change time INFINITI FX35 2008 Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: INFINITI, Model Year: 2008, Model line: FX35, Model: INFINITI FX35 2008Pages: 3924, PDF Size: 81.37 MB
Page 2890 of 3924

GI-28
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
ough understanding of system operation. Then you will be able to use the appropriate equipment and follow
the correct test procedure.
You may have to simulate vehicle vibrations while test ing electrical components. Gently shake the wiring har-
ness or electrical component to do this.
NOTE:
Refer to “How to Check Terminal” to probe or check terminal.
Testing for “Opens” in the Circuit
Before you begin to diagnose and test the system, you should rough sketch a schematic of the system. This
will help you to logically walk through the diagnosis process. Drawing the sketch will also reinforce your work-
ing knowledge of the system.
CONTINUITY CHECK METHOD
The continuity check is used to find an open in the circ uit. The digital multimeter (DMM) set on the resistance
function will indicate an open circuit as over limit (no beep tone or no ohms symbo\
l). Make sure to always start
with the DMM at the highest resistance level.
To help in understanding the diagnosis of open circui ts, please refer to the previous schematic.
Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Start at one end of the circuit and work your way to the other end. (At the fuse block in this example)
Connect one probe of the DMM to the fuse block terminal on the load side.
Connect the other probe to the fuse block (power) side of SW1. Little or no resistance will indicate that por-
tion of the circuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would indicate an over
limit or infinite resistance condition. (point A)
Connect the probes between SW1 and the relay. Little or no resistance will indicate that portion of the circuit
has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, t he DMM would indicate an over limit or infinite resis-
tance condition. (point B)
Connect the probes between the relay and the solenoid. Little or no resistance will indicate that portion of the
circuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the ci rcuit, the DMM would indicate an over limit or infi-
nite resistance condition. (point C)
Any circuit can be diagnosed using the approach in the previous example.
VOLTAGE CHECK METHOD
To help in understanding the diagnosis of open circui ts please refer to the previous schematic.
In any powered circuit, an open can be found by methodica lly checking the system for the presence of voltage.
This is done by switching the DMM to the voltage function.
Connect one probe of the DMM to a known good ground.
Begin probing at one end of the circuit and work your way to the other end.
With SW1 open, probe at SW1 to check for voltage.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than SW1.
no voltage; open is between fuse block and SW1 (point A).
Close SW1 and probe at relay.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than the relay.
no voltage; open is between SW1 and relay (point B).
OPEN A circuit is open when there is no continuity through a section of the circuit.
SHORT There are two types of shorts.
SHORT CIRCUIT
When a circuit contacts another circuit and causes the normal resistance to
change.
SHORT TO GROUND When a circuit contacts a ground source and grounds the circuit.
SGI846-A
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 2899 of 3924
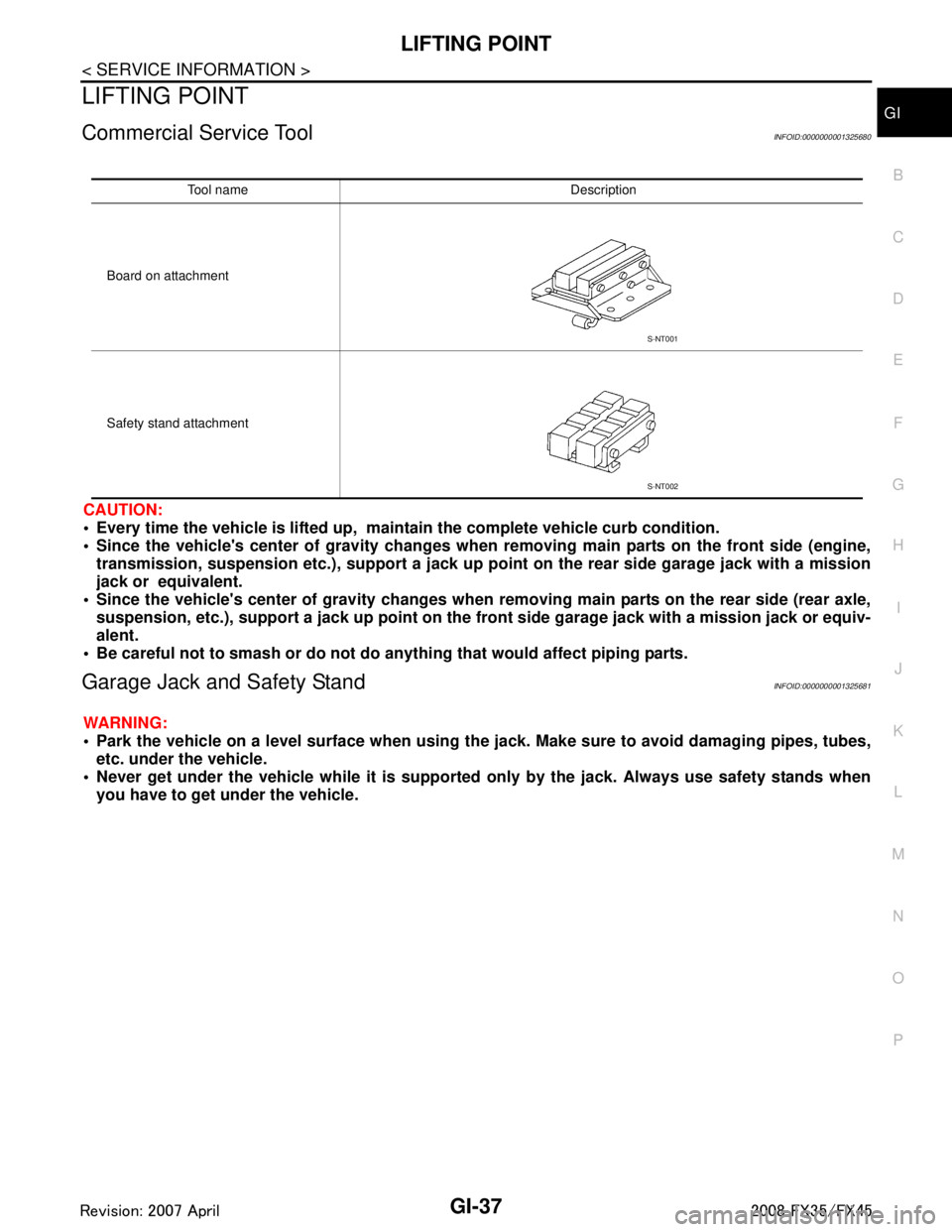
LIFTING POINTGI-37
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
DE
F
G H
I
J
K L
M B
GI
N
O PLIFTING POINT
Commercial Service ToolINFOID:0000000001325680
CAUTION:
Every time the vehicle is lifted up, main tain the complete vehicle curb condition.
Since the vehicle's center of gravity changes when removing main parts on the front side (engine,
transmission, suspension etc.), support a jack up poi nt on the rear side garage jack with a mission
jack or equivalent.
Since the vehicle's center of gravity changes when removing main parts on the rear side (rear axle,
suspension, etc.), support a jack up point on the fr ont side garage jack with a mission jack or equiv-
alent.
Be careful not to smash or do not do an ything that would affect piping parts.
Garage Jack and Safety StandINFOID:0000000001325681
WARNING:
Park the vehicle on a level surface when using th e jack. Make sure to avoid damaging pipes, tubes,
etc. under the vehicle.
Never get under the vehicle while it is supported only by the jack. Always use safety stands when
you have to get under the vehicle.
Tool name Description
Board on attachment
Safety stand attachment
S-NT001
S-NT002
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 2921 of 3924

GW-8
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
Most of these incidents can be repaired by adjusting, securing or insulatingthe item(s) or component(s) caus-
ing the noise.
SUNROOF/HEADLINING
Noises in the sunroof/headlining area c an often be traced to one of the following:
1. Sunroof lid, rail, linkage or seals making a rattle or light knockingnoise
2. Sunvisor shaft shaking in the holder
3. Front or rear windshield touching headlining and squeaking
Again, pressing on the components to stop the noise while duplicatingthe conditions can isolate most of these
incidents. Repairs usually consistof insulating with felt cloth tape.
SEATS
When isolating seat noise it's important to note the pos ition the seatis in and the load placed on the seat when
the noise is present. These conditionsshould be duplic ated when verifying and isolating the cause of the
noise.
Cause of seat noise include:
1. Headrest rods and holder
2. A squeak between the seat pad cushion and frame
3. The rear seatback lock and bracket
These noises can be isolated by moving or pressing on the suspectedcomponents while duplicating the condi-
tions under which the noise occurs.Most of these incidents can be repaired by repositioning the component
orapplying urethane tape to the contact area.
UNDERHOOD
Some interior noise may be caused by components under the hood or onthe engine wall. The noise is then
transmitted into the passenger compartment.
Causes of transmitted underhood noise include:
1. Any component mounted to the engine wall
2. Components that pass through the engine wall
3. Engine wall mounts and connectors
4. Loose radiator mounting pins
5. Hood bumpers out of adjustment
6. Hood striker out of adjustment
These noises can be difficult to isolate since they cannot be reached from the interior of the vehicle. The best
method is to secure, move or insulate one component at a time and test drive the \
vehicle. Also, engine RPM
or load can be changed to isolate the noise. Repairs can usually be made by moving, adjusting, securing, or
insulating the component causing the noise.
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 2931 of 3924

GW-18
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
POWER WINDOW SYSTEM
The one is applied only for front doors and the other is for all doors.
POWER WINDOW SERIAL LINK
Power window main switch, front power window switch (passenger side), and BCM transmit and receive the
signal by power window serial link.
The under mentioned signal is transmitted from BCM to power window main switch and front power window
switch (passenger side)
Keyless power window down signal.
The under mentioned signal is transmitted from power window main switch to front power window switch (pas-
senger side)
Front passenger side door window operation signal.
Power window control by key cylinder switch signal.
Power window lock signal.
Retained power operation signal.
POWER WINDOW LOCK
The power window lock is designed to lock operation of all windows except for driver side door window.
When the lock position, ground of the rear power window switches in the power window main switch is discon-
nected. The power window lock signal is transmitted to front power window switch (passenger side) by power
window serial link. This prevents t he power window motors from operating.
RETAINED POWER OPERATION
When the ignition switch is turned to the OFF position from ON or START position.
Power is supplied for 45 seconds
through BCM terminal 53
to power window main switch terminal 10
to rear power window switch (LH and RH) terminals 1.
When power and ground are supplied, the BCM conti nues to be energized, and the power window can be
operated.
The retained power operation is canceled when the driver or passenger side door is opened.
RAP signal period can be changed by CONSULT-III. Refer to GW-26, "
CONSULT-III Function".
ANTI-PINCH SYSTEM
Power window main switch and front power window switch (passenger side) monitors the power window motor
operation and the power window position (full closed or other) for driver side and passenger side power win-
dow by the signals from encoder and limit switch in front power window motor (driver side and passenger
side).
When power window main switch detects inte rruption during the following close operation,
automatic close operation when igniti on switch is in the “ON” position
automatic close operation during retained power operation
manual close operation during retained power operation
power window main switch or front power window swit ch (passenger side) controls each power window motor
for open and the power window will be lowered about 150 mm (5.91 in).
POWER WINDOW CONTROL BY THE KEY CYLINDER SWITCH
When ignition key switch is OFF, front power window can be opened or closed by turning the key cylinder
switch UNLOCK / LOCK position more than 1.5 second over condition.
Power window can be opened as the door key cylinder is kept fully turning to the UNLOCK position.
Power window can be closed as the door key cylinder is kept fully turning to the LOCK position.
The power window DOWN stops when the following operations are carried out.
While performing open / close the window, power window is stopped at the position as the door key cylinder is placed on NEUTRAL.
When the ignition switch is turned ON while the power window DOWN is operated.
CAN Communication System DescriptionINFOID:0000000001327964
CAN (Controller Area Network) is a serial communication line for real time application. It is an on-vehicle mul-
tiplex communication line with high data communication s peed and excellent error detection ability. Many elec-
tronic control units are equipped onto a vehicle, and each control unit shares information and links with other
control units during operation (not independent). In CA N communication, control units are connected with 2
communication lines (CAN H line, CAN L line) allowing a high rate of information transmission with less wiring.
Each control unit transmits/receives data but selectively reads required data only.
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 2939 of 3924

GW-26
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
POWER WINDOW SYSTEM
CONSULT-III Function
INFOID:0000000001327971
ACTIVE TEST
WORK SUPPORT
DATE MONITOR
12 PU Encoder pulse signal Input When power window motor
operates.
15 GY Limit switch signal Input Passenger side door window
is between fully-open and just
before fully-closed position
(ON)
0
Passenger side door window
is between just before fully-
closed position and fully-
closed position (OFF) 5
16 Y Power window serial link Input/Output IGN SW ON or power window
timer operating.
Te r -
minal Wire
color Item Signal
Input/Output Condition Voltage [V]
(Approx.)
OCC3383D
PIIA2344J
BCM diagnostic test item Check item diagnostic test mode Content
RETAINED PWR Work support Changes setting of each function.
Data monitor Displays the input data of BCM in real time.
Active test Gives a drive signal to a load to check the operation.
Te s t I t e m D e s c r i p t i o n
RETAINED PWR This test is able to supply RAP signal (powe
r) from BCM (body control module) to power window
system and power sunroof system (if equipped). Those systems can be operated when turning on
“RETAINED PWR” on CONSULT-III screen even if the ignition switch is turned OFF.
NOTE:
During this test, CONSULT-III can be operated with ignition switch in “OFF” position. “RETAINED
PWR” should be turned “ON” or “OFF” on CONSULT-III screen when ignition switch is ON. Then
turn ignition switch OFF to check retained power operation. CONSULT-III might be stuck if “RE-
TAINED PWR” is turned to “ON” or “OFF” on CONSULT-III screen when ignition switch is OFF.
Work item Description
RETAINED PWR Rap signal’s power supply period can be changed by mode setting. Selects rap signal’s power sup-
ply period between three steps
MODE1 (45 sec.) / MODE2 (OFF) / MODE 3 (2 min.).
Work item Description
IGN ON SW Indicates (ON / OFF) condition of ignition switch
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 3008 of 3924

SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSESIP-7
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
DE
F
G H
J
K L
M A
B
IP
N
O P
Most of these incidents can be repaired by adjusting, se curing or insulating the item(s) or component(s) caus-
ing the noise.
SUNROOF/HEADLINING
Noises in the sunroof/headlining area can often be traced to one of the following:
1. Sunroof lid, rail, linkage or seals making a rattle or light knocking noise
2. Sunvisor shaft shaking in the holder
3. Front or rear windshield touching headlining and squeaking
Again, pressing on the components to stop the noise while duplicating the conditions can isolate most of these
incidents. Repairs usually consist of insulating with felt cloth tape.
SEATS
When isolating seat noise it's important to note the pos ition the seat is in and the load placed on the seat when
the noise is present. These conditions should be duplic ated when verifying and isolating the cause of the
noise.
Cause of seat noise include:
1. Headrest rods and holder
2. A squeak between the seat pad cushion and frame
3. The rear seatback lock and bracket
These noises can be isolated by moving or pressing on the suspected components while duplicating the con-
ditions under which the noise occurs. Most of thes e incidents can be repaired by repositioning the component
or applying urethane tape to the contact area.
UNDERHOOD
Some interior noise may be caused by components under the hood or on the engine wall. The noise is then
transmitted into the passenger compartment.
Causes of transmitted underhood noise include:
1. Any component mounted to the engine wall
2. Components that pass through the engine wall
3. Engine wall mounts and connectors
4. Loose radiator mounting pins
5. Hood bumpers out of adjustment
6. Hood striker out of adjustment
These noises can be difficult to isolate since they cannot be reached from the interior of the vehicle. The best
method is to secure, move or insulate one component at a time and test drive the vehicle. Also, engine RPM
or load can be changed to isolate the noise. Repairs c an usually be made by moving, adjusting securing, or
insulating the component causing the noise.
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 3103 of 3924

LT-1
ELECTRICAL
C
DE
F
G H
I
J
L
M
SECTION LT
A
B
LT
N
O P
CONTENTS
LIGHTING SYSTEM
SERVICE INFORMATION .. ..........................4
PRECAUTIONS .............................................. .....4
Precaution for Supplemental Restraint System
(SRS) "AIR BAG" and "SEAT BELT PRE-TEN-
SIONER" ............................................................. ......
4
General Precaution for Service Operation ................4
HEADLAMP - XENON TYPE - ............................5
Component Parts and Harness Connector Loca-
tion ...................................................................... ......
5
System Description ...................................................5
CAN Communication System Description .................7
CAN Communication Unit .........................................7
Schematic .................................................................8
Wiring Diagram - H/LAMP - .......................................9
Terminal and Reference Value for BCM .................12
Terminal and Reference Value for IPDM E/R .........14
How to Proceed with Trouble Diagnosis .................14
Preliminary Check ...................................................15
CONSULT-III Functions (BCM) ...............................16
CONSULT-III Functions (IPDM E/R) .......................17
Headlamp Does Not Change To High Beam (Both
Sides) ......................................................................
18
Headlamp Does Not Change To High Beam (One
Side) ........................................................................
20
Headlamp Low Beam Does Not Illuminate (Both
Sides) .................................................................. ....
21
Headlamp Low Beam Does Not Illuminate (One
Side) .................................................................... ....
23
Headlamp RH Low Beam and High Beam Does
Not Illuminate ..........................................................
24
Headlamp LH Low Beam and High Beam Does
Not Illuminate ..........................................................
25
Headlamps Does Not Turn OFF .............................26
General Information for Xenon Headlamp Trouble
Diagnosis ................................................................
26
Caution: ...................................................................26
Xenon Headlamp Trouble Diagnosis ......................27
Aiming Adjustment ..................................................27
Bulb Replacement ...................................................28
Removal and Installation ..................................... ....30
Disassembly and Assembly .....................................30
DAYTIME LIGHT SYSTEM ...............................32
Component Parts and Harness Connector Loca-
tion ....................................................................... ....
32
System Description ..................................................32
CAN Communication System Description ...............33
CAN Communication Unit ........................................33
Schematic ................................................................34
Wiring Diagram - DTRL - .........................................35
Terminal and Reference Value for BCM ..................38
How to Proceed with Trouble Diagnosis ..................41
Preliminary Check ...................................................41
CONSULT-III Functions (BCM) ...............................43
Daytime Light Control Does Not Operate Properly ....44
Aiming Adjustment ...................................................46
Bulb Replacement ...................................................46
Removal and Installation .........................................46
Disassembly and Assembly .....................................46
AUTO LIGHT SYSTEM .....................................47
Component Parts and Harness Connector Loca-
tion ...........................................................................
47
System Description ..................................................47
CAN Communication System Description ...............48
CAN Communication Unit ........................................48
Major Component and Functions ............................48
Schematic ................................................................49
Wiring Diagram - AUTO/L - .....................................50
Terminal and Reference Value for BCM ..................52
Terminal and Reference Value for IPDM E/R ..........54
How to Proceed with Trouble Diagnosis ..................54
Preliminary Check ...................................................55
CONSULT-III Functions (BCM) ...............................56
CONSULT-III Functions (IPDM E/R) .......................57
Symptom Chart ........................................................58
Lighting Switch Inspection .......................................58
Optical sensor System Inspection ...........................59
Removal and Installation of Optical Sensor .............60
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 3107 of 3924
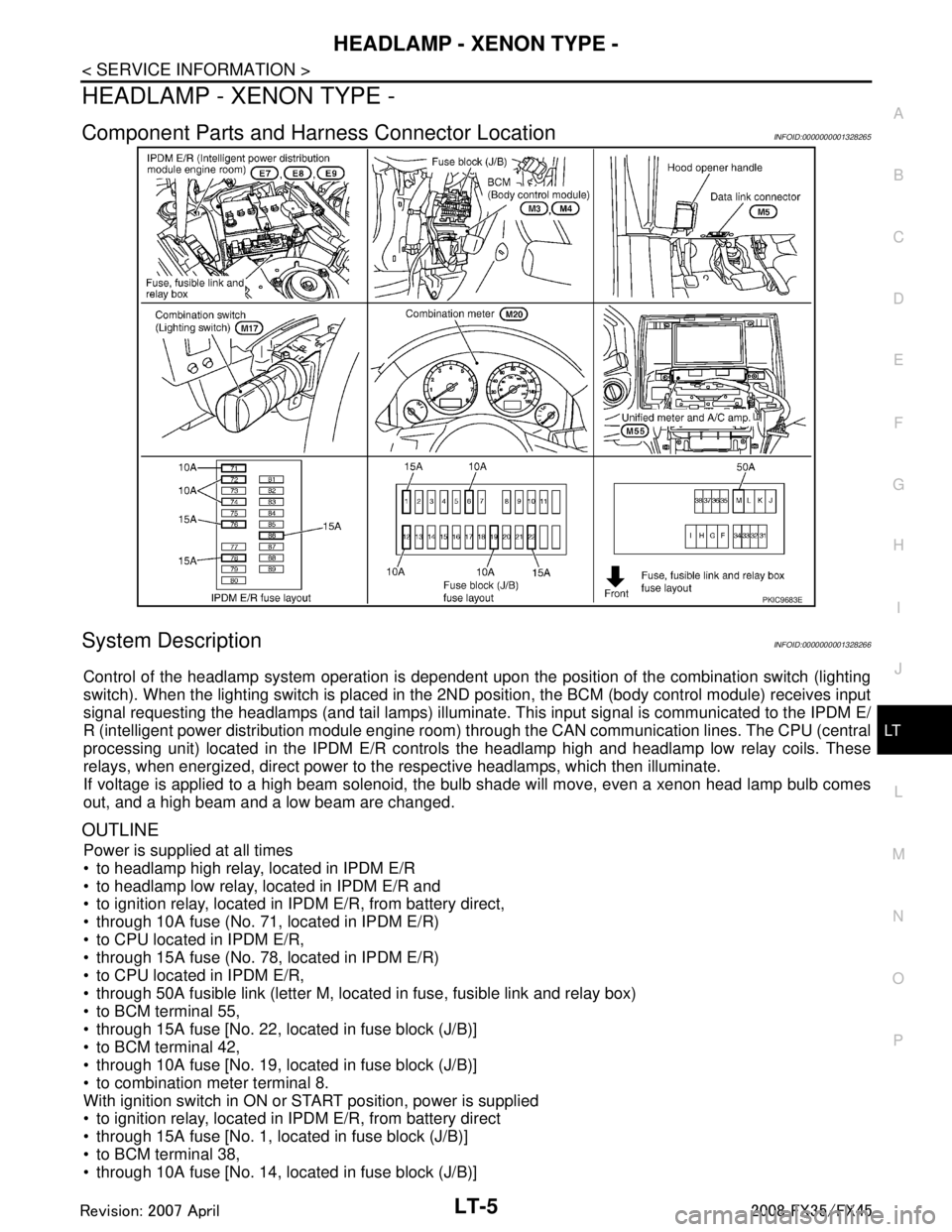
HEADLAMP - XENON TYPE -LT-5
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
DE
F
G H
I
J
L
M A
B
LT
N
O P
HEADLAMP - XENON TYPE -
Component Parts and Har ness Connector LocationINFOID:0000000001328265
System DescriptionINFOID:0000000001328266
Control of the headlamp system operation is dependent upon t he position of the combination switch (lighting
switch). When the lighting switch is placed in the 2ND position, the BCM (body control module) receives input
signal requesting the headlamps (and tail lamps) illuminate. This input signal is communicated to the IPDM E/
R (intelligent power distribution module engine room) through the CAN communication lines. The CPU (central
processing unit) located in the IPDM E/R contro ls the headlamp high and headlamp low relay coils. These
relays, when energized, direct power to the respective headlamps, which then illuminate.
If voltage is applied to a high beam solenoid, the bulb shade will move, even a xenon head lamp bulb comes
out, and a high beam and a low beam are changed.
OUTLINE
Power is supplied at all times
to headlamp high relay, located in IPDM E/R
to headlamp low relay, located in IPDM E/R and
to ignition relay, located in IPDM E/R, from battery direct,
through 10A fuse (No. 71, located in IPDM E/R)
to CPU located in IPDM E/R,
through 15A fuse (No. 78, located in IPDM E/R)
to CPU located in IPDM E/R,
through 50A fusible link (letter M, located in fuse, fusible link and relay box)
to BCM terminal 55,
through 15A fuse [No. 22, located in fuse block (J/B)]
to BCM terminal 42,
through 10A fuse [No. 19, located in fuse block (J/B)]
to combination meter terminal 8.
With ignition switch in ON or START position, power is supplied
to ignition relay, located in IPDM E/R, from battery direct
through 15A fuse [No. 1, located in fuse block (J/B)]
to BCM terminal 38,
through 10A fuse [No. 14, located in fuse block (J/B)]
PKIC9683E
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 3109 of 3924

HEADLAMP - XENON TYPE -LT-7
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
DE
F
G H
I
J
L
M A
B
LT
N
O P
Exterior lamp battery saver control mode can be changed by the function setting of CONSULT-III.
AUTO LIGHT OPERATION (IF EQUIPPED)
Refer to LT-47, "System Description".
VEHICLE SECURITY SYSTEM
The vehicle security system will flash the high beams if the system is triggered. Refer to BL-163.
XENON HEADLAMP
Xenon type lamps are used for to the low beam headlamps . Xenon bulbs do not use a filament. Instead, they
produce light when a high voltage current is passed between two tungsten electrodes through a mixture of
xenon (an inert gas) and certain other metal halides. In addition to strong lighting power, electronic control of
the power supply gives the headlamps stable quality and tone color.
Followings are some advantages of the xenon type headlamp.
The light produced by the headlamps is white color si milar to sunlight that is easy to the eyes.
Light output is nearly double that of halogen headl amps, affording increased area of illumination.
Counter-reflected luminance increases and the contrast enhances on the wet road in the rain. That makes
visibility go up more than the increase of the light volume.
Power consumption is approximately 25 percent less than halogen headlamps, reducing battery load.
CAN Communication System DescriptionINFOID:0000000001328267
CAN (Controller Area Network) is a serial communication li ne for real time application. It is an on-vehicle mul-
tiplex communication line with high data communication speed and excellent error detection ability. Many elec-
tronic control units are equipped onto a vehicle, and each control unit shares information and links with other
control units during operation (not independent). In CAN communication, control units are connected with 2
communication lines (CAN H line, CAN L line) allowing a high rate of information transmission with less wiring.
Each control unit transmits/receives data but selectively reads required data only.
CAN Communication UnitINFOID:0000000001328268
Refer to LAN-43, "CAN System Specification Chart".
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 3118 of 3924

LT-16
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
HEADLAMP - XENON TYPE -
Check continuity between BCM harness connector and ground.
OK or NG
OK >> INSPECTION END
NG >> Repair harness or connector.
CONSULT-III Functions (BCM)INFOID:0000000001328275
CONSULT-III can display each diagnostic item using the diagnostic test mode shown following.
CONSULT-III BASIC OPERATION
Refer to GI-34, "Description".
WORK SUPPORT
Display Item List
DATA MONITOR
Display Item List
BCM connector Terminal
GroundContinuity
M4 49
Ye s
52
SKIA5294E
BCM diagnosis part Diagnosis mode Description
HEADLAMP WORK SUPPORT Changes the setting for each function.
DATA MONITOR Displays BCM input data in real time. ACTIVE TEST Operation of electrical loads can be checked by sending drive signal to them.
BCM SELF-DIAG RESULTS BCM performs self-diagnosis of CAN communication.
CAN DIAG SUPPORT MNTR The result of transmit/receive diagnosis of CAN communication can be read.
Item Description CONSULT-III Factory setting
BATTERY SAVER SET Exterior lamp battery saver control mode can be changed in this mode.
Selects exterior lamp battery saver control mode between two ON/OFF. ON
×
OFF —
Monitor item Contents
IGN ON SW “ON/OFF” Displays “IGN posi tion (ON)/OFF, ACC position (OFF)” judged from ignition switch signal.
ACC ON SW “ON/OFF” Displays “ACC (ON)/O FF, Ignition OFF (OFF)” status judged from ignition switch signal.
HI BEAM SW “ON/OFF” Displays status (high beam switch: ON/Others: OFF) of high beam switch judged from light-
ing switch signal.
HEAD LAMP SW 1 “ON/OFF” Displays status (headlamp switch 1: ON/Others: OFF) of headlamp switch 1 judged from
lighting switch signal.
HEAD LAMP SW 2 “ON/OFF” Displays status (headlamp switch 2: ON/Others: OFF) of headlamp switch 2 judged from
lighting switch signal.
LIGHT SW 1 ST “ON/OFF” Displays status (lighting switch 1ST or 2ND position: ON/Others: OFF) of lighting switch
judged from lighting switch signal.
AUTO LIGHT SW
NOTE 1 “ON/OFF” Displays status of lighting switch as judged from lighting switch signal. (AUTO position: ON/
Other than AUTO position: OFF)
PASSING SW “ON/OFF” Displays status (flash-to-pass switch: ON/Others: OFF) of flash-to-pass switch judged from
lighting switch signal.
FR FOG SW “ON/OFF” Displays status (front fog lamp switch: ON/Others: OFF) of front fog lamp switch judged
from lighting switch signal.
RR FOG SW
NOTE 3“OFF” —
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C