Differential level JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 1530 of 2199

FOURTH GEAR POWERFLOW
Fourth gear overdrive range is electronically con-
trolled and hydraulically activated. Various sensor
inputs are supplied to the powertrain control module
to operate the overdrive solenoid on the valve body.
The solenoid contains a check ball that opens and
closes a vent port in the 3-4 shift valve feed passage.
The overdrive solenoid (and check ball) are not ener-
gized in first, second, third, or reverse gear. The vent
port remains open, diverting line pressure from the
2-3 shift valve away from the 3-4 shift valve. The
overdrive control switch must be in the ON position
to transmit overdrive status to the PCM. A 3-4
upshift occurs only when the overdrive solenoid is
energized by the PCM. The PCM energizes the over-
drive solenoid during the 3-4 upshift. This causes the
solenoid check ball to close the vent port allowing
line pressure from the 2-3 shift valve to act directly
on the 3-4 upshift valve. Line pressure on the 3-4
shift valve overcomes valve spring pressure moving
the valve to the upshift position. This action exposes
the feed passages to the 3-4 timing valve, 3-4 quick
fill valve, 3-4 accumulator, and ultimately to the
overdrive piston. Line pressure through the timing
valve moves the overdrive piston into contact with
the overdrive clutch. The direct clutch is disengaged
before the overdrive clutch is engaged. The boost
valve provides increased fluid apply pressure to the
overdrive clutch during 3-4 upshifts, and when accel-
erating in fourth gear. The 3-4 accumulator cushions
overdrive clutch engagement to smooth 3-4 upshifts.
The accumulator is charged at the same time as
apply pressure acts against the overdrive piston.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
Automatic transmission problems can be a result of
poor engine performance, incorrect fluid level, incor-
rect linkage or cable adjustment, band or hydraulic
control pressure adjustments, hydraulic system mal-
functions or electrical/mechanical component mal-
functions. Begin diagnosis by checking the easily
accessible items such as: fluid level and condition,
linkage adjustments and electrical connections. A
road test will determine if further diagnosis is neces-
sary.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRELIMINARY
Two basic procedures are required. One procedure
for vehicles that are drivable and an alternate proce-
dure for disabled vehicles (will not back up or move
forward).
VEHICLE IS DRIVEABLE
(1) Check for transmission fault codes using DRBt
scan tool.
(2) Check fluid level and condition.
(3) Adjust throttle and gearshift linkage if com-
plaint was based on delayed, erratic, or harsh shifts.
(4) Road test and note how transmission upshifts,
downshifts, and engages.
(5) Perform hydraulic pressure test if shift prob-
lems were noted during road test.
(6) Perform air-pressure test to check clutch-band
operation.
VEHICLE IS DISABLED
(1) Check fluid level and condition.
(2) Check for broken or disconnected gearshift or
throttle linkage.
(3) Check for cracked, leaking cooler lines, or loose
or missing pressure-port plugs.
(4) Raise and support vehicle on safety stands,
start engine, shift transmission into gear, and note
following:
(a) If propeller shaft turns but wheels do not,
problem is with differential or axle shafts.
(b) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is noisy, stop engine. Remove oil pan, and
check for debris. If pan is clear, remove transmis-
sion and check for damaged drive plate, converter,
oil pump, or input shaft.
(c) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is not noisy, perform hydraulic-pressure test to
determine if problem is hydraulic or mechanical.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TESTING
Before road testing, be sure the fluid level and con-
trol cable adjustments have been checked and
adjusted if necessary. Verify that diagnostic trouble
codes have been resolved.
Observe engine performance during the road test.
A poorly tuned engine will not allow accurate analy-
sis of transmission operation.
Operate the transmission in all gear ranges. Check
for shift variations and engine flare which indicates
slippage. Note if shifts are harsh, spongy, delayed,
early, or if part throttle downshifts are sensitive.
Slippage indicated by engine flare, usually means
clutch, band or overrunning clutch problems. If the
condition is advanced, an overhaul will be necessary
to restore normal operation.
A slipping clutch or band can often be determined
by comparing which internal units are applied in the
various gear ranges. The Clutch and Band Applica-
tion chart provides a basis for analyzing road test
results.
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 11
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1606 of 2199

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - OVERDRIVE
ELECTRICAL CONTROLS
The overdrive off switch, valve body solenoid, case
connectors and related wiring can all be tested with
a 12 volt test lamp or a volt/ohmmeter. Check conti-
nuity of each component when diagnosis indicates
this is necessary.
Switch and solenoid continuity should be checked
whenever the transmission fails to shift into fourth
gear range.
OVERDRIVE UNIT
REMOVAL
(1) Shift transmission into PARK.
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) Remove transfer case, if equipped.
(4) Mark propeller shaft universal joint(s) and axle
pinion yoke, or the companion flange and flange
yoke, for alignment reference at installation, if necc-
esary.
(5) Disconnect and remove the rear propeller shaft,
if necessary. (Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIV-
ELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT -
REMOVAL)
(6) Remove transmission oil pan, remove gasket,
drain oil and reinstall pan.
(7) If overdrive unit had malfunctioned, or if fluid
is contaminated, remove entire transmission. If diag-
nosis indicated overdrive problems only, remove just
the overdrive unit.
(8) Support transmission with transmission jack.
(9) Remove bolts attaching overdrive unit to trans-
mission (Fig. 126).
CAUTION: Support the overdrive unit with a jack
before moving it rearward. This is necessary to pre-
vent damaging the intermediate shaft. Do not allow
the shaft to support the entire weight of the over-
drive unit.(10) Carefully work overdrive unit off intermediate
shaft. Do not tilt unit during removal. Keep it as
level as possible.
(11) If overdrive unit does not require service,
immediately insert Alignment Tool 6227-2 in splines
of planetary gear and overrunning clutch to prevent
splines from rotating out of alignment. If misalign-
ment occurs, overdrive unit will have to be disassem-
bled in order to realign splines.
(12) Remove and retain overdrive piston thrust
bearing. Bearing may remain on piston or in clutch
hub during removal.
(13) Position drain pan on workbench.
(14) Place overdrive unit over drain pan. Tilt unit
to drain residual fluid from case.
(15) Examine fluid for clutch material or metal
fragments. If fluid contains these items, overhaul will
be necessary.
(16) If overdrive unit does not require any service,
leave alignment tool in position. Tool will prevent
accidental misalignment of planetary gear and over-
running clutch splines.Fig. 126 Overdrive Unit Bolts
1 - OVERDRIVE UNIT
2 - ATTACHING BOLTS (7)
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 87
OVERDRIVE OFF SWITCH (Continued)
Page 1699 of 2199

Diagnosis of these problems should always begin
by checking the easily accessible variables: fluid level
and condition, gearshift cable adjustment. Then per-
form a road test to determine if the problem has been
corrected or if more diagnosis is necessary. If the
problem persists after the preliminary tests and cor-
rections are completed, hydraulic pressure checks
should be performed.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRELIMINARY
Two basic procedures are required. One procedure for
vehicles that are drivable and an alternate procedure for
disabled vehicles (will not back up or move forward).
VEHICLE IS DRIVABLE
(1) Check for transmission fault codes using DRBt
scan tool.
(2) Check fluid level and condition.
(3) Adjust gearshift cable if complaint was based
on delayed, erratic, or harsh shifts.
(4) Road test and note how transmission upshifts,
downshifts, and engages.
(5) Perform stall test if complaint is based on slug-
gish acceleration. Or, if abnormal throttle opening is
needed to maintain normal speeds with a properly
tuned engine.
(6) Perform hydraulic pressure test if shift prob-
lems were noted during road test.
(7)
Perform air-pressure test to check clutch operation.
VEHICLE IS DISABLED
(1) Check fluid level and condition.
(2)
Check for broken or disconnected gearshift cable.
(3) Check for cracked, leaking cooler lines, or loose
or missing pressure-port plugs.(4) Raise and support vehicle on safety stands,
start engine, shift transmission into gear, and note
following:
(a) If propeller shaft turns but wheels do not,
problem is with differential or axle shafts.
(b) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is noisy, stop engine. Remove oil pan, and
check for debris. If pan is clear, remove transmis-
sion and check for damaged driveplate, converter,
oil pump, or input shaft.
(c) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is not noisy, perform hydraulic-pressure test to
determine if problem is hydraulic or mechanical.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TESTING
Before road testing, be sure the fluid level and con-
trol cable adjustments have been checked and
adjusted if necessary. Verify that all diagnostic trou-
ble codes have been resolved.
Observe engine performance during the road test.
A poorly tuned engine will not allow accurate analy-
sis of transmission operation.
Operate the transmission in all gear ranges. Check
for shift variations and engine flare which indicates
slippage. Note if shifts are harsh, spongy, delayed,
early, or if part throttle downshifts are sensitive.
Slippage indicated by engine flare, usually means
clutch, overrunning clutch, or line presure problems.
A slipping clutch can often be determined by com-
paring which internal units are applied in the vari-
ous gear ranges. The Clutch Application chart
provides a basis for analyzing road test results.
CLUTCH APPLICATION CHART
SLP UD OD R 2C 4C L/R OVERRUNNING
P±PARKON
R±REVERSEON ON
N-NEUTRALON
D±OVERDRIVE
FIRSTON ON* ON
SECONDON ON
SECOND PRIMEON ON
THIRDON ON
FOURTHON ON
FIFTHON ON
LIMP-INON ON
2±FIRSTON ON* ON
SECONDON ON
LIMP-INON ON
1±LOWON ON ON
*L/R clutch is on only with the output shaft speed below 150 rpm.
21 - 180 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE (Continued)
Page 1826 of 2199

NV242HD REAR RETAINER
(1) Apply bead of MopartSealer, or LoctiteŸ
Ultra Gray, to mating surface of rear retainer. Sealer
bead should be a maximum of 3/16 in.
(2) Install rear retainer on rear case. Tighten
retainer bolts to 20-27 N´m (15-20 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install new output shaft bearing snap-ring
(Fig. 91). Lift mainshaft slightly to seat snap-ring in
shaft groove, if necessary.
(4) Apply 3 mm (1/8 in.) wide bead of Mopartgas-
ket maker or silicone adhesive sealer to mounting
surface of extension housing. Allow sealer to set-up
slightly before proceeding.(5) Install extension housing on rear retainer.
(6) Install extension housing bolts and tighten to
35-46 N´m (26-34 ft. lbs.).
COMPANION FLANGE
(1) Lubricate companion flange hub with transmis-
sion fluid and install flange on front shaft.
(2) Install new seal washer on front shaft.
(3) Install flange on front shaft and tighten nut to
122-176 N´m (90-130 ft. lbs.).
INSTALLATION
(1) Mount transfer case on a transmission jack.
(2) Secure transfer case to jack with chains.
(3) Position transfer case under vehicle.
(4) Align transfer case and transmission shafts
and install transfer case on transmission.
(5) Install and tighten transfer case attaching nuts
to 35 N´m (26 ft. lbs.) torque (Fig. 4).
(6) Align and connect propeller shafts. (Refer to 3 -
DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER
SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT - INSTALLATION)
(7) Fill transfer case with correct fluid. Check
transmission fluid level. Correct as necessary.
(8) Install rear crossmember and skid plate, if
equipped. Tighten crossmember bolts to 41 N´m (30
ft. lbs.) torque.
(9) Remove transmission jack and support stand.
(10) Connect shift rod to transfer case range lever.
(11) Connect transfer case vent hose and transfer
case position sensor.
(12) Adjust transfer case shift cable.
(13) Lower vehicle and verify transfer case shift
operation.
Fig. 91 Install Output Bearing Snap-ring
1 - REAR RETAINER
2 - SNAP-RING
3 - REAR BEARING
WJTRANSFER CASE - NV242 21 - 307
TRANSFER CASE - NV242 (Continued)
Page 1832 of 2199

(5) Install the rear propeller shaft. (Refer to 3 -
DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER
SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT - INSTALLATION)
(6) Verify proper fluid level.
(7) Lower vehicle.
SHIFT CABLE
REMOVAL
(1) Shift transfer case into NEUTRAL.
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) Disconnect the shift cable eyelet from the
transfer case shift lever (Fig. 101).
(4) Remove shift cable from the cable support
bracket.
(5) Lower vehicle.
(6) Remove any necessary console parts for access
to shift lever assembly and shift cable.(7) Disconnect cable at shift lever and shifter
assembly bracket (Fig. 102).
(8) Remove the nuts holding the shift cable seal
plate to the floor pan (Fig. 103).
(9) Pull cable through floor panel opening.
(10) Remove transfer case shift cable from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Route cable through hole in floor pan.
(2) Install seal plate to studs in floor pan.
(3) Install nuts to hold seal plate to floor pan (Fig.
103). Tighten nuts to 7 N´m (65 in.lbs.).
Fig. 100 Install Rear Retainer Seal
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4171
2 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3995-A
Fig. 101 Transfer Case Shift Cable at Transfer Case
1 - TRANSFER CASE SHIFT LEVER
2 - TRANSFER CASE SHIFT CABLE
Fig. 102 Transfer Case Shift Cable at Shifter
1 - CLIP
2 - SHIFTER
3 - TRANSFER CASE SHIFT LEVER PIN
4 - TRANSFER CASE SHIFT CABLE
Fig. 103 Shift Cables at Floor Pan
1 - SEAL PLATES
2 - TRANSMISSION SHIFT CABLE
3 - TRANSFER CASE SHIFT CABLE
WJTRANSFER CASE - NV242 21 - 313
REAR RETAINER BUSHING AND SEAL - NV242HD (Continued)
Page 1836 of 2199

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
NOISY INÐOR JUMPS OUT OF
4WD LOW RANGE1. Transfer case not completely
engaged in 4WD LOW (possibly
from shift to 4L while rolling)1. Stop vehicle, shift transfer case
to neutral, then shift back to 4WD
LOW
2. Shift linkage loose, binding, or is
misadjusted2. Tighten, lubricate, or repair
linkage as necessary. Adjust linkage
if necessary
3. Range fork cracked, inserts
worn, or fork is binding on shift rail3. Disassemble unit and repair as
necessary
4. Annulus gear or lockplate worn
or damaged4. Disassemble unit and repair as
necessary
LUBRICANT LEAKING FROM
OUTPUT SHAFT SEALS OR FROM
VENT1. Transfer case over filled 1. Drain to correct level
2. Vent closed or restricted 2. Clear or replace vent if necessary
3. Output shaft seals damaged or
installed correctly3. Replace seals. Be sure seal lip
faces interior of case when installed.
Also be sure yoke seal surfaces are
not scored or nicked. Remove
scores and nicks with fine
sandpaper or replace yoke(s) if
necessary.
REMOVAL
(1) Shift transfer case into NEUTRAL.
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) Remove transfer case drain plug and drain
transfer case lubricant.
(4) Mark front and rear propeller shaft yokes for
alignment reference.
(5) Support transmission with jack stand.
(6) Remove rear crossmember and skid plate, if
equipped (Fig. 4).
(7) Disconnect front propeller shaft from transfer
case at companion flange. Remove rear propeller
shaft from vehicle. (Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL &
DRIVELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT/PROPELLER
SHAFT - REMOVAL)
CAUTION: Do not allow propshafts to hang at
attached end. Damage to joint can result.
(8) Disconnect transfer case cable from range
lever.
(9) Disconnect transfer case vent hose (Fig. 5).
(10) Support transfer case with transmission jack.
(11) Secure transfer case to jack with chains.
(12) Remove nuts attaching transfer case to trans-
mission.
(13) Pull transfer case and jack rearward to disen-
gage transfer case (Fig. 5).
(14) Remove transfer case from under vehicle.
DISASSEMBLY
Position transfer case on shallow drain pan.
Remove drain plug and drain lubricant remaining in
case.
Fig. 4 Crossmember Removal
1 - CROSSMEMBER
2 - REAR TRANSMISSION MOUNT
WJTRANSFER CASE - NV247 21 - 317
TRANSFER CASE - NV247 (Continued)
Page 1855 of 2199
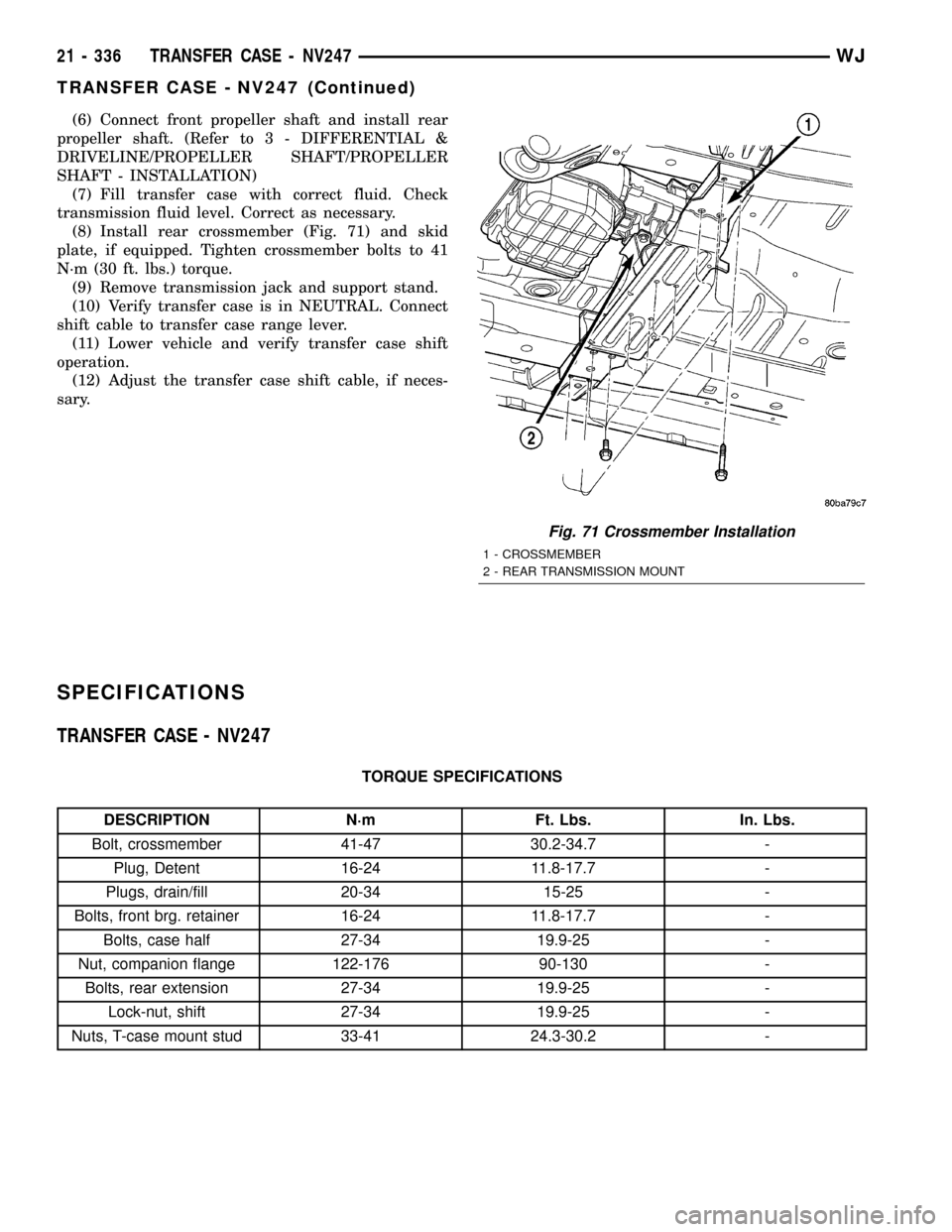
(6) Connect front propeller shaft and install rear
propeller shaft. (Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL &
DRIVELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT/PROPELLER
SHAFT - INSTALLATION)
(7) Fill transfer case with correct fluid. Check
transmission fluid level. Correct as necessary.
(8) Install rear crossmember (Fig. 71) and skid
plate, if equipped. Tighten crossmember bolts to 41
N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(9) Remove transmission jack and support stand.
(10) Verify transfer case is in NEUTRAL. Connect
shift cable to transfer case range lever.
(11) Lower vehicle and verify transfer case shift
operation.
(12) Adjust the transfer case shift cable, if neces-
sary.
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSFER CASE - NV247
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Bolt, crossmember 41-47 30.2-34.7 -
Plug, Detent 16-24 11.8-17.7 -
Plugs, drain/fill 20-34 15-25 -
Bolts, front brg. retainer 16-24 11.8-17.7 -
Bolts, case half 27-34 19.9-25 -
Nut, companion flange 122-176 90-130 -
Bolts, rear extension 27-34 19.9-25 -
Lock-nut, shift 27-34 19.9-25 -
Nuts, T-case mount stud 33-41 24.3-30.2 -
Fig. 71 Crossmember Installation
1 - CROSSMEMBER
2 - REAR TRANSMISSION MOUNT
21 - 336 TRANSFER CASE - NV247WJ
TRANSFER CASE - NV247 (Continued)
Page 1867 of 2199

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRESSURE
GAUGES
A quality air pressure gauge is recommended to
check tire pressure. After checking the air pressure,
replace valve cap finger tight.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TREAD WEAR
INDICATORS
Tread wear indicators are molded into the bottom
of the tread grooves. When tread depth is 1.6 mm
(1/16 in.), the tread wear indicators will appear as a
13 mm (1/2 in.) band (Fig. 15).
Tire replacement is necessary when indicators
appear in two or more grooves or if localized balding
occurs.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE WEAR
PATTERNS
Under inflation will cause wear on the shoulders of
tire. Over inflation will cause wear at the center of
tire.
Excessive camber causes the tire to run at an
angle to the road. One side of tread is then worn
more than the other (Fig. 16).
Excessive toe-in or toe-out causes wear on the
tread edges and a feathered effect across the tread
(Fig. 16).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE NOISE OR
VIBRATION
Radial-ply tires are sensitive to force impulses
caused by improper mounting, vibration, wheel
defects, or possibly tire imbalance.
To find out if tires are causing the noise or vibra-
tion, drive the vehicle over a smooth road at varying
speeds. Note the noise level during acceleration and
deceleration. The engine, differential and exhaust
noises will change as speed varies, while the tire
noise will usually remain constant.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIRING LEAKS
For proper repairing, a radial tire must be removed
from the wheel. Repairs should only be made if the
defect, or puncture, is in the tread area (Fig. 17). The
tire should be replaced if the puncture is located in
the sidewall.
Deflate tire completely before removing the tire
from the wheel. Use lubrication such as a mild soap
solution when dismounting or mounting tire. Use
tools free of burrs or sharp edges which could dam-
age the tire or wheel rim.
Before mounting tire on wheel, make sure all rust
is removed from the rim bead and repaint if neces-
sary.
Install wheel on vehicle, and tighten to proper
torque specification (Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS/
WHEELS - SPECIFICATIONS).
Fig. 15 Tread Wear Indicators
1 - TREAD ACCEPTABLE
2 - TREAD UNACCEPTABLE
3 - WEAR INDICATOR
22 - 8 TIRES/WHEELSWJ
Page 2133 of 2199

(a) If the refrigerant system fails to reach the
specified vacuum, the system has a leak that must
be corrected. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CON-
DITIONING/PLUMBING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM LEAKS)
(b) If the refrigerant system maintains the spec-
ified vacuum for five minutes, restart the vacuum
pump, open the suction and discharge valves and
evacuate the system for an additional ten minutes.
(3) Close all of the valves, and turn off the charg-
ing station vacuum pump.
(4) The refrigerant system is now ready to be
charged with R-134a refrigerant. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM CHARGE)
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM CHARGE
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
After the refrigerant system has been tested for
leaks and evacuated, a refrigerant charge can be
injected into the system. (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - SPECIFICA-
TIONS - CHARGE CAPACITY)
A R-134a refrigerant recovery/recycling/charging
station that meets SAE Standard J2210 must be
used to charge the refrigerant system with R-134a
refrigerant. Refer to the operating instructions sup-
plied by the equipment manufacturer for proper care
and use of this equipment.
PARTIAL CHARGE METHOD
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
The partial charge method is used to add a partial
charge to a refrigerant system that is low on refrig-
erant. To perform this procedure the evaporator inlet
and outlet tube temperatures are measured. The
temperature difference is measured with a tempera-
ture meter with one or two clamp-on thermocouple
probes. The difference between the evaporator inlet
and outlet tube temperatures will determine the
amount of refrigerant needed.Before adding a partial refrigerant charge, check
for refrigerant system leaks. (Refer to 24 - HEATING
& AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM LEAKS)
If a leak is found, make the necessary repairs before
attempting a full or partial refrigerant charge.
(1) Attach a manifold gauge set to the refrigerant
system service ports.
(2) Attach the two clamp-on thermocouple probes
to the inlet and outlet tubes of the evaporator coil.
²If a single thermocouple probe is used, attach
the probe to the evaporator inlet tube just before the
collar of the refrigerant line connector fitting. The
probe must make contact with the bottom surface of
the evaporator inlet tube.
²If dual thermocouple probes are used, attach
probe 1 to the evaporator inlet tube, and probe 2 to
the evaporator outlet tube. Attach both probes to the
evaporator tubes just before the collar of the refrig-
erant line connector fittings. The probes must make
contact with the bottom surfaces of the evaporator
inlet and outlet tubes.
(3) Open all of the windows or doors of the passen-
ger compartment.
(4) Set the A/C button on the A/C Heater controls
to the on position, the temperature control knob in
the full cool position, select Recirculation Mode, and
place the blower motor switch in the highest speed
position.
(5) Start the engine and hold the engine idle speed
at 1,000 rpm. Allow the engine to warm up to normal
operating temperature.
(6) The compressor clutch may cycle, depending
upon ambient temperature, humidity, and the refrig-
erant system charge level.
(7) Hold the engine idle speed at 1,000 rpm.
(8) Allow three to five minutes for the refrigerant
system to stabilize, then record the temperatures of
the evaporator inlet and outlet tubes.
²If a single probe is used, record the temperature
of the evaporator inlet tube. Then remove the probe
from the inlet tube and attach it to the evaporator
outlet tube just before the collar of the refrigerant
line connector fitting. The probe must make contact
with the bottom surface of the evaporator outlet tube.
Allow the thermocouple and meter time to stabilize,
then record the temperature of the evaporator outlet
tube. Subtract the inlet tube temperature reading
from the outlet tube temperature reading.
²If dual probes are used, record the temperatures
of both the evaporator inlet and outlet tubes. Then
subtract the inlet tube temperature reading from the
outlet tube temperature reading.
(9) If the measured temperature differential is
higher than 22É C to 26É C (40É F to 47É F), add 0.4
kilograms (14 ounces) of refrigerant.
24 - 56 PLUMBINGWJ
PLUMBING (Continued)