Electric plug ins JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 1375 of 2199

(5) With a wiping cloth, clean the gasket sealing
surface of oil and grime.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lightly lubricate oil filter gasket with engine
oil.
(2) Thread filter onto adapter nipple. When gasket
makes contact with sealing surface, (Fig. 94)hand
tighten filter one full turn, do not over tighten.
(3) Add oil, verify crankcase oil level and start
engine. Inspect for oil leaks.
OIL PAN
DESCRIPTION
The engine oil pan is made of laminated steel and
has a single plane sealing surface. The sandwich
style oil pan gasket has an integrated windage tray
and steel carrier. The sealing area of the gasket is
molded with rubber and is designed to be reused as
long as the gasket is not cut, torn or ripped.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3) Remove structural cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/STRUCTURAL COVER - REMOV-
AL).
(4) Remove exhaust system Y-pipe.
(5) Remove starter (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
STARTING/STARTER MOTOR - REMOVAL).
(6) Drain engine oil.
(7) Un-clip transmission lines from support on oil
pan stud. Move lines for oil pan clearance.
CAUTION: DO NOT pry on the oil pan gasket when
removing the oil pan, The oil pan gasket is mounted
to the cylinder block in three locations and will
remain attached to block when lowering oil pan.
Gasket can not be removed with oil pan.
(8) Remove oil pan bolts and oil pan.
(9) Remove oil pump pickup tube.
(10) Remove oil pan gasket.
CLEANING
(1) Clean oil pan in solvent and wipe dry with a
clean cloth.
(2) Clean the oil pan gasket surface.DO NOTuse
a grinder wheel or other abrasive tool to clean seal-
ing surface.
(3) Clean oil screen and tube thoroughly in clean
solvent.
INSPECTION
(1) Inspect oil drain plug and plug hole for
stripped or damaged threads. Repair as necessary.
(2) Inspect the oil pan mounting flange for bends
or distortion. Straighten flange, if necessary.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean oil pan and all sealing surfaces. Inspect
oil pan gasket and replace as necessary.
(2) Install oil pan gasket.
Fig. 93 Oil Filter - 4.7L Engine
1 - ENGINE OIL FILTER
Fig. 94 Oil Filter Sealing SurfaceÐTypical
1 - SEALING SURFACE
2 - RUBBER GASKET
3 - OIL FILTER
9 - 132 ENGINE - 4.7LWJ
OIL FILTER (Continued)
Page 1426 of 2199

(3) Apply a small amount of clean engine oil to
o-rings.
(4) Position filter/regulator to body and install 2
bolts. Tighten bolts to 3 N´m (30 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Connect 3 fittings. Refer to Quick-Connect Fit-
tings.
(6) Connect negative battery cable to battery.
(7) Start engine and check for leaks.
FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT /
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor) is
attached to the side of the fuel pump module. The
sending unit consists of a float, an arm, and a vari-
able resistor track (card).
OPERATION
The fuel pump module has 4 different circuits
(wires). Two of these circuits are used for the fuel
gauge sending unit for fuel gauge operation, and for
certain OBD II emission requirements. The other 2
wires are used for electric fuel pump operation.
For Fuel Gauge Operation:A constant input
voltage source of about 12 volts (battery voltage) is
supplied to the resistor track on the fuel gauge send-
ing unit. This is fed directly from the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM).NOTE: For diagnostic pur-
poses, this 12V power source can only be veri-fied with the circuit opened (fuel pump module
electrical connector unplugged). With the con-
nectors plugged, output voltages will vary from
about 0.6 volts at FULL, to about 8.6 volts at
EMPTY (about 8.6 volts at EMPTY for Jeep
models, and about 7.0 volts at EMPTY for
Dodge Truck models).The resistor track is used to
vary the voltage (resistance) depending on fuel tank
float level. As fuel level increases, the float and arm
move up, which decreases voltage. As fuel level
decreases, the float and arm move down, which
increases voltage. The varied voltage signal is
returned back to the PCM through the sensor return
circuit.
Both of the electrical circuits between the fuel
gauge sending unit and the PCM are hard-wired (not
multi-plexed). After the voltage signal is sent from
the resistor track, and back to the PCM, the PCM
will interpret the resistance (voltage) data and send
a message across the multi-plex bus circuits to the
instrument panel cluster. Here it is translated into
the appropriate fuel gauge level reading. Refer to
Instrument Panel for additional information.
For OBD II Emission Monitor Requirements:
The PCM will monitor the voltage output sent from
the resistor track on the sending unit to indicate fuel
level. The purpose of this feature is to prevent the
OBD II system from recording/setting false misfire
and fuel system monitor diagnostic trouble codes.
The feature is activated if the fuel level in the tank
is less than approximately 15 percent of its rated
capacity. If equipped with a Leak Detection Pump
(EVAP system monitor), this feature will also be acti-
vated if the fuel level in the tank is more than
approximately 85 percent of its rated capacity.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL LEVEL
SENDING UNIT
The fuel level sending unit contains a variable
resistor (track). As the float moves up or down, elec-
trical resistance will change. Refer to Instrument
Panel and Gauges for Fuel Gauge testing. To test the
gauge sending unit only, it must be removed from
vehicle. The unit is part of the fuel pump module.
Refer to Fuel Pump Module Removal/Installation for
procedures. Measure the resistance across the send-
ing unit terminals. With float in up position, resis-
tance should be 20 ohms (+/- 5%). With float in down
position, resistance should be 270 ohms (+/- 5%).
REMOVAL
The fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor) and
float assembly is located on the side of fuel pump
module (Fig. 6). The fuel pump module is located
within the fuel tank.
Fig. 5 Fuel Filter/Fuel Pressure Regulator Removal/
Installation
1 - FUEL FILTER/FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS (2)
WJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 7
FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE REGULATOR (Continued)
Page 1428 of 2199

OPERATION
Voltage to operate the electric pump is supplied
through the fuel pump relay.
Fuel is drawn in through a filter at the bottom of
the module and pushed through the electric motor
gearset to the pump outlet.
Check Valve Operation:The pump outlet con-
tains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel flow back
into the tank and to maintain fuel supply line pres-
sure (engine warm) when pump is not operational. It
is also used to keep the fuel supply line full of gaso-
line when pump is not operational. After the vehicle
has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop to 0 psi
(cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline will remain
in fuel supply line between the check valve and fuel
injectors.Fuel pressure that has dropped to 0
psi on a cooled down vehicle (engine off) is a
normal condition.Refer to the Fuel Pressure Leak
Down Test for more information.
The electric fuel pump is not a separate, service-
able component.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
CAPACITY TEST
Before performing this test, verify fuel pump
pressure. Refer to Fuel Pump Pressure Test.
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pres-
sure Leak Down Test.
(1) Release fuel system pressure. Refer to Fuel
Pressure Release Procedure.
(2) Disconnect fuel supply line at fuel rail. Refer to
Quick-Connect Fittings. Some engines may require
air cleaner housing removal before line disconnection.
(3) Obtain correct Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter
Tool Hose. Tool number 6539 is used for 5/16º fuel
lines and tool number 6631 is used for 3/8º fuel lines.
(4) Connect correct Fuel Line Pressure Test
Adapter Tool Hose into disconnected fuel supply line.
Insert other end of Adaptor Tool Hose into a gradu-
ated container.
(5) Remove fuel fill cap.
(6) To activate fuel pump and pressurize system,
obtain DRBtscan tool and actuate ASD Fuel System
Test.
(7) A good fuel pump will deliver at least 1/4 liter
of fuel in 7 seconds. Do not operate fuel pump for
longer than 7 seconds with fuel line disconnected as
fuel pump module reservoir may run empty.
(a) If capacity is lower than specification, but
fuel pump can be heard operating through fuel fill
cap opening, check for a kinked/damaged fuel sup-
ply line somewhere between fuel rail and fuel
pump module.(b) If line is not kinked/damaged, and fuel pres-
sure is OK, but capacity is low, replace fuel filter/
fuel pressure regulator. The filter/regulator may be
serviced separately on certain applications. Refer
to Fuel Filter/Fuel Pressure Regulator Removal/In-
stallation for additional information.
(c) If both fuel pressure and capacity are low,
replace fuel pump module assembly. Refer to Fuel
Pump Module Removal/Installation.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
AMPERAGE TEST
This amperage (current draw) test is to be done in
conjunction with the Fuel Pump Pressure Test, Fuel
Pump Capacity Test and Fuel Pressure Leak Down
Test. Before performing the amperage test, be sure
the temperature of the fuel tank is above 50É F (10É
C).
The DRBtScan Tool along with the DRB Low Cur-
rent Shunt (LCS) adapter (Fig. 8) and its test leads
will be used to check fuel pump amperage specifica-
tions.
(1) Be sure fuel tank contains fuel before starting
test. If tank is empty or near empty, amperage read-
ings will be incorrect.
(2) Obtain LCS adapter.
(3) Plug cable from LCS adapter into DRB scan
tool at SET 1 receptacle.
(4) Plug DRB into vehicle 16±way connector (data
link connector).
Fig. 8 LOW CURRENT SHUNT
1 - LOW CURRENT SHUNT ADAPTER
2 - PLUG TO DRB
3 - TEST LEAD RECEPTACLES
WJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 9
FUEL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1457 of 2199

(23) Inspect for pinched or leaking fuel tubes/lines.
Inspect for pinched, cracked or leaking fuel hoses.
(24) Inspect for exhaust system restrictions such
as pinched exhaust pipes, collapsed muffler or
plugged catalytic convertor.
(25) If equipped with automatic transmission, ver-
ify electrical harness is firmly connected to park/neu-
tral switch and to transmission components.
(26) Verify fuel pump module pigtail harness elec-
trical connector (Fig. 15) is firmly connected to body
harness connector.
(27) Inspect fuel line harness (from fuel pump
module) at fuel filter/fuel pressure regulator (Fig. 15)
for chaffing, cracks or leaks.
(28) Verify battery cable and solenoid feed wire
connections to starter solenoid are tight and clean.
(29) Inspect for chaffed wires or wires rubbing up
against other components.
(30) Inspect for chaffed vacuum lines or lines rub-
bing up against other components.
Fig. 15 Fuel Filter/Fuel Pressure Regulator Location
1 - FUEL RETURN LINE
2 - FUEL SUPPLY LINE (TO FUEL RAIL)
3 - FUEL FILTER/FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
4 - FUEL PRESSURE LINE
5 - REAR AXLE
6 - ELEC. CONNECTOR
7 - EVAP LINE
14 - 38 FUEL INJECTIONWJ
FUEL INJECTION (Continued)
Page 1530 of 2199

FOURTH GEAR POWERFLOW
Fourth gear overdrive range is electronically con-
trolled and hydraulically activated. Various sensor
inputs are supplied to the powertrain control module
to operate the overdrive solenoid on the valve body.
The solenoid contains a check ball that opens and
closes a vent port in the 3-4 shift valve feed passage.
The overdrive solenoid (and check ball) are not ener-
gized in first, second, third, or reverse gear. The vent
port remains open, diverting line pressure from the
2-3 shift valve away from the 3-4 shift valve. The
overdrive control switch must be in the ON position
to transmit overdrive status to the PCM. A 3-4
upshift occurs only when the overdrive solenoid is
energized by the PCM. The PCM energizes the over-
drive solenoid during the 3-4 upshift. This causes the
solenoid check ball to close the vent port allowing
line pressure from the 2-3 shift valve to act directly
on the 3-4 upshift valve. Line pressure on the 3-4
shift valve overcomes valve spring pressure moving
the valve to the upshift position. This action exposes
the feed passages to the 3-4 timing valve, 3-4 quick
fill valve, 3-4 accumulator, and ultimately to the
overdrive piston. Line pressure through the timing
valve moves the overdrive piston into contact with
the overdrive clutch. The direct clutch is disengaged
before the overdrive clutch is engaged. The boost
valve provides increased fluid apply pressure to the
overdrive clutch during 3-4 upshifts, and when accel-
erating in fourth gear. The 3-4 accumulator cushions
overdrive clutch engagement to smooth 3-4 upshifts.
The accumulator is charged at the same time as
apply pressure acts against the overdrive piston.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
Automatic transmission problems can be a result of
poor engine performance, incorrect fluid level, incor-
rect linkage or cable adjustment, band or hydraulic
control pressure adjustments, hydraulic system mal-
functions or electrical/mechanical component mal-
functions. Begin diagnosis by checking the easily
accessible items such as: fluid level and condition,
linkage adjustments and electrical connections. A
road test will determine if further diagnosis is neces-
sary.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRELIMINARY
Two basic procedures are required. One procedure
for vehicles that are drivable and an alternate proce-
dure for disabled vehicles (will not back up or move
forward).
VEHICLE IS DRIVEABLE
(1) Check for transmission fault codes using DRBt
scan tool.
(2) Check fluid level and condition.
(3) Adjust throttle and gearshift linkage if com-
plaint was based on delayed, erratic, or harsh shifts.
(4) Road test and note how transmission upshifts,
downshifts, and engages.
(5) Perform hydraulic pressure test if shift prob-
lems were noted during road test.
(6) Perform air-pressure test to check clutch-band
operation.
VEHICLE IS DISABLED
(1) Check fluid level and condition.
(2) Check for broken or disconnected gearshift or
throttle linkage.
(3) Check for cracked, leaking cooler lines, or loose
or missing pressure-port plugs.
(4) Raise and support vehicle on safety stands,
start engine, shift transmission into gear, and note
following:
(a) If propeller shaft turns but wheels do not,
problem is with differential or axle shafts.
(b) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is noisy, stop engine. Remove oil pan, and
check for debris. If pan is clear, remove transmis-
sion and check for damaged drive plate, converter,
oil pump, or input shaft.
(c) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is not noisy, perform hydraulic-pressure test to
determine if problem is hydraulic or mechanical.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TESTING
Before road testing, be sure the fluid level and con-
trol cable adjustments have been checked and
adjusted if necessary. Verify that diagnostic trouble
codes have been resolved.
Observe engine performance during the road test.
A poorly tuned engine will not allow accurate analy-
sis of transmission operation.
Operate the transmission in all gear ranges. Check
for shift variations and engine flare which indicates
slippage. Note if shifts are harsh, spongy, delayed,
early, or if part throttle downshifts are sensitive.
Slippage indicated by engine flare, usually means
clutch, band or overrunning clutch problems. If the
condition is advanced, an overhaul will be necessary
to restore normal operation.
A slipping clutch or band can often be determined
by comparing which internal units are applied in the
various gear ranges. The Clutch and Band Applica-
tion chart provides a basis for analyzing road test
results.
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 11
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1536 of 2199
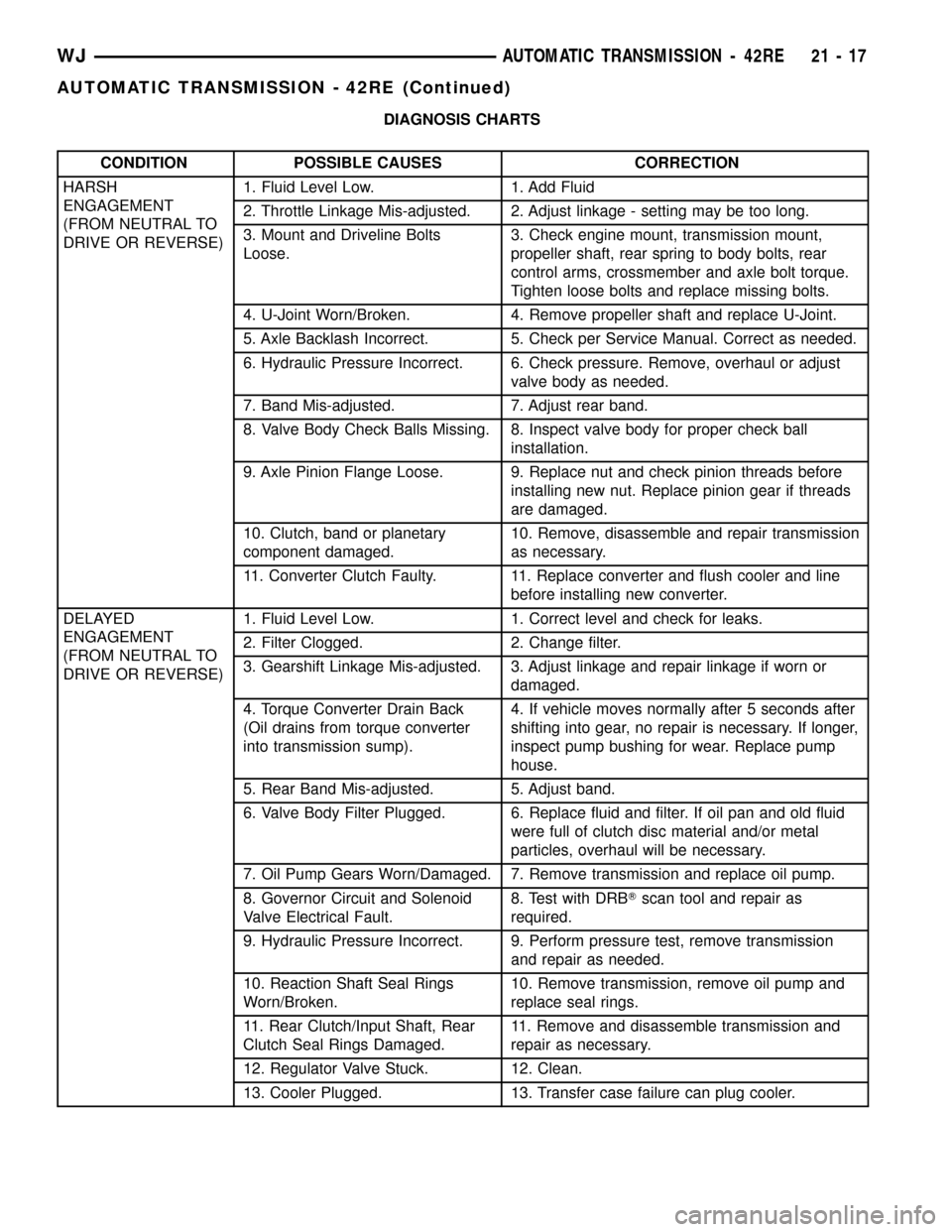
DIAGNOSIS CHARTS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
HARSH
ENGAGEMENT
(FROM NEUTRAL TO
DRIVE OR REVERSE)1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add Fluid
2. Throttle Linkage Mis-adjusted. 2. Adjust linkage - setting may be too long.
3. Mount and Driveline Bolts
Loose.3. Check engine mount, transmission mount,
propeller shaft, rear spring to body bolts, rear
control arms, crossmember and axle bolt torque.
Tighten loose bolts and replace missing bolts.
4. U-Joint Worn/Broken. 4. Remove propeller shaft and replace U-Joint.
5. Axle Backlash Incorrect. 5. Check per Service Manual. Correct as needed.
6. Hydraulic Pressure Incorrect. 6. Check pressure. Remove, overhaul or adjust
valve body as needed.
7. Band Mis-adjusted. 7. Adjust rear band.
8. Valve Body Check Balls Missing. 8. Inspect valve body for proper check ball
installation.
9. Axle Pinion Flange Loose. 9. Replace nut and check pinion threads before
installing new nut. Replace pinion gear if threads
are damaged.
10. Clutch, band or planetary
component damaged.10. Remove, disassemble and repair transmission
as necessary.
11. Converter Clutch Faulty. 11. Replace converter and flush cooler and line
before installing new converter.
DELAYED
ENGAGEMENT
(FROM NEUTRAL TO
DRIVE OR REVERSE)1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Correct level and check for leaks.
2. Filter Clogged. 2. Change filter.
3. Gearshift Linkage Mis-adjusted. 3. Adjust linkage and repair linkage if worn or
damaged.
4. Torque Converter Drain Back
(Oil drains from torque converter
into transmission sump).4. If vehicle moves normally after 5 seconds after
shifting into gear, no repair is necessary. If longer,
inspect pump bushing for wear. Replace pump
house.
5. Rear Band Mis-adjusted. 5. Adjust band.
6. Valve Body Filter Plugged. 6. Replace fluid and filter. If oil pan and old fluid
were full of clutch disc material and/or metal
particles, overhaul will be necessary.
7. Oil Pump Gears Worn/Damaged. 7. Remove transmission and replace oil pump.
8. Governor Circuit and Solenoid
Valve Electrical Fault.8. Test with DRBTscan tool and repair as
required.
9. Hydraulic Pressure Incorrect. 9. Perform pressure test, remove transmission
and repair as needed.
10. Reaction Shaft Seal Rings
Worn/Broken.10. Remove transmission, remove oil pump and
replace seal rings.
11. Rear Clutch/Input Shaft, Rear
Clutch Seal Rings Damaged.11. Remove and disassemble transmission and
repair as necessary.
12. Regulator Valve Stuck. 12. Clean.
13. Cooler Plugged. 13. Transfer case failure can plug cooler.
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 17
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1538 of 2199
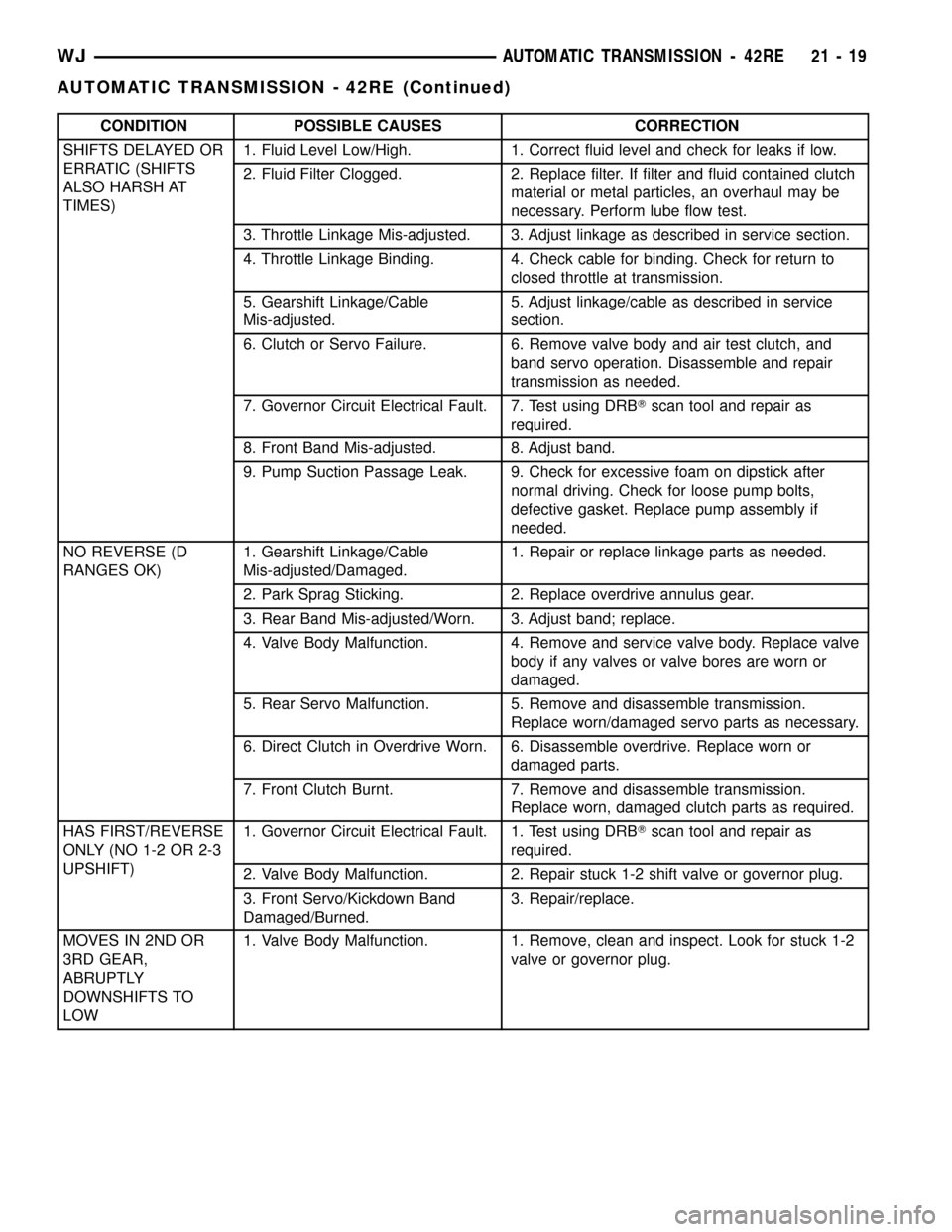
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
SHIFTS DELAYED OR
ERRATIC (SHIFTS
ALSO HARSH AT
TIMES)1. Fluid Level Low/High. 1. Correct fluid level and check for leaks if low.
2. Fluid Filter Clogged. 2. Replace filter. If filter and fluid contained clutch
material or metal particles, an overhaul may be
necessary. Perform lube flow test.
3. Throttle Linkage Mis-adjusted. 3. Adjust linkage as described in service section.
4. Throttle Linkage Binding. 4. Check cable for binding. Check for return to
closed throttle at transmission.
5. Gearshift Linkage/Cable
Mis-adjusted.5. Adjust linkage/cable as described in service
section.
6. Clutch or Servo Failure. 6. Remove valve body and air test clutch, and
band servo operation. Disassemble and repair
transmission as needed.
7. Governor Circuit Electrical Fault. 7. Test using DRBTscan tool and repair as
required.
8. Front Band Mis-adjusted. 8. Adjust band.
9. Pump Suction Passage Leak. 9. Check for excessive foam on dipstick after
normal driving. Check for loose pump bolts,
defective gasket. Replace pump assembly if
needed.
NO REVERSE (D
RANGES OK)1. Gearshift Linkage/Cable
Mis-adjusted/Damaged.1. Repair or replace linkage parts as needed.
2. Park Sprag Sticking. 2. Replace overdrive annulus gear.
3. Rear Band Mis-adjusted/Worn. 3. Adjust band; replace.
4. Valve Body Malfunction. 4. Remove and service valve body. Replace valve
body if any valves or valve bores are worn or
damaged.
5. Rear Servo Malfunction. 5. Remove and disassemble transmission.
Replace worn/damaged servo parts as necessary.
6. Direct Clutch in Overdrive Worn. 6. Disassemble overdrive. Replace worn or
damaged parts.
7. Front Clutch Burnt. 7. Remove and disassemble transmission.
Replace worn, damaged clutch parts as required.
HAS FIRST/REVERSE
ONLY (NO 1-2 OR 2-3
UPSHIFT)1. Governor Circuit Electrical Fault. 1. Test using DRBTscan tool and repair as
required.
2. Valve Body Malfunction. 2. Repair stuck 1-2 shift valve or governor plug.
3. Front Servo/Kickdown Band
Damaged/Burned.3. Repair/replace.
MOVES IN 2ND OR
3RD GEAR,
ABRUPTLY
DOWNSHIFTS TO
LOW1. Valve Body Malfunction. 1. Remove, clean and inspect. Look for stuck 1-2
valve or governor plug.
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 19
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1539 of 2199
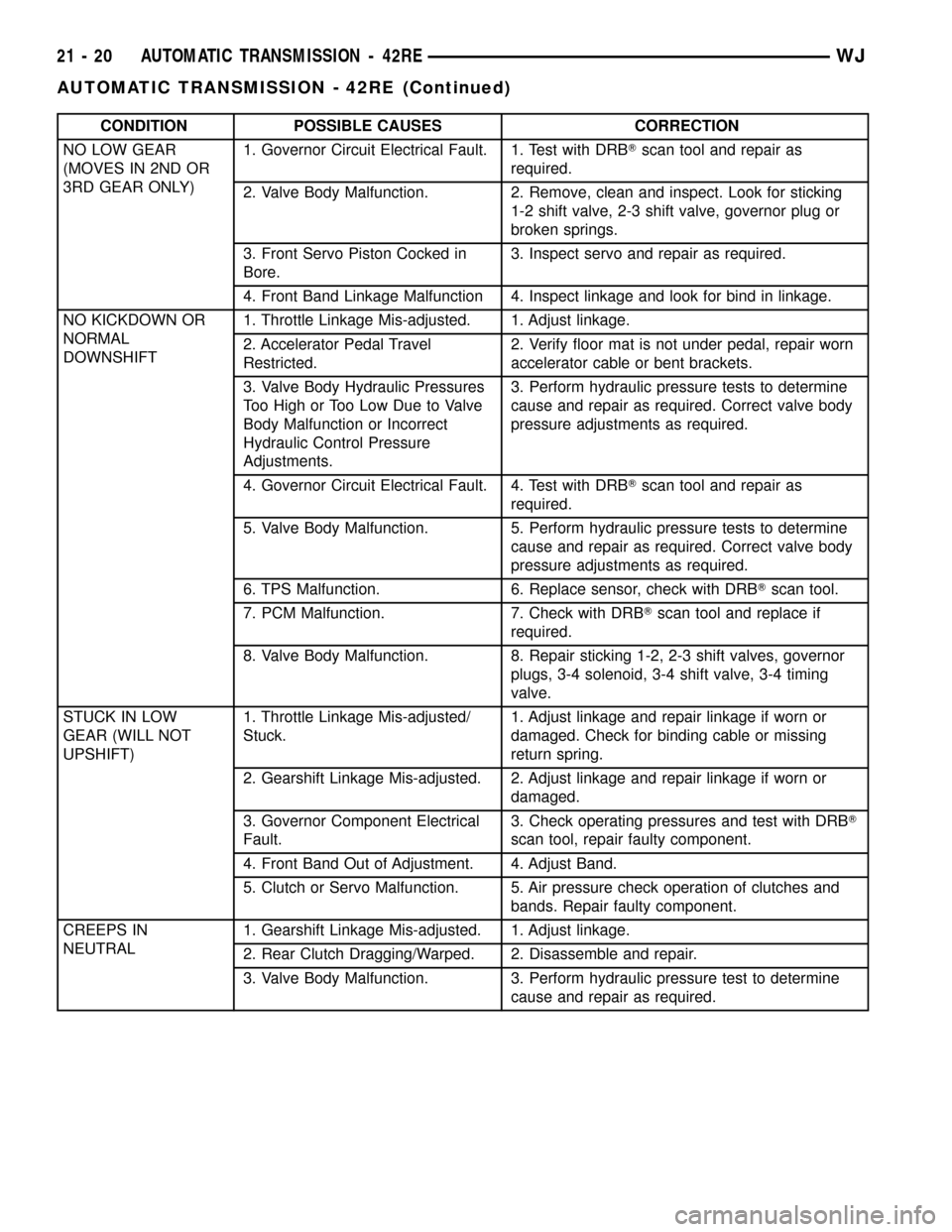
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NO LOW GEAR
(MOVES IN 2ND OR
3RD GEAR ONLY)1. Governor Circuit Electrical Fault. 1. Test with DRBTscan tool and repair as
required.
2. Valve Body Malfunction. 2. Remove, clean and inspect. Look for sticking
1-2 shift valve, 2-3 shift valve, governor plug or
broken springs.
3. Front Servo Piston Cocked in
Bore.3. Inspect servo and repair as required.
4. Front Band Linkage Malfunction 4. Inspect linkage and look for bind in linkage.
NO KICKDOWN OR
NORMAL
DOWNSHIFT1. Throttle Linkage Mis-adjusted. 1. Adjust linkage.
2. Accelerator Pedal Travel
Restricted.2. Verify floor mat is not under pedal, repair worn
accelerator cable or bent brackets.
3. Valve Body Hydraulic Pressures
Too High or Too Low Due to Valve
Body Malfunction or Incorrect
Hydraulic Control Pressure
Adjustments.3. Perform hydraulic pressure tests to determine
cause and repair as required. Correct valve body
pressure adjustments as required.
4. Governor Circuit Electrical Fault. 4. Test with DRBTscan tool and repair as
required.
5. Valve Body Malfunction. 5. Perform hydraulic pressure tests to determine
cause and repair as required. Correct valve body
pressure adjustments as required.
6. TPS Malfunction. 6. Replace sensor, check with DRBTscan tool.
7. PCM Malfunction. 7. Check with DRBTscan tool and replace if
required.
8. Valve Body Malfunction. 8. Repair sticking 1-2, 2-3 shift valves, governor
plugs, 3-4 solenoid, 3-4 shift valve, 3-4 timing
valve.
STUCK IN LOW
GEAR (WILL NOT
UPSHIFT)1. Throttle Linkage Mis-adjusted/
Stuck.1. Adjust linkage and repair linkage if worn or
damaged. Check for binding cable or missing
return spring.
2. Gearshift Linkage Mis-adjusted. 2. Adjust linkage and repair linkage if worn or
damaged.
3. Governor Component Electrical
Fault.3. Check operating pressures and test with DRBT
scan tool, repair faulty component.
4. Front Band Out of Adjustment. 4. Adjust Band.
5. Clutch or Servo Malfunction. 5. Air pressure check operation of clutches and
bands. Repair faulty component.
CREEPS IN
NEUTRAL1. Gearshift Linkage Mis-adjusted. 1. Adjust linkage.
2. Rear Clutch Dragging/Warped. 2. Disassemble and repair.
3. Valve Body Malfunction. 3. Perform hydraulic pressure test to determine
cause and repair as required.
21 - 20 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1796 of 2199

CLEANING
Clean the valve housings, valves, plugs, springs,
and separator plates with a standard parts cleaning
solution only. Do not use gasoline, kerosene, or any
type of caustic solution. (Fig. 131)
Do not immerse any of the electrical components in
cleaning solution. Clean the electrical components by
wiping them off with dry shop towels only.
Dry all except the electrical parts with compressed
air. Make sure all passages are clean and free from
obstructions.Do not use rags or shop towels to
dry or wipe off valve body components. Lint
from these materials can stick to valve body
parts, interfere with valve operation, and clog
filters and fluid passages.
INSPECTION
Inspect all of the valve body mating surfaces for
scratches, nicks, burrs, or distortion. Use a straight-edge to check surface flatness. Minor scratches may
be removed with crocus cloth using only very light
pressure.
Minor distortion of a valve body mating surface
may be corrected by smoothing the surface with a
sheet of crocus cloth. Position the crocus cloth on a
surface plate, sheet of plate glass or equally flat sur-
face. If distortion is severe or any surfaces are
heavily scored, the valve body will have to be
replaced.
Inspect the valves and plugs (Fig. 132) for
scratches, burrs, nicks, or scores. Minor surface
scratches on steel valves and plugs can be removed
with crocus cloth butdo not round off the edges
of the valve or plug lands.Maintaining sharpness
of these edges is vitally important. The edges prevent
foreign matter from lodging between the valves and
plugs and the bore.
Fig. 130 Valve Body Components
1 - SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
2 - MANUAL VALVE
3 - LOW REVERSE SWITCH VALVE
4 - LOW REVERSE ACCUMULATOR
5 - 2ND CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR
6 - UNDERDRIVE ACCUMULATOR
7 - OVERDRIVE ACCUMULATOR
8 - 4TH CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR
9 - CHECK BALLS (7)
Fig. 131 Valve Body Components
1 - SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
2 - MANUAL VALVE
3 - LOW REVERSE SWITCH VALVE
4 - LOW REVERSE ACCUMULATOR
5 - 2ND CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR
6 - UNDERDRIVE ACCUMULATOR
7 - OVERDRIVE ACCUMULATOR
8 - 4TH CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR
9 - CHECK BALLS (7)
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 277
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1874 of 2199

BODY
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BODY
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
WATER LEAKS........................1
WIND NOISE..........................2
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BODY
LUBRICATION.........................2
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRILLING AND
WELDING............................3
SPECIFICATIONS
BODY LUBRICANTS....................3
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE.............4
SPECIAL TOOLS
BODY...............................4DECKLID/HATCH/LIFTGATE/TAILGATE........5
DOOR - FRONT.........................11
DOORS - REAR.........................19
EXTERIOR.............................25
HOOD.................................33
INSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEM.............36
INTERIOR..............................69
PAINT.................................81
SEATS................................83
STATIONARY GLASS.....................93
SUNROOF.............................96
WEATHERSTRIP/SEALS..................105
BODY STRUCTURE.....................112
BODY
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
WATER LEAKS
Water leaks can be caused by poor sealing,
improper body component alignment, body seam
porosity, missing plugs, or blocked drain holes. Cen-
trifugal and gravitational force can cause water to
drip from a location away from the actual leak point,
making leak detection difficult. All body sealing
points should be water tight in normal wet-driving
conditions. Water flowing downward from the front of
the vehicle should not enter the passenger or luggage
compartment. Moving sealing surfaces will not
always seal water tight under all conditions. At
times, side glass or door seals will allow water to
enter the passenger compartment during high pres-
sure washing or hard driving rain (severe) condi-
tions. Overcompensating on door or glass
adjustments to stop a water leak that occurs under
severe conditions can cause premature seal wear and
excessive closing or latching effort. After completing
a repair, water test vehicle to verify leak has stopped
before returning vehicle to use.
VISUAL INSPECTION BEFORE WATER LEAK TESTS
Verify that floor and body plugs are in place, body
drains are clear, and body components are properly
aligned and sealed. If component alignment or seal-
ing is necessary, refer to the appropriate section of
this group for proper procedures.
WATER LEAK TESTS
WARNING: DO NOT USE ELECTRIC SHOP LIGHTS
OR TOOLS IN WATER TEST AREA. PERSONAL
INJURY CAN RESULT.
When the conditions causing a water leak have
been determined, simulate the conditions as closely
as possible.
²If a leak occurs with the vehicle parked in a
steady light rain, flood the leak area with an open-
ended garden hose.
²If a leak occurs while driving at highway speeds
in a steady rain, test the leak area with a reasonable
velocity stream or fan spray of water. Direct the
spray in a direction comparable to actual conditions.
²If a leak occurs when the vehicle is parked on an
incline, hoist the end or side of the vehicle to simu-
late this condition. This method can be used when
the leak occurs when the vehicle accelerates, stops or
turns. If the leak occurs on acceleration, hoist the
front of the vehicle. If the leak occurs when braking,
hoist the back of the vehicle. If the leak occurs on left
turns, hoist the left side of the vehicle. If the leak
occurs on right turns, hoist the right side of the vehi-
cle. For hoisting recommendations refer to Group 0,
Lubrication and Maintenance, General Information
section.
WATER LEAK DETECTION
To detect a water leak point-of-entry, do a water
test and watch for water tracks or droplets forming
on the inside of the vehicle. If necessary, remove inte-
rior trim covers or panels to gain visual access to the
WJBODY 23 - 1