rain sensor JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 383 of 2199
OK, repair the shorted circuit or component as
required and replace the faulty fuse.
(2) Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
Check for battery voltage at the fused ignition switch
output (run) fuse in the junction block. If OK, go to
Step 3. If not OK, repair the open fused ignition
switch output (run) circuit to the ignition switch as
required.
(3) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Remove the lower center bezel from the instru-
ment panel and disconnect the instrument panel wire
harness connectors from both heated seat switch con-
nector receptacles. Check for continuity between the
ground circuit cavity of the instrument panel wire
harness connector for the inoperative heated seat
switch(es) and a good ground. There should be conti-
nuity. If OK, go to Step 4. If not OK, repair the open
ground circuit to ground as required.
(4) Reconnect the battery negative cable. Turn the
ignition switch to the On position. Check for battery
voltage at the fused ignition switch output (run) cir-
cuit cavity of the instrument panel wire harness con-
nector for the inoperative heated seat switch(es). If
OK, turn the ignition switch to the Off position, dis-
connect and isolate the battery negative cable, and go
to Step 5. If not OK, repair the open fused ignition
switch output (run) circuit to the junction block fuse
as required.
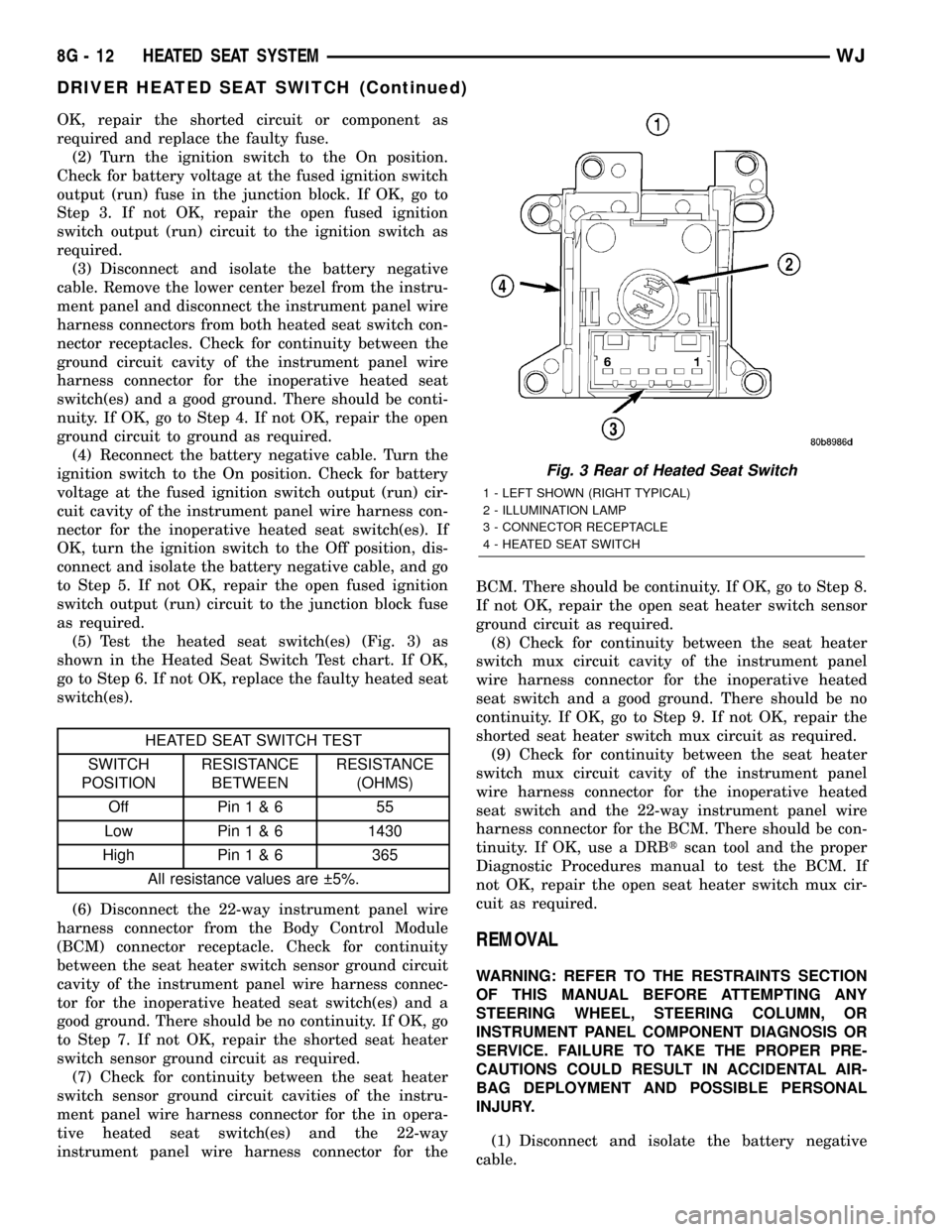
(5) Test the heated seat switch(es) (Fig. 3) as
shown in the Heated Seat Switch Test chart. If OK,
go to Step 6. If not OK, replace the faulty heated seat
switch(es).
HEATED SEAT SWITCH TEST
SWITCH
POSITIONRESISTANCE
BETWEENRESISTANCE
(OHMS)
Off Pin1&6 55
Low Pin1&61430
High Pin1&6 365
All resistance values are 5%.
(6) Disconnect the 22-way instrument panel wire
harness connector from the Body Control Module
(BCM) connector receptacle. Check for continuity
between the seat heater switch sensor ground circuit
cavity of the instrument panel wire harness connec-
tor for the inoperative heated seat switch(es) and a
good ground. There should be no continuity. If OK, go
to Step 7. If not OK, repair the shorted seat heater
switch sensor ground circuit as required.
(7) Check for continuity between the seat heater
switch sensor ground circuit cavities of the instru-
ment panel wire harness connector for the in opera-
tive heated seat switch(es) and the 22-way
instrument panel wire harness connector for theBCM. There should be continuity. If OK, go to Step 8.
If not OK, repair the open seat heater switch sensor
ground circuit as required.
(8) Check for continuity between the seat heater
switch mux circuit cavity of the instrument panel
wire harness connector for the inoperative heated
seat switch and a good ground. There should be no
continuity. If OK, go to Step 9. If not OK, repair the
shorted seat heater switch mux circuit as required.
(9) Check for continuity between the seat heater
switch mux circuit cavity of the instrument panel
wire harness connector for the inoperative heated
seat switch and the 22-way instrument panel wire
harness connector for the BCM. There should be con-
tinuity. If OK, use a DRBtscan tool and the proper
Diagnostic Procedures manual to test the BCM. If
not OK, repair the open seat heater switch mux cir-
cuit as required.
REMOVAL
WARNING: REFER TO THE RESTRAINTS SECTION
OF THIS MANUAL BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY
STEERING WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, OR
INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
Fig. 3 Rear of Heated Seat Switch
1 - LEFT SHOWN (RIGHT TYPICAL)
2 - ILLUMINATION LAMP
3 - CONNECTOR RECEPTACLE
4 - HEATED SEAT SWITCH
8G - 12 HEATED SEAT SYSTEMWJ
DRIVER HEATED SEAT SWITCH (Continued)
Page 388 of 2199

(6) Disconnect the 22-way instrument panel wire
harness connector from the Body Control Module
(BCM) connector receptacle. Check for continuity
between the seat heater switch sensor ground circuit
cavity of the instrument panel wire harness connec-
tor for the inoperative heated seat switch(es) and a
good ground. There should be no continuity. If OK, go
to Step 7. If not OK, repair the shorted seat heater
switch sensor ground circuit as required.
(7) Check for continuity between the seat heater
switch sensor ground circuit cavities of the instru-
ment panel wire harness connector for the in opera-
tive heated seat switch(es) and the 22-way
instrument panel wire harness connector for the
BCM. There should be continuity. If OK, go to Step 8.
If not OK, repair the open seat heater switch sensor
ground circuit as required.
(8) Check for continuity between the seat heater
switch mux circuit cavity of the instrument panel
wire harness connector for the inoperative heated
seat switch and a good ground. There should be no
continuity. If OK, go to Step 9. If not OK, repair the
shorted seat heater switch mux circuit as required.
(9) Check for continuity between the seat heater
switch mux circuit cavity of the instrument panel
wire harness connector for the inoperative heated
seat switch and the 22-way instrument panel wire
harness connector for the BCM. There should be con-
tinuity. If OK, use a DRBtscan tool and the proper
Diagnostic Procedures manual to test the BCM. If
not OK, repair the open seat heater switch mux cir-
cuit as required.
REMOVAL
WARNING: REFER TO THE RESTRAINTS SECTION
OF THIS MANUAL BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY
STEERING WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, OR
INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the center lower bezel from the instru-
ment panel. Refer toInstrument Panel CenterLower Bezelin the Body section of this manual for
the procedure.
(3) Remove the four screws that secure the heated
seat switch to the back of the instrument panel cen-
ter lower bezel (Fig. 9).
(4) Remove the heated seat switch from the back
of the instrument panel center lower bezel.INSTALLATION
(1) Position the heated seat switch onto the back
of the instrument panel center lower bezel.
(2) Install and tighten the four screws that secure
the heated seat switch to the back of the instrument
panel center lower bezel. Tighten the screws to 1.5
N´m (13 in. lbs.).
(3) Install the center lower bezel onto the instru-
ment panel. Refer toInstrument Panel Center
Lower Bezelin the Body section of this manual for
the procedure.
(4) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
Fig. 9 Heated Seat Switch Remove/Install
1 - HEATED SEAT SWITCHES
2 - SCREWS (4)
3 - CENTER LOWER BEZEL
4 - CIGAR LIGHTER
5 - ILLUMINATION LAMPS
6 - POWER OUTLET
WJHEATED SEAT SYSTEM 8G - 17
PASSENGER HEATED SEAT SWITCH (Continued)
Page 390 of 2199
HORN
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HORN SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HORN SYSTEM . . . 2
HORN
DESCRIPTION..........................3
OPERATION............................3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HORN..........3
REMOVAL.............................3
INSTALLATION..........................4
HORN RELAY
DESCRIPTION..........................4OPERATION............................4
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HORN RELAY....4
REMOVAL.............................5
INSTALLATION..........................5
HORN SWITCH
DESCRIPTION..........................6
OPERATION............................6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HORN SWITCH . . . 6
REMOVAL.............................7
INSTALLATION..........................7
HORN SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
A dual-note electric horn system is standard facto-
ry-installed equipment on this model. The standard
equipment horn system features one low-note horn
unit and one high-note horn unit. The horn system
allows the vehicle operator to provide an audible
warning of the presence or approach of the vehicle to
pedestrians and the drivers of other vehicles in near
proximity. The horn system uses a non-switched
source of battery current so that the system will
remain functional, regardless of the ignition switch
position.
The horn system can also be activated by the Body
Control Module (BCM). The BCM is programmed to
activate the horns in order to provide the following
features:
²Remote Keyless Entry (RKE) system lock
request audible verification (except export)
²RKE system panic mode audible alert
²Vehicle Theft Security System (VTSS) audible
alarm.
This vehicle also offers several customer program-
mable features, which allows the selection of several
optional electronic features to suit individual prefer-
ences. Refer to Overhead Console for more informa-
tion on the customer programmable feature options.
Customer programmable feature options affecting the
horn system include:
²Sound Horn on Lock- Allows the option of
having the horn sound a short chirp as an audible
verification that the RKE system received a valid
Lock request from the RKE transmitter, or having no
audible verification.The horn system includes the following compo-
nents:
²Clockspring
²Horns
²Horn relay
²Horn switch
Certain functions and features of the horn system
rely upon resources shared with other electronic
modules in the vehicle over the Programmable Com-
munications Interface (PCI) data bus network. The
PCI data bus network allows the sharing of sensor
information. This helps to reduce wire harness com-
plexity, internal controller hardware, and component
sensor current loads. At the same time, this system
provides increased reliability, enhanced diagnostics,
and allows the addition of many new feature capabil-
ities. For diagnosis of these electronic modules or of
the PCI data bus network, the use of a DRB scan
tool and the proper Diagnostic Procedures manual
are recommended.
The other electronic modules that may affect horn
system operation are as follows:
²Body Control Module (BCM)(Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-
ULES/BODY CONTROL/CENTRAL TIMER MODUL
- DESCRIPTION) for more information.
²Electronic Vehicle Information Center
(EVIC)(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/OVERHEAD
CONSOLE/ELECTRONIC VEHICLE INFO CENTER
- DESCRIPTION) for more information.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS/CLOCK-
SPRING - DESCRIPTION) for more information on
this component. Refer to the appropriate wiring
information. The wiring information includes wiring
diagrams, proper wire and connector repair proce-
dures, details of wire harness routing and retention,
WJHORN 8H - 1
Page 399 of 2199

The ignition system is controlled by the powertrain
control module (PCM) on all engines.
The ignition system consists of:
²Spark Plugs
²Ignition Coil(s)
²Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
²Crankshaft Position Sensor
²Camshaft Position Sensor
²The MAP, TPS, IAC and ECT also have an effect
on the control of the ignition system.
SPECIFICATIONS
ENGINE FIRING ORDER - 4.0L 6-CYLINDER
ENGINEENGINE FIRING ORDERÐ4.7L V-8 ENGINE
IGNITION COIL RESISTANCE - 4.0L ENGINE
PRIMARY RESISTANCE 21-27ÉC (70-80ÉF)
0.71 - 0.88 Ohms
IGNITION COIL RESISTANCEÐ4.7L V-8
ENGINE
PRIMARY RESISTANCE
21-27ÉC (70-80ÉF)SECONDARY
RESISTANCE 21-27ÉC
(70-80ÉF)
0.6 - 0.9 Ohms 6,000 - 9,000 Ohms
IGNITION TIMING
All ignition timing functions are controlled by the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM). Mechanical
adjustments are not needed and can't be made.
On the 4.0L 6±cylinder engine, do not attempt to
rotate the oil pump drive to adjust timing. This
adjustment is used for fuel synchronization after
camshaft position sensor replacement.
8I - 2 IGNITION CONTROLWJ
IGNITION CONTROL (Continued)
Page 400 of 2199

SPARK PLUGS
ENGINE PLUG TYPE ELECTRODE GAP
4.0L 6-CYL. RC12ECC 0.89 mm (.035 in.)
4.7L V-8 (Exc. HO) RC12MCC4 1.01 mm (.040 in.)
4.7L V-8 High
Output (HO)RC7PYCB4 1.01 mm (.040 in.)
TORQUE - IGNITION SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION N-m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Crankshaft Position Sensor
Bolts - 4.0L Engine7- 60
Crankshaft Position Sensor
Bolt - 4.7L V-8 Engine28 21 -
Camshaft Position
Sensor±to±base bolts - 4.0L
Engine2- 15
Camshaft Position Sensor
Bolt - 4.7L V-8 Engine12 - 106
Oil Pump Drive Hold-down
Bolt - 4.0L Engine23 17 -
Ignition Coil Rail Mounting
Bolts - 4.0L Engine29 - 250
Ignition Coil Mounting Nut -
4.7L V-8 Engine8- 70
* Knock Sensor Bolt - 4.7L
HO V-8 Engine*20 *15 -
Spark Plugs - 4.0L Engine 35-41 26-30 -
Spark Plugs - 4.7L V-8
Engine24-30 18-22 -
* Do not apply any sealant,
thread-locker or adhesive to
bolts. Poor sensor
performance may result.
Refer to Removal / Installation
for additional information.
AUTO SHUT DOWN RELAY
DESCRIPTION - PCM OUTPUT
The 5±pin, 12±volt, Automatic Shutdown (ASD)
relay is located in the Power Distribution Center
(PDC). Refer to label on PDC cover for relay location.
OPERATION
OPERATION - PCM OUTPUT
The ASD relay supplies battery voltage (12+ volts)
to the fuel injectors and ignition coil(s). With certain
emissions packages it also supplies 12±volts to the
oxygen sensor heating elements.
The ground circuit for the coil within the ASD
relay is controlled by the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). The PCM operates the ASD relay by switch-
ing its ground circuit on and off.
WJIGNITION CONTROL 8I - 3
IGNITION CONTROL (Continued)
Page 401 of 2199
The ASD relay will be shut±down, meaning the
12±volt power supply to the ASD relay will be de-ac-
tivated by the PCM if:
²the ignition key is left in the ON position. This
is if the engine has not been running for approxi-
mately 1.8 seconds.
²there is a crankshaft position sensor signal to
the PCM that is lower than pre-determined values.
OPERATION - ASD SENSE - PCM INPUT
A 12 volt signal at this input indicates to the PCM
that the ASD has been activated. The relay is used to
connect the oxygen sensor heater element, ignition
coil and fuel injectors to 12 volt + power supply.
This input is used only to sense that the ASD relay
is energized. If the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) does not see 12 volts at this input when the
ASD should be activated, it will set a Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC).
REMOVAL
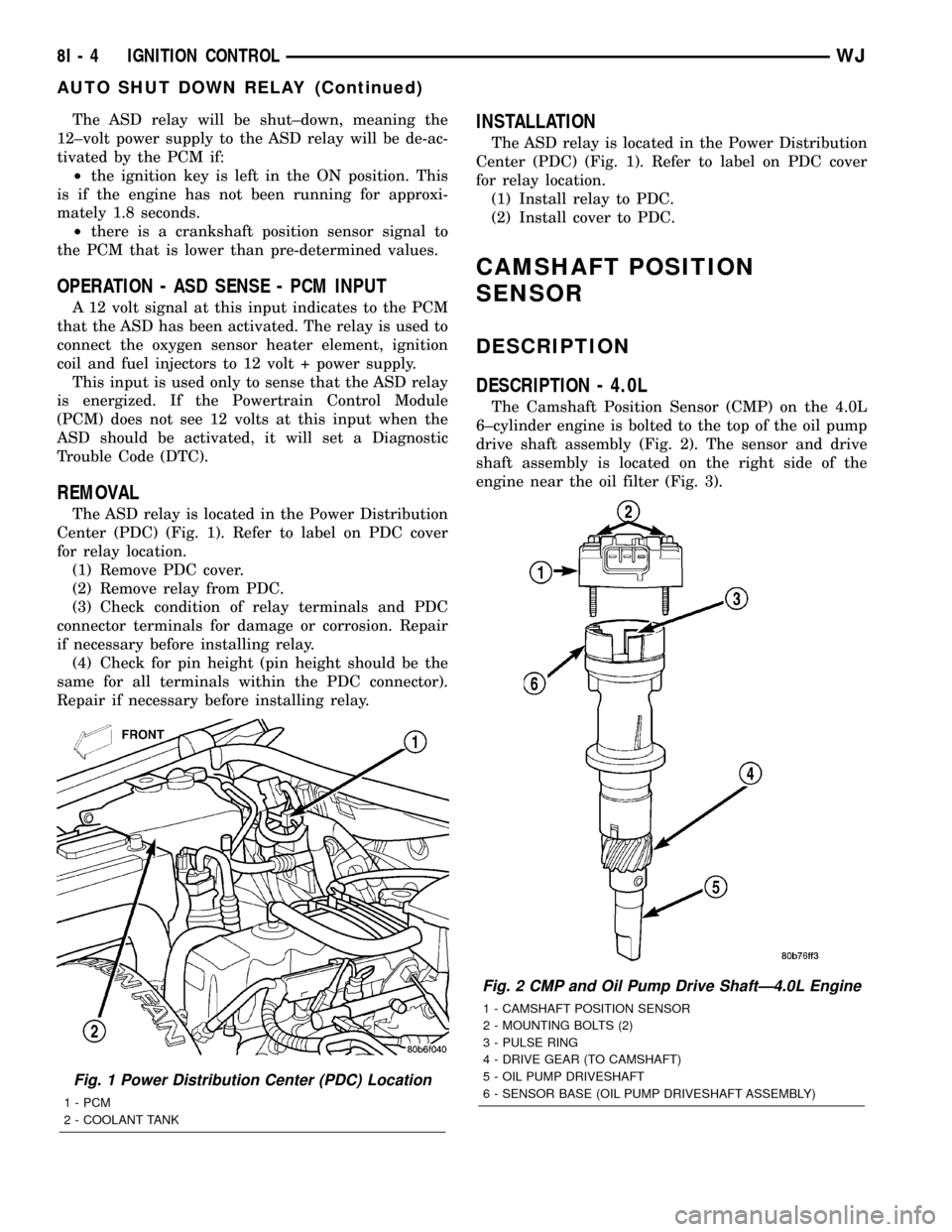
The ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution
Center (PDC) (Fig. 1). Refer to label on PDC cover
for relay location.
(1) Remove PDC cover.
(2) Remove relay from PDC.
(3) Check condition of relay terminals and PDC
connector terminals for damage or corrosion. Repair
if necessary before installing relay.
(4) Check for pin height (pin height should be the
same for all terminals within the PDC connector).
Repair if necessary before installing relay.
INSTALLATION
The ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution
Center (PDC) (Fig. 1). Refer to label on PDC cover
for relay location.
(1) Install relay to PDC.
(2) Install cover to PDC.
CAMSHAFT POSITION
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - 4.0L
The Camshaft Position Sensor (CMP) on the 4.0L
6±cylinder engine is bolted to the top of the oil pump
drive shaft assembly (Fig. 2). The sensor and drive
shaft assembly is located on the right side of the
engine near the oil filter (Fig. 3).
Fig. 1 Power Distribution Center (PDC) Location
1 - PCM
2 - COOLANT TANK
Fig. 2 CMP and Oil Pump Drive ShaftÐ4.0L Engine
1 - CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS (2)
3 - PULSE RING
4 - DRIVE GEAR (TO CAMSHAFT)
5 - OIL PUMP DRIVESHAFT
6 - SENSOR BASE (OIL PUMP DRIVESHAFT ASSEMBLY)
8I - 4 IGNITION CONTROLWJ
AUTO SHUT DOWN RELAY (Continued)
Page 406 of 2199

(14) If a plus (+) or a minus (-) is displayed next to
degree number, and/or the degree displayed is not
zero, loosen but do not remove hold-down clamp bolt.
Rotate oil pump drive until IN RANGE appears on
screen. Continue to rotate oil pump drive until
achieving as close to 0É as possible.
The degree scale on SET SYNC screen of DRB is
referring to fuel synchronization only.It is not
referring to ignition timing.Because of this, do
not attempt to adjust ignition timing using this
method. Rotating oil pump drive will have no effect
on ignition timing. All ignition timing values are con-
trolled by powertrain control module (PCM).
(15) Tighten hold-down clamp bolt to 23 N´m (17
ft. lbs.) torque.
INSTALLATION - 4.7L
The Camshaft Position Sensor (CMP) on the 4.7L
V±8 engine is bolted to the front/top of the right cyl-
inder head (Fig. 10).
(1) Clean out machined hole in cylinder head.
(2) Apply a small amount of engine oil to sensor
o-ring.
(3) Install sensor into cylinder head with a slight
rocking action. Do not twist sensor into position as
damage to o-ring may result.
CAUTION: Before tightening sensor mounting bolt,
be sure sensor is completely flush to cylinder head.
If sensor is not flush, damage to sensor mounting
tang may result.
(4) Install mounting bolt and tighten to 12 N´m
(106 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Connect electrical connector to sensor.
(6) Lower vehicle.
COIL RAIL
DESCRIPTION
A one-piece coil rail assembly containing three
individual coils is used on the 4.0L 6±cylinder engine
(Fig. 11). The coil rail must be replaced as one
assembly. The bottom of the coil is equipped with 6
individual rubber boots (Fig. 11) to seal the 6 spark
plugs to the coil. Inside each rubber boot is a spring.
The spring is used for a mechanical contact between
the coil and the top of the spark plug. These rubber
boots and springs are a permanent part of the coil
and are not serviced separately.
(1) The coil is bolted directly to the cylinder head
(Fig. 12). One electrical connector (located at rear of
coil) is used for all three coils.
Fig. 11 Ignition Coil AssemblyÐ4.0L 6±Cylinder
Engine
1 - CYL. #6
2 - CYL. #5
3 - CYL. #4
4 - CYL. #3
5 - CYL. #2
6 - CYL. #1
7 - COILS (3)
8 - MOUNTING BOLTS (4)
9 - BOLT BASES (4)
10 - RUBBER BOOTS (6)
Fig. 12 Coil LocationÐ4.0L Engine
1 - COIL RAIL
2 - COIL MOUNTING BOLTS (4)
3 - COIL
4 - COIL ELECTRICAL CONNECTION
WJIGNITION CONTROL 8I - 9
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR (Continued)
Page 410 of 2199

IGNITION COIL CAPACITOR
DESCRIPTION
Two coil capacitors are used. One of them is
located near the center of, and on the left side of the
intake manifold (Fig. 20). The other capacitor is
located near the center of, and on the right side of
the intake manifold.
OPERATION
The 2 coil capacitors are used to prevent high-volt-
age spikes from interfering with the operation of cer-
tain powertrain sensors. They are also used to help
prevent radio interference.
REMOVAL
Two coil capacitors are used. One of them is
located near the center of, and on the left side of the
intake manifold (Fig. 21). The other capacitor is
located near the center of, and on the right side of
the intake manifold.
(1) Disconnect electrical connector at coil capacitor
(Fig. 21).
(2) Remove mounting nut.
(3) Remove capacitor from mounting stud.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position capacitor to manifold mounting stud.(2) Install nut and tighten to 8 N´m (70 in. lbs.)
torque.
(3) Connect electrical connector to capacitor (Fig.
21).
KNOCK SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
4.7L High-Output Engine
The 2 knock sensors are bolted into the cylinder
block under the intake manifold.
OPERATION
4.7L High-Output Engine
Two knock sensors are used on the 4.7L V-8 engine
if equipped with the high-output package; one for
each cylinder bank. When the knock sensor detects a
knock in one of the cylinders on the corresponding
bank, it sends an input signal to the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM). In response, the PCM retards
ignition timing for all cylinders by a scheduled
amount.
Knock sensors contain a piezoelectric material
which constantly vibrates and sends an input voltage
(signal) to the PCM while the engine operates. As the
intensity of the crystal's vibration increases, the
knock sensor output voltage also increases.
Fig. 20 Coil Capacitor (Left Side Shown)
1 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
2 - COIL CAPACITOR
3 - MOUNTING NUT
Fig. 21 Coil Capacitor (Left Side Shown)
1 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
2 - COIL CAPACITOR
3 - MOUNTING NUT
WJIGNITION CONTROL 8I - 13
Page 411 of 2199

The voltage signal produced by the knock sensor
increases with the amplitude of vibration. The PCM
receives the knock sensor voltage signal as an input.
If the signal rises above a predetermined level, the
PCM will store that value in memory and retard
ignition timing to reduce engine knock. If the knock
sensor voltage exceeds a preset value, the PCM
retards ignition timing for all cylinders. It is not a
selective cylinder retard.
The PCM ignores knock sensor input during engine
idle conditions. Once the engine speed exceeds a
specified value, knock retard is allowed.
Knock retard uses its own short term and long
term memory program.
Long term memory stores previous detonation
information in its battery-backed RAM. The maxi-
mum authority that long term memory has over tim-
ing retard can be calibrated.
Short term memory is allowed to retard timing up
to a preset amount under all operating conditions (as
long as rpm is above the minimum rpm) except at
Wide Open Throttle (WOT). The PCM, using short
term memory, can respond quickly to retard timing
when engine knock is detected. Short term memory
is lost any time the ignition key is turned off.
NOTE: Over or under tightening the sensor mount-
ing bolts will affect knock sensor performance, pos-
sibly causing improper spark control. Always use
the specified torque when installing the knock sen-
sors.
REMOVAL
4.7L High-Output Engine Only
The 2 knock sensors are bolted into the cylinder
block under the intake manifold (Fig. 22).
NOTE: The left sensor is identified by an identifica-
tion tag (LEFT). It is also identified by a larger bolt
head. The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) must
have and know the correct sensor left/right posi-
tions. Do not mix the sensor locations.
(1) Disconnect knock sensor dual pigtail harness
connector from engine wiring harness connector. This
connection is made near the right/rear of intake man-
ifold (Fig. 23).
(2) Remove intake manifold. Refer to Engine sec-
tion.
(3) Remove sensor mounting bolts (Fig. 22). Note
foam strip on bolt threads. This foam is used only to
retain the bolts to sensors for plant assembly. It is
not used as a sealant. Do not apply any adhesive,
sealant or thread locking compound to these bolts.
(4) Remove sensors from engine.
Fig. 22 KNOCK SENSOR LOCATION - 4.7L H.O.
1 - KNOCK SENSORS (2)
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS
3 - INTAKE MANIFOLD (CUTAWAY)
4 - PIGTAIL CONNECTOR
Fig. 23 KNOCK SENSOR ELEC. CONNECTOR - 4.7L
H.O.
1 - KNOCK SENSOR PIGTAIL HARNESS CONNECTOR
2 - ENGINE WIRING HARNESS
8I - 14 IGNITION CONTROLWJ
KNOCK SENSOR (Continued)
Page 412 of 2199

INSTALLATION
4.7L High-Output Engine Only
NOTE: The left sensor is identified by an identifica-
tion tag (LEFT). It is also identified by a larger bolt
head. The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) must
have and know the correct sensor left/right posi-
tions. Do not mix the sensor locations.
(1) Thoroughly clean knock sensor mounting holes.
(2) Install sensors (Fig. 22) into cylinder block.
NOTE: Over or under tightening the sensor mount-
ing bolts will affect knock sensor performance, pos-
sibly causing improper spark control. Always use
the specified torque when installing the knock sen-
sors. The torque for the knock senor bolt is rela-
tively light for an 8mm bolt.
NOTE: Note foam strip on bolt threads. This foam is
used only to retain the bolts to sensors for plant
assembly. It is not used as a sealant. Do not apply
any adhesive, sealant or thread locking compound
to these bolts.
(3) Install and tighten mounting bolts.Bolt
torque is critical.Refer to torque specification.
(4) Install intake manifold. Refer to Engine sec-
tion.
(5) Connect knock sensor pigtail wiring harness to
engine wiring harness near right / rear of intake
manifold (Fig. 23).
SPARK PLUG
DESCRIPTION
Both the 4.0L 6-cylinder and the 4.7L V-8 engine
use resistor type spark plugs. Standard 4.7L V-8
engines are equipped with ªfired in suppressor sealº
type spark plugs using a copper core ground elec-
trode. High-Output (H.O.) 4.7L V-8 engines are
equipped with unique plugs using a platinum rivet
located on the tip of the center electrode.
Because of the use of an aluminum cylinder head
on the 4.7L engine, spark plug torque is very critical.
To prevent possible pre-ignition and/or mechanical
engine damage, the correct type/heat range/number
spark plug must be used.Do not substitute any
other spark plug on the 4.7L H.O. engine. Seri-
ous engine damage may occur.
Plugs on both engines have resistance values rang-
ing from 6,000 to 20,000 ohms (when checked with at
least a 1000 volt spark plug tester).Do not use an
ohmmeter to check the resistance values of thespark plugs. Inaccurate readings will result.
Remove the spark plugs and examine them for
burned electrodes and fouled, cracked or broken por-
celain insulators. Keep plugs arranged in the order
in which they were removed from the engine. A sin-
gle plug displaying an abnormal condition indicates
that a problem exists in the corresponding cylinder.
Replace spark plugs at the intervals recommended in
Group O, Lubrication and Maintenance.
EXCEPT 4.7L H.O. ENGINE :Spark plugs that
have low mileage may be cleaned and reused if not
otherwise defective, carbon or oil fouled. Also refer to
Spark Plug Conditions.4.7L H.O. ENGINE :Never
clean spark plugs on the 4.7L H.O. engine. Damage
to the platinum rivet will result.
CAUTION: EXCEPT 4.7L H.O. ENGINE : Never use a
motorized wire wheel brush to clean the spark
plugs. Metallic deposits will remain on the spark
plug insulator and will cause plug misfire.
H.O. Gap Adjustment:If equipped with the 4.7L
H.O. engine, do not use a wire-type gapping tool as
damage to the platinum rivet on the center electrode
may occur. Use a tapered-type gauge (Fig. 24).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SPARK PLUG
CONDITIONS
NORMAL OPERATING
The few deposits present on the spark plug will
probably be light tan or slightly gray in color. This is
evident with most grades of commercial gasoline
Fig. 24 PLUG GAP - 4.7L H.O.
1 - TAPER GAUGE
WJIGNITION CONTROL 8I - 15
KNOCK SENSOR (Continued)