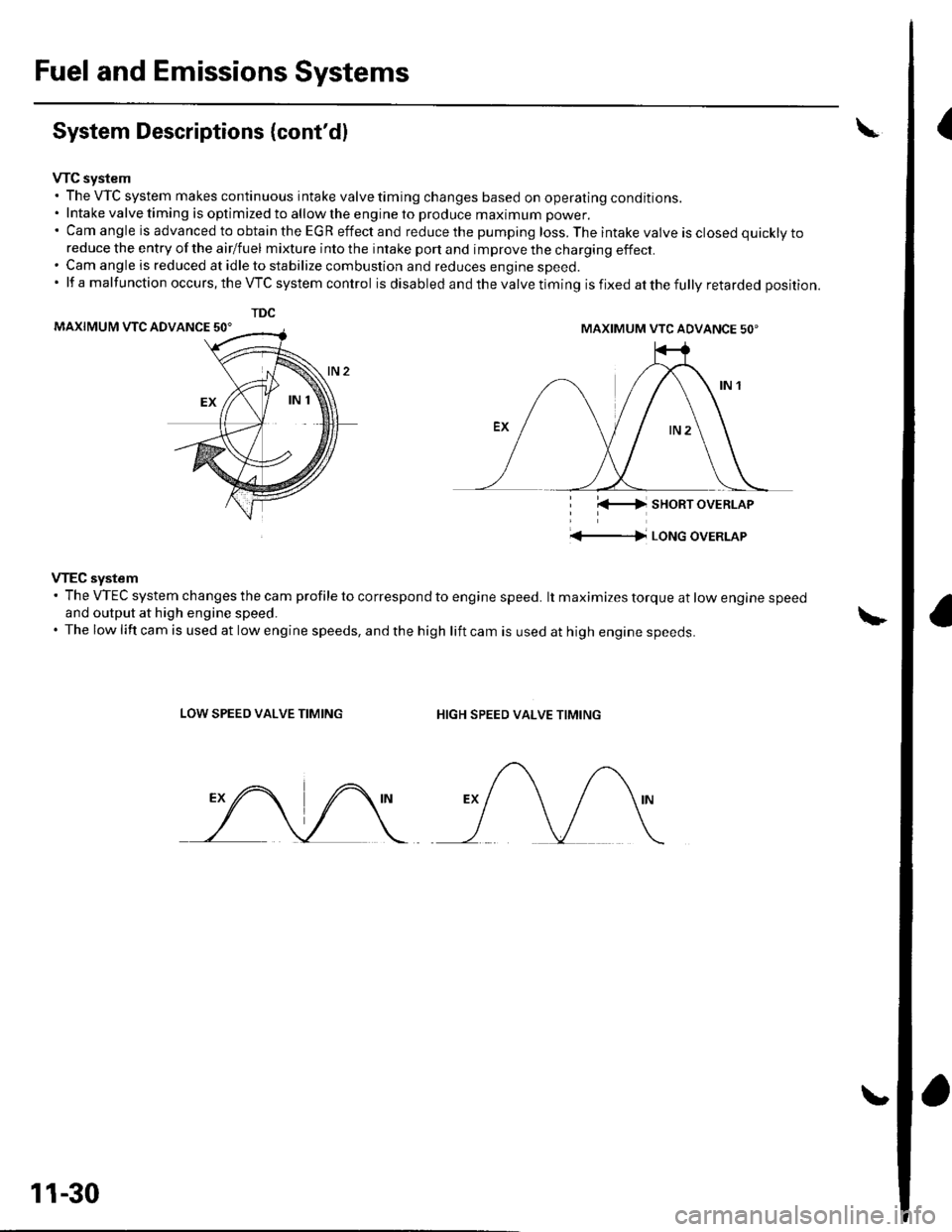
Fuel and Emissions Systems
(System Descriptions (cont'dl
VTC system. The VTC system makes continuous intake valve timing changes based on operating conditions.. Intake valve timing is optimized to allow the engine to produce maximum power.'CamangleisadvancedtoobtaintheEGReffectandreducethepumpingloss.Theintakevalveisclosedquicklyto
reduce the entry of the airlfuel mixture into the intake port and improve the charging effect.. Cam angle is reduced at idle to stabilize combustion and reduces engine speed.'lfamalfunctionoccurs,theVTCsystemcontrol is disabled and the valve timing is fixed at the fully retarded position.
MAXIMUM VTC ADVANCE 50'
i l(-4 sHoRT oVERLAP
'+-|l LoNG oVERLAP
VTEC system' The VTEC system changes the cam profile to correspond to engine speed. lt maximizes torque at low engine speedand output at high engine speed.. The low lift cam is used at low engine speeds, and the high lift cam is used at high engine speeds.
LOW SPEED VALVE TIMINGHIGH SPEED VALVE TIMING
TDC
MAXIMUM VTC ADVANCE 50'
11-30
Page 238 of 1139
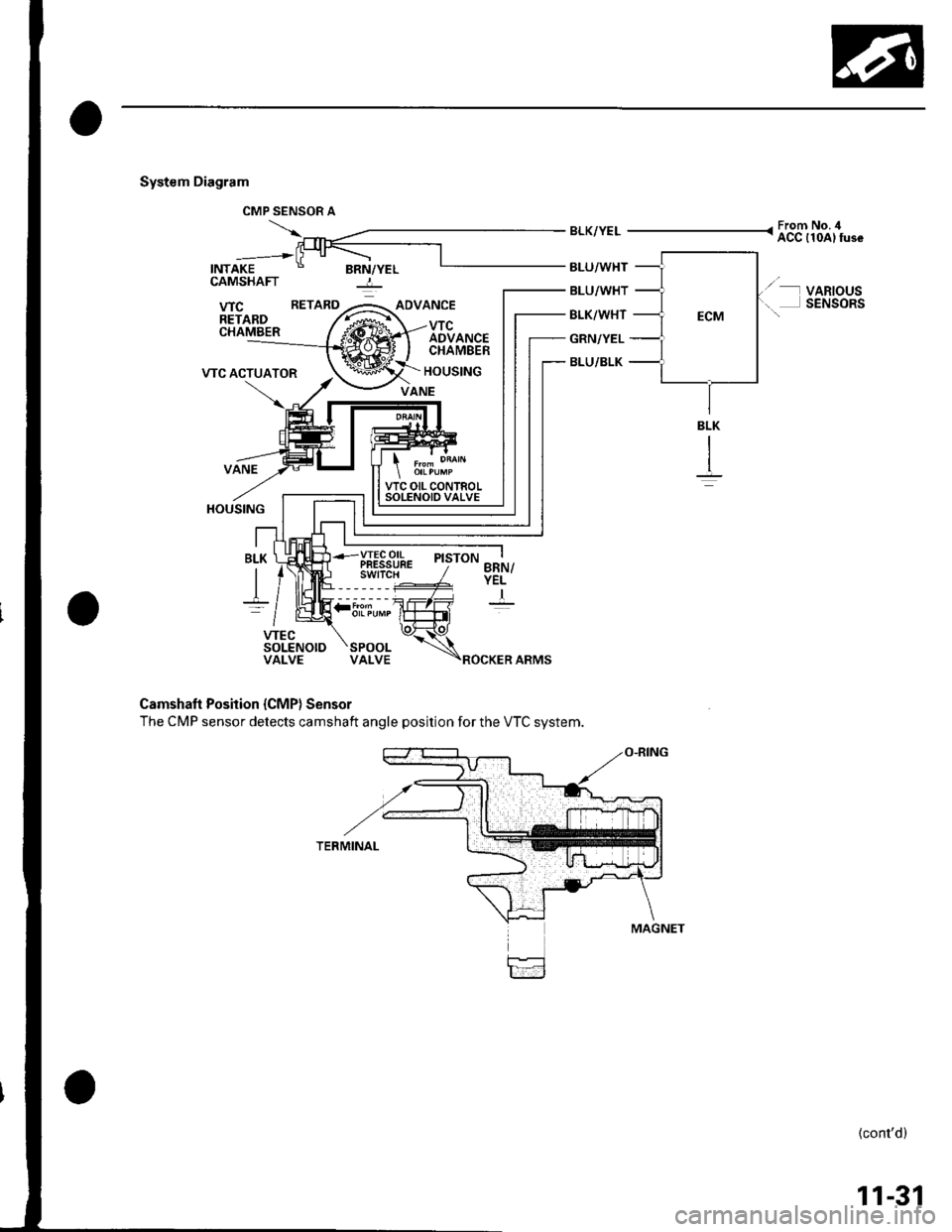
System Diagram
INTAKE
CMP SENSOR A
BRN/YELBLU/WHT
BLU/WHT
BLK/WHT
GRN/YEL
BLU/BLK
From No. ilACC {10A) fuse
VARIOUSSENSORS
CAMSHAFT -:-
BLK
It
Camshaft Position {CMP} Sensor
The CMP sensor detects camshaft angle position for the VTC system.
{cont'd}
11-31
:5i.T,""