abs ring replace JEEP CHEROKEE 1995 Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1995, Model line: CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP CHEROKEE 1995Pages: 2198, PDF Size: 82.83 MB
Page 143 of 2198

pedal. The proper course of action is to bleed the sys-
tem, or replace thin drums and suspect quality brake
lines and hoses.
HARD PEDAL OR HIGH PEDAL EFFORT
A hard pedal or high pedal effort may be due to lin-
ing that is water soaked, contaminated, glazed, or
badly worn. The power booster or check valve could
also be faulty. Test the booster and valve as described
in this section.
BRAKE DRAG
Brake drag occurs when the lining is in constant
contact with the rotor or drum. Drag can occur at one
wheel, all wheels, fronts only, or rears only. It is a
product of incomplete brakeshoe release. Drag can be
minor or severe enough to overheat the linings, ro-
tors and drums. A drag condition also worsens as
temperature of the brake parts increases.
Brake drag also has a direct effect on fuel economy.
If undetected, minor brake drag can be misdiagnosed
as an engine or transmission/torque converter prob-
lem.
Minor drag will usually cause slight surface char-
ring of the lining. It can also generate hard spots in
rotors and drums from the overheat/cool down pro-
cess. In most cases, the rotors, drums, wheels and
tires are quite warm to the touch after the vehicle is
stopped.
Severe drag can char the brake lining all the way
through. It can also distort and score rotors and
drums to the point of replacement. The wheels, tires
and brake components will be extremely hot. In se-
vere cases, the lining may generate smoke as it chars
from overheating.
An additional cause of drag involves the use of in-
correct length caliper mounting bolts. Bolts that are
too long can cause a partial apply condition. The cor-
rect caliper bolts have a shank length of 67 mm
(2.637 in.), plus or minus 0.6 mm (0.0236 in.). Refer
to the Disc Brake service section for more detail on
caliper bolt dimensions and identification.
Some common causes of brake drag are:
²loose or damaged wheel bearing
²seized or sticking caliper or wheel cylinder piston
²caliper binding on bolts or slide surfaces
²wrong length caliper mounting bolts (too long)
²loose caliper mounting bracket
²distorted rotor, brake drum, or shoes
²brakeshoes binding on worn/damaged support
plates
²severely rusted/corroded components
²misassembled components.
If brake drag occurs at all wheels, the problem may
be related to a blocked master cylinder compensatorport or faulty power booster (binds-does not release).
The condition will worsen as brake temperature in-
creases.
The brakelight switch can also be a cause of drag.
An improperly mounted or adjusted brakelight
switch can prevent full brake pedal return. The re-
sult will be the same as if the master cylinder com-
pensator ports are blocked. The brakes would be
partially applied causing drag.
BRAKE FADE
Brake fade is a product of overheating caused by
brake drag. However, overheating and subsequent
fade can also be caused by riding the brake pedal,
making repeated high deceleration stops in a short
time span, or constant braking on steep roads. Refer
to the Brake Drag information in this section for
causes.
PEDAL PULSATION (NON-ABS BRAKES ONLY)
Pedal pulsation is caused by parts that are loose,
or beyond tolerance limits. This type of pulsation is
constant and will occur every time the brakes are ap-
plied.
Disc brake rotors with excessive lateral runout or
thickness variation, or out of round brake drums are
the primary causes of pulsation.
On vehicles with ABS brakes, remember that pedal
pulsation is normal during antilock mode brake
stops. If pulsation occurs during light to moderate
brake stops, a standard brake part is either loose, or
worn beyond tolerance.
BRAKE PULL
A front pull condition could be the result of:
²contaminated lining in one caliper
²seized caliper piston
²binding caliper
²wrong caliper mounting bolts (too long)
²loose caliper
²loose or corroded mounting bolts
²improper brakeshoes
²damaged rotor
²incorrect wheel bearing adjustment (at one wheel)
A worn, damaged wheel bearing or suspension com-
ponent are further causes of pull. A damaged front
tire (bruised, ply separation) can also cause pull.
Wrong caliper bolts (too long) will cause a partial ap-
ply condition and pull if only one caliper is involved.
A common and frequently misdiagnosed pull condi-
tion is where direction of pull changes after a few
stops. The cause is a combination of brake drag fol-
lowed by fade at the dragging brake unit.
As the dragging brake overheats, efficiency is so re-
duced that fade occurs. If the opposite brake unit is
still functioning normally, its braking effect is magni-
5 - 6 SERVICE BRAKE DIAGNOSISJ
Page 147 of 2198

BRAKE FLUIDÐBRAKE BLEEDINGÐBRAKELINES AND HOSES
INDEX
page page
Brake Bleeding (With ABS Brakes)............ 11
Brake Bleeding (With Standard Brakes)......... 11
Brake Bleeding Recommendations............ 10
Brake Fluid Contamination.................. 10Brake Fluid Level......................... 10
Brakeline Charts.......................... 12
Brakelines and Hoses...................... 12
Recommended Brake Fluid.................. 10
RECOMMENDED BRAKE FLUID
Recommended brake fluid for Jeep vehicles is Mo-
par brake fluid, or an equivalent fluid meeting SAE
J1703 and DOT 3 standards. The recommendation
applies to models with standard or ABS brakes.
Use new brake fluid to top off the master cyl-
inder or refill the system. Never use reclaimed
fluid, fluid not meeting the SAE/DOT standards
or fluid from an unsealed container. Do not use
fluid from any container that has been left
open for any length of time. Fluid in open con-
tainers can absorb moisture.
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL
Always clean the master cylinder reservoir and
cover or cap before adding fluid. This avoids having
dirt from the cap or reservoir exterior fall into the
fluid.
If the vehicle has a one piece master cylinder, cor-
rect fluid level is to within 6 mm (1/4 in.) of the res-
ervoir rim (Fig. 1).
If the vehicle has a plastic reservoir with a single
cap, preferred fluid level is to the FULL mark (Fig.
2).
CAUTION: Do not allow brake fluid to contact
painted surfaces. Fluid spills must be cleaned up
immediately as brake fluid can loosen and lift paint.
BRAKE FLUID CONTAMINATION
Oil in the fluid will cause brake system rubber
seals to soften and swell. The seals may also become
porous and begin to deteriorate.If fluid contamination is suspected, drain off a sam-
ple from the master cylinder. A suction gun or similar
device can be used for this purpose.
Empty the drained fluid into a glass container.
Contaminants in the fluid will cause the fluid to sep-
arate into distinct layers. If contamination has oc-
curred, the system rubber seals, hoses and cups must
be replaced and the system thoroughly flushed with
clean brake fluid.
BRAKE BLEEDING RECOMMENDATIONS
²Use Mopar DOT 3 brake fluid, or an equivalent
meeting SAE/DOT standards J1703-F and DOT 3, to
fill and bleed the system.
²Bleeding can be performed manually, or with vac-
uum or pressure equipment. Vacuum and pressure
bleeding equipment are both available. Both types
are effective but should be used only as described in
the manufacturers instructions.
²Do not allow the master cylinder to run out of
fluid when bleeding the brakes. An empty cylinder
will allow additional air to be drawn into the system.
Check fluid level frequently during bleed operations.
²Do not pump the brake pedal at any time while
bleeding. Air in system will be compressed into small
Fig. 1 Correct Fluid Level (4-Cylinder Models)
Fig. 2 Correct Fluid Level (All Except 4-Cylinder
Models)
5 - 10 BRAKE FLUIDÐBRAKE BLEEDINGÐBRAKELINES AND HOSESJ
Page 149 of 2198
connect scan tool and proceed to next step.
(7)Repeatconventional bleed procedure described
in steps (4) and (5).
(8) Top off master cylinder fluid level and verify
proper brake operation before moving vehicle.
BRAKELINES AND HOSES
Metal brakelines and rubber brake hoses should be
inspected periodically and replaced if damaged.
Rubber brake hoses should be replaced if cut,
cracked, swollen, or leaking. Rubber hoses must be
replaced as they are not repairable.
Steel brakelines should be inspected any time the
vehicle is in for normal maintenance. This is impor-
tant on high mileage vehicles. It is especially impor-
tant when the vehicle is operated on roads that are
salted during winter months.
Heavily rusted/corroded brake rotors, drums,
support plates, and brakelines should be
cleaned and carefully inspected. Heavy rust
buildup can hide severe damage to a compo-
nent. Severely rusted parts should be replaced
if condition is suspect.
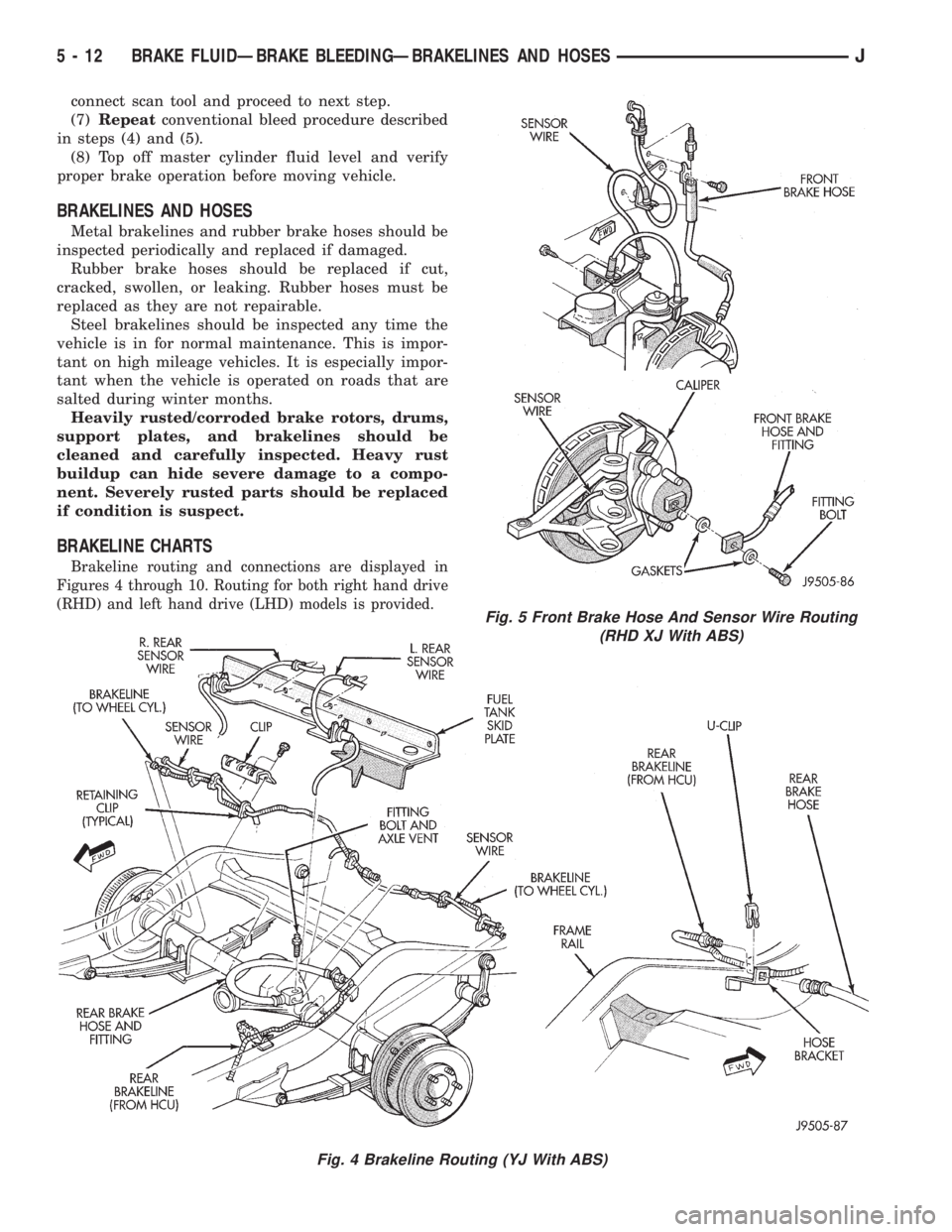
BRAKELINE CHARTS
Brakeline routing and connections are displayed in
Figures 4 through 10. Routing for both right hand drive
(RHD) and left hand drive (LHD) models is provided.
Fig. 4 Brakeline Routing (YJ With ABS)
Fig. 5 Front Brake Hose And Sensor Wire Routing
(RHD XJ With ABS)
5 - 12 BRAKE FLUIDÐBRAKE BLEEDINGÐBRAKELINES AND HOSESJ
Page 152 of 2198

MASTER CYLINDERÐCOMBINATION VALVE
INDEX
page page
Combination Valve Replacement (Non-ABS)..... 16
General Service Information................. 15
Master Cylinder and Combination Valve Installation
(With ABS)............................. 20
Master Cylinder and Combination Valve Removal
(With ABS)............................. 17Master Cylinder Bench Bleeding.............. 21
Master Cylinder Installation (Non-ABS)......... 16
Master Cylinder Overhaul (4-Cylinder Models).... 16
Master Cylinder Removal (Non-ABS)........... 15
Reservoir Replacement (2-Piece Master Cylinder) . 19
GENERAL SERVICE INFORMATION
Master Cylinder
Two different master cylinders are used. A one-piece
cast aluminum cylinder is used on 4-cylinder YJ models
(Fig. 1). All other models have a two-piece master cylin-
der with removable nylon reservoir (Fig. 2).
The two master cylinders are serviced differently.
The reservoir and grommets are the only replaceable
parts on the two-piece master cylinder. The one-piece
master cylinder can be overhauled when necessary.
Combination Valve
A combination valve is used in all models. The
valve contains a pressure differential valve and
switch and a rear brake proportioning valve. The
valve is not repairable. It must be replaced if diagno-
sis indicates this is necessary.
The pressure differential switch is connected to the
brake warning light. The switch is actuated by move-
ment of the switch valve. The switch monitors fluid
pressure in the separate front/rear brake hydraulic cir-
cuits.
A decrease or loss of fluid pressure in either hydraulic
circuit will cause the switch valve to shuttle to the low
pressure side. Movement of the valve pushes the switch
plunger upward. This action closes the switch internal
contacts completing the electrical circuit to the red
warning light. The switch valve will remain in an actu-
ated position until repairs are made.
The rear proportioning valve is used to balance front-
rear brake action. The valve allows normal fluid flow
during moderate effort brake stops. The valve only con-
trols (meters) fluid flow during high effort brake stops.
MASTER CYLINDER REMOVAL (NON-ABS)
(1) Remove air cleaner hose, cover and housing.
Fig. 1 Master Cylinder And Combination Valve
(4-Cyl. YJ Models)
Fig. 2 Master Cylinder And Combination Valve (All
Except 4-Cyl. YJ Models)
JMASTER CYLINDERÐCOMBINATION VALVE 5 - 15
Page 153 of 2198

(2) Disconnect brake lines at master cylinder and
combination valve.
(3) Remove nuts attaching master cylinder to
booster studs.
(4) Remove master cylinder.
(5) Remove cylinder cover and drain fluid.
(6) If two-piece master cylinder reservoir requires
service, refer to reservoir replacement procedure in
this section.
MASTER CYLINDER INSTALLATION (NON-ABS)
(1) Bleed master cylinder on bench before installa-
tion. Refer to procedure in this section.
(2) If new two-piece master cylinder is being in-
stalled, remove plastic protective sleeve from primary
piston shank. Also check condition of seal at rear of
cylinder body. Reposition seal if dislodged. Replace
seal if cut, or torn.
(3) Clean cylinder mounting surface of brake booster.
Use shop towel wetted with brake cleaner for this pur-
pose. Dirt, grease, or similar materials will prevent
proper cylinder seating and could result in vacuum leak.
(4) Slide master cylinder onto brake booster studs.
(5) Install nuts attaching master cylinder to booster
studs. Tighten nuts to 25 Nzm (220 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) Connect brakelines to master cylinder and com-
bination valve (Figs. 1 and 2).
(7) Fill and bleed brake system.
COMBINATION VALVE REPLACEMENT (NON-ABS)
The combination valve is not a repairable compo-
nent. The valve is serviced as an assembly whenever
diagnosis indicates replacement is necessary.
(1) Remove air cleaner cover and hose for access to
valve, if necessary.
(2) Disconnect differential pressure switch wire at
combination valve. Do not pull switch wire to discon-
nect. Unsnap connecter lock tabs to remove.
(3) Disconnect brakelines at combination valve and
remove valve.
(4) Connect brakelines to replacement valve. Start
line fittings by hand to avoid cross threading.
Tighten fittings snug but not to required torque at
this time.
(5) Connect wire to pressure differential switch.
(6) Bleed brakes.
(7) Tighten brakeline fittings to 18-24 Nzm
(160-210 in. lbs.) torque after bleeding.
MASTER CYLINDER OVERHAUL (4-CYLINDER
MODELS)
CYLINDER DISASSEMBLY
(1) Examine cylinder cover seal. Discard seal if
torn or distorted.
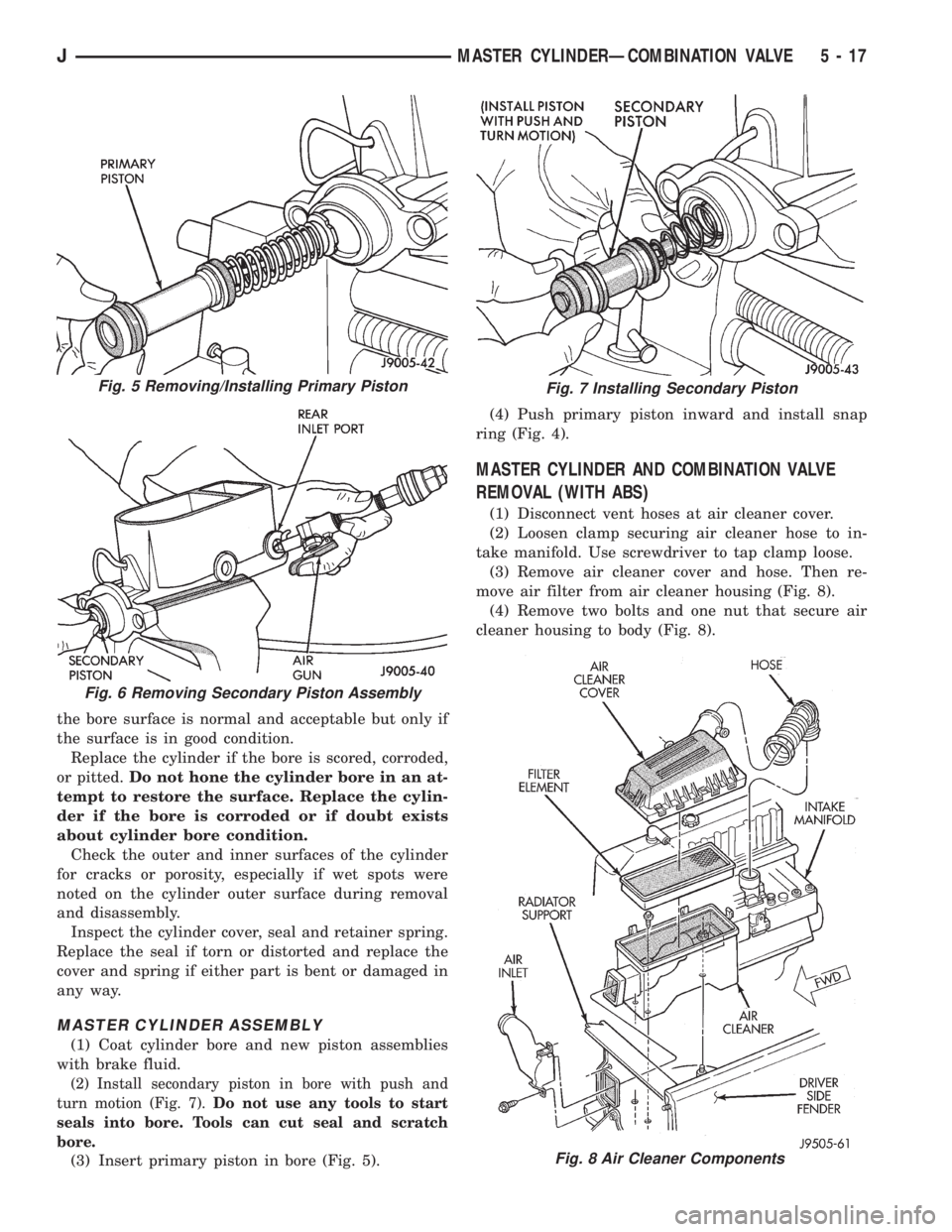
(2) Clamp cylinder in vise (Fig. 3).(3) Remove piston retaining snap ring. Press and
hold primary piston inward with wood dowel or sim-
ilar tool. Then remove snap ring (Fig. 4).
(4) Remove and discard primary piston (Fig. 5).
Piston is serviced only as assembly.
(5) Remove secondary piston (Fig. 6). Apply air
pressure through rear outlet port to ease piston out
of bore. Cover small ports at bottom of rear reservoir
with towel to prevent air leakage.
(6) Discard secondary piston. Do not disassemble
piston as components are only serviced as assembly.
MASTER CYLINDER CLEANING AND
INSPECTION
Clean the cylinder with Mopar brake cleaning sol-
vent or clean brake fluid. Remove cleaning residue
with compressed air.
Inspect the cylinder bore. A light discoloration of
Fig. 3 Mounting Cylinder In Vise
Fig. 4 Removing/Installing Piston Snap Ring
5 - 16 MASTER CYLINDERÐCOMBINATION VALVEJ
Page 154 of 2198
the bore surface is normal and acceptable but only if
the surface is in good condition.
Replace the cylinder if the bore is scored, corroded,
or pitted.Do not hone the cylinder bore in an at-
tempt to restore the surface. Replace the cylin-
der if the bore is corroded or if doubt exists
about cylinder bore condition.
Check the outer and inner surfaces of the cylinder
for cracks or porosity, especially if wet spots were
noted on the cylinder outer surface during removal
and disassembly.
Inspect the cylinder cover, seal and retainer spring.
Replace the seal if torn or distorted and replace the
cover and spring if either part is bent or damaged in
any way.
MASTER CYLINDER ASSEMBLY
(1) Coat cylinder bore and new piston assemblies
with brake fluid.
(2) Install secondary piston in bore with push and
turn motion (Fig. 7).Do not use any tools to start
seals into bore. Tools can cut seal and scratch
bore.
(3) Insert primary piston in bore (Fig. 5).(4) Push primary piston inward and install snap
ring (Fig. 4).
MASTER CYLINDER AND COMBINATION VALVE
REMOVAL (WITH ABS)
(1) Disconnect vent hoses at air cleaner cover.
(2) Loosen clamp securing air cleaner hose to in-
take manifold. Use screwdriver to tap clamp loose.
(3) Remove air cleaner cover and hose. Then re-
move air filter from air cleaner housing (Fig. 8).
(4) Remove two bolts and one nut that secure air
cleaner housing to body (Fig. 8).
Fig. 8 Air Cleaner Components
Fig. 5 Removing/Installing Primary Piston
Fig. 6 Removing Secondary Piston Assembly
Fig. 7 Installing Secondary Piston
JMASTER CYLINDERÐCOMBINATION VALVE 5 - 17
Page 174 of 2198

WHEEL SPEED SENSOR OPERATION
Wheel speed input signals are generated by a sen-
sor and tone ring at each wheel. The sensors, which
are connected directly to the ECU, are mounted on
brackets attached to the front steering knuckles and
rear brake support plates.
The sensor triggering devices are the tone rings
which are similar in appearance to gears. The tone
rings are located on the outboard end of each front/rear axle shaft. The speed sensors generate a signal
whenever a tone ring tooth rotates past the sensor
pickup face.
The wheel speed sensors provide the input signal
to the ECU. If input signals indicate ABS mode brak-
ing, the ECU causes the HCU solenoids to decrease,
hold, or increase fluid apply pressure as needed.
The HCU solenoid valves are activated only when
wheel speed input signals indicate that a wheel is
approaching a high slip, or lockup condition. At this
point, the ECU will cycle the appropriate wheel con-
trol channel solenoid valves to prevent lockup.
The wheel sensors provide speed signals whenever
the vehicle wheels are rotating. The ECU examines
these signals for degree of deceleration and wheel
slip. If signals indicate normal braking, the solenoid
valves are not activated. However, when incoming
signals indicate the approach of wheel slip, or lockup,
the ECU cycles the solenoid valves as needed.
ACCELERATION SWITCH OPERATION
The ECU monitors the acceleration switch at all
times. The switch assembly contains three mercury
switches that monitor vehicle ride height and decel-
eration rates (G-force). Sudden, rapid changes in ve-
hicle and wheel deceleration rate, triggers the switch
sending a signal to the ECU. The switch assembly
provides three deceleration rates; two for forward
braking and one for rearward braking.
ECU OPERATION
The antilock ECU controls all phases of antilock
operation. It monitors and processes input signals
from the system sensors.
It is the ECU that activates the solenoid valves to
modulate apply pressure during antilock braking.
The ECU program is able to determine which wheel
control channel requires modulation and which fluid
pressure modulation cycle to use. The ECU cycles the
solenoid valves through the pressure decrease, hold
and increase phases.
ABS COMPONENT SERVICEABILITY
The ECU, acceleration sensor, wheel sensors, and
wire harnesses are serviced as assemblies only. The
axle shaft tone wheels are also not serviceable. If a
tone wheel becomes damaged, it will be necessary to
replace the axle shaft, or disc brake rotor and hub
assembly.
SPEED SENSOR AIR GAP
Front sensor air gap is fixed and not adjustable.
Only rear sensor air gap is adjustable.
Although front air gap is not adjustable, it can be
checked if diagnosis indicates this is necessary. Front
Fig. 7 Pressure Hold Cycle
Fig. 8 Pressure Increase Cycle
JABS OPERATION AND SERVICE 5 - 37
Page 175 of 2198

air gap should be 0.40 to 1.3 mm (0.0157 to 0.051
in.). If gap is incorrect, the sensor is either loose, or
damaged.
A rear sensor air gap adjustment is only needed
when reinstalling an original sensor. Replacement
sensors have an air gap spacer attached to the sensor
pickup face. The spacer establishes correct air gap
when pressed against the tone ring during installa-
tion. As the tone ring rotates, it peels the spacer off
the sensor to create the required air gap. Rear sensor
air gap is 0.92-1.45 mm (0.036-0.057 in.).
Sensor air gap measurement, or adjustment proce-
dures are provided in this section. Refer to the front,
or rear sensor removal and installation procedures as
required.
FRONT WHEEL SENSOR REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle and turn wheel outward for easier
access to sensor.
(2) Remove sensor wire from mounting brackets.
(3) Clean sensor and surrounding area with shop
towel before removal.
(4) Remove bolt attaching sensor to steering
knuckle and remove sensor.
(5) remove sensor wire from brackets on body and
steering knuckle.
(6) Unseat sensor wire grommet in wheel house
panel.
(7) In engine compartment, disconnect sensor wire
connector at harness plug. Then remove sensor and
wire.
FRONT WHEEL SENSOR INSTALLATION
(1) Iforiginalsensor will be installed, wipe all
traces of old spacer material off sensor pickup face.
Use a dry shop towel for this purpose.
(2) Apply Mopar Lock N' Seal or Loctite 242 to bolt
that secures sensor in steering knuckle. Use new
sensor bolt if original bolt is worn or damaged.
(3) Position sensor on steering knuckle. Seat sen-
sor locating tab in hole in knuckle and install sensor
attaching bolt finger tight.
(4) Tighten sensor attaching bolt to 14 Nzm (11 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(5) If original sensor has been installed, check sen-
sor air gap. Air gap should be 0.40 to 1.3 mm (0.0157
to 0.051 in.). If gap is incorrect, sensor is either loose,
or damaged.
(6) Secure sensor wire to steering knuckle and
body brackets.
(7) Route sensor wire forward and behind shock
absorber. Then attach sensor wire to spring seat
bracket with grommets on sensor wire.
(8) Route sensor wire to outer sill bracket. Remove
all twists or kinks from wire.
(9) Attach sensor wire to sill bracket with grom-
met. Be sure wire is free of twists and kinks.(10) Verify sensor wire routing. Wire should loop
forward and above sill bracket. Loose end of wire
should be below sill bracket and towards brake hose.
(11) Seat sensor wire grommet in body panel and
clip wire to brake line at grommet location.
(12) Connect sensor wire to harness in engine com-
partment.
REAR WHEEL SENSOR REMOVAL
(1) On XJ models, raise and fold rear seat forward
for access to rear sensor connectors (Fig. 9).
(2) Disconnect sensors at rear harness connectors.
(3) Push sensor grommets and sensor wires
through floorpan.
(4) Raise vehicle.
(5) Disconnect sensor wires at rear axle connectors.
(6) Remove wheel and tire assembly.
(7) Remove brake drum.
(8) Remove clips securing sensor wires to brake-
lines, rear axle and, brake hose.
(9) Unseat sensor wire support plate grommet.
(10) Remove bolt attaching sensor to bracket and
remove sensor.
REAR WHEEL SENSOR INSTALLATION AND
ADJUSTMENT
(1) Iforiginal sensoris being installed, remove
any remaining pieces of cardboard spacer from sen-
sor pickup face. Use dry shop towel only to remove
old spacer material.
(2) Insert sensor wire through support plate hole.
Then seat sensor grommet in support plate.
(3) Apply Mopar Lock N' Seal or Loctite 242 to
Fig. 9 Acceleration Switch And Rear Sensor
Connections (XJ)
5 - 38 ABS OPERATION AND SERVICEJ
Page 177 of 2198
CAUTION: The mercury switch (inside the accelera-
tion switch), will not function properly if the switch
is mispositioned. Verify that the switch locating ar-
row is pointing to the front of the vehicle.
(2) Position switch in mounting bracket.
(3) Install and tighten switch attaching screws to
2-4 Nzm (17-32 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Connect harness to switch. Be sure harness
connecter is firmly seated.
(5) Move seat back to normal position.
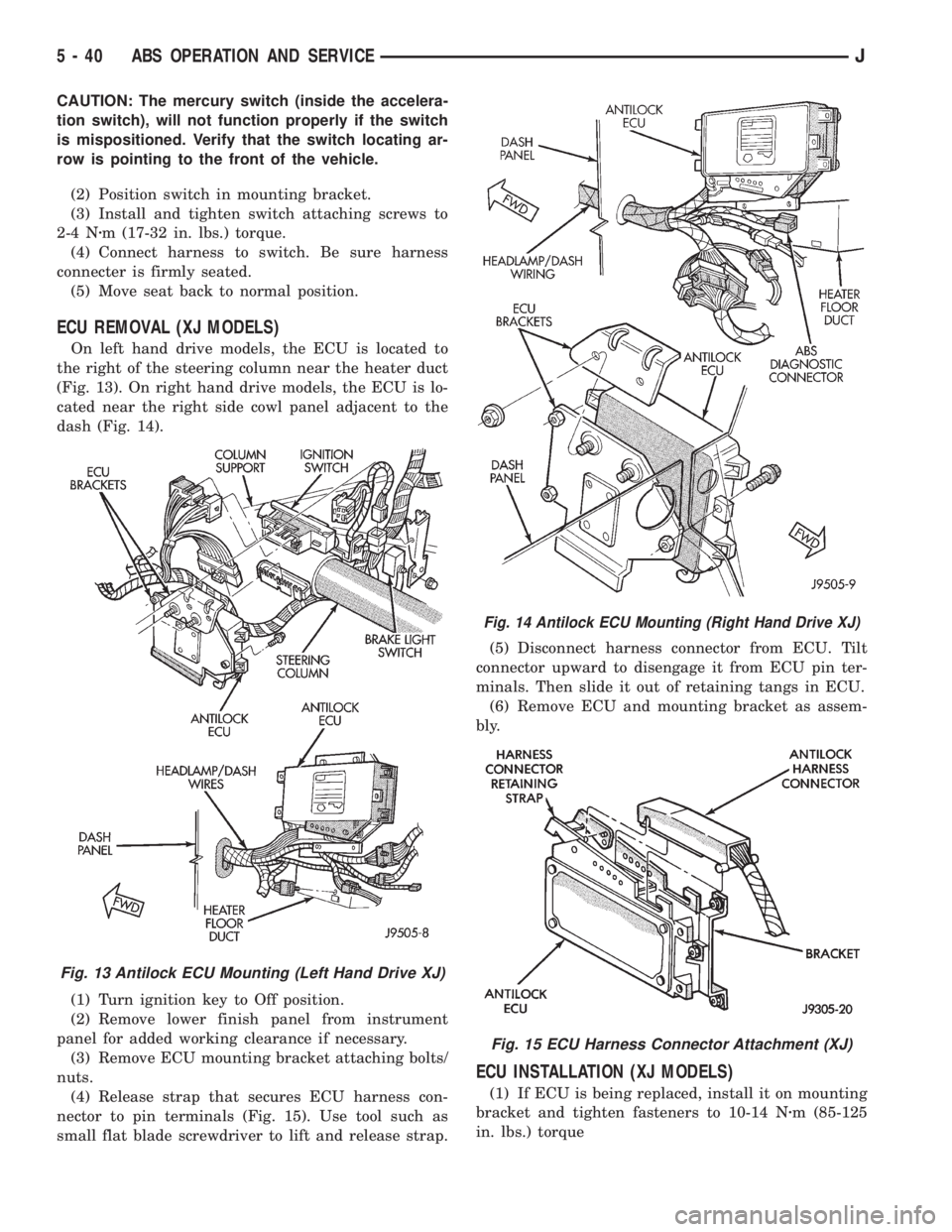
ECU REMOVAL (XJ MODELS)
On left hand drive models, the ECU is located to
the right of the steering column near the heater duct
(Fig. 13). On right hand drive models, the ECU is lo-
cated near the right side cowl panel adjacent to the
dash (Fig. 14).
(1) Turn ignition key to Off position.
(2) Remove lower finish panel from instrument
panel for added working clearance if necessary.
(3) Remove ECU mounting bracket attaching bolts/
nuts.
(4) Release strap that secures ECU harness con-
nector to pin terminals (Fig. 15). Use tool such as
small flat blade screwdriver to lift and release strap.(5) Disconnect harness connector from ECU. Tilt
connector upward to disengage it from ECU pin ter-
minals. Then slide it out of retaining tangs in ECU.
(6) Remove ECU and mounting bracket as assem-
bly.
ECU INSTALLATION (XJ MODELS)
(1) If ECU is being replaced, install it on mounting
bracket and tighten fasteners to 10-14 Nzm (85-125
in. lbs.) torque
Fig. 13 Antilock ECU Mounting (Left Hand Drive XJ)
Fig. 14 Antilock ECU Mounting (Right Hand Drive XJ)
Fig. 15 ECU Harness Connector Attachment (XJ)
5 - 40 ABS OPERATION AND SERVICEJ
Page 248 of 2198

WARNING: HOT, PRESSURIZED COOLANT CAN
CAUSE INJURY BY SCALDING.
Carefully remove the radiator pressure cap from
the filler neck and check the coolant level. Push
down on the cap to disengage it from the stop tabs.
Wipe the inner part of the filler neck and examine
the lower inside sealing seat for nicks, cracks, paint,
dirt and solder residue. Inspect the reserve/overflow
tank tube for internal obstructions. Insert a wire
through the tube to be sure it is not obstructed.
Inspect the cams on the outside part of the filler
neck. If the cams are bent, seating of pressure cap
valve and tester seal will be affected. Replace cap if
cams are bent.
Attach pressure tester 7700 (or an equivalent) to
the radiator filler neck (Fig. 21).Operate the tester pump to apply 124 kPa (18 psi)
pressure to the system. If the hoses enlarge exces-
sively or bulge while testing, replace as necessary.
Observe the gauge pointer and determine the condi-
tion of the cooling system according to the following
criteria:
²Holds Steady: If the pointer remains steady for
two minutes, there are no serious coolant leaks in
the system. However, there could be an internal leak
that does not appear with normal system test pres-
sure. Inspect for interior leakage or do the Internal
Leakage Test. Do this if it is certain that coolant is
being lost and no leaks can be detected.
²Drops Slowly: Shows a small leak or seepage is oc-
curring. Examine all connections for seepage or slight
leakage with a flashlight. Inspect the radiator, hoses,
gasket edges and heater. Seal any small leak holes
with a Sealer Lubricant or equivalent. Repair leak
holes and reinspect the system with pressure ap-
plied.
²Drops Quickly: Shows that a serious leakage is oc-
curring. Examine the system for serious external
leakage. If no leaks are visible, inspect for internal
leakage. Large radiator leak holes should be repaired
by a reputable radiator repair shop.
INTERNAL LEAKAGE INSPECTION
Remove the engine oil pan drain plug and drain a
small amount of engine oil. Coolant, being heavier
than engine oil, will drain first. Another way of test-
ing is to operate the engine and check for water glob-
ules on the engine oil dipstick. Also inspect the
automatic transmission oil dipstick for water glob-
ules. Inspect the automatic transmission fluid cooler
for leakage. Operate the engine without the pressure
cap on the radiator until thermostat opens.
Attach a pressure tester to the filler neck. If pres-
sure builds up quickly, a leak exists as a result of a
faulty cylinder head gasket or crack in the engine.
Repair as necessary.
WARNING: DO NOT ALLOW PRESSURE TO EX-
CEED 124 KPA (18 PSI). TURN THE ENGINE OFF.
TO RELEASE THE PRESSURE, ROCK THE TESTER
FROM SIDE TO SIDE. WHEN REMOVING THE
TESTER, DO NOT TURN THE TESTER MORE THAN
1/2 TURN IF THE SYSTEM IS UNDER PRESSURE.
If there is no immediate pressure increase, pump
the pressure tester until the indicated pressure is
within the system range. Vibration of the gauge
pointer indicates compression or combustion leakage
into the cooling system.
WARNING: DO NOT DISCONNECT THE SPARK
PLUG WIRES WHILE THE ENGINE IS OPERATING.
Fig. 20 Leak Detection Using Black LightÐTypical
Fig. 21 Pressurizing SystemÐTypical
JCOOLING SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURES 7 - 23