Pressure switch HONDA CR-V 1999 RD1-RD3 / 1.G Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HONDA, Model Year: 1999, Model line: CR-V, Model: HONDA CR-V 1999 RD1-RD3 / 1.GPages: 1395, PDF Size: 35.62 MB
Page 541 of 1395
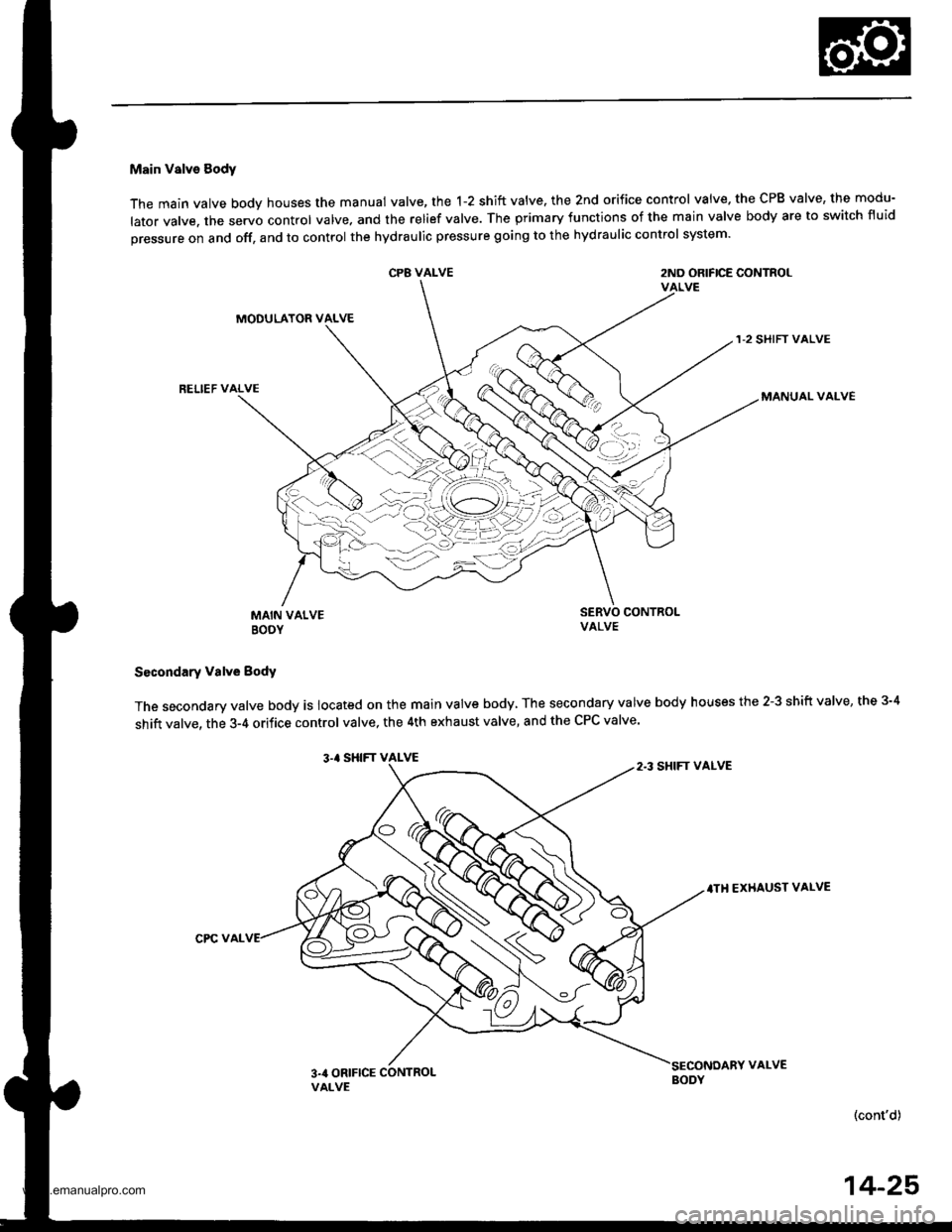
Main Valve Sody
The main valve body houses the manual valve, the 1-2 shift valve. the 2nd orifice control valve. the CPB valve, the modu-
lator valve. the servo control valve. and the relief valve. The primary functions of the main valve body are to switch fluid
pressure on and off, and to control the hydraulic pressure going to the hydraulic control system.
CP8 VALVE2ND ORIFICE CONTROLVALVE
MODULATOR VALVE
RELIEF VALVE
1-2 SHIFT VALVE
MANUAL VALVE
MAIN VALVEBOOY
SERVO CONTROI-VALVE
Secondary valve Body
The secondary valve body is located on the main valve body, The secondary valve body houses the 2-3 shift valve, the 3-4
shift valve, the 3-4 orifice control valve, the 4th exhaust valve, and the CPC valve'
3.' SHIFT VALVE
.TH EXHAUST VALVE
CPC VAL
(cont'd)
14-25
2.3 SHIFT VALVE
3na ORIFICE CONTROLVALVE
VALVE
www.emanualpro.com
Page 555 of 1395
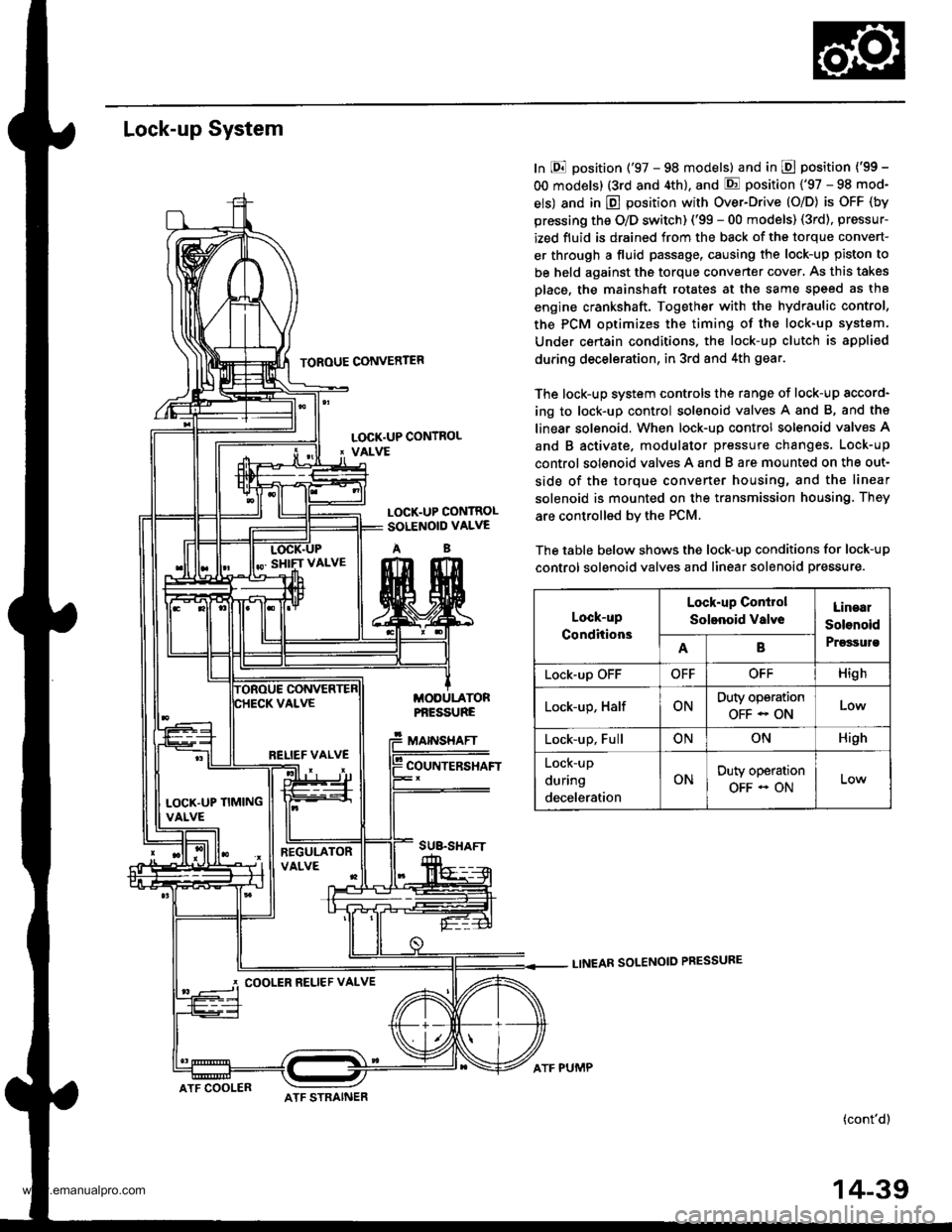
Lock-up System
TOROUE CONVERTER
In E position ('97 - 98 models) and in E position ('99 -
OO models) (3rd and 4th), and E position ('97 - 98 mod-
els) and in E position with Over-Drive (O/D) is OFF (by
pressing the O/D switch) ('99 - 00 models) (3rd), pressur-
ized fluid is drained from the back of the torque convert-
er through a fluid passage, causing the lock-up piston to
be held against the torque converter cover, As this takes
Dlace, the mainshaft rotates at the same speed as th8
engine crankshaft. Together with the hydraulic control,
the PCM optimizes the timing of the lock-up system.
Under certain condltions. the lock-up clutch is appli€d
during deceleration, in 3rd and 4th gear.
The lock-up system controls the range of lock-up sccord-
ing to lock-up control solenoid valves A and B, and ths
linear solenoid. When lock-up control solenoid valves A
and B activate. modulator pressure changes. Lock-up
control solenoid valves A and B are mounted on the out-
side of the torque converter housing, and the linear
solenoid is mounted on the transmission housing. They
are controlled bv the PCM.
The table below shows the lock-up conditions for lock-up
control solenoid valves and linear solenoid pressure.
LINEAR SOLENOID PRESSURE
(cont'd)
LOCK.UP CONTROL' VALVE
LOCK.UP CONTROLSOLENOID VALVE
AB
MODULATORPf,ESSURE
MAINSHAFT
COUNTERSHAFT
SUB.SHAFT
Lock-up
Conditions
Lock-up Conirol
Solenoid valveLinaal
Solenoid
PrgssulsAB
Lock-up OFFOFFOFFHigh
Lock-up, HalfONDuty operation
OFF - ONLow
Lock-up, FullONONHigh
Lock-up
during
deceleration
ONDuty operation
OFF - ON
RELIEF VALVE
LOCK'UP TIMINGVALVE
COOLER RELIEF VALVE
ATF COOLERATF STRAINER
ATF PUMP
14-39
www.emanualpro.com
Page 558 of 1395
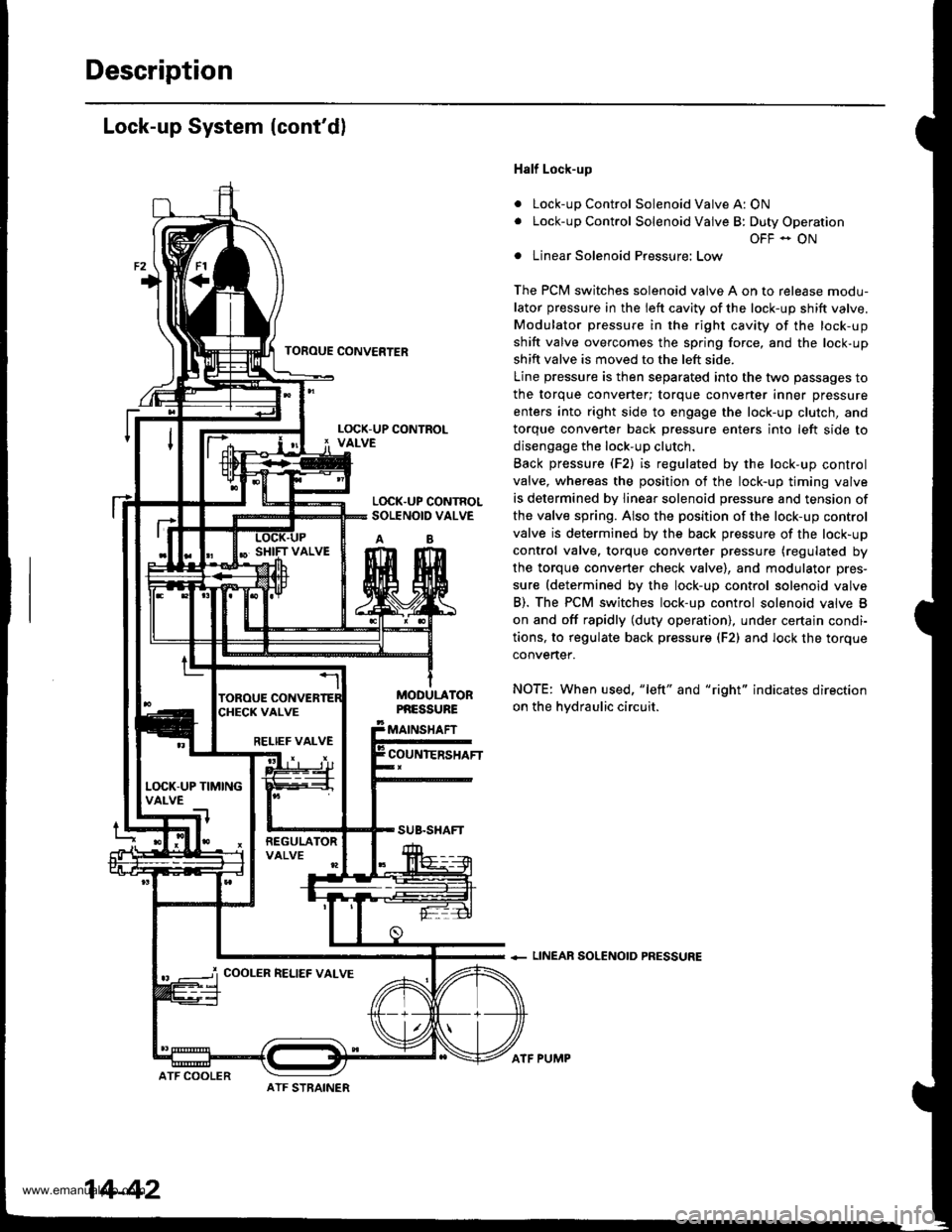
Description
Lock-up System (cont'dl
a
a
Half Lock-up
Lock-up Control Solenoid Valve A: ON
Lock-up Control Solenoid Valve B: Duty Operation
OFF - ON
Linear Solenoid Pressure: Low
The PCM switches solenoid valve A on to release modu-
lator pressure in the left cavity of the lock-up shift valve.
Modulator pressure in the right cavity of the lock-up
shift valve overcomes the spring force, and the lock-up
shift valve is moved to the left side.
Line pressure is then separated into the two passages to
the torque converter; torque converter inner pressure
enters into right side to engage the lock-up clutch, and
torque convener back Dressure enters into left side to
disengage the lock-up clutch.
Back pressure (F2) is regulated by the lock-up control
valve, whereas the position of the lock-up timing valve
is determined by linear solenoid pressure and tension of
the valve spring. Also the position of the lock-up control
valve is determined by the back pressure of the lock-up
control valve. torque converter pressure (regulated by
the torque converter check valve), and modulator pres-
sure (determined by the lock-up control solenoid valve
B). The PCM switches lock-up control solenoid valve B
on and off rapidly (duty operation), under certajn condi-
tions, to regulate back pressur€ (F2) and lock the torque
convertef.
NOTE: When used, "left" and "right" indicates direction
on the hvdraulic circuit.
+ LINEAR SOLENOID PRESSURE
TOFOUE CONVERTER
L(rcK.UP CONTROLSOLENOID VALVE
AB
MODULATORPNESSURE
MAINSHAFT
COUNIERSHAFTRELIEF VALVE
L(rcK-UP TIMINGVALVE
COOLER RELIEF VALVE
ATF STRAINER
14-42
ATF COOLER
ATF PUMP
www.emanualpro.com
Page 560 of 1395
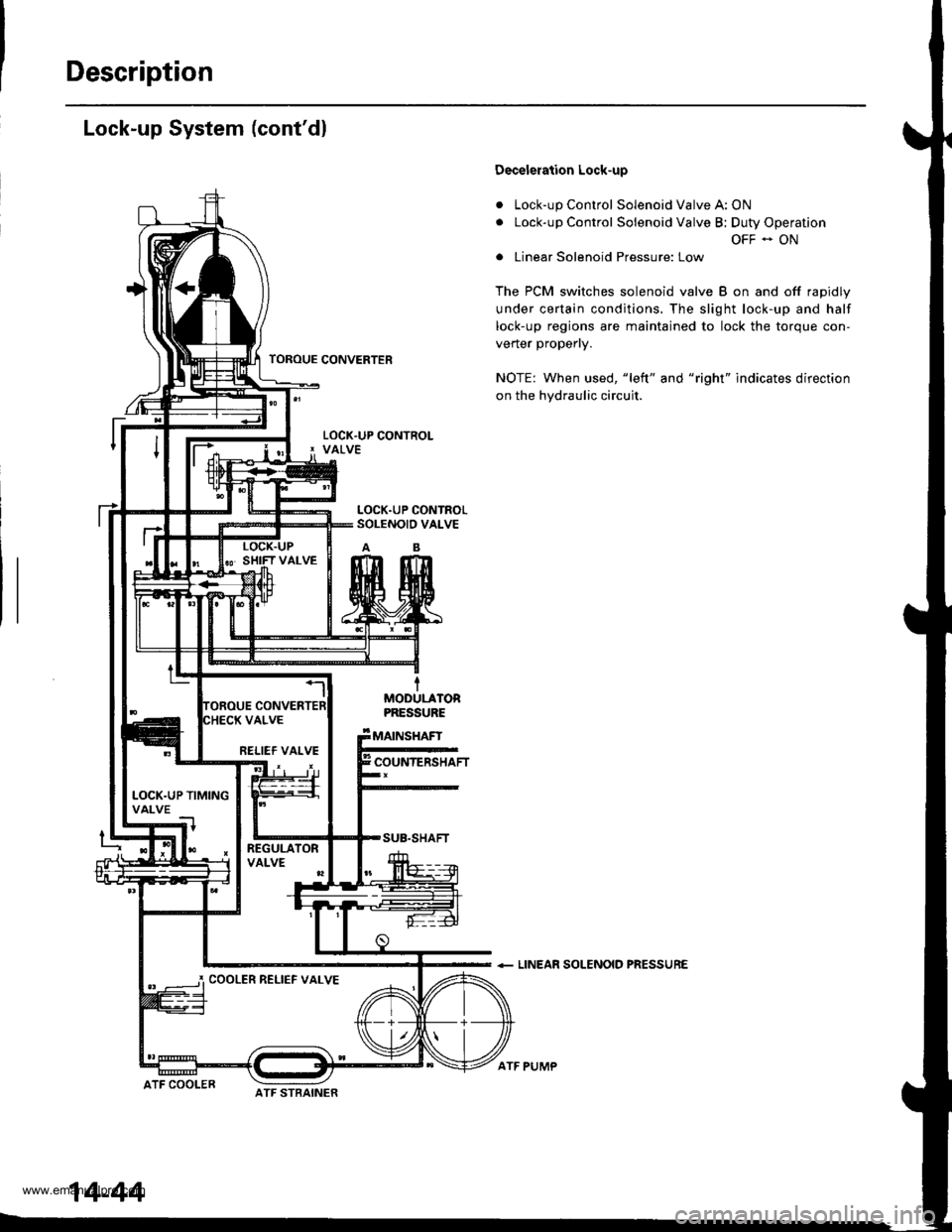
Description
Lock-up System (cont'dl
a
a
Decelelation Lock-up
Lock-up Control Solenoid Valve A: ON
Lock-up Control Solenoid Valve B; Duty Operation
OFF - ON
Linear Solenoid Pressure: Low
The PCM switches solenoid valve B on and off rapidly
under certain conditions. The slight lock-up and half
lock-up regions are maintained to lock the torque con-
vener propeny.
NOTE: When used, "left" and "right" indicates direction
on the hydraulic circuit.
+ LINEAR SOLENOID PRESSURE
TOROUE CONVERTER
tMOOULATORPRESSURE
MAINSHAFT
COUNTERSHAFT
SUB.SHAFT
ATF COOLER
RELIEF VALVE
LOCK.UP TIMINGVALVE
COOLER RELIEF VALVE
14-44
ATF STBAINER
ATF PUMP
www.emanualpro.com
Page 670 of 1395
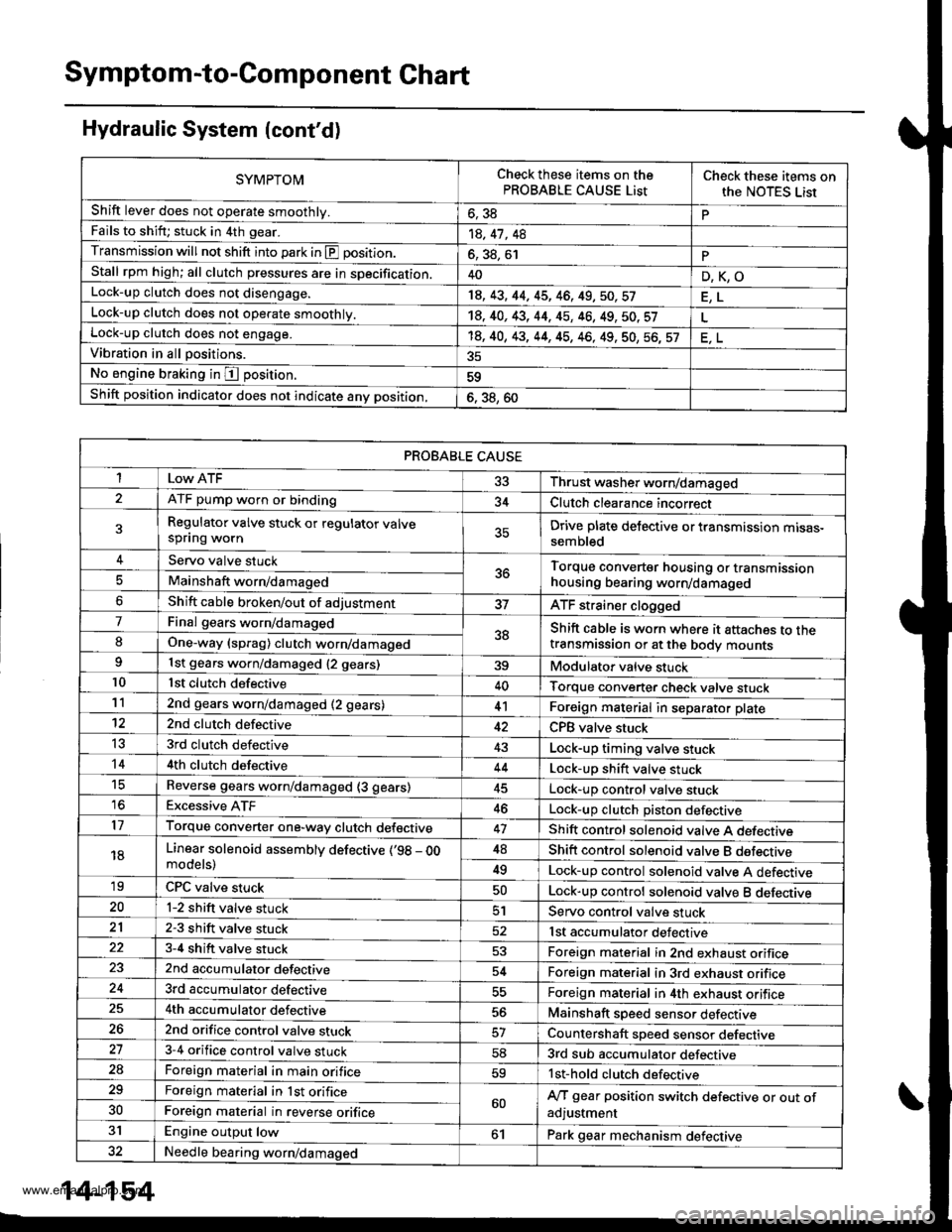
Symptom-to-Component Chart
Hydraulic System (cont'd)
SYMPTOMCheck these items on thePROBABLE CAUSE ListCheck these items onthe NOTES Lisr
Shift lever does not operate smoothly.o, JdPFails to shift; stuck in 4th gear.14, 41 , 48
Transmission will not shift into park in E position.6, 38, 61PStall rpm high; all clutch pressures are in specification.40D,K,OLock-up clutch does not disengage.18, 43, 44, 45, 46, 49,50,57
Lock-up clutch does not operate smoothly.14, 40, 43, 44, 45, 46, 49, 50. 57Lock-up clutch does not engage.'t8, 40, 43, 44, 45, 46, 49, 50, 56, 57Vibration in all positions.
No engine braking in I position.59
Shift position indicator does not indicate anv position,6. 38, 60
PROBABLE CAUSE
I 33 Thrust washer worn/damaged
ATF pump worn or binding34Clutch clearance incorrect
Regulator valve stuck or regulator valvespflng wornDrive plate delective or transmission mtsas-sembled
Servo valve stuck5ttTorque converter housing or transmissionhousing bearing worn/damagedMainshaft worn/damaged
Shift cable broken/out of adjustmentATF strainer clogged
7Final gears worn/damaged38Shift cable is worn where it attaches to thetransmission or at the body mountsIOne-way (sprag) clutch worn/damaged
1st gears worn/damaged {2 gears)39Modulator valve stuck10lst clutch defective40Torque converter check valve stuck112nd gears worn/damaged (2 gears)41Foreign material in separator plate't22nd clutch defectiveCPB valve stuck
t53rd clutch defective43Lock-up timing valve stuck144th clutch defective44Lock-up shift valve stucktcReverse gears worn/damaged (3 gears)Lock-up control valve stuck16Excessive ATF46Lock-up clutch Diston defective17Torque converter one-way clutch defective47Shift control solenoid valve A defecttve
18Linear solenoid assemblv defective (,98 - OOmodels)48Shift control solenoid valve B dsfectrve
49Lock-up control solenoid valve A defective'19CPC valve stuckLock-up control solenoid valve B deleqtve20l-2 shift valve stuck51Servo control valve stuck212-3 shift valve stuck52lst accumulator defective3-4 shift valve stuck53Foreign material in 2nd exhaust orifice2nd accumulator defective54Foreign material in 3rd exhaust orifice3rd accumulator defectiveForeign material in 4th exhaust orifice4th accumulator defective56Mainshaft speed sensor defective262nd orifice control valve stuckCountershaft speed sensor defective273-4 orifice control valve stuck583rd sub accumulator defective2aForeign material in main orifice59lst-hold clutch defective29Foreign material in lst orifice60A/T gear position switch defective or out ofadjustment30Foreign material in reverse orifice
31Engine output low61Park gear mechanism defective32Needle bearing worn/damaged
14-154
www.emanualpro.com
Page 675 of 1395

Stall Speed
Test
CAUTION:
. To prevent transmission damage, do not te3t stall speed for mors than 10 s€€onds at a time'
. Do not shift the lever while raising th€ engine spsed.
. Be sure to remove tho pressuro gauge bofore testing stall speed,
1. Before testing, check the transmission fluid level, s€e page 14-160.
2. Engage the parking brake and block all four wheels
3. Connect the tachometer, and start the engane.
4. Make sure the Ay'C switch is OFF
5. After the engine haswarmed upto normal operating temperature (the radiator fan comes on),shiftinto@ position.
6. Fully press the brake pedal and accelerator for 6 to 8 seconds, and note engine speed '
j. A|ow 2 minutes for cooling, then repeat the test in E, E ('97 - 98). E {'99 - 00}, and E positions. Stall speed should
be the same in E, E, E, tr. and E positions
Stall Speed rpm:
Specitication: 2,550 rpm
S€rvice Limit: ?,400 - 2.700 rpm
TROUBLEPROBAELE CAUSE
Stall rpm high in El, E, E, E and E
positions
ATF pump output is low
Clogged ATF strainer
Pressure regulator valve stuck closed
Slipping clutch
Stall rpm high in E positionSlippage of 1st clutch, 1st-hold clutch, or 1st gear one-way clutch
Stall rpm high in E positionSlippage of 2nd clutch
stall rpm high in E! or E positionSlippage of 1st clutch or 1st gear one-way clutch
Stall rpm high in E positionSlippage of 4th clutch
Stall rpm low in [dd, E. E, E, ana E
positions
. Engine output low
. Torque converter one-way clutch slipping
14-159
www.emanualpro.com
Page 679 of 1395
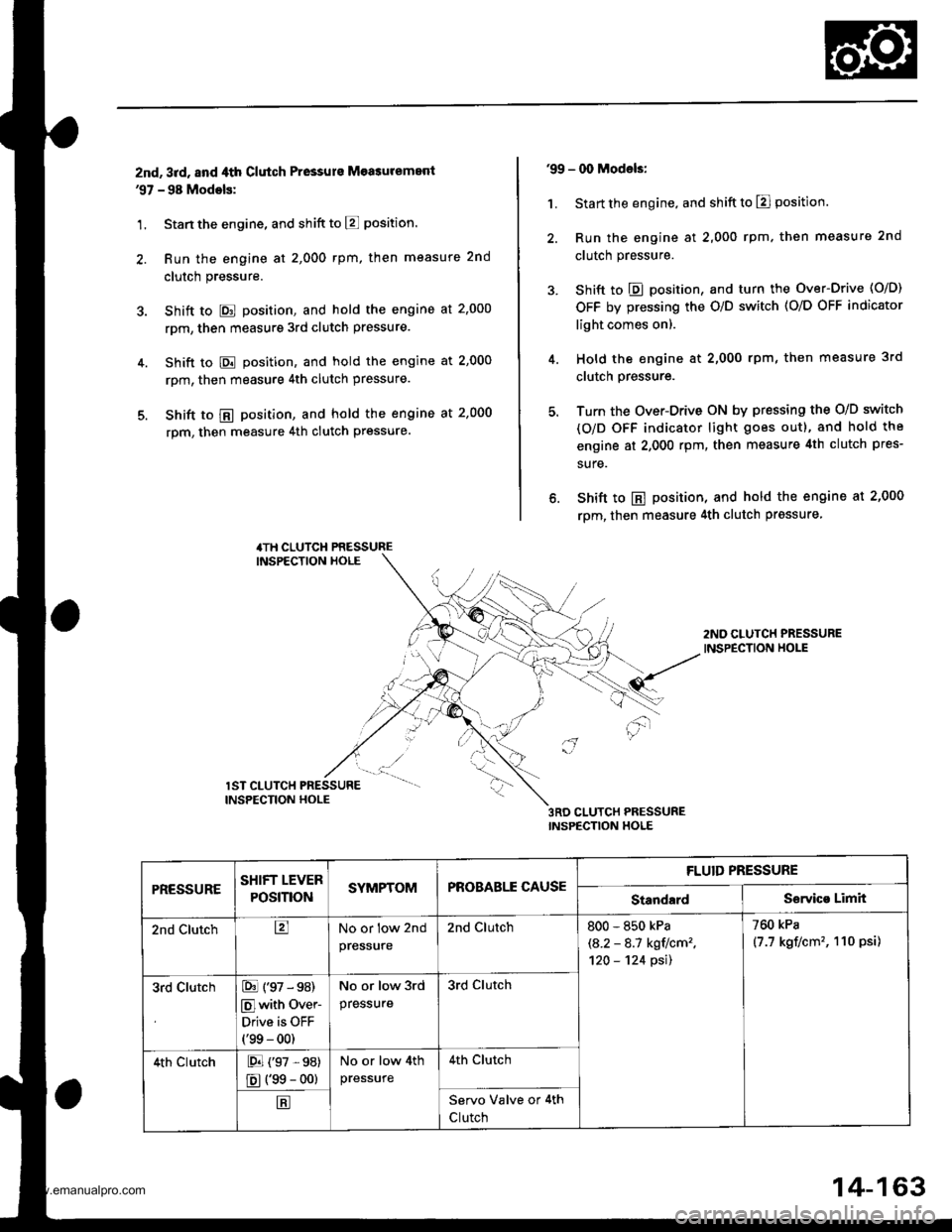
znd, 3rd, and ,lth Clutch Pressurs Measuremenl'97 - 98 Modols:
1. Stan the engine, and shift to E position.
2. Run the engine at 2,000 rpm, then measure 2nd
clutch pressure.
3. Shift to E position, and hold the engine at 2'000
rpm, then measure 3rd clutch pressure.
4. Shift to E position, and hold the engine at 2,000
rpm, then measure 4th clutch pressure.
5. Shift to @ position, and hold the engine at 2,000
rpm, then measure 4th clutch pressure.
4TH CLUTCH PRESSUREINSPECTION HOLE
'99 - 00 Models:
1. Start the engine, and shift to El position.
2. Run the engine at 2,000 rpm. then measure 2nd
clutch pressure.
3. Shift to E position, and turn the Over-Drive (O/D)
OFF by pressing the O/D switch (O/O OFF indicator
light comes on).
4. Hold the engine at 2,000 rpm, then measure 3rd
clutch Pressure.
5. Turn the Over-Drive ON by pressing the O/D switch
(O/D OFF indicator light goes out), and hold the
engine at 2,000 rpm, then measure 4th clutch pres-
sure.
6. Shift to E position, and hold the engine at 2,000
rpm, then measure 4th clutch prgssure
2ND CLUTCH PRESSUREINSPECTION HOLE
3RD CLUTCH PRESSUREINSPECTION HOLE
'"r.,-ur"" "..#
- -t"1' -.
INSPECTION HOLE
PRESSURESHIFT LEVER
POSmONSYMPTOMPROBABLE CAUSE
FLUID PRESSURE
StandardServico Limit
2nd ClutchtrNo or low 2nd
pres$ure
2nd Clutch800 - 850 kPa
\A.2 - 8.1 kgtlcm2,'120 - '124 psil
760 kPa
(7.7 kgf/cm'�, 110 psi)
3rd ClutchE (97 - s8)
Elwith Over-
Drive is OFF(99 - 00)
No or low 3rd
pressure
3rd clutch
4th clutchE (97 ,98)
E (99 - oo)
No or low 4th
pressure
4th Clutch
EServo Valve or 4th
Clutch
14-163
www.emanualpro.com
Page 794 of 1395

Description
Rear Differential
Outline
The Real-time 4WD-Dual Pump System model has a hydraulic clutch and a differential mechanism in the rear differential
assembly. Under normal conditions, the vehicle is driven by the front wheels. However, depending on to the driving force
of the front wheels and the road conditions. the system instantly transmits appropriate driving force to the rear wheels
without requiring the driver to switch between 2WD (tront wheel drive) and 4WD (four wheel drive). The switching mecha-
nism between 2WD and 4WD is integrated into the rear differential assembly to make the system light and compact.
ln addition, the dual-pump system switches off the rear-wheel-drive force when braking in a forward gear. This allows the
braking system to work properly on models equipped with an Anti-lock Braking System (ABS).
Construction
The rear differential assembly consists of the torque control differential case assembly and the rear differential carrier
assembly. The torque control differential case assembly consists of the differential clutch assembly, the companion
flange, and the oil pump body assembly. The rear differential carrier assembly consists of the differential mechanism. The
differential drive and driven gears are hypoid gears.
The oil pump body assembly consists of the front oil pump, the rear oil pump, the hydraulic control mechanism, and the
clutch piston. The clutch piston has a disc spring that constantly provides the differential clutch assembly with a preset
torque to Drevent abnormal sound.
The clutch guide in the differential clutch assembly is connected to the propeller shaft via the companion flange, and it
receives the driving force lrom the transfer assembly. The clutch guide rotates the clutch plate and the front oil pump in
the oil pump body.
The clutch hub in the differential clutch assembly has a clutch disc that is splined with the hypoid drive pinion gear. The
hypoid drive gear drives the rear oil pump.
The front and rear oil pumps are trochoidal pumps. The rear oil pump capacity is 2.5 percent larger that the front oil pump
to handle the rotation difference between the front and rear wheels caused by worn front tires and tight corner braking.
The oil pumps are designed so the fluid intake works as a fluid discharge when the oil pumps rotate in reverse. Genuine
Honda CVT fluid is used instead of differential fluid.
Operation
When there is a difference in rotation speed between the front wheels (clutch guide) and rear wheels (hypoid driven gear),
hydraulic pressure from the front and rear oil pumps engages the differential clutch, and drive force from the transler
assembly is applied to the rear wheels.
The hydraulic pressure control mechanism in the oil pump body selects 4WD mode when the vehicle is started abruptly,
or when accelerating in a forward or reverse gear (causing rotation difference between the front and rear wheels). or
when braking in reverse gear {when decelerating). lt switches to 2WD mode when the vehicle is driven at a constant speed
in forwar! or reverse gear (when there is no rotation difference between the front and rear wheels), or when braking in a
fo rwa rd gear (when decelerating).
To protect the system, the differential clutch assembly is lubricated by hydraulic pressure generated by the oil pumps in
both 4WD and 2WD modes. Also, the thermal switch relieves the hydraulic pressure on the clutch piston and cancels 4WD
mode if the temDerature of the differential fluid rises above normal.
www.emanualpro.com
Page 799 of 1395
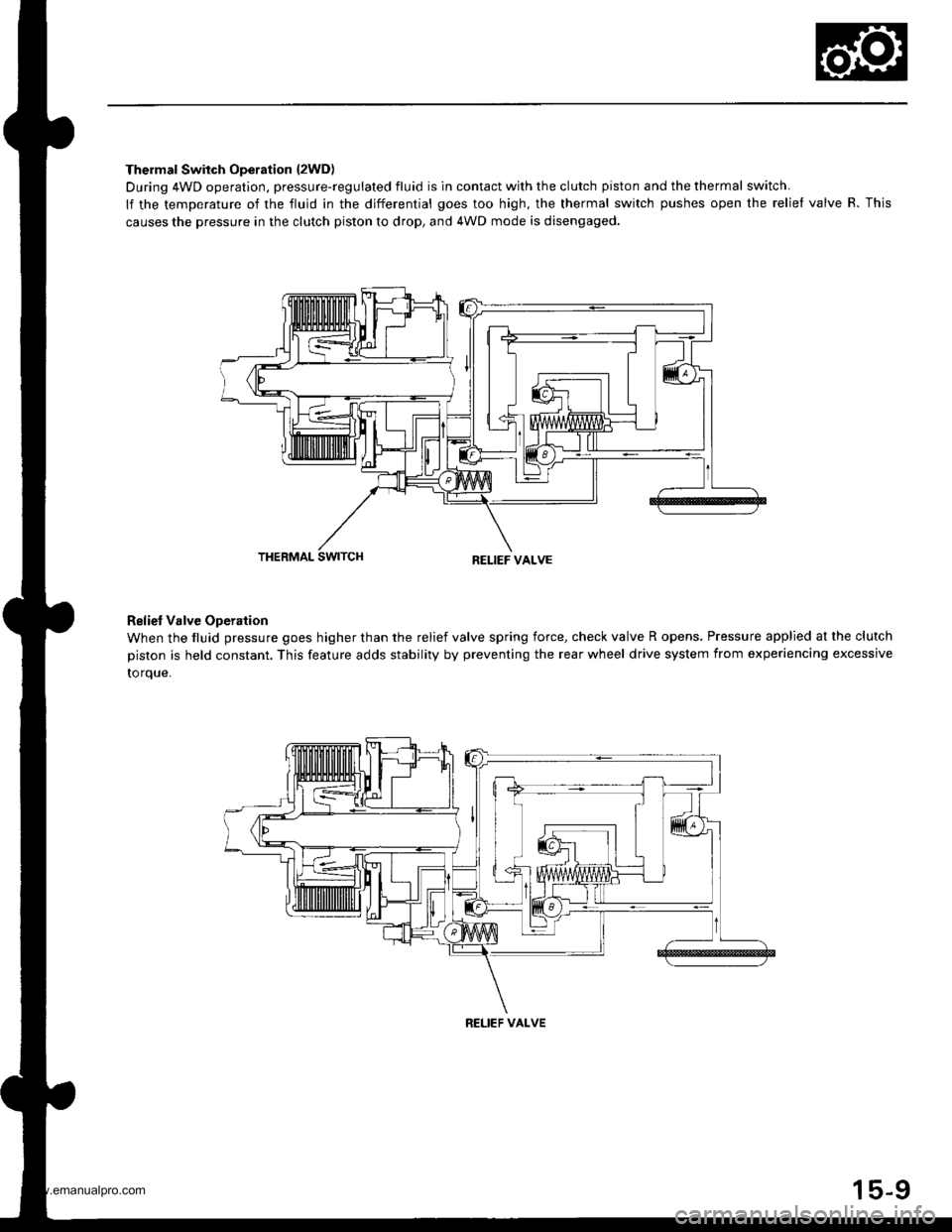
Thermal Switch Operation l2WD)
During 4WD operation, pressure-regulated fluid is in contact with the clutch piston and the thermal switch.
lf the temperature of the fluid in the differential goes too high, the thermal switch pushes open the relief valve R. This
causes the pressure in the clutch piston to drop, and 4WD mode is disengaged.
THERMAL SWITCHRELIEF VALVE
Reliet Valve Operation
When the fluid pressure goes higher than the relief valve spring force, check valve R opens. Pressure applied at the clutch
piston is held constant. This feature adds stability by preventing the rear wheel drive system from experiencing excessive
to rque.
RELIEF VALVE
15-9
www.emanualpro.com
Page 846 of 1395

Steering
Special Toofs ............. 17-2
Component Locations
Index ................ ....... 17-3
Troubleshooting
General Troubleshooting ................ 1 7-4
Noise and Vibration ......................... 17-8
Fluid Leaks ............. 17-10
Inspection and Adiustment
Steering Operation .......................... 17-12
Power Assist Check
With Vehicle Parked ....................
Steering Linkage and Gearbox .......
Pump Belt
Rack Guide Adjustment ...................
Fluid Rep|acement ...................,,.,....
Pump Pressure Check .................,,...
*Steering Wheel
Removal ................. 17-18
*Steering Column
Removal/lnstallation ................ ....... 17 -2O
lnspection .............. 17-21
Steering Lock Replacement ............ 17 -22
Power Steering Hoses, Lines
Ffuid Leakage Inspection ................. 17 -23
Repfacement .......... 17-23
Power Steering Pump
Repfacement .......... 17-24
Disassembly ...........17-25
fnspection .............. 17-26
Reassembly ............ 17-28
Power Steering Gearbox
Removal ................. 17-31
Disassembly ........... 17-34
Reassembly ............ 17-40
Ball Joint Boot Replacement .......... 17-50
Installation ............. 17-51
17-12
17-13
17-14
l7-15
17-15
17-16
Disassembly/Reassembly............... 17-18
4'%/b.......... -r'-7--a/
SUPPLEN\EN AL RES\RA(N SYSTES{ (SRS\
This model has an SRS which includes a driver's airbag in the steering wheel hub. a passenger's airbag in the dashboardabove the glove box ('97 - 00 models), and seat belt tensioners in the seat belt retractors ('98 - 00 models). Informationnecessary to safely service the SRS is included in this Service Manual. ltems marked with an asterisk (*) on the contentspage include, or are located near, SBS components. Servicing. disassembling or replacing these items will require specialprecautions and tools, and should only be done by an authorized Honda oearer.
To avoid rendering the SRS inoperative, which could lead to peFonal iniury or death in the event of a sevore trontalcollision. allSRS service work must be performod by an authorized Honda dealer.lmproper service procedurgs, including incorrect removal and installalion of the SRS, could lead to personal iniurycaused by unintontional deployment of th€ airbags {'97 - 00 models), and seat belt tensioners ('98 - 00 modelsl.Do not bump the SRS unit. Otherwise, the system may lail in case ot a collision, or the airbags may deploy when theignition switch is ON (lll.
SRS electrical wiring harnesses are identitied by yellow colof coding. Ralated components are located in the steeringcolumn, front console, dashboard, dashboard lower panel, and in the dashboard above the glove box. Do not use elec-trical test equipment on these cilcuits,
www.emanualpro.com