front lower control arm JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 623 of 2199

(3) Insert the hook formation on the tip of the
wiper arm through the opening in the wiper blade
superstructure ahead of the wiper blade pivot block/
latch unit far enough to engage the pivot block with
the hook (Fig. 10).
(4) Slide the wiper blade pivot block/latch up into
the hook formation on the tip of the wiper arm until
the latch release tab snaps into its locked position.
Latch engagement will be accompanied by an audible
click.
(5) Gently lower the wiper blade onto the glass.
FRONT WIPER MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The front wiper module is secured with four screws
through rubber isolators to the cowl plenum panel
beneath the cowl plenum cover/grille panel (Fig. 11).
The ends of the wiper pivot shafts that protrude
through dedicated openings in the cowl plenum cov-
er/grille panel to drive the wiper arms and blades are
the only visible components of the front wiper mod-
ule. The front wiper module consists of the following
major components:
²Bracket- The front wiper module bracket con-
sists of a long tubular steel main member that has a
stamped pivot bracket formation near each end
where the two wiper pivots are secured. A stamped
steel mounting plate for the wiper motor is secured
with welds near the center of the main member.
²Crank Arm- The front wiper motor crank arm
is a stamped steel unit with a slotted hole on the
driven end that is secured to the wiper motor outputshaft with a nut, and a ball stud secured to the drive
end.
²Linkage- Two stamped steel drive links con-
nect the wiper motor crank arm to the pivot lever
arms. The passenger side drive link has a plastic
socket-type bushing on each end. The driver side
drive link has a plastic socket-type bushing on one
end, and a plastic sleeve-type bushing on the other
end. The socket-type bushing on one end of each
drive link is snap-fit over the ball stud on the lever
arm of its respective pivot. The driver side drive link
sleeve-type bushing end is then fit over the motor
crank arm ball stud, and the other socket-type bush-
ing of the passenger side drive link is snap-fit over
the exposed end of the wiper motor crank arm ball
stud.
²Motor- The front wiper motor is secured with
three screws to the motor mounting plate near the
center of the wiper module bracket. The wiper motor
output shaft passes through a hole in the module
bracket, where a nut secures the wiper motor crank
arm to the motor output shaft. The two-speed perma-
nent magnet wiper motor features an integral trans-
mission, an internal park switch, and an internal
automatic resetting circuit breaker.
²Pivots- The two front wiper pivots are secured
to the ends of the wiper module bracket. The crank
arms that extend from the bottom of the pivot shafts
each have a ball stud on their end. The upper end of
each pivot shaft where the wiper arms will be fas-
tened each has an externally serrated drum with a
threaded stud secured to it.
The front wiper module cannot be adjusted or
repaired. If any component of the module is faulty or
damaged, the entire front wiper module unit must be
replaced. The reinforcement bracket and stud plate
are available for service replacement.OPERATION
The front wiper module operation is controlled by
the battery current inputs received by the wiper
motor from the wiper on/off and wiper high/low
relays. The wiper motor speed is controlled by cur-
rent flow to either the low speed or the high speed
set of brushes. The park switch is a single pole, sin-
gle throw, momentary switch within the wiper motor
that is mechanically actuated by the wiper motor
transmission components. The park switch alter-
nately closes the wiper park switch sense circuit to
ground or to battery current, depending upon the
position of the wipers on the glass. This feature
allows the motor to complete its current wipe cycle
after the wiper system has been turned Off, and to
park the wiper blades in the lowest portion of the
wipe pattern. The automatic resetting circuit breaker
protects the motor from overloads. The wiper motor
Fig. 11 Front Wiper Module
1 - FRONT WIPER MODULE
2 - SCREW (4)
3 - WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
4 - LOWER COWL PLENUM PANEL
8R - 16 FRONT WIPERS/WASHERSWJ
FRONT WIPER BLADE (Continued)
Page 640 of 2199

REAR WIPERS/WASHERS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
REAR WIPERS/WASHERS
DESCRIPTION.........................33
OPERATION...........................34
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR WIPER &
WASHER SYSTEM....................35
CLEANING - REAR WIPER & WASHER
SYSTEM............................37
INSPECTION - REAR WIPER & WASHER
SYSTEM............................37
REAR WASHER HOSES/TUBES
DESCRIPTION.........................38
OPERATION...........................39
REAR WASHER NOZZLE
DESCRIPTION.........................39
OPERATION...........................39
REMOVAL.............................39
INSTALLATION.........................40
REAR WASHER PUMP/MOTOR
DESCRIPTION.........................40
OPERATION...........................40REMOVAL.............................41
INSTALLATION.........................41
REAR WIPER ARM
DESCRIPTION.........................41
OPERATION...........................42
REMOVAL.............................42
INSTALLATION.........................42
REAR WIPER BLADE
DESCRIPTION.........................43
OPERATION...........................43
REMOVAL.............................44
INSTALLATION.........................44
REAR WIPER MODULE
DESCRIPTION.........................44
OPERATION...........................45
REMOVAL.............................45
INSTALLATION.........................45
WIPER ARM PARK RAMP
REMOVAL.............................46
INSTALLATION.........................46
REAR WIPERS/WASHERS
DESCRIPTION
An electrically operated fixed interval intermittent
rear wiper and washer system is standard factory-in-
stalled equipment on this model. The rear wiper and
washer system includes the following major compo-
nents, which are described in further detail else-
where in this service information:
²Rear Washer Nozzle- The rear washer nozzle
is secured by a snap fit onto the top of the liftgate
outer panel above the liftgate glass. The rear washer
nozzle includes an integral check valve. The rear
washer system plumbing is concealed within and
routed through the interior of the vehicle.
²Rear Washer Pump/Motor- The rear washer
pump/motor unit is located in a dedicated hole on the
lower outboard side of the washer reservoir, ahead of
the left front wheel housing. The rear washer pump
mounting hole is located higher on the reservoir than
the front washer pump mounting hole.
²Rear Wiper Arm- The single rear wiper arm is
secured by a nut directly to the rear wiper module
output shaft, which extends through the liftgate
outer panel near the base of the liftgate glass.²Rear Wiper Arm Park Ramp- The molded
rubber rear wiper arm park ramp is secured with a
screw to the liftgate outer panel, just below the right
side of the liftgate glass. When the rear wiper system
is not in operation, the rear wiper arm is parked on
this ramp so that it will not interfere with or be
damaged by liftgate flip-up glass operation.
²Rear Wiper Blade- The single rear wiper
blade is secured to the rear wiper arm, and is moved
off of the liftgate glass when the rear wiper system is
not in operation.
²Rear Wiper Module- The rear wiper module
output shaft is the only visible component of the rear
wiper module. The remainder of the module is con-
cealed within the liftgate beneath the liftgate glass
opening. The rear wiper module includes the module
bracket, the rear wiper motor, and the rear wiper
module electronic control circuitry.
²Right Multi-Function Switch- The right
(wiper) multi-function switch is secured to the right
side of the multi-function switch mounting housing
near the top of the steering column. Only the control
stalk for the right multi-function switch is visible,
the remainder of the switch is concealed beneath the
steering column shrouds. The right multi-function
switch contains all of the switches and control cir-
cuitry for both the front and rear wiper and washer
systems.
WJREAR WIPERS/WASHERS 8R - 33
Page 1177 of 2199
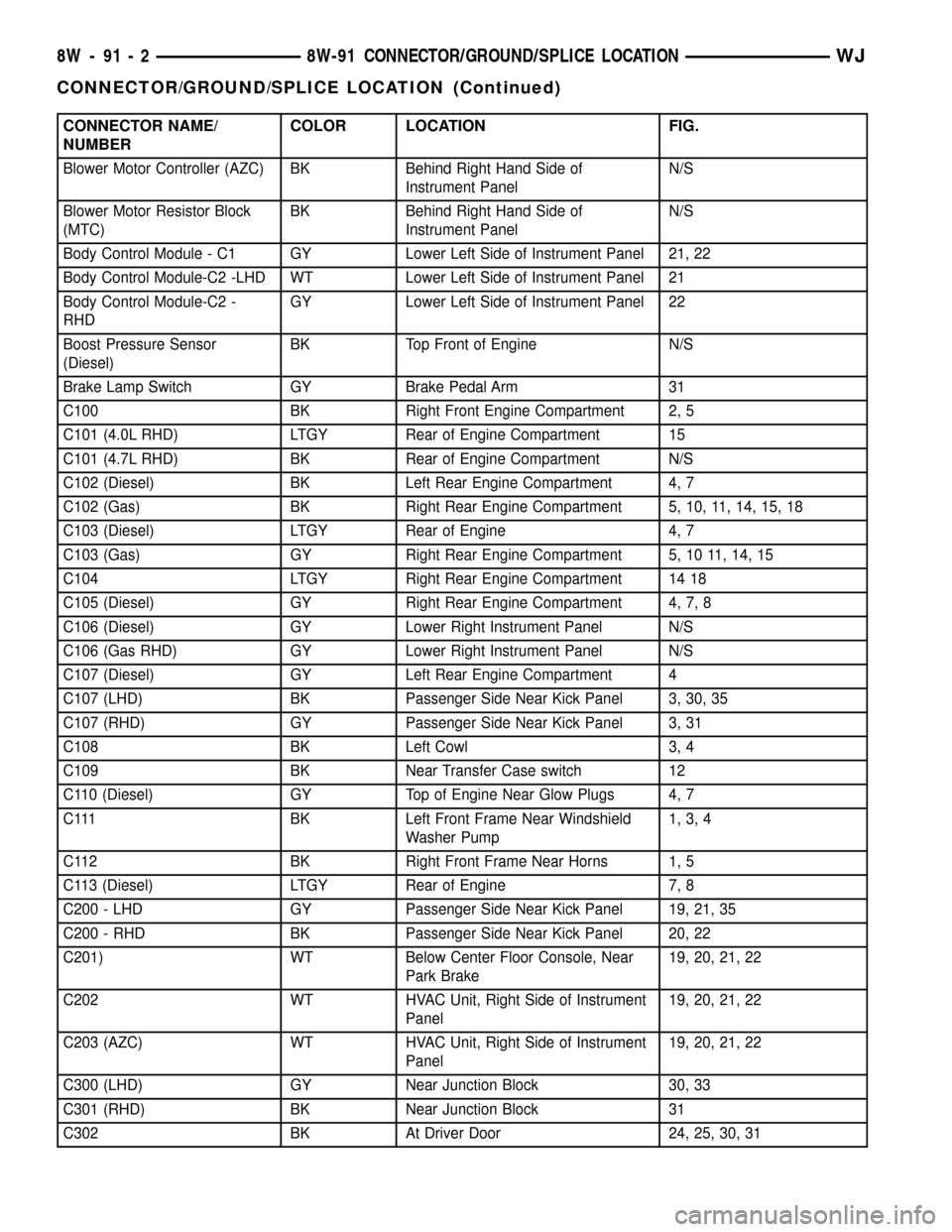
CONNECTOR NAME/
NUMBERCOLOR LOCATION FIG.
Blower Motor Controller (AZC) BK Behind Right Hand Side of
Instrument PanelN/S
Blower Motor Resistor Block
(MTC)BK Behind Right Hand Side of
Instrument PanelN/S
Body Control Module - C1 GY Lower Left Side of Instrument Panel 21, 22
Body Control Module-C2 -LHD WT Lower Left Side of Instrument Panel 21
Body Control Module-C2 -
RHDGY Lower Left Side of Instrument Panel 22
Boost Pressure Sensor
(Diesel)BK Top Front of Engine N/S
Brake Lamp Switch GY Brake Pedal Arm 31
C100 BK Right Front Engine Compartment 2, 5
C101 (4.0L RHD) LTGY Rear of Engine Compartment 15
C101 (4.7L RHD) BK Rear of Engine Compartment N/S
C102 (Diesel) BK Left Rear Engine Compartment 4, 7
C102 (Gas) BK Right Rear Engine Compartment 5, 10, 11, 14, 15, 18
C103 (Diesel) LTGY Rear of Engine 4, 7
C103 (Gas) GY Right Rear Engine Compartment 5, 10 11, 14, 15
C104 LTGY Right Rear Engine Compartment 14 18
C105 (Diesel) GY Right Rear Engine Compartment 4, 7, 8
C106 (Diesel) GY Lower Right Instrument Panel N/S
C106 (Gas RHD) GY Lower Right Instrument Panel N/S
C107 (Diesel) GY Left Rear Engine Compartment 4
C107 (LHD) BK Passenger Side Near Kick Panel 3, 30, 35
C107 (RHD) GY Passenger Side Near Kick Panel 3, 31
C108 BK Left Cowl 3, 4
C109 BK Near Transfer Case switch 12
C110 (Diesel) GY Top of Engine Near Glow Plugs 4, 7
C111 BK Left Front Frame Near Windshield
Washer Pump1, 3, 4
C112 BK Right Front Frame Near Horns 1, 5
C113 (Diesel) LTGY Rear of Engine 7, 8
C200 - LHD GY Passenger Side Near Kick Panel 19, 21, 35
C200 - RHD BK Passenger Side Near Kick Panel 20, 22
C201) WT Below Center Floor Console, Near
Park Brake19, 20, 21, 22
C202 WT HVAC Unit, Right Side of Instrument
Panel19, 20, 21, 22
C203 (AZC) WT HVAC Unit, Right Side of Instrument
Panel19, 20, 21, 22
C300 (LHD) GY Near Junction Block 30, 33
C301 (RHD) BK Near Junction Block 31
C302 BK At Driver Door 24, 25, 30, 31
8W - 91 - 2 8W-91 CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE LOCATIONWJ
CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE LOCATION (Continued)
Page 1315 of 2199

(13) Disconnect the engine block heater power
cable from the block heater.
(14) Lower vehicle.
(15) Remove throttle body resonator assembly and
inlet hose.
(16) Disconnect throttle and speed control cables.
(17) Disconnect tube from both the left and right
side crankcase breathers, then remove the breathers
(Fig. 5).
(18) Discharge A/C system (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).(19) Remove radiator fan (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - REMOVAL) and acces-
sory drive belt (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ACCESSORY
DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - REMOVAL).
(20) Remove A/C compressor (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C COM-
PRESSOR - REMOVAL).
(21) Disconnect transmission oil cooler lines at the
radiator.
(22) Disconnect radiator lower hose at the thermo-
stat housing.
(23) Remove A/C condenser (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C CON-
DENSER - REMOVAL).
(24) Remove radiator (Refer to 7 - COOLING/EN-
GINE/RADIATOR - REMOVAL).
(25) Remove generator (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
CHARGING/GENERATOR - REMOVAL).
(26) Disconnect the two heater hoses from the tim-
ing chain cover.
(27) Disconnect engine harness at the following
points :
²Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor (Fig. 6)
²Fuel Injectors
²Throttle Position (TPS) Switch
²Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor
²Engine Oil Pressure Switch
²Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
²Coil Over Plugs
(28) Release fuel rail pressure (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE) then disconnect the fuel supply quick connect
fitting at the fuel rail (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/
FUEL DELIVERY/QUICK CONNECT FITTING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(29) Remove power steering pump and position out
of the way.
(30) Disconnect ground straps from the left side of
the engine.
(31) Install Engine Lifting Fixture Special Tool
8347 (Fig. 7)following these steps.
²Holding the lifting fixture at a slight angle, slide
the large bore in the front plate over the hex portion
of the lifting stud.
²Position the two remaining fixture arms onto
the two lifting studs in the cylinder heads.
²Pull foward and upward on the lifting fixture so
that the lifting stud rest in the slotted area below the
large bore.
²Secure the lifting fixture to the three studs
using three 7/16 ± 14 N/C locknuts.
²Make sure the lifting loop in the lifting fixture is
in the last hole (closest to the throttle body) to min-
imize the angle of engine during removal.
Fig. 4 Crankshaft Position Sensor
1 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
2 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER
3 - CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
4 - RIGHT SIDE CYLINDER BLOCK
Fig. 5 Crankcase Breather Connection Points
1 - CRANKCASE BREATHERS
9 - 72 ENGINE - 4.7LWJ
ENGINE - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 1421 of 2199

FUEL DELIVERY
DESCRIPTION
The fuel delivery system consists of:
²the fuel pump module containing the electric
fuel pump, fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor)
and a separate fuel filter located at bottom of pump
module
²a separate combination fuel filter/fuel pressure
regulator
²fuel tubes/lines/hoses
²quick-connect fittings
²fuel injector rail
²fuel injectors
²fuel tank
²fuel tank filler/vent tube assembly
²fuel tank filler tube cap
²accelerator pedal
²throttle cable
OPERATION
The fuel tank assembly consists of: the fuel tank,
fuel tank shield, fuel tank straps, fuel pump module
assembly, fuel pump module locknut/gasket, and fuel
tank check valve (refer to Emission Control System
for fuel tank check valve information).
A fuel filler/vent tube assembly using a pressure/
vacuum, 1/4 turn fuel filler cap is used. The fuel
filler tube contains a flap door located below the fuel
fill cap.
Also to be considered part of the fuel system is the
evaporation control system. This is designed to
reduce the emission of fuel vapors into the atmo-
sphere. The description and function of the Evapora-
tive Control System is found in Emission Control
Systems.
Both fuel filters (at bottom of fuel pump module
and within fuel pressure regulator) are designed for
extended service. They do not require normal sched-
uled maintenance. Filters should only be replaced if
a diagnostic procedure indicates to do so.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
FUEL PRESSURE LEAK DOWN TEST
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pump
Pressure Test and Fuel Pump Capacity Test.
Check Valve Operation:The electric fuel pump
outlet contains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel
flow back into the tank and to maintain fuel supply
line pressure (engine warm) when pump is not oper-
ational. It is also used to keep the fuel supply line
full of gasoline when pump is not operational. After
the vehicle has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop
to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline willremain in fuel supply line between the check valve
and fuel injectors.Fuel pressure that has
dropped to 0 psi on a cooled down vehicle
(engine off) is a normal condition.When the elec-
tric fuel pump is activated, fuel pressure should
immediately(1±2 seconds) rise to specification.
Abnormally long periods of cranking to restart a
hotengine that has been shut down for a short
period of time may be caused by:
²Fuel pressure bleeding past a fuel injector(s).
²Fuel pressure bleeding past the check valve in
the fuel pump module.
²A defective fuel filter/pressure regulator.
Two #6539, 5/16º, Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter
Hose Tools are required for the following tests.
(1) Release fuel system pressure. Refer to Fuel
Pressure Release Procedure.
(2) Raise vehicle.
Fuel Line Identification:The fuel filter/pressure
regulator is located in front of the fuel tank and
above the rear axle. It is transversely mounted to a
chassis crossmember (left-to-right). The filter/regula-
tor is equipped with 3 fuel line fittings (2 at one end
and 1 at the other end). The single fitting facing the
left side of the vehicle is the supply line to the fuel
rail (Fig. 1) . The 2 fittings facing the right side of
the vehicle are connected to the fuel tank. Of these 2
fittings, the fitting towards thefrontis used for fuel
return to the fuel tank. The fitting towards therear
is a pressure line. Thisrearfitting must be discon-
nected for the following step.
(3) See previous step. Disconnect fuel pressure line
atrearof filter/regulator. This is a 5/169quick-con-
nect fitting (Fig. 1) . Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings
for procedures.
(4) Obtain correct Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter
Hose Tool # 6539 for 5/16º fuel lines. Connect one
end of this Special Tool into the disconnected fuel
pressure line. Connect the other end of the Tool into
fitting on filter/regulator.
(5) Lower vehicle.
(6) Disconnect the fuel inlet line at fuel rail. Refer
to Quick-Connect Fittings for procedures. On some
engines, air cleaner housing removal may be neces-
sary before fuel line disconnection.
(7) Obtain a second Fuel Line Pressure Test
Adapter Hose Tool # 6539 for 5/16º fuel lines. Con-
nect this tool between disconnected fuel line and fuel
rail (Fig. 2) .
(8) Connect the 0-414 kPa (0-60 psi) fuel pressure
test gauge (from Gauge Set 5069) to the test port on
the appropriate Adaptor Tool.NOTE: The DRB III
Scan Tool along with the PEP module, the 500
psi pressure transducer, and the transducer-to-
test port adapter may also be used in place of
the fuel pressure gauge.
14 - 2 FUEL DELIVERYWJ
Page 2026 of 2199

WELD LOCATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS
WELD LOCATIONS
INDEX
DESCRIPTION FIGURE
RADIATOR SUPPORT BRACKETS 49
FRONT SUSPENSION SUPPORT REINFORCEMENT 50
FRONT LOWER CROSSMEMBER TO COWL SIDE PANEL 51
FRONT SILL TO LOWER CROSSMEMBER 52
FRONT FENDER MOUNTING BRACKET AND REINFORCEMENT 53
FRONT SUSPENSION SUPPORT TO SILLS AND COWL SIDE PANEL 54
LEFT INSTRUMENT PANEL BRACKET TO COWL SIDE PANEL 55
COWL SIDE UPPER REINFORCEMENT TO COWL SIDE AND FRONT SUSPENSION
SUPPORT56
COWL SIDE PANEL TO DASH PANEL AND INNER BODYSIDE PANEL AND SILL 57
PLENUM ASSEMBLY TO COWL SIDE PANEL 58
FRONT LOWER CROSSMEMBER 59
FRONT SUSPENSION SUPPORT TO DASH 60
WIPER MOUNTING BRACKETS TO PLENUM ASSEMBLY 61
COWL TOP AND PLENUM ASSEMBLY 62
LOWER PLENUM REINFORCEMENT TO LOWER PLENUM PANEL 63
DASH PANEL TO LOWER PLENUM PANEL 64
PLENUM ASSEMBLY TO COWL 65
COWL PANEL TO BODYSIDE SILL 66
COWL PANEL TO FRONT FLOOR PAN 67
FRONT SILLS TO DASH AND FRONT FLOOR PAN 68
COWL SIDE PANEL DASH INNER BODYSIDE AND OUTER BODYSIDE PANELS 69
UPPER FRONT INNER PILLAR TO ROOF AND COWL 70
DOOR OPENINGS 71
B-PILLAR REINFORCEMENT TO INNER BODYSIDE APERTURE 72
REAR QUARTER WINDOW TO BODYSIDE APERTURE INNER AND OUTER 73
LOWER REAR QUARTER TO BODYSIDE APERTURE INNER AND OUTER 74
INNER TRACK BAR, LOWER CONTROL ARM AND TRANSMISSION CROSSMEMBER
BRACKETS TO FRONT SILLS75
TRANSMISSION CROSSMEMBER BRACKET AND REINFORCEMENT TO FRONT
SILLS76
UPPER SILLS AND UPPER CONTROL ARM REINFORCEMENT AND BRACKETS TO
FRONT SILLS77
REINFORCEMENT TO FRONT OUTER SILLS 78
FRONT INNER SILL TO FRONT OUTER SILL 79
OUTER TRACK BAR BRACKET TO FRONT OUTER SILL 80
WJBODY STRUCTURE 23 - 153
Page 2027 of 2199

DESCRIPTION FIGURE
REINFORCEMENT FOR FRONT ENGINE MOUNTING AND STEERING GEAR TO
FRONT INNER SILL81
LARGE AND SMALL SWAY BAR TAPPING PLATES TO FRONT INNER SILLS 82
FRONT AND REAR DOOR HINGE TAPPING PLATES 83
REAR DOOR STRIKER REINFORCEMENT 84
TAIL LAMP MOUNTING PANELS 85
ROOF PANEL TO BODYSIDE APERTURE 86
ROOF PANEL TO REAR HEADER 87
UPPER REAR HEADER TO LOWER HEADER 88
FRONT HEADER AND ROOF BOWS TO INNER PANEL 89
FRONT SEAT/SHOULDER BELT TO INNER PANEL REINFORCEMENT 90
REAR SEAT/SHOULDER BELT TO INNER PANEL REINFORCEMENT 91
FUEL FILLER GUSSET TO INNER QUARTER PANEL 92
FRONT FLOOR PAN TO SILL REINFORCEMENT 93
CENTER FLOOR PAN TO REAR SEAT CROSSMEMBER 94
FRONT FLOOR PAN TO FRONT SEAT REINFORCEMENT AND RAILS 95
CENTER FLOOR PAN TO UPPER CONTROL ARM CROSSMEMBER AND RAILS 96
REAR FLOOR PAN TO RAILS AND SPRING GUIDE CROSSMEMBER 97
REAR RAILS 98
UPPER CONTROL ARM CROSSMEMBER TO REAR RAIL 99
REAR RAIL REINFORCEMENT TO REAR RAILS 100
UPPER CONTROL ARM REINFORCEMENTS TO REAR RAIL 101
OUTER TRANSMISSION CROSSMEMBER REINFORCEMENT TO RAIL AND
BODYSIDE SILL102
BODYSIDE SILL TO FLOOR PAN 103
REAR RAILS TO REAR CROSSMEMBER 104
INNER WHEELHOUSE TO FLOOR PAN 105
INNER WHEELHOUSE TO INNER BODYSIDE APERTURE AND FLOOR PAN 106
OUTER WHEELHOUSE TO OUTER BODYSIDE APERTURE 107
OUTER WHEELHOUSE TO INNER BODYSIDE APERTURE 108
INNER BODYSIDE APERTURE TO OUTER BODYSIDE APERTURE 109
REAR INBOARD SEAT BELT REINFORCEMENT TO FLOOR PAN 110
23 - 154 BODY STRUCTUREWJ
WELD LOCATIONS (Continued)
Page 2048 of 2199
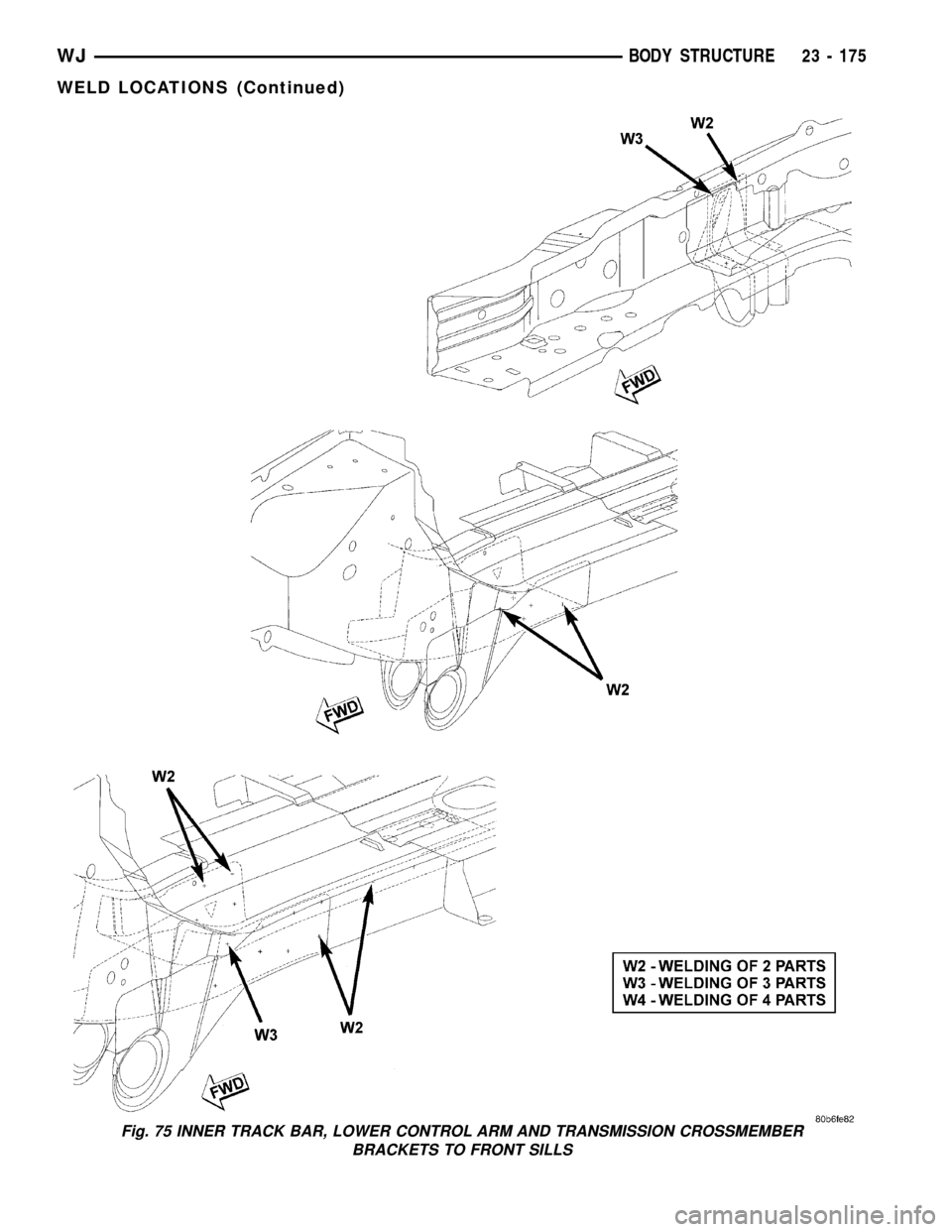
Fig. 75 INNER TRACK BAR, LOWER CONTROL ARM AND TRANSMISSION CROSSMEMBER
BRACKETS TO FRONT SILLS
WJBODY STRUCTURE 23 - 175
WELD LOCATIONS (Continued)
Page 2079 of 2199

OPERATION
OPERATION - HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONER
Outside fresh air enters the vehicle through the
cowl top opening at the base of the windshield, and
passes through a plenum chamber to the HVAC sys-
tem blower housing. Air flow velocity can then be
adjusted with the blower motor speed selector switch
on the a/c heater control panel. The air intake open-
ings must be kept free of snow, ice, leaves, and other
obstructions for the HVAC system to receive a suffi-
cient volume of outside air.
It is also important to keep the air intake openings
clear of debris because leaf particles and other debris
that is small enough to pass through the cowl ple-
num screen can accumulate within the HVAC hous-
ing. The closed, warm, damp and dark environment
created within the HVAC housing is ideal for the
growth of certain molds, mildews and other fungi.
Any accumulation of decaying plant matter provides
an additional food source for fungal spores, which
enter the housing with the fresh air. Excess debris,
as well as objectionable odors created by decaying
plant matter and growing fungi can be discharged
into the passenger compartment during HVAC sys-
tem operation.
Both the manual and AZC heater and air condi-
tioner are blend-air type systems. In a blend-air sys-
tem, a blend door controls the amount of
unconditioned air (or cooled air from the evaporator)
that is allowed to flow through, or around, the heater
core. A temperature control knob on the a/c heater
control panel determines the discharge air tempera-
ture by energizing the blend door actuator, which
operates the blend door. This allows an almost imme-
diate control of the output air temperature of the sys-
tem. The AZC system will have separate blend doors
and temperature controls for each front seat occu-
pant.
The mode control knob on the a/c heater control
panel is used to direct the conditioned air to the
selected system outlets. On manual temperature con-
trol systems, the mode control knob switches engine
vacuum to control the mode doors, which are oper-
ated by vacuum actuators. On AZC systems, the
mode control knob switches electrical current to con-
trol the mode doors, which are operated by electronic
actuators.
The outside air intake can be shut off on manual
temperature control systems by selecting the Recircu-
lation Mode with the mode control knob. The outside
air intake can be shut off on Automatic Zone Control
(AZC) type system by pushing the Recirculation
Mode button. This will operate the recirculation door
that closes off the outside fresh air intake and recir-
culates the air that is already inside the vehicle.The air conditioner for all models is designed for
the use of non-CFC, R-134a refrigerant. The air con-
ditioning system has an evaporator to cool and dehu-
midify the incoming air prior to blending it with the
heated air. This air conditioning system uses a ther-
mal expansion valve to meter refrigerant flow to the
evaporator coil. To maintain minimum evaporator
temperature and prevent evaporator freezing, the
system utilizes an evaporator thermister probe with
the appropriate operating logic located in the body
control module (BCM).
OPERATION - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM SERVICE
PORT
The high pressure service port is located on the liq-
uid line near the receiver/drier. The low pressure ser-
vice port is located on the suction line near the
evaporator at the rear of the engine compartment.
Each of the service ports has a threaded plastic
protective cap installed over it from the factory. After
servicing the refrigerant system, always reinstall
both of the service port caps.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C
PERFORMANCE
The air conditioning system is designed to provide
the passenger compartment with low temperature
and low specific humidity air. The evaporator, located
in the HVAC housing on the dash panel below the
instrument panel, is cooled to temperatures near the
freezing point. As warm damp air passes through the
cooled evaporator, the air transfers its heat to the
refrigerant in the evaporator and the moisture in the
air condenses on the evaporator fins. During periods
of high heat and humidity, an air conditioning sys-
tem will be more effective in the Recirculation Mode.
With the system in the Recirculation Mode, only air
from the passenger compartment passes through the
evaporator. As the passenger compartment air dehu-
midifies, the air conditioning system performance
levels improve.
Humidity has an important bearing on the tempera-
ture of the air delivered to the interior of the vehicle. It
is important to understand the effect that humidity has
on the performance of the air conditioning system.
When humidity is high, the evaporator has to perform a
double duty. It must lower the air temperature, and it
must lower the temperature of the moisture in the air
that condenses on the evaporator fins. Condensing the
moisture in the air transfers heat energy into the evap-
orator fins and tubing. This reduces the amount of heat
the evaporator can absorb from the air. High humidity
greatly reduces the ability of the evaporator to lower
the temperature of the air.
24 - 2 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGWJ
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2133 of 2199

(a) If the refrigerant system fails to reach the
specified vacuum, the system has a leak that must
be corrected. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CON-
DITIONING/PLUMBING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM LEAKS)
(b) If the refrigerant system maintains the spec-
ified vacuum for five minutes, restart the vacuum
pump, open the suction and discharge valves and
evacuate the system for an additional ten minutes.
(3) Close all of the valves, and turn off the charg-
ing station vacuum pump.
(4) The refrigerant system is now ready to be
charged with R-134a refrigerant. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM CHARGE)
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM CHARGE
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
After the refrigerant system has been tested for
leaks and evacuated, a refrigerant charge can be
injected into the system. (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - SPECIFICA-
TIONS - CHARGE CAPACITY)
A R-134a refrigerant recovery/recycling/charging
station that meets SAE Standard J2210 must be
used to charge the refrigerant system with R-134a
refrigerant. Refer to the operating instructions sup-
plied by the equipment manufacturer for proper care
and use of this equipment.
PARTIAL CHARGE METHOD
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
The partial charge method is used to add a partial
charge to a refrigerant system that is low on refrig-
erant. To perform this procedure the evaporator inlet
and outlet tube temperatures are measured. The
temperature difference is measured with a tempera-
ture meter with one or two clamp-on thermocouple
probes. The difference between the evaporator inlet
and outlet tube temperatures will determine the
amount of refrigerant needed.Before adding a partial refrigerant charge, check
for refrigerant system leaks. (Refer to 24 - HEATING
& AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM LEAKS)
If a leak is found, make the necessary repairs before
attempting a full or partial refrigerant charge.
(1) Attach a manifold gauge set to the refrigerant
system service ports.
(2) Attach the two clamp-on thermocouple probes
to the inlet and outlet tubes of the evaporator coil.
²If a single thermocouple probe is used, attach
the probe to the evaporator inlet tube just before the
collar of the refrigerant line connector fitting. The
probe must make contact with the bottom surface of
the evaporator inlet tube.
²If dual thermocouple probes are used, attach
probe 1 to the evaporator inlet tube, and probe 2 to
the evaporator outlet tube. Attach both probes to the
evaporator tubes just before the collar of the refrig-
erant line connector fittings. The probes must make
contact with the bottom surfaces of the evaporator
inlet and outlet tubes.
(3) Open all of the windows or doors of the passen-
ger compartment.
(4) Set the A/C button on the A/C Heater controls
to the on position, the temperature control knob in
the full cool position, select Recirculation Mode, and
place the blower motor switch in the highest speed
position.
(5) Start the engine and hold the engine idle speed
at 1,000 rpm. Allow the engine to warm up to normal
operating temperature.
(6) The compressor clutch may cycle, depending
upon ambient temperature, humidity, and the refrig-
erant system charge level.
(7) Hold the engine idle speed at 1,000 rpm.
(8) Allow three to five minutes for the refrigerant
system to stabilize, then record the temperatures of
the evaporator inlet and outlet tubes.
²If a single probe is used, record the temperature
of the evaporator inlet tube. Then remove the probe
from the inlet tube and attach it to the evaporator
outlet tube just before the collar of the refrigerant
line connector fitting. The probe must make contact
with the bottom surface of the evaporator outlet tube.
Allow the thermocouple and meter time to stabilize,
then record the temperature of the evaporator outlet
tube. Subtract the inlet tube temperature reading
from the outlet tube temperature reading.
²If dual probes are used, record the temperatures
of both the evaporator inlet and outlet tubes. Then
subtract the inlet tube temperature reading from the
outlet tube temperature reading.
(9) If the measured temperature differential is
higher than 22É C to 26É C (40É F to 47É F), add 0.4
kilograms (14 ounces) of refrigerant.
24 - 56 PLUMBINGWJ
PLUMBING (Continued)