reset JEEP CHEROKEE 1994 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1994, Model line: CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP CHEROKEE 1994Pages: 1784, PDF Size: 77.09 MB
Page 497 of 1784

FUSIBLE LINK REPLACEMENT
CAUTION: Do not replace blown fusible links with a
standard wire. Only use fusible type wire with hypa-
lon insulation or damage to the electrical system
could occur. Also make sure correct gauge of wir-
ing is used. Refer to the wiring diagrams for proper
gauge and color.
When a fusible link blows it is important to find
out what the problem is. They are placed in the elec-
trical system for protection against shorts to ground.
This can be caused by a component failure or various
wiring failures.Do not just replace the fusible
link to correct the problem.
When diagnosing a faulty fusible link it is impor-
tant to check the wire carefully. In some instances
the link may be blown and it will not show through
the insulation, the wire should be checked over its
entire length for internal breaks.
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Cut out the blown portion of the fusible link.
(3) Strip 1 inch of insulation from each end of the
existing fusible link.
(4) Place a piece of heat shrink tubing over one
side of the fusible link. Make sure the tubing will be
long enough to cover and seal the entire repair area.
(5) Cut a replacement piece of fusible link approx-
imately two inches longer than the piece removed.
(6) Remove one inch of insulation from each end of
the replacement fusible link.
(7) Spread the strands of wire apart on each of the
exposed wires (Fig. 7 example 1).
(8) Push the two ends of the wire together until
the strands of wire are close to the insulation (Fig. 7
example 2).
(9) Twist the wires together (Fig. 7 example 3).
(10) Solder the wires together using rosin core type
solder only.Do not use acid core type solder.
(11) Center the heat shrink tubing over the joint
and heat using a heat gun. Heat the joint until the
tubing is tightly sealed and sealant comes out of both
ends of the tubing.
(12) Secure the fusible link to the existing ones to
prevent chafing or damage to the insulation.
(13) Connect battery and test affected systems.
WIRING REPAIR
When replacing or repairing a wire, it is important
that the correct gauge be used as shown in the wir-
ing diagrams. The wires must also be held securely
in place to prevent damage to the insulation.
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove 1 inch of insulation from each end of
the wire.
(3) Place a piece of heat shrink tubing over one
side of the wire. Make sure the tubing will be long
enough to cover and seal the entire repair area.(4) Spread the strands of the wire apart on each of
the exposed wires (Fig. 7 example 1).
(5) Push the two ends of wire together until the
strands of wire are close to the insulation (Fig. 7 ex-
ample 2).
(6) Twist the wires together (Fig. 7 example 3).
(7) Solder the connection together using rosin core
type solder only.Do not use acid core solder.
(8) Center the heat shrink tubing over the joint
and heat using a heat gun. Heat the joint until the
tubing is tightly sealed and sealant comes out of both
ends of the tubing.
(9) Secure the wire to the existing ones to prevent
chafing or damage to the insulation.
(10) Connect battery and test affected systems.
CONNECTOR REPLACEMENT
(1) Disconnect battery.
(2) Disconnect the connector to be repaired from its
mating half.
(3) Remove connector locking wedge (Fig. 8).
(4) Position the connector locking finger away from
the terminal while pulling on the wire to remove the
terminal from the connector (Fig. 9).
(5) Reset the terminal locking tang, if it has one.
(6) Insert the removed wire in the same cavity on
the repair connector.
(7) Repeat steps four through six for each wire in
the connector, being sure that all wires are inserted
into the proper cavities. For additional connector pin
out identification refer to the wiring diagrams.
(8) Insert the connector locking wedge into the re-
paired connector.
(9) Connect connector to its mating half.
Fig. 7 Wire Repair
8W - 4 WIRING DIAGRAMSJ
Page 988 of 1784

SPEED CONTROLÐPCM OUTPUT
Speed control operation is regulated by the power-
train control module (PCM). The PCM controls the
vacuum to the throttle actuator through the speed
control vacuum and vent solenoids. Refer to Group
8H for speed control information.
TACHOMETERÐPCM OUTPUT
The powertrain control module (PCM) supplies en-
gine rpm values to the instrument cluster tachome-
ter (if equipped). Refer to Group 8E for tachometer
information.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH RELAYÐPCM
OUTPUT
ALL 2.5L 4 CYL. WITH 3-SPEED AUTO. TRANS
4.0L 6 CYL. YJ MODELS WITH 3-SPEED AUTO.
TRANS
The transmission mounted torque converter clutch
(TCC) solenoid is used to control the torque con-
verter. The solenoid is controlled through the power-
train control module (PCM) and by the TCC relay.
This relay is used only on vehicles equipped with a
3-speed automatic transmission.
An electrical output signal is sent from the PCM to
the TCC relay after the PCM receives information
from the vehicle speed, MAP, throttle position and
engine coolant temperature sensors. After the TCC
relay receives this necessary information, it will send
a signal to the torque converter clutch solenoid to
control the torque converter.
On YJ models the TCC relay is located in the en-
gine compartment, on the cowl panel and near the
battery (Fig. 24). On XJ models the TCC relay is lo-
cated in the power distribution center (PDC) (Fig.
23).
OPEN LOOP/CLOSED LOOP MODES OF
OPERATION
As input signals to the powertrain control module
(PCM) change, the PCM adjusts its response to the
output devices. For example, the PCM must calculate
different injector pulse width and ignition timing for
idle than it does for wide open throttle (WOT). There
are several different modes of operation that deter-
mine how the PCM responds to the various input sig-
nals.
MODES
²Open Loop
²Closed Loop
During Open Loop modes, the powertrain control
module (PCM) receives input signals and responds
only according to preset PCM programming. Input
from the oxygen (O2S) sensor is not monitored dur-
ing Open Loop modes.
During Closed Loop modes, the PCM will monitor
the oxygen (O2S) sensor input. This input indicates
to the PCM whether or not the calculated injector
pulse width results in the ideal air-fuel ratio. This
ratio is 14.7 parts air-to-1 part fuel. By monitoring
the exhaust oxygen content through the O2S sensor,
the PCM can fine tune the injector pulse width. This
is done to achieve optimum fuel economy combined
with low emission engine performance.
The fuel injection system has the following modes
of operation:
²Ignition switch ON
²Engine start-up (crank)
²Engine warm-up
²Idle
²Cruise
²Acceleration
²Deceleration
²Wide open throttle (WOT)
²Ignition switch OFF
The ignition switch On, engine start-up (crank),
engine warm-up, acceleration, deceleration and wide
open throttle modes are Open Loop modes. The idle
and cruise modes, (with the engine at operating tem-
perature) are Closed Loop modes.
IGNITION SWITCH (KEY-ON) MODE
This is an Open Loop mode. When the fuel system
is activated by the ignition switch, the following ac-
tions occur:
²The powertrain control module (PCM) pre-posi-
tions the idle air control (IAC) motor.
²The PCM determines atmospheric air pressure
from the MAP sensor input to determine basic fuel
strategy.
²The PCM monitors the engine coolant temperature
sensor input. The PCM modifies fuel strategy based
on this input.
Fig. 24 TCC Relay LocationÐYJ Models
JFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 27
Page 1095 of 1784
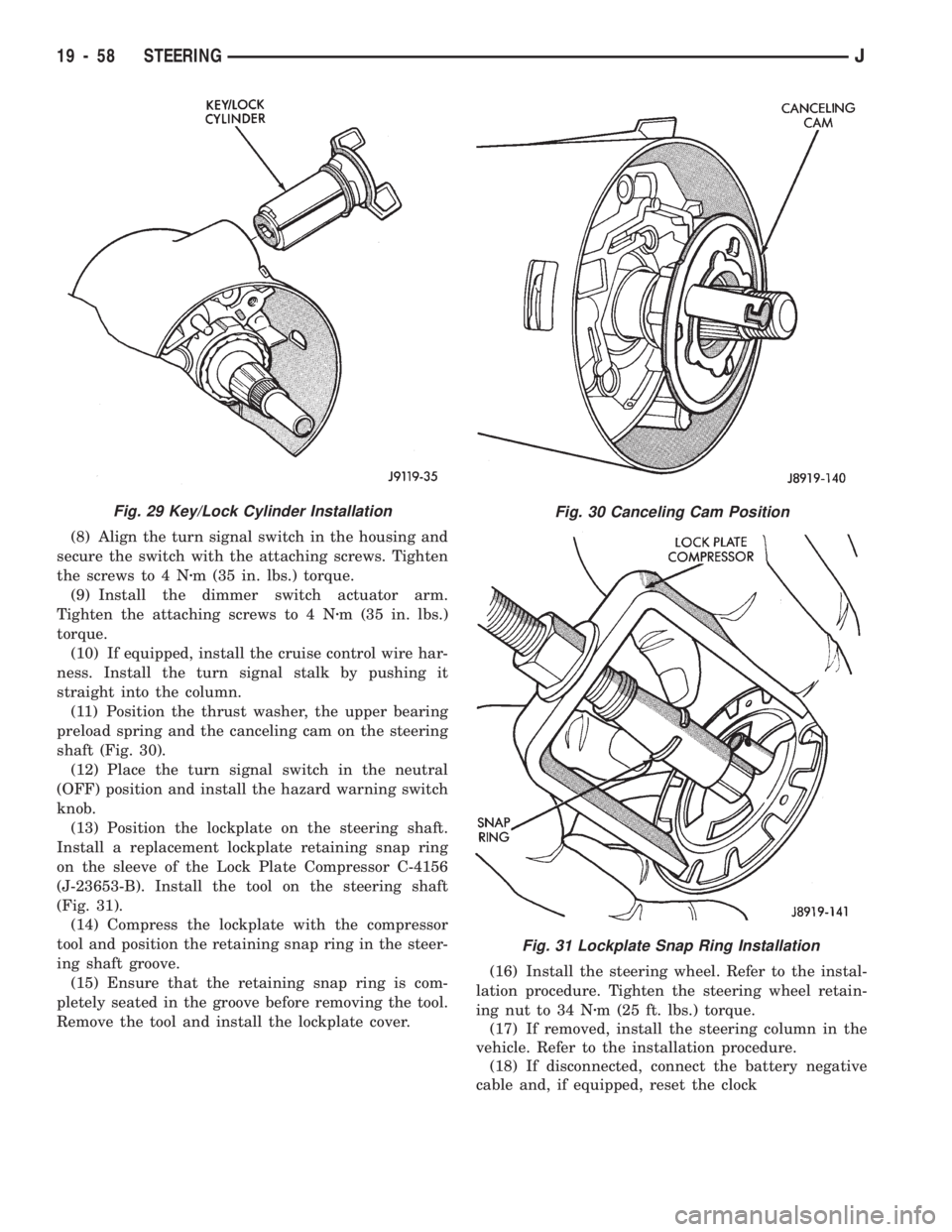
(8) Align the turn signal switch in the housing and
secure the switch with the attaching screws. Tighten
the screws to 4 Nzm (35 in. lbs.) torque.
(9) Install the dimmer switch actuator arm.
Tighten the attaching screws to 4 Nzm (35 in. lbs.)
torque.
(10) If equipped, install the cruise control wire har-
ness. Install the turn signal stalk by pushing it
straight into the column.
(11) Position the thrust washer, the upper bearing
preload spring and the canceling cam on the steering
shaft (Fig. 30).
(12) Place the turn signal switch in the neutral
(OFF) position and install the hazard warning switch
knob.
(13) Position the lockplate on the steering shaft.
Install a replacement lockplate retaining snap ring
on the sleeve of the Lock Plate Compressor C-4156
(J-23653-B). Install the tool on the steering shaft
(Fig. 31).
(14) Compress the lockplate with the compressor
tool and position the retaining snap ring in the steer-
ing shaft groove.
(15) Ensure that the retaining snap ring is com-
pletely seated in the groove before removing the tool.
Remove the tool and install the lockplate cover.(16) Install the steering wheel. Refer to the instal-
lation procedure. Tighten the steering wheel retain-
ing nut to 34 Nzm (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(17) If removed, install the steering column in the
vehicle. Refer to the installation procedure.
(18) If disconnected, connect the battery negative
cable and, if equipped, reset the clock
Fig. 30 Canceling Cam Position
Fig. 31 Lockplate Snap Ring Installation
Fig. 29 Key/Lock Cylinder Installation
19 - 58 STEERINGJ
Page 1281 of 1784

(8) Shift transmission into D range and record
time it takes for engagement. Repeat test two more
times.
(9) Reset stop watch and shift transmission back to
Neutral.
(10) Shift transmission into Reverse and record
time it takes for engagement. Repeat test two more
times.
(11) Engagement time in D range should be a max-
imum of 1.2 seconds. Engagement time for Reverse
should be a maximum of 1.5 seconds.
TIME LAG TEST ANALYSIS
If engagement time is longer than specified for D
range, check for the following:²shift cable misadjusted
²line pressure low
²forward clutch worn
²overdrive clutch worn or damaged
If engagement time is longer than specified for Re-
verse, check for the following:
²shift cable misadjusted
²line pressure low
²direct clutch worn
²first/reverse brake worn
²overdrive clutch worn or damaged
21 - 170 AW-4 TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSISJ
Page 1543 of 1784
The reinforcement bracket is held on the
frame rail with two blind rivets.
(2) Remove the bracket and tow hook from frame
rail.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position bracket and tow hook on the frame
rail.
(2) Install bolts that attach tow hook bracket to
frame rail and reinforcement bracket. Tighten bolts
to 75 Nzm (55 ft-lbs) torque.
TRAILER HITCHES
CLASS III HITCHÐXJ VEHICLES
A class III weight-distributing/equalizer type hitch
can be used to tow a trailer:
²having a maximum gross weight of 5,000 lbs/2250
kg, and
²having a maximum tongue weight of 750 lbs/332
kg).
The following vehicle basic equipment is required
for class III trailer towing:
²P205/75R15 or larger tires;
²full size spare tire;
²trailer sway control;
²trailer tow wire harness and connector;
²heavy duty turn signal flasher element;
²heavy duty axle (with synthetic lubricant);²heavy duty cooling system;
²heavy duty generator/battery;
²auxiliary automatic transmission fluid cooler; and
²I-6, 4.0L engine.
Wide-angle type door mirrors are recommended but
not required.
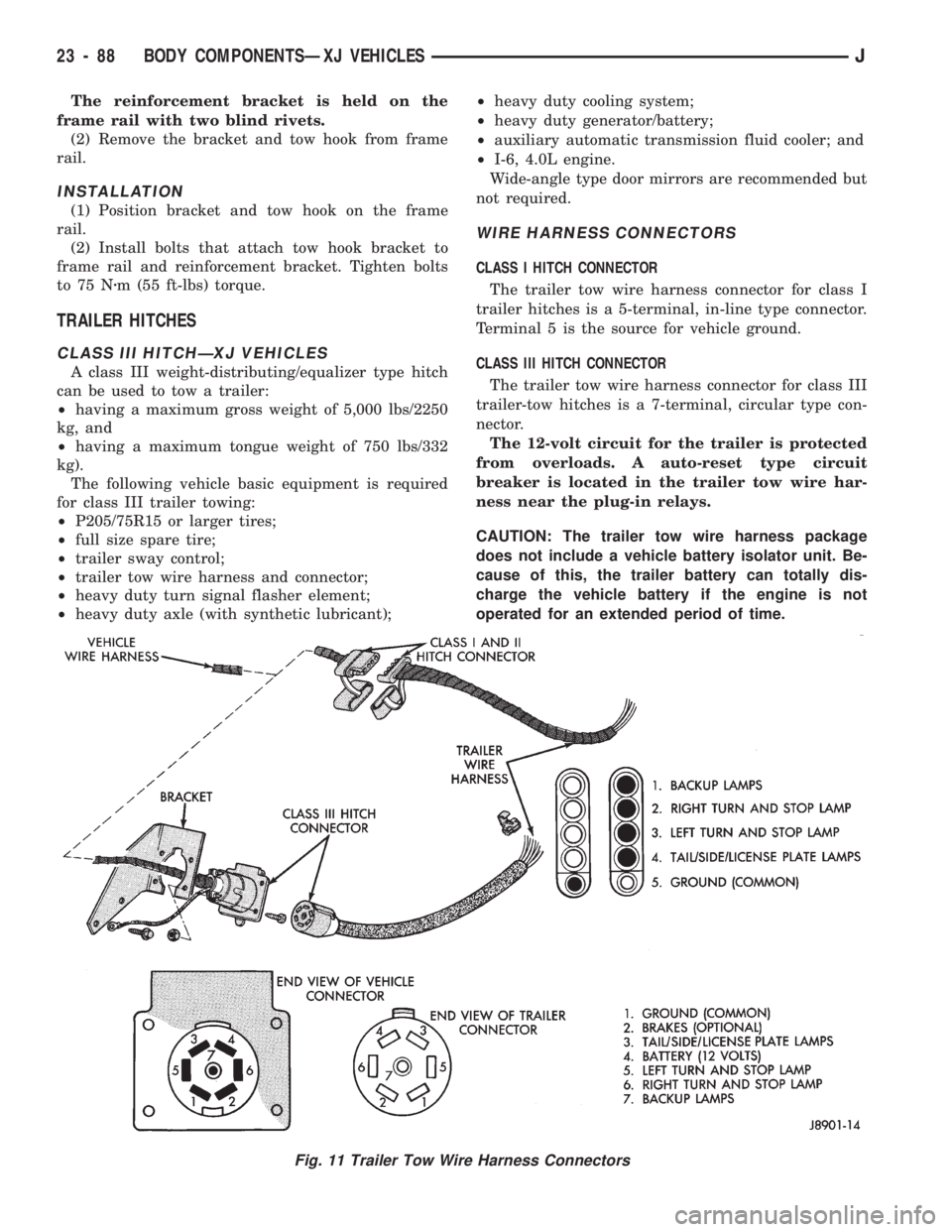
WIRE HARNESS CONNECTORS
CLASS I HITCH CONNECTOR
The trailer tow wire harness connector for class I
trailer hitches is a 5-terminal, in-line type connector.
Terminal 5 is the source for vehicle ground.
CLASS III HITCH CONNECTOR
The trailer tow wire harness connector for class III
trailer-tow hitches is a 7-terminal, circular type con-
nector.
The 12-volt circuit for the trailer is protected
from overloads. A auto-reset type circuit
breaker is located in the trailer tow wire har-
ness near the plug-in relays.
CAUTION: The trailer tow wire harness package
does not include a vehicle battery isolator unit. Be-
cause of this, the trailer battery can totally dis-
charge the vehicle battery if the engine is not
operated for an extended period of time.
Fig. 11 Trailer Tow Wire Harness Connectors
23 - 88 BODY COMPONENTSÐXJ VEHICLESJ