shift lock HONDA CR-V 1998 RD1-RD3 / 1.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HONDA, Model Year: 1998, Model line: CR-V, Model: HONDA CR-V 1998 RD1-RD3 / 1.GPages: 1395, PDF Size: 35.62 MB
Page 532 of 1395
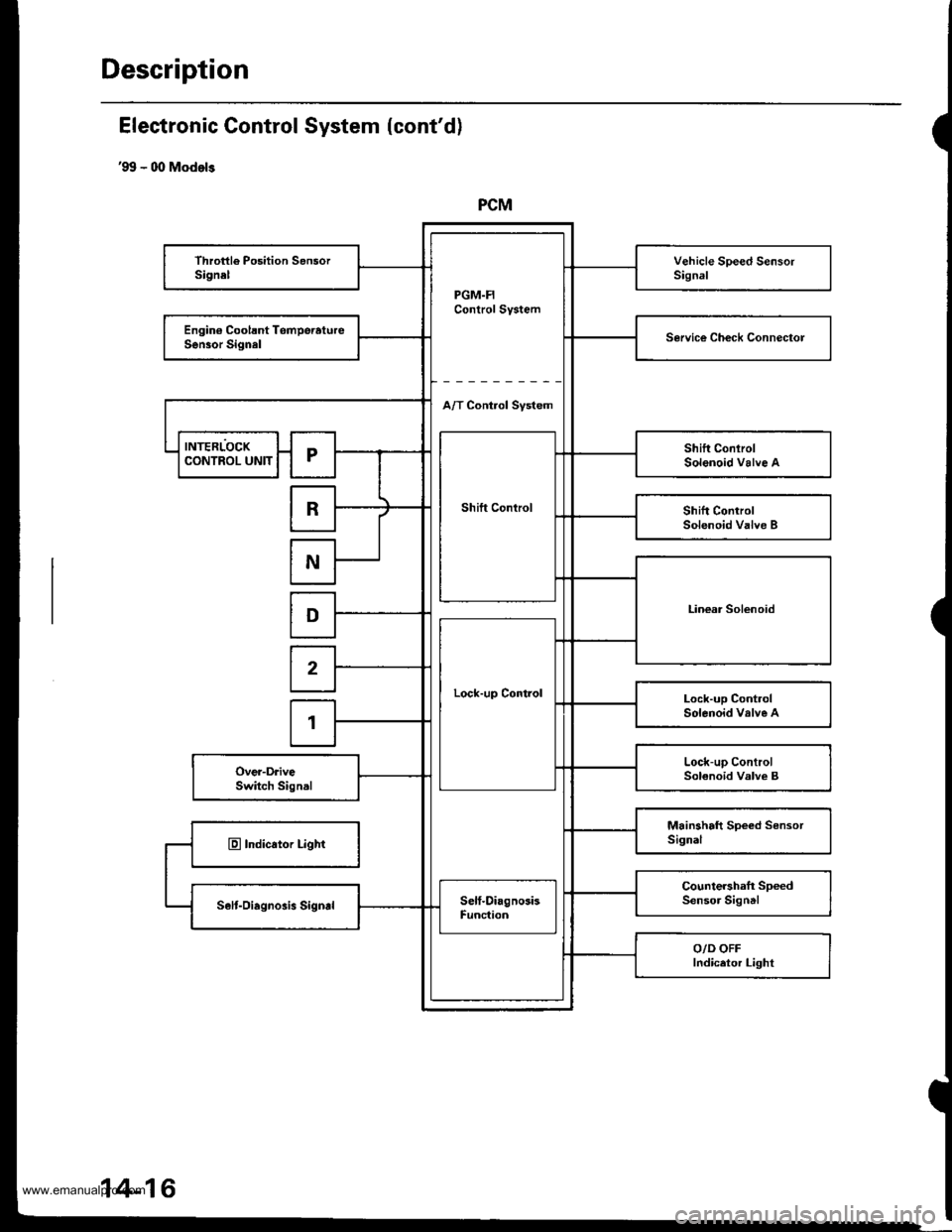
Description
PCM
PGM.FIControl System
Throttle Position SensorSignelVehicle Speed SensorSignal
Engin€ Coolsnt TomperatureSen30r SignalService Ch€ck Connectol
A/T Control Svstem
INTERLOCK
Shift Control
Shift ConlrolSolenoid Valve ACONTROL UNITr
RShift ControlSolenoid Valve B
N
Linear SolenoidD
Lock-up Control
2
Lock-up ControlSolenoid valve A1
Lock-up ControlSolenoid Valve BOver-DriveSwitch Signal
Mainshaft Speed SensorSignalE Indicator Light
Countershaft SpeedSensor SigntlSelt-Oiagnosis SigndSelf-DiagnosisFunc{ion
O/D OFFIndicetor Light
Electronic Gontrol System (cont'd)
'99 - 00 Models
14-16
www.emanualpro.com
Page 533 of 1395
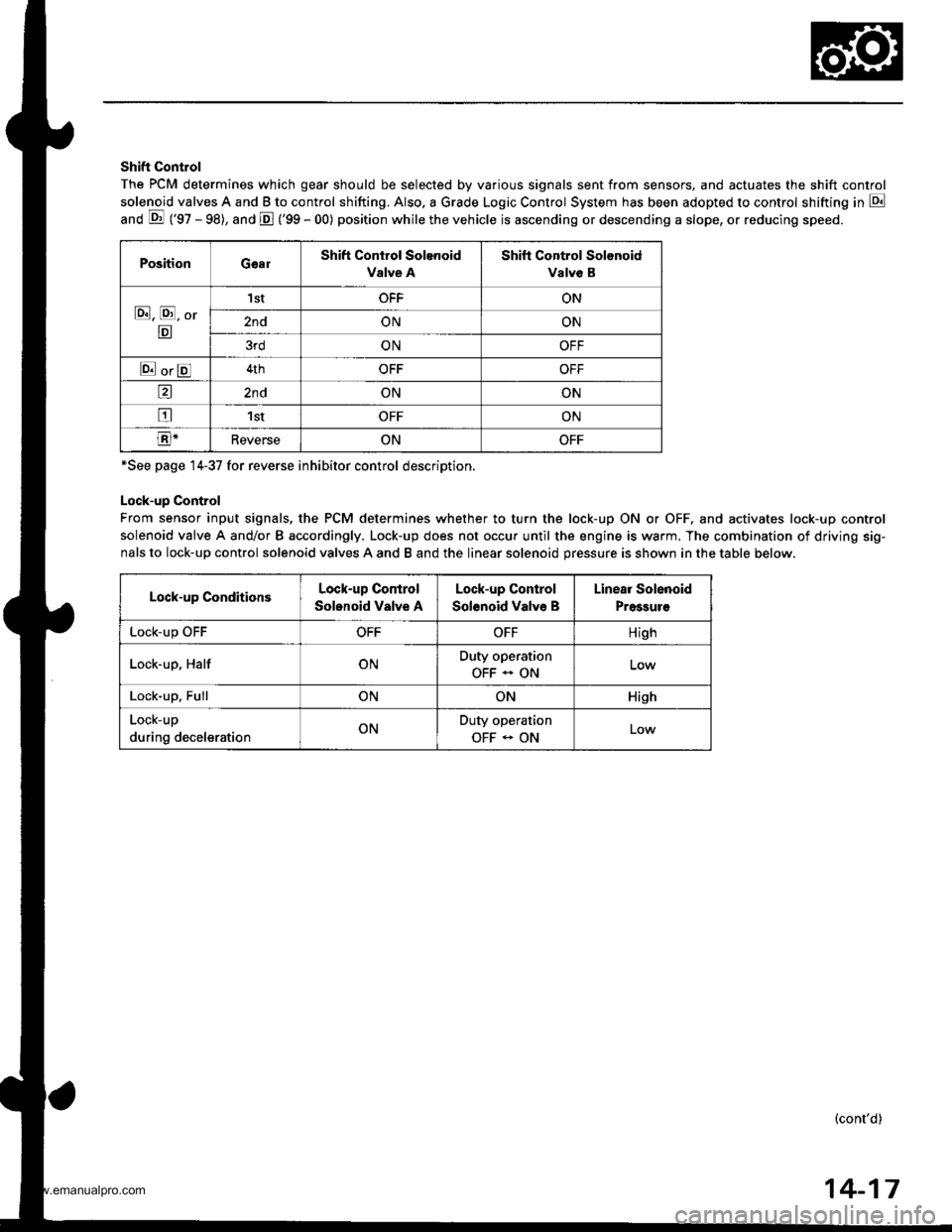
Shift Control
The PCM determines which gear should be selected by various signals sent from sensors, and actuates the shift control
solenoid valves A and B to control shifting. Also. a Grade Logic Control System has been adopted to control shifting in E
anO E ('gZ - gg), and E ('99 - 00) position while the vehicle is ascending or descending a slope, or reducing speeo.
PositionGearShift Control Solenoid
Valve A
Shift Control Solonoid
Valve B
E, E, Or
E
'I stOFFON
2ndONON
3rdONOFF
E orE4thOFFOFF
a2ndONON
tr1stOFFON
E-ReverseONOFF
*See page 14-37 for reverse inhibitor control description.
Lock-up Control
From sensor input signals, the PCM determines whether to turn the lock-up ON or OFF, and activates lock-up control
solenoid valve A and/or B accordingly. Lock-up does not occur until the engine is warm. The combination of driving sig-
nals to lock-up control solenoid valves A and B and the linear solenoid pressure is shown in the table below.
Lock-up ConditionsLock-up Control
Solonoid Valve A
Lock-up Control
Solenoid Valve B
Linear Solenoid
Pressuro
LOCK-Up \JrrOFFOFFHigh
Lock-up, HalfONDuty operation
OFF - ON
Lock-up, FullONONHish
Lock-up
during decelerationONDuty operation
OFF - ONLow
(cont'd)
14-17
www.emanualpro.com
Page 536 of 1395
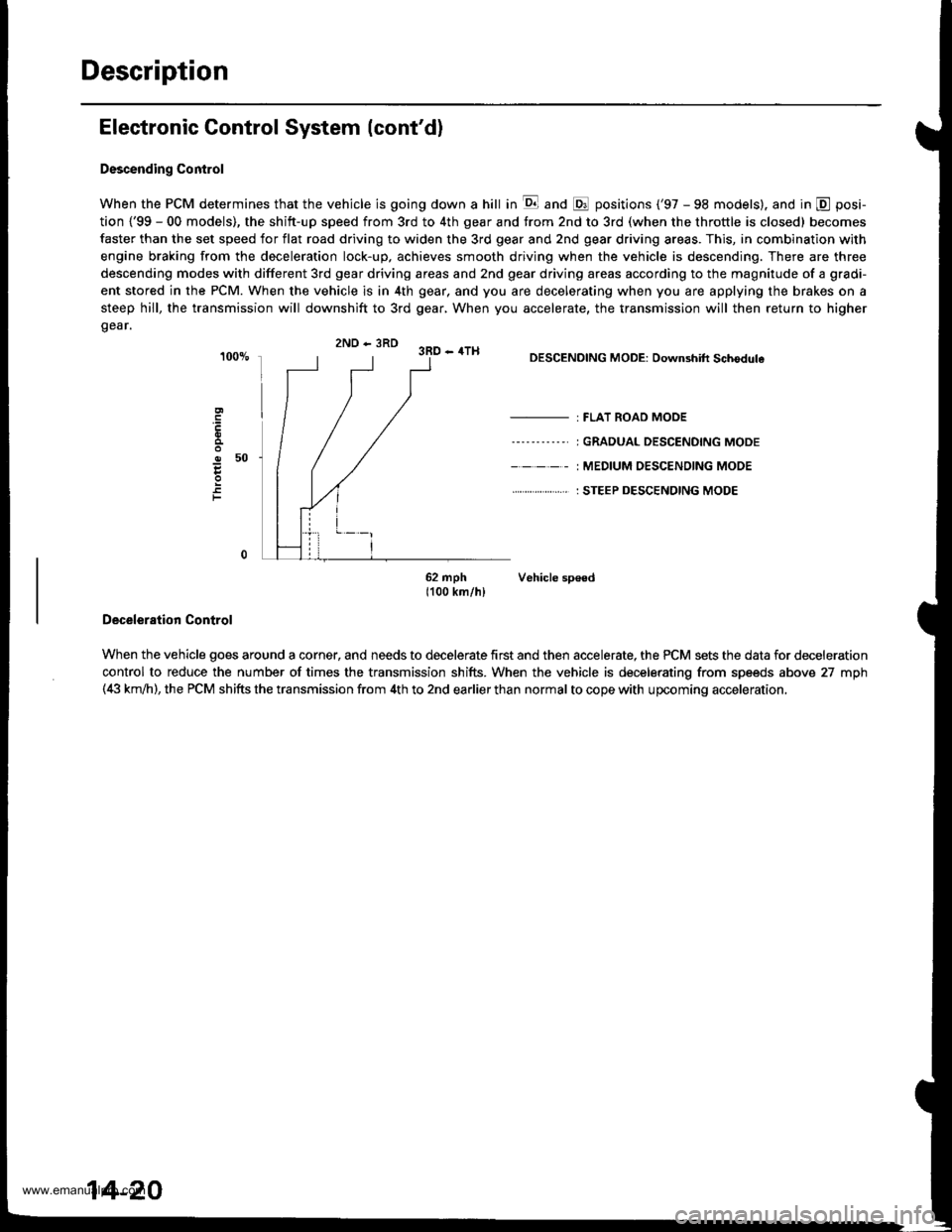
Description
Electronic Control System (cont'd)
Descending Control
When the PCM determines that the vehicle is going down a hill in E and @ positions ('97 - 98 models). and in @ posi-
tion {'99 - 00 models), the shitt-up speed from 3rd to 4th gear and from 2nd to 3rd (when the throttle is closed) becomes
faster than the set speed for flat road driving to widen the 3rd gear and 2nd gear driving areas. This, in combination with
engine braking from the deceleration lock-up, achieves smooth driving when the vehicle is descending. There are three
descending modes with different 3rd gear driving areas and 2nd gear driving areas according to the magnitude of a gradi-
ent stored in the PCM. When the vehicle is in 4th gear, and you are decelerating when you are applying the brakes on a
steep hill, the transmission will downshift to 3rd gear, When you accelerate, the transmission will then return to higher
gear.
2ND - 3RD 3RD - 4TH
o50
F
DESCENDING MODE: Downshift Schodule
- : FLAT ROAD MODE
----'-----' I GRADUAL DESCENDING MODE
- - - - - : MEDIUM OESC€NOING MODE
. . ... : STEEP DESCENDING MODE
62 mph Vehicle sp€ed1100 km/hl
Deceleration Control
When the vehicle goes around a corner, and needs to decelerate first and then accelerate, the PCM sets the data for deceleration
control to reduce the number of times the transmission shifts. When the vehicle is decelerating from speeds above 27 mph(4i| km,ih), the PCM shifts the transmission from 4th to 2nd earlier than normal to cope with upcoming acceleration,
14-20
www.emanualpro.com
Page 540 of 1395
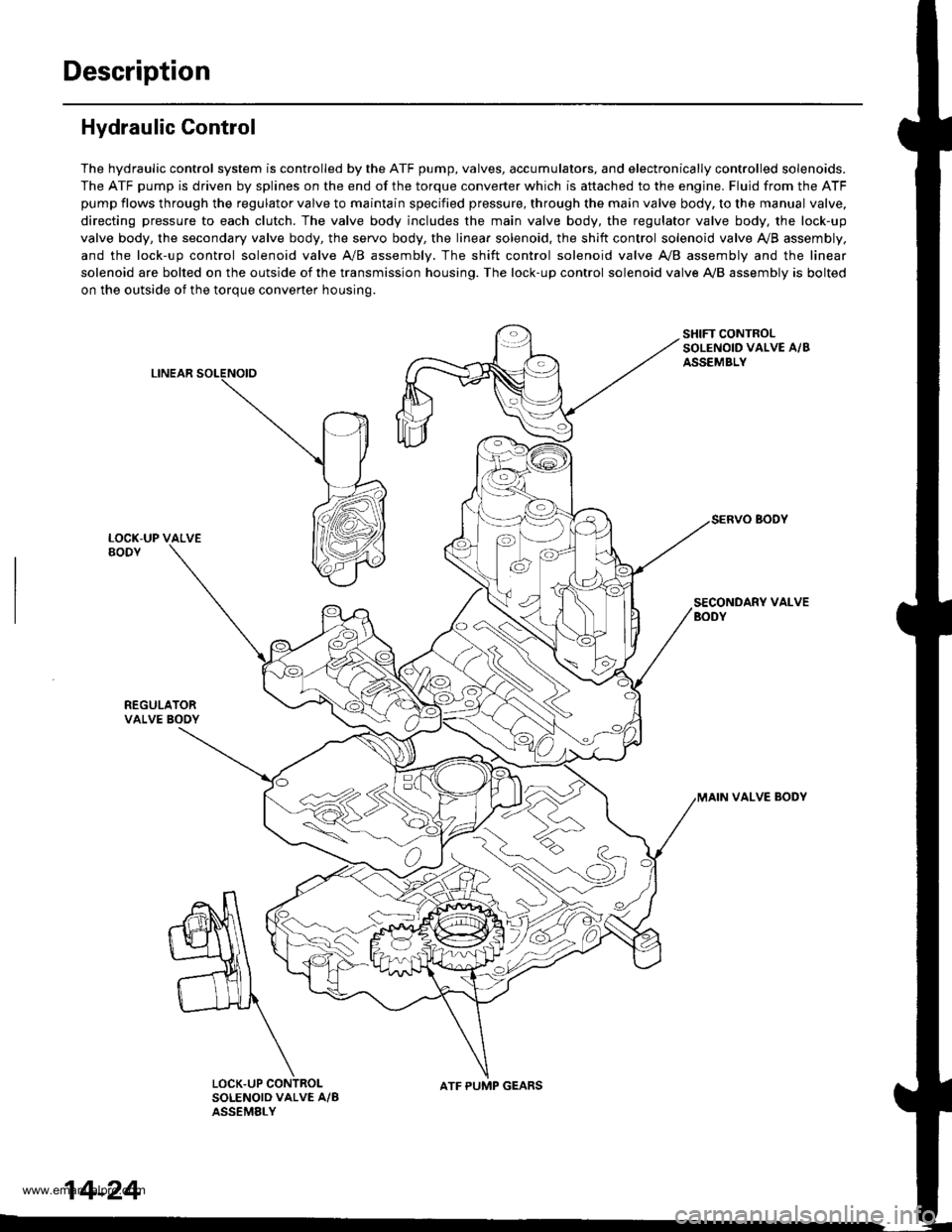
Description
Hydraulic Control
The hydraulic control system is controlled by the ATF pump, valves, accumulators, and electronically controlled solenoids.
The ATF pump is driven by splines on the end of the torque converter which is aftached to the engine. Fluid from the ATF
pump flows through the regulator valve to maintain specified pressure, through the main valve body, to the manual valve,
directing pressure to each clutch. The valve body includes the main valve body, the regulator valve body, the lock-up
valve body, the secondary valve body, the servo body, the linear solenoid, the shift control solenoid valve Ay'B assembly,
and the lock-up control solenoid valve A/B assembly. The shift control solenoid valve A,/B assembly and the linear
solenoid are bolted on the outside of the transmission housing. The lock-up control solenoid valve A,/B assembly is bolted
on the outside of the torque converter housing.
LINEAR
SHIFT CONTROLSOLENOID VALVE A/BASSEMBLY
SECONDARY VALVEBODY
REGULATORVALVE BOOY
VALVE BODY
SOLENOID VALVE A/BASSEMELY
N
ATF PUMP GEARS
14-24
www.emanualpro.com
Page 542 of 1395
Description
Hydraulic Control (cont'd)
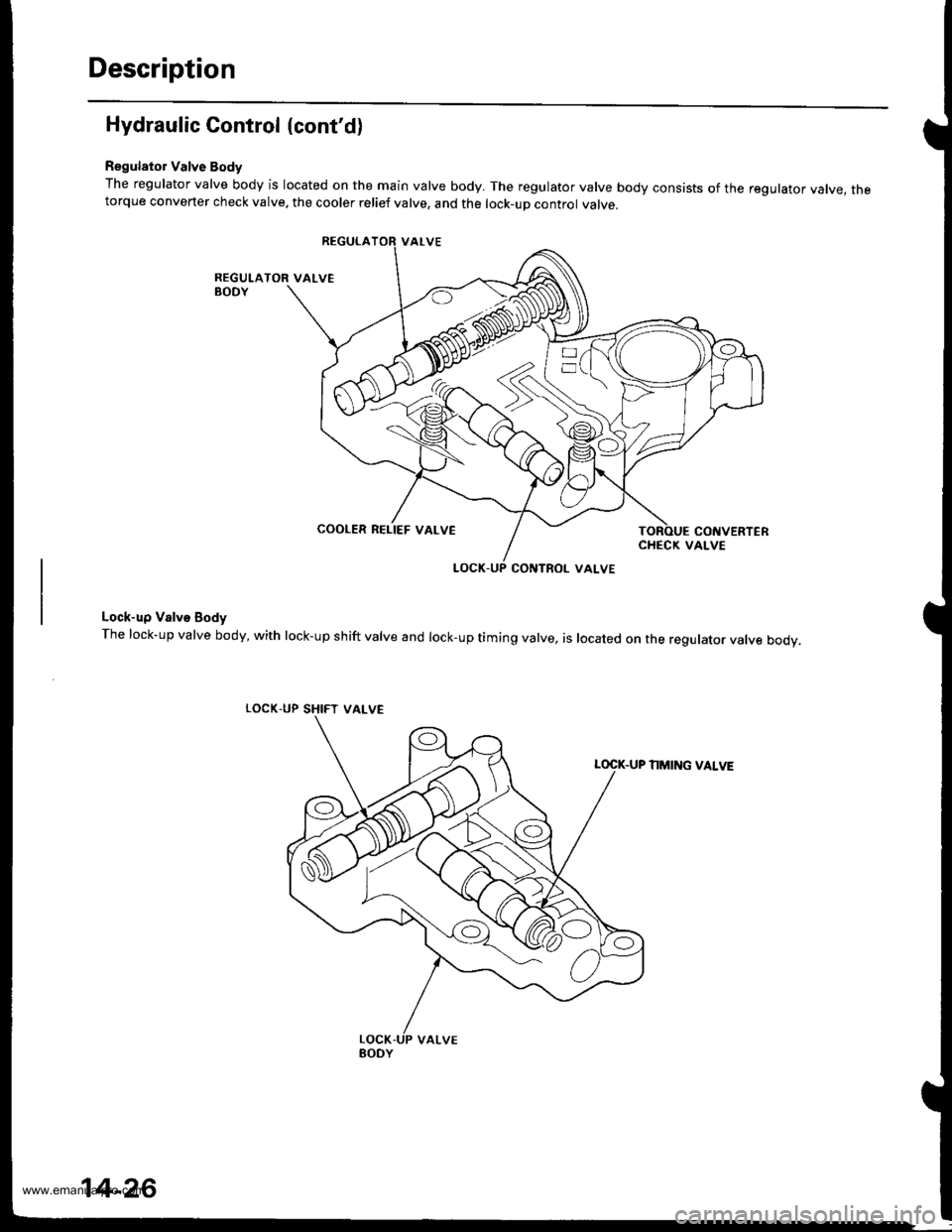
Regulator Valve Body
The regulator valve body is located on the main valve body. The regulator valve body consists of the regulator vatve, thetorque converter check valve. the cooler relief valve, and the lock-up control valve.
Lock-up Valve Body
The lock-up valve body, with lock-up shift valve and lock-up timing valve, is located on the regulator valve body.
LOCK.UP SHIFT
NMING VALVE
COOLER RELIEF VALVE
VALVE
14-26
www.emanualpro.com
Page 545 of 1395
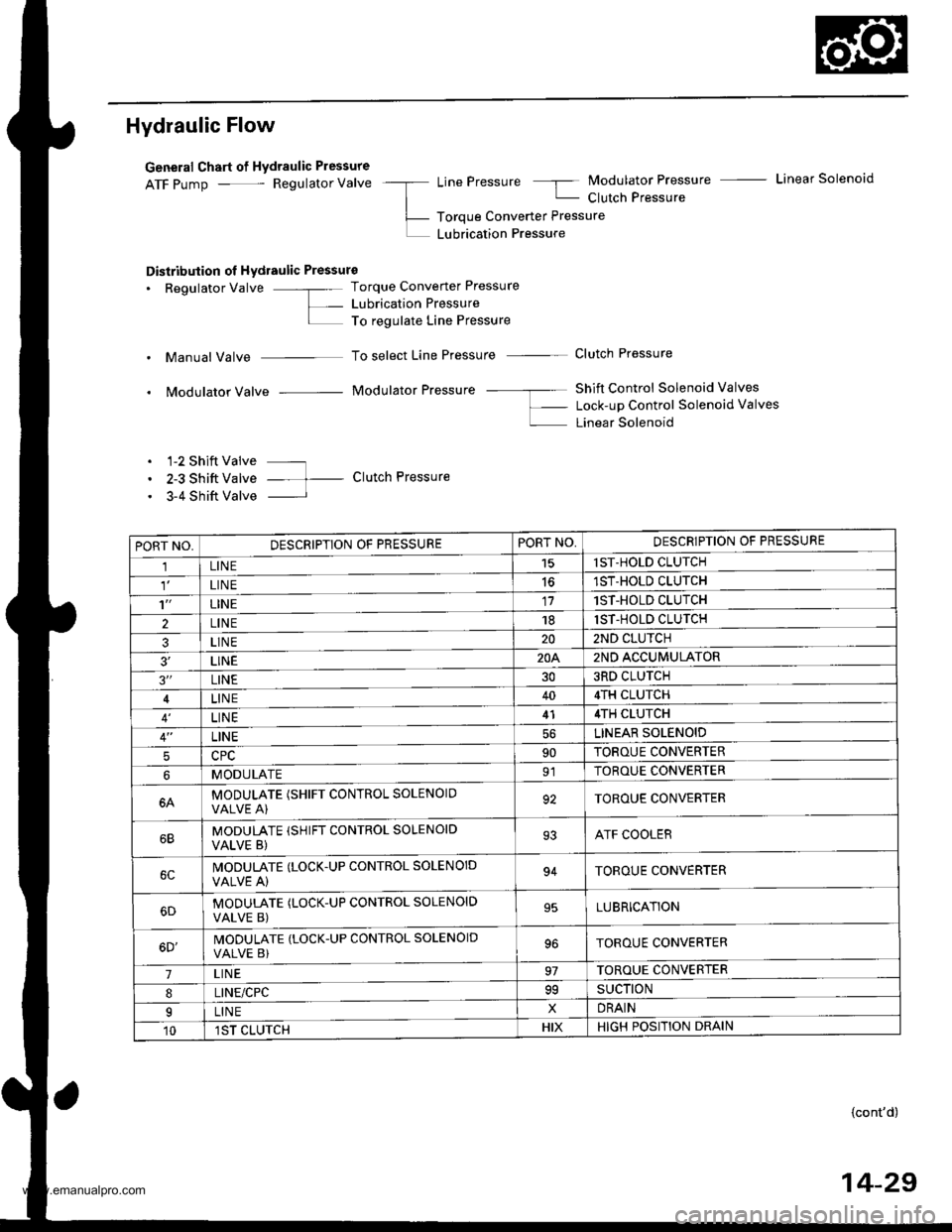
Hydraulic Flow
General Chart of Hydraulic Pressure
ATF pump - Regulator Valve -a LinePressure 5 Modulator Pressure - Linear Solenoid
| - Clutch Pressure
L- Toroue Converter Pressure
L LUbrication Pressure
Distribution ol Hydraulic Pressure
. Regulator Valve -"- Torque Converter Pressure
L- Lubrication PressureI To regulate Line Pressure
. Manual Valve To select Line Pressure - Clutch Pressure
. Modulator Valve Modulator Pressure -- ---- Shift Control Solenoid Valves
f- Lock-up Control Solenoid valves
L Linear Solenoid
. 1-2 Shift Valve ---
. 2-3 Shift Valve -- t- Clutch Pressure
. 3-4 Shift Valve I
PORT NO,DESCRIPTION OF PRESSUREPORT NO,DESCRIPTION OF PRESSURE
1LINE15lST-HOLD CLUTCH
LIN E1ST-HOLD CLUTCH
't'LINE171ST-HOLD CLUTCH
2LINE181ST-HOLD CLUTCH
3LINE202ND CLUTCH
3'�LINE20A2ND ACCUMULATOR
3"LINE303RD CLUTCH
LINE404TH CLUTCH
LINE414TH CLUTCH
LINELINEAR SOLENOID
590TOROUE CONVERTER
MODULATE91TOROUE CONVERTER
6AMODULATE (SHIFT CONTROL SOLENOIOVALVE A)92TOROUE CONVERTER
MODULATE (SHIFT CONTROL SOLENOID
VALVE B)93ATF COOLER
IVODULATE (LOCK.UP CONTROL SOLENOID
VALVE A)94TOROUE CONVERTER
MODUTATE (LOCK-UP CONTROL SOLENOID
VALVE B)95LUBRICATION
6D'MODULATE (LOCK-UP CONTROL SOLENOID
VALVE B)TOROUE CONVERTER
7LIN E97TOROUE CONVERTER
8LINE/CPC99SUCTION
ILINExDRAIN
101ST CLUTCHHIXHIGH POSITION DRAIN
{cont'd)
14-29
www.emanualpro.com
Page 546 of 1395
Description
Hydraulic Flow (cont'dl
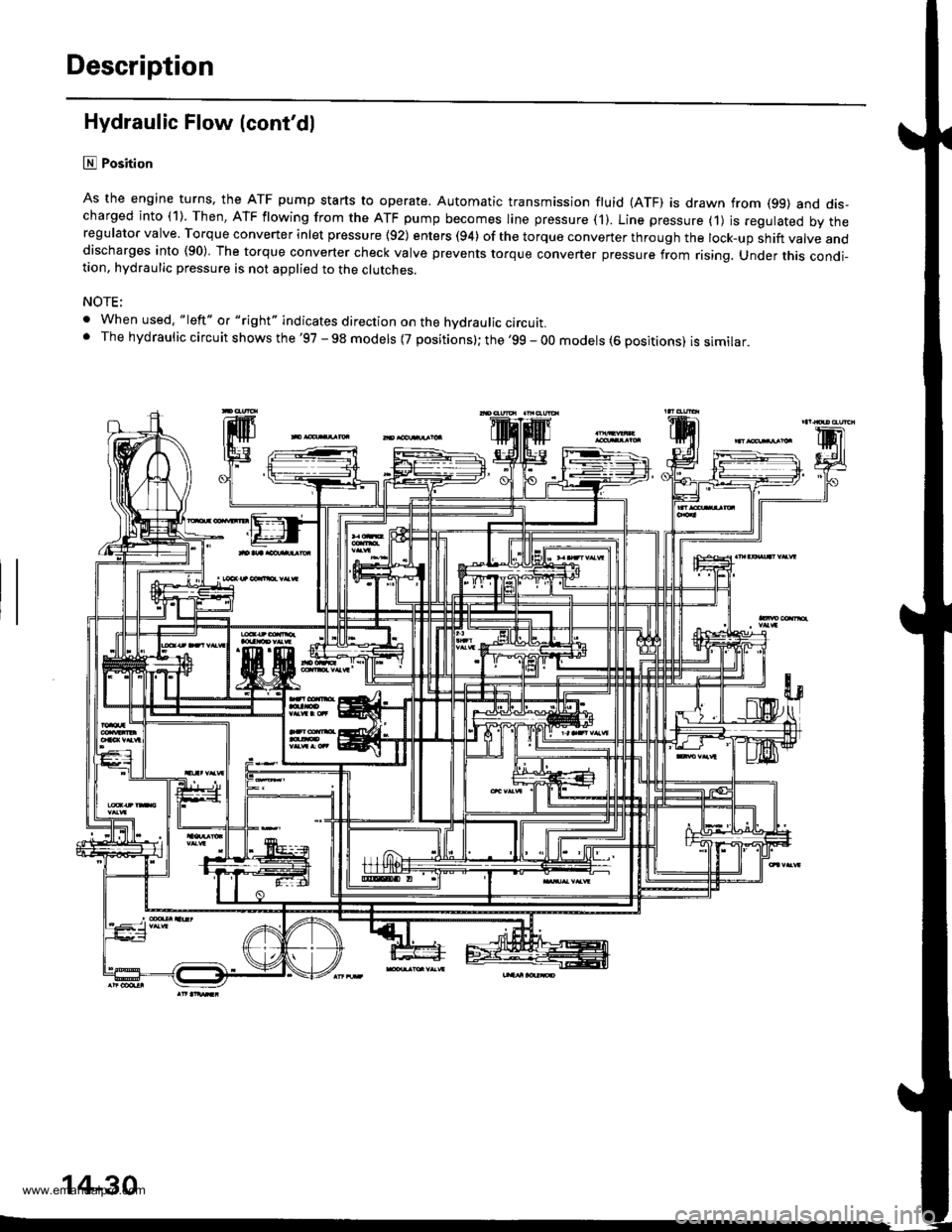
lll Position
As the engine turns, the ATF pump starts to operate. Automatic transmission fluid (ATF) is drawn from (99) and dis-charged into (1). Then, ATF flowing from the ATF pump becomes line pressure ('l). Line pressure (1) js regulated by theregulator valve. Torque converter inlet pressure {92) enters (94) of the torque conveTter through the lock-up shift valve anddischarges into (90) The torque converter check valve prevents torque converter pressure from rising. Under this condi-tion, hydraulic pressure is not applied to the clutches.
NOTE;
. When used. "|eft" o. "right" indicates direction on the hvdraulic circutt.. The hydraulic circuit shows the '97 - 98 models {7 positions}; the '99 - 00 models (6 positions) is similar.
'lF'.j.l
14-30
www.emanualpro.com
Page 557 of 1395
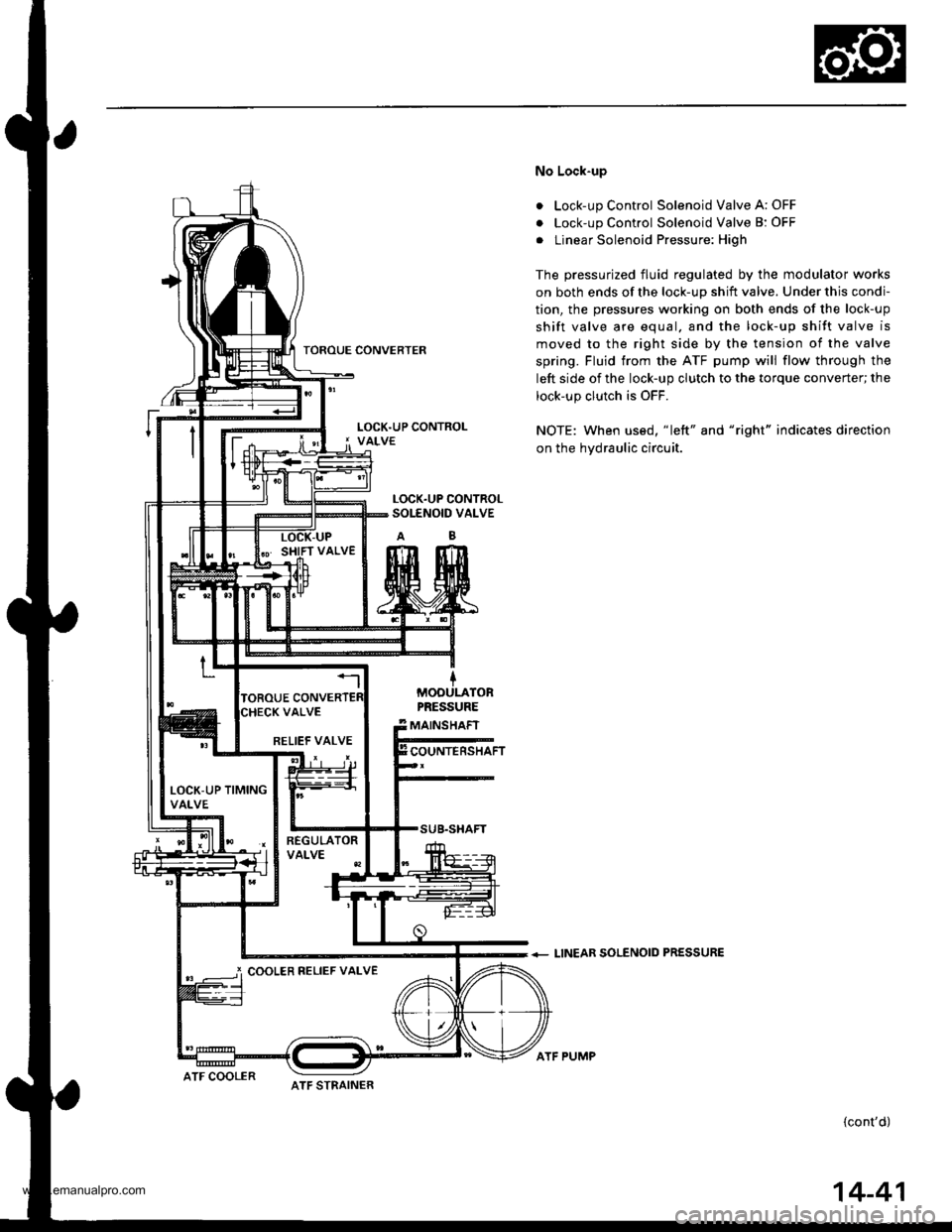
TOROUE CONVERTER
No Lock-up
. Lock-up Control Solenoid Valve A: OFF
. Lock-up Control Solenoid Valve B: OFF
. Linear Solenoid Pressure: High
The pressurized fluid regulated by the modulator works
on both ends of the lock-up shift valve. Under this condi-
tion, the pressures working on both ends of the lock-up
shift valve are equal. and the lock-up shift valve is
moved to the right side by the tension of the valve
spring. Fluid trom the ATF pump will flow through the
left side of the lock-up clutch to the torque converter; the
lock-up clutch is OFF.
NOTE: When us€d, "|eft" and "right" indicates direction
on the hydraulic circuit.
+ LINEAR SOLENOID PRESSURE
(cont'd)
LOCK.UP CONTROLSOI-ENOID VALVE
MOOULATORPRESSURE
MAINSHAFT
COUNTERSHAFTRELIEF VALVE
LOCK-UP TIMINGVALVE
i COOLER RELIEF VALVE
ATF STRAINERATF COOLER
ATF PUMP
14-41
www.emanualpro.com
Page 558 of 1395
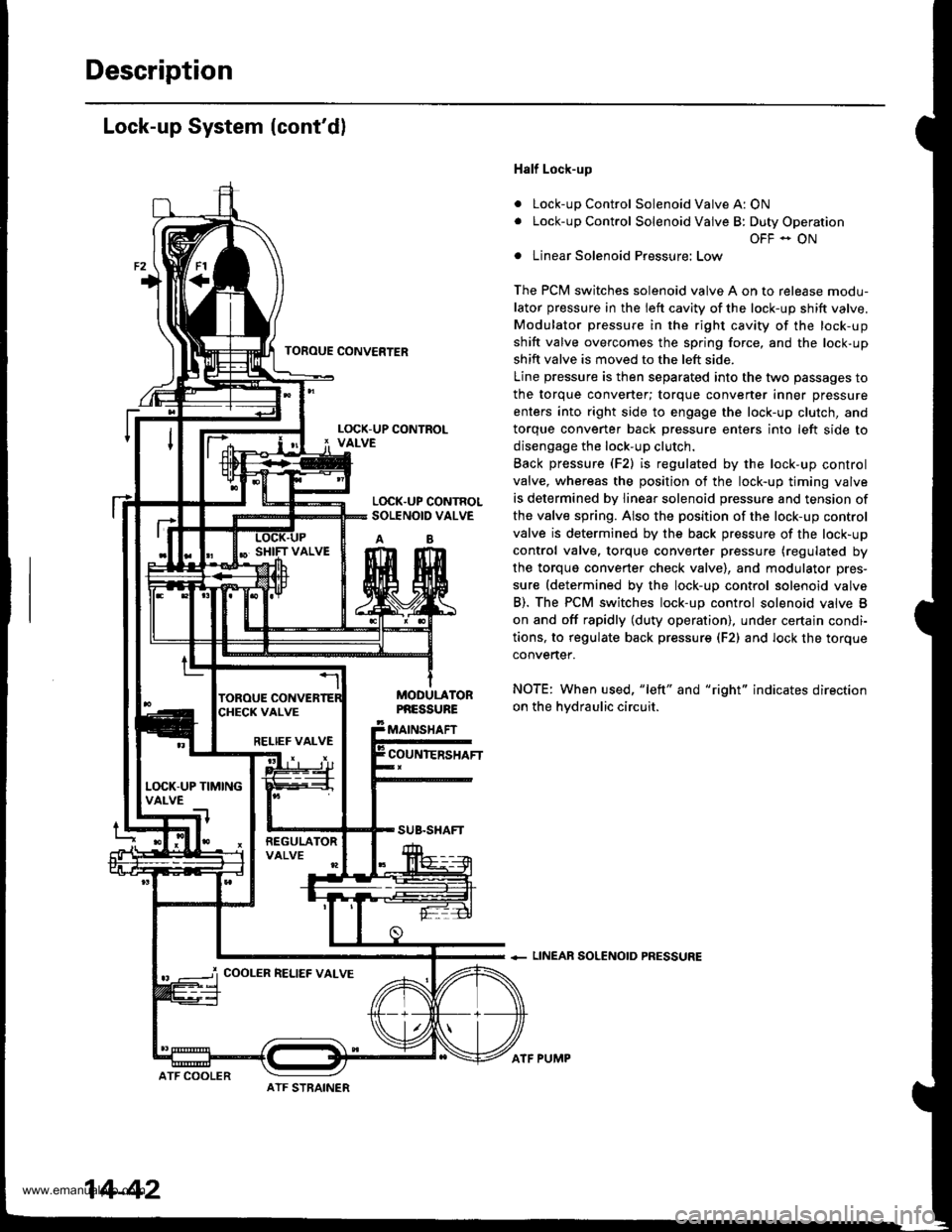
Description
Lock-up System (cont'dl
a
a
Half Lock-up
Lock-up Control Solenoid Valve A: ON
Lock-up Control Solenoid Valve B: Duty Operation
OFF - ON
Linear Solenoid Pressure: Low
The PCM switches solenoid valve A on to release modu-
lator pressure in the left cavity of the lock-up shift valve.
Modulator pressure in the right cavity of the lock-up
shift valve overcomes the spring force, and the lock-up
shift valve is moved to the left side.
Line pressure is then separated into the two passages to
the torque converter; torque converter inner pressure
enters into right side to engage the lock-up clutch, and
torque convener back Dressure enters into left side to
disengage the lock-up clutch.
Back pressure (F2) is regulated by the lock-up control
valve, whereas the position of the lock-up timing valve
is determined by linear solenoid pressure and tension of
the valve spring. Also the position of the lock-up control
valve is determined by the back pressure of the lock-up
control valve. torque converter pressure (regulated by
the torque converter check valve), and modulator pres-
sure (determined by the lock-up control solenoid valve
B). The PCM switches lock-up control solenoid valve B
on and off rapidly (duty operation), under certajn condi-
tions, to regulate back pressur€ (F2) and lock the torque
convertef.
NOTE: When used, "left" and "right" indicates direction
on the hvdraulic circuit.
+ LINEAR SOLENOID PRESSURE
TOFOUE CONVERTER
L(rcK.UP CONTROLSOLENOID VALVE
AB
MODULATORPNESSURE
MAINSHAFT
COUNIERSHAFTRELIEF VALVE
L(rcK-UP TIMINGVALVE
COOLER RELIEF VALVE
ATF STRAINER
14-42
ATF COOLER
ATF PUMP
www.emanualpro.com
Page 564 of 1395
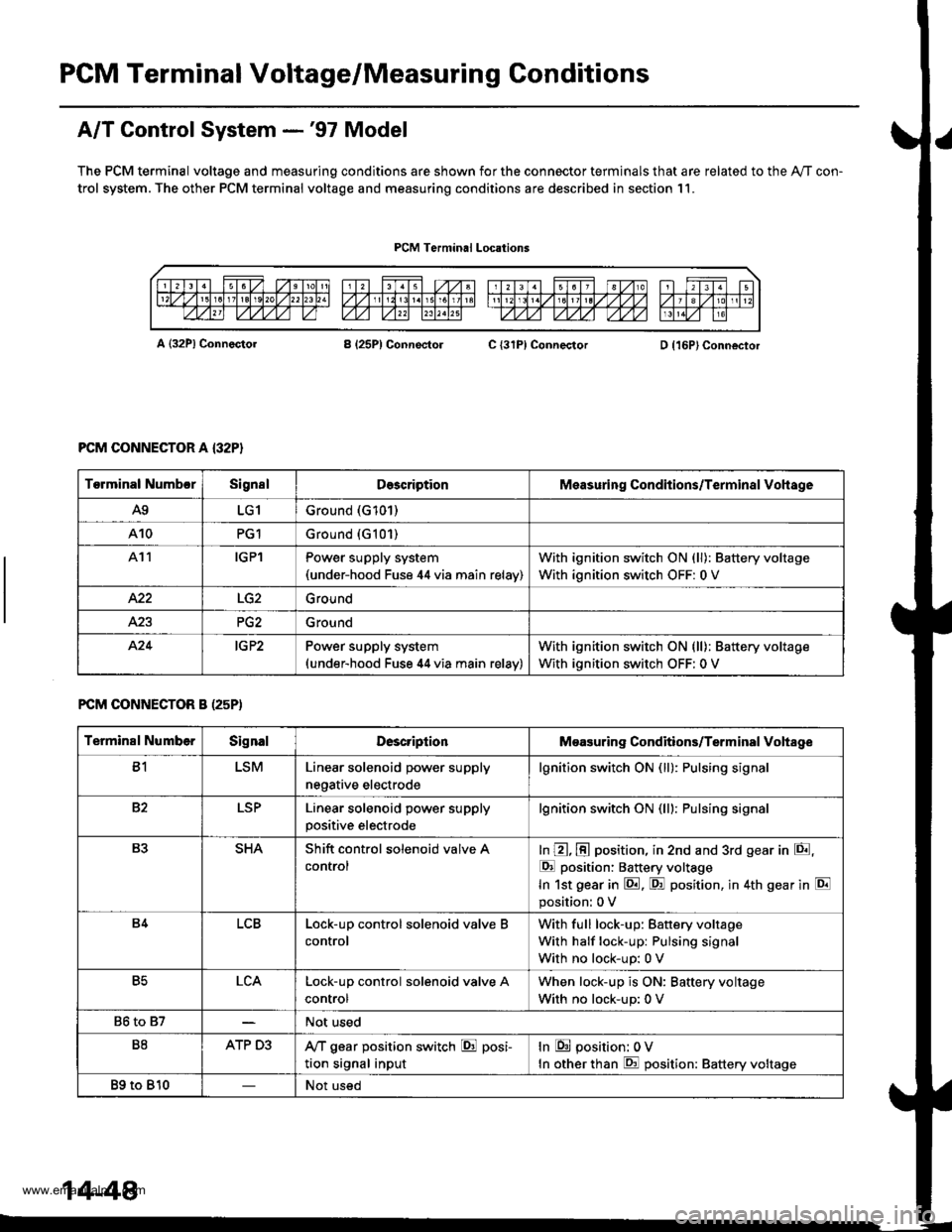
PGM Terminal Voltage/Measuring Conditions
A/T Control System -'97 Model
The PCM terminal voltage and measuring conditions are shown for the connector terminals that are related to the Ay'T con-
trol system. The other PCM terminal voltage and measuring conditions are described in section 11.
PCM Terminal Locations
A {32P} ConnectorB (25P1 ConnectolC {31PI ConnectorD {16P}Connector
PCM CONNECTOR A {32P}
FCM CONNECTOR B (25P)
Torminal NumbcrSignslDescriptionMeasuring Conditions/Terminal Vohage
A9LG1Ground (G101)
A10PG1Ground {G101)
At1IGPlPower supply system(under-hood Fuse 44 via main relav)
With ignition switch ON (ll): Battery voltage
With ignition switch OFF: 0 V
422Ground
Ground
424IG P2Power supply system(under-hood Fuse 44 via main relav)
With ignition switch ON (ll): Battery voltage
With ignition switch OFF: 0 V
Terminal NumberSignalDescriptionMeasuring Conditions/Terminal Vohage
B1LSMLinear solenoid power supply
negative electrode
lgnition switch ON (ll): Pulsing signa
82LSPLinear solenoid power supply
positive electrode
lgnition switch ON (lll: Pulsing signa
B3SHAShift control solenoid valve A
control
In @, @ position, in 2nd and 3rd gear in E,
E position: Battery voltage
In 1st gear in E. F! position, in 4th gear in E
position: 0 V
B4LCBLock-up control solenoid valve B
control
With full lock-up: Battery voltage
With half lock-up: Pulsing signal
With no lock-up: 0 V
B5LCALock-up control solenoid valve A
control
When lock-up is ON: Baftery voltage
With no lock-up: 0 V
86 to 87Not used
B8ATP D3,VT gear position switch E posi-
tion signal input
In E position: 0V
In other than E position: Battery voltage
89 to 810Not used
14-48
www.emanualpro.com