Back JEEP CHEROKEE 1995 Service Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1995, Model line: CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP CHEROKEE 1995Pages: 2198, PDF Size: 82.83 MB
Page 160 of 2198
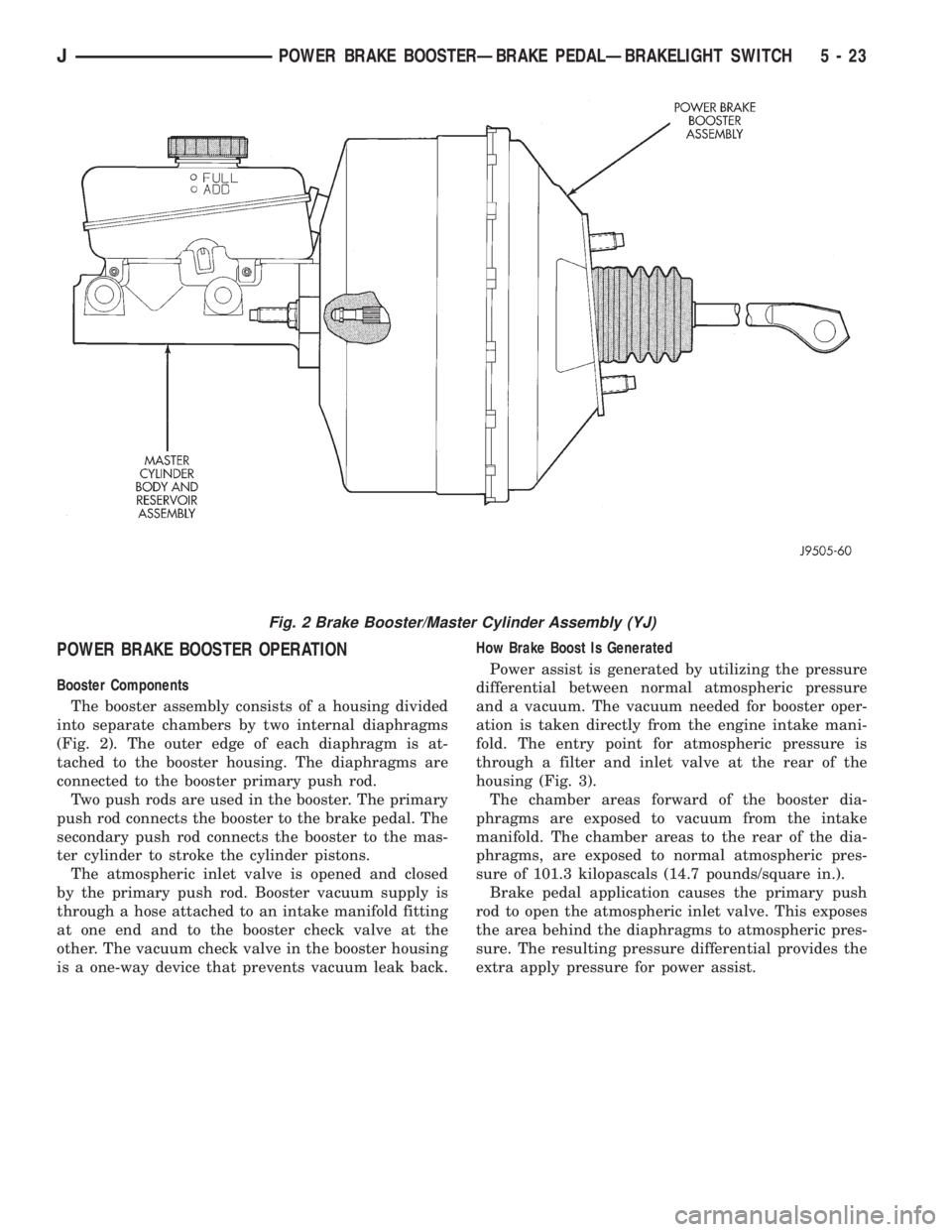
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER OPERATION
Booster Components
The booster assembly consists of a housing divided
into separate chambers by two internal diaphragms
(Fig. 2). The outer edge of each diaphragm is at-
tached to the booster housing. The diaphragms are
connected to the booster primary push rod.
Two push rods are used in the booster. The primary
push rod connects the booster to the brake pedal. The
secondary push rod connects the booster to the mas-
ter cylinder to stroke the cylinder pistons.
The atmospheric inlet valve is opened and closed
by the primary push rod. Booster vacuum supply is
through a hose attached to an intake manifold fitting
at one end and to the booster check valve at the
other. The vacuum check valve in the booster housing
is a one-way device that prevents vacuum leak back.How Brake Boost Is Generated
Power assist is generated by utilizing the pressure
differential between normal atmospheric pressure
and a vacuum. The vacuum needed for booster oper-
ation is taken directly from the engine intake mani-
fold. The entry point for atmospheric pressure is
through a filter and inlet valve at the rear of the
housing (Fig. 3).
The chamber areas forward of the booster dia-
phragms are exposed to vacuum from the intake
manifold. The chamber areas to the rear of the dia-
phragms, are exposed to normal atmospheric pres-
sure of 101.3 kilopascals (14.7 pounds/square in.).
Brake pedal application causes the primary push
rod to open the atmospheric inlet valve. This exposes
the area behind the diaphragms to atmospheric pres-
sure. The resulting pressure differential provides the
extra apply pressure for power assist.
Fig. 2 Brake Booster/Master Cylinder Assembly (YJ)
JPOWER BRAKE BOOSTERÐBRAKE PEDALÐBRAKELIGHT SWITCH 5 - 23
Page 177 of 2198
CAUTION: The mercury switch (inside the accelera-
tion switch), will not function properly if the switch
is mispositioned. Verify that the switch locating ar-
row is pointing to the front of the vehicle.
(2) Position switch in mounting bracket.
(3) Install and tighten switch attaching screws to
2-4 Nzm (17-32 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Connect harness to switch. Be sure harness
connecter is firmly seated.
(5) Move seat back to normal position.
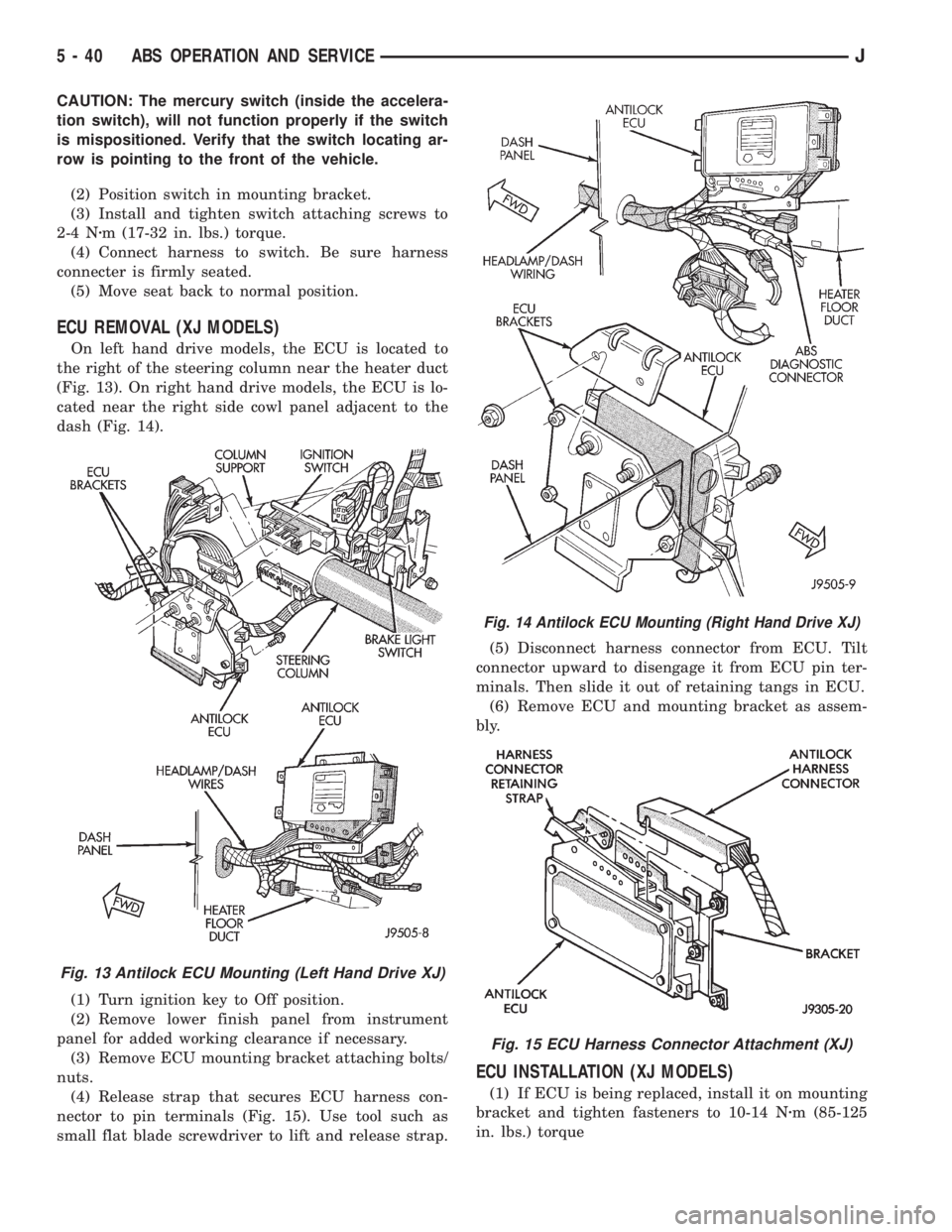
ECU REMOVAL (XJ MODELS)
On left hand drive models, the ECU is located to
the right of the steering column near the heater duct
(Fig. 13). On right hand drive models, the ECU is lo-
cated near the right side cowl panel adjacent to the
dash (Fig. 14).
(1) Turn ignition key to Off position.
(2) Remove lower finish panel from instrument
panel for added working clearance if necessary.
(3) Remove ECU mounting bracket attaching bolts/
nuts.
(4) Release strap that secures ECU harness con-
nector to pin terminals (Fig. 15). Use tool such as
small flat blade screwdriver to lift and release strap.(5) Disconnect harness connector from ECU. Tilt
connector upward to disengage it from ECU pin ter-
minals. Then slide it out of retaining tangs in ECU.
(6) Remove ECU and mounting bracket as assem-
bly.
ECU INSTALLATION (XJ MODELS)
(1) If ECU is being replaced, install it on mounting
bracket and tighten fasteners to 10-14 Nzm (85-125
in. lbs.) torque
Fig. 13 Antilock ECU Mounting (Left Hand Drive XJ)
Fig. 14 Antilock ECU Mounting (Right Hand Drive XJ)
Fig. 15 ECU Harness Connector Attachment (XJ)
5 - 40 ABS OPERATION AND SERVICEJ
Page 192 of 2198

DRUM BRAKES
INDEX
page page
Brake Drum Refinishing.................... 58
Drum Brake Adjustment.................... 57
Drum Brakeshoe Installation................. 55
Drum Brakeshoe Removal................... 55
Support Plate Replacement.................. 58Wheel Cylinder Installation.................. 58
Wheel Cylinder Overhaul.................... 57
Wheel Cylinder Removal.................... 57
Wheel Nut Tightening...................... 59
DRUM BRAKESHOE REMOVAL (Figs. 1 and 2)
(1) Raise vehicle and remove rear wheels.
(2) Remove and discard spring nuts securing
drums to wheel studs.
(3) Remove brake drums. If drums prove difficult
to remove, retract brakeshoes. Remove access plug at
the rear of backing plate and back off adjuster screw
with brake tool and screwdriver.
(4) Remove U-clip and washer securing adjuster
cable to parking brake lever.
(5) Remove primary and secondary return springs
from anchor pin with Brake Spring Plier Tool 8078.
(6) Remove holddown springs, retainers and pins
with standard retaining spring tool.
(7) Install spring clamps on wheel cylinders to hold
pistons in place.
(8) Remove adjuster lever, adjuster screw and
spring.
(9) Remove adjuster cable and cable guide.
(10) Remove brakeshoes and parking brake strut.(11) Disconnect cable from parking brake lever and
remove lever.
DRUM BRAKESHOE INSTALLATION
(1) Clean support plate with Mopar brake cleaner.
Replace support plate if worn, or rusted through at
any point. Do not attempt to salvage, or reuse a dam-
aged support plate.
(2) If new drums are being installed, remove pro-
tective coating with Mopar Carb cleaner followed by
final rinse with Mopar brake cleaner. A scotch brite
pad, or steel wool can also be used to help loosen and
remove coating if desired.It is not necessary to
machine drums to remove the coating.
(3) Clean and lubricate anchor pin with light coat
of Mopar multi-mileage grease.
(4) Apply Mopar multi-mileage grease to brakeshoe
contact surfaces of support plate (Figs. 3 and 4).
(5) Lubricate adjuster screw threads and pivot
with Mopar spray lube.
Fig. 1 Nine Inch Drum Brake Components
JDRUM BRAKES 5 - 55
Page 204 of 2198

PARKING BRAKE REAR CABLE REPLACEMENT (XJ)
(1) Raise vehicle and loosen equalizer nuts until
rear cables are slack.
(2) Disengage cable from equalizer and remove ca-
ble clip and spring (Fig. 15).
(3) Remove rear wheel and brake drum.
(4) Remove secondary brakeshoe and disconnect
cable from lever on brakeshoe.
(5) Compress cable retainer with worm drive hose
clamp (Fig. 16) and remove cable from backing plate.
(6) Install new cable in backing plate. Be sure ca-
ble retainer is seated.
(7) Attach cable to lever on brakeshoe and install
brakeshoe on backing plate.
(8) Adjust brakeshoes to drum with brake gauge.(9) Install brake drum and wheel.
(10) Engage cable in equalizer and install equal-
izer nuts (Fig. 15).
(11) Adjust parking brakes. Refer to procedure in
this section.
PARKING BRAKE FRONT CABLE REPLACEMENT
(YJ)
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Remove equalizer nuts (Fig. 17).
(3) Remove front cable from equalizer (Fig. 17).
(4) Remove cable-to-frame bracket clip.
(5) Lower vehicle.
(6) Move front carpeting away from pedal.
(7) Compress clip securing cable to pedal frame
(Fig. 17). Use hose clamp to compress clip.
(8) Disconnect cable from pedal retainer and re-
move cable.
(9) Remove grommet (Fig. 17) from old cable and
transfer it to new cable, if necessary.
(10) Install new cable in floorpan and connect it to
pedal assembly.
(11) Seat cable grommet in floorpan.
(12) Raise the vehicle.
(13) Install cable-to-frame retaining clip.
(14) Insert cable in equalizer and install equalizer
washer and nuts.
(15) Adjust parking brakes as described in Service
Adjustment section.
Fig. 14 Parking Brake Pedal Assembly (YJ)
Fig. 15 Parking Brake Cables (XJ)
Fig. 16 Compressing Rear Cable Retainer
JPARKING BRAKES 5 - 67
Page 205 of 2198
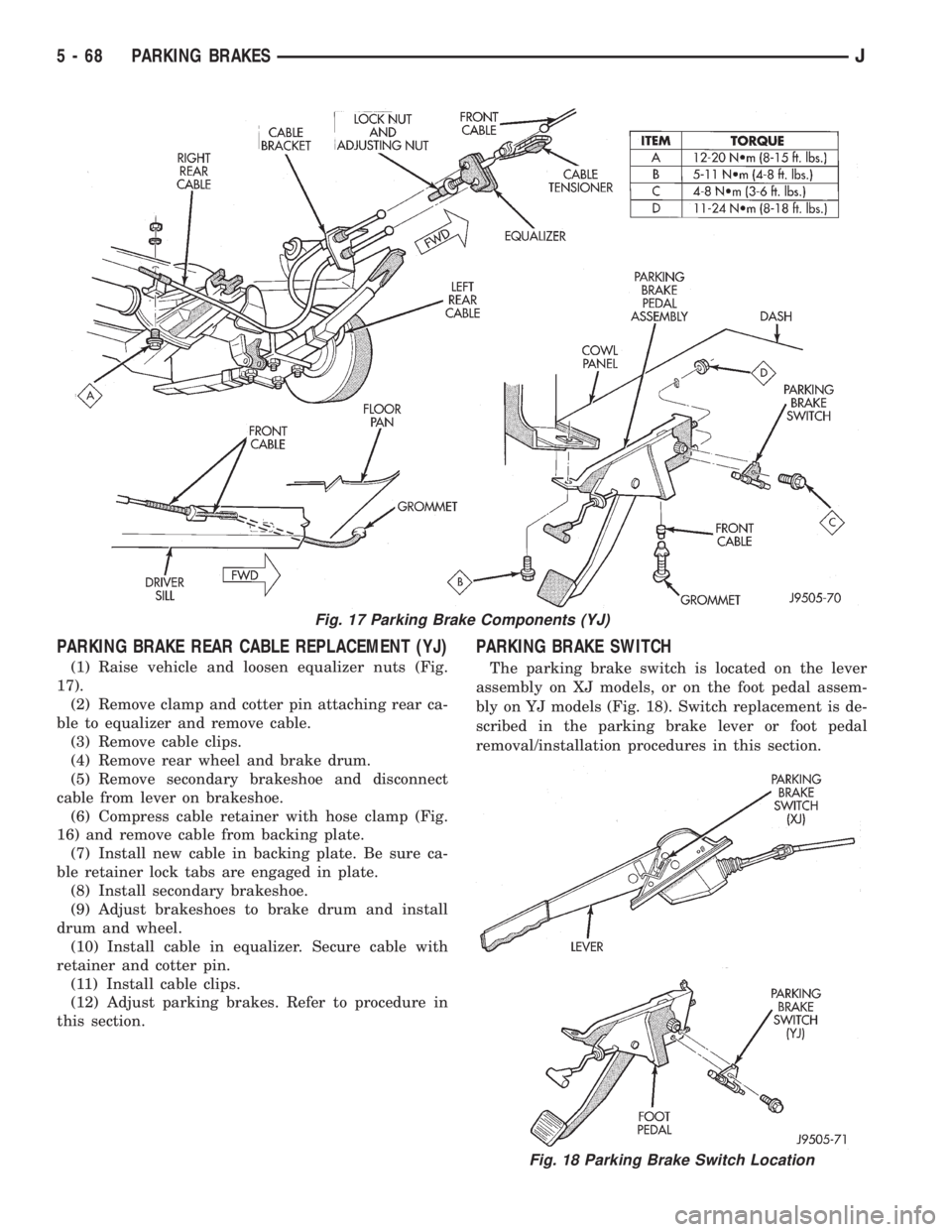
PARKING BRAKE REAR CABLE REPLACEMENT (YJ)
(1) Raise vehicle and loosen equalizer nuts (Fig.
17).
(2) Remove clamp and cotter pin attaching rear ca-
ble to equalizer and remove cable.
(3) Remove cable clips.
(4) Remove rear wheel and brake drum.
(5) Remove secondary brakeshoe and disconnect
cable from lever on brakeshoe.
(6) Compress cable retainer with hose clamp (Fig.
16) and remove cable from backing plate.
(7) Install new cable in backing plate. Be sure ca-
ble retainer lock tabs are engaged in plate.
(8) Install secondary brakeshoe.
(9) Adjust brakeshoes to brake drum and install
drum and wheel.
(10) Install cable in equalizer. Secure cable with
retainer and cotter pin.
(11) Install cable clips.
(12) Adjust parking brakes. Refer to procedure in
this section.
PARKING BRAKE SWITCH
The parking brake switch is located on the lever
assembly on XJ models, or on the foot pedal assem-
bly on YJ models (Fig. 18). Switch replacement is de-
scribed in the parking brake lever or foot pedal
removal/installation procedures in this section.
Fig. 17 Parking Brake Components (YJ)
Fig. 18 Parking Brake Switch Location
5 - 68 PARKING BRAKESJ
Page 206 of 2198

PARKING BRAKE CABLE TENSIONER ADJUSTMENT
(XJ/YJ)
Parking brake adjustment is only necessary
when the tensioner, or a cable has been re-
placed or disconnected for service. When ad-
justment is necessary, perform adjustment only
as described in the following procedure. This is
necessary to avoid faulty parking brake opera-
tion.
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Back off tensioner adjusting nut to create slack
in cables.
(3) Remove rear wheel/tire assemblies and remove
brake drums.
(4) Check rear brakeshoe adjustment with stan-
dard brake gauge. Also check condition of brake parts
as follows:
(a) Replace worn parts if necessary.Excessive
shoe-to-drum clearance, or worn brake com-
ponents will result in faulty parking brake
adjustment and operation.
(b) Verify that parking brake cables operate
freely and are not binding, or seized. Replace faulty
cables, before proceeding.
(c) Adjust rear brakeshoes shoes to drum.
(5) Reinstall brake drums and wheel/tire assem-
blies after brakeshoe adjustment is complete.
(6) Lower vehicle enough for access to parking
brake lever or foot pedal.Then fully apply parking
brakes. Leave brakes applied until adjustment
is complete.(7) Raise vehicle again.
(8) Mark tensioner rod 6.5 mm (1/4 in.) from ten-
sioner bracket (Fig. 19).
(9) Tighten adjusting nut at equalizer until mark
on tensioner rod moves into alignment with tensioner
bracket (Fig. 19).Do not loosen/tighten equalizer
adjusting nut for any reason after completing
adjustment.
(10) Lower vehicle until rear wheels are 15-20 cm
(6-8 in.) off shop floor.
(11) Release parking brake lever and verify that
rear wheels rotate freely without drag.
(12) Lower vehicle.
Fig. 19 Placing Adjustment Mark On Tensioner Rod
JPARKING BRAKES 5 - 69
Page 211 of 2198

when handling the cover and disc. Impact can distort
the cover, diaphragm spring, release fingers and the
hub of the clutch disc.
Use an alignment tool when positioning the disc on
the flywheel. The tool prevents accidental misalign-
ment which could result in cover distortion and disc
damage.
A frequent cause of clutch cover distortion (and
consequent misalignment) is improper bolt tighten-
ing. To avoid warping the cover, the bolts must tight-
ened alternately (diagonal pattern) and evenly (2-3
threads at a time) to specified torque.
CLUTCH HOUSING MISALIGNMENT
Clutch housing alignment is important to proper
clutch operation. The housing maintains alignment
between the crankshaft and transmission input
shaft. Misalignment can cause clutch noise, hard
shifting, incomplete release and chatter. It can also
result in premature wear of the pilot bearing, cover
release fingers and clutch disc. In severe cases, mis-
alignment can also cause premature wear of the
transmission input shaft and front bearing.
Housing misalignment is generally caused by incor-
rect seating on the engine or transmission, loose
housing bolts, missing alignment dowels, or housing
damage. Infrequently, misalignment may also be
caused by housing mounting surfaces that are not
completely parallel. Misalignment can be corrected
with shims.
INSTALLATION METHODS AND PARTS USAGE
Distortion of clutch components during installation
and the use of non-standard components are addi-
tional causes of clutch malfunction.Improper clutch cover bolt tightening can distort
the cover. The usual result is clutch grab, chatter
and rapid wear. Tighten the cover bolts as described
in Clutch Service section.
An improperly seated flywheel and/or clutch hous-
ing are additional causes of clutch failure. Improper
seating will produce misalignment and additional
clutch problems.
The use of non-standard or low quality parts will
also lead to problems and wear. Use recommended
factory quality parts to avoid comebacks.
A cocked pilot bearing is another cause of clutch
noise, drag, and hard shifting, and rapid bearing
wear. Always use an alignment tool to install a new
bearing. This practice helps avoid cocking the bear-
ing during installation.
INSPECTION AND DIAGNOSIS CHARTS
The clutch inspection chart (Fig. 1) outlines items
to be checked before and during clutch installation.
Use the chart as a check list to help avoid overlook-
ing potential problem sources during service opera-
tions.
The diagnosis charts describe common clutch prob-
lems, causes and correction. Fault conditions are
listed at the top of each chart. Conditions, causes and
corrective action are outlined in the indicated col-
umns.
The charts are provided as a convenient reference
when diagnosing faulty clutch operation.
6 - 4 CLUTCH DIAGNOSISJ
Page 238 of 2198

SERVICE PROCEDURES
INDEX
page page
Auxiliary Electric Cooling FanÐXJ Models with 4.0L
6-Cylinder Engine....................... 35
Coolant................................. 20
Coolant Reserve/Overflow System............. 24
Cooling System Cleaning/Reverse Flushing...... 22
Cooling System Fans...................... 32
Cooling System Hoses..................... 32
Draining Cooling System.................... 21
Radiator Pressure Cap..................... 25
Radiators............................... 26Refilling Cooling System.................... 21
Testing Cooling System for Leaks............. 22
Thermostat.............................. 17
Transmission Oil Coolers.................... 36
Viscous Fan Drive......................... 34
Water Pump Tests......................... 13
Water PumpsÐGeneral Information............ 13
Water PumpsÐRemoval/Installation........... 14
WATER PUMPSÐGENERAL INFORMATION
A centrifugal water pump circulates coolant
through the water jackets, passages, intake manifold,
radiator core, cooling system hoses and heater core.
The pump is driven from the engine crankshaft by a
drive belt on all engines.
The water pump impeller is pressed onto the rear
of a shaft that rotates in bearings pressed into the
housing. The housing has a small hole to allow seep-
age to escape. The water pump seals are lubricated
by the antifreeze in the coolant mixture. No addi-
tional lubrication is necessary.
CAUTION: All engines are equipped with a reverse
(counter-clockwise) rotating water pump and vis-
cous fan drive assembly. REVERSE is stamped or
imprinted on the cover of the viscous fan drive and
inner side of the fan. The letter R is stamped into
the back of the water pump impeller (Fig. 1).
Engines from previous model years, depending
upon application, may have been equipped with a for-
ward (clockwise) rotating water pump. Installation of
the wrong water pump will cause engine overheating.
A quick test to determine if the pump is working is
to check if the heater warms properly. A defective wa-
ter pump will not be able to circulate heated coolant
through the long heater hose to the heater core.
WATER PUMP TESTS
LOOSE IMPELLER
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If solution is
clean, drain coolant into a clean container for reuse.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER
PRESSURE. SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE COOL-
ANT CAN OCCUR.(1) Drain the cooling system.
(2) Loosen the fan belt(s).
(3) Disconnect the lower radiator hose from the
water pump.
(4) Bend a stiff clothes hanger or welding rod as
shown in (Fig. 2).
(5) Position the rod in the water pump inlet and
attempt to hold the impeller while turning the fan
blades. If equipped with a viscous fan drive, turn the
water pump shaft with a breaker bar and socket at-
tached to a mounting flange nut. If the impeller is
loose and can be held with the rod while the fan
blades are turning, the pump is defective. If the im-
peller turns, the pump is OK.
Connect the hose and install the coolant, or proceed
with repairs.
Fig. 1 Reverse Rotating Water PumpÐTypical
JCOOLING SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURES 7 - 13
Page 239 of 2198

INSPECTING FOR INLET RESTRICTIONS
Inadequate heater performance may be caused by a
metal casting restriction in the water pump heater
hose inlet.
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If solution is
clean, drain coolant into a clean container for reuse.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER
PRESSURE. SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE COOL-
ANT CAN OCCUR.
(1) Drain sufficient coolant from the radiator to de-
crease the level below the water pump heater hose
inlet.
(2) Remove the heater hose.
(3) Inspect the inlet for metal casting flash or
other restrictions.
Remove the pump from engine before remov-
ing restriction to prevent contamination of the
coolant with debris. Refer to Water Pump Re-
moval.
WATER PUMPSÐREMOVAL/INSTALLATION
REMOVALÐALL MODELS
CAUTION: If the water pump is replaced because of
mechanical damage, the fan blades and viscous fan
drive should also be inspected. These components
could have been damaged due to excessive vibra-
tion.The water pump on all models can be removed
without discharging the air conditioning system (if
equipped).
CAUTION: All engines have a reverse (counter-
clockwise) rotating water pump. The letter R is
stamped into the back of the water pump impeller
(Fig. 1) to identify. Engines from previous model
years, depending upon application, may be
equipped with a forward (clockwise) rotating water
pump. Installation of the wrong water pump will
cause engine over heating.
The water pump impeller is pressed on the rear of
the pump shaft and bearing assembly. The water
pump is serviced only as a complete assembly.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE BLOCK DRAIN
PLUG(S) OR LOOSEN RADIATOR DRAINCOCK
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE.
SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN OCCUR.
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If the solution
is clean, drain coolant into a clean container for re-
use.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Drain the cooling system. Refer to Draining
Cooling System in this group.
(3)XJ models with 4.0L 6-cylinder engine
equipped with A/C or heavy duty cooling sys-
tem:
Loosen (but do not remove at this time) the four
water pump pulley-to-water pump hub mounting
bolts (Fig. 3).
XJ models with 4.0L 6-cylinder engine with-
out A/C or heavy duty cooling system; or any
2.5L 4-cylinder engines; or any YJ models:
Loosen (but do not remove at this time) the four
fan hub-to-water pump pulley mounting nuts (Fig. 4).
Fig. 2 Impeller TestÐTypical
Fig. 3 Water Pump Pulley Bolts
7 - 14 COOLING SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURESJ
Page 251 of 2198

(4) When checking for vacuum leaks.
WARNING: IF VEHICLE HAS BEEN RUN RECENTLY,
WAIT AT LEAST 15 MINUTES BEFORE REMOVING
RADIATOR CAP. WITH A RAG, SQUEEZE RADIATOR
UPPER HOSE TO CHECK IF SYSTEM IS UNDER
PRESSURE. PLACE A RAG OVER THE CAP AND
WITHOUT PUSHING DOWN, ROTATE CAP
COUNTER-CLOCKWISE TO THE FIRST STOP. AL-
LOW FLUID TO ESCAPE THROUGH OVERFLOW
HOSE INTO COOLANT RESERVE/OVERFLOW
TANK. SQUEEZE RADIATOR UPPER HOSE TO DE-
TERMINE WHEN PRESSURE HAS BEEN RE-
LEASED. WHEN COOLANT AND STEAM STOP
BEING PUSHED INTO TANK AND SYSTEM PRES-
SURE DROPS, REMOVE RADIATOR CAP COM-
PLETELY.
PRESSURE TESTING RADIATOR CAPS
Remove cap from radiator. Be sure that sealing
surfaces are clean. Moisten rubber gasket with water
and install the cap on pressure tester (tool 7700 or
an equivalent) (Fig. 26).
Operate the tester pump and observe the gauge
pointer at its highest point. The cap release pressure
should be 83-to-110 kPa (12-to-16 psi). The cap is sat-
isfactory when the pressure holds steady. It is also
good if it holds pressure within the 83-to-110 kPa
(12-to-16 psi) range for 30 seconds or more. If the
pointer drops quickly, replace the cap.
CAUTION: Radiator pressure testing tools are very
sensitive to small air leaks, which will not causecooling system problems. A pressure cap that does
not have a history of coolant loss should not be re-
placed just because it leaks slowly when tested
with this tool. Add water to tool. Turn tool upside
down and recheck pressure cap to confirm that cap
needs replacement.
INSPECTION
Visually inspect the pressure valve gasket on the
cap. Replace cap if the gasket is swollen, torn or
worn. Inspect the area around radiator filler neck for
white deposits that indicate a leaking cap.
RADIATORS
GENERAL INFORMATION
All radiators are down flow types except XJ models
equipped with 4.0L 6-cylinder engines. Radiators in
XJ models equipped with the 4.0L 6-cylinder engine
are the cross flow type. Plastic tanks are used on all
radiators.
CAUTION: Plastic tanks, while stronger than brass,
are subject to damage by impact, such as
wrenches.
If the plastic tank has been damaged, the plastic
tank and/or o-rings are available for service repair.
Tank replacement should be done by qualified per-
sonal with proper equipment.
RADIATOR COOLANT FLOW CHECK
The following procedure will determine if coolant is
flowing through the cooling system.
If engine is cold, idle engine until normal operating
temperature is reached. Then feel the upper radiator
hose. If hose is hot, the thermostat is open and water
is circulating through cooling system.
RADIATOR CLEANING
The radiator and air conditioning fins should be
cleaned when an accumulation of bugs, leaves etc.
has occurred. Clean radiator fins are necessary for
good heat transfer. With the engine cold, apply cold
water and compressed air to the back (engine side) of
the radiator to flush the radiator and/or A/C con-
denser of debris.
RADIATOR REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS, RADIATOR CAP, OR
LOOSEN THE RADIATOR DRAINCOCK WITH THE
SYSTEM HOT AND PRESSURIZED. SERIOUS
BURNS FROM THE COOLANT CAN OCCUR.
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If solution is
clean, drain coolant into a clean container for reuse.
Fig. 26 Pressure Testing Radiator Pressure
CapÐTypical
7 - 26 COOLING SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURESJ