height Hyundai Elantra 2014 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HYUNDAI, Model Year: 2014, Model line: Elantra, Model: Hyundai Elantra 2014Pages: 668, PDF Size: 35.58 MB
Page 44 of 668

Seat Belt – Passenger’s 3-pointsystem with combination lockingretractor
This type of seat belt combines the
features of both an emergency lock-
ing retractor seat belt and an auto-
matic locking retractor seat belt.
Combination retractor type seat belts
are installed in the rear seat positions
to help accommodate the installation
of child restraint systems. Although a
combination retractor is also installed
in the front passenger seat position,
NEVER place any infant restraint sys-
tem in the front seat of the vehicle. To fasten your seat belt:
Pull the seat belt out of the retractor
and insert the metal tab into the
buckle. There will be an audible
"click" when the tab locks into the
buckle. When not securing a child
restraint, the seat belt operates in the
same way as the driver's seat belt
(Emergency Locking Retractor
Type). It automatically adjusts to the
proper length only after the lap belt
portion of the seat belt is adjusted
manually so that it fits snugly across
your hips.
When the seat belt is fully extended
from the retractor to allow the instal-
lation of a child restraint system, the
seat belt operation changes to allow
the belt to retract, but not to extend
(Automatic Locking Retractor Type).
Refer to “Using a Child Restraint
System” in this chapter.
Safety features of your vehicle
325
(Continued)
Position one arm under the
shoulder belt and the other over
the belt, as shown in the illus-
tration.
Always position the shoulder
belt anchor into the locked
position at the appropriate
height.
Never position the shoulder
belt across your neck or face.
Page 49 of 668

Safety features of your vehicle
30
3
Seat belt use and children
Infant and small children
All 50 states have child restraint laws
which require children to travel in
approved child restraint devices,
including booster seats. The age at
which seat belts can be used instead
of child restraints differs among
states, so you should be aware of the
specific requirements in your state,
and where you are travelling. Infant
and child restraints must be properly
placed and installed in a rear seat.
For more information refer to the
“Child Restraint Systems” in this
chapter. Small children are best protected
from injury in an accident when prop-
erly restrained in the rear seat by a
child restraint system that meets the
requirements of the Federal Motor
Vehicle Safety Standards. Before
buying any child restraint system,
make sure that it has a label certify-
ing that it meets Federal Motor
Vehicle Safety Standard 213. The
restraint must be appropriate for your
child's height and weight. Check the
label on the child restraint for this
information. Refer to “Child Restraint
Systems” in this chapter.WARNING
ALWAYS properly restrain infants
and small children in a child
restraint appropriate for the
child’s height and weight.
To reduce the risk of serious
injury or death to a child and
other passengers, NEVER hold a
child in your lap or arms when
the vehicle is moving. The violent
forces created during an acci-
dent will tear the child from your
arms and throw the child against
the interior of the vehicle.
Page 53 of 668

Safety features of your vehicle
34
3 Children under age 13 must always
ride in the rear seats and must
always be properly restrained to min-
imize the risk of injury in an accident,
sudden stop or sudden maneuver.
According to accident statistics, chil-
dren are safer when properly
restrained in the rear seats than in
the front seat.
Even with air bags,
children can be seriously injured
or killed. Children too large for a
child restraint must use the seat belts
provided.
All 50 states have child restraint laws
which require children to travel in
approved child restraint devices. The
laws governing the age or
height/weight restrictions at which
seat belts can be used instead of
child restraints differs among states,
so you should be aware of the spe-
cific requirements in your state, and
where you are travelling. Child restraint systems must be
properly placed and installed in the
rear seat. You must use a commer-
cially available child restraint system
that meets the requirements of the
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety
Standards (FMVSS).
Child restraint systems are generally
designed to be secured in a vehicle
seat by lap belt portion of a
lap/shoulder belt, or by a LATCH sys-
tem in the rear seats of the vehicle.
CHILD RESTRAINT SYSTEM (CRS)
WARNING
Always properly restrain chil-
dren in the rear seats of the
vehicle.
Children of all ages are safer
when restrained in the rear seat.
A child riding in the front pas-
senger seat can be forcefully
struck by an inflating air bag
resulting in SERIOUS INJURY
or DEATH.
Page 54 of 668
Safety features of your vehicle
335
Child restraint system (CRS)
Infants and younger children must be
restrained in an appropriate rear-fac-
ing or forward-facing CRS that has
first been properly secured to the
rear seat of the vehicle. Read and
comply with the instructions for
installation and use provided by the
manufacturer of the child restraint.
Selecting a Child Restraint
System (CRS)
When selecting a CRS for your child,
always:
Make sure the CRS has a labelcertifying that it meets applicable
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety
Standards (FMVSS 213).
Select a child restraint based on your child’s height and weight. The
required label or the instructions
for use typically provide this infor-
mation.
Select a child restraint that fits the vehicle seating position where it
will be used.
Read and comply with the warn- ings and instructions for installation
and use provided with the child
restraint system.
WARNING
An improperly secured child
restraint can increase the risk
of SERIOUS INJURY or DEATH
in an accident. Always take the
following precautions when
using a child restraint system:
NEVER install a child or infant
restraint in the front passen-
ger’s seat.
Always properly secure the
child restraint to a rear seat of
the vehicle.
(Continued)
(Continued)
Always follow the child
restraint system manufactur-
er’s instructions for installa-
tion and use.
Always properly restrain your
child in the child restraint.
Do not use an infant carrier or
a child safety seat that
“hooks” over a seatback, it
may not provide adequate
protection in an accident.
After an accident, have a
HYUNDAI dealer check the
child restraint system, seat
belts, tether anchors and
lower anchors.
Page 55 of 668

Safety features of your vehicle
36
3
Child restraint system types
There are three main types of child
restraint systems: rear-facing seats,
forward-facing seats, and booster
seats. They are classified according
to the child’s age, height and weight.
Rear-facing child seats A rear-facing child seat provides
restraint with the seating surface
against the back of the child. The har-
ness system holds the child in place,
and in an accident, acts to keep the
child positioned in the seat and
reduce the stress to the neck and
spinal cord.
All children under age one must
always ride in a rear-facing infant child
restraint.
Convertible and 3-in-1 child seats typ-
ically have higher height and weight
limits for the rear-facing position,
allowing you to keep your child rear-
facing for a longer period of time.Continue to use a rear-facing child
seat for as long as your child will fit
within the height and weight limits
allowed by the child seat manufactur-
er. It’s the best way to keep them
safe. Once your child has outgrown
the rear-facing child restraint, your
child is ready for a forward-facing
child restraint with a harness.
CRS09
WARNING
NEVER install a child or infant
restraint in the front passen-
ger’s seat.
Placing a rear-facing child
restraint in the front seat can
result in SERIOUS INJURY or
DEATH if the child restraint is
struck by an inflating air bag.
■
Rearward-facing child restraint system
WARNING
If the vehicle headrest prevents
proper installation of a child
seat, the headrest of the respec-
tive seating position shall be
readjusted or entirely removed.
Page 56 of 668

Safety features of your vehicle
337
Forward-facing child restraints
A forward-facing child seat provides
restraint for the child’s body with a
harness. Keep children in a forward-
facing child seat with a harness until
they reach the top height or weight
limit allowed by your child restraint’s
manufacturer.
Once your child outgrows the forward-
facing child restraint, your child is
ready for a booster seat.Booster seats
A booster seat is a restraint designed
to improve the fit of the vehicle’s seat
belt system. A booster seat positions
the seat belt so that it fits properly
over the lap of your child. Keep your
child in a booster seat until they are
big enough to sit in the seat without a
booster and still have the seat belt fit
properly.
For a seat belt to fit properly, the lap
belt must lie snugly across the upper
thighs, not the stomach. The shoulder
belt should lie snug across the shoul-
der and chest and not across the neck
or face. Children under age 13 must
always ride in the rear seats and must
always be properly restrained to mini-
mize the risk of injury.
Installing a Child Restraint
System (CRS)
OMD030019
WARNING
Before installing your child
restraint system always:
Read and follow the instruc-
tions provided by the manu-
facturer of the child restraint.
Read and follow the instruc-
tions regarding child restraint
systems in this manual.
Failure to follow all warnings
and instructions could increase
the risk of the SERIOUS INJURY
or DEATH if an accident occurs.
Page 85 of 668

Safety features of your vehicle
66
3
Additional safety precautions
Passengers should not move out of
or change seats while the vehicle is
moving. A passenger who is not
wearing a seat belt during a crash or
emergency stop can be thrown
against the inside of the vehicle,
against other occupants, or be ejected
from the vehicle.
Do not use any accessories on seat
belts. Devices claiming to improve
occupant comfort or reposition the
seat belt can reduce the protection
provided by the seat belt and increase
the chance of serious injury in a crash
Do not modify the front seats.
Modification of the front seats could
interfere with the operation of the sup-
plemental restraint system sensing
components or side air bags.
Do not place items under the front
seats. Placing items under the front
seats could interfere with the opera-
tion of the supplemental restraint sys-
tem sensing components and wiring
harnesses.
Do not cause impact to the doors.
Impact to the doors when the ignition
switch is in the ON position may cause
the air bags to inflate. Modifications to accommodate
disabilities.
If you require modifica-
tion to your vehicle to accommodate
a disability, contact the HYUNDAI
Customer Connect Center at 1-877-
378-8727.
Adding equipment to or modifying
your air bag equipped vehicle
If you modify your vehicle by changing
your vehicle's frame, bumper system,
front end or side sheet metal or ride
height, this may affect the operation of
your vehicle's air bag system.
(Continued)
If components of the air bag
system must be discarded, or if
the vehicle must be scrapped,
certain safety precautions
must be observed. Consult an
authorized HYUNDAI dealer for
the necessary information.
Failure to follow these precau-
tions could increase the risk of
personal injury.
Page 488 of 668

Driving your vehicle
32
5
Anti-lock Brake System (ABS)
ABS is an electronic braking system
that helps prevent a braking skid.
ABS allows the driver to steer and
brake at the same time.
Using ABS
To obtain the maximum benefit from
your ABS in an emergency situation,
do not attempt to modulate your
brake pressure and do not try to
pump your brakes. Depress your
brake pedal as hard as possible.
When you apply your brakes under
conditions which may lock the
wheels, you may hear sounds from
the brakes, or feel a corresponding
sensation in the brake pedal. This is
normal and it means your ABS is
active.
ABS does not reduce the time or dis-
tance it takes to stop the vehicle.
Always maintain a safe distance from
the vehicle in front of you.
ABS will not prevent a skid that
results from sudden changes in
direction, such as trying to take a
corner too fast or making a sudden
lane change. Always drive at a safe
speed for the road and weather con-
ditions.
WARNING
An Anti-Lock Braking System
(ABS) or an Electronic Stability
Control (ESC) system will not
prevent accidents due to
improper or dangerous driving
maneuvers. Even though vehi-
cle control is improved during
emergency braking, always
maintain a safe distance
between you and objects ahead
of you. Vehicle speeds should
always be reduced during
extreme road conditions. The
braking distance for cars
equipped with ABS or ESC may
be longer than for those without
these systems in the following
road conditions.
(Continued)
(Continued)
Drive your vehicle at reduced
speeds during the following
conditions:
Rough, gravel or snow-cov-ered roads.
On roads where the road sur- face is pitted or has different
surface height.
Tire chains are installed on your vehicle.
The safety features of an ABS
or ESC equipped vehicle should
not be tested by high speed
driving or cornering. This could
endanger the safety of yourself
or others.
UD(FL) HMA 5.qxp 6/26/2014 3:22 PM Page 32
Page 601 of 668
753
Maintenance
Tire maintenance
In addition to proper inflation, correct
wheel alignment helps to decrease
tire wear. If you find a tire is worn
unevenly, have your dealer check the
wheel alignment.
When you have new tires installed,
make sure they are balanced. This
will increase vehicle ride comfort and
tire life. Additionally, a tire should
always be rebalanced if it is removed
from the wheel.
Tire sidewall labeling
This information identifies and
describes the fundamental charac-
teristics of the tire and also provides
the tire identification number (TIN)
for safety standard certification. The
TIN can be used to identify the tire in
case of a recall.
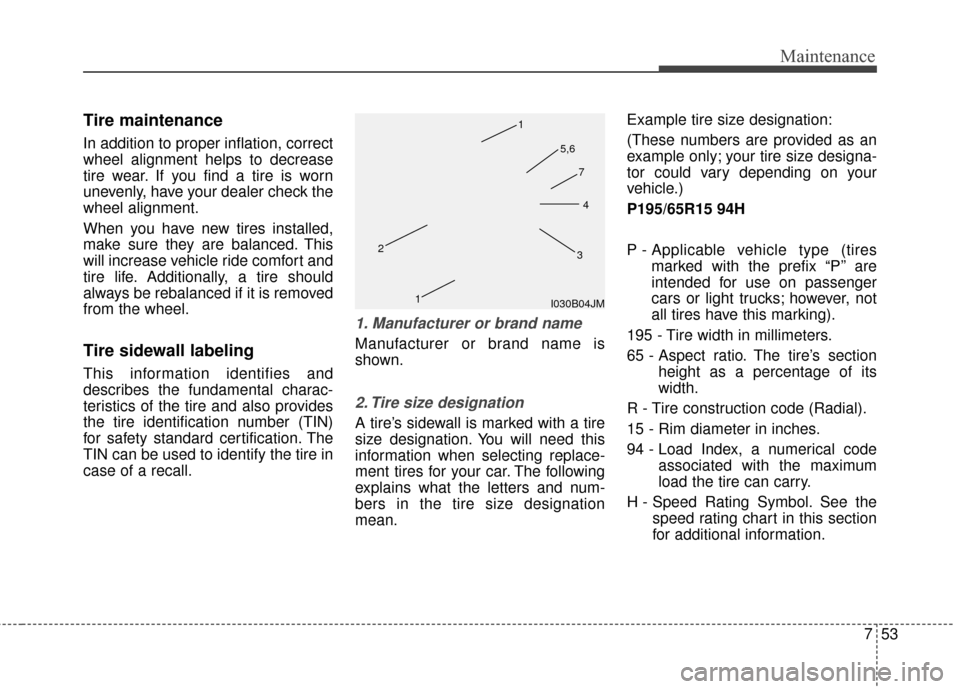
1. Manufacturer or brand name
Manufacturer or brand name is
shown.
2. Tire size designation
A tire’s sidewall is marked with a tire
size designation. You will need this
information when selecting replace-
ment tires for your car. The following
explains what the letters and num-
bers in the tire size designation
mean.Example tire size designation:
(These numbers are provided as an
example only; your tire size designa-
tor could vary depending on your
vehicle.)
P195/65R15 94H
P - Applicable vehicle type (tires
marked with the prefix “P’’ are
intended for use on passenger
cars or light trucks; however, not
all tires have this marking).
195 - Tire width in millimeters.
65 - Aspect ratio. The tire’s section height as a percentage of its
width.
R - Tire construction code (Radial).
15 - Rim diameter in inches.
94 - Load Index, a numerical code associated with the maximum
load the tire can carry.
H - Speed Rating Symbol. See the speed rating chart in this section
for additional information.
I030B04JM
1
1
2
34
5,6
7
Page 605 of 668
757
Maintenance
Tire terminology and defini-
tions
Air Pressure
The amount of air inside the tire
pressing outward on the tire. Air
pressure is expressed in pounds per
square inch (psi) or kilopascal (kPa).
Accessory Weight
This means the combined weight of
optional accessories. Some exam-
ples of optional accessories are
automatic transaxle, power seats,
and air conditioning.
Aspect Ratio
The relationship of a tire's height to
its width.
Belt
A rubber coated layer of cords that is
located between the plies and the
tread. Cords may be made from steel
or other reinforcing materials.
Bead
The tire bead contains steel wires
wrapped by steel cords that hold the
tire onto the rim.
Bias Ply Tire
A pneumatic tire in which the plies
are laid at alternate angles less than
90 degrees to the centerline of the
tread.
Cold Tire Pressure
The amount of air pressure in a tire,
measured in pounds per square inch
(psi) or kilopascals (kPa) before a tire
has built up heat from driving.
Curb Weight
This means the weight of a motor
vehicle with standard and optional
equipment including the maximum
capacity of fuel, oil and coolant, but
without passengers and cargo.
DOT Markings
A code molded into the sidewall of a
tire signifying that the tire is in com-
pliance with the U.S. Department of
Transportation motor vehicle safety
standards. The DOT code includes
the Tire Identification Number (TIN),
an alphanumeric designator which
can also identify the tire manufactur-
er, production plant, brand and date
of production.