fuel cap JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 1697 of 2199
INSTALLATION........................253
OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................254
OPERATION..........................254
REMOVAL............................254
INSTALLATION........................254
OVERDRIVE SWITCH
DESCRIPTION........................254
OPERATION..........................254
PARK LOCK CABLE
REMOVAL............................255
INSTALLATION........................255
PISTONS
DESCRIPTION........................256
OPERATION..........................256
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN
DESCRIPTION........................258
OPERATION..........................260
DISASSEMBLY........................260
CLEANING...........................260
INSPECTION.........................260
ASSEMBLY...........................261
SHIFT MECHANISM
DESCRIPTION........................261
OPERATION..........................261
REMOVAL............................261
INSTALLATION........................263
SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
DESCRIPTION........................263
OPERATION..........................263
SOLENOIDS
DESCRIPTION........................263OPERATION..........................264
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION........................264
OPERATION..........................268
REMOVAL............................269
INSTALLATION........................269
TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY
DESCRIPTION........................270
OPERATION..........................270
TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................270
OPERATION..........................270
TRANSMISSION SOLENOID/TRS ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION........................271
OPERATION..........................271
REMOVAL............................272
INSTALLATION........................272
TRANSMISSION TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................272
OPERATION..........................272
VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION........................273
OPERATION..........................273
REMOVAL............................274
DISASSEMBLY........................275
CLEANING...........................277
INSPECTION.........................277
ASSEMBLY...........................278
INSTALLATION........................279
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION -
545RFE
DESCRIPTION
The 545RFE automatic transmission is a sophisti-
cated, multi-range, electronically controlled transmis-
sion which combines optimized gear ratios for
responsive performance, state of the art efficiency
features and low NVH. Other features include driver
adaptive shifting and three planetary gear sets to
provide wide ratio capability with precise ratio steps
for optimum driveability. The three planetary gear
sets also make available a unique alternate second
gear ratio. The primary 2nd gear ratio fits between
1st and 3rd gears for normal through-gear accelera-
tions. The alternate second gear ratio (2prime) allows
smoother 4-2 kickdowns at high speeds to provide
2nd gear passing performance over a wider highway
cruising range. An additional overdrive ratio (0.67:1)
is also provided for greater fuel economy and less
NVH at highway speeds.The hydraulic portion of the transmission consists
of the transmission fluid, fluid passages, hydraulic
valves, and various line pressure control components.
The primary mechanical components of the trans-
mission consist of the following:
²Three multiple disc input clutches
²Three multiple disc holding clutches
²Five hydraulic accumulators
²Three planetary gear sets
²Dual Stage Hydraulic oil pump
²Valve body
²Solenoid pack
The TCM is the ªheartº or ªbrainº of the electronic
control system and relies on information from vari-
ous direct and indirect inputs (sensors, switches, etc.)
to determine driver demand and vehicle operating
conditions. With this information, the TCM can cal-
culate and perform timely and quality shifts through
various output or control devices (solenoid pack,
transmission control relay, etc.).
21 - 178 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
Page 1865 of 2199
TIRES
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - TIRES
Tires are designed and engineered for each specific
vehicle. They provide the best overall performance
for normal operation. The ride and handling charac-
teristics match the vehicle's requirements. With
proper care they will give excellent reliability, trac-
tion, skid resistance, and tread life.
Driving habits have more effect on tire life than
any other factor. Careful drivers will obtain in most
cases, much greater mileage than severe use or care-
less drivers. A few of the driving habits which will
shorten the life of any tire are:
²Rapid acceleration
²Severe brake applications
²High speed driving
²Excessive speeds on turns
²Striking curbs and other obstacles
Radial-ply tires are more prone to irregular tread
wear. It is important to follow the tire rotation inter-
val shown in the section on Tire Rotation.(Refer to 22
- TIRES/WHEELS - STANDARD PROCEDURE),
This will help to achieve a greater tread life.
TIRE IDENTIFICATION
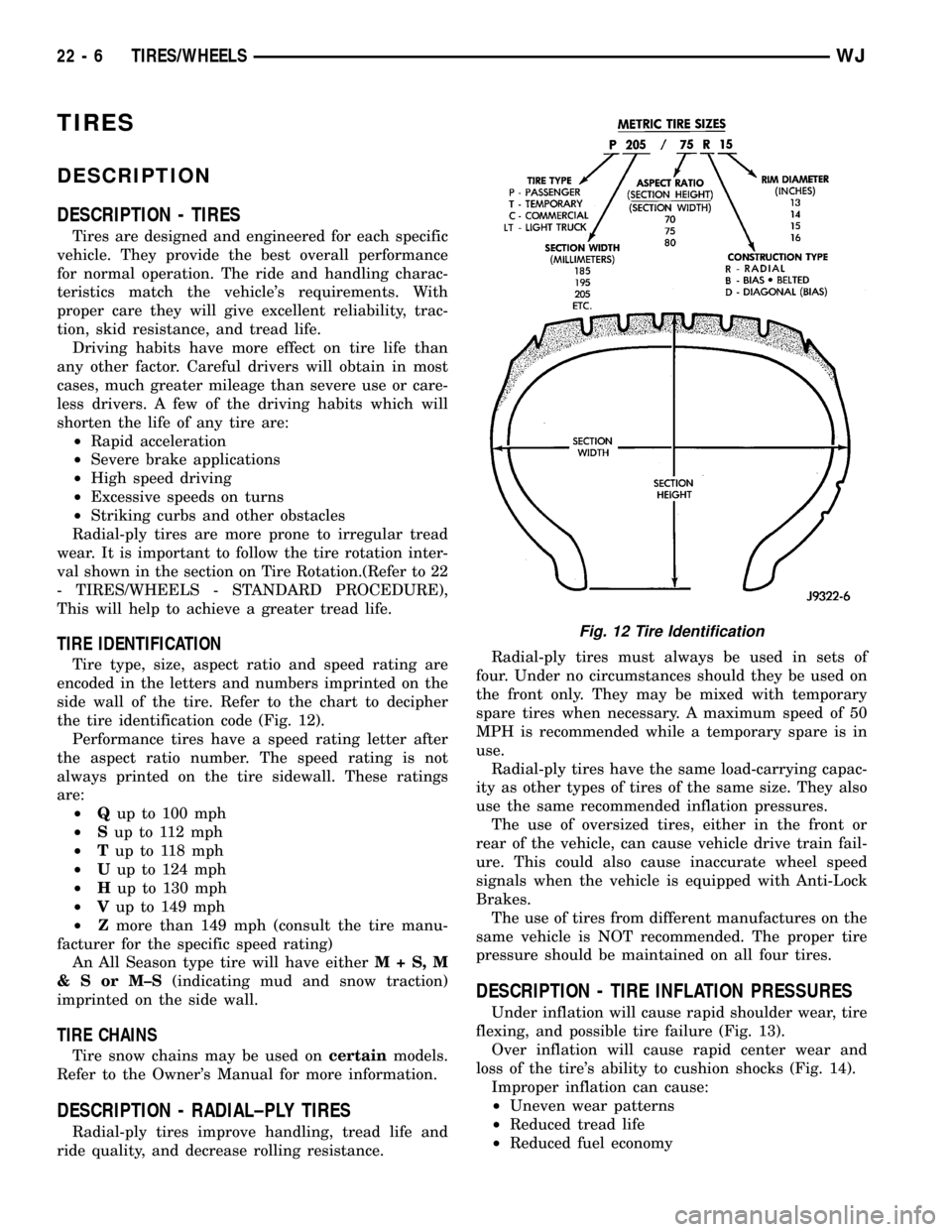
Tire type, size, aspect ratio and speed rating are
encoded in the letters and numbers imprinted on the
side wall of the tire. Refer to the chart to decipher
the tire identification code (Fig. 12).
Performance tires have a speed rating letter after
the aspect ratio number. The speed rating is not
always printed on the tire sidewall. These ratings
are:
²Qup to 100 mph
²Sup to 112 mph
²Tup to 118 mph
²Uup to 124 mph
²Hup to 130 mph
²Vup to 149 mph
²Zmore than 149 mph (consult the tire manu-
facturer for the specific speed rating)
An All Season type tire will have eitherM+S,M
&SorM±S(indicating mud and snow traction)
imprinted on the side wall.
TIRE CHAINS
Tire snow chains may be used oncertainmodels.
Refer to the Owner's Manual for more information.
DESCRIPTION - RADIAL±PLY TIRES
Radial-ply tires improve handling, tread life and
ride quality, and decrease rolling resistance.Radial-ply tires must always be used in sets of
four. Under no circumstances should they be used on
the front only. They may be mixed with temporary
spare tires when necessary. A maximum speed of 50
MPH is recommended while a temporary spare is in
use.
Radial-ply tires have the same load-carrying capac-
ity as other types of tires of the same size. They also
use the same recommended inflation pressures.
The use of oversized tires, either in the front or
rear of the vehicle, can cause vehicle drive train fail-
ure. This could also cause inaccurate wheel speed
signals when the vehicle is equipped with Anti-Lock
Brakes.
The use of tires from different manufactures on the
same vehicle is NOT recommended. The proper tire
pressure should be maintained on all four tires.
DESCRIPTION - TIRE INFLATION PRESSURES
Under inflation will cause rapid shoulder wear, tire
flexing, and possible tire failure (Fig. 13).
Over inflation will cause rapid center wear and
loss of the tire's ability to cushion shocks (Fig. 14).
Improper inflation can cause:
²Uneven wear patterns
²Reduced tread life
²Reduced fuel economy
Fig. 12 Tire Identification
22 - 6 TIRES/WHEELSWJ
Page 1933 of 2199

(5) Reach under the steering column opening cover
to access and remove the screw that secures the cour-
tesy lamp bracket and the inboard side of the JB to
the instrument panel steering column support
bracket.
(6) Remove the courtesy lamp bracket from the
inboard side of the JB and the instrument panel
steering column support bracket.
INSTALLATION
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Reach under the instrument panel to position
the upper end of the courtesy lamp bracket to the
inboard side of the Junction Block (JB) and the
instrument panel steering column support bracket
(Fig. 30).(2) Install and tighten the screw that secures the
courtesy lamp bracket and the inboard side of the JB
to the instrument panel steering column support
bracket. Tighten the screw to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.).
(3) Position the courtesy lamp to the lower end of
the courtesy lamp bracket.
(4) Install and tighten the screw that secures the
courtesy lamp to the lower end of the courtesy lamp
bracket. Tighten the screw to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.).
(5) Reinstall the instrument panel fuse cover to
the bottom of the JB and Body Control Module
(BCM) unit. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER
DISTRIBUTION/FUSE COVER - INSTALLATION).
(6) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
INSTRUMENT PANEL
INTERMEDIATE BRACKET
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the accelerator pedal assembly from
the shoulder studs on the dash panel. (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/ACCELERATOR
PEDAL - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the instrument panel from the vehicle.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL -
REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the one nut that secures the instru-
ment panel intermediate bracket to the stud on the
dash panel (Fig. 31).
(5) Remove the instrument panel intermediate
bracket from the two shoulder studs and the one
stud on the dash panel.
Fig. 30 Instrument Panel Courtesy Lamp Bracket
Remove/Install
1 - STEERING COLUMN
2 - SCREW
3 - COURTESY LAMP BRACKET
4 - DRIVER SIDE COURTESY LAMP
5 - JUNCTION BLOCK
6 - SCREW
23 - 60 INSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEMWJ
INSTRUMENT PANEL COURTESY LAMP BRACKET (Continued)
Page 1934 of 2199

INSTALLATION
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Position the instrument panel intermediate
bracket to the two shoulder studs and the one stud
on the dash panel (Fig. 31).
(2) Loosely install the one nut that secures the
intermediate bracket to the one stud on the dash
panel.
(3) Reinstall the instrument panel into the vehicle.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL -
INSTALLATION).
(4) Reinstall the accelerator pedal assembly onto
the shoulder studs on the dash panel. (Refer to 14 -FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/ACCELERATOR
PEDAL - INSTALLATION).
(5) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
INSTRUMENT PANEL LOWER
RIGHT CENTER BEZEL
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Unlatch and open the glove box.
(3) Remove the three screws that secure the lower
right center bezel to the instrument panel glove box
opening (Fig. 32).
(4) Pull the lower right center bezel straight back
from the instrument panel to disengage the two snap
clips that secure it to the receptacles in the instru-
ment panel top pad.
(5) Remove the lower right center bezel from the
instrument panel.
INSTALLATION
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Be certain that the glove box catch bumper is
installed in the mounting hole nearest the inboard
Fig. 31 Instrument Panel Intermediate Bracket
Remove/Install
1 - STUD
2 - DASH PANEL
3 - NUT (2)
4 - INTERMEDIATE BRACKET
5 - NUT (2)
6 - ACCELERATOR PEDAL
7 - SHOULDER STUDS
WJINSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEM 23 - 61
INSTRUMENT PANEL INTERMEDIATE BRACKET (Continued)
Page 2174 of 2199

and deteriorate engine performance, driveability and
fuel economy.
The catalyst monitor uses dual oxygen sensors
(O2S's) to monitor the efficiency of the converter. The
dual O2S's sensor strategy is based on the fact that
as a catalyst deteriorates, its oxygen storage capacity
and its efficiency are both reduced. By monitoring
the oxygen storage capacity of a catalyst, its effi-
ciency can be indirectly calculated. The upstream
O2S is used to detect the amount of oxygen in the
exhaust gas before the gas enters the catalytic con-
verter. The PCM calculates the A/F mixture from the
output of the O2S. A low voltage indicates high oxy-
gen content (lean mixture). A high voltage indicates a
low content of oxygen (rich mixture).
When the upstream O2S detects a lean condition,
there is an abundance of oxygen in the exhaust gas.
A functioning converter would store this oxygen so it
can use it for the oxidation of HC and CO. As the
converter absorbs the oxygen, there will be a lack of
oxygen downstream of the converter. The output of
the downstream O2S will indicate limited activity in
this condition.
As the converter loses the ability to store oxygen,
the condition can be detected from the behavior of
the downstream O2S. When the efficiency drops, no
chemical reaction takes place. This means the con-
centration of oxygen will be the same downstream as
upstream. The output voltage of the downstream
O2S copies the voltage of the upstream sensor. The
only difference is a time lag (seen by the PCM)
between the switching of the O2S's.
To monitor the system, the number of lean-to-rich
switches of upstream and downstream O2S's is
counted. The ratio of downstream switches to
upstream switches is used to determine whether the
catalyst is operating properly. An effective catalyst
will have fewer downstream switches than it has
upstream switches i.e., a ratio closer to zero. For a
totally ineffective catalyst, this ratio will be one-to-
one, indicating that no oxidation occurs in the device.
The system must be monitored so that when cata-
lyst efficiency deteriorates and exhaust emissions
increase to over the legal limit, the MIL will be illu-
minated.
DESCRIPTION - TRIP DEFINITION
The term ªTripº has different meanings depending
on what the circumstances are. If the MIL (Malfunc-
tion Indicator Lamp) is OFF, a Trip is defined as
when the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and the Catalyst
Monitor have been completed in the same drive cycle.
When any Emission DTC is set, the MIL on the
dash is turned ON. When the MIL is ON, it takes 3
good trips to turn the MIL OFF. In this case, itdepends on what type of DTC is set to know what a
ªTripº is.
For the Fuel Monitor or Mis-Fire Monitor (contin-
uous monitor), the vehicle must be operated in the
ªSimilar Condition Windowº for a specified amount of
time to be considered a Good Trip.
If a Non-Contiuous OBDII Monitor fails twice in a
row and turns ON the MIL, re-running that monitor
which previously failed, on the next start-up and
passing the monitor, is considered to be a Good Trip.
These will include the following:
²Oxygen Sensor
²Catalyst Monitor
²Purge Flow Monitor
²Leak Detection Pump Monitor (if equipped)
²EGR Monitor (if equipped)
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
If any other Emission DTC is set (not an OBDII
Monitor), a Good Trip is considered to be when the
Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst Monitor have
been completed; or 2 Minutes of engine run time if
the Oxygen Sensor Monitor or Catalyst Monitor have
been stopped from running.
It can take up to 2 Failures in a row to turn on the
MIL. After the MIL is ON, it takes 3 Good Trips to
turn the MIL OFF. After the MIL is OFF, the PCM
will self-erase the DTC after 40 Warm-up cycles. A
Warm-up cycle is counted when the ECT (Engine
Coolant Temperature Sensor) has crossed 160ÉF and
has risen by at least 40ÉF since the engine has been
started.
DESCRIPTION - COMPONENT MONITORS
There are several components that will affect vehi-
cle emissions if they malfunction. If one of these com-
ponents malfunctions the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) will illuminate.
Some of the component monitors are checking for
proper operation of the part. Electrically operated
components now have input (rationality) and output
(functionality) checks. Previously, a component like
the Throttle Position sensor (TPS) was checked by
the PCM for an open or shorted circuit. If one of
these conditions occurred, a DTC was set. Now there
is a check to ensure that the component is working.
This is done by watching for a TPS indication of a
greater or lesser throttle opening than MAP and
engine rpm indicate. In the case of the TPS, if engine
vacuum is high and engine rpm is 1600 or greater
and the TPS indicates a large throttle opening, a
DTC will be set. The same applies to low vacuum if
the TPS indicates a small throttle opening.
All open/short circuit checks or any component that
has an associated limp in will set a fault after 1 trip
with the malfunction present. Components without
WJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 19
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2179 of 2199

EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - EVAPORATION CONTROL
SYSTEM............................24
DESCRIPTION - CCV SYSTEM...........25
DESCRIPTION - PCV SYSTEM...........25
OPERATION
OPERATION - 4.0L CCV SYSTEM.........26
OPERATION - 4.7L PCV SYSTEM.........26
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE - EVAPORATION SYSTEM.......27
CCV HOSE
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CCV SYSTEM -
4.0L................................28
REMOVAL - FIXED ORIFICE FITTING........28
INSTALLATION - FIXED ORIFICE FITTING....29
EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION.........................29
OPERATION...........................29
REMOVAL.............................29
INSTALLATION.........................29
FUEL FILLER CAP
DESCRIPTION.........................29
OPERATION...........................29REMOVAL.............................29
LEAK DETECTION PUMP
DESCRIPTION.........................30
OPERATION...........................31
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENABLING
CONDITIONS TO RUN EVAP LEAK
DETECTION TEST.....................32
REMOVAL.............................35
INSTALLATION.........................35
ORVR
DESCRIPTION.........................37
OPERATION...........................37
P C V VA LV E
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PCV VALVE/PCV
SYSTEM - 4.7L.......................37
REMOVAL - PCV VALVE - 4.7L.............39
INSTALLATION - PCV VALVE - 4.7L.........39
VACUUM LINES
DESCRIPTION.........................39
VAPOR CANISTER
DESCRIPTION.........................39
OPERATION...........................39
REMOVAL.............................40
INSTALLATION.........................40
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - EVAPORATION CONTROL
SYSTEM
The evaporation control system prevents the emis-
sion of fuel tank vapors into the atmosphere. When
fuel evaporates in the fuel tank, the vapors pass
through the control valve, through the fuel manage-
ment valve, and through vent hoses and tubes to a
charcoal filled evaporative canister. The canister tem-
porarily holds the vapors. The Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) allows intake manifold vacuum todraw vapors into the combustion chambers during
certain operating conditions.
Gas powered engines use a duty cycle purge sys-
tem. The PCM controls vapor flow by operating the
duty cycle EVAP purge solenoid. Refer to Duty Cycle
EVAP Canister Purge Solenoid.
When equipped with certain emissions packages, a
Leak Detection Pump (LDP) will be used as part of
the evaporative system for OBD II requirements.
Also refer to Leak Detection Pump.
Vehicles powered with gasoline engines are also
equipped with ORVR (On-Board Refueling Vapor
Recovery). Refer to ORVR for additional information.
25 - 24 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSWJ
Page 2184 of 2199

INSTALLATION - FIXED ORIFICE FITTING
When installing fixed orifice fitting, be sure loca-
tions of fixed orifice fitting and air inlet fitting (Fig.
9) have not been inadvertently exchanged. The fixed
orifice fitting is light grey in color and is located at
rearof valve cover. The air inlet fitting is black in
color and is located atfrontof valve cover.
(1) Connect fitting to CCV breather tube.
(2) Return fixed orifice fitting to valve cover grom-
met.
EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION
The duty cycle EVAP canister purge solenoid (DCP)
regulates the rate of vapor flow from the EVAP can-
ister to the intake manifold. The Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) operates the solenoid.
OPERATION
During the cold start warm-up period and the hot
start time delay, the PCM does not energize the sole-
noid. When de-energized, no vapors are purged. The
PCM de-energizes the solenoid during open loop oper-
ation.
The engine enters closed loop operation after it
reaches a specified temperature and the time delay
ends. During closed loop operation, the PCM cycles
(energizes and de-energizes) the solenoid 5 or 10
times per second, depending upon operating condi-
tions. The PCM varies the vapor flow rate by chang-
ing solenoid pulse width. Pulse width is the amount
of time that the solenoid is energized. The PCM
adjusts solenoid pulse width based on engine operat-
ing condition.
REMOVAL
The duty cycle evaporative (EVAP) canister purge
solenoid is located in the engine compartment near
the brake master cylinder (Fig. 10).
(1) Disconnect electrical connector at solenoid.
(2) Disconnect vacuum lines at solenoid.
(3) Lift solenoid slot (Fig. 10) from mounting
bracket for removal.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position solenoid slot to mounting bracket.
(2) Connect vacuum lines to solenoid. Be sure vac-
uum lines are firmly connected and not leaking or
damaged. If leaking, a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) may be set with certain emission packages.
(3) Connect electrical connector to solenoid.
FUEL FILLER CAP
DESCRIPTION
The plastic fuel tank filler tube cap is threaded
onto the end of the fuel fill tube. Certain models are
equipped with a 1/4 turn cap.
OPERATION
The loss of any fuel or vapor out of fuel filler tube
is prevented by the use of a pressure-vacuum fuel fill
cap. Relief valves inside the cap will release fuel tank
pressure at predetermined pressures. Fuel tank vac-
uum will also be released at predetermined values.
This cap must be replaced by a similar unit if
replacement is necessary. This is in order for the sys-
tem to remain effective.
CAUTION: Remove fill cap before servicing any fuel
system component to relieve tank pressure. If
equipped with a California emissions package and a
Leak Detection Pump (LDP), the cap must be tight-
ened securely. If cap is left loose, a Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) may be set.
REMOVAL
If replacement of the 1/4 turn fuel tank filler tube
cap is necessary, it must be replaced with an identi-
cal cap to be sure of correct system operation.
Fig. 10 EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID LOCATION
1 - BRAKE MASTER CYLINDER
2 - EVAP SOLENOID
3 - SLOT
4 - ELEC. CONNEC.
5 - VACUUM LINE CONNEC.
6 - TEST PORT
WJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 29
CCV HOSE (Continued)
Page 2185 of 2199

CAUTION: Remove the fuel tank filler tube cap to
relieve fuel tank pressure. The cap must be
removed prior to disconnecting any fuel system
component or before draining the fuel tank.
LEAK DETECTION PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The evaporative emission system is designed to
prevent the escape of fuel vapors from the fuel sys-
tem (Fig. 11). Leaks in the system, even small ones,
can allow fuel vapors to escape into the atmosphere.
Government regulations require onboard testing to
make sure that the evaporative (EVAP) system is
functioning properly. The leak detection system tests
for EVAP system leaks and blockage. It also performs
self-diagnostics. During self-diagnostics, the Power-
train Control Module (PCM) first checks the Leak
Detection Pump (LDP) for electrical and mechanical
faults. If the first checks pass, the PCM then uses
the LDP to seal the vent valve and pump air into the
system to pressurize it. If a leak is present, the PCM
will continue pumping the LDP to replace the air
that leaks out. The PCM determines the size of the
leak based on how fast/long it must pump the LDP
as it tries to maintain pressure in the system.
EVAP LEAK DETECTION SYSTEM COMPONENTS
Service Port: Used with special tools like the Miller
Evaporative Emissions Leak Detector (EELD) to test
for leaks in the system.
EVAP Purge Solenoid: The PCM uses the EVAP
purge solenoid to control purging of excess fuel
vapors stored in the EVAP canister. It remains closed
during leak testing to prevent loss of pressure.
EVAP Canister: The EVAP canister stores fuel
vapors from the fuel tank for purging.
EVAP Purge Orifice: Limits purge volume.
EVAP System Air Filter: Provides air to the LDP
for pressurizing the system. It filters out dirt while
allowing a vent to atmosphere for the EVAP system.
Fig. 11 TYPICAL SYSTEM COMPONENTS
1 - Throttle Body
2 - Service Vacuum Supply Tee (SVST)
3 - LDP Solenoid
4 - EVAP System Air Filter
5 - LDP Vent Valve
6 - EVAP Purge Orifice
7 - EVAP Purge Solenoid
8 - Service Port
9 - To Fuel Tank
10 - EVAP Canister
11 - LDP
12 - Intake Air Plenum
25 - 30 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSWJ
FUEL FILLER CAP (Continued)
Page 2190 of 2199

set a temporary fault without turning on the MIL
and continue the leak portion of the test. However,
the PCM will assume that the system is already
pressurized and skip the rapid pump cycles.
Always diagnose leaks, if possible, before discon-
necting connections. Disconnecting connections may
mask a leak condition.
Keep in mind that if the purge solenoid seat is
leaking, it could go undetected since the leak would
end up in the intake manifold. Disconnect the purge
solenoid at the manifold when leak checking. In addi-
tion, a pinched hose fault (P1486) could set if the
purge solenoid does not purge the fuel system prop-
erly (blocked seat). The purge solenoid must vent the
fuel system prior to the LDP system test. If the
purge solenoid cannot properly vent the system the
LDP cannot properly complete the test for P1486 and
this fault can set due to pressure being in the EVAP
system during the test sequence.
Multiple actuation's of the DRB IIItLeak Detec-
tion Pump (LDP) Monitor Test can hide a 0.020 leak
because of excess vapor generation. Additionally, any
source for additional vapor generation can hide a
small leak in the EVAP system. Excess vapor gener-
ation can delay the fall of the LDP diaphragm thus
hiding the small leak. An example of this condition
could be bringing a cold vehicle into a warm shop for
testing or high ambient temperatures.
Fully plugged and partially plugged underhood
vacuum lines have been known to set MIL condi-
tions. P1494 and P0456 can be set for this reason.
Always, thoroughly, check plumbing for pinches or
blockage before condemning components.
TEST EQUIPMENT The Evaporative Emission
Leak Detector (EELD) Miller Special Tool 8404 is
capable of visually detecting leaks in the evaporative
system and will take the place of the ultrasonic leak
detector 6917A. The EELD utilizes shop air and a
smoke generator to visually detect leaks down to
0.020 or smaller. The food grade oil used to make the
smoke includes an UV trace dye that will leave tell-
tale signs of the leak under a black light. This is
helpful when components have to be removed to
determine the exact leak location. For detailed test
instructions, follow the operators manual packaged
with the EELD.
NOTE: Be sure that the PCM has the latest software
update. Reprogram as indicated by any applicable
Technical Service Bulletin. After LDP repairs are
completed, verify the repair by running the DRB IIIT
Leak Detection Pump (LDP) Monitor Test as
described in Technical Service Bulletin 18-12-99.REMOVAL
The Leak Detection Pump (LDP) is located under
the left quarter panel behind the left/rear wheel (Fig.
16). It is attached to a two-piece support bracket
(Fig. 17). The LDP and LDP filter are replaced (ser-
viced) as one unit.
(1) Remove stone shield behind left/rear wheel
(Fig. 18). Drill out plastic rivets for removal.
(2) Remove 3 LDP mounting bolts (Fig. 19).
(3) Remove support bracket brace bolt (Fig. 17).
(4) Loosen, but do not remove 2 support bracket
nuts at frame rail (Fig. 19).
(5) To separate and lower front section of two-piece
support bracket, remove 3 attaching bolts on bottom
of support bracket (Fig. 17). While lowering support
bracket, disconnect LDP wiring clip (Fig. 20).
(6) Disconnect electrical connector at LDP (Fig.
20).
(7) Carefully remove vapor/vacuum lines at LDP
(Fig. 20).
(8) Remove LDP.
INSTALLATION
The LDP is located in the left quarter panel behind
the left/rear wheel. It is attached to a two-piece sup-
port bracket (Fig. 17). The LDP and LDP filter are
replaced (serviced) as one unit.
(1) Position LDP and carefully install vapor/vac-
uum lines to LDP and LDP filter.The vapor/vac-
uum lines and hoses must be firmly connected.
Fig. 16 LOCATION, LDP / EVAP CANISTER
1 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP
2 - EVAP CANISTER
WJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 35
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 2192 of 2199

Check the vapor/vacuum lines at the LDP, LDP
filter and EVAP canister purge solenoid for
damage or leaks. If a leak is present, a Diagnos-
tic Trouble Code (DTC) may be set.
(2) Connect electrical connector to LDP.
(3) While raising front section of support bracket,
connect LDP wiring clip (Fig. 20).
(4) Install 3 LDP mounting bolts (Fig. 19). Refer to
Torque Specifications.
(5) Join front and rear sections of two-piece sup-
port bracket by installing 3 bolts on bottom of sup-
port bracket (Fig. 17). Do not tighten bolts at this
time.
(6) Install support bracket brace bolt (Fig. 17). Do
not tighten bolt at this time.
(7) Tighten 2 support bracket nuts at frame rail
(Fig. 19). Refer to Torque Specifications.
(8) Tighten 3 support bracket bolts and brace bolt.
Refer to Torque Specifications.
(9) Position stone shield behind left/rear wheel
(Fig. 18). Install new plastic rivets.
ORVR
DESCRIPTION
The ORVR (On-Board Refueling Vapor Recovery)
system consists of a unique fuel tank, flow manage-
ment valve, fluid control valve, one-way check valve
and vapor canister. Certain ORVR components can be
found in (Fig. 1).
OPERATION
The ORVR (On-Board Refueling Vapor Recovery)
system is used to remove excess fuel tank vapors.
This is done while the vehicle is being refueled. Cer-
tain ORVR components can be found in (Fig. 1).
Fuel flowing into the fuel filler tube (approx. 1º
I.D.) creates an aspiration effect drawing air into the
fuel fill tube. During refueling, the fuel tank is
vented to the EVAP canister to capture escaping
vapors. With air flowing into the filler tube, there are
no fuel vapors escaping to the atmosphere. Once the
refueling vapors are captured by the EVAP canister,
the vehicle's computer controlled purge system draws
vapor out of the canister for the engine to burn. The
vapor flow is metered by the purge solenoid so that
there is no, or minimal impact on driveability or
tailpipe emissions.As fuel starts to flow through the fuel fill tube, it
opens the normally closed check valve and enters the
fuel tank. Vapor or air is expelled from the tank
through the control valve and on to the vapor canis-
ter. Vapor is absorbed in the EVAP canister until
vapor flow in the lines stops. This stoppage occurs
following fuel shut-off, or by having the fuel level in
the tank rise high enough to close the control valve.
This control valve contains a float that rises to seal
the large diameter vent path to the EVAP canister.
At this point in the refueling process, fuel tank pres-
sure increases, the check valve closes (preventing liq-
uid fuel from spiting back at the operator), and fuel
then rises up the fuel filler tube to shut off the dis-
pensing nozzle.
PCV VALVE
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PCV VALVE/PCV
SYSTEM - 4.7L
(1) Disconnect PCV line/hose (Fig. 21) by discon-
necting rubber connecting hose at PCV valve fitting.
(2) Remove PCV valve at oil filler tube by rotating
PCV valve downward until locating tabs have been
freed at cam lock (Fig. 21). After tabs have cleared,
pull valve straight out from filler tube.To prevent
damage to PCV valve locating tabs, valve must
be pointed downward for removal. Do not force
valve from oil filler tube.
(3) After valve is removed, check condition of valve
o-ring (Fig. 21). Also, PCV valve should rattle when
shaken.
(4) Reconnect PCV valve to its connecting line/
hose.
(5) Start engine and bring to idle speed.
(6) If valve is not plugged, a hissing noise will be
heard as air passes through valve. Also, a strong vac-
uum should be felt with a finger placed at valve
inlet.
(7) If vacuum is not felt at valve inlet, check line/
hose for kinks or for obstruction. If necessary, clean
out intake manifold fitting at rear of manifold. Do
this by turning a 1/4 inch drill (by hand) through the
fitting to dislodge any solid particles. Blow out the
fitting with shop air. If necessary, use a smaller drill
to avoid removing any metal from the fitting.
WJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 37
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)