Lever JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 211 of 2199

(9) Compress the cable retainers with a 13 mm
wrench (Fig. 70). Remove the cable from parking
brake lever bracket and equalizer bracket.
REMOVAL - REAR PARKING BRAKE CABLES
(1) Remove center console, (Refer to 23 - BODY/
INTERIOR/FLOOR CONSOLE - REMOVAL).
(2) Lift up rear seat and carpet covering the park-
ing brake cables.
(3) Place a screw driver through the front cable
eyelet (Fig. 71) and pry back on the front cable.(4) Have an assistant pry down the lock out spring
through the hole in the side of the park brake lever
(Fig. 72) with a small screw driver. Then slowly
release the front cable.
NOTE: Their should be slack in the cable if the lock
out spring is engaged.
(5) Disengage rear cables ends from the equalizer.
(6) Compress the cable retainers with a 13 mm
wrench (Fig. 73) and remove the cable from equalizer
bracket.
Fig. 70 Brake Lever Bracket
1 - FRONT CABLE
2 - WRENCH
Fig. 71 Front Cable Eyelet
1 - REAR CABLES
2 - FRONT CABLE EYELET
3 - FRONT CABLE
4 - EQUALIZER
Fig. 72 Lock Out Spring
1 - LOCK OUT SPRING
Fig. 73 Cable Retainers
1 - CABLE RETAINER
2 - WRENCH
3 - FRONT CABLE
4 - REAR CABLES
5 - 36 BRAKES - BASEWJ
CABLES (Continued)
Page 212 of 2199

(7) Raise and support the vehicle.
(8) Remove the wheel and tire assemblies.
(9) Remove the brake calipers, caliper anchors and
rotors.
(10) Remove the ABS sensor wiring harness (Fig.
74)from the rear brake cables.
(11) Remove the cable retainer bolts (Fig. 74) from
the rear spring pads.
(12) Pull the cables out of the upper suspension
arm brackets.
(13) Push the cable in and lift up the end of cable
with a small screw driver to disengage the cable from
the parking brake actuator (Fig. 75).
(14) Remove the cable from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - FRONT PARKING BRAKE
CABLE
(1) Install thecable into the parking brake lever
bracket and equalizer bracket.
(2) Install the front cable to the floor pan and
install retainer nuts.
(3) Engage the front cable ends to the parking
brake lever and equalizer.
(4) Install the front carpet, (Refer to 23 - BODY/
INTERIOR/CARPETS AND FLOOR MATS -
INSTALLATION).
(5) Pull on the lever to release the lock out spring.
(6) Install the center console, (Refer to 23 - BODY/
INTERIOR/FLOOR CONSOLE - INSTALLATION).
(7) Fold down the rear carpet cover and rear seat.
INSTALLATION - REAR PARKING BRAKE
CABLES
(1) Install the cables through the caliper anchor
mount. Then push the end of cable strand in to
engage the cable end to the parking brake actuator.
(2) Feed the other end of the cables through the
body and into the equalizer bracket (Fig. 76).
Fig. 74 Left Rear Parking Brake Cable
1 - CABLE BRACKET
2 - UPPER SUSPENSION ARM
3 - PARKING BRAKE CABLE
4 - CABLE RETAINER
5 - ABS SENSOR WIRING
Fig. 75 Parking Brake
1 - CABLE END
2 - SCREW DRIVER
3 - PARKING BRAKE ACTUATOR
4 - BRAKE SHOES
Fig. 76 Equalizer Bracket
1 - EQUALIZER
2 - RIGHT REAR CABLE
3 - LEFT REAR CABLE
4 - FRONT CABLE
WJBRAKES - BASE 5 - 37
CABLES (Continued)
Page 213 of 2199

(3) Push the cables into the upper suspension arm
brackets.
(4) Install the cable retainer bolts to the rear
spring pads.
(5) Install the ABS sensor wiring harness to the
rear brake cables.
(6) Install the rotors, caliper anchors and brake
calipers.
(7) Install the wheel and tire assemblies.
(8) Remove support and lower the vehicle.
(9) Engage the cable ends into the parking brake
equalizer.
(10) Pull on the lever to release the lock out
spring.
(11) Install center console, (Refer to 23 - BODY/IN-
TERIOR/FLOOR CONSOLE - INSTALLATION).
(12) Fold down the rear carpet cover and rear seat.
(13) Verify parking brake operation.
LEVER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove center console,(Refer to 23 - BODY/IN-
TERIOR/FLOOR CONSOLE - REMOVAL).
(2) Lift up rear seat and carpet covering the park-
ing brake cables.
(3) Place a screw driver through the front cable
eyelet (Fig. 77) and pry back on the front cable.(4) Have an assistant pry down the lock out spring
through the hole in the side of the park brake lever
(Fig. 78) with a small screw driver. Then slowly
release the front cable.
NOTE: Their should be slack in the cable if the lock
out spring is engaged.
(5) Disconnect parking brake switch wiring con-
nector.
(6) Disengage front cable end from parking brake
lever.
(7) Compress the cable retainer with a 13 mm
wrench (Fig. 79) and remove the cable from the park-
ing brake lever bracket.
Fig. 77 FRONT CABLE
1 - REAR CABLES
2 - FRONT CABLE EYELET
3 - FRONT CABLE
4 - EQUALIZER
Fig. 78 Lock Out Spring
1 - LOCK OUT SPRING
Fig. 79 Parking Brake Lever Bracket
1 - FRONT CABLE
2 - WRENCH
5 - 38 BRAKES - BASEWJ
CABLES (Continued)
Page 214 of 2199

(8) Remove the park brake lever mounting nuts
and console bracket (Fig. 80).
(9) Lift the lever assembly off the mounting studs
and pull the front cable out of the lever bracket.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the lever assembly on the mounting
studs while feeding the front cable into the lever
bracket.
(2) Install the console bracket (Fig. 80) and mount-
ing nuts.
(3) Engage the front cable end to the lever.
(4) Connect parking brake switch wire connector.
(5) Pull on the lever to release the lock out spring.
(6) Install center console,(Refer to 23 - BODY/IN-
TERIOR/FLOOR CONSOLE - INSTALLATION).
(7) Fold down the rear carpet cover and rear seat.
SHOES
REMOVAL
(1) Lock out park brake lever (Fig. 81).
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) Remove rear wheel and tire assembly.
(4) Remove caliper and anchor as an assembly.
(5) Remove rubber access plug from back of rear
disc brake splash shield.
(6) If necessary retract parking brake shoes with
brake adjuster tool (Fig. 82). Position tool at top of
star wheel and rotate wheel.
(7) Remove rotor from axle hub flange.
(8) Remove the lower shoe to shoe spring/adjuster
spring with needle nose pliers (Fig. 83).
(9) Remove the upper shoe to shoe spring/return
spring with brake pliers (Fig. 84).(10) Remove shoe hold-down clips and pins (Fig.
85). Clip is held in place by pin which fits in clip
notch. To remove clip, first push clip ends together
and slide clip until head of pin clears narrow part of
notch. Then remove clip and pin.
(11) Remove shoes and adjuster.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install shoes on splash shield with hold down
clips and pins. Be sure shoes are properly engaged in
the park brake actuator.
(2) Lubricate and install adjuster screw assembly.
Be sure notched ends of screw assembly are properly
seated on shoes and that star wheel is aligned with
access hole in shield.
Fig. 80 Parking Brake Lever Mounting
1 - MOUNTING NUT
2 - PARK BRAKE LEVER
Fig. 81 Lock Out Spring
1 - LOCK OUT SPRING
Fig. 82 Retracting Parking Brake Shoes
1 - ACCESS HOLE
2 - BRAKE ADJUSTING TOOL
3 - SPLASH SHIELD
WJBRAKES - BASE 5 - 39
LEVER (Continued)
Page 215 of 2199

(3) Install lower shoe to shoe spring/adjuster
spring. Needle nose pliers can be used to connect
spring to each shoe.
(4) Install the upper shoe to shoe spring/return
spring with brake pliers (Fig. 83).
(5) Install rotor and caliper anchor assembly.
(6) Install anchor bolts and tighten to 90-115 N´m
(66-85 ft. lbs.).
(7) Actuate park brake lever to unlock the park
brake system.
(8) Adjust the parking brake shoes (Fig. 82).
(9) Install wheel and tire assembly.
(10) Lower vehicle and verify correct parking
brake operation.
ADJUSTMENTS - PARKING BRAKE SHOE
(1) Remove wheel and tire assemblies.
(2) Secure rotor with two wheel nuts.
(3) Remove rubber access plug from back of splash
shield.
(4) Insert brake tool through access hole in splash
shield (Fig. 86). Position tool at bottom of star wheel.
(5) Rotate star wheel upward direction to expand
shoes (while facing front of vehicle).
(6) Expand shoes until light drag is experienced.
Then back off adjuster screw only enough to elimi-
nate drag.
(7) Install plug in splash shield access hole.
(8) Install wheel and tire assemblies.
Fig. 83 Lower Spring
1 - REAR SHOE
2 - NEEDLENOSE PLIERS
3 - ADJUSTER SCREW
4 - LOWER SPRING
Fig. 84 Upper Spring
1 - BRAKE PLIERS
2 - REAR SHOE
3 - UPPER SPRING
Fig. 85 Hold-Down Clip And Pin
1 - HOLD-DOWN CLIP
2 - HOLD-DOWN PIN
Fig. 86 Park Brake Shoe Adjustment
1 - ACCESS HOLE
2 - BRAKE ADJUSTING TOOL
3 - SPLASH SHIELD
5 - 40 BRAKES - BASEWJ
SHOES (Continued)
Page 320 of 2199

Programmable Communications Interface (PCI) data
bus network.
For diagnosis of the HSM, MHSM or the PCI data
bus, a DRBIIItscan tool and the proper Diagnostic
Procedures manual are recommended. The HSM or
MHSM cannot be repaired and, if faulty or damaged,
it must be replaced.
OPERATION
The MSM receives hard wired inputs from the
power seat switch and the potentiometers on each of
the driver side power seat motors. The MSM receives
messages over the PCI data bus from the Driver
Door Module (DDM) (memory switch status), the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) (vehicle speed sta-
tus), and the Body Control Module (seat belt switch
status).The MSM will prevent the seat memory recall
function from being initiated if the driver side seat
belt is buckled, if the transmission gear selector lever
is not in the Park or Neutral positions, or if the vehi-
cle is moving.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATED SEAT
MODULE
Visually inspect the related wiring harness connec-
tors. Look for broken, bent, pushed out, or corroded
terminals. If any of the above conditions are present,
repair as necessary. If not, use a DRBIIItscan tool
and the proper Diagnostic Procedures Manual to test
the HSM or MHSM. For complete circuit diagrams,
refer toPower Seat Premium I/IIIin Wiring Dia-
grams.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the driver side front bucket seat from
the power seat track unit. Refer toBucket Seat
Track Adjusterin Body for the procedure.
(3) Lift the heated seat module off of the power
seat track and disconnect the power seat wire har-
ness connectors (Fig. 10).
(4) Remove the module from the bracket.
Fig. 9 Heated Seat Module Remove/Install
1 - NUT (4)
2 - SEAT CUSHION FRAME
3 - POWER SEAT TRACK
4 - STUD (4)
5 - MODULE
6 - BRACKET
Fig. 10 Heated Seat Module Remove/Install
1 - NUT (4)
2 - SEAT CUSHION FRAME
3 - POWER SEAT TRACK
4 - STUD (4)
5 - MODULE
6 - BRACKET
WJELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E - 11
MEMORY HEATED SEAT/MIRROR MODULE (Continued)
Page 330 of 2199
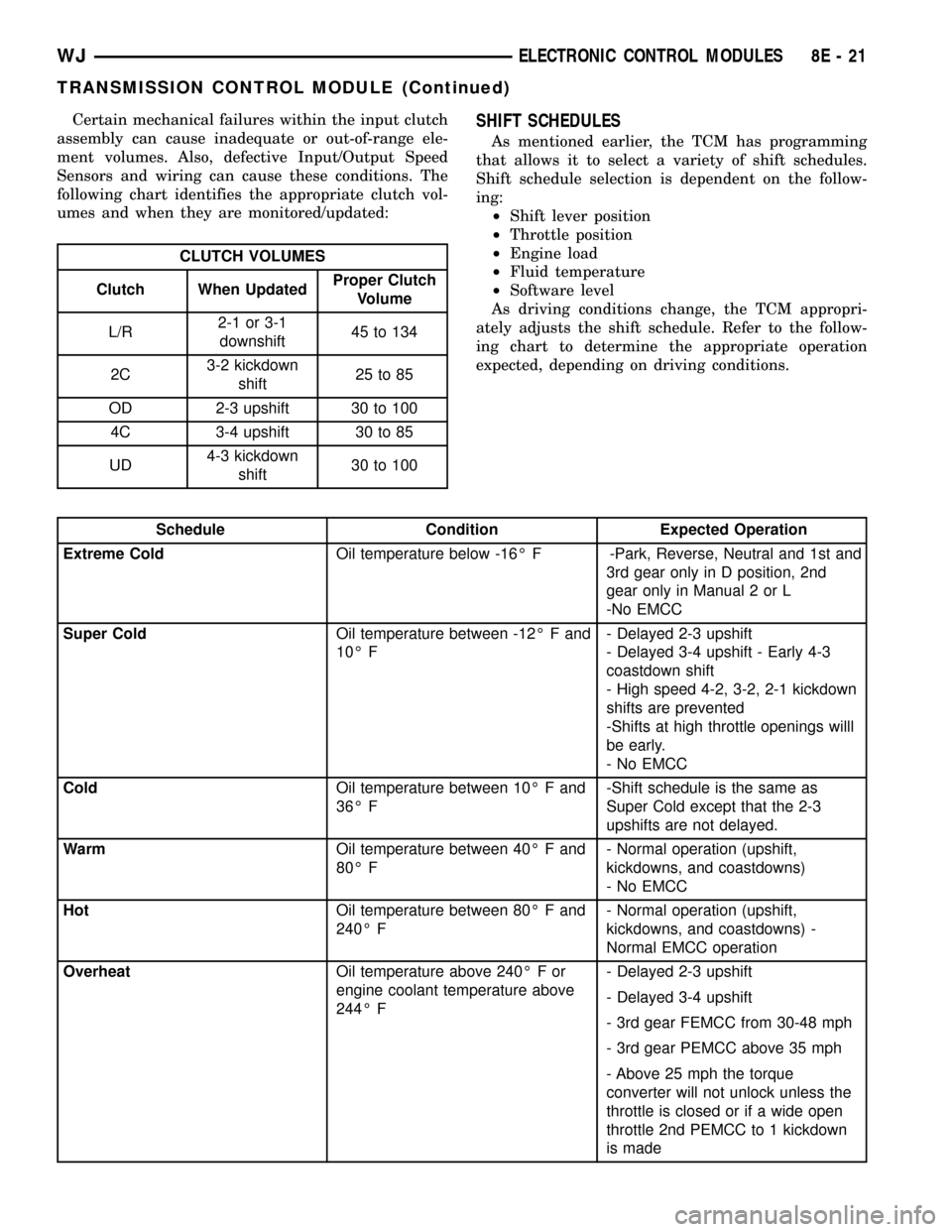
Certain mechanical failures within the input clutch
assembly can cause inadequate or out-of-range ele-
ment volumes. Also, defective Input/Output Speed
Sensors and wiring can cause these conditions. The
following chart identifies the appropriate clutch vol-
umes and when they are monitored/updated:
CLUTCH VOLUMES
Clutch When UpdatedProper Clutch
Volume
L/R2-1 or 3-1
downshift45 to 134
2C3-2 kickdown
shift25 to 85
OD 2-3 upshift 30 to 100
4C 3-4 upshift 30 to 85
UD4-3 kickdown
shift30 to 100
SHIFT SCHEDULES
As mentioned earlier, the TCM has programming
that allows it to select a variety of shift schedules.
Shift schedule selection is dependent on the follow-
ing:
²Shift lever position
²Throttle position
²Engine load
²Fluid temperature
²Software level
As driving conditions change, the TCM appropri-
ately adjusts the shift schedule. Refer to the follow-
ing chart to determine the appropriate operation
expected, depending on driving conditions.
Schedule Condition Expected Operation
Extreme ColdOil temperature below -16É F -Park, Reverse, Neutral and 1st and
3rd gear only in D position, 2nd
gear only in Manual 2 or L
-No EMCC
Super ColdOil temperature between -12É F and
10É F- Delayed 2-3 upshift
- Delayed 3-4 upshift - Early 4-3
coastdown shift
- High speed 4-2, 3-2, 2-1 kickdown
shifts are prevented
-Shifts at high throttle openings willl
be early.
- No EMCC
ColdOil temperature between 10É F and
36É F-Shift schedule is the same as
Super Cold except that the 2-3
upshifts are not delayed.
WarmOil temperature between 40É F and
80É F- Normal operation (upshift,
kickdowns, and coastdowns)
- No EMCC
HotOil temperature between 80É F and
240É F- Normal operation (upshift,
kickdowns, and coastdowns) -
Normal EMCC operation
OverheatOil temperature above 240É F or
engine coolant temperature above
244É F- Delayed 2-3 upshift
- Delayed 3-4 upshift
- 3rd gear FEMCC from 30-48 mph
- 3rd gear PEMCC above 35 mph
- Above 25 mph the torque
converter will not unlock unless the
throttle is closed or if a wide open
throttle 2nd PEMCC to 1 kickdown
is made
WJELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E - 21
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 331 of 2199

STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TCM QUICK LEARN
The quick learn procedure requires the use of the
DRBIIItscan tool.
This program allows the electronic transmission
system to recalibrate itself. This will provide the
proper transmission operation. The quick learn pro-
cedure should be performed if any of the following
procedures are performed:
²Transmission Assembly Replacement
²Transmission Control Module Replacement
²Solenoid Pack Replacement
²Clutch Plate and/or Seal Replacement
²Valve Body Replacement or ReconditionTo perform the Quick Learn Procedure, the follow-
ing conditions must be met:
²The brakes must be applied
²The engine speed must be above 500 rpm
²The throttle angle (TPS) must be less than 3
degrees
²The shift lever position must stay in PARK until
prompted to shift to overdrive
²The shift lever position must stay in overdrive
after the Shift to Overdrive prompt until the DRBt
indicates the procedure is complete
²The calculated oil temperature must be above
60É and below 200É
8E - 22 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESWJ
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 349 of 2199

The battery cables (Fig. 17) or (Fig. 18) are large
gauge, stranded copper wires sheathed within a
heavy plastic or synthetic rubber insulating jacket.
The wire used in the battery cables combines excel-
lent flexibility and reliability with high electrical cur-
rent carrying capacity. Refer toWiring Diagrams
for battery cable wire gauge information.
A clamping type female battery terminal made of
soft lead is die cast onto one end of the battery cable
wire. A square headed pinch-bolt and hex nut are
installed at the open end of the female battery termi-
nal clamp. Large eyelet type terminals are crimped
onto the opposite end of the battery cable wire and
then solder-dipped. The battery positive cable wires
have a red insulating jacket to provide visual identi-
fication and feature a larger female battery terminal
clamp to allow connection to the larger battery posi-
tive terminal post. The battery negative cable wires
have a black insulating jacket and a smaller female
battery terminal clamp.
The battery cables cannot be repaired and, if dam-
aged or faulty they must be replaced. Both the bat-
tery positive and negative cables are available for
service replacement only as a unit with the battery
wire harness, which may include portions of the wir-
ing circuits for the generator and other components
on some models. Refer toWiring Diagramsfor more
information on the various wiring circuits included in
the battery wire harness for the vehicle being ser-
viced.
OPERATION
The battery cables connect the battery terminal
posts to the vehicle electrical system. These cables
also provide a path back to the battery for electrical
current generated by the charging system for restor-
ing the voltage potential of the battery. The female
battery terminal clamps on the ends of the battery
cable wires provide a strong and reliable connection
of the battery cable to the battery terminal posts.
The terminal pinch bolts allow the female terminal
clamps to be tightened around the male terminal
posts on the top of the battery. The eyelet terminals
secured to the opposite ends of the battery cable
wires from the female battery terminal clamps pro-
vide secure and reliable connection of the battery
cables to the vehicle electrical system.
The battery positive cable terminal clamp is die
cast onto the ends of two wires. One wire has an eye-
let terminal that connects the battery positive cable
to the B(+) terminal stud of the Power Distribution
Center (PDC), and the other wire has an eyelet ter-
minal that connects the battery positive cable to the
B(+) terminal stud of the engine starter motor sole-
noid. The battery negative cable terminal clamp is
also die cast onto the ends of two wires. One wirehas an eyelet terminal that connects the battery neg-
ative cable to the vehicle powertrain through a stud
on the right side of the engine cylinder block. The
other wire has an eyelet terminal that connects the
battery negative cable to the vehicle body through a
ground screw on the right front fender inner shield,
near the battery.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BATTERY CABLES
A voltage drop test will determine if there is exces-
sive resistance in the battery cable terminal connec-
tions or the battery cable. If excessive resistance is
found in the battery cable connections, the connec-
tion point should be disassembled, cleaned of all cor-
rosion or foreign material, then reassembled.
Following reassembly, check the voltage drop for the
battery cable connection and the battery cable again
to confirm repair.
When performing the voltage drop test, it is impor-
tant to remember that the voltage drop is giving an
indication of the resistance between the two points at
which the voltmeter probes are attached.EXAM-
PLE:When testing the resistance of the battery pos-
itive cable, touch the voltmeter leads to the battery
positive cable terminal clamp and to the battery pos-
itive cable eyelet terminal at the starter solenoid
B(+) terminal stud. If you probe the battery positive
terminal post and the battery positive cable eyelet
terminal at the starter solenoid B(+) terminal stud,
you are reading the combined voltage drop in the
battery positive cable terminal clamp-to-terminal
post connection and the battery positive cable.
VOLTAGE DROP TEST
The following operation will require a voltmeter
accurate to 1/10 (0.10) volt. Before performing this
test, be certain that the following procedures are
accomplished:
²The battery is fully-charged and load tested.
Refer to Standard Procedures for the proper battery
charging and load test procedures.
²Fully engage the parking brake.
²If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic
transmission, place the gearshift selector lever in the
Park position. If the vehicle is equipped with a man-
ual transmission, place the gearshift selector lever in
the Neutral position and block the clutch pedal in the
fully depressed position.
²Verify that all lamps and accessories are turned
off.
²To prevent the engine from starting, remove the
Automatic Shut Down (ASD) relay. The ASD relay is
located in the Power Distribution Center (PDC), in
the engine compartment. See the fuse and relay lay-
out label affixed to the underside of the PDC cover
for ASD relay identification and location.
8F - 18 BATTERY SYSTEMWJ
BATTERY CABLE (Continued)
Page 361 of 2199

OPERATION
The starting system components form two separate
circuits. A high-amperage feed circuit that feeds the
starter motor between 150 and 350 amperes, and a
low-amperage control circuit that operates on less
than 20 amperes. The high-amperage feed circuit
components include the battery, the battery cables,
the contact disc portion of the starter solenoid, and
the starter motor. The low-amperage control circuit
components include the ignition switch, the park/
neutral position switch, the starter relay, the electro-
magnetic windings of the starter solenoid, and the
connecting wire harness components.
Battery voltage is supplied through the low-amper-
age control circuit to the coil battery terminal of the
starter relay when the ignition switch is turned to
the momentary Start position. The park/neutral posi-
tion switch is installed in series between the starter
relay coil ground terminal and ground. This normally
open switch prevents the starter relay from being
energized and the starter motor from operating
unless the automatic transmission gear selector is in
the Neutral or Park positions.
When the starter relay coil is energized, the nor-
mally open relay contacts close. The relay contacts
connect the relay common feed terminal to the relay
normally open terminal. The closed relay contacts
energize the starter solenoid coil windings.
The energized solenoid pull-in coil pulls in the sole-
noid plunger. The solenoid plunger pulls the shift
lever in the starter motor. This engages the starter
overrunning clutch and pinion gear with the starter
ring gear on the automatic transmission torque con-
verter drive plate.
As the solenoid plunger reaches the end of its
travel, the solenoid contact disc completes the high-
amperage starter feed circuit and energizes the sole-
noid plunger hold-in coil. Current now flows between
the solenoid battery terminal and the starter motor,
energizing the starter.Once the engine starts, the overrunning clutch pro-
tects the starter motor from damage by allowing the
starter pinion gear to spin faster than the pinion
shaft. When the driver releases the ignition switch to
the On position, the starter relay coil is de-energized.
This causes the relay contacts to open. When the
relay contacts open, the starter solenoid plunger
hold-in coil is de-energized.
When the solenoid plunger hold-in coil is de-ener-
gized, the solenoid plunger return spring returns the
plunger to its relaxed position. This causes the con-
tact disc to open the starter feed circuit, and the shift
lever to disengage the overrunning clutch and pinion
gear from the starter ring gear.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTING
SYSTEM
The battery, starting, and charging systems oper-
ate with one another, and must be tested as a com-
plete system. In order for the vehicle to start and
charge properly, all of the components involved in
these systems must perform within specifications.
Group 8A covers the Battery, Group 8B covers the
Starting Systems, and Group 8C covers the Charging
System. We have separated these systems to make it
easier to locate the information you are seeking
within this Service Manual. However, when attempt-
ing to diagnose any of these systems, it is important
that you keep their interdependency in mind.
The diagnostic procedures used in these groups
include the most basic conventional diagnostic meth-
ods, to the more sophisticated On-Board Diagnostics
(OBD) built into the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). Use of an induction-type milliampere amme-
ter, volt/ohmmeter, battery charger, carbon pile rheo-
stat (load tester), and 12-volt test lamp may be
required.
All OBD-sensed systems are monitored by the
PCM. Each monitored circuit is assigned a Diagnos-
tic Trouble Code (DTC). The PCM will store a DTC in
electronic memory for any failure it detects. Refer to
On-Board Diagnostic Test For Charging System
in the Diagnosis and Testing section of Group 8C -
Charging System for more information.
8F - 30 STARTINGWJ
STARTING (Continued)