tire pressure ISUZU TROOPER 1998 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 1998, Model line: TROOPER, Model: ISUZU TROOPER 1998Pages: 3573, PDF Size: 60.36 MB
Page 30 of 3573
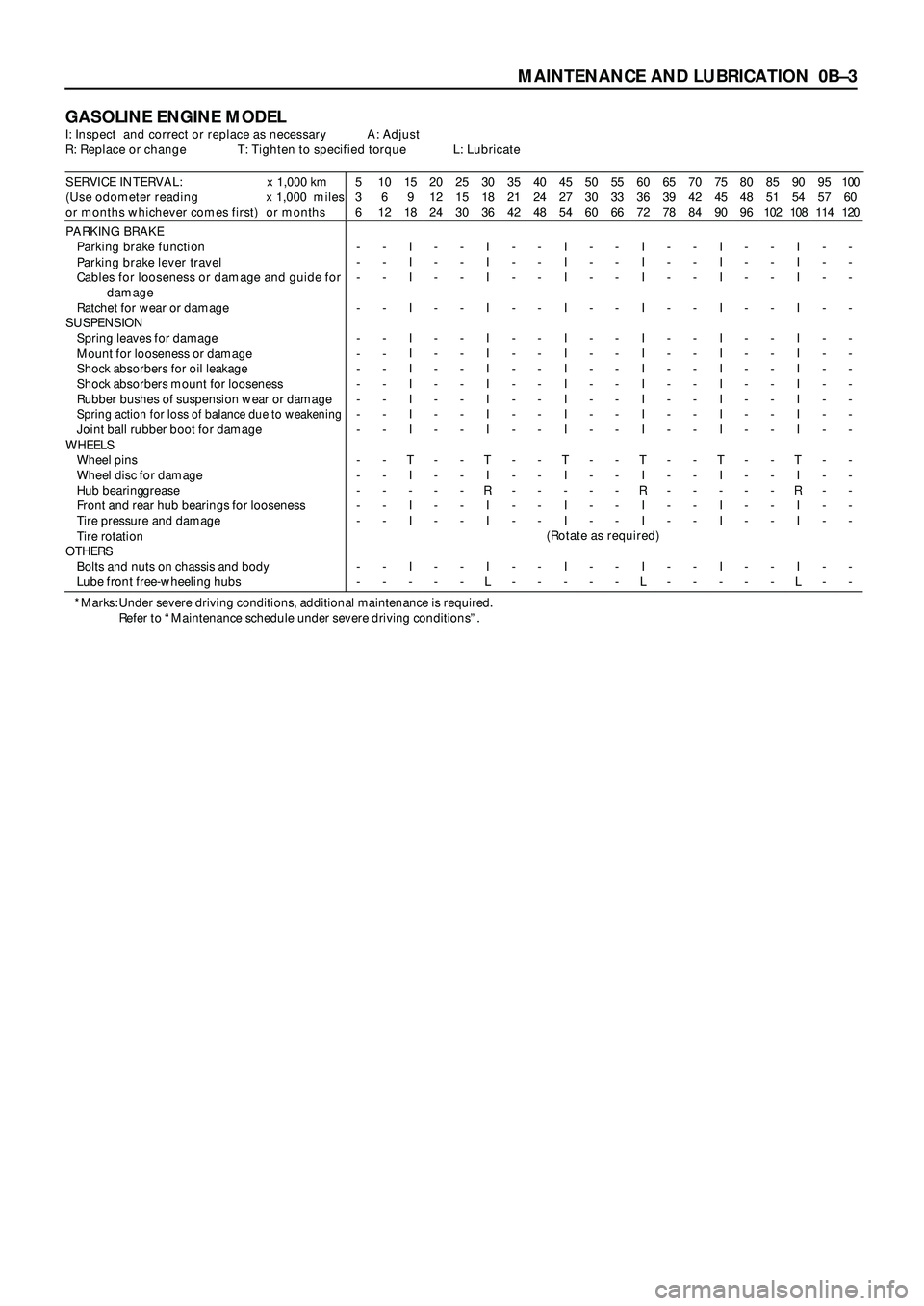
MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION 0BÐ3
GASOLINE ENGINE MODELI: Inspect and correct or replace as necessary A: Adjust
R: Replace or change T: Tighten to specified torque L: Lubricate
SERVICE INTERVAL: x 1,000 km
(Use odometer reading x 1,000 miles
or months whichever comes first) or months5
3
610
6
1215
9
1820
12
2425
15
3030
18
3635
21
4240
24
4845
27
5450
30
6055
33
6660
36
7265
39
7870
42
8475
45
9080
48
9685
51
10290
54
10895
57
114100
60
120
PARKING BRAKE
Parking brake function
Parking brake lever travel
Cables for looseness or damage and guide for
damage
Ratchet for wear or damage
SUSPENSION
Spring leaves for damage
Mount for looseness or damage
Shock absorbers for oil leakage
Shock absorbers mount for looseness
Rubber bushes of suspension wear or damage
Spring action for loss of balance due to weakeningJoint ball rubber boot for damage
WHEELS
Wheel pins
Wheel disc for damage
Hub bearing grease
Front and rear hub bearings for looseness
Tire pressure and damage
Tire rotation
OTHERS
Bolts and nuts on chassis and body
Lube front free-wheeling hubs-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
--
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
T
I
-
I
I
I
--
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
--
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
T
I
R
I
I
I
L-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
--
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
T
I
-
I
I
I
--
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
--
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
T
I
R
I
I
I
L-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
--
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
T
I
-
I
I
I
--
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
--
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
T
I
R
I
I
I
L-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
--
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
(Rotate as required)
*Marks: Under severe driving conditions, additional maintenance is required.
Refer to “Maintenance schedule under severe driving conditions”.
Page 32 of 3573
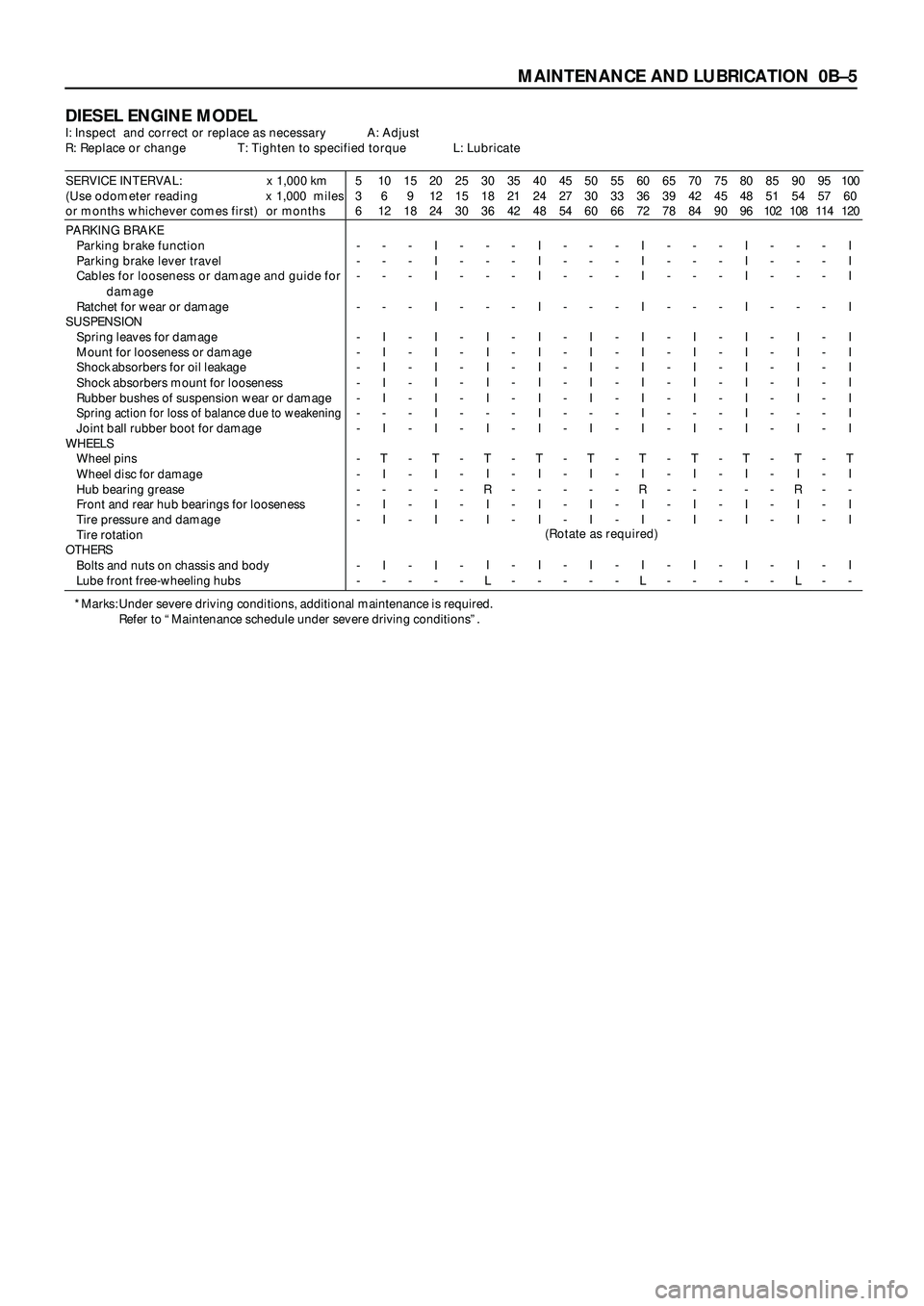
MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION 0BÐ5
DIESEL ENGINE MODELI: Inspect and correct or replace as necessary A: Adjust
R: Replace or change T: Tighten to specified torque L: Lubricate
SERVICE INTERVAL: x 1,000 km
(Use odometer reading x 1,000 miles
or months whichever comes first) or months5
3
610
6
1215
9
1820
12
2425
15
3030
18
3635
21
4240
24
4845
27
5450
30
6055
33
6660
36
7265
39
7870
42
8475
45
9080
48
9685
51
10290
54
10895
57
114100
60
120
PARKING BRAKE
Parking brake function
Parking brake lever travel
Cables for looseness or damage and guide for
damage
Ratchet for wear or damage
SUSPENSION
Spring leaves for damage
Mount for looseness or damage
Shock absorbers for oil leakage
Shock absorbers mount for looseness
Rubber bushes of suspension wear or damage
Spring action for loss of balance due to weakeningJoint ball rubber boot for damage
WHEELS
Wheel pins
Wheel disc for damage
Hub bearing grease
Front and rear hub bearings for looseness
Tire pressure and damage
Tire rotation
OTHERS
Bolts and nuts on chassis and body
Lube front free-wheeling hubs-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
--
-
-
-
I
I
I
I
I
-
I
T
I
-
I
I
I
--
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
T
I
-
I
I
I
--
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
--
-
-
-
I
I
I
I
I
-
I
T
I
R
I
I
I
L-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
T
I
-
I
I
I
--
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
--
-
-
-
I
I
I
I
I
-
I
T
I
-
I
I
I
--
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
T
I
R
I
I
I
L-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
--
-
-
-
I
I
I
I
I
-
I
T
I
-
I
I
I
--
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
T
I
-
I
I
I
--
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
--
-
-
-
I
I
I
I
I
-
I
T
I
R
I
I
I
L-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
T
I
-
I
I
I
-
(Rotate as required)
*Marks: Under severe driving conditions, additional maintenance is required.
Refer to “Maintenance schedule under severe driving conditions”.
Page 286 of 3573

Problem Possible Cause Correction
00 – 4 SERVICE INFORMATION
GENERAL INFORMATION
Since the problems in steering, suspension,
wheels and tires involve several systems, they
must all be considered when diagnosing a
complaint. To identify the symptom, always road
test the vehicle first.
Proceed with the following preliminary inspections
and correct any defects which are found.1. Inspect tires for proper pressure and uneven
wear.
2. Raise vehicle on a hoist and inspect front and
rear suspension and steering linkage for loose
or damaged parts.
3. Spin front wheels. Inspect for out-of-round
tires, out-of-balance tires, loose and/or rough
wheel bearings.
GENERAL TROUBLESHOOTING
Vehicle Pulls
Abnormal or Excessive
Tire Wear
Shimmy, Shake or
Vibration1. Mismatched or uneven tires.
2. Tires not adequately inflated.
3. Broken or sagging springs.
4. Radial tire lateral force.
5. Improper wheel alignment.
6. Brake dragging in one wheel.
7. Loose, bent or broken front or rear
suspension parts.
8. Faulty shock absorbers.
1. Sagging or broken spring.
2. Tire out of balance.
3. Improper wheel alignment.
4. Faulty shock absorber.
5. Hard driving.
6. Overloaded vehicle.
7. Tires not rotated periodically.
8. Worn or loose road wheel bearings.
9. Wobbly wheel or tires.
10. Tires not adequately inflated.
1. Tire or wheel out of balance.
2. Loose wheel bearings.
3. Worn steering linkage ball joints.
4. Worn upper or lower end ball joints.
5. Excessively upper wheel runout.
6. Blister or bump on tire.
7. Excessive loaded radial run out of
tire/wheel assembly.
8. Improper wheel alignment.
9. Loose or worn steering linkage.
10. Loose steering gear.
11. Tires not adequately inflated.
12. Loose, bent or broken front or rear
suspension parts.
13. Faulty shock absorber.
14. Hub bearing preload misadjustment.Replace tire.
Adjust tire pressure.
Replace spring.
Replace tire.
Adjust wheel alignment.
Repair brake.
Tighten or replace the
appropriate suspension part(s).
Replace shock absorber.
Replace spring.
Balance or replace tire.
Check front end alignment.
Replace shock absorber.
Replace tire.
Replace tire and reduce load.
Replace or rotate tire.
Replace wheel bearing.
Replace wheel or tire.
Adjust the pressure.
Balance wheels or replace
tire/or wheel.
Replace wheel bearing.
Replace ball joints.
Replace ball joints.
Repair or replace wheel
and/or tire.
Replace tire.
Replace tire or wheel.
Check wheel alignment.
Tighten or replace steering
linkage.
Tighten housing bolts.
Adjust tire pressure.
Tighten or replace the
appropriate suspension parts.
Replace shock absorber.
Adjust preload.
Page 287 of 3573
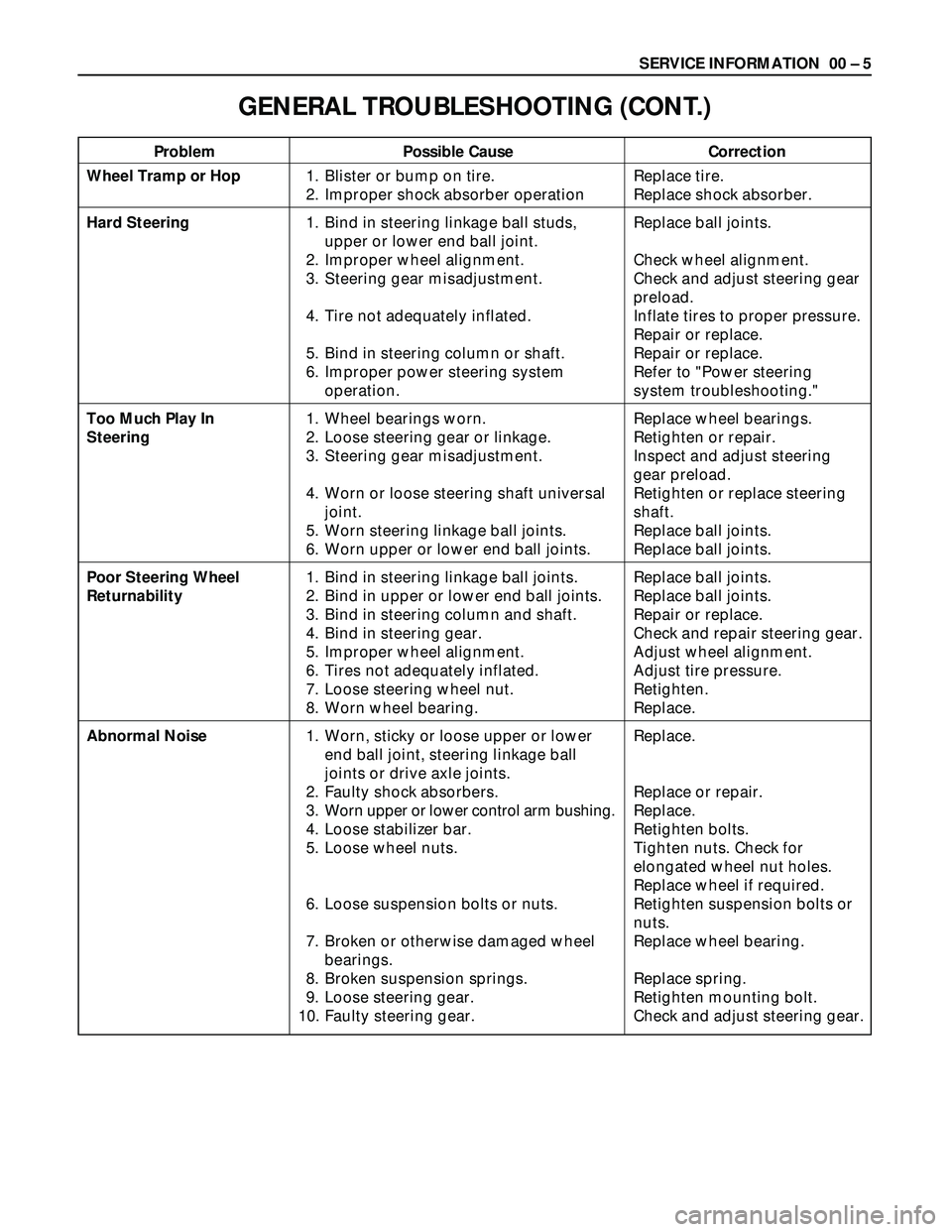
SERVICE INFORMATION 00 – 5
Problem Possible Cause Correction
GENERAL TROUBLESHOOTING (CONT.)
Wheel Tramp or Hop
Hard Steering
Too Much Play In
Steering
Poor Steering Wheel
Returnability
Abnormal Noise1. Blister or bump on tire.
2. Improper shock absorber operation
1. Bind in steering linkage ball studs,
upper or lower end ball joint.
2. Improper wheel alignment.
3. Steering gear misadjustment.
4. Tire not adequately inflated.
5. Bind in steering column or shaft.
6. Improper power steering system
operation.
1. Wheel bearings worn.
2. Loose steering gear or linkage.
3. Steering gear misadjustment.
4. Worn or loose steering shaft universal
joint.
5. Worn steering linkage ball joints.
6. Worn upper or lower end ball joints.
1. Bind in steering linkage ball joints.
2. Bind in upper or lower end ball joints.
3. Bind in steering column and shaft.
4. Bind in steering gear.
5. Improper wheel alignment.
6. Tires not adequately inflated.
7. Loose steering wheel nut.
8. Worn wheel bearing.
1. Worn, sticky or loose upper or lower
end ball joint, steering linkage ball
joints or drive axle joints.
2. Faulty shock absorbers.
3. Worn upper or lower control arm bushing.
4. Loose stabilizer bar.
5. Loose wheel nuts.
6. Loose suspension bolts or nuts.
7. Broken or otherwise damaged wheel
bearings.
8. Broken suspension springs.
9. Loose steering gear.
10. Faulty steering gear.Replace tire.
Replace shock absorber.
Replace ball joints.
Check wheel alignment.
Check and adjust steering gear
preload.
Inflate tires to proper pressure.
Repair or replace.
Repair or replace.
Refer to "Power steering
system troubleshooting."
Replace wheel bearings.
Retighten or repair.
Inspect and adjust steering
gear preload.
Retighten or replace steering
shaft.
Replace ball joints.
Replace ball joints.
Replace ball joints.
Replace ball joints.
Repair or replace.
Check and repair steering gear.
Adjust wheel alignment.
Adjust tire pressure.
Retighten.
Replace.
Replace.
Replace or repair.
Replace.
Retighten bolts.
Tighten nuts. Check for
elongated wheel nut holes.
Replace wheel if required.
Retighten suspension bolts or
nuts.
Replace wheel bearing.
Replace spring.
Retighten mounting bolt.
Check and adjust steering gear.
Page 288 of 3573
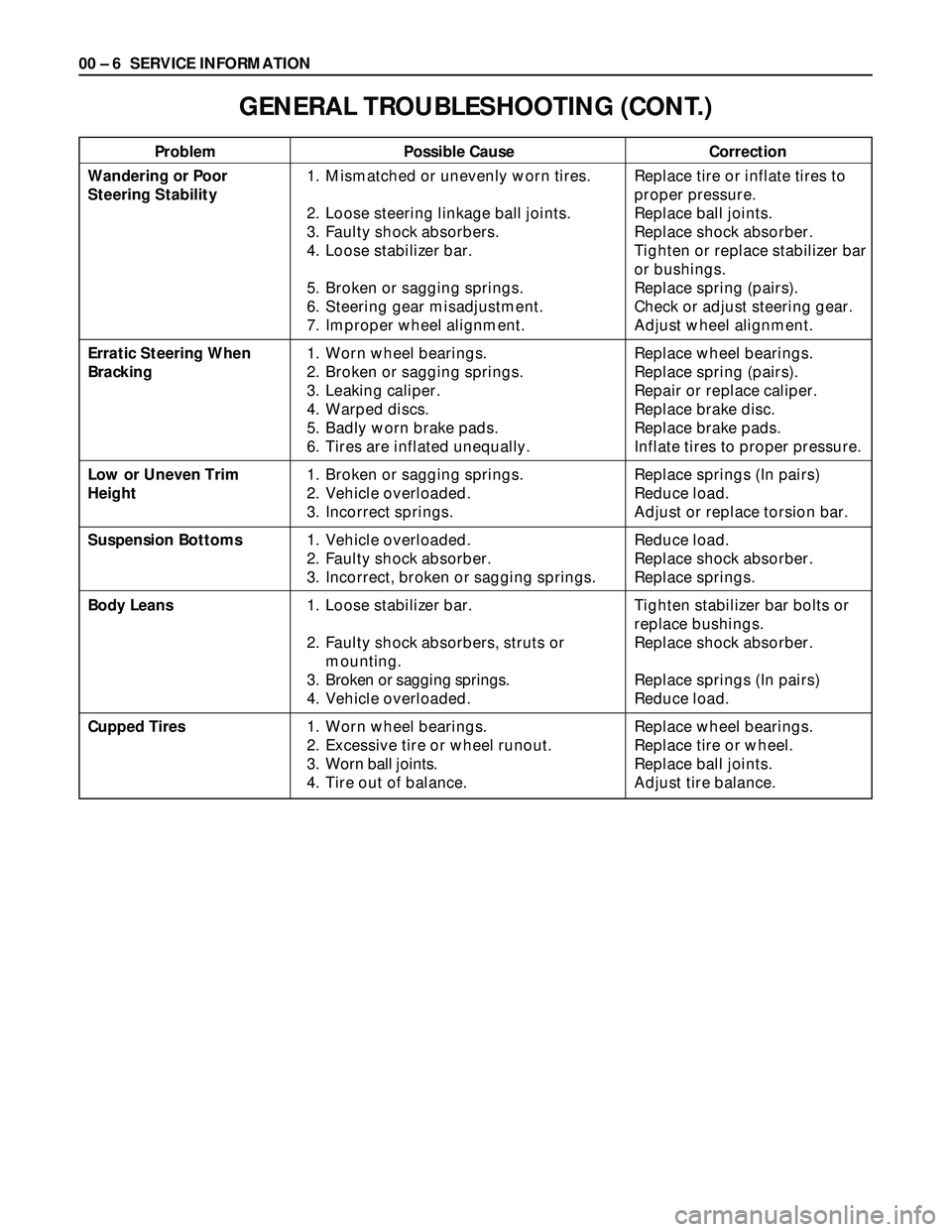
00 – 6 SERVICE INFORMATION
Problem Possible Cause Correction
GENERAL TROUBLESHOOTING (CONT.)
Wandering or Poor
Steering Stability
Erratic Steering When
Bracking
Low or Uneven Trim
Height
Suspension Bottoms
Body Leans
Cupped Tires1. Mismatched or unevenly worn tires.
2. Loose steering linkage ball joints.
3. Faulty shock absorbers.
4. Loose stabilizer bar.
5. Broken or sagging springs.
6. Steering gear misadjustment.
7. Improper wheel alignment.
1. Worn wheel bearings.
2. Broken or sagging springs.
3. Leaking caliper.
4. Warped discs.
5. Badly worn brake pads.
6. Tires are inflated unequally.
1. Broken or sagging springs.
2. Vehicle overloaded.
3. Incorrect springs.
1. Vehicle overloaded.
2. Faulty shock absorber.
3. Incorrect, broken or sagging springs.
1. Loose stabilizer bar.
2. Faulty shock absorbers, struts or
mounting.
3. Broken or sagging springs.
4. Vehicle overloaded.
1. Worn wheel bearings.
2. Excessive tire or wheel runout.
3. Worn ball joints.
4. Tire out of balance.Replace tire or inflate tires to
proper pressure.
Replace ball joints.
Replace shock absorber.
Tighten or replace stabilizer bar
or bushings.
Replace spring (pairs).
Check or adjust steering gear.
Adjust wheel alignment.
Replace wheel bearings.
Replace spring (pairs).
Repair or replace caliper.
Replace brake disc.
Replace brake pads.
Inflate tires to proper pressure.
Replace springs (In pairs)
Reduce load.
Adjust or replace torsion bar.
Reduce load.
Replace shock absorber.
Replace springs.
Tighten stabilizer bar bolts or
replace bushings.
Replace shock absorber.
Replace springs (In pairs)
Reduce load.
Replace wheel bearings.
Replace tire or wheel.
Replace ball joints.
Adjust tire balance.
Page 305 of 3573
INSPECTION
Before making any adjustments affecting caster, camber
or toe-in, the following front end inspection should be
made.
INSPECT
1. Tires for proper inflation pressure. Refer to “Wheels
and Tires” in section 3E.
2. Front wheel bearings for proper adjustment. Refer to
“Front Wheel Drive” in section 4C.
3. Ball joints, tie rod ends and relay rods. If excessive
looseness is noted, correct before adjusting. Refer to
“Steering Linkage” in section 2A.
4. Wheel and tires for run-out. Refer to “Wheels and
Tires”in section 3E.
5. Trim height. If not within specifications, the
correction must be made before adjusting caster.
6. Steering gear for looseness at the frame.
7. Shock absorbers for leaks or any noticeable noise.
Refer to “Front Suspension” in section 3C.
8. Control arms or stabilizer bar attachment for
looseness. Refer to “Front Suspension“ in section 3C.
9. Alignment equipment. Follow the manufacturer’s
instructions.
10. Level of the vehicle. The vehicle must be on a level
surface.
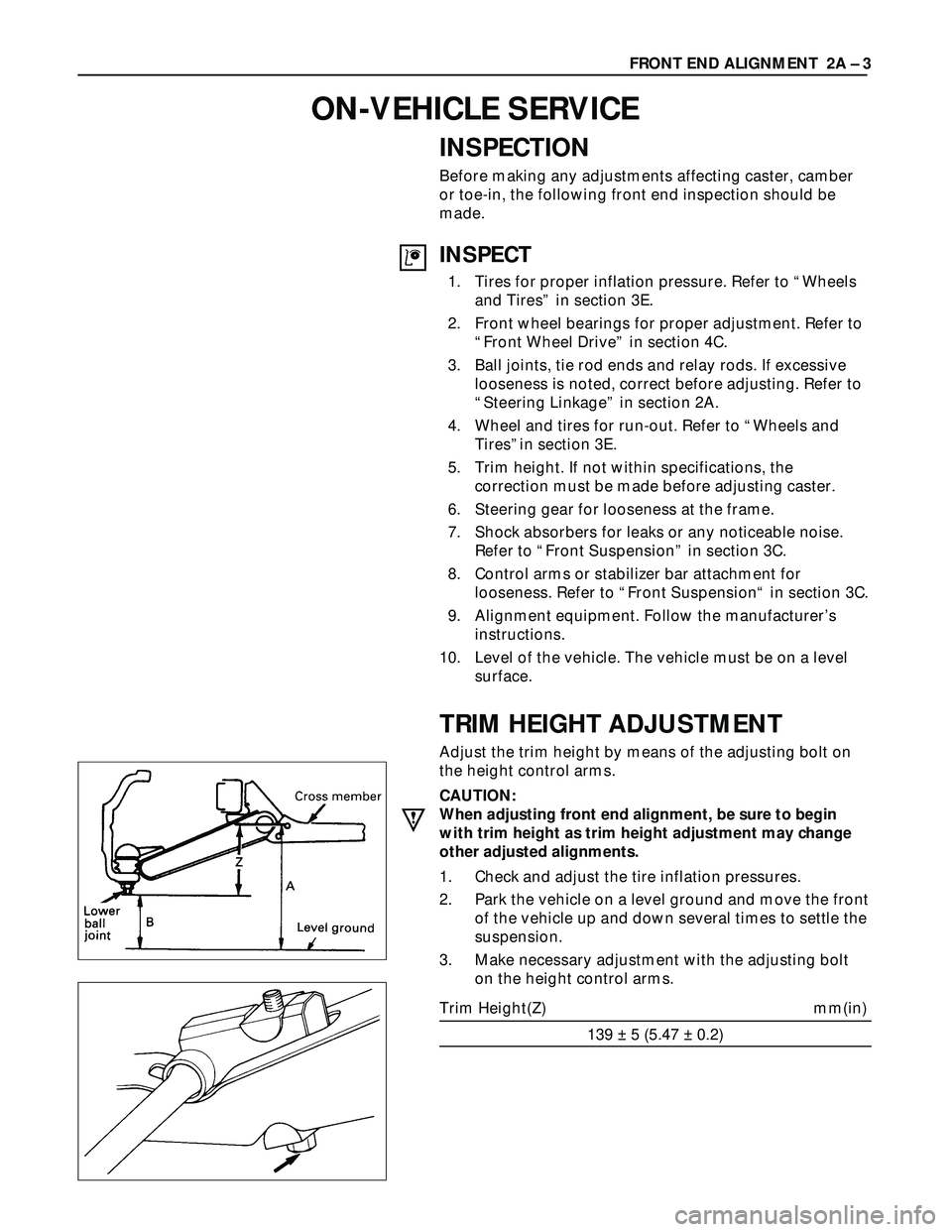
TRIM HEIGHT ADJUSTMENT
Adjust the trim height by means of the adjusting bolt on
the height control arms.
CAUTION:
When adjusting front end alignment, be sure to begin
with trim height as trim height adjustment may change
other adjusted alignments.
1. Check and adjust the tire inflation pressures.
2. Park the vehicle on a level ground and move the front
of the vehicle up and down several times to settle the
suspension.
3. Make necessary adjustment with the adjusting bolt
on the height control arms.
Trim Height(Z) mm(in)
139 ± 5 (5.47 ± 0.2)FRONT END ALIGNMENT 2A – 3
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
Page 433 of 3573
3E – 2 WHEELS AND TIRES
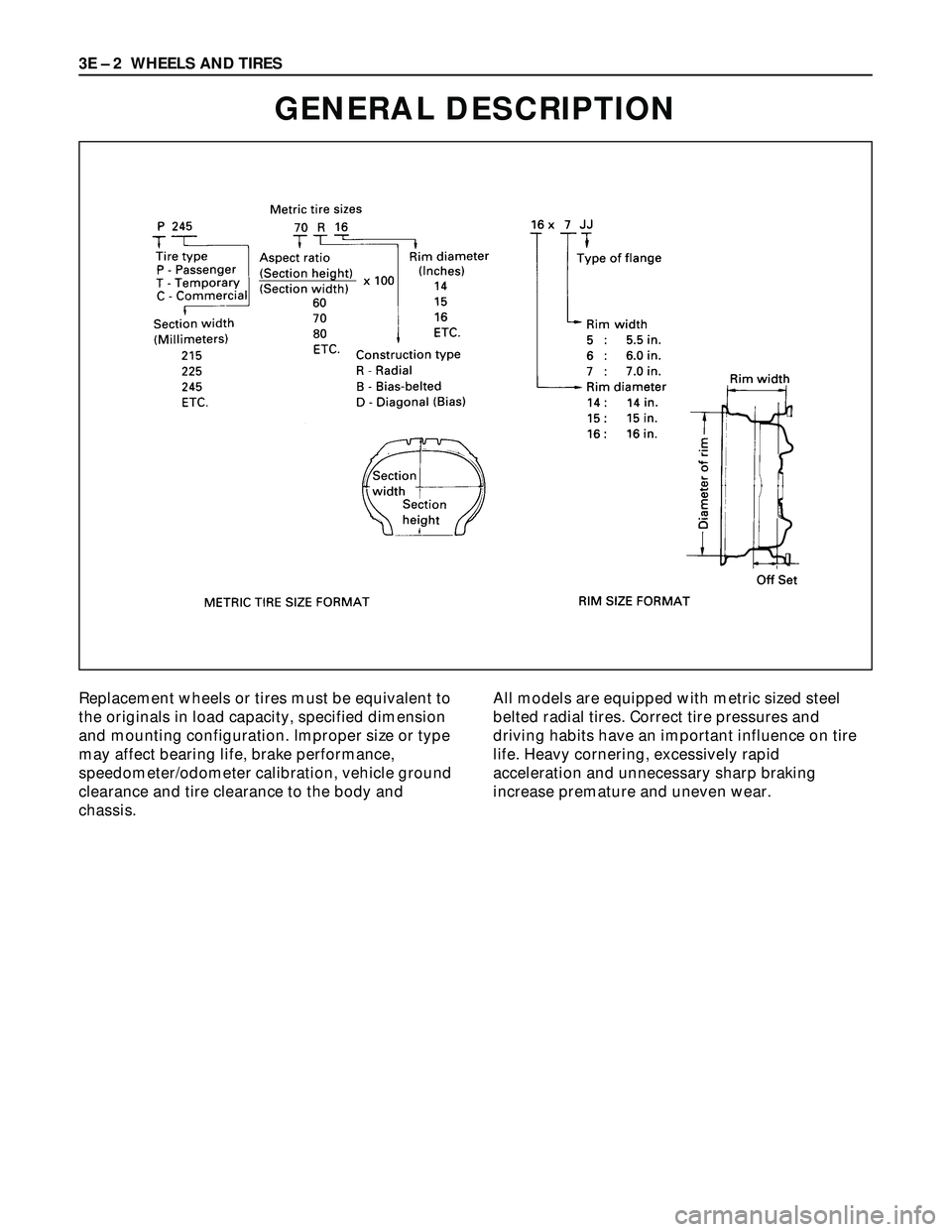
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Replacement wheels or tires must be equivalent to
the originals in load capacity, specified dimension
and mounting configuration. Improper size or type
may affect bearing life, brake performance,
speedometer/odometer calibration, vehicle ground
clearance and tire clearance to the body and
chassis.All models are equipped with metric sized steel
belted radial tires. Correct tire pressures and
driving habits have an important influence on tire
life. Heavy cornering, excessively rapid
acceleration and unnecessary sharp braking
increase premature and uneven wear.
Page 435 of 3573

3E – 4 WHEELS AND TIRES
TIRES
REPLACEMENT
When replacement is necessary, the original metric size
should be used. Most metric tire sizes do not have exact
corresponding alphanumeric tire sizes. It is recommended
that new tires be installed in pairs on the same axle. If
necessary to replace only one tire, it should be paired with
tire having the most tread, to equalize braking traction.
CAUTION:
Do not mix different types of tires such as radial, bias and
bias-belted tires except in emergencies, because vehicle
handling may be seriously affected and may result in loss
of control.
TIRE MOUNTING
Remove valve cap on valve stem and deflate the tire.
Then use a tire changing machine to mount or dismount
tires.
Follow the equipment manufacturer’s instruction. Do not
use hand tools or tire lever alone to change tires as they
may damage the tire beads or wheel rim.
TIRE DISMOUNTING
Rim bead seats should be cleaned with a wire brush or
coarse steel wool to remove lubricants, and light rust.
Before mounting a tire, the bead area should be well
lubricated with an approved tire lubricant.
After mounting, inflate the tire to 196 kPa (28 psi) so that
beads are completely seated. Inflate the air to specified
pressure and install valve cap to the stem
WARNING:
NEVER STAND OVER TIRE WHEN INFLATING. BEAD MAY
BREAK WHEN BEAD SNAPS OVER RIM’S SAFETY HUMP
AND CAUSE SERIOUS PERSONAL INJURY.
NEVER EXCEED 240 kPa (35 psi) PRESSURE WHEN
INFLATING. IF 240 kPa (35 psi) PRESSURE WILL NOT
SEAT BEADS, DEFLATE, RE-LUBRICATE AND RE-INFLATE.
OVER INFLATION MAY CAUSE THE BEAD TO BREAK AND
CAUSE SERIOUS PERSONAL INJURY.
TIRE REPAIR
There are many different materials on the market used to
repair tires.
Manufacturers have published detailed instructions on
how and when to repair tires. These instructions can be
obtained from the tire manufacturer if they are not
included with the repair kit.
UNIT REPAIR
Page 436 of 3573
WHEELS AND TIRES 3E – 5
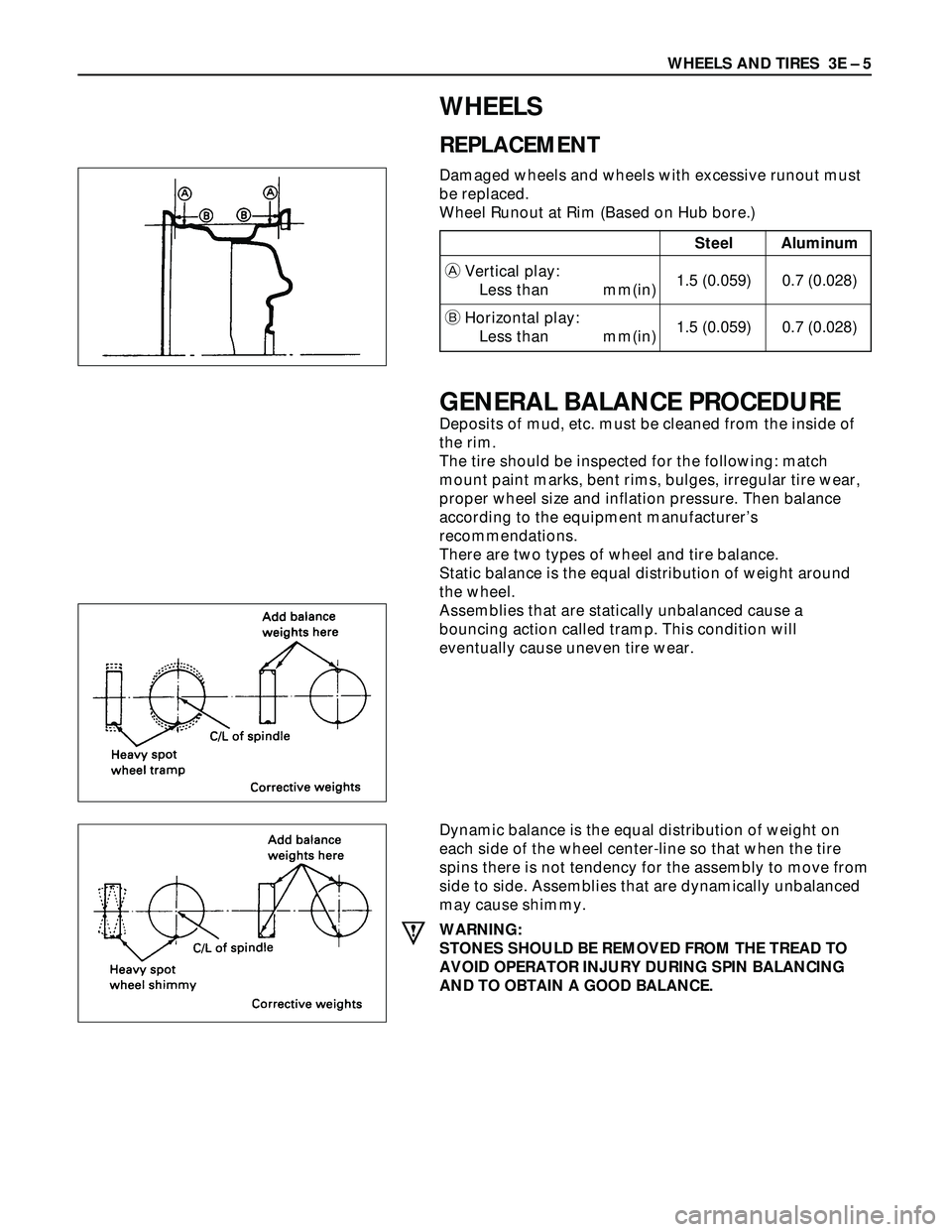
WHEELS
REPLACEMENT
Damaged wheels and wheels with excessive runout must
be replaced.
Wheel Runout at Rim (Based on Hub bore.)
GENERAL BALANCE PROCEDURE
Deposits of mud, etc. must be cleaned from the inside of
the rim.
The tire should be inspected for the following: match
mount paint marks, bent rims, bulges, irregular tire wear,
proper wheel size and inflation pressure. Then balance
according to the equipment manufacturer’s
recommendations.
There are two types of wheel and tire balance.
Static balance is the equal distribution of weight around
the wheel.
Assemblies that are statically unbalanced cause a
bouncing action called tramp. This condition will
eventually cause uneven tire wear.
Dynamic balance is the equal distribution of weight on
each side of the wheel center-line so that when the tire
spins there is not tendency for the assembly to move from
side to side. Assemblies that are dynamically unbalanced
may cause shimmy.
WARNING:
STONES SHOULD BE REMOVED FROM THE TREAD TO
AVOID OPERATOR INJURY DURING SPIN BALANCING
AND TO OBTAIN A GOOD BALANCE.
Steel Aluminum
AVertical play:
Less than mm(in)1.5 (0.059) 0.7 (0.028)
BHorizontal play:
Less than mm(in)1.5 (0.059) 0.7 (0.028)
Page 470 of 3573

DIFFERENTIAL (REAR 220mm)
4A2A±3
Diagnosis
Many noises that seem to come from the rear axle
actually originate from other sources such as tires, road
surface, wheel bearings, engine, transmission, muffler, or
body drumming. Investigate to find the source of the
noise before disassembling the rear axle. Rear axles, like
any other mechanical device, are not absolutely quiet but
should be considered quiet unless some abnormal noise
is present.
To make a systematic check for axle noise, observe the
following:
1. Select a level asphalt road to reduce tire noise and
body drumming.
2. Check rear axle lubricant level to assure correct level,
and then drive the vehicle far enough to thoroughly
warm up the rear axle lubricant.
3. Note the speed at which noise occurs. Stop the
vehicle and put the transmission in neutral. Run the
engine speed slowly up and down to determine if the
noise is caused by exhaust, muffler noise, or other
engine conditions.
4. Tire noise changes with different road surfaces; axle
noises do not. Temporarily inflate all tires to 344 kPa
(3.5kg/cm
2, 50 psi) (for test purposes only). This will
change noise caused by tires but will not affect noise
caused by the rear axle.
Rear axle noise usually stops when coasting at
speeds under 48 km/h (30 mph); however, tire noise
continues with a lower tone. Rear axle noise usually
changes when comparing pull and coast, but tire
noise stays about the same.
Distinguish between tire noise and rear axle noise by
noting if the noise changes with various speeds or
sudden acceleration and deceleration. Exhaust and
axle noise vary under these conditions, while tire
noise remains constant and is more pronounced at
speeds of 32 to 48 km/h (20 to 30 mph). Further check
for tire noise by driving the vehicle over smooth
pavements or dirt roads (not gravel) with the tires at
normal pressure. If the noise is caused by tires, it will
change noticeably with changes in road surface.
5. Loose or rough front wheel bearings will cause noise
which may be confused with rear axle noise; however,
front wheel bearing noise does not change when
comparing drive and coast. Light application of the
brake while holding vehicle speed steady will often
cause wheel bearing noise to diminish. Front wheel
bearings may be checked for noise by jacking up the
wheels and spinning them or by shaking the wheels to
determine if bearings are loose.
6. Rear suspension rubber bushings and spring
insulators dampen out rear axle noise when correctly
installed. Check to see that there is no link or rod
loosened or metal±to±metal contact.
7. Make sure that there is no metal±to±metal contact
between the floor and the frame.
After the noise has been determined to be in the axle, the
type of axle noise should be determined, in order to make
any necessary repairs.
Gear Noise
Gear noise (whine) is audible from 32 to 89 km/h (20 to 55
mph) under four driving conditions.
1. Driving under acceleration or heavy pull.
2. Driving under load or under constant speed.
3. When using enough throttle to keep the vehicle from
driving the engine while the vehicle slows down
gradually (engine still pulls slightly).
4. When coasting with the vehicle in gear and the throttle
closed. The gear noise is usually more noticeable
between 48 and 64 km/h (30 and 40 mph) and 80 and
89 km/h (50 and 55 mph).
Bearing Noise
Bad bearings generally produce a rough growl or grating
sound, rather than the whine typical of gear noise.
Bearing noise frequently ªwow±wowsº at bearing rpm,
indicating a bad pinion or rear axle side bearing. This
noise can be confused with rear wheel bearing noise.
Rear Wheel Bearing Noise
Rear wheel bearing noise continues to be heard while
coasting at low speed with transmission in neutral. Noise
may diminish by gentle braking. Jack up the rear wheels,
spin them by hand and listen for noise at the hubs.
Replace any faulty wheel bearings.
Knock At Low Speeds
Low speed knock can be caused by worn universal joints
or a side gear hub counter bore in the cage that is worn
oversize. Inspect and replace universal joints or cage and
side gears as required.
Backlash Clunk
Excessive clunk on acceleration and deceleration can be
caused by a worn rear axle pinion shaft, a worn cage,
excessive clearance between the axle and the side gear
splines, excessive clearance between the side gear hub
and the counterbore in the cage, worn pinion and side
gear teeth, worn thrust washers, or excessive drive pinion
and ring gear backlash. Remove worn parts and replace
as required. Select close±fitting parts when possible.
Adjust pinion and ring gear backlash.