temperature JEEP CHEROKEE 1995 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1995, Model line: CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP CHEROKEE 1995Pages: 2198, PDF Size: 82.83 MB
Page 16 of 2198

ENGINE MAINTENANCE
INDEX
page page
Accessory Drive Belt....................... 21
Air Cleaner Element....................... 18
Air-Conditioner Compressor.................. 21
Battery................................. 20
Crankcase Ventilation System................ 19
Emission Control System................... 20
Engine Break-In.......................... 15
Engine Cooling System..................... 18
Engine Oil.............................. 15Engine Oil Change and Filter Replacement...... 16
Engine Oil Filter.......................... 17
Engine Supports.......................... 21
Exhaust System.......................... 21
Fuel Filter............................... 19
Fuel Usage StatementÐGas Engines.......... 19
Ignition Cables, Distributor Cap and Rotor....... 20
Rubber and Plastic Component Inspection....... 20
Spark Plugs............................. 20
ENGINE BREAK-IN
CAUTION: Wide open throttle operation in low
gears, before engine break-in period is complete,
can damage engine.
After first starting a new engine, allow it to idle for
15 seconds before shifting into a drive gear. Also:
²Drive the vehicle at varying speeds less than 88
km/h (55 mph) for the first 480 km (300 miles).
²Avoid fast acceleration and sudden stops.
²Do not drive at full-throttle for extended periods of
time.
²Do not drive at constant speeds.
²Do not idle the engine excessively.
A special break-in engine oil is not required. The
original engine oil installed is a high quality, energy
conserving lubricant. Special break-in oils are not
recommended. These oils could interfere with the
normal piston ring seating process.
New engines tend to consume more fuel and oil un-
til after the break-in period has ended.
ENGINE OIL
WARNING: NEW OR USED ENGINE OIL CAN BE IR-
RITATING TO THE SKIN. AVOID PROLONGED OR
REPEATED SKIN CONTACT WITH ENGINE OIL.
CONTAMINANTS IN USED ENGINE OIL, CAUSED BY
INTERNAL COMBUSTION, CAN BE HAZARDOUS TO
YOUR HEALTH. THOROUGHLY WASH EXPOSED
SKIN WITH SOAP AND WATER.
DO NOT WASH SKIN WITH GASOLINE, DIESEL
FUEL, THINNER, OR SOLVENTS, HEALTH PROB-
LEMS CAN RESULT.
DO NOT POLLUTE, DISPOSE OF USED ENGINE
OIL PROPERLY. CONTACT YOUR DEALER OR GOV-
ERNMENT AGENCY FOR LOCATION OF COLLEC-
TION CENTER IN YOUR AREA.
ENGINE OIL SPECIFICATION
CAUTION: Do not use non-detergent or straight
mineral oil when adding or changing crankcase lu-
bricant. Engine failure can result.
API SERVICE GRADE CERTIFIED
Use an engine oil that is API Service Grade Certi-
fied or an oil that conforms to the API Service Grade
SH or SH/CD. MOPAR provides engine oils that con-
form to all of these service grades.
SAE VISCOSITY
An SAE viscosity grade is used to specify the vis-
cosity grade of engine oil. SAE 30 specifies a single
viscosity engine oil. Engine oils also have multiple
viscosities. These are specified with a dual SAE vis-
cosity grade which indicates the cold-to-hot tempera-
ture viscosity range. Select an engine oil that is best
suited to your particular temperature range and vari-
ation (Fig.1).
ENERGY CONSERVING OIL
An Energy Conserving type oil is recommeded for
gasoline engines. They are designated as either EN-
ERGY CONSERVING or ENERGY CONSERVING
II.
Fig. 1 Temperature/Engine Oil Viscosity
JLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 15
Page 19 of 2198

USED ENGINE OIL DISPOSAL
Care should be exercised when disposing used en-
gine oil after it has been drained from a vehicle en-
gine. Refer to the WARNING listed above.
ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
WARNING: ANTIFREEZE IS AN ETHYLENE GLYCOL
BASE COOLANT AND IS HARMFUL IF SWAL-
LOWED OR INHALED. IF SWALLOWED, DRINK
TWO GLASSES OF WATER AND INDUCE VOMIT-
ING. IF INHALED, MOVE TO FRESH AIR AREA.
SEEK MEDICAL ATTENTION IMMEDIATELY. DO NOT
STORE IN OPEN OR UNMARKED CONTAINERS.
WASH SKIN AND CLOTHING THOROUGHLY AFTER
COMING IN CONTACT WITH ETHYLENE GLYCOL.
KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN.
DISPOSE OF GLYCOL BASE COOLANT PROP-
ERLY, CONTACT YOUR DEALER OR GOVERNMENT
AGENCY FOR LOCATION OF COLLECTION CENTER
IN YOUR AREA.
DO NOT OPEN A COOLING SYSTEM WHEN THE
ENGINE IS AT RUNNING TEMPERATURE, PER-
SONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
AVOID RADIATOR COOLING FAN WHEN ENGINE
COMPARTMENT RELATED SERVICE IS PER-
FORMED, PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
CAUTION: Do not use straight antifreeze as engine
coolant, inadequate engine running temperatures
can result.
Do not operate vehicle without proper concentra-
tion of recommended ethylene glycol coolant, high
running temperatures and cooling system corrosion
can result.
The engine cooling system will develop internal
pressure of 97 to 123 kPa (14 to 18 psi) at normal op-
erating temperature. Allow the vehicle approximately
one half hour to cool off before opening the cooling
system. As an indicator of pressure, squeeze the up-
per radiator hose between index finger and thumb. If
it collapses with little effort the system would have
low internal pressure and should be safe to open to
the first safety notch of the radiator cap. Refer to
Group 7, Cooling System.
COOLING SYSTEM INSPECTION
Coolant level should be inspected when other en-
gine compartment service is performed or when cool-
ant leak is suspected. With the engine at normal
operating temperature, observe the coolant level in
thecoolant recovery bottle. The coolant level mustbe at least above the ADD mark and preferably at
the FULL mark. Add coolant to the coolant recovery
bottleonly, if necessary.
Cooling system freeze protection should be tested
at the onset of the winter season or every 12 months.
Service is required if coolant is low, contaminated,
rusty or freeze protection is inadequate. To properly
test cooling system, see Group 7, Cooling System.
The cooling system factory fill is a mixture of 50%
Ethylene Glycol based antifreeze and 50% water. Us-
ing a suitable hydrometer, measure antifreeze con-
centration in the radiator when the engine is cool. If
the cooling system has recently been serviced, allow
coolant to circulate for at least 20 minutes before
taking hydrometer reading. Properly mixed coolant
will protect the cooling system to -37ÉC (-35ÉF). If the
freeze protection is above -28ÉC (-20ÉF), drain enough
coolant from the cooling system to allow room to add
antifreeze to achieve adequate protection. A mix table
on the coolant container indicates the amount of an-
tifreeze required to winterize the cooling system
based on the capacity, see Capacity Chart in General
Information section of this group.
ANTIFREEZE SPECIFICATION
Chrysler Corporation recommends the use of Mo-
par Antifreeze/Coolant or a high quality, ethylene
glycol base antifreeze/coolant, with a silicate inhibi-
tor.
COOLING SYSTEM SERVICE
The cooling system should be drained, flushed and
filled with the proper coolant mixture at the inter-
vals described in the Lubrication and Maintenance
Schedules. Refer to General Information section of
this group. For proper service instructions see Group
7, Cooling System.
AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
The air cleaner element should be serviced at the
intervals described in the Lubrication and Mainte-
nance Schedules sections of this group. Additional in-
formation can be found in Group 14, Fuel System
and Group 25, Emission System. Inspect all air
cleaner hoses or tubes for damage or leaks when
other engine compartment service is performed. Re-
place faulty components.
FILTER ELEMENT SERVICE/REPLACEMENT
CAUTION: The air cleaner cover must be installed
properly for the emissions system and engine con-
troller to function correctly.
Do not immerse paper air filter element in clean-
ing solvents, damage can result.
(1) Remove the air cleaner cover from the body/
housing (Fig. 9).
0 - 18 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCEJ
Page 24 of 2198

If the transmission is warm, lube oil could
drip out of the fill hole. This is acceptable but
the lube oil should not gush out of the fill hole.
(2) If not acceptable, raise the lube oil level to the
bottom edge of the transmission fill hole.
Add lube oil in small amounts to raise the
level.
(3) Install the fill-hole plug in the transmission.
Tighten the plug with 37 Nzm (27 ft. lbs.) torque.
LUBE OIL CHANGE
When it becomes necessary to change manual
transmission lube oil, use the following procedure.
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the fill-hole plug from the transmis-
sion.
(3) Place a container to collect the lube oil under
the transmission drain-hole plug.
(4) Remove the drain-hole plug and drain the lube
oil from the transmission into the container.
Care should be exercised when disposing
used lube oil after it has been drained from a
transmission.
(5) Install the drain-hole plug in the transmission.
Tighten the plug with 37 Nzm (27 ft. lbs.) torque.
(6) Fill the transmission until the lube oil begins to
drip out of the fill hole.
(7) Install the fill-hole plug in the transmission.
Tighten the plug with 37 Nzm (27 ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Remove the support and lower the vehicle.
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
The automatic transmission fluid should be
changed and bands adjusted at the intervals de-
scribed in the Maintenance Schedules section of this
Group. The automatic transmission should be in-
spected for fluid leaks and proper fluid level whenother under hood service is performed. Refer to
Group 21, Transmission for proper service proce-
dures.
CAUTION: To minimize fluid contamination, verify
that dipstick is seated in the fill tube after fluid level
reading is taken.
TO INSPECT THE TRANSMISSION FLUID
LEVEL
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE DRIVE BELT, PULLEYS OR FAN
BLADE. DO NOT STAND IN A DIRECT LINE WITH
THE FAN BLADE.
(1) Be sure transmission fluid is at normal operat-
ing temperature. Normal operating temperature is
reached after approximately 15 miles (25km) of oper-
ation.
(2) Position the vehicle on a level surface. This is
important for an accurate fluid level check.
(3) While sitting in driver seat, apply brakes and
place gear selector in each position, then move the
selector to:
²XJ vehicles-P (Park).
²YJ vehicles-N (Neutral).
(4) Apply parking brake.
(5) Raise hood and wipe off dipstick handle to pre-
vent dirt from entering fill tube. Then remove trans-
mission fluid level indicator (dipstick) and wipe clean
with a wiping cloth.
(6) Install dipstick and verify it is seated in fill
hole or tube.
(7) Remove dipstick, with handle above tip, take
fluid level reading. If the vehicle has been driven for
at least 15 minutes before inspecting fluid level,
transmission can be considered hot and reading
should be in the OK area. If vehicle has run for less
than 15 minutes and more than 60 seconds transmis-
sion can be considered warm and reading should be
above MIN mark. Add fluid only if level is below
MIN mark on dipstick when transmission is warm
(Fig. 4).
CAUTION: Do not overfill automatic transmission,
leakage or damage can result.
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION FLUID
SPECIFICATION
When it becomes necessary to add fluid or when
the ATF is replaced, use:
²MOPAR Dexron IIE/Mercon ATFonlyfor AW-4
automatic transmissions (XJ vehicles).
²MOPAR ATF PLUS type 7176 (YJ vehicles).
Fig. 3 Manual Transmission Fill- & Drain-Hole
PlugsÐTypical
JLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 23
Page 31 of 2198

FLUID LEVEL
The fluid level indicator (dipstick) is attached to
the reservoir cap (Fig. 6). The fluid level in the res-
ervoir can be determined with the fluid either hot or
cold.
(1) Remove the cap from the reservoir.
(2) Depending on fluid temperature, if the level is
below the FULL HOT mark or the FULL COLD
mark on the dipstick, add power steering fluid.
(3) Install the cap on the reservoir.CAUTION: Do not over fill power steering reservoir
when adding fluid, seal damage and leakage can re-
sult.
MANUAL STEERING GEAR
The manual steering gear should be inspected for
damage at the same time as the engine oil is
changed and the oil filter is replaced. Refer to Group
19, Steering for additional information and service
procedures.
POWER BRAKE SYSTEM
RECOMMENDED MAINTENANCE
The brake fluid level (Fig. 8) should be inspected
when other underhood service is done. With disc-
brakes, the fluid level can be expected to fall as the
brake pads wear. However, a low fluid level can also
be caused by a leak, and repair will then be neces-
sary. Refer to Group 5, Brakes for proper service pro-
cedures.
In addition, the brake system should be operation-
ally tested periodically to ensure that it is function-
ing normally.
FLUID SPECIFICATION
Jeep power brake systems require MOPAR Heavy-
Duty Brake Fluid, or an equivalent product identified
as conforming to FMVSS No. 116, DOT-3 and SAE
J-1703 specifications.
Use brake fluid from properly sealed container
when adding fluid to the reservoir. Never use re-
claimed fluid or fluid that does not conform to the
DOT/SAE Standards.
CAUTION: Use of a brake fluid that has a lower ini-
tial boiling point then specified by FMVSS No. 116,
DOT 3 and SAE J-1703 could result in sudden brake
failure during hard, prolonged braking.
Do not allow petroleum base fluids to contaminate
the brake fluid. Seal damage will result.
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL
STANDARD POWER BRAKE SYSTEM
(1) Clean the cover and the sides of the brake fluid
reservoir.
(2) Detach the bail retainer from the reservoir
cover and remove the cover from the reservoir.
(3) The brake fluid level should be 6 mm (1/4 in)
below the rim of each reservoir well for XJ and YJ
Vehicles (Fig. 7 and 8). If not, add brake fluid as nec-
essary.
(4) Inspect the reservoir cover bail retainer for ten-
sion and the cover for proper fit. The cover should fit
tight and have a good seal.
Fig. 5 Power Steering SystemÐYJ Vehicles
Fig. 6 Power Steering Fluid Reservoir DipstickÐ
Typical
0 - 30 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCEJ
Page 53 of 2198

AXLE NOISE/VIBRATION DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page page
Driveline Snap........................... 19
Gear and Bearing Noise.................... 18
General Information....................... 18Low Speed Knock......................... 19
Vibration................................ 19
GENERAL INFORMATION
Axle bearing problem conditions are usually caused
by:
²Insufficient or incorrect lubricant
²Foreign matter/water contamination
²Incorrect bearing preload torque adjustment
²Incorrect backlash (to tight)
When serviced, the bearings must be cleaned thor-
oughly. They should be dried with lint-free shop tow-
els.Never dry bearings with compressed air.
This will overheat them and brinell the bearing
surfaces. This will result in noisy operation af-
ter repair.
Axle gear problem conditions are usually the result
of:
²Insufficient lubrication
²Incorrect or contaminated lubricant
²Overloading (excessive engine torque) or exceeding
vehicle weight capacity
²Incorrect clearance or backlash adjustment
Insufficient lubrication is usually the result of a
housing cover leak. It can also be from worn axle
shaft or pinion gear seals. Check for cracks or porous
areas in the housing or tubes.
Using the wrong lubricant will cause overheating
and gear failure. Gear tooth cracking and bearing
spalling are indicators of this.
Axle component breakage is most often the result
of:
²Severe overloading
²Insufficient lubricant
²Incorrect lubricant
²Improperly tightened components
Overloading occurs when towing heavier than rec-
ommended loads. Component breakage can occur
when the wheels are spun excessively. Incorrect lu-
bricant quantity contributes to breakage. Loose dif-
ferential components can also cause breakage.
Incorrect bearing preload or gear backlash will not
result in component breakage. Mis-adjustment will
produce enough noise to cause service repair before a
failure occurs. If a mis-adjustment condition is not
corrected, component failure can result.
Excessive bearing preload may not be noisy. This
condition will cause high temperature which can re-
sult in bearing failure.
GEAR AND BEARING NOISE
GEAR NOISE
Axle gear noise can be caused by insufficient lubri-
cant. Incorrect backlash, tooth contact, or worn/dam-
aged gears can cause noise.
Gear noise usually happens at a specific speed
range. The range is 30 to 40 mph, or above 50 mph.
The noise can also occur during a specific type of
driving condition. These conditions are acceleration,
deceleration, coast, or constant load.
When road testing, accelerate the vehicle to the
speed range where the noise is the greatest. Shift
out-of-gear and coast through the peak-noise range.
If the noise stops or changes greatly, check for insuf-
ficient lubricant. Incorrect ring gear backlash, or
gear damage can cause noise changes.
Differential side and pinion gears can be checked
by turning the vehicle. They usually do not cause
noise in straight-ahead driving. These gears are
loaded during vehicle turns. If noise does occur dur-
ing vehicle turns, the side or pinion gears could be
worn or damaged. A worn pinion gear mate shaft can
also cause a snapping or a knocking noise.
BEARING NOISE
The axle shaft, differential and pinion gear bear-
ings can all produce noise when worn or damaged.
Bearing noise can be either a whining, or a growling
sound.
Pinion gear bearings have a constant-pitch noise.
This noise changes only with vehicle speed. Pinion
bearing noise will be higher because it rotates at a
faster rate. Drive the vehicle and load the differen-
tial. If bearing noise occurs the pinion rear bearing is
the source of the noise. If the bearing noise is heard
during a coast, front bearing is the source.
Worn, damaged differential bearings usually pro-
duce a low pitch noise. Differential bearing noise is
similar to pinion bearing. The pitch of differential
bearing noise is also constant and varies only with
vehicle speed.
2 - 18 FRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLEJ
Page 57 of 2198

MODEL 30 AXLE AND TUBE AXLE (2WD)
INDEX
page page
Axle Bushing Replacement.................. 34
Axle ShaftÐCardan U-Joint.................. 26
Backlash and Contact Pattern Analysis......... 45
Cleaning/Inspection........................ 37
Differential and Pinion Measurement........... 40
Differential Assembly....................... 38
Differential Disassembly.................... 35
Differential Installation...................... 44
Differential Removal....................... 34
Differential Shim Pack Measurement and
Adjustment............................ 43
Drive Axle Assembly ReplacementÐXJ Vehicles . . 23
Drive Axle Assembly ReplacementÐYJ Vehicles . . 24Final Assembly........................... 46
Hub Bearing and Axle Shaft................. 25
Information.............................. 22
Inner Axle Shaft Oil Seal Replacement......... 35
Lubricant Change......................... 23
Lubricant Specifications..................... 22
Pinion Gear Assembly/Installation............. 42
Pinion Gear Depth Information............... 39
Pinion Removal/Disassembly................. 36
Pinion Seal Replacement................... 25
Steering Knuckle and Ball Studs.............. 32
Vacuum Disconnect AxleÐYJ Vehicles......... 27
INFORMATION
The Model 30 front axles consists of a cast iron dif-
ferential housing with axle shaft tubes extending
from either side. The tubes are pressed into the dif-
ferential housing and welded.
The integral type housing, hypoid gear design has
the centerline of the pinion set above the centerline
of the ring gear.
The axle has a fitting for a vent hose used to re-
lieve internal pressure caused by lubricant vaporiza-
tion and internal expansion.
The axles are equipped with semi-floating axle
shafts, meaning that loads are supported by the hub
bearings. The axle shafts are retained by nuts at the
hub bearings. The hub bearings are bolted to the
steering knuckle at the outboard end of the axle tube
yoke. The hub bearings are serviced as an assembly.
The axles are equipped with ABS brake sensors.
The sensors are attached to the knuckle assemblies
and tone rings are pressed on the axle shaft.Use
care when removing axle shafts as NOT to dam-
age the tone wheel or the sensor.
The stamped steel cover provides a means for in-
spection and servicing the differential.
The Model 30 axle has the assembly part number
and gear ratio listed on a tag. The tag is attached to
the housing cover. Build date identification codes are
stamped on the axle shaft tube cover side.
The differential case is a one-piece design. The dif-
ferential pinion mate shaft is retained with a roll
pin. Differential bearing preload and ring gear back-
lash is adjusted by the use of shims (select thick-
ness). The shims are located between the differential
bearing cones and case. Pinion bearing preload is set
and maintained by the use of collapsible spacer.
COMMAND-TRACÐYJ VEHICLES
The Command-Trac system is a vacuum disconnect
axle. The system has a two-piece axle shaft coupled
together by a shift collar. For two-wheel drive opera-
tion, the vacuum motor and shift fork disengages the
axle shaft splines. For four-wheel drive operation, the
vacuum motor and shift fork engages the axle
splines.
SELEC-TRACÐXJ VEHICLES
The Selec-Trac system is a non-disconnect axle.
Shifting from two-wheel to four-wheel drive is done
at the transfer case.
For XJ vehicles equipped withSelec-Tracand
ABS brake system, refer to Group 5ÐBrakes for ad-
ditional service information.
LUBRICANT SPECIFICATIONS
Multi-purpose, hypoid gear lubricant should be
used for Model 30 axles. The lubricant should have
MIL-L-2105C and API GL 5 quality specifications.
MOPARtHypoid Gear Lubricant conforms to both of
these specifications.
²The factory fill for the Model 30 axle is SAE Ther-
mally Stable 80W-90 gear lubricant.Do not use
heavier weight lubricant, this will cause axle
engagement difficulties.
²The factory installed lubricant quantity for the
NON-DISCONNECT TYPE AXLE is 1.48 L (3.13
pts.).
²The factory installed lubricant quantity for the
VACUUM-DISCONNECT TYPE AXLE is 1.65 L (3.76
pts.).
Refer to Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance for
additional information regarding temperature range,
viscosity and fluid level.
2 - 22 FRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLEJ
Page 94 of 2198

AXLE NOISE/VIBRATION DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page page
Driveline Snap........................... 10
Gear and Bearing Noise..................... 9
General Information........................ 9
Limited Slip Differential..................... 10Low Speed Knock......................... 10
Rear Axle Alignment....................... 10
Vibration................................ 10
GENERAL INFORMATION
Axle bearing problem conditions are usually caused
by:
²Insufficient or incorrect lubricant
²Foreign matter/water contamination
²Incorrect bearing preload torque adjustment
²Incorrect backlash (to tight)
When serviced, the bearings must be cleaned thor-
oughly. They should be dried with lint-free shop tow-
els.Never dry bearings with compressed air.
This will overheat them and brinell the bearing
surfaces. This will result in noisy operation af-
ter repair.
Axle gear problem conditions are usually the result of:
²Insufficient lubrication
²Incorrect or contaminated lubricant
²Overloading (excessive engine torque) or exceeding
vehicle weight capacity
²Incorrect clearance or backlash adjustment
Insufficient lubrication is usually the result of a
housing cover leak. It can also be from worn axle
shaft or pinion gear seals. Check for cracks or porous
areas in the housing or tubes.
Using the wrong lubricant will cause overheating
and gear failure. Gear tooth cracking and bearing
spalling are indicators of this.
Axle component breakage is most often the result of:
²Severe overloading
²Insufficient lubricant
²Incorrect lubricant
²Improperly tightened components
Overloading occurs when towing heavier than rec-
ommended loads. Component breakage can occur
when the wheels are spun excessively. Incorrect lu-
bricant quantity contributes to breakage. Loose dif-
ferential components can also cause breakage.
Incorrect bearing preload or gear backlash will not
result in component breakage. Mis-adjustment will
produce enough noise to cause service repair before a
failure occurs. If a mis-adjustment condition is not
corrected, component failure can result.
Excessive bearing preload may not be noisy. This
condition will cause high temperature which can re-
sult in bearing failure.
GEAR AND BEARING NOISE
GEAR NOISE
Axle gear noise can be caused by insufficient lubri-
cant. Incorrect backlash, tooth contact, or worn/dam-
aged gears can cause noise.
Gear noise usually happens at a specific speed
range. The range is 30 to 40 mph, or above 50 mph.
The noise can also occur during a specific type of
driving condition. These conditions are acceleration,
deceleration, coast, or constant load.
When road testing, accelerate the vehicle to the
speed range where the noise is the greatest. Shift
out-of-gear and coast through the peak-noise range.
If the noise stops or changes greatly, check for insuf-
ficient lubricant. Incorrect ring gear backlash, or
gear damage can cause noise changes.
Differential side and pinion gears can be checked
by turning the vehicle. They usually do not cause
noise in straight-ahead driving. These gears are
loaded during vehicle turns. If noise does occur dur-
ing vehicle turns, the side or pinion gears could be
worn or damaged. A worn pinion gear mate shaft can
also cause a snapping or a knocking noise.
BEARING NOISE
The axle shaft, differential and pinion gear bear-
ings can all produce noise when worn or damaged.
Bearing noise can be either a whining, or a growling
sound.
Pinion gear bearings have a constant-pitch noise.
This noise changes only with vehicle speed. Pinion
bearing noise will be higher because it rotates at a
faster rate. Drive the vehicle and load the differen-
tial. If bearing noise occurs the pinion rear bearing is
the source of the noise. If the bearing noise is heard
during a coast, front bearing is the source.
Worn, damaged differential bearings usually pro-
duce a low pitch noise. Differential bearing noise is
similar to pinion bearing. The pitch of differential
bearing noise is also constant and varies only with
vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearings produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
JREAR SUSPENSION AND AXLES 3 - 9
Page 123 of 2198

(6) If removed, heat ring gear with a heat lamp or
by immersing in a hot fluid. The temperature should
not exceed 149ÉC (300ÉF).Do not use a torch to
heat the ring gear.
(7) Position heated rear gear on case. Use two
equally spaced Pilot Studs C-3288-B to align the gear
with the flange holes (Fig. 18).
(8) Install replacement ring gear bolts (with left
hand threads). Alternately and evenly tighten each
bolt to 95 Nzm (70 ft. lbs.) torque.
CAUTION: When installing a differential bearing,
never apply force to the bearing cage because bear-
ing damage will result.
(9) Install a differential bearing on each hub with
Installer C-4340 and Handle C-4171 (Fig. 19).PINION DEPTH MEASUREMENT AND
ADJUSTMENT WITH GAUGE SET 6575
(1) Use pinion gear adjustment gauge set 6575
(Fig. 20) and continue the assembly:
(2) Install front (outer) bearing cup use Installer
D-130 and Handle C-4171.
(3) Install rear (inner) bearing cup use Installer
C-4308 and Handle C-4171.
Assemble tools as described;
²Position Spacer (SP-6030) over Shaft (SP-5385)
²Position pinion rear bearing on shaft
²Position tools (with bearing) in the housing
²Install Sleeve (SP-5382)
²Install pinion front bearing
²Install Spacer (SP-6022)
²Install Sleeve (SP-3194-B), Washer (SP-534) and
Nut (SP-3193)
(4) Prevent compression sleeve tool from turning
with Wrench C-3281.
Tighten the nut to seat the pinion bearings in the
housing (Fig. 21). Allow the sleeve to turn several
times during the tightening to prevent brinelling the
bearing cups or bearings.
Depth shim(s) are positioned between the pin-
ion gear rear bearing and pinion gear. The re-
quired thickness of the depth shim(s) is
determined according to the following informa-
tion.
(5) Loosen the compression nut tool. Lubricate the
pinion gear front and rear bearings with gear lubri-
cant. Re-tighten the compression nut tool to 1 to 3
Nzm (15 to 25 in. lbs.) torque. Rotate the pinion gear
several complete revolutions to align the bearing roll-
ers.
(6) Install Gauge Block SP-5383 at the end of SP-
5385. Install Cap Screw (SP-536) and tighten.
(7) Position Arbor (SP-6029) in the differential
housing (Fig. 22).
Fig. 18 Case-To-Ring Gear Alignment
Fig. 19 Differential Bearing Installation
Fig. 20 Axle Adjustment ToolsÐ8 1/4
3 - 38 REAR SUSPENSION AND AXLESJ
Page 143 of 2198

pedal. The proper course of action is to bleed the sys-
tem, or replace thin drums and suspect quality brake
lines and hoses.
HARD PEDAL OR HIGH PEDAL EFFORT
A hard pedal or high pedal effort may be due to lin-
ing that is water soaked, contaminated, glazed, or
badly worn. The power booster or check valve could
also be faulty. Test the booster and valve as described
in this section.
BRAKE DRAG
Brake drag occurs when the lining is in constant
contact with the rotor or drum. Drag can occur at one
wheel, all wheels, fronts only, or rears only. It is a
product of incomplete brakeshoe release. Drag can be
minor or severe enough to overheat the linings, ro-
tors and drums. A drag condition also worsens as
temperature of the brake parts increases.
Brake drag also has a direct effect on fuel economy.
If undetected, minor brake drag can be misdiagnosed
as an engine or transmission/torque converter prob-
lem.
Minor drag will usually cause slight surface char-
ring of the lining. It can also generate hard spots in
rotors and drums from the overheat/cool down pro-
cess. In most cases, the rotors, drums, wheels and
tires are quite warm to the touch after the vehicle is
stopped.
Severe drag can char the brake lining all the way
through. It can also distort and score rotors and
drums to the point of replacement. The wheels, tires
and brake components will be extremely hot. In se-
vere cases, the lining may generate smoke as it chars
from overheating.
An additional cause of drag involves the use of in-
correct length caliper mounting bolts. Bolts that are
too long can cause a partial apply condition. The cor-
rect caliper bolts have a shank length of 67 mm
(2.637 in.), plus or minus 0.6 mm (0.0236 in.). Refer
to the Disc Brake service section for more detail on
caliper bolt dimensions and identification.
Some common causes of brake drag are:
²loose or damaged wheel bearing
²seized or sticking caliper or wheel cylinder piston
²caliper binding on bolts or slide surfaces
²wrong length caliper mounting bolts (too long)
²loose caliper mounting bracket
²distorted rotor, brake drum, or shoes
²brakeshoes binding on worn/damaged support
plates
²severely rusted/corroded components
²misassembled components.
If brake drag occurs at all wheels, the problem may
be related to a blocked master cylinder compensatorport or faulty power booster (binds-does not release).
The condition will worsen as brake temperature in-
creases.
The brakelight switch can also be a cause of drag.
An improperly mounted or adjusted brakelight
switch can prevent full brake pedal return. The re-
sult will be the same as if the master cylinder com-
pensator ports are blocked. The brakes would be
partially applied causing drag.
BRAKE FADE
Brake fade is a product of overheating caused by
brake drag. However, overheating and subsequent
fade can also be caused by riding the brake pedal,
making repeated high deceleration stops in a short
time span, or constant braking on steep roads. Refer
to the Brake Drag information in this section for
causes.
PEDAL PULSATION (NON-ABS BRAKES ONLY)
Pedal pulsation is caused by parts that are loose,
or beyond tolerance limits. This type of pulsation is
constant and will occur every time the brakes are ap-
plied.
Disc brake rotors with excessive lateral runout or
thickness variation, or out of round brake drums are
the primary causes of pulsation.
On vehicles with ABS brakes, remember that pedal
pulsation is normal during antilock mode brake
stops. If pulsation occurs during light to moderate
brake stops, a standard brake part is either loose, or
worn beyond tolerance.
BRAKE PULL
A front pull condition could be the result of:
²contaminated lining in one caliper
²seized caliper piston
²binding caliper
²wrong caliper mounting bolts (too long)
²loose caliper
²loose or corroded mounting bolts
²improper brakeshoes
²damaged rotor
²incorrect wheel bearing adjustment (at one wheel)
A worn, damaged wheel bearing or suspension com-
ponent are further causes of pull. A damaged front
tire (bruised, ply separation) can also cause pull.
Wrong caliper bolts (too long) will cause a partial ap-
ply condition and pull if only one caliper is involved.
A common and frequently misdiagnosed pull condi-
tion is where direction of pull changes after a few
stops. The cause is a combination of brake drag fol-
lowed by fade at the dragging brake unit.
As the dragging brake overheats, efficiency is so re-
duced that fade occurs. If the opposite brake unit is
still functioning normally, its braking effect is magni-
5 - 6 SERVICE BRAKE DIAGNOSISJ
Page 218 of 2198
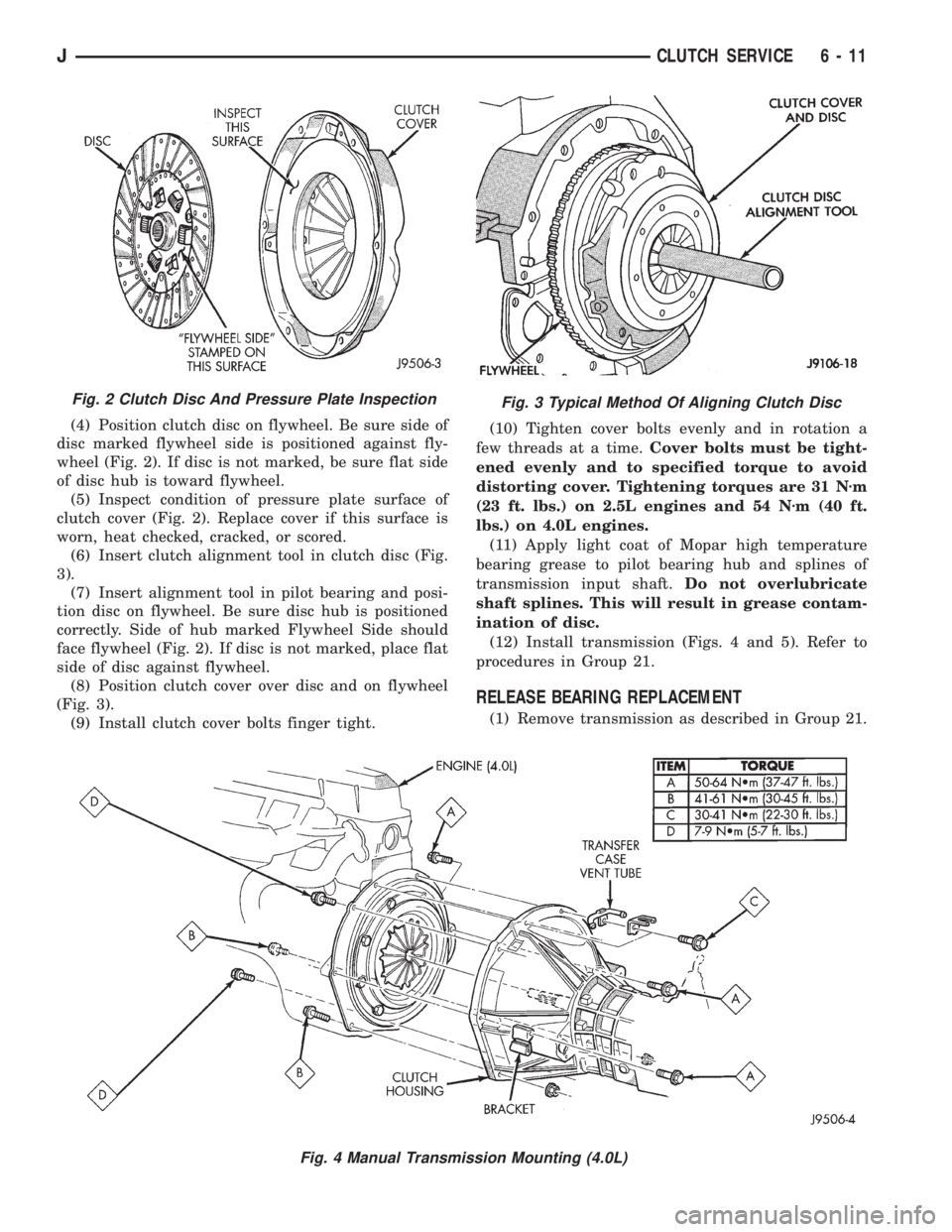
(4) Position clutch disc on flywheel. Be sure side of
disc marked flywheel side is positioned against fly-
wheel (Fig. 2). If disc is not marked, be sure flat side
of disc hub is toward flywheel.
(5) Inspect condition of pressure plate surface of
clutch cover (Fig. 2). Replace cover if this surface is
worn, heat checked, cracked, or scored.
(6) Insert clutch alignment tool in clutch disc (Fig.
3).
(7) Insert alignment tool in pilot bearing and posi-
tion disc on flywheel. Be sure disc hub is positioned
correctly. Side of hub marked Flywheel Side should
face flywheel (Fig. 2). If disc is not marked, place flat
side of disc against flywheel.
(8) Position clutch cover over disc and on flywheel
(Fig. 3).
(9) Install clutch cover bolts finger tight.(10) Tighten cover bolts evenly and in rotation a
few threads at a time.Cover bolts must be tight-
ened evenly and to specified torque to avoid
distorting cover. Tightening torques are 31 Nzm
(23 ft. lbs.) on 2.5L engines and 54 Nzm (40 ft.
lbs.) on 4.0L engines.
(11) Apply light coat of Mopar high temperature
bearing grease to pilot bearing hub and splines of
transmission input shaft.Do not overlubricate
shaft splines. This will result in grease contam-
ination of disc.
(12) Install transmission (Figs. 4 and 5). Refer to
procedures in Group 21.
RELEASE BEARING REPLACEMENT
(1) Remove transmission as described in Group 21.
Fig. 2 Clutch Disc And Pressure Plate InspectionFig. 3 Typical Method Of Aligning Clutch Disc
Fig. 4 Manual Transmission Mounting (4.0L)
JCLUTCH SERVICE 6 - 11