4.0 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 1590 of 2199

PROCEDURE TWO
(1) Start engine and apply parking brake.
(2) Shift the transmission into DRIVE for approxi-
mately 2 seconds.
(3) Shift the transmission into REVERSE for
approximately 2 seconds.
(4) Shift the transmission into PARK.
(5) Hook up DRBtscan tool and select engine.
(6) Select sensors.
(7) Read the transmission temperature value.
(8) Compare the fluid temperature value with the
figure. (Fig. 88)
(9) Adjust transmission fluid level shown on the
dipstick according to the figure.NOTE: After adding any fluid to the transmission,
wait a minimum of 2 minutes for the oil to fully
drain from the fill tube into the transmission before
rechecking the fluid level.
(10) Check transmission for leaks.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND FILTER
REPLACEMENT
For proper service intervals (Refer to LUBRICA-
TION & MAINTENANCE/MAINTENANCE SCHED-
ULES - DESCRIPTION). The service fluid fill after a
filter change is approximately 3.8 liters (4.0 quarts).
REMOVAL
(1) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
(2) Place a large diameter shallow drain pan
beneath the transmission pan.
(3) Remove bolts holding front and sides of pan to
transmission (Fig. 89).
(4) Loosen bolts holding rear of pan to transmis-
sion.
(5) Slowly separate front of pan and gasket away
from transmission allowing the fluid to drain into
drain pan.
(6) Hold up pan and remove remaining bolt hold-
ing pan to transmission.
Fig. 88 42/44RE Fluid Fill Graph
Fig. 87 Dipstick Fluid Level Marks - Typical
1 - DIPSTICK
2 - MAXIMUM CORRECT FLUID LEVEL
3 - ACCEPTABLE FLUID LEVEL
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 71
FLUID AND FILTER (Continued)
Page 1863 of 2199

STANDARD PROCEDURE - MATCH MOUNTING
Tires and wheels are currently not match mounted
at the factory. Match mounting is a technique used to
reduce runout in the wheel/tire assembly. This means
that the high spot of the tire is aligned with the low
spot on the wheel rim. The high spot on the tire is
marked with a paint mark or a bright colored adhe-
sive label on the outboard sidewall. The low spot on
the rim is identified with a label on the outside of the
rim and a dot on the inside of the rim. If the outside
label has been removed the tire will have to be
removed to locate the dot on the inside of the rim.
Before dismounting a tire from its wheel, a refer-
ence mark should be placed on the tire at the valve
stem location. This reference will ensure that it is
remounted in the original position on the wheel.
(1) Use a dial indicator to locate the high spot of
the tire on the center tread rib (Fig. 6). Record the
indicator reading and mark the high spot on the tire.
Place a mark on the tire at the valve stem location
(Fig. 7).
(2) Break down the tire and remount it 180
degrees on the rim (Fig. 8).
(3) Measure the total runout again and mark the
tire to indicate the high spot.
(4) If runout is still excessive use the following
procedures.
(a) If the high spot is within 101.6 mm (4.0 in.)
of the first spot and is still excessive, replace the
tire.
(b) If the high spot is within 101.6 mm (4.0 in.)
of the first spot on the wheel, the wheel may be out
of specifications,(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
(c) If the high spot is NOT within 101.6 mm (4.0
in.) of either high spot, draw an arrow on the tread
from second high spot to first. Break down the tire
and remount it 90 degrees on rim in that direction
(Fig. 9). This procedure will normally reduce the
runout to an acceptable amount.
Fig. 6 Dial Indicator
Fig. 7 First Measurement On Tire
1 - REFERENCE MARK
2 - 1ST MEASUREMENT
HIGH SPOT MARK TIRE AND RIM
3 - WHEEL
4 - VALVE STEM
Fig. 8 Remount Tire 180 Degrees
1 - VALVE STEM
2 - REFERENCE MARK
22 - 4 TIRES/WHEELSWJ
TIRES/WHEELS (Continued)
Page 1868 of 2199

CLEANING
Remove the protective coating on the tires before
delivery of a vehicle. This coating may cause deteri-
oration of the tires.
To remove the protective coating, apply warm
water and let it soak for a few minutes. Afterwards,
scrub the coating away with a soft bristle brush.
Steam cleaning may also be used to remove the coat-
ing.
NOTE: DO NOT use gasoline, mineral oil, oil-based
solvent or a wire brush for cleaning.
SPECIFICATIONS
TIRES
SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
TIRE P225/75R16
TIRE P245/70R16
TIRE P235/65R17
SPECIFICATIONS -
SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION - RIM SPECIFICATION - TIRE
BASE LAREDO (2.7L &
4.0L)
16x7P225/75R16
OPTIONAL LAREDO
(2.7L, 4.0L, 4.7L)
16x7P245/70R16
LAREDO 4.7L (JAPAN &
AUSTRALIA)
17x7.5P235/65R17
OPTIONAL LAREDO (UP
COUNTRY)
17x7.5P235/65R17
BASE LIMITED
17x7.5P235/65R17
OPTIONAL LIMITED (UP
COUNTRY)
& OVERLAND
17x7.5P235/65R17
BASE WHEEL / SNOW
TIREP235/65R17
Fig. 16 Tire Wear Patterns
Fig. 17 Tire Repair Area
1 - REPAIRABLE AREA
WJTIRES/WHEELS 22 - 9
TIRES (Continued)
Page 2085 of 2199
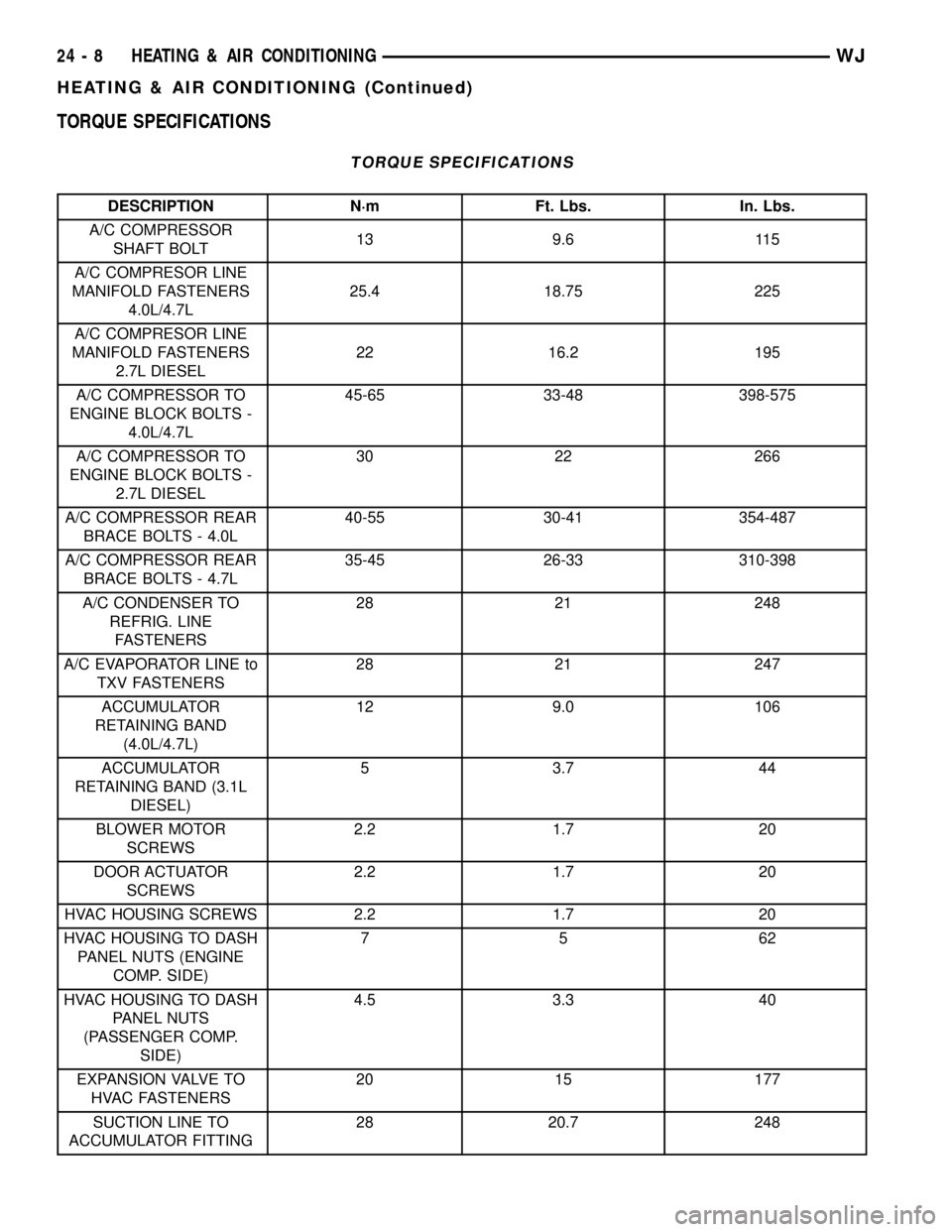
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
A/C COMPRESSOR
SHAFT BOLT13 9.6 115
A/C COMPRESOR LINE
MANIFOLD FASTENERS
4.0L/4.7L25.4 18.75 225
A/C COMPRESOR LINE
MANIFOLD FASTENERS
2.7L DIESEL22 16.2 195
A/C COMPRESSOR TO
ENGINE BLOCK BOLTS -
4.0L/4.7L45-65 33-48 398-575
A/C COMPRESSOR TO
ENGINE BLOCK BOLTS -
2.7L DIESEL30 22 266
A/C COMPRESSOR REAR
BRACE BOLTS - 4.0L40-55 30-41 354-487
A/C COMPRESSOR REAR
BRACE BOLTS - 4.7L35-45 26-33 310-398
A/C CONDENSER TO
REFRIG. LINE
FASTENERS28 21 248
A/C EVAPORATOR LINE to
TXV FASTENERS28 21 247
ACCUMULATOR
RETAINING BAND
(4.0L/4.7L)12 9.0 106
ACCUMULATOR
RETAINING BAND (3.1L
DIESEL)5 3.7 44
BLOWER MOTOR
SCREWS2.2 1.7 20
DOOR ACTUATOR
SCREWS2.2 1.7 20
HVAC HOUSING SCREWS 2.2 1.7 20
HVAC HOUSING TO DASH
PANEL NUTS (ENGINE
COMP. SIDE)75 62
HVAC HOUSING TO DASH
PANEL NUTS
(PASSENGER COMP.
SIDE)4.5 3.3 40
EXPANSION VALVE TO
HVAC FASTENERS20 15 177
SUCTION LINE TO
ACCUMULATOR FITTING28 20.7 248
24 - 8 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGWJ
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2136 of 2199

(5) Remove the (2) refrigerant line retaining bolts
that secure the suction line and discharge line to the
compressor. Install plugs in, or tape over all of the
opened refrigerant fittings.
(6) Remove the bolts that secure the compressor
(Fig. 2) or (Fig. 3) and (Fig. 4).
(7) Remove the compressor.
Fig. 2 COMPRESSOR REMOVE/INSTALL - 4.0L
ENGINE
1 - POWER STEERING PUMP MOUNTING BRACKET
2 - BOLT
3 - BRACE
4 - BOLT
5 - BOLT
6 - A/C COMPRESSOR
7 - BOLT
Fig. 3 COMPRESSOR AND A/C LINES - V8
1 - DISCHARGE LINE
2 - A/C COMPRESSOR
3 - SUCTION LINE
4 - A/C/ CONDENSOR
5 - DISCHARGE LINE TO CONDENSOR
6 - A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER SWITCH
7 - A/C/ SERVICE PORT
8 - RECEIVER DRIER
Fig. 4 COMPRESSOR REMOVE/INSTALL - V8
ENGINE - RIGHT VIEW
1 - BOLT
2 - A/C COMPRESSOR
3 - BOLT
WJPLUMBING 24 - 59
A/C COMPRESSOR (Continued)
Page 2138 of 2199

INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
Any kinks or sharp bends in the refrigerant plumb-
ing will reduce the capacity of the entire air condi-
tioning system. Kinks and sharp bends reduce the
flow of refrigerant in the system. A good rule for the
flexible hose refrigerant lines is to keep the radius of
all bends at least ten times the diameter of the hose.
In addition, the flexible hose refrigerant lines should
be routed so they are at least 80 millimeters (3
inches) from the exhaust manifold.
High pressures are produced in the refrigerant sys-
tem when the air conditioning compressor is operat-
ing. Extreme care must be exercised to make sure
that each of the refrigerant system connections is
pressure-tight and leak free. It is a good practice to
inspect all flexible hose refrigerant lines at least once
a year to make sure they are in good condition and
properly routed.
NOTE: If a replacement compressor is being
installed, be certain to check the refrigerant oil
level. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING/REFRIGERANT OIL - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE) Use only refrigerant oil of the type
recommended for the compressor in the vehicle.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING/REFRIGERANT OIL - DESCRIPTION)
(1) Install the compressor. Tighten the 4.0L
mounting bolts fastening the compressor to the block
to 45-65 N´m (35-50 ft. lbs.). Tighten the mounting
bolts holding the rear brace to the compressor and
block to 40-55 N´m (30-40 ft. lbs.). Tighten the 4.7L
compressor front mounting screws to 45-65 N´m
(35-50 ft. lbs.), and the rear mounting screws to
35-45 N´m (25-35 ft. lbs.).
(2) Remove the tape or plugs from all of the
opened refrigerant line fittings. Install the suction
line and discharge line fittings to the manifold on the
compressor. Tighten the mounting bolts to 25.4 N´m
(225 in. lbs.).
(3) Install the serpentine drive belt. Refer to Cool-
ing for the procedures.
(4) Plug in the compressor clutch coil wire harness
connector.
(5) Connect the battery negative cable.(6) Evacuate the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM EVACUATE)
(7) Charge the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM CHARGE)
INSTALLATION - 2.7L TURBO DIESEL
CAUTION: Check the oil level before installing the
new compressor. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/REFRIGERANT OIL -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
Any kinks or sharp bends in the refrigerant plumb-
ing will reduce the capacity of the entire air condi-
tioning system. Kinks and sharp bends reduce the
flow of refrigerant in the system. A good rule for the
flexible hose refrigerant lines is to keep the radius of
all bends at least ten times the diameter of the hose.
In addition, the flexible hose refrigerant lines should
be routed so they are at least 80 millimeters (3
inches) from the exhaust manifold.
High pressures are produced in the refrigerant sys-
tem when the air conditioning compressor is operat-
ing. Extreme care must be exercised to make sure
that each of the refrigerant system connections is
pressure-tight and leak free. It is a good practice to
inspect all flexible hose refrigerant lines at least once
a year to make sure they are in good condition and
properly routed.
(1) Lift the compressor into position and install
the (4) mounting bolts. Torque the bolts to 41 N´m
(30 ft. lbs.).
(2) Connect the compressor clutch electrical con-
nector.
(3) Install both refrigerant lines on the compressor.
Make certain the sealing 0-rings are free of tears and
well lubricated with R-134a refrigerant oil. Torque
the line retaining bolts to 22 N´m (200 in. lbs.).
(4) Install the front splash shield (if equipped).
(5) Lower the vehicle from the hoist.
(6) Install the accessory drive belt on the compres-
sor clutch. Refer to Cooling for the procedure.
(7) Evacuate the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
WJPLUMBING 24 - 61
A/C COMPRESSOR (Continued)
Page 2179 of 2199

EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - EVAPORATION CONTROL
SYSTEM............................24
DESCRIPTION - CCV SYSTEM...........25
DESCRIPTION - PCV SYSTEM...........25
OPERATION
OPERATION - 4.0L CCV SYSTEM.........26
OPERATION - 4.7L PCV SYSTEM.........26
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE - EVAPORATION SYSTEM.......27
CCV HOSE
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CCV SYSTEM -
4.0L................................28
REMOVAL - FIXED ORIFICE FITTING........28
INSTALLATION - FIXED ORIFICE FITTING....29
EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION.........................29
OPERATION...........................29
REMOVAL.............................29
INSTALLATION.........................29
FUEL FILLER CAP
DESCRIPTION.........................29
OPERATION...........................29REMOVAL.............................29
LEAK DETECTION PUMP
DESCRIPTION.........................30
OPERATION...........................31
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENABLING
CONDITIONS TO RUN EVAP LEAK
DETECTION TEST.....................32
REMOVAL.............................35
INSTALLATION.........................35
ORVR
DESCRIPTION.........................37
OPERATION...........................37
P C V VA LV E
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PCV VALVE/PCV
SYSTEM - 4.7L.......................37
REMOVAL - PCV VALVE - 4.7L.............39
INSTALLATION - PCV VALVE - 4.7L.........39
VACUUM LINES
DESCRIPTION.........................39
VAPOR CANISTER
DESCRIPTION.........................39
OPERATION...........................39
REMOVAL.............................40
INSTALLATION.........................40
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - EVAPORATION CONTROL
SYSTEM
The evaporation control system prevents the emis-
sion of fuel tank vapors into the atmosphere. When
fuel evaporates in the fuel tank, the vapors pass
through the control valve, through the fuel manage-
ment valve, and through vent hoses and tubes to a
charcoal filled evaporative canister. The canister tem-
porarily holds the vapors. The Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) allows intake manifold vacuum todraw vapors into the combustion chambers during
certain operating conditions.
Gas powered engines use a duty cycle purge sys-
tem. The PCM controls vapor flow by operating the
duty cycle EVAP purge solenoid. Refer to Duty Cycle
EVAP Canister Purge Solenoid.
When equipped with certain emissions packages, a
Leak Detection Pump (LDP) will be used as part of
the evaporative system for OBD II requirements.
Also refer to Leak Detection Pump.
Vehicles powered with gasoline engines are also
equipped with ORVR (On-Board Refueling Vapor
Recovery). Refer to ORVR for additional information.
25 - 24 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSWJ
Page 2180 of 2199

NOTE: The evaporative system uses specially man-
ufactured lines/hoses. If replacement becomes nec-
essary, only use fuel resistant, low permeation
hose.
Certain components can be found in (Fig. 1).
DESCRIPTION - CCV SYSTEM
The 4.0L 6±cylinder engine is equipped with a
Crankcase Ventilation (CCV) system. The system
consists of:
²A fixed orifice fitting of a calibrated size. This
fitting is pressed into a rubber grommet located on
the top/rear of cylinder head (valve) cover (Fig. 2).
²a pair of breather tubes (lines) to connect the
system components.
²the air cleaner housing.
²an air inlet fitting (Fig. 2).
DESCRIPTION - PCV SYSTEM
The 4.7L V-8 engine is equipped with a closed
crankcase ventilation system and a Positive Crank-
case Ventilation (PCV) valve.
This system consists of:
Fig. 1 ORVR / LDP COMPONENTS
1 - FUEL TANK (LEFT SIDE) 6 - EVAP CANISTER
2 - FRAME RAIL (LEFT-REAR OUTSIDE) 7 - LDP FILTER
3 - FUEL VENT TUBE 8 - TWO-PIECE SUPPORT BRACKET
4 - FUEL FILL TUBE 9 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP (LDP)
5 - CONTROL VALVE
Fig. 2 CCV SystemÐ4.0L Engine
1 - AIR INLET FITTING
2 - FIXED ORIFICE FITTING
3 - CCV BREATHER TUBE (REAR)
4 - INT. MAN. FITTING
5 - CCV BREATHER TUBE (FRONT)
WJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 25
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS (Continued)
Page 2181 of 2199

²a PCV valve mounted to the oil filler housing
(Fig. 3). The PCV valve is sealed to the oil filler
housing with an o-ring.
²the air cleaner housing
²two interconnected breathers threaded into the
rear of each cylinder head (Fig. 4).
²tubes and hose to connect the system compo-
nents.
OPERATION
OPERATION - 4.0L CCV SYSTEM
The CCV system performs the same function as a
conventional PCV system, but does not use a vacuum
controlled PCV valve.
The fixed orifice fitting meters the amount of
crankcase vapors drawn out of the engine.
When the engine is operating, fresh air enters the
engine and mixes with crankcase vapors. Engine vac-uum draws the vapor/air mixture through the fixed
orifice and into the intake manifold. The vapors are
then consumed during engine combustion.
OPERATION - 4.7L PCV SYSTEM
The PCV system operates by engine intake mani-
fold vacuum. Filtered air is routed into the crankcase
through the air cleaner hose and crankcase breath-
ers. The metered air, along with crankcase vapors,
are drawn through the PCV valve and into a passage
in the intake manifold. The PCV system manages
crankcase pressure and meters blow-by gases to the
intake system, reducing engine sludge formation.
The PCV valve contains a spring loaded plunger.
This plunger meters the amount of crankcase vapors
routed into the combustion chamber based on intake
manifold vacuum.
TYPICALPCV valves are shown in (Fig. 5), (Fig.
6) and (Fig. 7).
When the engine is not operating, or during an
engine pop-back, the spring forces the plunger back
against the seat (Fig. 5). This will prevent vapors
from flowing through the valve.
Fig. 3 PCV Valve/Oil Filler Tube (Housing)Ð4.7L
Engine
1 - O-RING
2 - LOCATING TABS
3 - CAM LOCK
4 - OIL FILLER TUBE
5 - PCV LINE/HOSE
6 - P C V VA LV E
Fig. 4 PCV System Hoses/TubesÐ4.7L Engine
1 - FRESH AIR FITTING
2 - CONNECTING TUBES/HOSES
3 - CRANKCASE BREATHERS (2)
4 - RUBBER HOSE
5 - AIR CLEANER RESONATOR
25 - 26 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSWJ
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS (Continued)
Page 2183 of 2199

CCV HOSE
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CCV SYSTEM -
4.0L
Before attempting diagnosis, be sure locations of
fixed orifice fitting and air inlet fitting (Fig. 8) have
not been inadvertently exchanged. The fixed orifice
fitting is light grey in color and is located atrearof
valve cover. The air inlet fitting is black in color and
is located atfrontof valve cover.
(1) Pull fixed orifice fitting (Fig. 8) from valve
cover and leave tube attached.
(2) Start engine and bring to idle speed.
(3) If fitting is not plugged, a hissing noise will be
heard as air passes through fitting orifice. Also, a
strong vacuum should be felt with a finger placed at
fitting inlet.
(4) If vacuum is not present, remove fitting orifice
fitting from tube. Start engine. If vacuum can now be
felt, replace fixed orifice fitting. Do not attempt to
clean plastic fitting.
(5) If vacuum is still not felt at hose, check line/
hose for kinks or for obstruction. If necessary, clean
out intake manifold fitting at intake manifold. Do
this by turning a 1/4 inch drill (by hand) through the
fitting to dislodge any solid particles. Blow out thefitting with shop air. If necessary, use a smaller drill
to avoid removing any metal from the fitting.
(6) Return fixed orifice fitting to valve cover and
leave tube attached.
(7) Disconnect air inlet fitting and its attached
hose at front of valve cover (Fig. 8). Start engine and
bring to idle speed. Hold a piece of stiff paper (such
as a parts tag) loosely over the rubber grommet
(opening) of the disconnected air inlet fitting.
(8) The paper should be drawn against the rubber
grommet with noticeable force. This will be after
allowing approximately one minute for crankcase
pressure to reduce.
(9) If vacuum is not present, check breather hoses/
tubes/lines for obstructions or restrictions.
(10) After testing, reconnect all system hoses/
tubes/lines.
REMOVAL - FIXED ORIFICE FITTING
When installing fixed orifice fitting, be sure loca-
tions of fixed orifice fitting and air inlet fitting (Fig.
9) have not been inadvertently exchanged. The fixed
orifice fitting is light grey in color and is located at
rearof valve cover. The air inlet fitting is black in
color and is located atfrontof valve cover.
(1) Pull fixed orifice fitting (Fig. 9) from valve
cover grommet.
(2) Separate fitting from CCV breather tube.
Fig. 8 Fixed Orifice Fitting and CCV SystemÐ4.0L
Engine
1 - AIR INLET FITTING
2 - FIXED ORIFICE FITTING
3 - CCV BREATHER TUBE (REAR)
4 - INT. MAN. FITTING
5 - CCV BREATHER TUBE (FRONT)
Fig. 9 FIXED ORIFICE FITTING - 4.0L
1 - AIR INLET FITTING
2 - FIXED ORIFICE FITTING
3 - CCV BREATHER TUBE (REAR)
4 - INT. MAN. FITTING
5 - CCV BREATHER TUBE (FRONT)
25 - 28 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSWJ