electrical system ISUZU TROOPER 1998 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 1998, Model line: TROOPER, Model: ISUZU TROOPER 1998Pages: 3573, PDF Size: 60.36 MB
Page 3489 of 3573

RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM 9J1±2
Diagnostic Information
CAUTION: When fasteners are removed, always
reinstall them at the same location from which they
were removed. if a fastener needs to be replaced, use
the correct part number fastener for that application.
if the correct part number fastener is not available, a
fastener of equal size and strength (or stronger) may
be used. fasteners that are not reused, and those
requiring thread locking compound will be called
out. the correct torque value must be used when
installing fasteners that require it. if the above
conditions are not followed, parts or system damage
could result.
Diagnostic Procedures
WARNING: T O AV O I D D E P L O Y M E N T W H E N
TROUBLESHOOTING THE SRS, DO NOT USE
ELECTRICAL TEST EQUIPMENT SUCH AS A
BATTERY±POWERED OR AC±POWERED
VOLTMETER, OHMMETER, ETC., OR ANY TYPE OF
ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT OTHER THAN THAT
SPECIFIED IN THIS MANUAL. DO NOT USE A NON
POWERED, PROBE±TYPE TESTER.
INSTRUCTIONS IN THIS MANUAL MUST BE
FOLLOWED CAREFULLY, OTHERWISE PERSONAL
INJURY MAY RESULT.
The diagnostic procedures used in this section are
designed to aid in finding and repairing SRS problems.
Outlined below are the steps to find and repair SRS
problems quickly and effectively. Failure to carefully
follow these procedures may result in extended
diagnostic time, incorrect diagnosis and incorrect parts
replacement.
1.Perform The ªSRS Diagnostic System Checkº.
The ªSRS Diagnostic System Checkº should always
be the starting point of any SRS diagnostics. The
ªSRS Diagnostic System Checkº checks for proper
ªAIR BAGº warning lamp operation and checks for
SRS trouble codes using both ªFlash Codeº and
ªScan Toolº Methods.
2.Refer To The Proper Diagnostic Chart As Directed
By The ªSRS Diagnostic System Checkº.
The ªSRS Diagnostic System Checkº will lead you to
the correct chart to diagnose any SRS problems.
Bypassing these procedures may result in extended
diagnostic time, incorrect diagnosis and incorrect
parts replacement.
3.Repeat The ªSRS Diagnostic System Checkº
After Any Repair Or Diagnostic Procedures Have
Been Performed.
Preforming the ªSRS Diagnostic System Checkº after
all repair or diagnostic procedures will assure that the
repair has been made correctly and that no other
conditions exist.
Diagnostic Codes
The Sensing and Diagnostic Module (SDM) maintains a
history record of all diagnostic codes that have beendetected since the SRS codes were last cleared during
service.
1. Active Codes Ð Faults that are presently detected
this ignition cycle. Active codes are stored in RAM
(Random Access Memory).
2. History Codes Ð All faults detected since the last
time the history fault memory was cleared. History
codes are stored in EEPROM. (Electronically
Erasable Programmable Read only Memory)
How To Read Trouble Codes
All codes (Active and history) can be read (or cleared) by
using a scan tool or equivalent.
If a PDT is not available, have the vehicle serviced by
ISUZU dealer.
How To Clear Trouble Codes
Trouble codes can only be cleared by using a Scan Tool.
If a ªscan toolº is not available then inform the owner of the
stored codes and suggest that the codes are cleared
upon the next visit to an Isuzu dealership.
Scan Tool Diagnostics
A scan tool can be used to read current and history codes
and to clear all history codes after a repair is complete.
The scan tool must be updated to communicate with the
SRS through a memory card or a manufacturer's update
before it can be used for SRS diagnostics. To use the
scan tool, connect it to the DLC connector and turn the
ignition switch ªONº. Then follow the manufacturer's
directions for communication with the SRS. The scan tool
reads serial data from the SDM ªSerial Dataº output
(terminal 24) to the DLC connector (terminal 9).
Basic Knowledge Required
Before using this section of the Service Manual, there is
some basic knowledge which will be required. Without
this knowledge, you will have trouble using the diagnostic
procedures in this section. Use care to prevent harm or
unwanted deployment. Read all cautions in the service
manual and on warning labels attached to SRS
components.
Basic Electrical Circuits
You should understand the basic theory of electricity
including series and parallel circuits, and understand the
voltage drops across series resistors. You should know
the meaning of voltage (volts), current (amps), and
resistance (ohms). You should understand what happens
in a circuit with an open or a shorted wire. You should be
able to read and understand a wiring diagram.
ªFlash Codeº Diagnostics
Flash code diagnostics can be used to read active codes
and to determine if history codes are present but cannot
be used to clear codes or read history codes. Flash code
diagnostics is enabled by grounding by terminal 4
shorting to terminal 13 of the DLC connector with the
ignition switch ªONº. Grounding terminal 4 of the DLC
connector pulls the ªDiagnostics Requestº input (Terminal
1) of the SDM low and signals the SDM to enter the flash
code diagnostic display mode.
Page 3492 of 3573
9J1±5
RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM
diagnostic trouble codes in the order specified may result in extended diagnostic time, incorrect diagnosis and
incorrect parts replacement.
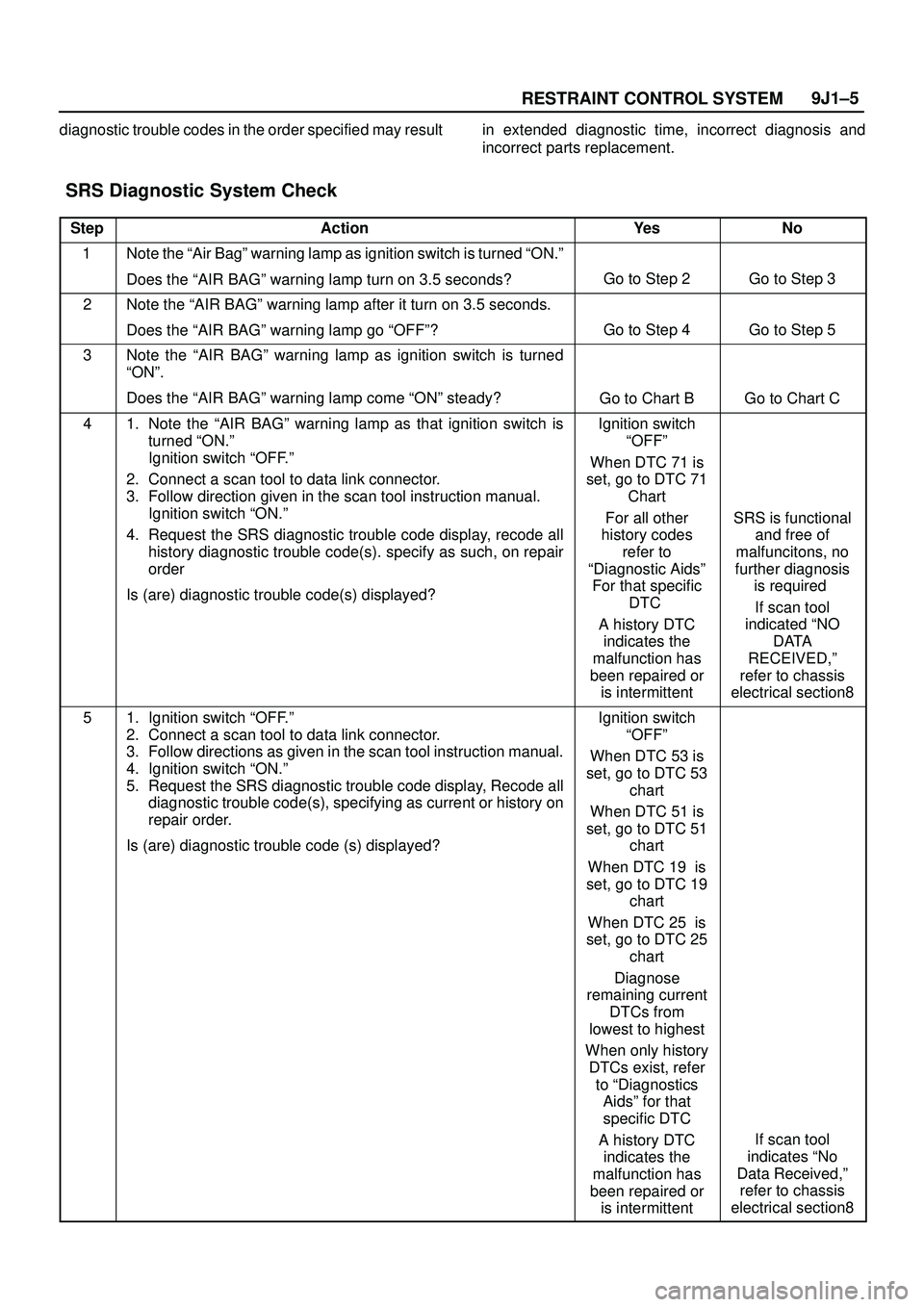
SRS Diagnostic System Check
StepActionYe sNo
1Note the ªAir Bagº warning lamp as ignition switch is turned ªON.º
Does the ªAIR BAGº warning lamp turn on 3.5 seconds?
Go to Step 2Go to Step 3
2Note the ªAIR BAGº warning lamp after it turn on 3.5 seconds.
Does the ªAIR BAGº warning lamp go ªOFFº?
Go to Step 4Go to Step 5
3Note the ªAIR BAGº warning lamp as ignition switch is turned
ªONº.
Does the ªAIR BAGº warning lamp come ªONº steady?
Go to Chart BGo to Chart C
41. Note the ªAIR BAGº warning lamp as that ignition switch is
turned ªON.º
Ignition switch ªOFF.º
2. Connect a scan tool to data link connector.
3. Follow direction given in the scan tool instruction manual.
Ignition switch ªON.º
4. Request the SRS diagnostic trouble code display, recode all
history diagnostic trouble code(s). specify as such, on repair
order
Is (are) diagnostic trouble code(s) displayed?Ignition switch
ªOFFº
When DTC 71 is
set, go to DTC 71
Chart
For all other
history codes
refer to
ªDiagnostic Aidsº
For that specific
DTC
A history DTC
indicates the
malfunction has
been repaired or
is intermittent
SRS is functional
and free of
malfuncitons, no
further diagnosis
is required
If scan tool
indicated ªNO
DATA
RECEIVED,º
refer to chassis
electrical section8
51. Ignition switch ªOFF.º
2. Connect a scan tool to data link connector.
3. Follow directions as given in the scan tool instruction manual.
4. Ignition switch ªON.º
5. Request the SRS diagnostic trouble code display, Recode all
diagnostic trouble code(s), specifying as current or history on
repair order.
Is (are) diagnostic trouble code (s) displayed?Ignition switch
ªOFFº
When DTC 53 is
set, go to DTC 53
chart
When DTC 51 is
set, go to DTC 51
chart
When DTC 19 is
set, go to DTC 19
chart
When DTC 25 is
set, go to DTC 25
chart
Diagnose
remaining current
DTCs from
lowest to highest
When only history
DTCs exist, refer
to ªDiagnostics
Aidsº for that
specific DTC
A history DTC
indicates the
malfunction has
been repaired or
is intermittent
If scan tool
indicates ªNo
Data Received,º
refer to chassis
electrical section8
Page 3522 of 3573
9J1±35
RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM
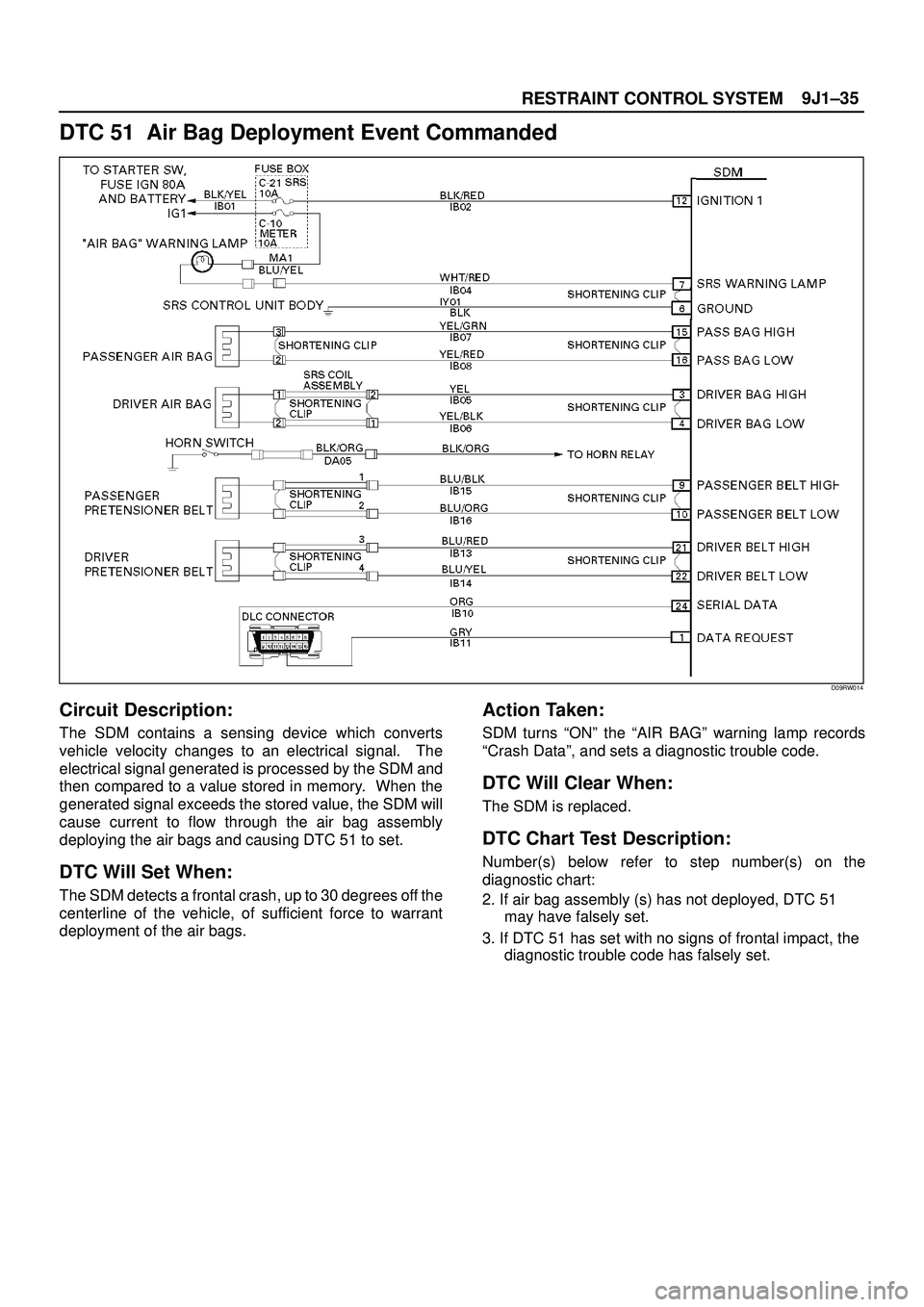
DTC 51 Air Bag Deployment Event Commanded
D09RW014
Circuit Description:
The SDM contains a sensing device which converts
vehicle velocity changes to an electrical signal. The
electrical signal generated is processed by the SDM and
then compared to a value stored in memory. When the
generated signal exceeds the stored value, the SDM will
cause current to flow through the air bag assembly
deploying the air bags and causing DTC 51 to set.
DTC Will Set When:
The SDM detects a frontal crash, up to 30 degrees off the
centerline of the vehicle, of sufficient force to warrant
deployment of the air bags.
Action Taken:
SDM turns ªONº the ªAIR BAGº warning lamp records
ªCrash Dataº, and sets a diagnostic trouble code.
DTC Will Clear When:
The SDM is replaced.
DTC Chart Test Description:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the
diagnostic chart:
2. If air bag assembly (s) has not deployed, DTC 51
may have falsely set.
3. If DTC 51 has set with no signs of frontal impact, the
diagnostic trouble code has falsely set.
Page 3524 of 3573
9J1±37
RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM
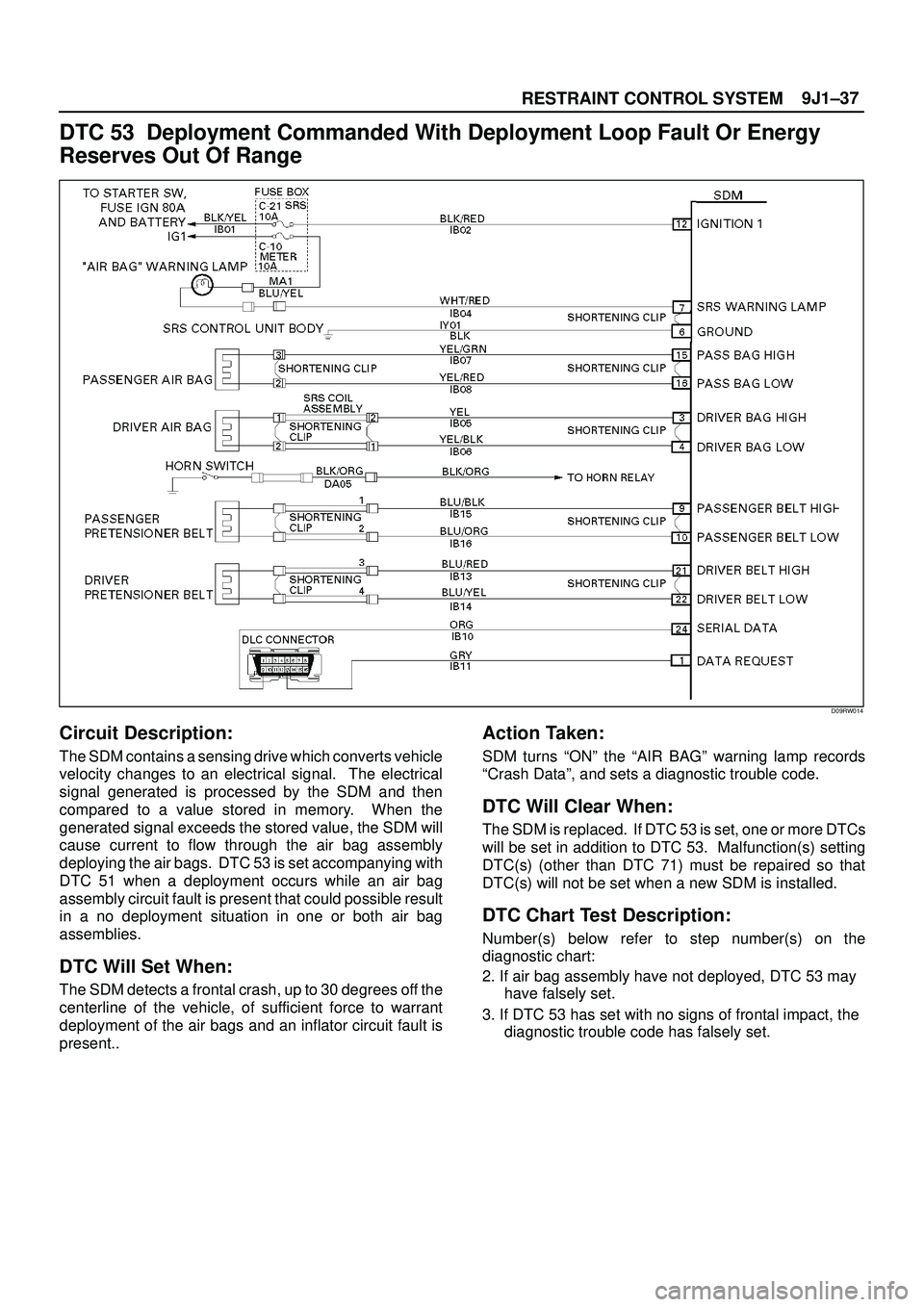
DTC 53 Deployment Commanded With Deployment Loop Fault Or Energy
Reserves Out Of Range
D09RW014
Circuit Description:
The SDM contains a sensing drive which converts vehicle
velocity changes to an electrical signal. The electrical
signal generated is processed by the SDM and then
compared to a value stored in memory. When the
generated signal exceeds the stored value, the SDM will
cause current to flow through the air bag assembly
deploying the air bags. DTC 53 is set accompanying with
DTC 51 when a deployment occurs while an air bag
assembly circuit fault is present that could possible result
in a no deployment situation in one or both air bag
assemblies.
DTC Will Set When:
The SDM detects a frontal crash, up to 30 degrees off the
centerline of the vehicle, of sufficient force to warrant
deployment of the air bags and an inflator circuit fault is
present..
Action Taken:
SDM turns ªONº the ªAIR BAGº warning lamp records
ªCrash Dataº, and sets a diagnostic trouble code.
DTC Will Clear When:
The SDM is replaced. If DTC 53 is set, one or more DTCs
will be set in addition to DTC 53. Malfunction(s) setting
DTC(s) (other than DTC 71) must be repaired so that
DTC(s) will not be set when a new SDM is installed.
DTC Chart Test Description:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the
diagnostic chart:
2. If air bag assembly have not deployed, DTC 53 may
have falsely set.
3. If DTC 53 has set with no signs of frontal impact, the
diagnostic trouble code has falsely set.
Page 3550 of 3573
9J1±63
RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM
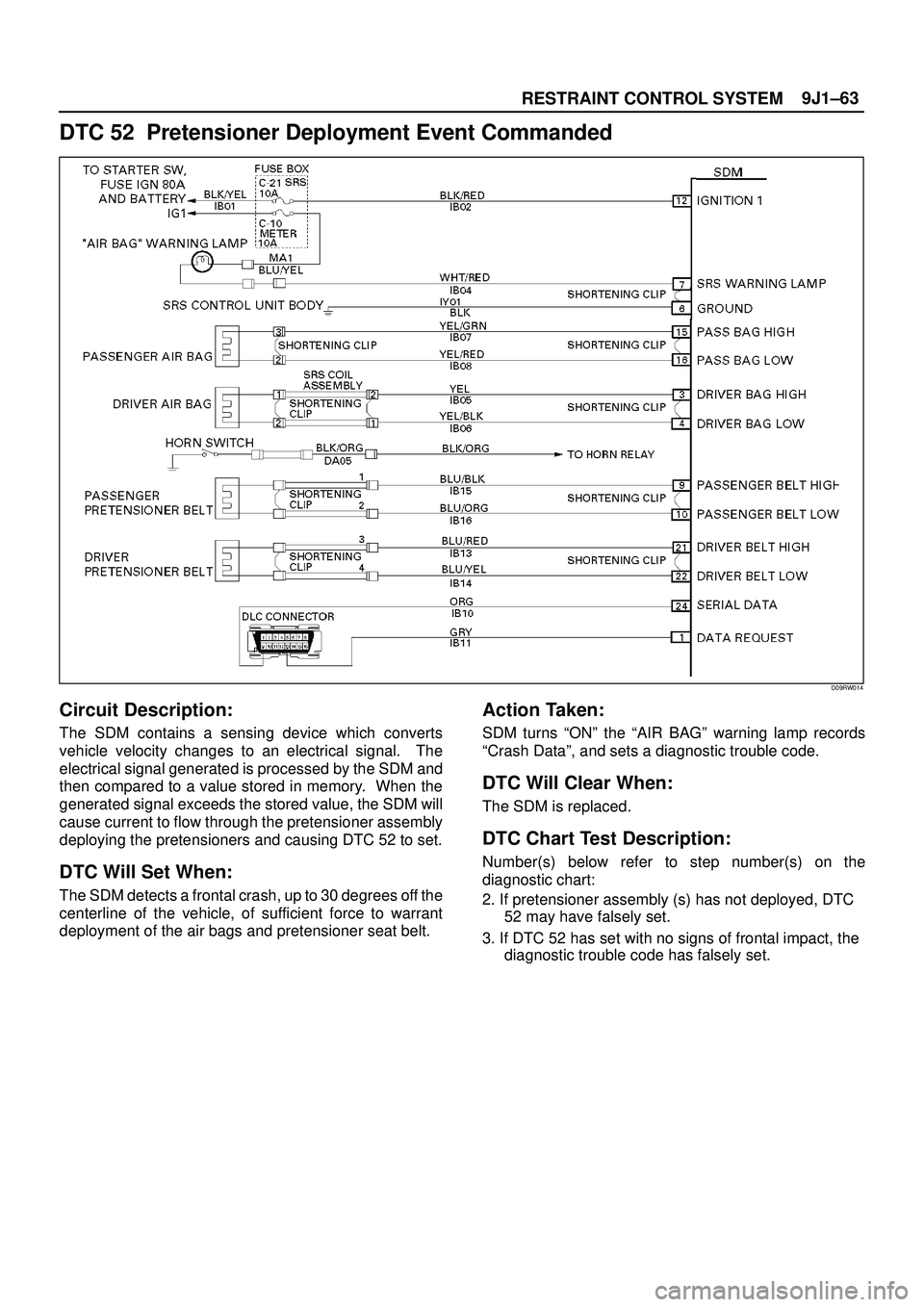
DTC 52 Pretensioner Deployment Event Commanded
D09RW014
Circuit Description:
The SDM contains a sensing device which converts
vehicle velocity changes to an electrical signal. The
electrical signal generated is processed by the SDM and
then compared to a value stored in memory. When the
generated signal exceeds the stored value, the SDM will
cause current to flow through the pretensioner assembly
deploying the pretensioners and causing DTC 52 to set.
DTC Will Set When:
The SDM detects a frontal crash, up to 30 degrees off the
centerline of the vehicle, of sufficient force to warrant
deployment of the air bags and pretensioner seat belt.
Action Taken:
SDM turns ªONº the ªAIR BAGº warning lamp records
ªCrash Dataº, and sets a diagnostic trouble code.
DTC Will Clear When:
The SDM is replaced.
DTC Chart Test Description:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the
diagnostic chart:
2. If pretensioner assembly (s) has not deployed, DTC
52 may have falsely set.
3. If DTC 52 has set with no signs of frontal impact, the
diagnostic trouble code has falsely set.
Page 3566 of 3573
PAGE BACK PAGE NEXT
THIS MALUAL INCLUDES THE FOLLOWING SECTIONS:
6VD1/6VE1
SECTION No. CONTRNTS
6A ENGINE MECHANICAL
6B ENGINE COOLING
6C ENGINE FUEL
6D1 ENGINE ELECTRICAL
6D2 IGNITION SYSTEM
6D3 STARTING AND CHARGING SYSTEM
6E ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
6F ENGINE EXHAUST
6G ENGINE LUBRICATION
6H ENGINE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM
6J INDUCTION
Page 3567 of 3573
PAGE BACK PAGE NEXT
4JG2
4JX1 SECTION No. CONTRNTS
00 SERVICE INFORMATION
6A ENGINE MECHANICAL
6A2 4JG2-NA / 4JG2-TURBO ENGINE
6B ENGINE COOLING
6C FUEL SYSTEM
6D ENGINE ELECTRICAL
6E -
6F EXHAUST
6G -
SECTION No. CONTRNTS
6A ENGINE MECHANICAL
6B ENGINE COOLING
6C ENGINE FUEL
6D ENGINE ELECTRICAL
6E ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
6F ENGINE EXHAUST
6G ENGINE LUBRICATION
6H ENGINE SPEED CONTROL
6J INDUCTION