sensor HONDA CRV 2023 Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HONDA, Model Year: 2023, Model line: CRV, Model: HONDA CRV 2023Pages: 719, PDF Size: 13.43 MB
Page 36 of 719
35
Quick Reference Guide
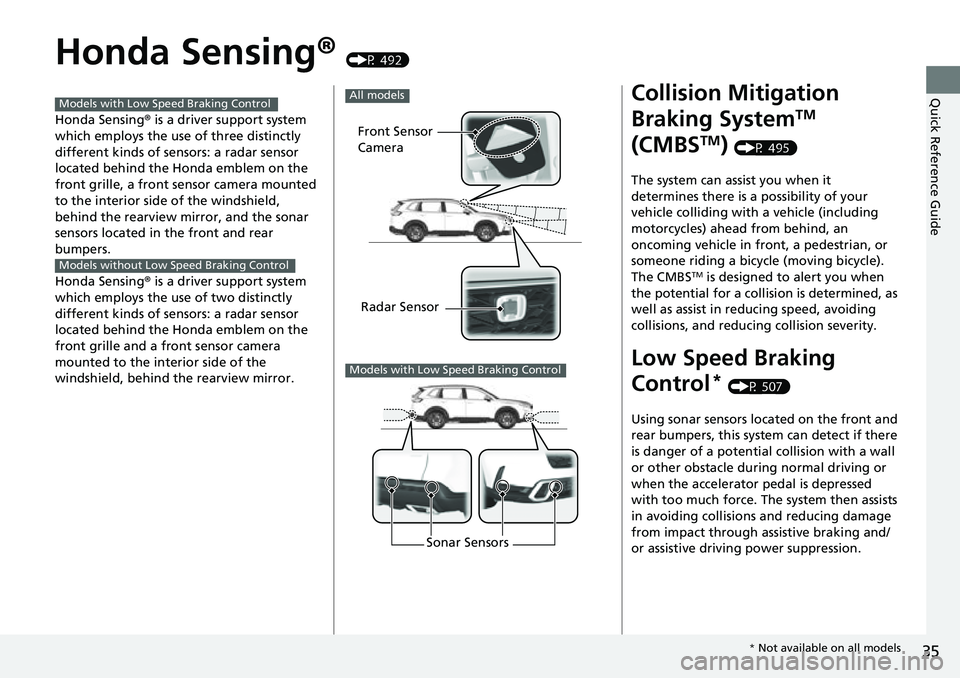
Honda Sensing® (P 492)
Honda Sensing ® is a driver support system
which employs the use of three distinctly
different kinds of sensors: a radar sensor
located behind the Honda emblem on the
front grille, a front sensor camera mounted
to the interior side of the windshield,
behind the rearview mirror, and the sonar
sensors located in the front and rear
bumpers.
Honda Sensing ® is a driver support system
which employs the use of two distinctly
different kinds of sensors: a radar sensor
located behind the Honda emblem on the
front grille and a front sensor camera
mounted to the interior side of the
windshield, behind the rearview mirror.
Models with Low Speed Braking Control
Models without Low Speed Braking Control
Front Sensor
Camera
Radar Sensor
All models
Models with Low Speed Braking Control
Sonar Sensors
Collision Mitigation
Braking System
TM
(CMBS
TM) (P 495)
The system can assist you when it
determines there is a possibility of your
vehicle colliding with a vehicle (including
motorcycles) ahead from behind, an
oncoming vehicle in front, a pedestrian, or
someone riding a bicycle (moving bicycle).
The CMBS
TM is designed to alert you when
the potential for a collision is determined, as
well as assist in reducing speed, avoiding
collisions, and reducing collision severity.
Low Speed Braking
Control
* (P 507)
Using sonar sensors located on the front and
rear bumpers, this system can detect if there
is danger of a potential collision with a wall
or other obstacle during normal driving or
when the accelerator pedal is depressed
with too much force. The system then assists
in avoiding collisions and reducing damage
from impact through assistive braking and/
or assistive driving power suppression.
* Not available on all models
Page 52 of 719

Continued51
uuSeat Belts uAbout Your Seat Belts
Safe Driving■Front seats
The seat belt system includes an indicator on
the instrument panel to remind the driver or a
front passenger or both to fasten their seat
belts.
If the power mode is set to ON and a seat belt
is not fastened, a beeper will sound and the
indicator will blink. After a few seconds, the
beeper will stop and the indicator will come
on and remain illuminated until the seat belt is
fastened.
The beeper will periodically sound and the
indicator will blink while the vehicle is moving
until the seat belt is fastened.
■Seat Belt Reminder1 Seat Belt Reminder
The indicator will also co me on if a front passenger
does not fasten their seat belt within six seconds after
the power mode is set to ON.
When no one is sitting in th e front passenger’s seat,
the indicator will not come on and the beeper will not
sound.
The indicator also may no t come on and the beeper
may not sound when the occupant is not heavy
enough to trigger the weight sensor. Such occupants
(e.g., infants and smaller children) should be moved
to the rear seat as a deploying front airbag likely will
injure or kill them.
2 Protecting Child Passengers P. 79
The driver information interface uses colors to aid the
driver in checking the st atus of the passengers.
For the front seating positions:
•Green indicates the seat belt is fastened.
•An unfastened gray graphic indicates the seat belt
is not fastened and an occupant has not been
detected.
•An unfastened red graphic i ndicates the seat belt is
unfastened and an occupa nt has been detected.
Page 61 of 719
60
uuAirbags uAirbag System Components
Safe Driving
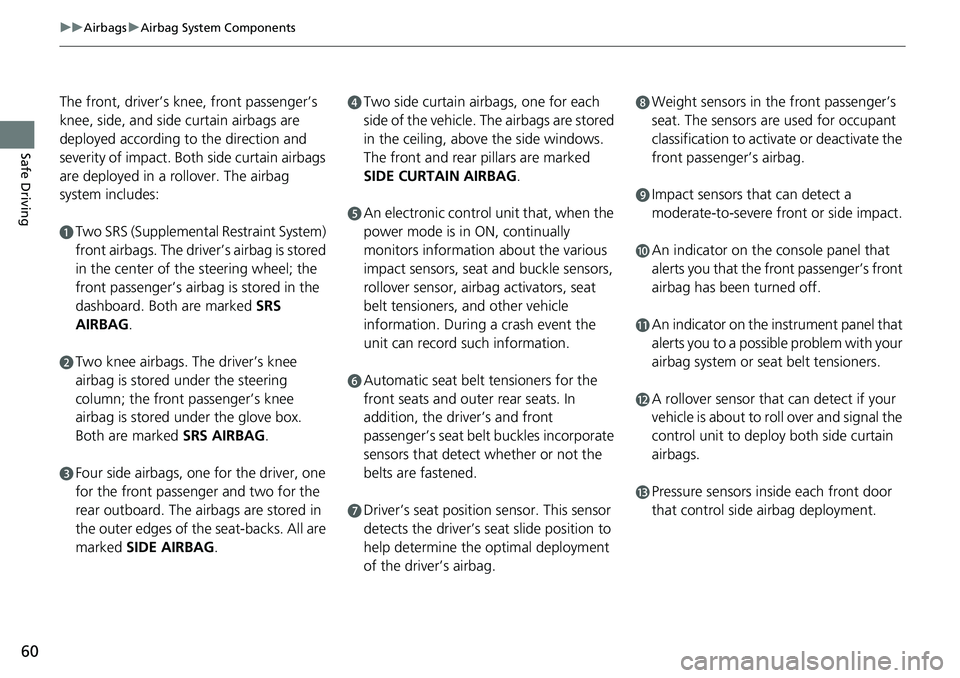
The front, driver’s knee, front passenger’s
knee, side, and side curtain airbags are
deployed according to the direction and
severity of impact. Both side curtain airbags
are deployed in a ro llover. The airbag
system includes:
aTwo SRS (Supplemental Restraint System)
front airbags. The driver’s airbag is stored
in the center of the steering wheel; the
front passenger’s airbag is stored in the
dashboard. Both are marked SRS
AIRBAG.
bTwo knee airbags. Th e driver’s knee
airbag is stored under the steering
column; the front passenger’s knee
airbag is stored under the glove box.
Both are marked SRS AIRBAG.
cFour side airbags, one for the driver, one
for the front passenger and two for the
rear outboard. The airbags are stored in
the outer edges of the seat-backs. All are
marked SIDE AIRBAG .
dTwo side curtain airbags, one for each
side of the vehicle. The airbags are stored
in the ceiling, above the side windows.
The front and rear pillars are marked
SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG .
eAn electronic control unit that, when the
power mode is in ON, continually
monitors information about the various
impact sensors, seat and buckle sensors,
rollover sensor, airbag activators, seat
belt tensioners, and other vehicle
information. During a crash event the
unit can record such information.
fAutomatic seat belt tensioners for the
front seats and outer rear seats. In
addition, the driver’s and front
passenger’s seat belt buckles incorporate
sensors that detect whether or not the
belts are fastened.
gDriver’s seat position sensor. This sensor
detects the driver’s seat slide position to
help determine the optimal deployment
of the driver’s airbag.
hWeight sensors in the front passenger’s
seat. The sensors are used for occupant
classification to activa te or deactivate the
front passenger’s airbag.
iImpact sensors that can detect a
moderate-to-severe front or side impact.
jAn indicator on the console panel that
alerts you that the front passenger’s front
airbag has been turned off.
kAn indicator on the instrument panel that
alerts you to a possib le problem with your
airbag system or seat belt tensioners.
lA rollover sensor that can detect if your
vehicle is about to roll over and signal the
control unit to deploy both side curtain
airbags.
mPressure sensors inside each front door
that control side airbag deployment.
Page 64 of 719

Continued63
uuAirbags uFront Airbags (SRS)
Safe DrivingFront airbags are designed to inflate duri ng moderate-to-severe frontal collisions.
When the vehicle decelerates suddenly, the sensors send information to the control
unit which signals one or both front airbags to inflate.
A frontal collision can be either head-on or angled between two vehicles, or when a
vehicle crashes into a stationary object, such as a concrete wall.
While your seat belt restrains your torso, the
front airbag provides supplemental protection
for your head and chest.
The front airbags deflate immediately so that
they won’t interfere with the driver’s visibility
or the ability to steer or operate other
controls.
The total time for inflation and deflation is so fast that most occupants are not
aware that the airbags deployed until th ey see them lying in front of them.
■Operation
■How the Front Airbags Work1How the Front Airbags Work
Although the driver’s and fr ont passenger’s airbags
normally inflate within a spli t second of each other, it
is possible for only one airbag to deploy. This can
happen if the severity of a collision is at the margin,
or threshold that determines whether or not the
airbags will deploy. In such cases, the seat belt will
provide sufficient protec tion, and the supplemental
protection offered by the airbag would be minimal.
Page 65 of 719

64
uuAirbags uFront Airbags (SRS)
Safe Driving
■When front airbags should not deploy
Minor frontal crashes: Front airbags were designed to supplement seat belts and
help save lives, not to prevent minor scrape s, or even broken bones that might occur
during a less than moderate-to-severe frontal crash.
Side impacts: Front airbags can provide protection when a sudden deceleration
causes a driver or front passenger to move toward the front of the vehicle. Side
airbags and side curtain airb ags have been specifically designed to help reduce the
severity of injuries that can occur during a moderate-to-severe side impact which
can cause the driver or passenger to move toward the side of the vehicle.
Rear impacts: Head restraints and seat belts are your best protection during a rear
impact. Front airbags cannot provide any si gnificant protection and are not designed
to deploy in such collisions.
Rollovers: In a rollover, your best form of protection is a seat belt or, if your vehicle
is equipped with a rollover sensor, both a se at belt and a side curtain airbag. Front
airbags, however, are not designed to deploy in a rollover as they would provide
little if any protection.
■When front airbags deploy with little or no visible damage
Because the airbag system senses sudden deceleration, a strong impact to the
vehicle framework or suspension might caus e one or more of the airbags to deploy.
Examples include running into a curb, the edge of a hole, or other low fixed object
that causes a sudden deceleration in th e vehicle chassis. Since the impact is
underneath the vehicle, damage may not be readily apparent.
■When front airbags may not deploy, even though exterior damage
appears severe
Since crushable body parts absorb crash energy during an impact, the amount of
visible damage does not always indicate proper airbag operation. In fact, some
collisions can result in severe damage but no airbag deployment because the airbags
would not have been needed or would not have provided protection even if they
had deployed.
Page 66 of 719
Continued65
uuAirbags uFront Airbags (SRS)
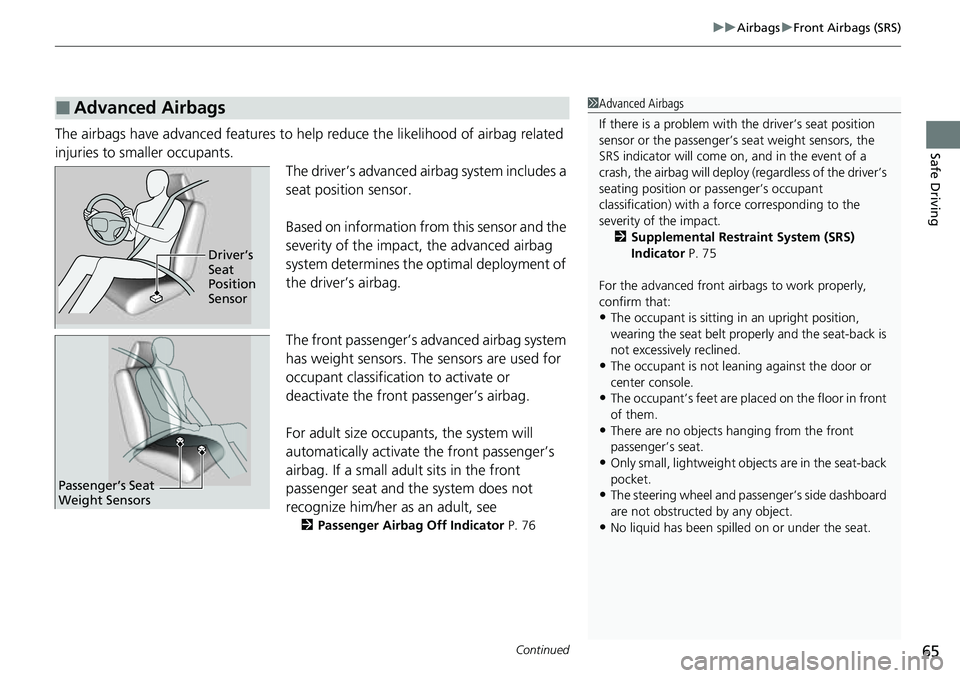
Safe DrivingThe airbags have advanced features to he lp reduce the likelihood of airbag related
injuries to smaller occupants. The driver’s advanced airbag system includes a
seat position sensor.
Based on information from this sensor and the
severity of the impact, the advanced airbag
system determines the optimal deployment of
the driver’s airbag.
The front passenger’s ad vanced airbag system
has weight sensors. The sensors are used for
occupant classification to activate or
deactivate the front passenger’s airbag.
For adult size occupant s, the system will
automatically activate the front passenger’s
airbag. If a small adult sits in the front
passenger seat and the system does not
recognize him/her as an adult, see
2 Passenger Airbag Off Indicator P. 76
■Advanced Airbags1Advanced Airbags
If there is a problem with the driver’s seat position
sensor or the passenger’s s eat weight sensors, the
SRS indicator will come on, and in the event of a
crash, the airbag will deploy (regardless of the driver’s
seating position or passenger’s occupant
classification) with a force corresponding to the
severity of the impact. 2 Supplemental Restraint System (SRS)
Indicator P. 75
For the advanced front airbags to work properly,
confirm that:
•The occupant is sitting in an upright position,
wearing the seat belt prope rly and the seat-back is
not excessively reclined.
•The occupant is not leaning against the door or
center console.
•The occupant’s feet are plac ed on the floor in front
of them.
•There are no objects ha nging from the front
passenger’s seat.
•Only small, lightweight objects are in the seat-back
pocket.
•The steering wheel and passenger’s side dashboard
are not obstructed by any object.
•No liquid has been spille d on or under the seat.
Driver’s
Seat
Position
Sensor
Passenger’s Seat
Weight Sensors
Page 67 of 719

uuAirbags uFront Airbags (SRS)
66
Safe Driving
We advise against allowing a child age 12 or under to ride in the front passenger’s
seat. However, if you do allow a small child or infant to ride in the front passenger’s
seat, the system is designed to automaticall y deactivate the front passenger’s airbag.
Do not let a small child or infant ride in the front passenger’s seat if the airbag does
not automatically deactivate.1 Advanced Airbags
•There is no child seat or other object pressing
against the rear of the seat or seat-back.
•There is no rear passenger pushing or pulling on
the back of the front passenger’s seat.
•There are no objects placed under or beside the
front passenger’s seat . Improperly positioned
objects can interfere with the advanced airbag
sensors.
•The head restraint is not contacting the roof.
2 Passenger Airbag Off Indicator P. 76
•The floor mat behind the front passenger’s seat is
set in the correct position evenly on the floor. An
improperly placed mat can interfere with the
advanced airbag sensors. 2Floor Mats P. 645
Page 71 of 719
70
uuAirbags uSide Airbags
Safe Driving
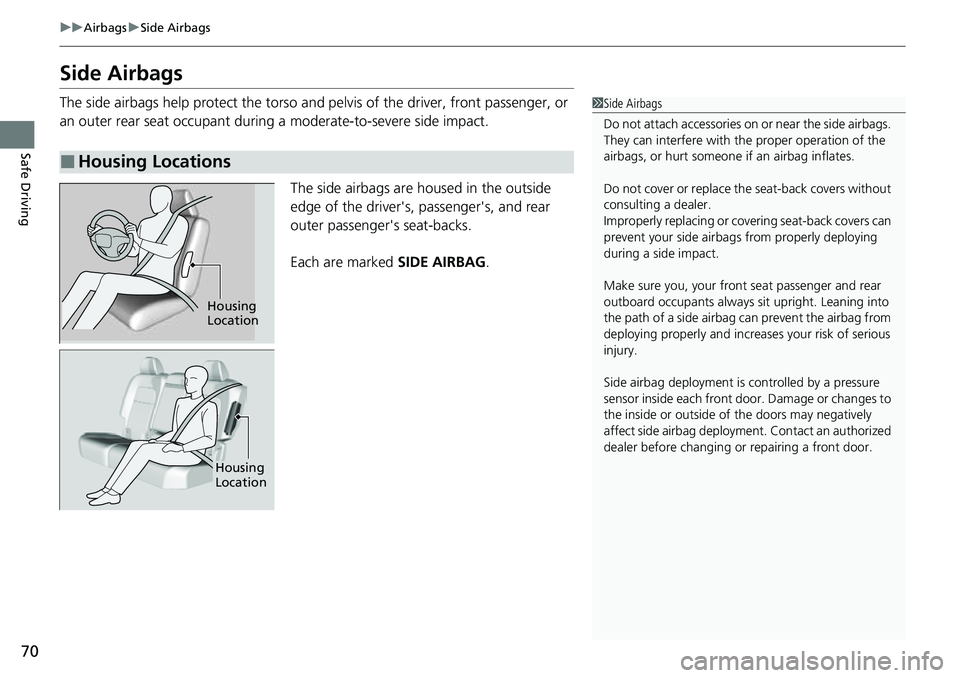
Side Airbags
The side airbags help protect the torso and pelvis of the driver, front passenger, or
an outer rear seat occupant during a moderate-to-severe side impact.
The side airbags are housed in the outside
edge of the driver's, passenger's, and rear
outer passenger's seat-backs.
Each are marked SIDE AIRBAG.
■Housing Locations
1Side Airbags
Do not attach accessories on or near the side airbags.
They can interfere with the proper operation of the
airbags, or hurt someone if an airbag inflates.
Do not cover or replace th e seat-back covers without
consulting a dealer.
Improperly replacing or covering seat-back covers can
prevent your side airbag s from properly deploying
during a side impact.
Make sure you, your front seat passenger and rear
outboard occupants always sit upright. Leaning into
the path of a side airbag can prevent the airbag from
deploying properly and increa ses your risk of serious
injury.
Side airbag deploy ment is controlled by a pressure
sensor inside each front door . Damage or changes to
the inside or outside of the doors may negatively
affect side airbag deployment. Contact an authorized
dealer before ch anging or repairing a front door.
Housing
Location
Housing
Location
Page 72 of 719

71
uuAirbags uSide Airbags
Continued
Safe DrivingWhen the sensors detect a moderate-to-
severe side impact, the control unit signals the
side airbag on the impact side to immediately
inflate.
■Operation
When
inflated
Side
Airbag
Side
Airbag
When
inflated
Page 73 of 719

72
uuAirbags uSide Airbags
Safe Driving
■When a side airbag deploys with little or no visible damage
Because the airbag system senses sudden acceleration, a strong impact to the side
of the vehicle’s framework can cause a side airbag to deploy. In such cases, there
may be little or no damage, but the side impact sensors detected a severe enough
impact to deploy the airbag.
■When a side airbag may not deploy, even though visible damage appears
severe
It is possible for a side airbag not to deploy during an impact that results in
apparently severe damage. This can occur when the point of impact was toward the
far front or rear of the vehicle, or when the vehicle’s crushable body parts absorbed
most of the crash energy. In either case , the side airbag would not have been
needed nor provided protection even if it had deployed.