automatic transmission HYUNDAI ELANTRA SEL 2021 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HYUNDAI, Model Year: 2021, Model line: ELANTRA SEL, Model: HYUNDAI ELANTRA SEL 2021Pages: 570, PDF Size: 52.21 MB
Page 300 of 570

06
6-41
Various driving situations, which you may
encounter in SMART mode
• The driving mode automatically
changes to SMART ECO mode after
a certain period of time, when you
gently depress the accelerator pedal
(Your driving is categorized to be
economic.).
• The driving mode automatically
changes from SMART ECO mode to
SMART NORMAL mode after a certain
period of time, when you sharply or
repetitively depress the accelerator
pedal.
• The driving mode automatically
changes to SMART NORMAL mode
with the same driving patterns, when
the vehicle starts to drive on an
upward slope of a certain angle. The
driving mode automatically returns to
SMART ECO mode, when the vehicle
enters a leveled road.
• The driving mode automatically
changes to SMART SPORT, when
you abruptly accelerate the vehicle
or repetitively operate the steering
wheel (Your driving is categorized
to be sporty.). In this mode, your
vehicle drives in a lower gear for
abrupt accelerating/decelerating
and increases the engine brake
performance.
• You may still sense the engine
braking performance, even when
you release the accelerator pedal in
SMART SPORT mode. It is because
your vehicle remains in lower gear
over a certain period of time for next
acceleration. Thus, it is a normal
driving situation, not indicating any
malfunction. •
The driving mode automatically
changes to SMART SPORT mode
only in harsh driving situations. In
most of the normal driving situations,
the driving mode sets to be either
in SMART ECO mode or in SMART
NORMAL mode.
Limitation of SMART mode
The SMART mode may be limited in
following situations. (The OFF indicator
illuminates in those situations.)
• The cruise control is activated :
The cruise control system may
deactivate the SMART mode when
the vehicle is controlled by the set
speed of Smart Cruise Control system.
(SMART mode is not deactivated
just by activating the cruise control
system.)
• The transmission oil temperature is
either extremely low or extremely
high :
The SMART mode can be active in
most of the normal driving situations.
However, an extremely high/ low
transmission oil temperature may
temporarily deactivate the SMART
mode, because the transmission
condition is out of normal operation
condition.
Page 482 of 570
08
8-19
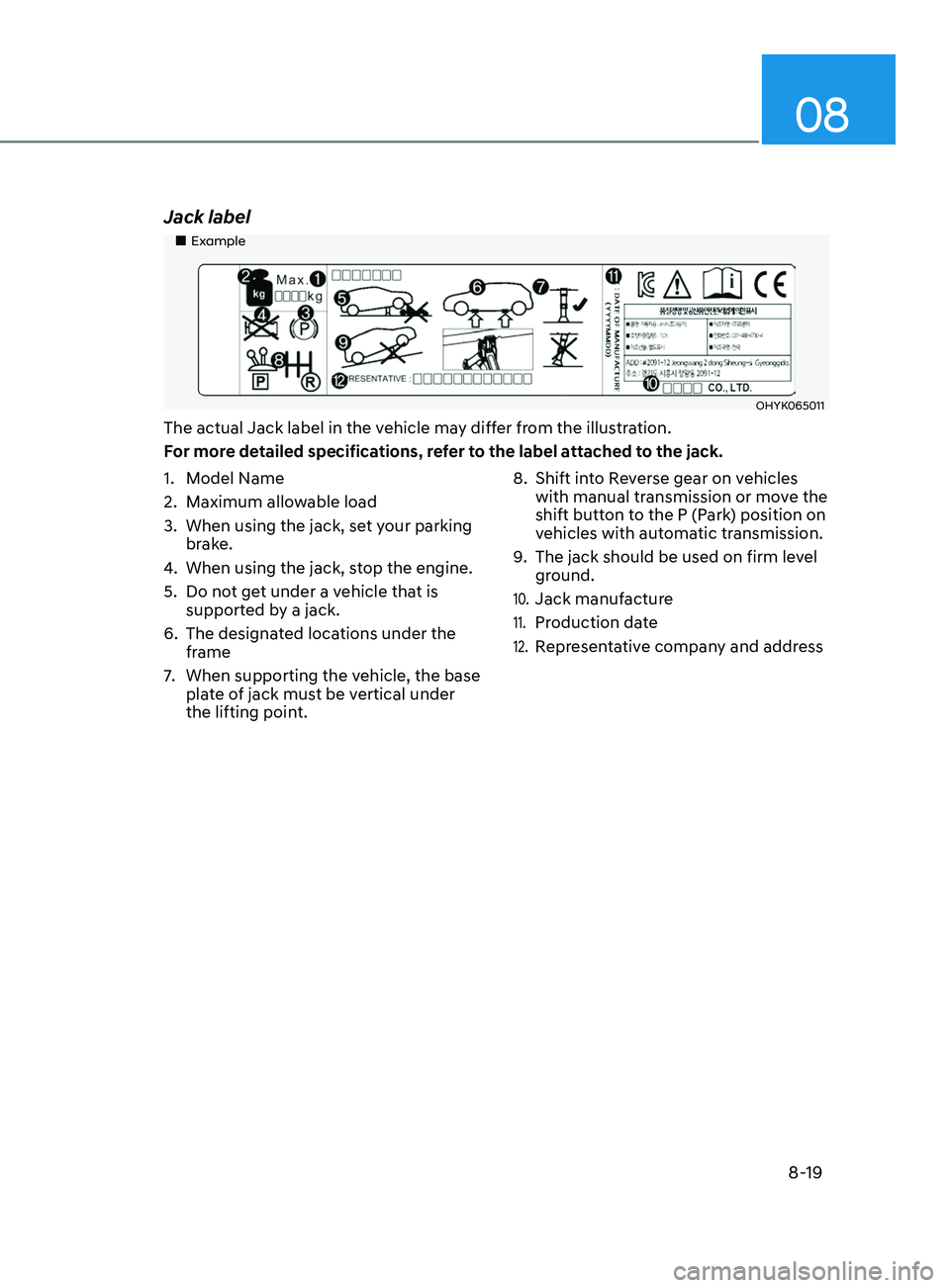
Jack label
„„Example
OHYK065011
The actual Jack label in the vehicle may differ from the illustration.
For more detailed specifications, refer to the label attached to the jack.
1.
Model Name
2.
Maximum allow
able load
3.
When using the jack, set y
our parking
brake.
4.
When using the jack, st
op the engine.
5.
Do not ge
t under a vehicle that is
supported by a jack.
6.
The designat
ed locations under the
frame
7.
When supporting the vehicle, the base
pla
te of jack must be vertical under
the lifting point. 8.
Shift int
o Reverse gear on vehicles
with manual transmission or move the
shift button to the P (Park) position on
vehicles with automatic transmission.
9.
The jack should be used on firm lev
el
ground.
10. Jack manufacture
11. Production date
12. Representative company and address
Page 521 of 570

09
9-35
Temperature A, B & C
The temperature grades are A (the
highest), B and C representing the tire’s
resistance to the generation of heat
and its ability to dissipate heat when
tested under controlled conditions on a
specified indoor laboratory test wheel.
Sustained high temperature can cause
the material of the tire to degenerate
and reduce tire life, and excessive
temperature can lead to sudden tire
failure. Grade C responds to a level
of performance which all passenger
car tires must meet under the Federal
Motor Vehicle Safety Standard No. 109.
Grades B and A represent higher levels
of performance on the laboratory test
wheel than the minimum required by
law.
WARNING
The temperature grade for this tire is
established for a tire that is properly
inflated and not overloaded. Excessive
speed, under-inflation, over-inflation,
or excessive loading, either separately
or in combination, can cause heat build-
up and possible sudden tire failure.
This may cause loss of vehicle control
resulting in an accident.
Tire Terminology and Definitions
Air Pressure
The amount of air inside the tire pressing
outward on the tire. Air pressure is
expressed in pounds per square inch
(psi) or kilopascal (kPa).
Accessory Weight
This means the combined weight of
optional accessories. Some examples
of optional accessories are automatic
transmission, power seats, and air
conditioning.
Aspect Ratio
The relationship of a tire’s height to its
width.
Belt
A rubber coated layer of cords that is
located between the plies and the tread.
Cords may be made from steel or other
reinforcing materials.
Bead
The tire bead contains steel wires
wrapped by steel cords that hold the tire
onto the rim.
Bias Ply Tire
A pneumatic tire in which the plies are
laid at alternate angles less than 90
degrees to the centerline of the tread.
Cold Tire Pressure
The amount of air pressure in a tire,
measured in pounds per square inch (psi)
or kilopascals (kPa) before a tire has built
up heat from driving.