Acc HYUNDAI TUCSON 2011 Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HYUNDAI, Model Year: 2011, Model line: TUCSON, Model: HYUNDAI TUCSON 2011Pages: 382, PDF Size: 5.43 MB
Page 332 of 382

Maintenance
46
7
Temperature -A, B & C
The temperature grades are A (the highest), B and C representing the
tire’s resistance to the generation ofheat and its ability to dissipate heatwhen tested under controlled condi-
tions on a specified indoor laboratorytest wheel.
Sustained high temperature can
cause the material of the tire to
degenerate and reduce tire life, and
excessive temperature can lead to
sudden tire failure. The grade C cor-
responds to a level of performance
which all passenger car tires must
meet under the Federal Motor
Vehicle Safety Standard No. 109.
Grades B and A represent higher
levels of performance on the labora-
tory test wheel than the minimum
required by law. Tire terminology and definitions Air Pressure
: The amount of air
inside the tire pressing outward on
the tire. Air pressure is expressed inpounds per square inch (psi) or kilo-
pascal (kPa).
Accessory Weight : This means the
combined weight of optional acces-
sories. Some examples of optional
accessories are, automatic transaxle,
power seats, and air conditioning. Aspect Ratio : The relationship of a
tire's height to its width.Belt: A rubber coated layer of cords
that is located between the plies and
the tread. Cords may be made from
steel or other reinforcing materials. Bead : The tire bead contains steel
wires wrapped by steel cords that
hold the tire onto the rim.
Bias Ply Tire : A pneumatic tire in
which the plies are laid at alternate
angles less than 90 degrees to the
centerline of the tread.WARNING - Tire temperature
The temperature grade for this
tire is established for a tire that
is properly inflated and not
overloaded. Excessive speed,
underinflation, or excessive
loading, either separately or in
combination, can cause heat
build-up and possible sudden
tire failure. This can cause loss
of vehicle control and serious
injury or death.
Page 333 of 382

747
Maintenance
Cold Tire Pressure: The amount of
air pressure in a tire, measured in pounds per square inch (psi) or kilo-
pascals (kPa) before a tire has built
up heat from driving.
Curb Weight : This means the weight
of a motor vehicle with standard and optional equipment including the
maximum capacity of fuel, oil and
coolant, but without passengers and
cargo.
DOT Markings : A code molded into
the sidewall of a tire signifying that
the tire is in compliance with the U.S.
Department of Transportation motor
vehicle safety standards. The DOT
code includes the Tire Identification
Number (TIN), an alphanumeric des-ignator which can also identify the
tire manufacturer, production plant,
brand and date of production. GVWR : Gross Vehicle Weight Rating
GAWR FRT : Gross Axle Weight
Rating for the Front Axle.
GAWR RR : Gross Axle Weight
Rating for the Rear axle. Intended Outboard Sidewall
: The
side of an asymmetrical tire, that
must always face outward when
mounted on a vehicle.
Kilopascal (kPa) : The metric unit for
air pressure.
Load Index : An assigned number
ranging from 1 to 279 that corre-
sponds to the load carrying capacity
of a tire.
Maximum Inflation Pressure : The
maximum air pressure to which a
cold tire may be inflated. The maxi-
mum air pressure is molded onto the
sidewall.
Maximum Load Rating : The load
rating for a tire at the maximum per-
missible inflation pressure for that
tire.
Maximum Loaded Vehicle Weight :
The sum of curb weight; accessory
weight; vehicle capacity weight; and
production options weight.
Normal Occupant Weight :The
number of occupants a vehicle is
designed to seat multiplied by 150pounds (68 kg). Occupant Distribution
: Designated
seating positions.
Outward Facing Sidewall: The side
of a asymmetrical tire that has a par-
ticular side that faces outward when
mounted on a vehicle. The outward
facing sidewall bears white lettering
or bears manufacturer, brand, and/ormodel name molding that is higher ordeeper than the same moldings on
the inner facing sidewall.
Passenger (P-Metric) Tire : A tire
used on passenger cars and some
light duty trucks and multipurpose
vehicles. Recommended Inflation Pressure :
Vehicle manufacturer's recommend-
ed tire inflation pressure and shownon the tire placard.
Radial Ply Tire : A pneumatic tire in
which the ply cords that extend to the
beads are laid at 90 degrees to the
centerline of the tread. Rim : A metal support for a tire and
upon which the tire beads are seat- ed.
Sidewall : The portion of a tire
between the tread and the bead.
Page 334 of 382

Maintenance
48
7
Speed Rating : An alphanumeric
code assigned to a tire indicating the
maximum speed at which a tire can
operate.
Traction : The friction between the
tire and the road surface. The
amount of grip provided.
Tr e a d : The portion of a tire that
comes into contact with the road.
Treadwear Indicators : Narrow
bands, sometimes called "wear
bars," that show across the tread of atire when only 2/32 inch of tread
remains. UTQGS : Uniform Tire Quality
Grading Standards, a tire information
system that provides consumers with
ratings for a tire's traction, tempera-
ture and treadwear. Ratings are
determined by tire manufacturers
using government testing proce-
dures. The ratings are molded into
the sidewall of the tire.
Vehicle Capacity Weight : The num-
ber of designated seating positions
multiplied by 150 lbs. (68 kg) plus the
rated cargo and luggage load. Vehicle Maximum Load on theTire
: Load on an individual tire due to
curb and accessory weight plus
maximum occupant and cargo
weight.
Vehicle Normal Load on the Tire :
Load on an individual tire that is
determined by distributing to each
axle its share of the curb weight,
accessory weight, and normal occu-
pant weight and dividing by 2.
Vehicle Placard : A label permanent-
ly attached to a vehicle showing the
original equipment tire size and rec-
ommended inflation pressure. All season tires
HYUNDAI specifies all season tires
on some models to provide good
performance for use all year round,
including snowy and icy road condi-
tions. All season tires are identified
by ALL SEASON and/or M+S (Mud
and Snow) on the tire sidewall. Snow
tires have better snow traction than
all season tires and may be more
appropriate in some areas. Summer tires
HYUNDAI specifies summer tires on
some models to provide superior
performance on dry roads. Summer
tire performance is substantially
reduced in snow and ice. Summer
tires do not have the tire traction rat-
ing M+S (Mud and Snow) on the tire
side wall. if you plan to operate your
vehicle in snowy or icy conditions.
HYUNDAI recommends the use of
snow tires or all season tires on all
four wheels.
Snow tires
If you equip your car with snow tires,
they should be the same size and
have the same load capacity as the
original tires. Snow tires should be
installed on all four wheels; other-
wise, poor handling may result.
Snow tires should carry 4 psi (28
kPa) more air pressure than the
pressure recommended for the stan-
dard tires on the tire label on the dri-
ver's side of the center pillar, or up to
the maximum pressure shown on the
tire sidewall, whichever is less.
Page 335 of 382

749
Maintenance
Do not drive faster than 75 mph (120
km/h) when your vehicle is equipped
with snow tires.
Tire chains
Tire chains, if necessary, should be
installed on the drive wheels as fol-
lows.
2WD : Front wheels
AWD : All four wheelsIf a full set of chains is not
available for a AWD vehicle,
chains may be installed on
the front wheels only.
Be sure that the chains are installed
in accordance with the manufactur-
er's instructions.
To minimize tire and chain wear, do
not continue to use tire chains when
they are no longer needed.Radial-ply tires
Radial-ply tires provide improved
tread life, road hazard resistance and
smoother high speed ride. The radi-
al-ply tires used on this vehicle are of
belted construction, and are selected
to complement the ride and handling
characteristics of your vehicle.
Radial-ply tires have the same load
carrying capacity, as bias-ply or bias
belted tires of the same size, and use the same recommended inflation
pressure. Mixing of radial-ply tireswith bias-ply or bias belted tires is
not recommended. Any combina-
tions of radial-ply and bias-ply or biasbelted tires when used on the same
vehicle will seriously deteriorate
vehicle handling. The best rule to fol-
low is: Identical radial-ply tires should
always be used as a set of four.
Longer wearing tires can be more
susceptible to irregular tread wear. It
is very important to follow the tire
rotation interval shown in this section
to achieve the tread life potential of
these tires. Cuts and punctures in
radial-ply tires are repairable only in
the tread area, because of sidewall
flexing. Consult your tire dealer for
radial-ply tire repairs.WARNING- Snow or ice
When driving on roads cov- ered with snow or ice, drive at less than 20 mph (30 km/h).
Use the SAE “S” class or wire chains.
If you hear noise caused by chains contacting the body,
retighten the chain to avoid
contact with the vehicle body.
To prevent body damage, retighten the chains after driv-ing 0.3~0.6 miles (0.5~1.0 km).
Do not use tire chains on vehicles equipped with alu-
minum wheels. In unavoid-
able circumstance, use a wire
type chain.
Use wire chains less than 0.59 inches (15 mm) to prevent
damage to the chain’s con-nection.
Page 336 of 382
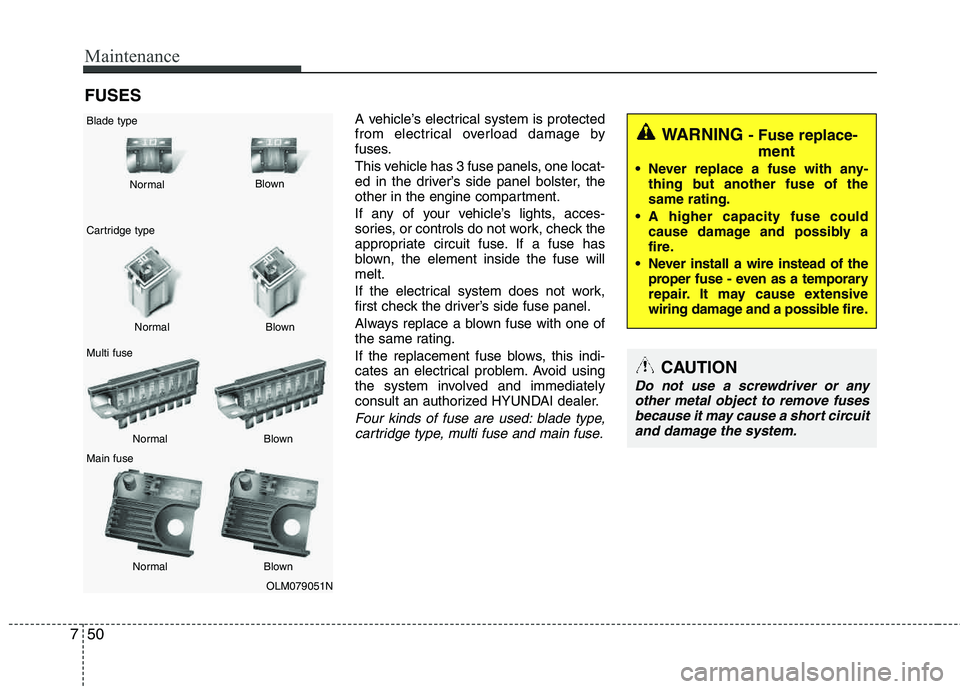
Maintenance
50
7
FUSES
A vehicle’s electrical system is protected
from electrical overload damage by
fuses.
This vehicle has 3 fuse panels, one locat-
ed in the driver’s side panel bolster, the
other in the engine compartment.
If any of your vehicle’s lights, acces-
sories, or controls do not work, check the
appropriate circuit fuse. If a fuse has
blown, the element inside the fuse willmelt.
If the electrical system does not work,
first check the driver’s side fuse panel.
Always replace a blown fuse with one of
the same rating.
If the replacement fuse blows, this indi-
cates an electrical problem. Avoid using
the system involved and immediately
consult an authorized HYUNDAI dealer.
Four kinds of fuse are used: blade type,cartridge type, multi fuse and main fuse.
WARNING - Fuse replace-
ment
Never replace a fuse with any- thing but another fuse of the same rating.
A higher capacity fuse could cause damage and possibly a
fire.
Never install a wire instead of the proper fuse - even as a temporary
repair. It may cause extensive
wiring damage and a possible fire.
CAUTION
Do not use a screwdriver or any
other metal object to remove fuses
because it may cause a short circuitand damage the system.
OLM079051N
Normal
Normal
Blade type
Cartridge type Multi fuse Main fuse Blown
Blown
Normal Blown
Normal Blown
Page 340 of 382
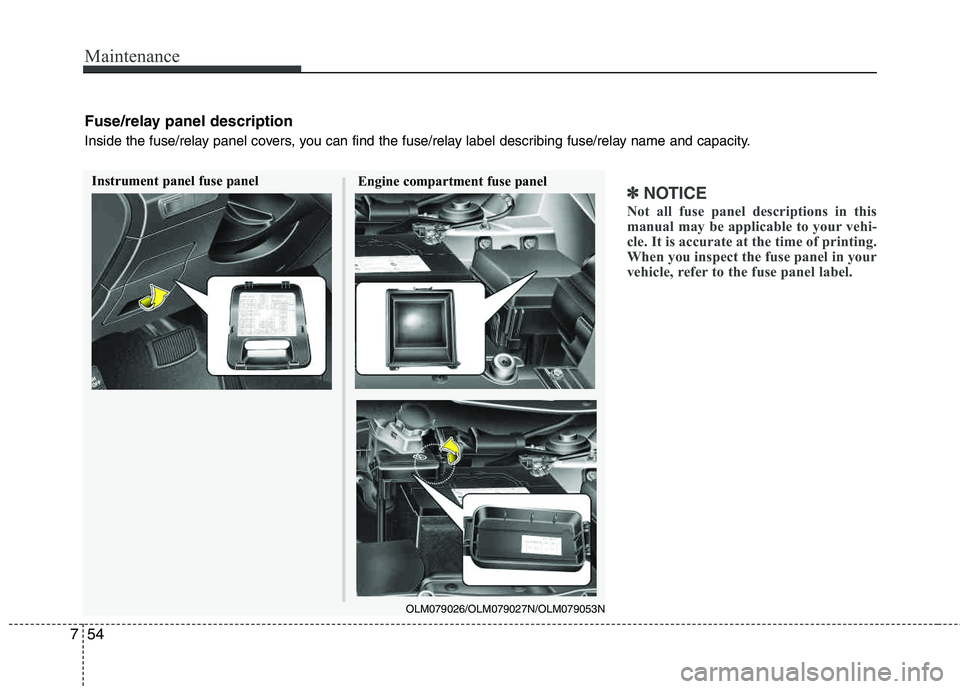
Maintenance
54
7
✽✽
NOTICE
Not all fuse panel descriptions in this
manual may be applicable to your vehi-
cle. It is accurate at the time of printing.
When you inspect the fuse panel in your
vehicle, refer to the fuse panel label.Instrument panel fuse panel Engine compartment fuse panel
OLM079026/OLM079027N/OLM079053N
Fuse/relay panel description
Inside the fuse/relay panel covers, you can find the fuse/relay label describing fuse/relay name and capacity.
Page 352 of 382

Maintenance
66
7
APPEARANCE CARE
WARNING - Wet brakes
After washing the vehicle, test the
brakes while driving slowly to see if
they have been affected by water. If
braking performance is impaired,
dry the brakes by applying them
lightly while maintaining a slow for-
ward speed.
Exterior care
Exterior general caution
It is very important to follow the label
directions when using any chemical
cleaner or polish. Read all warning andcaution statements that appear on the label.
Finish maintenance
Washing
To help protect your vehicle’s finish from
rust and deterioration, wash it thoroughly and frequently at least once a month with
lukewarm or cold water.
If you use your vehicle for off-road driv-
ing, you should wash it after each off-
road trip. Pay special attention to the
removal of any accumulation of salt, dirt,
mud, and other foreign materials. Make
sure the drain holes in the lower edges of
the doors and rocker panels are kept clear and clean.
Insects, tar, tree sap, bird droppings,
industrial pollution and similar deposits
can damage your vehicle’s finish if not
removed immediately. Even prompt washing with plain water
may not completely remove all these
deposits. A mild soap, safe for use on
painted surfaces, may be used.
After washing, rinse the vehicle thor-
oughly with lukewarm or cold water. Do
not allow soap to dry on the finish.
CAUTION
Do not use strong soap, chemical
detergents or hot water, and donot wash the vehicle in directsunlight or when the body of the
vehicle is warm.
Be careful when washing the side windows of your vehicle.
Especially, with high-pressurewater. Water may leak through thewindows and wet the interior.
To prevent damage to the plastic parts, do not clean with chemicalsolvents or strong detergents.
Page 354 of 382

Maintenance
68
7
Bright-metal maintenance
To remove road tar and insects, use a
tar remover, not a scraper or other
sharp object.
To protect the surfaces of bright-metal parts from corrosion, apply a coating of
wax or chrome preservative and rub to
a high luster.
During winter weather or in coastal areas, cover the bright metal parts with
a heavier coating of wax or preserva-
tive. If necessary, coat the parts with
non-corrosive petroleum jelly or other
protective compound.
Underbody maintenance
Corrosive materials used for ice and
snow removal and dust control may col-
lect on the underbody. If these materials
are not removed, accelerated rusting can
occur on underbody parts such as the
fuel lines, frame, floor pan and exhaust
system, even though they have been
treated with rust protection.
Thoroughly flush the vehicle underbody
and wheel openings with lukewarm or
cold water once a month, after off-road
driving and at the end of each winter. Payspecial attention to these areas because
it is difficult to see all the mud and dirt. It
will do more harm than good to wet down
the road grime without removing it. The
lower edges of doors, rocker panels, and
frame members have drain holes that
should not be allowed to clog with dirt;
trapped water in these areas can cause
rusting.
Aluminum wheel maintenance
The aluminum wheels are coated with a
clear protective finish.
Do not use any abrasive cleaner, pol-ishing compound, solvent, or wire
brushes on aluminum wheels. They
may scratch or damage the finish.
Use only a mild soap or neutral deter- gent, and rinse thoroughly with water.
Also, be sure to clean the wheels after
driving on salted roads. This helps pre-
vent corrosion.
Avoid washing the wheels with high- speed car wash brushes.
Do not use any cleaners containing acid or acid detergents. It may damage
and corrode the aluminum wheels
coated with a clear protective finish.
WARNING
After washing the vehicle, test the
brakes while driving slowly to see if
they have been affected by water. If
braking performance is impaired,
dry the brakes by applying them
lightly while maintaining a slow for-
ward speed.
Page 355 of 382
769
Maintenance
Corrosion protection
Protecting your vehicle from corrosion
By using the most advanced design and
construction practices to combat corro-
sion, we produces cars of the highest
quality. However, this is only part of the
job. To achieve the long-term corrosion
resistance your vehicle can deliver, the
owner's cooperation and assistance is also required.
Common causes of corrosion The most common causes of corrosion
on your car are:
allowed to accumulate underneath the
vehicle.
Removal of paint or protective coatings by stones, gravel, abrasion or minor
scrapes and dents which leave unpro-
tected metal exposed to corrosion. High-corrosion areas
If you live in an area where your vehicle
is regularly exposed to corrosive materi-
als, corrosion protection is particularly
important. Some of the common causes
of accelerated corrosion are road salts,
dust control chemicals, ocean air and
industrial pollution.
Moisture breeds corrosion Moisture creates the conditions in which
corrosion is most likely to occur. For
example, corrosion is accelerated by
high humidity, particularly when tempera-
tures are just above freezing. In such
conditions, the corrosive material is kept
in contact with the car surfaces by mois-
ture that is slow to evaporate.
Mud is particularly corrosive because it is
slow to dry and holds moisture in contact
with the vehicle. Although the mud
appears to be dry, it can still retain themoisture and promote corrosion.
High temperatures can also accelerate
corrosion of parts that are not properly
ventilated so the moisture can be dis-
persed. For all these reasons, it is par-
ticularly important to keep your vehicle
clean and free of mud or accumulations
of other materials. This applies not only
to the visible surfaces but particularly to
the underside of the vehicle.
Page 356 of 382

Maintenance
70
7
To help prevent corrosion
You can help prevent corrosion from get-
ting started by observing the following:
Keep your car clean
The best way to prevent corrosion is to
keep your vehicle clean and free of cor-
rosive materials. Attention to the under-
side of the vehicle is particularly impor- tant.
If you live in a high-corrosion area —
where road salts are used, near the
ocean, areas with industrial pollution,
acid rain, etc.—, you should take extra
care to prevent corrosion. In winter,
hose off the underside of your vehicleat least once a month and be sure to clean the underside thoroughly when
winter is over. When cleaning underneath the vehicle,
give particular attention to the compo-
nents under the fenders and other
areas that are hidden from view. Do a
thorough job; just dampening the accu-
mulated mud rather than washing it
away will accelerate corrosion rather
than prevent it. Water under high pres-
sure and steam are particularly effec-
tive in removing accumulated mud and
corrosive materials.
rocker panels and frame members, be
sure that drain holes are kept open sothat moisture can escape and not be
trapped inside to accelerate corrosion.
Keep your garage dry
Don't park your car in a damp, poorly
ventilated garage. This creates a favor-
able environment for corrosion. This is
particularly true if you wash your vehicle
in the garage or drive it into the garage
when it is still wet or covered with snow,
ice or mud. Even a heated garage can
contribute to corrosion unless it is well
ventilated so moisture is dispersed. Keep paint and trim in good condition
Scratches or chips in the finish should be
covered with "touch-up" paint as soon as
possible to reduce the possibility of cor-
rosion. If bare metal is showing through,the attention of a qualified body and paint shop is recommended.
Bird droppings : Bird droppings are high-
ly corrosive and may damage painted
surfaces in just a few hours. Always
remove bird droppings as soon as possi-
ble. Don't neglect the interior Moisture can collect under the floor mats
and carpeting to cause corrosion. Check
under the mats periodically to be sure
the carpeting is dry. Use particular care if
you carry fertilizers, cleaning materials or
chemicals in the vehicle.
These should be carried only in proper
containers and any spills or leaks should
be cleaned up, flushed with clean water
and thoroughly dried.