battery JEEP CHEROKEE 1995 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1995, Model line: CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP CHEROKEE 1995Pages: 2198, PDF Size: 82.83 MB
Page 242 of 2198

INSTALLATIONÐALL MODELS
(1) If pump is being replaced, install the heater
hose fitting to the pump. Use a sealant on the fitting
such as MoparŸ Thread Sealant With Teflon. Refer
to the directions on the package.
(2) Clean the gasket mating surfaces. If the origi-
nal pump is used, remove any deposits or other for-
eign material. Inspect the cylinder block and water
pump mating surfaces for erosion or damage from
cavitation.
(3) Install the gasket and water pump. The silicone
bead on the gasket should be facing the water pump.
Also, the gasket is installed dry. Tighten mounting
bolts to 30 Nzm (22 ft. lbs.) torque. Rotate the shaft
by hand to be sure it turns freely.
(4) Connect the radiator and heater hoses to the
water pump.
(5) Position water pump pulley to water pump hub.
(6) If equipped with a water pump mounted fan,
install fan and four nuts to water pump hub. If not
equipped with a water pump mounted fan, install
four pump hub bolts. Tighten bolts (or nuts) to 27
Nzm (20 ft. lbs.) torque.
(7) Position power steering pump bracket to en-
gine. Install bolts E, F and G (Fig. 7). Tighten bolts F
andGto38Nzm (28 ft. lbs.) torque. Tighten bolt E to
27 Nzm (20 ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Position power steering pump to mounting
bracket. Install pivot bolt B (Fig. 6) finger tight. In-
stall locknut C and adjustment bolt D (Figs. 6 or 7)
finger tight.
(9) Install two adjustment bolts A (Fig. 6) finger
tight.
(10) Install idler pulley.
CAUTION: When installing the serpentine engine
accessory drive belt, the belt MUST be routed cor-
rectly. If not, the engine may overheat due to the
water pump rotating in the wrong direction. Refer to
figures 11, 12, 13 or 14 for appropriate belt routing.
You may also refer to the Belt Routing Label in the ve-
hicle engine compartment.
(11) Position drive belt to pulleys.
(12) Tighten belt adjustment bolt D (Fig. 5) to the
proper tension. Refer to the Specifications section at
the end of this group for belt tension.
(13) Tighten bolts A (Fig. 5) to 27 Nzm (20 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(14) Tighten pivot bolt B (Fig. 6) to 27 Nzm (20 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(15) Tighten locknut C (Fig. 6) to 27 Nzm (20 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(16) After the power steering pump has been tight-
ened, recheck belt tension.
(17) Fill cooling system with coolant and check for
leaks. Refer to Refilling Cooling System in this
group.(18) Connect battery cable to battery.
(19) Start and warm the engine. Check for leaks.
THERMOSTAT
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
A pellet-type thermostat controls the operating
temperature of the engine by controlling the amount
of coolant flow to the radiator. On all engines the
thermostat is closed below 195ÉF (90ÉC). Above this
Fig. 11 YJ Models with 4.0L Engine, and XJ Models
with 2.5L 4-Cylinder EngineÐWith A/C
Fig. 12 YJ Models With 2.5L or 4.0L Engine, and XJ
Models with 2.5L EngineÐWithout A/C
JCOOLING SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURES 7 - 17
Page 252 of 2198

WARNING: CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMPS
ARE USED ON MOST COOLING SYSTEM HOSES.
WHEN REMOVING OR INSTALLING, USE ONLY
TOOLS DESIGNED FOR SERVICING THIS TYPE OF
CLAMP, SUCH AS SPECIAL CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER
6094) (FIG. 27). SNAP-ON CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER
HPC-20) MAY BE USED FOR LARGER CLAMPS. AL-
WAYS WEAR SAFETY GLASSES WHEN SERVICING
CONSTANT TENSION CLAMPS.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps (Fig. 28). If re-
placement is necessary, use only an original equip-
ment clamp with matching number or letter.XJ MODELS WITH 2.5L 4-CYLINDER ENGINE
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Observe the previousWARNINGS.Remove ra-
diator cap.
(3) Position drain pan under draincock. Open radi-
ator draincock. Drain radiator.
(4) Remove radiator upper and lower hose clamps
(Figs. 27 and 28). Remove hoses.
(5) Remove E-clip from alignment dowel at radia-
tor lower mounting bracket (Fig. 29).
(6) Disconnect coolant reserve/overflow tank hose
from radiator.
(7) Remove four radiator fan shroud mounting
bolts (Fig. 29). Push shroud back against front of en-
gine.
(8) If equipped, disconnect and plug automatic
transmission fluid cooler lines. Refer to Group 21,
Transmission for procedures.
(9) Remove two radiator top mounting bolts (Fig.
29).
(10) (a) If equipped with air conditioning, remove
the radiator grille mounting screws and remove grill.
Refer to Group 23, Body for procedures.
(b) If equipped, remove the air conditioning con-
denser-to-radiator mounting bolt. Use an open end
wrench to remove bottom bolts (Fig. 30).
(11) Lift radiator straight up and out of vehicle.
Take care not to damage radiator fins. When remov-
ing radiator, note position of the rubber seals located
on the top, bottom and sides of radiator (Fig. 29). To
prevent possible overheating, these seals must be in-
stalled to their original positions.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install radiator behind air conditioning con-
denser with bottom alignment dowel inserted into ra-
diator lower mounting bracket (Fig. 29).
(2) Install E-clip to radiator alignment dowel (Fig.
29).
(3) Tighten the four condenser-to-radiator mount-
ing bolts to 6.2 Nzm (55 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) If removed, install radiator grille.
(5) Tighten radiator top mounting bolts to 6 Nzm
(55 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) If equipped, connect automatic transmission
fluid cooler lines to radiator. Refer to Group 21,
Transmission for procedures.
(7) Install the radiator fan shroud.
(8) Connect the coolant reserve/overflow tank hose.
(9) Connect radiator hoses and install hose clamps.
(10) Connect negative battery cable.
(11) Close the draincock.
(12) Fill cooling system with correct coolant.
(13) Install radiator cap.
(14) Check and adjust automatic transmission
fluid level (if equipped).
Fig. 27 Hose Clamp ToolÐTypical
Fig. 28 Clamp Number/Letter Location
JCOOLING SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURES 7 - 27
Page 253 of 2198
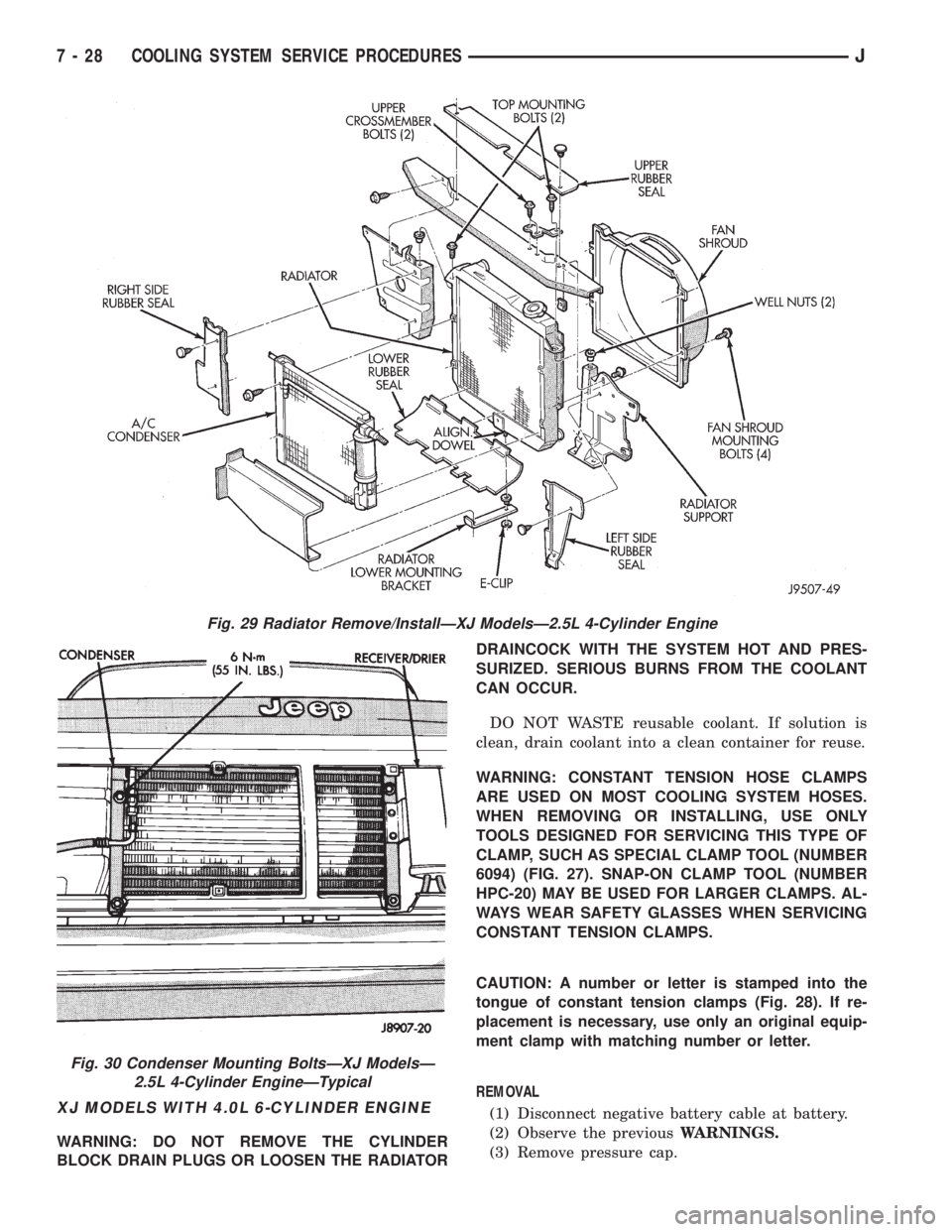
XJ MODELS WITH 4.0L 6-CYLINDER ENGINE
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATORDRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND PRES-
SURIZED. SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE COOLANT
CAN OCCUR.
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If solution is
clean, drain coolant into a clean container for reuse.
WARNING: CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMPS
ARE USED ON MOST COOLING SYSTEM HOSES.
WHEN REMOVING OR INSTALLING, USE ONLY
TOOLS DESIGNED FOR SERVICING THIS TYPE OF
CLAMP, SUCH AS SPECIAL CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER
6094) (FIG. 27). SNAP-ON CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER
HPC-20) MAY BE USED FOR LARGER CLAMPS. AL-
WAYS WEAR SAFETY GLASSES WHEN SERVICING
CONSTANT TENSION CLAMPS.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps (Fig. 28). If re-
placement is necessary, use only an original equip-
ment clamp with matching number or letter.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Observe the previousWARNINGS.
(3) Remove pressure cap.
Fig. 29 Radiator Remove/InstallÐXJ ModelsÐ2.5L 4-Cylinder Engine
Fig. 30 Condenser Mounting BoltsÐXJ ModelsÐ
2.5L 4-Cylinder EngineÐTypical
7 - 28 COOLING SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURESJ
Page 255 of 2198

(13) Remove four radiator upper crossmember
bolts (Fig. 32) and remove upper crossmember.
(14) If equipped with air conditioning, separate ra-
diator from condenser by removing condenser-to-radi-
ator mounting brackets (Fig. 33).
(15) Lift radiator straight up and out of engine
compartment taking care not to damage fins.
INSTALLATION
The radiator is supplied with two alignment dowels
(Figs. 32 or 34). They are located on the bottom tank
and fit into rubber grommets in the radiator lower
crossmember.
(1) Lower radiator into engine compartment. Posi-
tion alignment dowels into rubber grommets in radi-
ator lower crossmember (Figs. 32 or 34).
(2) If equipped with air conditioning, attach con-
denser to radiator with mounting brackets (Fig. 33).
(3) Install radiator upper crossmember and four
mounting bolts.
(4) Install radiator upper crossmember-to-isolator
nuts. Tighten nuts to 10 Nzm (86 in. lbs.) torque. If
isolator-to-radiator nuts had been removed, tighten
them to 5 Nzm (47 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Install hood latch striker. Note previously
marked position.
(6) Connect radiator upper and lower hoses.
(7) If equipped, connect automatic transmission
fluid cooler lines. Refer to Group 21, Transmissions
for procedures. If equipped with remote cooler, attach
cooler line to bracket at bottom of radiator.
(8) Install electric cooling fan (if equipped). Insert
alignment tabs at bottom of fan shroud into slots inbracket at bottom of radiator. Tighten mounting bolts
to3Nzm (31 in. lbs.) torque.
(9) Connect electric cooling fan electrical connector.
(10) Install mechanical cooling fan shroud. Insert
alignment tabs at bottom of shroud into slots in
bracket at bottom of radiator. Tighten mounting bolts
to3Nzm (31 in. lbs.) torque.
(11) Close radiator draincock.
(12) Install grille.
(13) Connect negative battery cable.
(14) Fill cooling system with correct coolant. Refer
to the Coolant section of this group.
(15) Install pressure cap.
(16) Check and adjust automatic transmission
fluid level (if equipped).
YJ MODELS
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND PRES-
SURIZED. SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE COOLANT
CAN OCCUR.
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If solution is
clean, drain coolant into a clean container for reuse.
WARNING: CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMPS
ARE USED ON MOST COOLING SYSTEM HOSES.
WHEN REMOVING OR INSTALLING, USE ONLY
TOOLS DESIGNED FOR SERVICING THIS TYPE OF
CLAMP, SUCH AS SPECIAL CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER
6094) (FIG. 27). SNAP-ON CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER
HPC-20) MAY BE USED FOR LARGER CLAMPS. AL-
Fig. 33 Condenser-to-Radiator Mounting BracketsÐ
XJ with 4.0L 6- Cylinder Engine
Fig. 34 Radiator InstallationÐXJ Models with 4.0L
6-Cylinder Engine
7 - 30 COOLING SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURESJ
Page 256 of 2198

WAYS WEAR SAFETY GLASSES WHEN SERVICING
CONSTANT TENSION CLAMPS.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps (Fig. 28). If re-
placement is necessary, use only an original equip-
ment clamp with matching number or letter.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Observe the previousWARNINGS.Remove the
radiator cap.
(3) Position drain pan under draincock. Open radi-
ator draincock and drain radiator.
(4) Remove radiator upper and lower hose clamps
(Figs 27 and 28). Remove radiator hoses.
(5) Disconnect coolant reserve/overflow tank hose
from radiator.
(6) Remove the four fan shroud mounting bolts
(Fig. 35). On some models the power steering fluid
reservoir tank is attached to the side of the fan
shroud. Tie the reservoir back to prevent spillage. Po-
sition the fan shroud back over the fan blades.
(7) If equipped, disconnect and plug automatic
transmission fluid cooler lines.(8) Remove six radiator mounting bolts. Position
the front axle vent hose (Fig. 35) to the side.
(9) Lift radiator straight up and out of vehicle tak-
ing care not to damage radiator fins.
When removing radiator, note position of the rub-
ber seals located on the top and bottom of radiator
(figure 35 on certain models only). To prevent possi-
ble overheating, these seals must be installed to their
original positions.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the radiator. Install and tighten the
six mounting bolts (Fig. 35) to 8 Nzm (72 in. lbs.)
torque.
(2) Close radiator draincock.
(3) Position fan shroud and power steering reser-
voir tank (if equipped). Install and tighten four
mounting bolts to 8 Nzm (72 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) If equipped, remove plugs and connect auto-
matic transmission fluid cooler lines.
(5) Connect radiator hoses and install hose clamps.
(6) Connect negative battery cable.
(7) Fill cooling system with correct coolant. Refer
to the Coolant section of this group.
(8) Connect reserve/overflow tank hose.
(9) Install radiator cap.
Fig. 35 RadiatorÐRemove/InstallÐYJ Models
JCOOLING SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURES 7 - 31
Page 260 of 2198

(5) Be sure that the air conditioner (if equipped) is
turned off.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A DI-
RECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR FAN. DO
NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(6) Start the engine and operate at 2400 rpm.
Within ten minutes the air temperature (indicated on
the dial thermometer) should be up to 88É C (190É F).
Fan driveengagementshould have started to occur
at between 74É to 82É C (165É to 180É F). Engage-
ment is distinguishable by a definiteincreasein fan
flow noise (roaring). The timing light also will indi-
cate an increase in the speed of the fan.
(7) When the air temperature reaches 88É C (190É
F), remove the plastic sheet. Fan drivedisengage-
mentshould have started to occur at between 57É to
79É C (135É to 175É F). A definitedecreaseof fan
flow noise (roaring) should be noticed. If not, replace
the defective viscous fan drive unit.
VISCOUS FAN DRIVE REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
Refer to the previous section on Cooling System
Fan for removal and installation procedures of the
viscous drive unit.
Viscous Fan Drive Fluid Pump Out Require-
ment:After installing anewviscous fan drive, bring
the engine speed up to approximately 2000 rpm and
hold for approximately two minutes. This will ensure
proper fluid distribution within the drive.
AUXILIARY ELECTRIC COOLING FANÐXJ MODELS
WITH 4.0L 6-CYLINDER ENGINE
OPERATION
XJ models equipped with a 4.0L 6-cylinder engine
may also have an auxiliary electrical cooling fan.
This is with models that have air conditioning and/or
heavy duty cooling. The fan is controlled by the cool-
ing fan relay, which is located in the power distribu-
tion center (PDC). For the location of relay within
the PDC (Fig. 41), refer to the label on PDC cover.
When coolant temperature is above 88ÉC (190ÉF),
the powertrain control module (PCM) provides a
ground path for the fan relay. This ground is pro-
vided through pin/connector #31 of the PCM 60-way
connector. Battery voltage is then applied to the fan
through the relay. When coolant temperature is be-
low 88ÉC (190ÉF), the PCM opens the ground path to
the relay. This will prevent the cooling fan from be-
ing energized.
Whenever the air conditioning is operated, the
PCM engages the auxiliary cooling fan. It provides aground path to the cooling fan relay. This ground is
provided through pin/connector #31 of the PCM 60-
way connector.
DIAGNOSIS AND RELAY TESTING
The powertrain control module (PCM) will enter a
diagnostic trouble code (DTC) number 35 in memory
if it detects a problem in the auxiliary cooling fan re-
lay or circuit. This will be read as a flashing signal
at the instrument panel mounted Malfunction Indica-
tor Lamp (displayed on the instrument panel as the
CHECK ENGINE lampÐfigure 42). Refer to On-
Board Diagnostics in Group 14, Fuel Systems for in-
formation on accessing a DTC.
The DTC can also be accessed through the DRB
scan tool. Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diag-
Fig. 41 PDCÐXJ Models
Fig. 42 Check Engine LampÐXJ ModelsÐTypical
JCOOLING SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURES 7 - 35
Page 272 of 2198

ELECTRICAL
GROUP INDEX
Group Group
AUDIO SYSTEMS........................ 8F
BATTERY/STARTER/GENERATOR SERVICE.... 8B
BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS
DIAGNOSTICS......................... 8A
CHIME/BUZZER WARNING SYSTEMS........ 8U
HORNS................................ 8G
IGNITION SYSTEMS...................... 8D
INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGES......... 8E
LAMPS................................ 8L
OVERHEAD CONSOLE.................... 8C
POWER LOCKS.......................... 8P
POWER MIRRORS....................... 8TPOWER SEATS.......................... 8R
POWER WINDOWS....................... 8S
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER............... 8N
RESTRAINT SYSTEMS................... 8M
TURN SIGNAL AND HAZARD WARNING
SYSTEMS............................. 8J
VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM......... 8H
WIPER AND WASHER SYSTEMS............ 8K
XJ WIRING DIAGRAMS-LEFT HAND DRIVE . . . 8W
XJ WIRING DIAGRAMS-RIGHT HAND DRIVE . 8W
YJ WIRING DIAGRAMS.................. 8W
BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS
CONTENTS
page page
BATTERY............................... 2
CHARGING SYSTEM..................... 17
IGNITION-OFF DRAW.................... 10SPECIFICATIONS........................ 23
STARTING SYSTEM...................... 11
USING ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM.... 22
GENERAL INFORMATION
The battery, starting, and charging systems operate
with one another; therefore, they must be tested as a
complete system. In order for the vehicle to start and
charge properly, all of the components involved in
these systems must perform within specifications.
Group 8A covers battery, starting (Fig. 1) and
charging (Fig. 2) system diagnostic procedures. These
procedures include the most basic conventional diag-
nostic methods, to On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) builtinto the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). Use of an
induction milliamp ammeter, volt/ohmmeter, battery
charger, carbon pile rheostat (load tester), and 12-
volt test lamp will be required.
All OBD-sensed systems are monitored by the
PCM. Each monitored circuit is assigned a Diagnos-
tic Trouble Code (DTC). The PCM will store a DTC in
electronic memory for any failure it detects. See Us-
ing On-Board Diagnostic System in this group for
more information.
JELECTRICAL 8A - 1
Page 273 of 2198
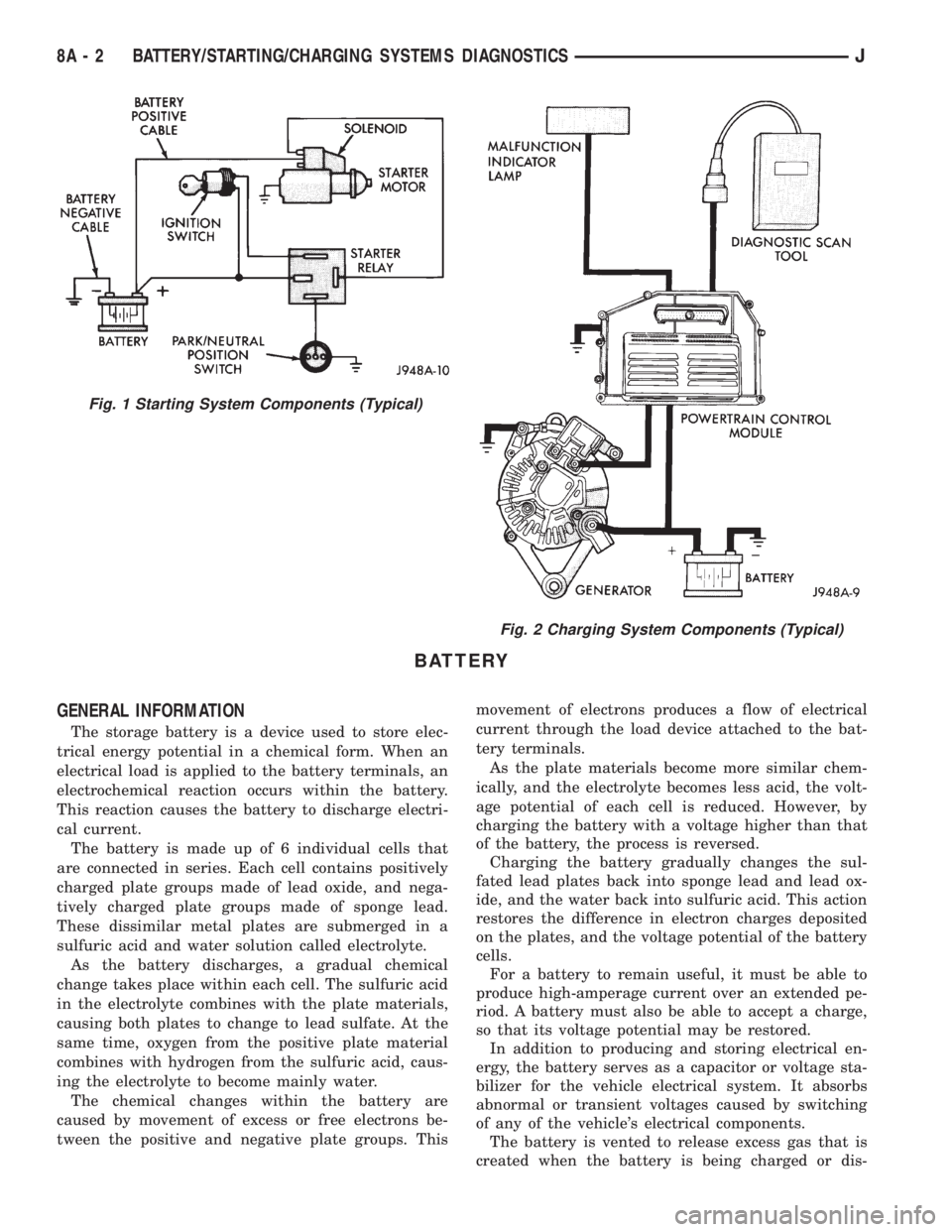
BATTERY
GENERAL INFORMATION
The storage battery is a device used to store elec-
trical energy potential in a chemical form. When an
electrical load is applied to the battery terminals, an
electrochemical reaction occurs within the battery.
This reaction causes the battery to discharge electri-
cal current.
The battery is made up of 6 individual cells that
are connected in series. Each cell contains positively
charged plate groups made of lead oxide, and nega-
tively charged plate groups made of sponge lead.
These dissimilar metal plates are submerged in a
sulfuric acid and water solution called electrolyte.
As the battery discharges, a gradual chemical
change takes place within each cell. The sulfuric acid
in the electrolyte combines with the plate materials,
causing both plates to change to lead sulfate. At the
same time, oxygen from the positive plate material
combines with hydrogen from the sulfuric acid, caus-
ing the electrolyte to become mainly water.
The chemical changes within the battery are
caused by movement of excess or free electrons be-
tween the positive and negative plate groups. Thismovement of electrons produces a flow of electrical
current through the load device attached to the bat-
tery terminals.
As the plate materials become more similar chem-
ically, and the electrolyte becomes less acid, the volt-
age potential of each cell is reduced. However, by
charging the battery with a voltage higher than that
of the battery, the process is reversed.
Charging the battery gradually changes the sul-
fated lead plates back into sponge lead and lead ox-
ide, and the water back into sulfuric acid. This action
restores the difference in electron charges deposited
on the plates, and the voltage potential of the battery
cells.
For a battery to remain useful, it must be able to
produce high-amperage current over an extended pe-
riod. A battery must also be able to accept a charge,
so that its voltage potential may be restored.
In addition to producing and storing electrical en-
ergy, the battery serves as a capacitor or voltage sta-
bilizer for the vehicle electrical system. It absorbs
abnormal or transient voltages caused by switching
of any of the vehicle's electrical components.
The battery is vented to release excess gas that is
created when the battery is being charged or dis-
Fig. 1 Starting System Components (Typical)
Fig. 2 Charging System Components (Typical)
8A - 2 BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICSJ
Page 274 of 2198

charged. However, even with these vents, hydrogen
gas can collect in or around the battery. If hydrogen
gas is exposed to flame or sparks, it can ignite.
If the electrolyte level is low, the battery could arc
internally and explode. If the battery is equipped
with removable cell caps, add distilled water when-
ever the electrolyte level is below the top of the
plates. If the battery cell caps cannot be removed, the
battery must be replaced when the electrolyte level is
low.
WARNING: DO NOT ATTEMPT TO ASSIST BOOST,
CHARGE, OR TEST BATTERY WHEN ELECTRO-
LYTE LEVEL IS BELOW THE TOP OF THE PLATES.
PERSONAL INJURY MAY OCCUR.
BATTERY RATINGS
Currently, there are 2 commonly accepted methods
for rating and comparing battery performance. These
ratings are called Cold Cranking Amperage (CCA),
and Reserve Capacity (RC). Be certain that a replace-
ment battery has CCA and RC ratings that equal or
exceed the original equipment specification for the
vehicle being serviced. See Battery Classifications
and Ratings charts in Specifications at the back of
this group.
COLD CRANKING AMPERAGE
The Cold Cranking Amperage (CCA) rating speci-
fies how much current (in amperes) the battery can
deliver for 30 seconds at -17.7ÉC (0ÉF). Terminal volt-
age must not fall below 7.2 volts during or after the
30 second discharge. The CCA required is generally
higher as engine displacement increases, depending
also upon the starter current draw requirements.
RESERVE CAPACITY
The Reserve Capacity (RC) rating specifies the
time (in minutes) it takes for battery terminal volt-
age to fall below 10.2 volts at a discharge rate of 25
amps. RC is determined with the battery fully-
charged at 26.7ÉC (80ÉF). This rating estimates how
long the battery might last after a charging system
failure, under minimum electrical load.
DIAGNOSIS
The battery must be completely charged and the
top, posts, and terminal clamps should be properly
cleaned before diagnostic procedures are performed.
Refer to Group 8B - Battery/Starter/Generator Ser-
vice for more information.
The condition of a battery is determined by two cri-
teria:
(1)State-Of-ChargeThis can be determined by
viewing the built-in test indicator, by checking spe-
cific gravity of the electrolyte (hydrometer test), or by
checking battery voltage (open circuit voltage test).(2)Cranking CapacityThis can be determined
by performing a battery load test, which measures
the ability of the battery to supply high-amperage
current.
If the battery has a built-in test indicator, use this
test first. If it has no test indicator, but has remov-
able cell caps, perform the hydrometer test first. If
cell caps are not removable, or a hydrometer is not
available, perform the open circuit voltage test first.
The battery must be charged before proceeding
with a load test if:
²the built-in test indicator has a black or dark color
visible
²the temperature corrected specific gravity is less
than 1.235
²the open circuit voltage is less than 12.4 volts.
A battery that will not accept a charge is faulty
and further testing is not required. A battery that is
fully-charged, but does not pass the load test is
faulty and must be replaced.
Completely discharged batteries may take
several hours to accept a charge. See Charging
Completely Discharged Battery.
A battery is fully-charged when:
²all cells are gassing freely during charging
²a green color is visible in the sight glass of the
built-in test indicator
²three corrected specific gravity tests, taken at
1-hour intervals, indicate no increase in specific grav-
ity
²open circuit voltage is 12.4 volts or greater.
ABNORMAL BATTERY DISCHARGING
Any of the following conditions can result in abnor-
mal battery discharging:
(1) Corroded battery posts and terminals.
(2) Loose or worn generator drive belt.
(3) Electrical loads that exceed the output of the
charging system, possibly due to equipment installed
after manufacture or repeated short trip use.
(4) Slow driving speeds (heavy traffic conditions) or
prolonged idling with high-amperage draw systems
in use.
(5) Faulty circuit or component causing excessive
ignition-off draw. See Ignition-Off Draw in this group
for diagnosis.
(6) Faulty charging system.
(7) Faulty or incorrect battery.
BUILT-IN TEST INDICATOR
A test indicator (hydrometer) built into the top of
the battery case, provides visual information for bat-
tery testing (Fig. 1). It is important when using the
test indicator that the battery be level and have a
clean sight glass to see correct indications. Additional
light may be required to view indicator.
JBATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS 8A - 3
Page 275 of 2198
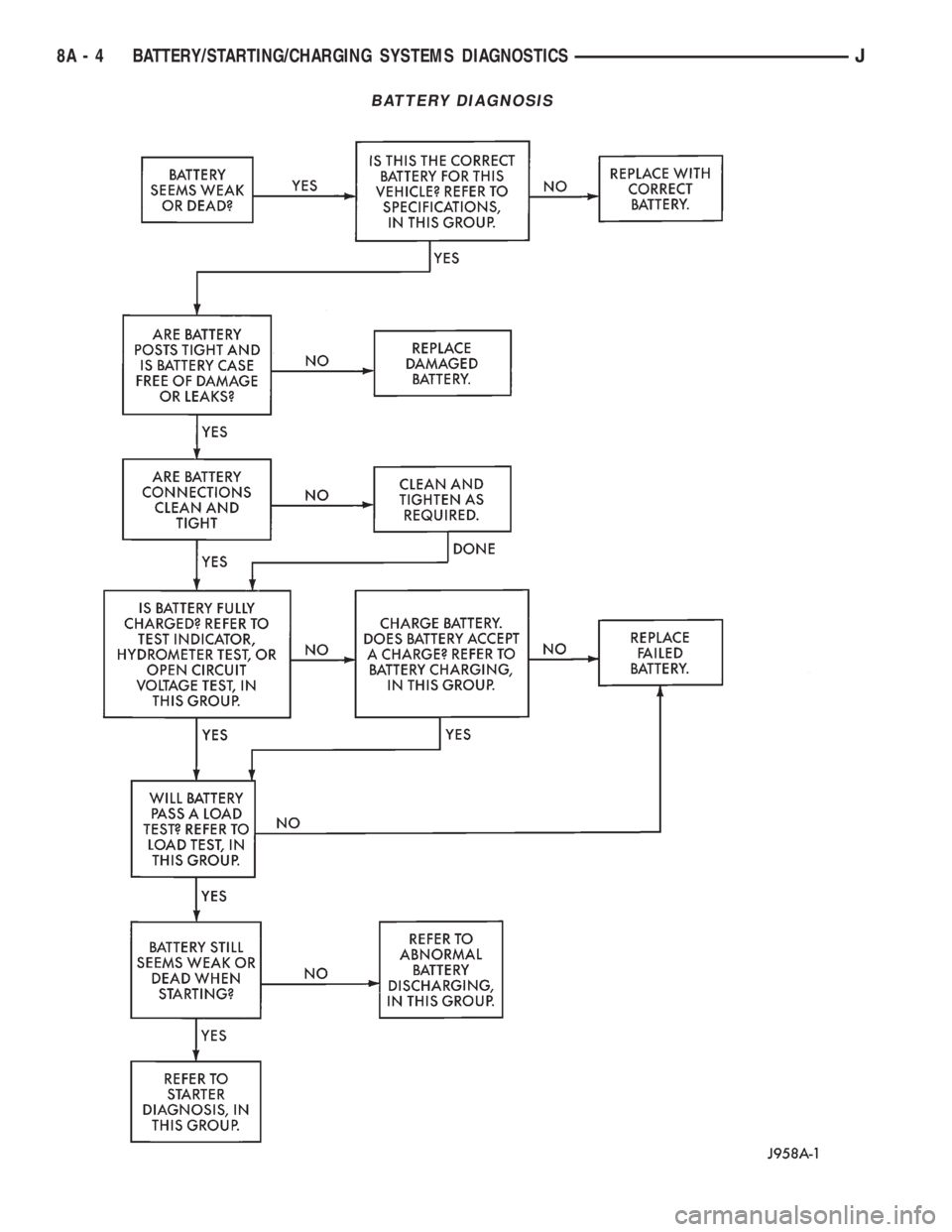
BATTERY DIAGNOSIS
8A - 4 BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICSJ