lock JAGUAR S TYPE 2005 1.G Technical Guide Update
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2005, Model line: S TYPE, Model: JAGUAR S TYPE 2005 1.GPages: 133, PDF Size: 3.48 MB
Page 37 of 133
JAGUARS-TYPEOccupant Protection
32
Seatbelts
D.501.1777
REAR SEAT BELT RETRACTOR ASSEMBLIES
D.501.1465
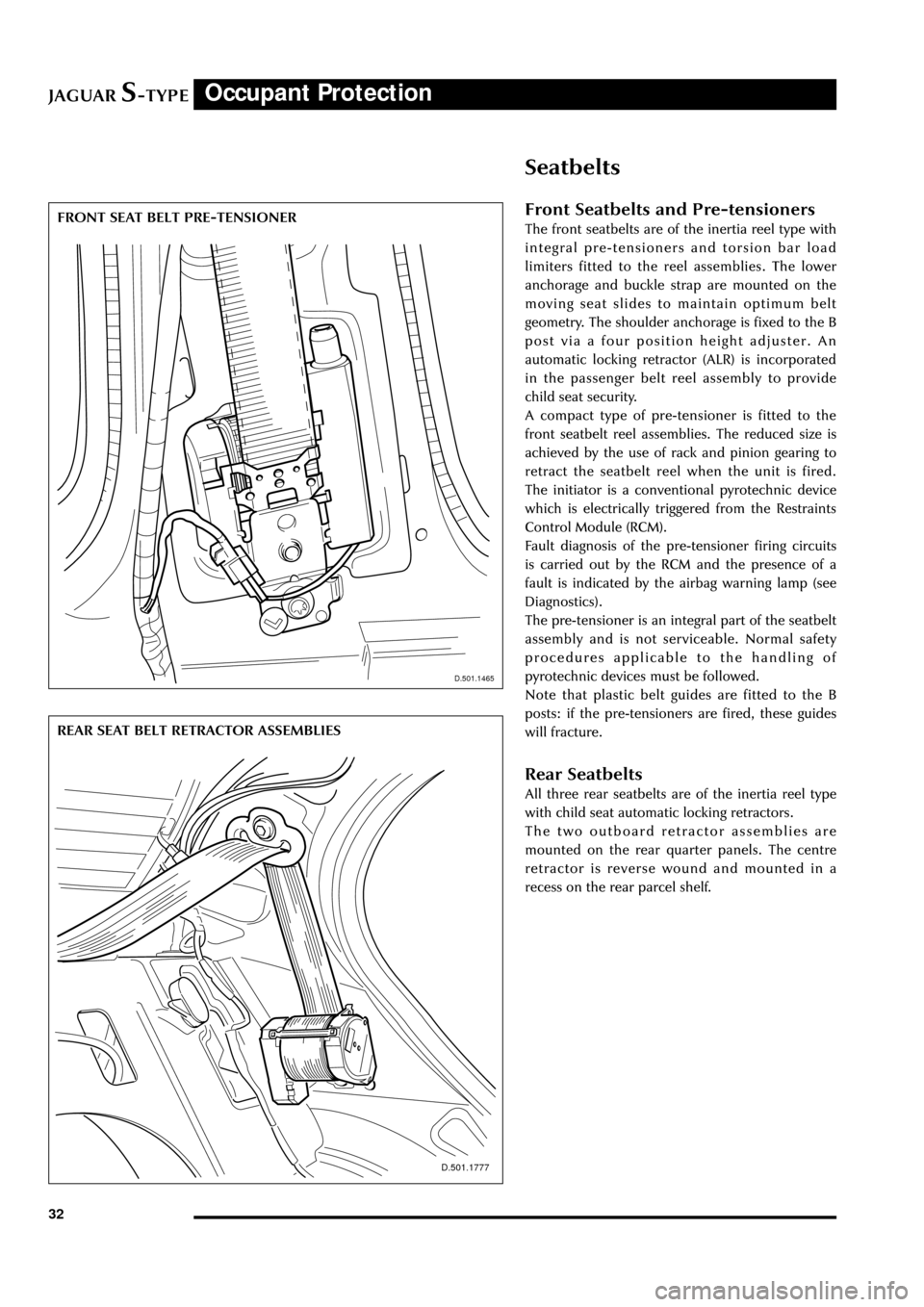
FRONT SEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONERFront Seatbelts and Pre-tensioners
The front seatbelts are of the inertia reel type with
integral pre-tensioners and torsion bar load
limiters fitted to the reel assemblies. The lower
anchorage and buckle strap are mounted on the
moving seat slides to maintain optimum belt
geometry. The shoulder anchorage is fixed to the B
post via a four position height adjuster. An
automatic locking retractor (ALR) is incorporated
in the passenger belt reel assembly to provide
child seat security.
A compact type of pre-tensioner is fitted to the
front seatbelt reel assemblies. The reduced size is
achieved by the use of rack and pinion gearing to
retract the seatbelt reel when the unit is fired.
The initiator is a conventional pyrotechnic device
which is electrically triggered from the Restraints
Control Module (RCM).
Fault diagnosis of the pre-tensioner firing circuits
is carried out by the RCM and the presence of a
fault is indicated by the airbag warning lamp (see
Diagnostics).
The pre-tensioner is an integral part of the seatbelt
assembly and is not serviceable. Normal safety
procedures applicable to the handling of
pyrotechnic devices must be followed.
Note that plastic belt guides are fitted to the B
posts: if the pre-tensioners are fired, these guides
will fracture.
Rear Seatbelts
All three rear seatbelts are of the inertia reel type
with child seat automatic locking retractors.
The two outboard retractor assemblies are
mounted on the rear quarter panels. The centre
retractor is reverse wound and mounted in a
recess on the rear parcel shelf.
D.501.1465
Page 46 of 133

JAGUARS-TYPEFuel System
41
JOL.062
INERTIA SWITCH operating fuel level sender assembly mounted on
the respective module assembly.
Control and Operation
The speed of the fuel pump is varied under closed
loop control so as to deliver the required fuel rail
injection pressure in accordance with factors such
as driver demand, manifold pressure and
temperature changes. The control loop sensors,
providing feedback information to the powertrain
control module (PCM), are the engine fuel
temperature (EFT) sensor and the injection
pressure (IP) sensor which are both mounted
directly on the engine fuel rail (see
S-TYPE Powertrain Technical Guide). The IP sensor
also has a vacuum feed from the intake manifold
so as to measure the pressure differential.
The required fuel flow is determined by the PCM
and sent to the rear electronic control module
(RECM) which is the power driver for the fuel
pump. The PCM demand to the RECM is a pulse
width modulated (PWM) signal over a single line
at a frequency of approximately 256 Hz and a
duty cycle of 0-50%. The RECM effecively
amplifies this signal by increasing the frequency
by 64 and doubling the duty cycle, thus providing
the necessary high current drive for the fuel
pump. The fuel pump relay, located in the rear
power distribution box, is energised by the PCM
relay and provides a dedicated fused supply to the
RECM for the pump drive.
When the ignition switch is turned from OFF to
RUN or START, the PCM primes the system by
running the pump for 1 second at full speed. The
pump is switched off 1 second after the engine is
stopped. During hot starts, fuel pressure is
increased to prevent vapour lock.
Fuel pump drive status is monitored by the RECM
and communicated to the PCM via the SCP
network.
Outputs from the fuel senders are connected by
independent wires to the RECM which sends the
data to the instrument pack and the PCM.
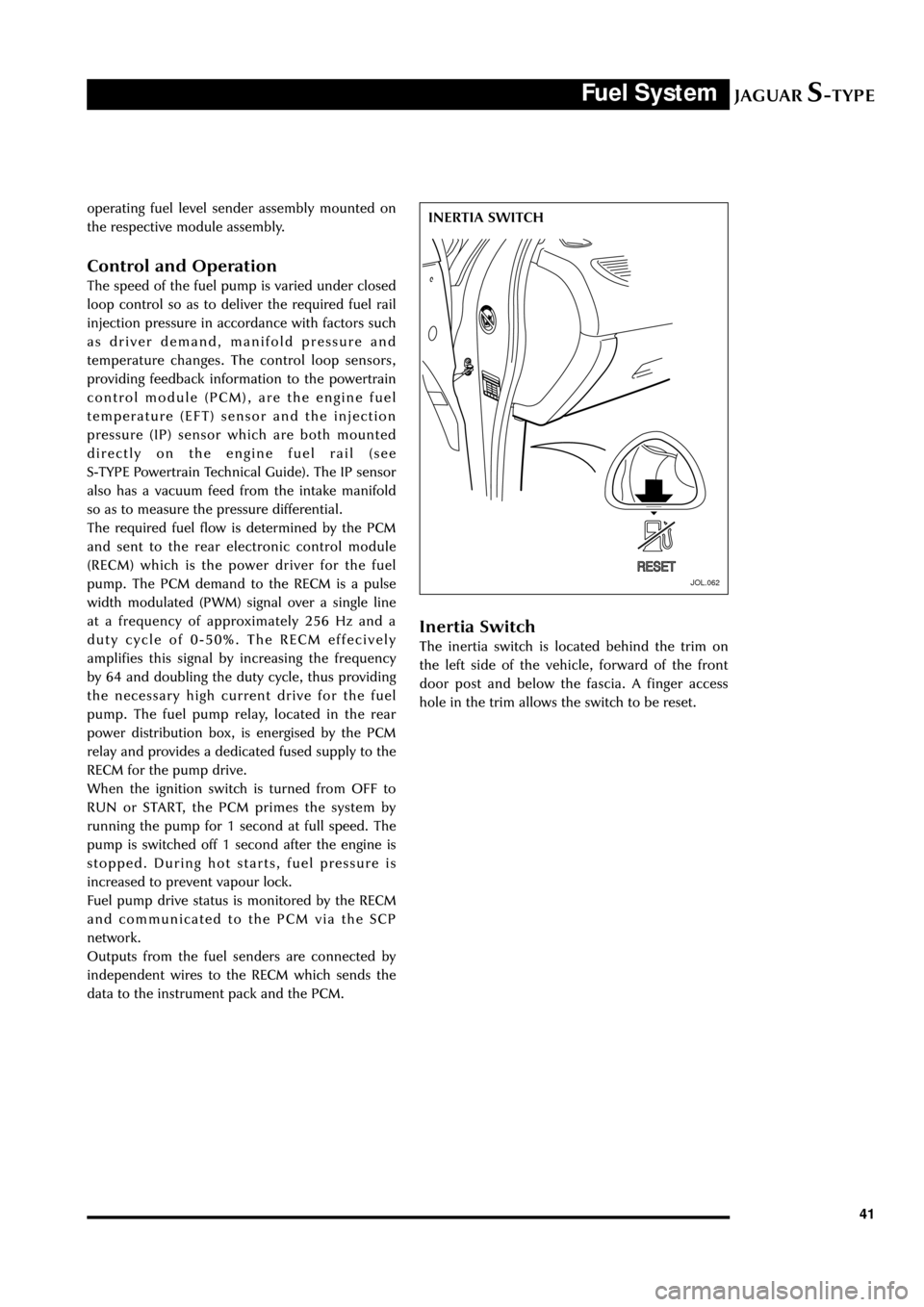
Inertia Switch
The inertia switch is located behind the trim on
the left side of the vehicle, forward of the front
door post and below the fascia. A finger access
hole in the trim allows the switch to be reset.
Page 50 of 133

JAGUARS-TYPETransmission
45
Introduction
The automatic and manual transmission units are
described in the ÔS-TYPE Sports Sedan Powertrain
IntroductionÕ Technical Guide.
J-Gate
The J-gate assembly is mounted on the
transmission tunnel by four bolts and has a
similar operating mechanism to the XJ/XK Series
vehicles. The selector gate positions are, P-R-N-D
on one side of the ÔJÕ and manual gear positions
4-3-2 on the other side. Movement of the gear
selector lever up and down these positions is
transmitted mechanically to a cable assembly
which then rotates the digital range switch on the
side of the automatic transmission housing (see
ÔS-TYPE Powertrain IntroductionÕ Technical
Guide). Movement across the gate between D and
4 operates an electrical switch (without cable
movement).
In the P position with the ignition off, the gear
selector lever is locked by a solenoid plunger
which inhibits a lock plate fixed to the selector
mechanism. When the ignition is switched on,pressing the brake pedal energises the solenoid
and releases the lock plate, allowing the selector
lever to be moved from the P position.
For NAS markets only, the J-gate slider actuator is
linked to the ignition switch barrel to provide a
mechanical interlock. The interlock lever and
cable are driven by the J-gate slider to operate a
locking plunger in the ignition barrel. If the gear
selector lever is in any position other than P, the
ignition key cannot be removed. Note when
servicing, that the interlock cable adjustment is
critical and the JTIS service instructions must be
followed. Where the interlock function is not
fitted, the interlock lever is retained without the
operating cable.
D.307.324
J-GATE
Ignition Switch
Interlock Cable
(NAS markets only)
Interlock Lever
(NAS markets only)
D.307.324
Page 57 of 133
JAGUARS-TYPE
Wheels and Tyres
Chassis
52
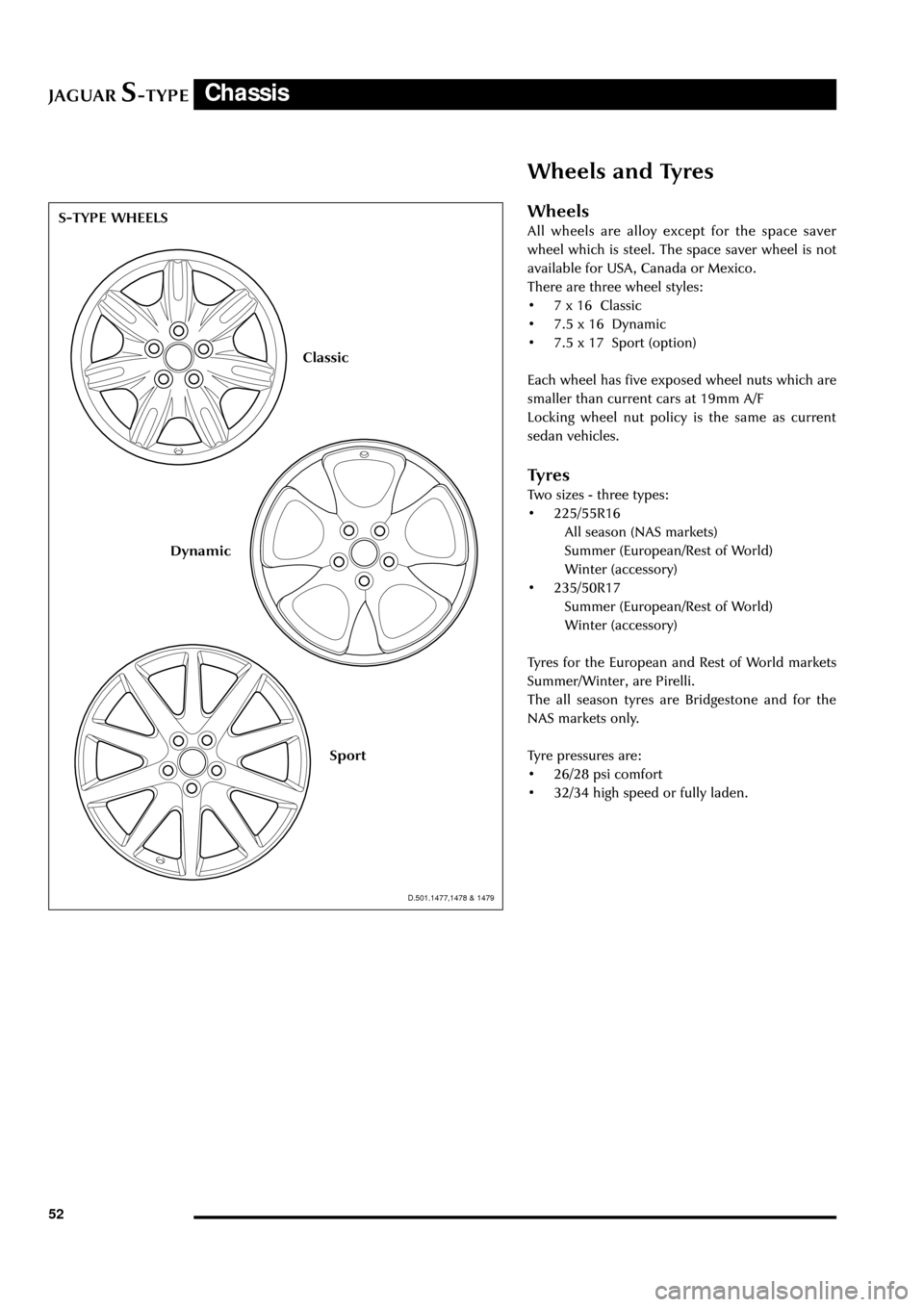
Wheels
All wheels are alloy except for the space saver
wheel which is steel. The space saver wheel is not
available for USA, Canada or Mexico.
There are three wheel styles:
¥ 7 x 16 Classic
¥ 7.5 x 16 Dynamic
¥ 7.5 x 17 Sport (option)
Each wheel has five exposed wheel nuts which are
smaller than current cars at 19mm A/F
Locking wheel nut policy is the same as current
sedan vehicles.
Ty r e s
Two sizes - three types:
¥ 225/55R16
All season (NAS markets)
Summer (European/Rest of World)
Winter (accessory)
¥ 235/50R17
Summer (European/Rest of World)
Winter (accessory)
Tyres for the European and Rest of World markets
Summer/Winter, are Pirelli.
The all season tyres are Bridgestone and for the
NAS markets only.
Tyre pressures are:
¥ 26/28 psi comfort
¥ 32/34 high speed or fully laden.
D.501.1477
S-TYPE WHEELS
D.501.1477,1478 & 1479
Classic
Sport
Dynamic
D.501.1478
D.501.1479
Page 58 of 133

JAGUARS-TYPEChassis
53
Driveline
Introduction
The driveline is a standard type with the engine
position at the front and driven rear axle. This will
be the first time that Jaguar has used in-plant
driveline balancing to improve noise, vibration
and handling. The driveline is finely balanced at
the rear driveshaft joint. The centre bearing is
laser aligned during initial factory build.
The alloy rear engine mountings have two
variants, one for automatic transmission and one
for manual transmission. They are both
serviceable items. The V6 auto is the same as the
V8 but rotated in plan by 180 degrees. The rubber
mountings are carry over concept from the
current XJ and XK Series vehicles but are not
D.307.322
DRIVELINE ARRANGEMENTinterchangeable with them. Both automatic
transmission rubber mountings are common but
with a softer unique mount for the manual V6
transmission.
In service if they are replaced, ensure that there
are buffer gaps and that they are approximately
equal. Neither will be contaminated by lubricant
or automatic transmission fluid.
Driveshaft
The S-TYPE has a two-piece welded steel tube
driveshaft with a splined centre slip joint and
locking collar, the whole being aligned with the
body centreline. The driveshaft has rubber flex
couplings and a rubber, body-mounted, centre
bearing. For safety, the front tube is collapsible.
Page 60 of 133

JAGUARS-TYPEChassis
55
Brakes
Brake Control Module
Brakes are controlled with a Teeves Mk 20E brake
modulator.
The anti-lock brake/traction control, control
module (ABS/TCCM) contains the integral software
for ABS and traction control, similar to current XJ
and XK Series vehicles. It is supplied as a 10 valve,
4-channel module and calibration is the same to
all powertrains. It is connected to the SCP bus for
traction control, warnings and vehicle speed.
Dynamic Stability Control
Dynamic stability control (DSC) is a new Jaguar
safety feature, which uses ABS and traction
control to control yaw movements of the vehicle.
Yaw is the rotary motion of the vehicle on its
vertical axis, a force that would cause oversteer or
oversteer or sideslip. The dynamic stability
control module (DSCM) contains the same
software as described but with the addition of IVD
software. The modulator is supplied as a 12 valve,
4-channel module calibrated for base suspension
only. The connectors differ between the two; the
10 valve unit has a 25-way with sliding cam, as
D.206.254
D.206.175
BRAKE CONTROL MODULE
BRAKE SYSTEM LAYOUT
Page 63 of 133

JAGUARS-TYPEChassis
58
Power Assisted Steering
Introduction
The Jaguar S-TYPE has a variable assist rack and
pinion steering gear and variable rack ratio. The
variable steering rack ratio reduces the number of
turns from lock to lock (2.8) to enhance parking
manoeuvrability whilst maintaining the on-centre
steering precision required at high speed. Full
power assistance is provided for parking. Steering
assistance decreases smoothly at a calibrated rate
to raise driver steering efforts as vehicle speed
increases.
Servicing
There are no carry over parts from XK or XJ Series
vehicles.
The rack is mounted to the rear of cross member
Number 2. The PAS pump is belt driven. A PAS
cooler matrix is located within the radiator
package.
Low PAS pump speeds problems are prevented by
increasing engine speed. A power steering
pressure (PSP) switch senses the demand on the
pump at low engine speeds and increases the
speed to a pre-set minimum.
Hose connections to the pump and the steering
gear are quickfit connectors. The quick connect
tube must be pushed into the existing tube nut
port, along the centreline. The assembly is
complete when the tube end bottoms out in the
port with an audible click/snap. Correct assembly
should be verified by pulling the quickfit tube end.
Servicing of the PAS line involves removal of the
quickfit nut. Replacement PAS lines are supplied
complete with quickfit nut and sealing washer. If
the joint is disturbed it is compulsory to replace
the PTFE sealing ring otherwise leaks are
inevitable. Replacement sealing washers may be
installed with the use of Service tool
D90P-3517-A.
Care must be taken when removing the quickfit
nut from the V6 engine pump as the pulley is
PHENOLIC and is susceptible to damage. The V8
pump installation provides a short jumper tube
from the pump to improve accessibility to the
high-pressure hose connection. The PAS pulley
D.211.247
PA S R AC K
D.211.258
POWER STEERING PRESSURE SWITCH
Page 64 of 133

JAGUARS-TYPEChassis
59
D.211.248
FRONT STEERING ARM requires a Service tool to assist removal. Low-
pressure hose connections are made using
Constant Tension (CT) clamps. Pinion hydraulic
connections are orientated with the bottom
connector low pressure with the longer nut, as
current vehicles.
The PAS fluid is for PAS only; it is not to be used
for transmissions. After manual filling, the system
must be bled using a vacuum pump to remove all
the air from the system to prevent system noises.
Fluid level is checked through a sight window on
the reservoir.
Components replaceable are complete pump,
steering rack, reservoir or hose assembly.
A non-serviceable 10-micron filter is located
within the reservoir to maintain fluid cleanliness
throughout the life of the vehicle. It is essential as
with all Jaguars that the system does not become
contaminated. Cap all ports on disassembly to
prevent contamination ingress. As with current
vehicles, the fluid and reservoir must be renewed
if any major component is replaced i.e. Rack,
pump or cooler.
The road wheels should be set straight ahead and
the steering wheel locked (using service tool
F7LC-3F732-BF) when removal and assembly of
the steering gear or intermediate shaft is required.
This is necessary to prevent damage to the air bag
clock spring within the steering upper column
assembly. The intermediate shaft can only be
assembled to its mating components in one
location. Steering wheel alignment can only be
achieved by adjustment at the tie-rods. A
dimensional check of the steering rack position
may be necessary to verify rack centre.
Steering Column
The steering column assembly is completely new
and uses no parts from previous Jaguar
assemblies:
¥ Construction of the upper column assembly is
based on the use of aluminium extrusions and
castings.
¥ A two shaft lower column assembly is used.
¥ The electronically controlled steering lock, the
steering column lock module (SCLM), is a
physically separate component from the
ignition switch which is fascia mounted.
¥ The dynamic stability control (DSC) steering
wheel position sensor is fitted to the upper
column assembly.
Steering Wheel
The steering wheel consists of a magnesium
armature with a central steel insert. The steering
column and wheel insert are splined with a flat so
that the wheel can only be fitted in one position.
Any misalignment of the steering wheel is
corrected by adjusting the tie rods. The splined
fitting also has a locking taper which requires the
use of a 2 legged puller to remove the wheel.
The steering wheel incorporates the the airbag
module, horn mechanism and the optional cruise
control and audio/phone switches.
Page 66 of 133

JAGUARS-TYPEChassis
61
D.211.253
LOWER STEERING COLUMN
Lower Steering Column Assembly
The adjustable column assembly is connected to
the steering rack via a lower assembly consisting
of two shafts linked by a universal joint. The lower
shaft incorporates a sliding section which is
secured by a pinch bolt on installation. To stabilise
the shaft to shaft joint, the upper of the two shafts
is supported by a bearing assembly where it passes
through the bulkhead.
Gaiter
Bearing and Seal
Slider
¥ Steering column lock module (SCLM) with
splined locking collar on the column.
¥ The retractor box, mounted on the underside
of the lower extrusion, houses the column
wiring harness and connectors with sufficient
cable to allow for column telescopic
movement.
Page 67 of 133

JAGUARS-TYPEChassis
62
J.211.257
STEERING COLUMN LOCK MODULE
Steering Column Lock (where fitted)
Lock Operation
The steering column lock module (SCLM) and
ignition key switch are separate assemblies and
activation of the lock is remotely controlled by the
instrument pack, GECM and RECM. The column is
unlocked on insertion of the ignition key and is
locked when the key is withdrawn.
The SCLM is mounted on top of the lower casting,
on the upper column assembly, by two shear
bolts. A locking bolt projects down from the SCLM
through a hole in the lower casting to engage into
a splined collar on the steering column. The SCLM
is an integrated non-serviceable assembly, housinga motor and worm drive for the locking bolt and
also an electronic printed circuit board. When
activated, the locking bolt is driven positively in
both the lock (down) and unlock (up) directions
and has a spring to help locate it into the trough
of the splined collar. When disengaging, the
locking bolt is driven upwards until it operates a
microswitch (within the SCLM) which causes the
motor to stop and also signals via the SCP bus that
the steering lock is off. To engage the lock, the
motor is energised for 350ms to lower the bolt.
System Control
The lock motor is powered by a switched 12V line
from the RECM and switched ground line from the
GECM, with both supplies being applied only
during lock operation. Initiation of motor drive
and direction and power supply switching is
controlled by the instrument pack via the SCP bus
when ignition key insertion or withdrawal is
detected. Identification is checked between the
SCLM and the other modules and the system will
not operate if, for example, a module has been
replaced and not re-programmed. System
diagnostics include defective modules and
incorrect module identification and also certain
SCLM faults, ie unconfimed lock or unlock
conditions and failed microswitch.
Steering Column Shrouds
The upper part of the column assembly is
enclosed by two plastic shrouds, upper and lower.
The steering column adjust switch, controlling tilt
and reach for the electrically powered steering
column assembly, is mounted on the side of the
lower shroud.
SCLM