wheel torque JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 140 of 2199
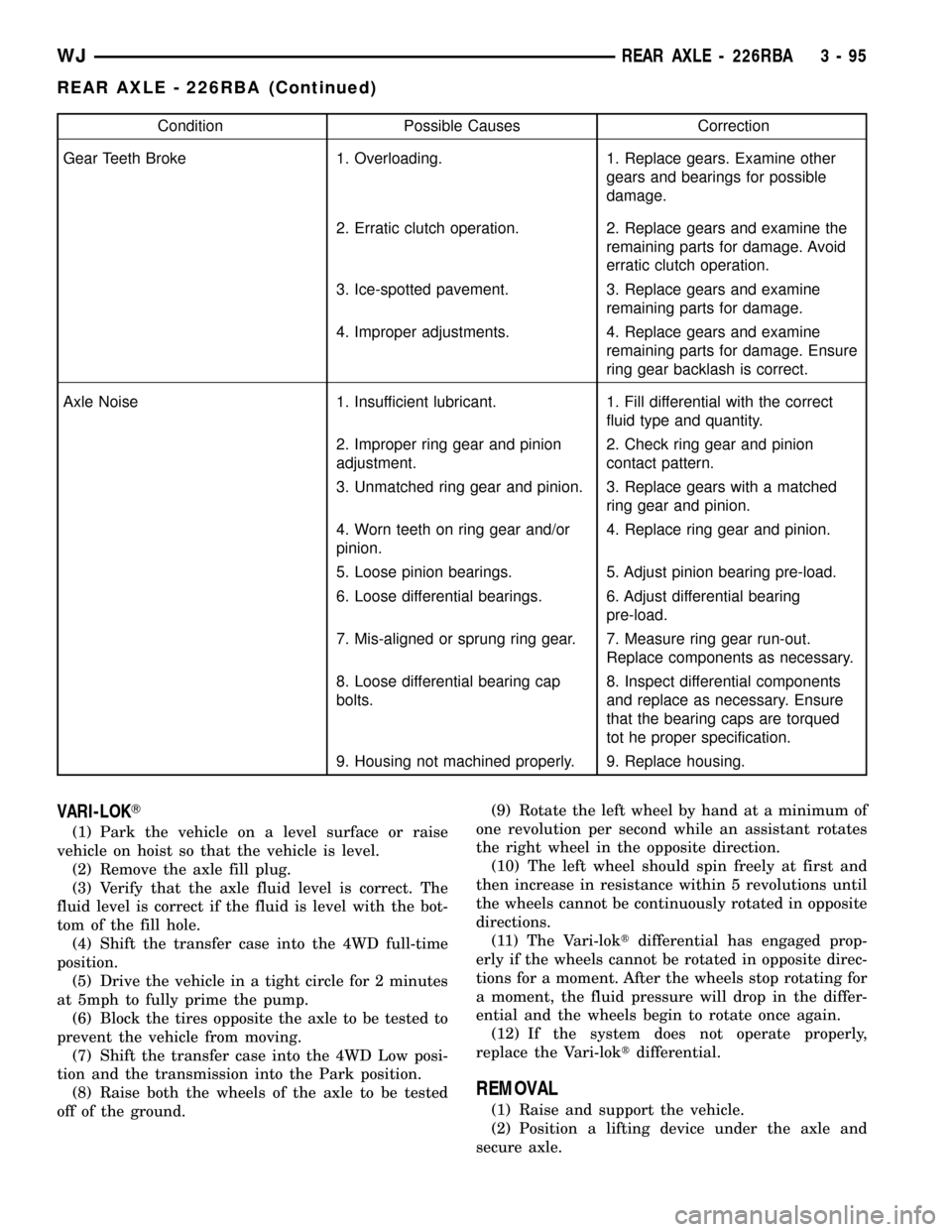
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Gear Teeth Broke 1. Overloading. 1. Replace gears. Examine other
gears and bearings for possible
damage.
2. Erratic clutch operation. 2. Replace gears and examine the
remaining parts for damage. Avoid
erratic clutch operation.
3. Ice-spotted pavement. 3. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage.
4. Improper adjustments. 4. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage. Ensure
ring gear backlash is correct.
Axle Noise 1. Insufficient lubricant. 1. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
2. Improper ring gear and pinion
adjustment.2. Check ring gear and pinion
contact pattern.
3. Unmatched ring gear and pinion. 3. Replace gears with a matched
ring gear and pinion.
4. Worn teeth on ring gear and/or
pinion.4. Replace ring gear and pinion.
5. Loose pinion bearings. 5. Adjust pinion bearing pre-load.
6. Loose differential bearings. 6. Adjust differential bearing
pre-load.
7. Mis-aligned or sprung ring gear. 7. Measure ring gear run-out.
Replace components as necessary.
8. Loose differential bearing cap
bolts.8. Inspect differential components
and replace as necessary. Ensure
that the bearing caps are torqued
tot he proper specification.
9. Housing not machined properly. 9. Replace housing.
VARI-LOKT
(1) Park the vehicle on a level surface or raise
vehicle on hoist so that the vehicle is level.
(2) Remove the axle fill plug.
(3) Verify that the axle fluid level is correct. The
fluid level is correct if the fluid is level with the bot-
tom of the fill hole.
(4) Shift the transfer case into the 4WD full-time
position.
(5) Drive the vehicle in a tight circle for 2 minutes
at 5mph to fully prime the pump.
(6) Block the tires opposite the axle to be tested to
prevent the vehicle from moving.
(7) Shift the transfer case into the 4WD Low posi-
tion and the transmission into the Park position.
(8) Raise both the wheels of the axle to be tested
off of the ground.(9) Rotate the left wheel by hand at a minimum of
one revolution per second while an assistant rotates
the right wheel in the opposite direction.
(10) The left wheel should spin freely at first and
then increase in resistance within 5 revolutions until
the wheels cannot be continuously rotated in opposite
directions.
(11) The Vari-loktdifferential has engaged prop-
erly if the wheels cannot be rotated in opposite direc-
tions for a moment. After the wheels stop rotating for
a moment, the fluid pressure will drop in the differ-
ential and the wheels begin to rotate once again.
(12) If the system does not operate properly,
replace the Vari-loktdifferential.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Position a lifting device under the axle and
secure axle.
WJREAR AXLE - 226RBA 3 - 95
REAR AXLE - 226RBA (Continued)
Page 156 of 2199

(7) Press metal retaining ring onto axle shaft with
Installer 7913 and a press (Fig. 30).
(8) Install axle in vehicle.
PINION SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove wheel and tire assemblies.
(3) Remove rear brake calipers and rotors.
(4) Mark propeller shaft and pinion yoke for
installation reference.
(5) Remove the propeller shaft from the yoke.
(6) Rotate pinion gear three or four times and ver-
ify that pinion rotates smoothly.
(7) Record torque necessary to rotate the pinion
gear with a inch pound dial-type torque wrench.
(8) Using a short piece of pipe and Spanner
Wrench 6958 to hold the pinion yoke and remove pin-
ion nut and washer (Fig. 31).
(9) Remove pinion companion flange with Remover
C-452 and Flange Wrench C-3281. (Fig. 32)
Fig. 30 BEARING RETAINING RING
1 - PRESS
2 - AXLE
3 - AXLE BEARING
4 - INSTALLER
5 - METAL RETAINING RING
Fig. 31 Pinion Yoke Holder
1 - PIPE
2 - PINION YOKE
3 - SPANNER WRENCH
4 - LOWER CONTROL ARM
Fig. 32 Pinion Yoke Remover
1 - FLANGE WRENCH
2 - YOKE
3 - YOKE PULLER
WJREAR AXLE - 226RBA 3 - 111
AXLE BEARINGS/SEALS (Continued)
Page 158 of 2199

(5) If rotating torque is low, use Wrench 6958 to
hold the pinion yoke (Fig. 37) and tighten the pinion
shaft nut in 6.8 N´m (5 ft. lbs.) increments until
rotating torque is achieved.
CAUTION: If the maximum tightening torque is
reached prior to reaching the required rotating
torque, the collapsible spacer may have been dam-
aged. Replace the collapsible spacer.
(6) Install propeller shaft with reference marks
aligned.
(7) Fill differential with gear lubricant.
(8) Install the brake rotors and calipers.
(9) Install wheel and tire assemblies.
(10) Lower the vehicle.
COLLAPSIBLE SPACER
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove wheel and tire assemblies.
(3) Remove rear brake calipers and rotors.
(4) Mark propeller shaft and pinion yoke for
installation reference and remove propeller shaft.
(5) Rotate pinion gear a minimum of ten times and
verify pinion rotates smoothly.
(6) Record rotate torque of the pinion gear, with an
inch pound torque wrench.
(7) Hold pinion yoke with Spanner Wrench 6958
and remove pinion nut and washer (Fig. 38).
(8) Remove pinion yoke with Remover C-452 and
Wrench C-3281 (Fig. 39).
Fig. 37 PINION SHAFT NUT
1 - SPANNER WRENCH
2 - PIPE
3 - TORQUE WRENCH
Fig. 38 PINION YOKE HOLDER
1 - 1 in. PIPE
2 - PINION YOKE
3 - SPANNER WRENCH
4 - LOWER CONTROL ARM
Fig. 39 PINION YOKE PULLER
1 - WRENCH
2 - PINION YOKE
3 - PULLER
WJREAR AXLE - 226RBA 3 - 113
PINION SEAL (Continued)
Page 160 of 2199

NOTE: If more than 380 N´m (280 ft. lbs.) torque is
required to crush the collapsible spacer, the spacer
is defective and must be replaced.
(7) Check rotating torque with an inch pound
torque wrench (Fig. 44). The rotating torque of the
pinion gear should be, the reading recorded during
removal plus an additional 0.56 N´m (5 in. lbs.).
(8)
Install propeller shaft with reference marks align.
(9) Install rear brake rotors and calipers.
(10) Add gear lubricant, if necessary.
(11) Install wheel and tire assemblies.
(12) Remove supports and lower vehicle.
DIFFERENTIAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove fill hole plug from the differential
housing cover.
(3) Remove differential housing cover and drain
fluid.
(4) Clean the housing cavity with flushing oil, light
engine oil or lint free cloth.
NOTE: Do not use water, steam, kerosene or gaso-
line for cleaning.
(5) Remove axle shafts.(6)
Note the reference letters stamped on the bearing
caps and housing machined sealing surface (Fig. 45).
(7) Loosen the differential bearing cap bolts.
(8) Position Spreader W-129-B with Adapter Kit
6987B on differential locating holes (Fig. 46). Install
holddown clamps and tighten the turnbuckle finger-
tight.
Fig. 44 PINION ROTATING TORQUE
1 - TORQUE WRENCH
2 - PINION YOKE
Fig. 45 BEARING CAP REFERENCE
1 - REFERENCE LETTERS
2 - REFERENCE LETTERS
Fig. 46 SPREADER LOCATION
1 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
2 - DOWEL
3 - SAFETY HOLD DOWN
4 - SPREADER
5 - TURNBUCKLE
WJREAR AXLE - 226RBA 3 - 115
COLLAPSIBLE SPACER (Continued)
Page 164 of 2199

(12) Install cover and tighten bolts in a criss-cross
pattern to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.).
(13) Refill the differential with Mopar Hypoid
Gear Lubricant or equivalent to bottom of the fill
plug hole.
(14) Install fill hole plug.
(15) Remove support and lower the vehicle.
DIFFERENTIAL - TRAC-LOK
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
The most common problem is a chatter noise when
turning corners. Before removing the unit for repair,
drain, flush and refill the axle with the specified
lubricant. A container of Mopar Trac-loktLubricant
(friction modifier) should be added after repair ser-
vice or during a lubricant change.
After changing the lubricant, drive the vehicle and
make 10 to 12 slow, figure-eight turns. This maneu-
ver will pump lubricant through the clutches. This
will correct the condition in most instances. If the
chatter persists, clutch damage could have occurred.
DIFFERENTIAL TEST
The differential can be tested without removing the
differential case by measuring rotating torque. Make
sure brakes are not dragging during this measure-
ment.
(1) Place blocks in front and rear of both front
wheels.
(2) Raise one rear wheel until it is completely off
the ground.
(3) Engine off, transmission in neutral, and park-
ing brake off.
(4) Remove wheel and bolt Special Tool 6790 or
equivalent tool to studs.
(5) Use torque wrench on special tool to rotate
wheel and read rotating torque (Fig. 56).
(6) If rotating torque is less than 41 N´m (56 ft.
lbs.) or more than 271 N´m (200 ft. lbs.) on either
wheel the unit should be serviced.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Clamp side gear Holding Fixture 6965 in a vise
and position the differential case on the Holding Fix-
ture (Fig. 57).
(2) Remove ring gear if the ring gear is to be
replaced. The Trac-loktdifferential can be serviced
with the ring gear installed.
Fig. 56 ROTATING TORQUE TEST
1 - SPECIAL TOOL WITH BOLT IN CENTER HOLE
2 - TORQUE WRENCH
Fig. 57 DIFFERENTIAL CASE FIXTURE
1 - HOLDING FIXTURE
2 - VISE
3 - DIFFERENTIAL
WJREAR AXLE - 226RBA 3 - 119
DIFFERENTIAL (Continued)
Page 183 of 2199

ADJUSTABLE PEDAL SWITCH
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the steering column opening cover
(Fig. 2)(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/
STEERING COLUMN OPENING COVER - REMOV-
AL).
(2) Disconnect the electrical connector from the
adjustable pedal switch.
(3) Remove the switch from the steering column
opening cover by squeezing the retaining clips
together and pushing the switch outwards (Fig. 3).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the switch to the steering column open-
ing cover by pushing the switch inwards seating the
retaining clips to the steering column opening cover
(Fig. 3).
(2) Reconnect the electrical connector to the
adjustable pedal switch.
(3) Install the steering column opening cover (Fig.
2)(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/
STEERING COLUMN OPENING COVER - INSTAL-
LATION).
BRAKE LINES
DESCRIPTION
Flexible rubber hose is used at both front brakes,
rear brakes and at the rear axle junction block. Dou-
ble walled steel tubing is used. Double inverted style
and ISO style flares are used on the brake lines.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE HOSES
AND LINES
Flexible rubber hose is used at both front and rear
brakes and at the rear axle junction block. Inspect
the hoses whenever the brake system is serviced, at
every engine oil change, or whenever the vehicle is in
for service.
Inspect the hoses for surface cracking, scuffing, or
worn spots. Replace any brake hose immediately if
the fabric casing of the hose is exposed due to cracks
or abrasions.
Also check brake hose installation. Faulty installa-
tion can result in kinked, twisted hoses, or contact
with the wheels and tires or other chassis compo-
nents. All of these conditions can lead to scuffing,
cracking and eventual failure.
The steel brake lines should be inspected periodi-
cally for evidence of corrosion, twists, kinks, leaks, or
other damage. Heavily corroded lines will eventually
rust through causing leaks. In any case, corroded or
damaged brake lines should be replaced.
Factory replacement brake lines and hoses are rec-
ommended to ensure quality, correct length and supe-
rior fatigue life. Care should be taken to make sure
that brake line and hose mating surfaces are clean
and free from nicks and burrs. Also remember that
right and left brake hoses are not interchangeable.
Use new copper gaskets at all caliper connections.
Be sure brake line connections are properly made
(not cross threaded) and tightened to recommended
torque.
Fig. 2 STEERING COLUMN OPENING COVER
REMOVAL/INSTALL
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL TOP PAD
2 - STEERING COLUMN OPENING COVER
3 - SCREW (3)
Fig. 3 ADJUSTABLE PEDAL SWITCH
1 - RETAINING CLIPS
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTION
5 - 8 BRAKES - BASEWJ
Page 216 of 2199

BRAKES - ABS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BRAKES - ABS
DESCRIPTION.........................41
OPERATION...........................41
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ANTILOCK
BRAKES............................42
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BLEEDING ABS
BRAKE SYSTEM......................42
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART......................42
ELECTRIC BRAKE
DESCRIPTION.........................43
OPERATION...........................43
FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................43
OPERATION...........................43
REMOVAL.............................43INSTALLATION.........................43
G-SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................44
OPERATION...........................44
REMOVAL.............................44
INSTALLATION.........................44
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................45
OPERATION...........................45
REMOVAL.............................45
INSTALLATION.........................46
HCU (HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT)
DESCRIPTION.........................46
OPERATION...........................46
REMOVAL.............................47
INSTALLATION.........................47
BRAKES - ABS
DESCRIPTION
The purpose of the antilock system is to prevent
wheel lockup during periods of high wheel slip. Pre-
venting lockup helps maintain vehicle braking action
and steering control.
The hydraulic system is a three channel design.
The front brakes are controlled individually and the
rear brakes in tandem.
The ABS electrical system is separate from other
vehicle electrical circuits. A separate controller oper-
ates the system.
OPERATION
The antilock CAB activates the system whenever
sensor signals indicate periods of high wheel slip.
High wheel slip can be described as the point where
wheel rotation begins approaching 20 to 30 percent of
actual vehicle speed during braking. Periods of high
wheel slip occur when brake stops involve high pedal
pressure and rate of vehicle deceleration.
Battery voltage is supplied to the CAB ignition ter-
minal when the ignition switch is turned to Run posi-
tion. The CAB performs a system initialization
procedure at this point. Initialization consists of a
static and dynamic self check of system electrical
components.
The static check occurs after the ignition switch is
turned to Run position. The dynamic check occurs
when vehicle road speed reaches approximately 30kph (18 mph). During the dynamic check, the CAB
briefly cycles the pump and solenoids to verify oper-
ation.
If an ABS component exhibits a fault during ini-
tialization, the CAB illuminates the amber warning
light and registers a fault code in the microprocessor
memory.
ANTILOCK BRAKING
The antilock system prevents lockup during high
slip conditions by modulating fluid apply pressure to
the wheel brake units.
Brake fluid apply pressure is modulated according
to wheel speed, degree of slip and rate of decelera-
tion. A sensor at each wheel converts wheel speed
into electrical signals. These signals are transmitted
to the CAB for processing and determination of
wheel slip and deceleration rate.
The ABS system has three fluid pressure control
channels. The front brakes are controlled separately
and the rear brakes in tandem. A speed sensor input
signal indicating a high slip condition activates the
CAB antilock program.
Two solenoid valves are used in each antilock con-
trol channel. The valves are all located within the
HCU valve body and work in pairs to either increase,
hold, or decrease apply pressure as needed in the
individual control channels.
The solenoid valves are not static during antilock
braking. They are cycled continuously to modulate
pressure. Solenoid cycle time in antilock mode can be
measured in milliseconds.
WJBRAKES - ABS 5 - 41
Page 217 of 2199

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ANTILOCK
BRAKES
The ABS brake system performs several self-tests
every time the ignition switch is turned on and the
vehicle is driven. The CAB monitors the systems
input and output circuits to verify the system is oper-
ating correctly. If the on board diagnostic system
senses that a circuit is malfunctioning the system
will set a trouble code in its memory.
NOTE: An audible noise may be heard during the
self-test. This noise should be considered normal.
NOTE: The MDS or DRB III scan tool is used to
diagnose the ABS system. For additional informa-
tion refer to the Electrical section. For test proce-
dures refer to the Chassis Diagnostic Manual.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BLEEDING ABS
BRAKE SYSTEM
ABS system bleeding requires conventional bleed-
ing methods plus use of the DRB scan tool. The pro-cedure involves performing a base brake bleeding,
followed by use of the scan tool to cycle and bleed the
HCU pump and solenoids. A second base brake bleed-
ing procedure is then required to remove any air
remaining in the system.
(1) Perform base brake bleeding. (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES - STANDARD PROCEDURE) OR (Refer to
5 - BRAKES - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Connect scan tool to the Data Link Connector.
(3) Select ANTILOCK BRAKES, followed by MIS-
CELLANEOUS, then ABS BRAKES. Follow the
instructions displayed. When scan tool displays TEST
COMPLETE, disconnect scan tool and proceed.
(4) Perform base brake bleeding a second time.
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
OR (Refer to 5 - BRAKES - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(5) Top off master cylinder fluid level and verify
proper brake operation before moving vehicle.
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
G-Sensor Bolt 5.6 Ð 50
Hydraulic Control Unit/Controller
Antilock Brakes
Mounting Bolts12 9 125
Hydraulic Control Unit/Controller
Antilock Brakes
Brake Lines16 Ð 144
Hydraulic Control Unit/Controller
Antilock Brakes
CAB Screws1.8 Ð 16
Wheel Speed Sensors
Front Sensor Bolt12-14 106-124 Ð
Wheel Speed Sensors
Rear Sensor Bolt12-14 106-124 Ð
5 - 42 BRAKES - ABSWJ
BRAKES - ABS (Continued)
Page 412 of 2199

INSTALLATION
4.7L High-Output Engine Only
NOTE: The left sensor is identified by an identifica-
tion tag (LEFT). It is also identified by a larger bolt
head. The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) must
have and know the correct sensor left/right posi-
tions. Do not mix the sensor locations.
(1) Thoroughly clean knock sensor mounting holes.
(2) Install sensors (Fig. 22) into cylinder block.
NOTE: Over or under tightening the sensor mount-
ing bolts will affect knock sensor performance, pos-
sibly causing improper spark control. Always use
the specified torque when installing the knock sen-
sors. The torque for the knock senor bolt is rela-
tively light for an 8mm bolt.
NOTE: Note foam strip on bolt threads. This foam is
used only to retain the bolts to sensors for plant
assembly. It is not used as a sealant. Do not apply
any adhesive, sealant or thread locking compound
to these bolts.
(3) Install and tighten mounting bolts.Bolt
torque is critical.Refer to torque specification.
(4) Install intake manifold. Refer to Engine sec-
tion.
(5) Connect knock sensor pigtail wiring harness to
engine wiring harness near right / rear of intake
manifold (Fig. 23).
SPARK PLUG
DESCRIPTION
Both the 4.0L 6-cylinder and the 4.7L V-8 engine
use resistor type spark plugs. Standard 4.7L V-8
engines are equipped with ªfired in suppressor sealº
type spark plugs using a copper core ground elec-
trode. High-Output (H.O.) 4.7L V-8 engines are
equipped with unique plugs using a platinum rivet
located on the tip of the center electrode.
Because of the use of an aluminum cylinder head
on the 4.7L engine, spark plug torque is very critical.
To prevent possible pre-ignition and/or mechanical
engine damage, the correct type/heat range/number
spark plug must be used.Do not substitute any
other spark plug on the 4.7L H.O. engine. Seri-
ous engine damage may occur.
Plugs on both engines have resistance values rang-
ing from 6,000 to 20,000 ohms (when checked with at
least a 1000 volt spark plug tester).Do not use an
ohmmeter to check the resistance values of thespark plugs. Inaccurate readings will result.
Remove the spark plugs and examine them for
burned electrodes and fouled, cracked or broken por-
celain insulators. Keep plugs arranged in the order
in which they were removed from the engine. A sin-
gle plug displaying an abnormal condition indicates
that a problem exists in the corresponding cylinder.
Replace spark plugs at the intervals recommended in
Group O, Lubrication and Maintenance.
EXCEPT 4.7L H.O. ENGINE :Spark plugs that
have low mileage may be cleaned and reused if not
otherwise defective, carbon or oil fouled. Also refer to
Spark Plug Conditions.4.7L H.O. ENGINE :Never
clean spark plugs on the 4.7L H.O. engine. Damage
to the platinum rivet will result.
CAUTION: EXCEPT 4.7L H.O. ENGINE : Never use a
motorized wire wheel brush to clean the spark
plugs. Metallic deposits will remain on the spark
plug insulator and will cause plug misfire.
H.O. Gap Adjustment:If equipped with the 4.7L
H.O. engine, do not use a wire-type gapping tool as
damage to the platinum rivet on the center electrode
may occur. Use a tapered-type gauge (Fig. 24).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SPARK PLUG
CONDITIONS
NORMAL OPERATING
The few deposits present on the spark plug will
probably be light tan or slightly gray in color. This is
evident with most grades of commercial gasoline
Fig. 24 PLUG GAP - 4.7L H.O.
1 - TAPER GAUGE
WJIGNITION CONTROL 8I - 15
KNOCK SENSOR (Continued)
Page 415 of 2199

SPARK PLUG OVERHEATING
Overheating is indicated by a white or gray center
electrode insulator that also appears blistered (Fig.
31). The increase in electrode gap will be consider-
ably in excess of 0.001 inch per 2000 miles of opera-
tion. This suggests that a plug with a cooler heat
range rating should be used. Over advanced ignition
timing, detonation and cooling system malfunctions
can also cause spark plug overheating.
CAUTION: If the engine is equipped with copper
core ground electrode, or platinum tipped spark
plugs, they must be replaced with the same type/
number spark plug as the original. If another spark
plug is substituted, pre-ignition will result.
REMOVAL
CAUTION: If equipped with a 4.7L H.O. (High-Out-
put) engine, never substitute the original platinum
tipped spark plug with a different part number. Seri-
ous engine damage may result.
On the 4.0L 6±cylinder engine, the spark plugs are
located below the coil rail assembly. On the 4.7L V±8
engine, each individual spark plug is located under
each ignition coil.
(1) 4.0L 6±Cylinder Engine: Prior to removing
spark plug, spray compressed air around spark plug
hole and area around spark plug. This will help pre-
vent foreign material from entering combustion
chamber.
(2) 4.7L V±8 Engine: Prior to removing spark plug,
spray compressed air around base of ignition coil at
cylinder head. This will help prevent foreign material
from entering combustion chamber.
(3) On the 4.0L engine the coil rail assembly must
be removed to gain access to any/all spark plug.
Refer to Ignition Coil Removal/Installation. On the4.7L V-8 engine each individual ignition coil must be
removed to gain access to each spark plug. Refer to
Ignition Coil Removal/Installation.
(4) Remove spark plug from cylinder head using a
quality socket with a rubber or foam insert. If
equipped with a 4.7L V-8 engine, also check condition
of coil o-ring and replace as necessary.
(5) Inspect spark plug condition. Refer to Spark
Plug Conditions.
CLEANING
Except 4.7L H.O. Engine:The plugs may be
cleaned using commercially available spark plug
cleaning equipment. After cleaning, file center elec-
trode flat with a small point file or jewelers file
before adjusting gap.
CAUTION: Never use a motorized wire wheel brush
to clean spark plugs. Metallic deposits will remain
on spark plug insulator and will cause plug misfire.
4.7L H.O. Engine:Never clean spark plugs on the
4.7L H.O. engine. Damage to the platinum rivet on
the center electrode will result.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: The standard 4.7L V-8 engine is
equipped with copper core ground electrode spark
plugs. They must be replaced with the same type/
number spark plug as the original. If another spark
plug is substituted, pre-ignition will result.
CAUTION: If equipped with a 4.7L H.O. (High-Out-
put) engine, never substitute the original platinum
tipped spark plug with a different type/part number.
Serious engine damage may result.
Special care should be taken when installing spark
plugs into cylinder head spark plug wells. Be sure
plugs do not drop into plug wells as ground straps
may be bent resulting in a change in plug gap, or
electrodes can be damaged.
Always tighten spark plugs to specified torque. Over
tightening can cause distortion resulting in a change
in spark plug gap or a cracked porcelain insulator.
(1) Start spark plug into cylinder head by hand to
avoid cross threading.
(2) 4.0L 6±Cylinder Engine: Tighten spark plugs to
35-41 N´m (26-30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) 4.7L V±8 Engine: Tighten spark plugs to 27
N´m (20 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4)
4.7L V±8 Engine: Before installing coil(s), check
condition of coil o-ring and replace as necessary. To aid
in coil installation, apply silicone to coil o-ring.
(5) Install ignition coil(s). Refer to Ignition Coil
Removal/Installation.
Fig. 31 SPARK PLUG OVERHEATING
1 - BLISTERED WHITE OR GRAY COLORED INSULATOR
8I - 18 IGNITION CONTROLWJ
SPARK PLUG (Continued)