injector ISUZU TF SERIES 2004 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2004, Model line: TF SERIES, Model: ISUZU TF SERIES 2004Pages: 4264, PDF Size: 72.63 MB
Page 2679 of 4264
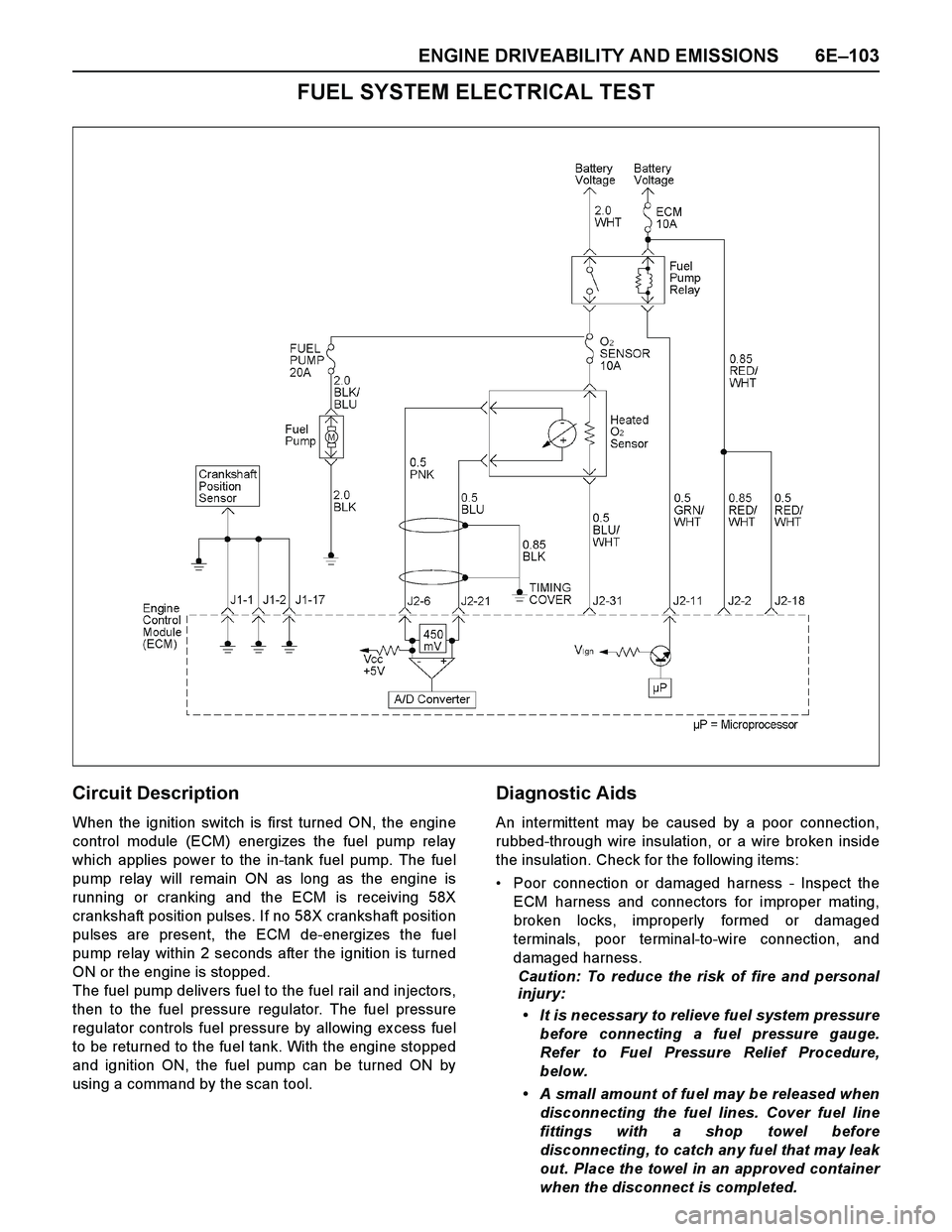
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–103
FUEL SYSTEM ELECTRICAL TEST
Circuit Description
When the ignition switch is first turned ON, the engine
control module (ECM) energizes the fuel pump relay
which applies power to the in-tank fuel pump. The fuel
pump relay will remain ON as long as the engine is
running or cranking and the ECM is receiving 58X
crankshaft position pulses. If no 58X crankshaft position
pulses are present, the ECM de-energizes the fuel
pump relay within 2 seconds after the ignition is turned
ON or the engine is stopped.
The fuel pump delivers fuel to the fuel rail and injectors,
then to the fuel pressure regulator. The fuel pressure
regulator controls fuel pressure by allowing ex cess fuel
to be returned to the fuel tank. With the engine stopped
and ignition ON, the fuel pump can be turned ON by
using a command by the scan tool.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed-through wire insulation, or a wire broken inside
the insulation. Check for the following items:
Poor connection or damaged harness - Inspect the
ECM harness and connectors for improper mating,
broken locks, improperly formed or damaged
terminals, poor terminal-to-wire connection, and
damaged harness.
Caution: To reduce the risk of fire and personal
injury:
It is necessary to relieve fuel system pressure
before connecting a fuel pressure gauge.
Refer to Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure,
below.
A small amount of fuel may be released when
disconnecting the fuel lines. Cover fuel line
fittings with a shop towel before
disconnecting, to catch any fuel that may leak
out. Place the towel in an approved container
when the disconnect is completed.
Page 2684 of 4264
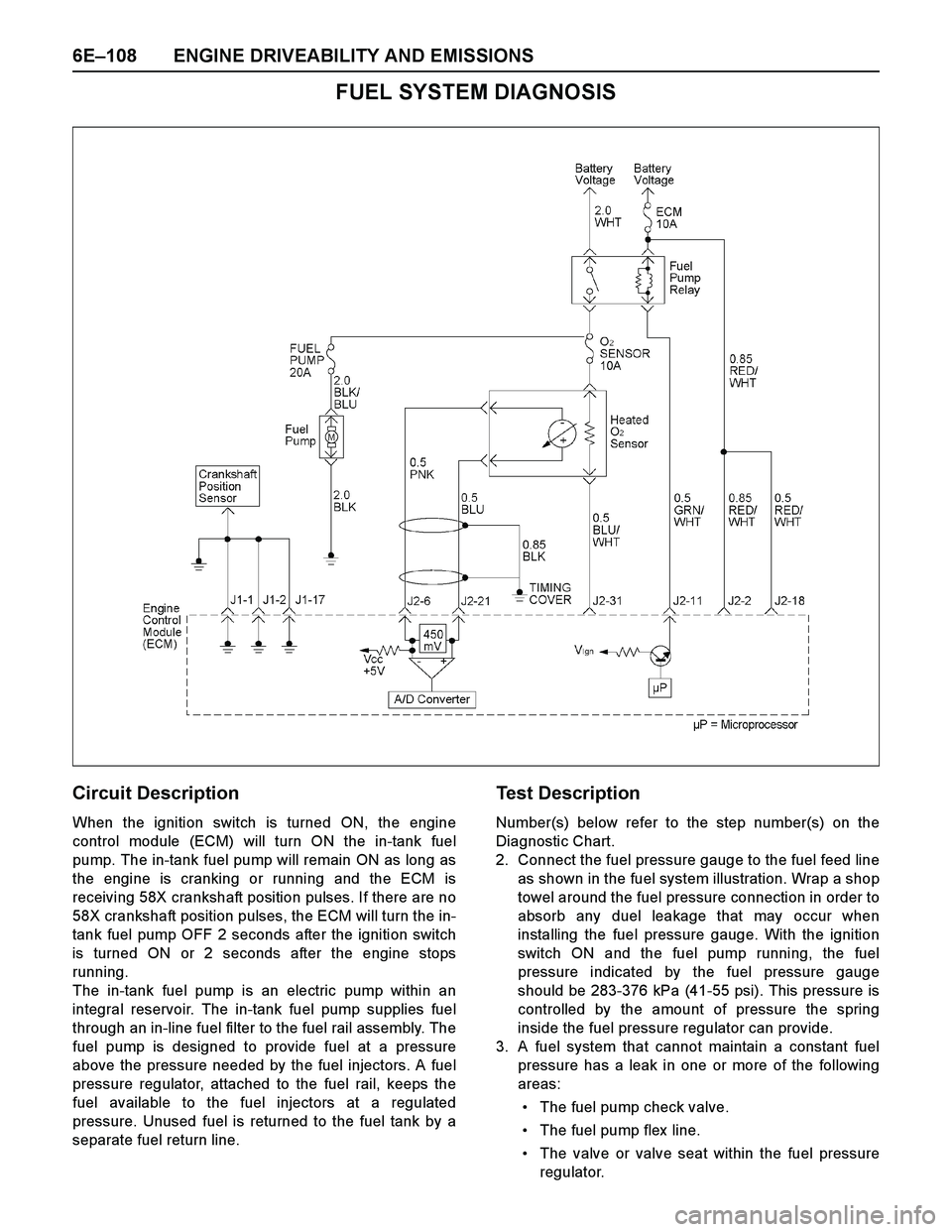
6E–108 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
FUEL SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
Circuit Description
When the ignition switch is turned ON, the engine
control module (ECM) will turn ON the in-tank fuel
pump. The in-tank fuel pump will remain ON as long as
the engine is cranking or running and the ECM is
receiving 58X crankshaft position pulses. If there are no
58X crankshaft position pulses, the ECM will turn the in-
tank fuel pump OFF 2 seconds after the ignition switch
is turned ON or 2 seconds after the engine stops
running.
The in-tank fuel pump is an electric pump within an
integral reservoir. The in-tank fuel pump supplies fuel
through an in-line fuel filter to the fuel rail assembly. The
fuel pump is designed to provide fuel at a pressure
above the pressure needed by the fuel injectors. A fuel
pressure regulator, attached to the fuel rail, keeps the
fuel available to the fuel injectors at a regulated
pressure. Unused fuel is returned to the fuel tank by a
separate fuel return line.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
2. Connect the fuel pressure gauge to the fuel feed line
as shown in the fuel system illustration. Wrap a shop
towel around the fuel pressure connection in order to
absorb any duel leakage that may occur when
installing the fuel pressure gauge. With the ignition
switch ON and the fuel pump running, the fuel
pressure indicated by the fuel pressure gauge
should be 283-376 kPa (41-55 psi). This pressure is
controlled by the amount of pressure the spring
inside the fuel pressure regulator can provide.
3. A fuel system that cannot maintain a constant fuel
pressure has a leak in one or more of the following
areas:
The fuel pump check valve.
The fuel pump flex line.
The valve or valve seat within the fuel pressure
regulator.
Page 2685 of 4264

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–109
The fuel injector(s).
4. Fuel pressure that drops off during acceleration,
cruise, or hard cornering may case a lean condition.
A lean condition can cause a loss of power, surging,
or misfire. A lean condition can be diagnosed using a
Tech 2 Scan Tool.
Following are applicable to the vehicle with
closed Loop System:
If an ex tremely lean condition occurs, the ox ygen
sensor(s) will stop toggling. The ox ygen sensor
output voltage(s) will drop below 500 mV. Also, the
fuel injector pulse width will increase.
Important: Make sure the fuel system is not
operating in the “Fuel Cut-Off Mode.”
When the engine is at idle, the manifold pressure is
low (high vacuum). This low pressure (high vacuum)
is applied to the fuel pressure regulator diaphragm.
The low pressure (high vacuum) will offset the
pressure being applied to the fuel pressure regulator
diaphragm by the spring inside the fuel pressure
regulator. When this happens, the result is lower fuel
pressure. The fuel pressure at idle will vary slightly
as the barometric pressure changes, but the fuel
pressure at idle should always be less than the fuel
pressure noted in step 2 with the engine OFF.
16.Check the spark plug associated with a particular
fuel injector for fouling or saturation in order to
determine if that particular fuel injector is leaking. If
checking the spark plug associated with a particular
fuel injector for fouling or saturation does not
determine that a particular fuel injector is leaking,
use the following procedure:
Remove the fuel rail, but leave the fuel lines and
injectors connected to the fuel rail. Refer to Fuel
Rail Assembly in On-Vehicle Service.
Lift the fuel rail just enough to leave the fuel
injector nozzles in the fuel injector ports.
Caution: In order to reduce the risk of fire and
personal injury that may result from fuel
spraying on the engine, verify that the fuel rail is
positioned over the fuel injector ports and verify
that the fuel injector retaining clips are intact.
Pressurize the fuel system by connecting a 20
amp fused jumper between B+ and the fuel
pump relay connector.
Visually and physically inspect the fuel
injector nozzles for leaks.
17.A rich condition may result from the fuel pressure
being above 376 kPa (55 psi). A rich condition may
cause a 45 to set. Driveability conditions associatedwith rich conditions can include hard starting
(followed by black smoke) and a strong sulfur smell
in the ex haust.
20.This test determines if the high fuel pressure is due
to a restricted fuel return line or if the high fuel
pressure is due to a faulty fuel pressure regulator.
21.A lean condition may result from fuel pressure below
333 kPa (48 psi). A lean condition may cause a 44 to
set. Driveability conditions associated with lean
conditions can include hard starting (when the
engine is cold), hesitation, poor driveability, lack of
power, surging, and misfiring.
22.Restricting the fuel return line causes the fuel
pressure to rise above the regulated fuel pressure.
Command the fuel pump ON with the scan tool. The
fuel pressure should rise above 376 kPa (55 psi) as
the fuel return line becomes partially closed.
NOTE: Do not allow the fuel pressure to exceed 414
kPa (60 psi). Fuel pressure in excess of 414 kPa (60
psi) may damage the fuel pressure regulator.
Caution: To reduce the risk of fire and personal
injury:
It is necessary to relieve fuel system pressure
before connecting a fuel pressure gauge.
Refer to Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure,
below.
A small amount of fuel may be released when
disconnecting the fuel lines. Cover fuel line
fittings with a shop towel before
disconnecting, to catch any fuel that may leak
out. Place the towel in an approved container
when the disconnect is completed.
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure
1. Remove the fuel cap.
2. Located on the intake manifold which is at the top
right part of the engine.
3. Start the engine and allow it to stall.
4. Crank the engine for an additional 3 seconds.
Fuel Pressure Gauge Installation
1. Remove the fuel pressure fitting cap.
2. Install fuel pressure gauge 5-8840-0378-0 to the
fuel feed line located on the upper right side of the
engine.
3. Reinstall the fuel pump relay.
Page 2687 of 4264
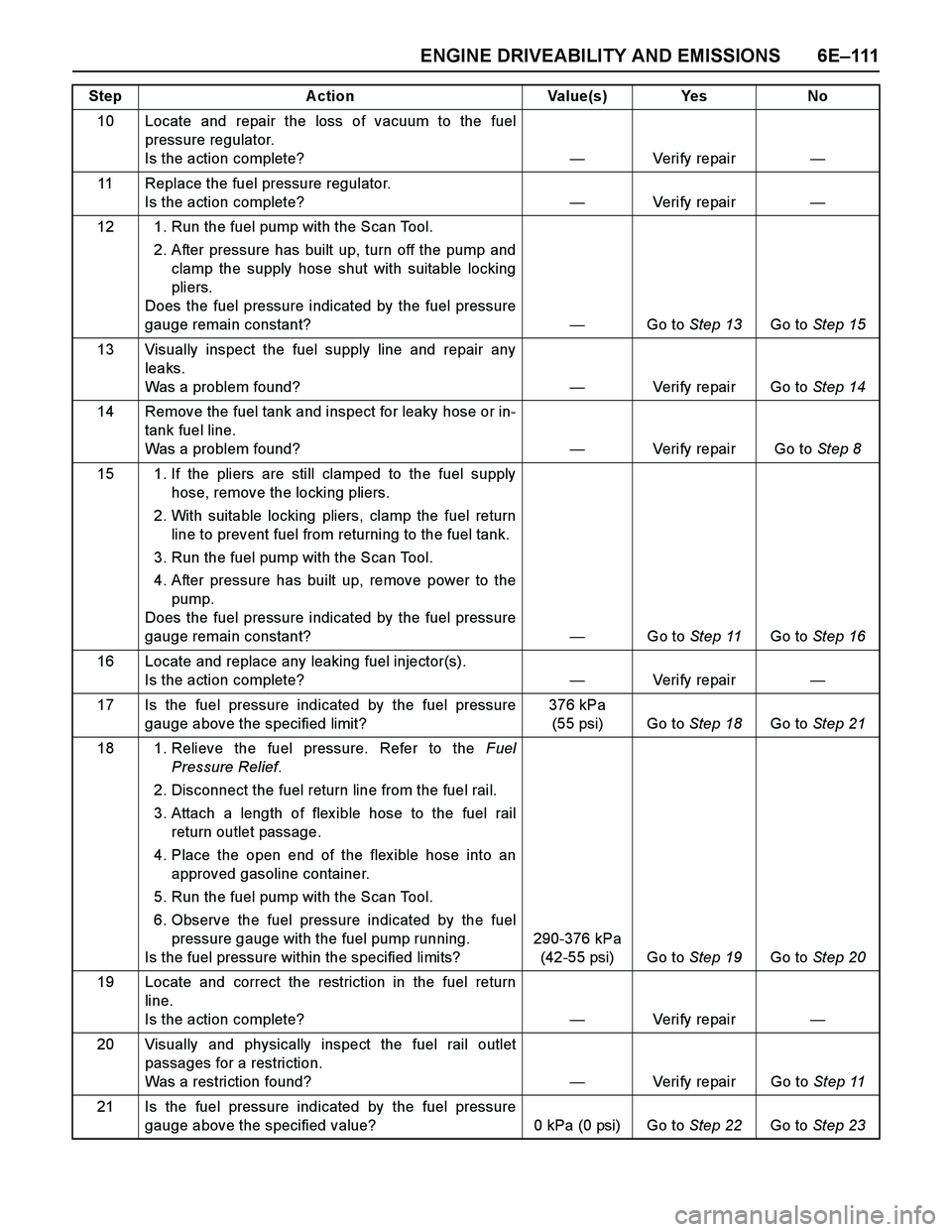
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–111
10 Locate and repair the loss of vacuum to the fuel
pressure regulator.
Is the action complete?—Veri fy repai r—
11 Replace the fuel pressure regulator.
Is the action complete?—Veri fy repai r—
12 1. Run the fuel pump with the Scan Tool.
2. After pressure has built up, turn off the pump and
clamp the supply hose shut with suitable locking
pliers.
Does the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel pressure
gauge remain constant?—Go to Step 13Go to Step 15
13 Visually inspect the fuel supply line and repair any
leaks.
Was a problem found?—Verify repair Go to Step 14
14 Remove the fuel tank and inspect for leaky hose or in-
tank fuel line.
Was a problem found?—Verify repair Go to Step 8
15 1. If the pliers are still clamped to the fuel supply
hose, remove the locking pliers.
2. With suitable locking pliers, clamp the fuel return
line to prevent fuel from returning to the fuel tank.
3. Run the fuel pump with the Scan Tool.
4. After pressure has built up, remove power to the
pump.
Does the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel pressure
gauge remain constant?—Go to Step 11Go to Step 16
16 Locate and replace any leaking fuel injector(s).
Is the action complete?—Veri fy repai r—
17 Is the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel pressure
gauge above the specified limit?376 kPa
(55 psi) Go to Step 18Go to Step 21
18 1. Relieve the fuel pressure. Refer to the Fuel
Pressure Relief.
2. Disconnect the fuel return line from the fuel rail.
3. Attach a length of flex ible hose to the fuel rail
return outlet passage.
4. Place the open end of the flex ible hose into an
approved gasoline container.
5. Run the fuel pump with the Scan Tool.
6. Observe the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel
pressure gauge with the fuel pump running.
Is the fuel pressure within the specified limits?290-376 kPa
(42-55 psi) Go to Step 19Go to Step 20
19 Locate and correct the restriction in the fuel return
line.
Is the action complete?—Veri fy repai r—
20 Visually and physically inspect the fuel rail outlet
passages for a restriction.
Was a restriction found?—Verify repair Go to Step 11
21 Is the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel pressure
gauge above the specified value? 0 kPa (0 psi) Go to Step 22Go to Step 23 Step Action Value(s) Yes No
Page 2691 of 4264
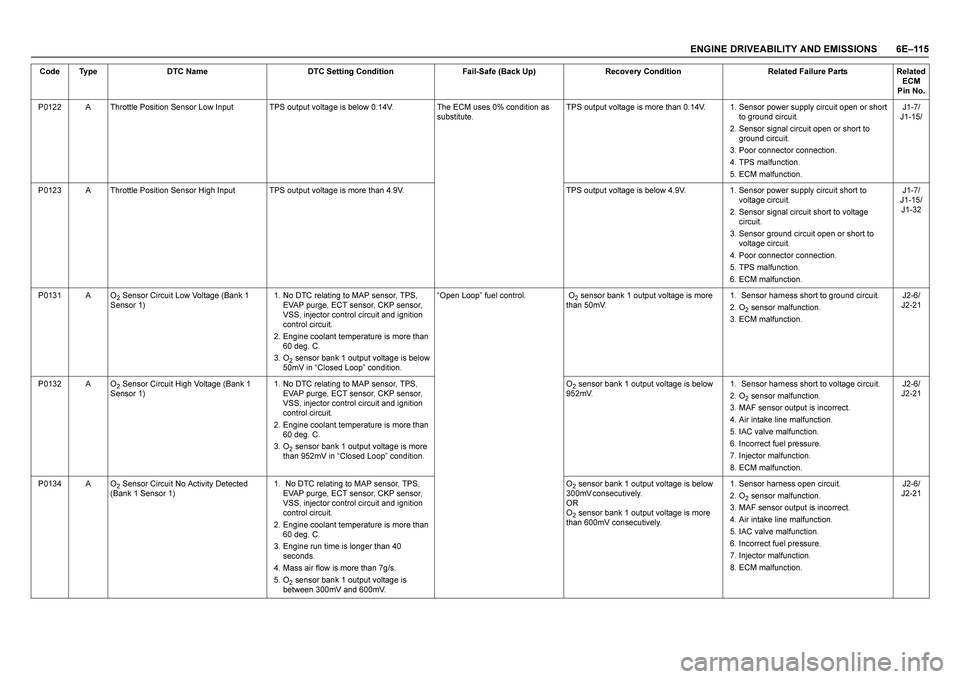
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–115
P0122 A Throttle Position Sensor Low Input TPS output voltage is below 0.14V. The ECM uses 0% condition as
substitute.TPS output voltage is more than 0.14V. 1. Sensor power supply circuit open or short
to ground circuit.
2. Sensor signal circuit open or short to
ground circuit.
3. Poor connector connection.
4. TPS malfunction.
5. ECM malfunction.J1-7/
J1-15/
P0123 A Throttle Position Sensor High Input TPS output voltage is more than 4.9V. TPS output voltage is below 4.9V. 1. Sensor power supply circuit short to
voltage circuit.
2. Sensor signal circuit short to voltage
circuit.
3. Sensor ground circuit open or short to
voltage circuit.
4. Poor connector connection.
5. TPS malfunction.
6. ECM malfunction.J1-7/
J1-15/
J1-32
P0131 A O
2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1
Sensor 1)1. No DTC relating to MAP sensor, TPS,
EVAP purge, ECT sensor, CKP sensor,
VSS, injector control circuit and ignition
control circuit.
2. Engine coolant temperature is more than
60 deg. C.
3. O
2 sensor bank 1 output voltage is below
50mV in “Closed Loop” condition. “Open Loop” fuel control. O
2 sensor bank 1 output voltage is more
than 50mV.1. Sensor harness short to ground circuit.
2. O
2 sensor malfunction.
3. ECM malfunction.J2-6/
J2-21
P0132 A O
2 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1
Sensor 1)1. No DTC relating to MAP sensor, TPS,
EVAP purge, ECT sensor, CKP sensor,
VSS, injector control circuit and ignition
control circuit.
2. Engine coolant temperature is more than
60 deg. C.
3. O
2 sensor bank 1 output voltage is more
than 952mV in “Closed Loop” condition. O
2 sensor bank 1 output voltage is below
952mV.1. Sensor harness short to voltage circuit.
2. O
2 sensor malfunction.
3. MAF sensor output is incorrect.
4. Air intake line malfunction.
5. IAC valve malfunction.
6. Incorrect fuel pressure.
7. Injector malfunction.
8. ECM malfunction.J2-6/
J2-21
P0134 A O
2 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected
(Bank 1 Sensor 1)1. No DTC relating to MAP sensor, TPS,
EVAP purge, ECT sensor, CKP sensor,
VSS, injector control circuit and ignition
control circuit.
2. Engine coolant temperature is more than
60 deg. C.
3. Engine run time is longer than 40
seconds.
4. Mass air flow is more than 7g/s.
5. O
2 sensor bank 1 output voltage is
between 300mV and 600mV.O
2 sensor bank 1 output voltage is below
3 0 0 m V c o n s e c u t i v e l y .
O R
O2 sensor bank 1 output voltage is more
than 600mV consecutively.1. Sensor harness open circuit.
2. O
2 sensor malfunction.
3. MAF sensor output is incorrect.
4. Air intake line malfunction.
5. IAC valve malfunction.
6. Incorrect fuel pressure.
7. Injector malfunction.
8. ECM malfunction.J2-6/
J2-21 Code Type DTC Name DTC Setting Condition Fail-Safe (Back Up) Recovery Condition Related Failure Parts Related
ECM
Pin No.
Page 2692 of 4264

6E–116 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONSP0135 A O
2 Sensor Heater Circuit (Bank 1 Sensor
1)1. No DTC relating to MAP sensor and ECT
sensor.
2. Engine coolant temperature is more than
60 deg. C.
3. Engine run time is longer than 20
seconds.
4. MAP sensor output is more than 70kPa.
5. O
2 sensor bank 1 heater current more
than 10mA.No fail-safe function. O
2 sensor bank 1 heater circuit is correct
condition.1. Heater harness open, short to ground or
short to voltage circuit.
2. O
2 sensor heater malfunction.
3. ECM malfunction.J2-31
P0201 A Injector 1 Control Circuit 1. Engine is running.
2. Engine speed is more than 1000rpm.
3. Injector voltage does not meet to the
battery voltage when the injector is
commanded Off or does not meet to the
0V when the injector is commanded On.Injector circuit is correct condition. 1. Injector harness open circuit, short to
ground or short to voltage circuit.
2. Injector malfunction.
3. ECM malfunction.J1-9
P0202 A Injector 2 Control CircuitJ1-22
P0203 A Injector 3 Control CircuitJ1-8
P0204 A Injector 4 Control CircuitJ1-11
P0325 B Knock Sensor Module Circuit 1. No DTC relating to MAP sensor.
2. Engine coolant temperature is more than
50 deg. C.
3. Engine speed is more than 1600rpm.
4. Knock sensor filter module integrated
circuit malfunction.ECM retards ignition timing 4 deg.
C.Knock sensor is correct condition. 1. KS harness open circuit.
2. Poor connector connection.
3. KS sensor malfunction.
4. ECM malfunction.J1-3/
J1-32
P0327 A Knock Sensor Circuit 1. No DTC relating to MAP sensor.
2. Engine coolant temperature is more than
50 deg. C.
3. Engine speed is more than 1600rpm.
4. Knock sensor harness short to ground or
short to voltage circuit.1. KS harness short to ground or short to
voltage circuit.
2. Poor connector connection.
3. KS sensor malfunction.
4. ECM malfunction.J1-3/
J1-32
P0336 B Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit Range/
Performance (58X)1. Engine is running.
2. Extra or missing pulse is detected
consecutively. No fail-safe function. Correct pulse is detected consecutively. 1. CKP sensor harness open circuit, short to
ground or short to voltage circuit.
2. Poor connector connection.
3. CKP sensor malfunction.
4. Pulse sensing gap incorrect.
5. Pluser malfunction.
6. Electrical interference.
7. Magnetic interference.
8. ECM malfunction.J1-6/
J1-21
P0337 B Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit Low
Input (58X)No pulse is detected during engine cranking.1. CKP sensor harness open circuit, short to
ground or short to voltage.
2. Poor connector connection.
3. CKP sensor malfunction.
4. Pulse sensing gap incorrect.
5. Pluser malfunction.
6. Electrical interference.
7. Magnetic interference.
8. ECM malfunction.J1-6/
J1-21 Code Type DTC Name DTC Setting Condition Fail-Safe (Back Up) Recovery Condition Related Failure Parts Related
ECM
Pin No.
Page 2693 of 4264

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–117
P0351 A Ignition 1 Control Circuit #1 or #4cylinder ignition signals are not
detected consecutively.No fail-safe function. Consecutive ignition signals are detected. 1. Ignition coil module 1 harness open
circuit, short to ground or short to voltage
circuit.
2. Ignition coil module malfunction.
3. ECM malfunction.J1-19
P0352 A Ignition 2 Control Circuit #2 or #3 cylinder ignition signals are not
detected consecutively.1. Ignition coil module 2 harness open circuit,
short to ground or short to voltage circuit.
2. Ignition coil module malfunction.
3. ECM malfunction.J1-18
P0443 B EVAP Emission Control System Purge
Control CircuitEVAP purge solenoid circuit open, short to
ground or short to voltage circuit.No fail-safe function. EVAP purge solenoid circuit is correct
condition.1. Solenoid harness open circuit, short to
ground or short to voltage circuit.
2. Solenoid malfunction.
3. ECM malfunction.J1-5
P0502 B Vehicle Speed Sensor Circuit Low Input 1. No DTC relating to MAP sensor, TPS,
ECT sensor, injector control circuit and
ignition control circuit.
2. Engine is running.
3. Vehicle speed is below 3km/h in power
condition or 2km/h in deceleration
condition.ECM uses 0km/h condition as
substitute.VSS circuit correct condition. 1. Sensor harness open circuit, short to
ground circuit or short to voltage circuit.
2. Poor connector connection.
3. VSS malfunction.
4. ECM malfunction.J2-23
P0562 D System Voltage Low Battery voltage is below 11V. No fail-safe function. Battery voltage is between 11V and 16V. 1. Battery power feed harness open circuit
or short to ground circuit.
2. ECM ground harness open or poor
connection.
3. Poor connector connection.
4. Battery malfunction.
5. Charge system malfunction.
6. ECM malfunction.-
P0563 A System Voltage High Battery voltage is above 16V.1. Charge system malfunction.
2. Battery jump start cable misconnect.
3. ECM malfunction.-
P0601 A ECM Memory Checksum ECM memory area error. Engine control disabled. Memory are is OK. ECM malfunction. -
P0602 - ECU Programming Error ECM memory area error. Engine control disabled. Memory are is OK. ECM is not programmed. -
P0650 A Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) Control
Circuit MalfunctionCheck engine lamp circuit open, short to
ground or short to voltage circuit.No fail-safe function. Check engine lamp circuit is correct
condition.1. Solenoid harness open circuit, short to
ground or short to voltage circuit.
2. Solenoid malfunction.
3. ECM malfunction.J2-32 Code Type DTC Name DTC Setting Condition Fail-Safe (Back Up) Recovery Condition Related Failure Parts Related
ECM
Pin No.
Page 2694 of 4264

6E–118 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONSP1167 D Fuel Supply System Rich During
Deceleration Fuel Cutoff1. No DTC relating to MAP sensor, TPS,
EVAP purge, ECT sensor, CKP sensor,
VSS, injector control circuit and ignition
control circuit.
2. O
2 sensor bank 1 output voltage is more
than 550mV in deceleration fuel cutoff
mode.No fail-safe function. O
2 sensor output voltage is below 550mV. 1. Sensor harness open or short to ground
circuit.
2. O
2 sensor malfunction.
3. MAF sensor output is incorrect.
4. Air intake line malfunction.
5. IAC valve malfunction.
6. Low fuel pressure.
7. Injector malfunction.
8. EVAP purge solenoid valve malfunction.
9. Ignition system malfunction.
10. Spark plug malfunction.
11. ECM malfunction.J2-6/
J2-21
P1171 D Fuel Supply System Lean During Power
Enrichment 1. No DTC relating to MAP sensor, TPS,
EVAP purge, ECT sensor, CKP sensor,
VSS, injector control circuit and ignition
control circuit.
2. Engine coolant temperature is more than
60deg. C.
3. Mass air flow is below 13.5m/s.
4. O
2 sensor bank 1 output voltage is below
350mV in power enrichment mode. No fail-safe function. O
2 sensor output voltage is more than
350mV.1. Sensor harness open or short to ground
circuit.
2. O
2 sensor malfunction.
3. MAF sensor output is incorrect.
4. Air intake line malfunction.
5. IAC valve malfunction.
6. Low fuel pressure.
7. Injector malfunction.
8. ECM malfunction.J2-6/
J2-21
P1625 B ECM System Reset ECM reset has occurred other than “On”. Engine control disabled. Memory are is OK. 1. Electrical interference.
2. Magnetic interference.
3. ECM malfunction.-
P1626 - Immobilizer No Signal No response from immobilizer control unit. 1. Engine does not start.
2. Check engine lamp flash.No recovery. 1. ECM and immobilizer control unit
communication circuit open circuit, short to
ground circuit or short to voltage circuit.
2. ECM malfunction.
3. Immobilizer control unit malfunction.
4. Transponder key malfunction.J2-23/
J2-32
P1631 - Immobilizer Wrong Signal Received response is not correct.1. ECM malfunction.
2. Immobilizer control unit malfunction.
3. Transponder key malfunction.-
P1648 - Wrong Security Code Entered Received incorrect security code.1. ECM malfunction.
2. Immobilizer control unit malfunction.
3. Transponder key malfunction.-
P1649 - Immobilizer Function Not Programmed Immobilizer function is not programmed in the
ECM.ECM malfunction. -
P1693 B Tachometer Output Low Voltage Tacho output circuit short to ground circuit. No fail-safe function. Tacho output circuit is correct condition. 1. Tacho output circuit short to ground circuit.
2. Poor connector connection.
3. ECM malfunction.J2-25 Code Type DTC Name DTC Setting Condition Fail-Safe (Back Up) Recovery Condition Related Failure Parts Related
ECM
Pin No.
Page 2727 of 4264

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–151
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0131 O2 SENSOR CIRCUIT LOW
VOLTAGE (BANK 1 SENSOR 1)
Condition for setting the DTC and action taken when the DTC sets
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) supplies a bias
voltage of about 450 mV between the heated ox ygen
sensor (HO2S) signal and low circuits. The ox ygen
sensor varies the voltage within a range of about 1000
mV when the ex haust is rich, down through about 10
mV when ex haust is lean. The ECM constantly monitors
the HO2S signal during “Closed Loop” operation and
compensates for a rich or lean condition by decreasing
or increasing injector pulse width as necessary. If theBank 1 HO2S 1 voltage remains ex cessively low for an
ex tended period of time, Diagnostic Trouble Code
P0131 will be set.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Heated oxygen sensor wiring - The sensor pigtail
may be routed incorrectly and/or contacting the
exhaust system. Also, check for shorts to ground,
shorts to battery positive and open circuits.
Code Type DTC Name DTC Setting Condition Fail-Safe (Back Up)
P0131 A O
2 SensorCircuit Low Voltage (Bank 1
Se nsor 1)1. No DTC re lating to MAP senso r, TPS,
EVAP purge, ECT sensor, CKP sensor,
VSS, injecto r contro l circuit and ignitio n
co ntro l circuit.
2. Engine coolant temperature is more than
60 de g. C.
3. O
2 sensor bank 1 output voltage is below
50mV in “Closed Loop” condition. “Ope n Lo op” fuel control.
Page 2728 of 4264

6E–152 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Poor ECM to engine block grounds.
Fuel pressure - The system will go lean if pressure is
too low. The ECM can compensate for some
decrease. However, if fuel pressure is too low, a
Diagnostic Trouble Code P0131 may be set. Refer to
Fuel System Diagnosis.
Lean injector(s) - Perform “I njector Balance Test.”
Vacuum leaks - Check for disconnected or damaged
vacuum hoses and for vacuum leaks at the intake
manifold, throttle body, EGR system, and PCV
system.Ex haust leaks - An ex haust leak may cause outside
air to be pulled into the ex haust gas stream past the
HO2S, causing the system to appear lean. Check for
exhaust leaks that may cause a false lean condition
to be indicated.
Fuel contamination - Water, even in small amounts,
can be delivered to the fuel injectors. The water can
cause a lean ex haust to be indicated. Ex cessive
alcohol in the fuel can also cause this condition. For
the procedure to check for fuel contamination, Refer
to Fuel System Diagnosis.
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0131
O
2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
Step A ction Value(s) Yes No
1 Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2Go to On Board
Diagnostic
(OBD) System
Check
2 1. Connect the Tech 2.
2. Review and record the failure information.
3. Select “F0: Read DTC Infor By Priority” in “F0:
Diagnostic Trouble Code”.
Is the DTC P0131 stored as “Present Failure”?—Go to Step 3Refer to
Diagnostic Aids
and Go to Step
3
3 1. Using the Tech2, ignition “On” and engine “Off”.
2. Select “Clear DTC Information” with the Tech2 and
clear the DTC information.
3. Operate the vehicle and monitor the “F5: Failed
This Ignition” in “F2: DTC Information”.
Was the DTC P0131 stored in this ignition cycle?—Go to Step 4Refer to
Diagnostic Aids
and Go to Step
4
4 Check for poor/faulty connection at the O
2 sensor or
ECM connector. If a poor/faulty connection is found,
repair as necessary.
Was the problem found?
—Verify repair Go to Step 5
5 Using the DVM and check the O
2 sensor circuit.
1. Ignition “On”, engine “Off”.
2. Disconnect the O
2 sensor connector.
3. Check the circuit for short to heater ground or
ground circuit.
Was the DVM indicated specified value?
Approximatly
450mV Go to Step 7Go to Step 6
C56(J2) E77
31 216
V
2 1
E77