fuel HONDA PRELUDE 1998 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HONDA, Model Year: 1998, Model line: PRELUDE, Model: HONDA PRELUDE 1998Pages: 278, PDF Size: 2.61 MB
Page 196 of 278
Tires
To safely operate your vehicle, your tires must be the proper type and
size, in good condition with adequate
tread, and correctly inflated. The
following pages give more detailed information on how and when to
check air pressure, how to inspect
your tires for damage and wear, and
what to do when your tires need to
be replaced.
Inflation
Keeping the tires properly inflated
provides the best combination of
handling, tread life and riding comfort. Underinflated tires wear
unevenly, adversely affect handlingand fuel economy, and are more
likely to fail from being overheated. Overinflated tires can make your
vehicle ride more harshly, are more prone to damage from road hazards,and wear unevenly.
We recommend that you visually check your tires every day. If you
think a tire might be low, check it immediately with a tire gauge.
Use a gauge to measure the air
pressure at least once a month. Even
tires that are in good condition may
lose one to two psi (10 to 20 kPa, 0.1
to 0.2 kgf/cm2) per month. Remember to check the spare tire at
the same time you check all the other tires. Check the pressure in the tires when
they are cold. This means the vehicle
has been parked for at least three
hours. If you have to drive the
vehicle before checking the tire pressure, the tires can still be
considered "cold" if you drive less
than 1 mile (1.6km).
If you check the pressure when the
tires are hot (the vehicle has been driven several miles), you will see
readings 4 to 6 psi (30 to 40 kPa, 0.3
to 0.4 kgf/cm2) higher than the cold
reading. This is normal. Do not let air out to match the specified cold
pressure. The tire will be
underinflated.
You should get your own tire pressure gauge and use it whenever
you check your tire pressures. This
will make it easier for you to tell if a pressure loss is due to a tire problemand not due to a variation between
gauges.
Maintenance
CONTINUED
Using tires that are excessively
worn or improperly inflated can
cause a crash in which you can
be seriously hurt or killed.
Follow all instructions in this
owner's manual regarding tire
inflation and maintenance.ProCarManuals.comMain Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 204 of 278
Lights
Headlight Aiming
The headlights were properly aimed
when your vehicle was new. You should check their aim if you
regularly carry heavy items in the
trunk or pull a trailer. Each headlight
assembly has horizontal and vertical
adjustment indicators. These are set to their "0" positions after the
headlights are aimed at the factory.
To check these settings:
1. Make sure the fuel tank is full. Park the vehicle on level ground.
2. The driver or someone who weighs the same should be sitting
in the driver's seat for all checks
and adjustments.Load the trunk with the items you
normally carry. If you usually pull a trailer, load it as
you would normally and attach it to the vehicle. Push down on the frontand rear bumpers several times tomake sure the vehicle is sitting
normally.
3. Open the hood.
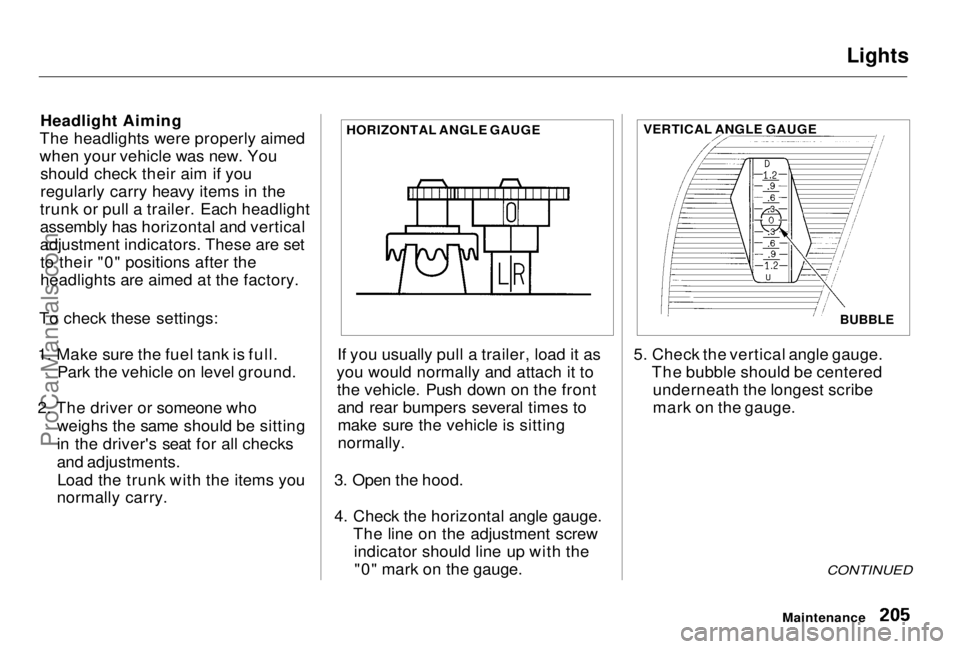
4. Check the horizontal angle gauge. The line on the adjustment screwindicator should line up with the"0" mark on the gauge. 5. Check the vertical angle gauge.
The bubble should be centeredunderneath the longest scribe
mark on the gauge.
CONTINUED
Maintenance
HORIZONTAL ANGLE GAUGE
BUBBLE
VERTICAL ANGLE GAUGEProCarManuals.comMain Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 216 of 278
Storing Your Vehicle
If you need to park your vehicle for
an extended period (more than one
month), there are several things you should do to prepare it for storage.
Proper preparation helps prevent
deterioration and makes it easier to
get your vehicle back on the road. If
possible, store your vehicle indoors. Fill the fuel tank.
Change the engine oil and filter
(see page 175). Wash and dry the exterior
completely.
Clean the interior. Make sure the
carpeting, floor mats, etc. are
completely dry.
Leave the parking brake off. Put
the transmission in Reverse (5- speed manual) or Park (automatic). Block the rear wheels. If the vehicle is to be stored for a
longer period, it should be supported on jackstands so the
tires are off the ground. Leave one window open slightly (if
the vehicle is being stored
indoors).
Disconnect the battery.
Support the front wiper blade
arms with a folded towel or rag so
they do not touch the windshield.
To minimize sticking, apply a silicone spray lubricant to all door
and trunk seals. Also, apply a
vehicle body wax to the painted surfaces that mate with the door
and trunk seals. Cover the vehicle with a
"breathable" vehicle cover, one
made from a porous material such as cotton. Nonporous materials,such as plastic sheeting, trap
moisture, which can damage the
paint. If possible, run the engine for a
while periodically (preferably once a month).
If you store your vehicle for 12
months or longer, have your Honda dealer perform the inspections called
for in the 24 months/30,000 miles (48,000 km) maintenance schedule
(Normal Conditions) as soon as you
take it out of storage (see page 164).
The replacements called for in the maintenance schedule are not
needed unless the vehicle hasactually reached that time or mileage.
MaintenanceProCarManuals.comMain Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 233 of 278
If Your Engine Won't Start, Jump Starting
The Starter Operates Normally In this case, the starter motor'sspeed sounds normal, or even faster
than normal, when you turn the
ignition switch to START (III), but
the engine does not run. Are you using the proper starting
procedure? Refer to Starting the
Engine on page 133.
Do you have fuel? Turn the
ignition switch to ON (II) for a
minute and watch the fuel gauge.
The low fuel level warning light
may not be working, so you were
not reminded to fill the tank.
There may be an electrical
problem, such as no power to the
fuel pump. Check all the fuses
(see page 245).
If you find nothing wrong, you will
need a qualified technician to find
the problem. See Towing on page
250. Jump Starting
If your vehicle's battery has rundown, you may be able to start the
engine by using a booster battery.
Although this seems like a simple procedure, you should take several
precautions.
You cannot start a Honda with an automatic transmission by pushing
or pulling it. To jump start your vehicle, follow
these directions closely:
1. Open the hood and check the physical condition of the battery(see page 190). In very cold
weather, check the condition of
the electrolyte. If it seems slushy or like ice, do not try jump starting
until it thaws.
If a battery sits in extreme cold, the
electrolyte inside can freeze.
Attempting to jump start with a frozen
battery can cause it to rupture.
2. Turn off all the electrical acces- sories: heater, A/C, stereo system,
lights, etc.
Put the transmission in Neutral or
Park and set the parking brake.
Taking Care of the Unexpected
NOTICE
A battery can explode if you do
not follow the correct procedure,
seriously injuring anyone nearby.
Keep all sparks, open flames,
and smoking materials away
from the battery.ProCarManuals.comMain Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 239 of 278
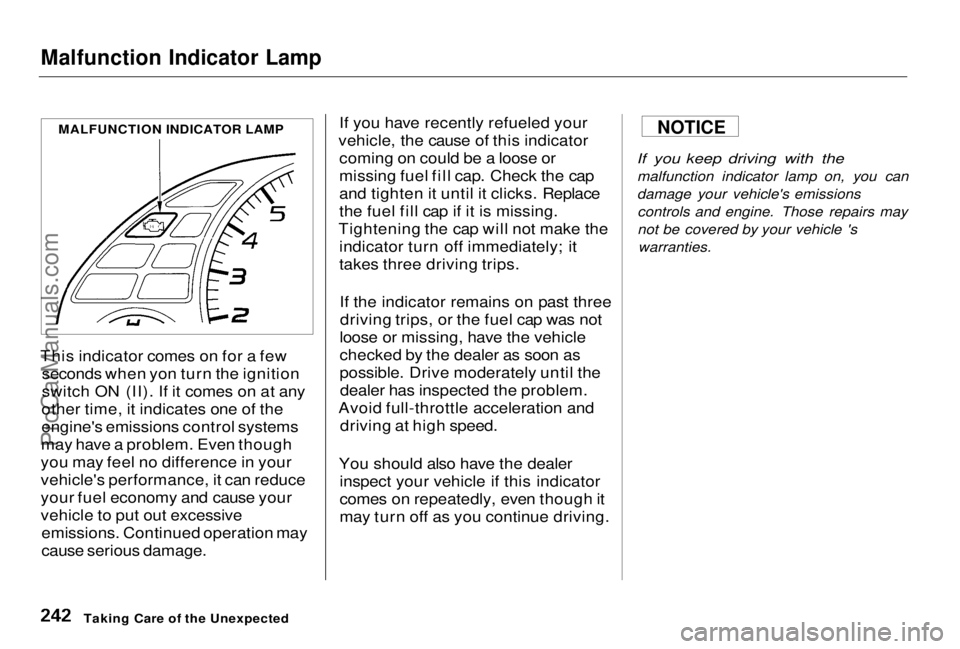
Malfunction Indicator Lamp
This indicator comes on for a few seconds when yon turn the ignition
switch ON (II). If it comes on at any
other time, it indicates one of the
engine's emissions control systems
may have a problem. Even though
you may feel no difference in your
vehicle's performance, it can reduce
your fuel economy and cause your
vehicle to put out excessive emissions. Continued operation may
cause serious damage. If you have recently refueled your
vehicle, the cause of this indicator coming on could be a loose or
missing fuel fill cap. Check the cap
and tighten it until it clicks. Replace
the fuel fill cap if it is missing.
Tightening the cap will not make the indicator turn off immediately; it
takes three driving trips.
If the indicator remains on past threedriving trips, or the fuel cap was not
loose or missing, have the vehicle
checked by the dealer as soon as
possible. Drive moderately until the dealer has inspected the problem.
Avoid full-throttle acceleration and driving at high speed.
You should also have the dealer inspect your vehicle if this indicator
comes on repeatedly, even though it
may turn off as you continue driving.If you keep driving with the
malfunction indicator lamp on, you can
damage your vehicle's emissionscontrols and engine. Those repairs may
not be covered by your vehicle 's warranties.
Taking Care of the Unexpected
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP
NOTICE
ProCarManuals.comMain Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 248 of 278
Technical Information
The diagrams in this section give you the dimensions and capacities of
your Honda, and the locations of the identification numbers. The expla-
nations of several electronic and mechanical systems on your Honda
are for the more technically-oriented
owner. Identification Numbers................. 252
Specifications................................. 254
Tire Information............................ 256 Tire Size Designation................ 256
Wheel Size Designation............ 256
Tire Speed Ratings.................... 256 Tire Pressure Adjustment For High Speed Driving........ 257
DOT Tire Quality Grading....... 257 Treadwear.............................. 257
Traction.................................. 258
Temperature.......................... 258 Oxygenated Fuels.......................... 259
Driving in Foreign Countries....... 260
Emissions Controls........................ 261
The Clean Air Act...................... 261Crankcase Emissions Control System..................................... 261
Evaporative Emissions Control System..................................... 261
Exhaust Emissions Controls.... 262 PGM-FI System..................... 262
Ignition Timing ControlSystem................................. 262
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System.................... 262
Three Way Catalytic
Converter............................ 262
Replacement Parts..................... 262
Three Way Catalytic Converter... 263
Technical InformationProCarManuals.comMain Menu s t
Page 256 of 278
Oxygenated Fuels
Some conventional gasolines are
being blended with alcohol or an
ether compound. These gasolines
are collectively referred to as
oxygenated fuels. To meet clean air
standards, some areas of the United
States and Canada use oxygenated
fuels to help reduce emissions.
If you use an oxygenated fuel, be
sure it is unleaded and meets the
minimum octane rating requirement.
Before using an oxygenated fuel, try
to confirm the fuel's contents. Some
states/provinces require this
information to be posted on the
pump.
The following are the EPA-approved
percentages of oxygenates:
ETHANOL (ethyl or grain alcohol)
You may use gasoline containing up to 10 percent ethanol by volume.Gasoline containing ethanol may be
marketed under the name "Gasohol."
MTBE (Methyl Tertiary Butyl Ether)
You may use gasoline containing up to 15 percent MTBE by volume.
METHANOL (methyl or wood
alcohol)
You may use gasoline containing up to 5 percent methanol by volume as
long as it also contains cosolvents and corrosion inhibitors to protect
the fuel system. Gasoline containing more than 5 percent methanol by
volume may cause starting and/or performance problems. It may alsodamage metal, rubber and plastic
parts of your fuel system. If you notice any undesirable
operating symptoms, try another
service station or switch to another
brand of gasoline.
Fuel system damage or performance
problems resulting from the use ofan oxygenated fuel containing more
than the percentages of oxygenates
given above are not covered under
warranty.
Technical InformationProCarManuals.comMain Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 257 of 278

Driving in Foreign Countries
If you are planning to take your
Honda outside the U.S. or Canada,
contact the tourist bureaus in theareas you will be traveling in to find
out about the availability of unleaded
gasoline with the proper octane
rating.
If unleaded gasoline is not available,
be aware that using leaded gasoline in your Honda will affect perfor-
mance and fuel mileage, and damage
its emissions controls. It will no
longer comply with U.S. andCanadian emissions regulations, and
will be illegal to operate in North
America. To bring your vehicle back into compliance will require the re-
placement of several components, such as the oxygen sensors and the
three way catalytic converter. These replacements are not covered under
warranty.
Technical InformationProCarManuals.comMain Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 258 of 278

Emissions Controls
The burning of gasoline in your vehicle's engine produces several by-products. Some of these are carbon
monoxide (CO), oxides of nitrogen (NOx) and hydrocarbons (HC).
Gasoline evaporating from the tank
also produces hydrocarbons. Con-
trolling the production of NOx, CO, and HC is important to the environ-
ment. Under certain conditions of sunlight and climate, NOx and HC
react to form photochemical "smog." Carbon monoxide does not contri-
bute to smog creation, but it is a
poisonous gas. The Clean Air Act
The United States Clean Air Act* sets standards for automobile
emissions. It also requires that
automobile manufacturers explain to
owners how their emissions controls
work and what to do to maintain them. This section summarizes how
the emissions controls work.Scheduled maintenance is on page 164.
* In Canada, Honda vehicles comply
with the Canadian Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (CMVSS) forEmissions valid at the time they are
manufactured. Crankcase Emissions Control
System
Your vehicle has a Positive Crankcase Ventilation System. This
keeps gasses that build up in the engine's crankcase from going into
the atmosphere. The Positive Crank- case Ventilation valve routes them
from the crankcase back to the intake manifold. They are thendrawn into the engine and burned.
Evaporative Emissions Control
System
As gasoline evaporates in the fuel tank, an evaporative emissions
control canister filled with charcoaladsorbs the vapor. It is stored in this
canister while the engine is off. After
the engine is started and warmed up,
the vapor is drawn into the engine and burned during driving.
Technical InformationProCarManuals.comMain Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 259 of 278
Emissions Controls
Exhaust Emissions Controls
The exhaust emissions controls include four systems: PGM-FI,
Ignition Timing Control, ExhaustGas Recirculation and Three Way
Catalytic Converter. These four
systems work together to control the
engine's combustion and minimize
the amount of HC, CO, and NOx that comes out the tailpipe. The exhaust
emissions control systems are
separate from the crankcase and
evaporative emissions control
systems.
PGM-FI System
The PGM-FI System uses sequential multiport fuel injection.
It has three subsystems: Air Intake,
Engine Control, and Fuel Control.
The Engine Control Module (ECM) uses various sensors to determine
how much air is going into the engine. It then controls how much
fuel to inject under all operating conditions. Ignition Timing Control System
This system constantly adjusts the ignition timing, reducing the amount
of HC, CO and NOx produced.
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
System
The Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system takes some of the
exhaust gas and routes it back into
the intake manifold. Adding exhaust
gas to the air/fuel mixture reduces the amount of NOx produced when
the fuel is burned.
Three Way Catalytic Converter
The three way catalytic converter is in the exhaust system. Through
chemical reactions, it converts HC,CO, and NOx in the engine's exhaust
to carbon dioxide (C02), dinitrogen
(
N2), and water vapor.
Replacement Parts
The emissions control systems are designed and certified to work to-
gether in reducing emissions to
levels that comply with the Clean Air
Act. To make sure the emissions remain low, you should use only newGenuine Honda replacement parts or
their equivalent for repairs. Using
lower quality parts may increase the emissions from your vehicle.
The emissions control systems are covered by warranties separate from
the rest of your vehicle. Read your
warranty manual for more informa-
tion.
Technical Information
ProCarManuals.comMain Menu Table of Contents s t