page 1 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 360 of 2199

STARTING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
STARTING
DESCRIPTION.........................29
OPERATION...........................30
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTING
SYSTEM............................30
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE - STARTER...................35
STARTER MOTOR - GAS POWERED......35
STARTER MOTOR
DESCRIPTION.........................35
OPERATION...........................36DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTER
MOTOR .............................36
REMOVAL.............................37
INSTALLATION.........................38
STARTER MOTOR RELAY
DESCRIPTION.........................38
OPERATION...........................38
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTER RELAY . 38
REMOVAL.............................39
INSTALLATION.........................40
STARTING
DESCRIPTION
An electrically operated engine starting system is
standard factory-installed equipment on this model.
The starting system is designed to provide the vehi-
cle operator with a convenient, efficient and reliable
means of cranking and starting the internal combus-
tion engine used to power the vehicle and all of its
accessory systems from within the safe and secure
confines of the passenger compartment. See the own-
er's manual in the vehicle glove box for more infor-
mation and instructions on the recommended use
and operation of the factory-installed starting sys-
tem.
The starting system consists of the following com-
ponents:
²Battery
²Starter relay
²Starter motor (including an integral starter sole-
noid)
²Ignition switch
²Park/neutral position switch
²Wire harnesses and connections (including the
battery cables).
This group provides complete service information
for the starter motor and the starter relay. Complete
service information for the other starting system
components can be located as follows:
²Refer toBatteryin the proper section of Group
8A - Battery for complete service information for the
battery.
²Refer toIgnition Switch and Key Lock Cyl-
inderin the proper section of Group 8D - Ignition
System for complete service information for the igni-
tion switch.²Refer toPark/Neutral Position Switchin the
proper section of Group 21 - Transmission for com-
plete service information for the park/neutral posi-
tion switch.
²Refer to the proper section ofGroup 8W - Wir-
ing Diagramsfor complete service information and
circuit diagrams for the starting system wiring com-
ponents.
Group 8A covers the Battery, Group 8B covers the
Starting Systems, and Group 8C covers the Charging
System. We have separated these systems to make it
easier to locate the information you are seeking
within this Service Manual. However, when attempt-
ing to diagnose any of these systems, it is important
that you keep their interdependency in mind.
The battery, starting, and charging systems in the
vehicle operate with one another, and must be tested
as a complete system. In order for the vehicle to start
and charge properly, all of the components that are
used in these systems must perform within specifica-
tions.
The diagnostic procedures used in each of these
groups include the most basic conventional diagnostic
methods, to the more sophisticated On-Board Diag-
nostics (OBD) built into the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM). Use of an induction-type milliampere
ammeter, volt/ohmmeter, battery charger, carbon pile
rheostat (load tester), and 12-volt test lamp may be
required.
All OBD-sensed systems are monitored by the
PCM. Each monitored circuit is assigned a Diagnos-
tic Trouble Code (DTC). The PCM will store a DTC in
electronic memory for any failure it detects. Refer to
On-Board Diagnostic Test For Charging System
in the Diagnosis and Testing section of Group 8C -
Charging System for more information.
WJSTARTING 8F - 29
Page 372 of 2199

HEATED SYSTEMS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HEATED GLASS........................... 1
HEATED MIRRORS......................... 8HEATED SEAT SYSTEM..................... 9
HEATED GLASS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HEATED GLASS
DESCRIPTION - REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER . . 1
OPERATION - REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER....2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR WINDOW
DEFOGGER SYSTEM...................2
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER GRID
DESCRIPTION..........................3
OPERATION............................3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR WINDOW
DEFOGGER GRID......................3
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REAR GLASS
HEATING GRID REPAIR.................4
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER RELAY
DESCRIPTION..........................5OPERATION............................5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR WINDOW
DEFOGGER RELAY.....................5
REMOVAL.............................6
INSTALLATION..........................6
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER SWITCH
DESCRIPTION..........................6
OPERATION............................7
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR WINDOW
DEFOGGER SWITCH...................7
REMOVAL.............................7
HEATED GLASS
DESCRIPTION - REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER
An electrically heated rear window defogger is
standard factory-installed equipment on this model.
Electrically heated outside rear view mirrors are
available factory-installed optional equipment. When
the rear window defogger system is turned on, elec-
tric heater grids on the liftgate flip-up glass and
behind both outside rear view mirror glasses are
energized. These electric heater grids produce heat to
help clear the rear window glass and the outside rear
view mirrors of ice, snow, or fog. The rear window
defogger system control circuit uses ignition switched
battery current, so the system will only operate when
the ignition switch is in the On position.
This group covers the following components of the
rear window defogger system:
²Rear glass heating grid
²Rear window defogger relay²Rear window defogger switch.
Certain functions and features of the rear window
defogger system rely upon resources shared with
other electronic modules in the vehicle over the Pro-
grammable Communications Interface (PCI) data bus
network. The PCI data bus network allows the shar-
ing of sensor information. This helps to reduce wire
harness complexity, internal controller hardware, and
component sensor current loads. At the same time,
this system provides increased reliability, enhanced
diagnostics, and allows the addition of many new fea-
ture capabilities. For diagnosis of these electronic
modules or of the PCI data bus network, use a
DRBIIItscan tool and (Refer to Appropriate Diagnos-
tic Information).
The other electronic modules that may affect
proper system operation are:
²Body Control Module (BCM)- Refer to Elec-
tronic Control Modules for more information.
²Driver Door Module (DDM)- Refer to Elec-
tronic Control Modules for more information.
WJHEATED SYSTEMS 8G - 1
Page 379 of 2199

HEATED MIRRORS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HEATED MIRRORS
DESCRIPTION..........................8
OPERATION............................8DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATED
MIRRORS............................8
HEATED MIRRORS
DESCRIPTION
Electrically heated outside rear view mirrors are
optional equipment on this model. These mirrors fea-
ture an electric heating grid located behind the mir-
ror glass of each power operated outside rear view
mirror. These heating grids consist of a single resis-
tor wire routed in a grid-like pattern and captured
between two thin sheets of plastic. When electrical
current is passed through the resistor wire, it pro-
duces enough heat energy to clear the outside mirror
glass of ice, snow or fog. Battery current is directed
to the outside mirror heating grid only when the rear
window defogger switch is in the On position.
If the outside mirror heating grids and the rear
window heating grid are all inoperative, (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/HEATED GLASS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING - REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER SYSTEM).
If the outside mirror heating grids are inoperative,
but the rear window heating grid is operating as
designed, (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/HEATED MIR-
RORS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
The heating grid behind each outside mirror glass
cannot be repaired and, if faulty or damaged, the
entire power mirror unit must be replaced. Refer to
Power Mirrors for the procedures.
OPERATION
The outside mirror heating grids are energized and
de-energized by the Driver Door Module (DDM) and
the Passenger Door Module (PDM) based upon the
rear window defogger switch status. The Body Con-
trol Module (BCM) monitors the rear window defog-ger switch. When the BCM receives an input from
the switch, it sends a defogger switch status message
to the DDM and the PDM over the Programmable
Communications Interface data bus. The DDM and
PDM respond to the defogger switch status messages
by energizing or de-energizing the battery current
feed to their respective outside rear view mirror
heating grids.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATED MIRRORS
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, (Refer to
Appropriate Wiring Information).
(1) If both mirror heaters are inoperative, check
for proper operation of the Rear Window Defogger
System. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/HEATED GLASS
- DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR WINDOW
DEFOGGER SYSTEM). If Rear Window Defogger
System operates correctly, or if only one mirror
heater is inoperative, go to Step 2.
(2) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Remove the front door trim panel on the side
of the inoperative mirror heater. Go to Step 3.
(3) Disconnect the door wire harness connector
from the door module connector receptacle. Check for
continuity between the mirror heater 12 volt supply,
and the mirror heater ground. There should be con-
tinuity. If OK, go to Step 4. If not OK, check for con-
tinuity of the individual circuits between the power
mirror and the door module, and of the mirror heater
grid right at the power mirror.
(4) Use a DRB IIItand (Refer to Appropriate
Diagnostic Information) to test the door module and
the PCI data bus.
8G - 8 HEATED MIRRORSWJ
Page 380 of 2199
HEATED SEAT SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HEATED SEAT SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION..........................9
OPERATION...........................10
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATED SEAT
SYSTEM............................10
DRIVER HEATED SEAT SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................11
OPERATION...........................11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DRIVER HEATED
SEAT SWITCH........................11
REMOVAL.............................12
INSTALLATION.........................13
HEATED SEAT ELEMENT
DESCRIPTION.........................13
OPERATION...........................13
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATED SEAT
ELEMENT...........................14REMOVAL.............................14
INSTALLATION.........................14
HEATED SEAT SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATED SEAT
SENSOR............................15
REMOVAL.............................15
PASSENGER HEATED SEAT SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................15
OPERATION...........................16
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PASSENGER
HEATED SEAT SWITCH.................16
REMOVAL.............................17
INSTALLATION.........................17
HEATED SEAT SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
Individually controlled driver and passenger side
electrically heated front seats are available factory-
installed optional equipment on this model, when it
is also equipped with the power seat option. The
heated seat system allows both the driver and the
front seat passenger the option to select one of two
seat heating ranges, Low or High, or to turn the indi-
vidual seat heaters Off using the heated seat
switches located in the center lower bezel near the
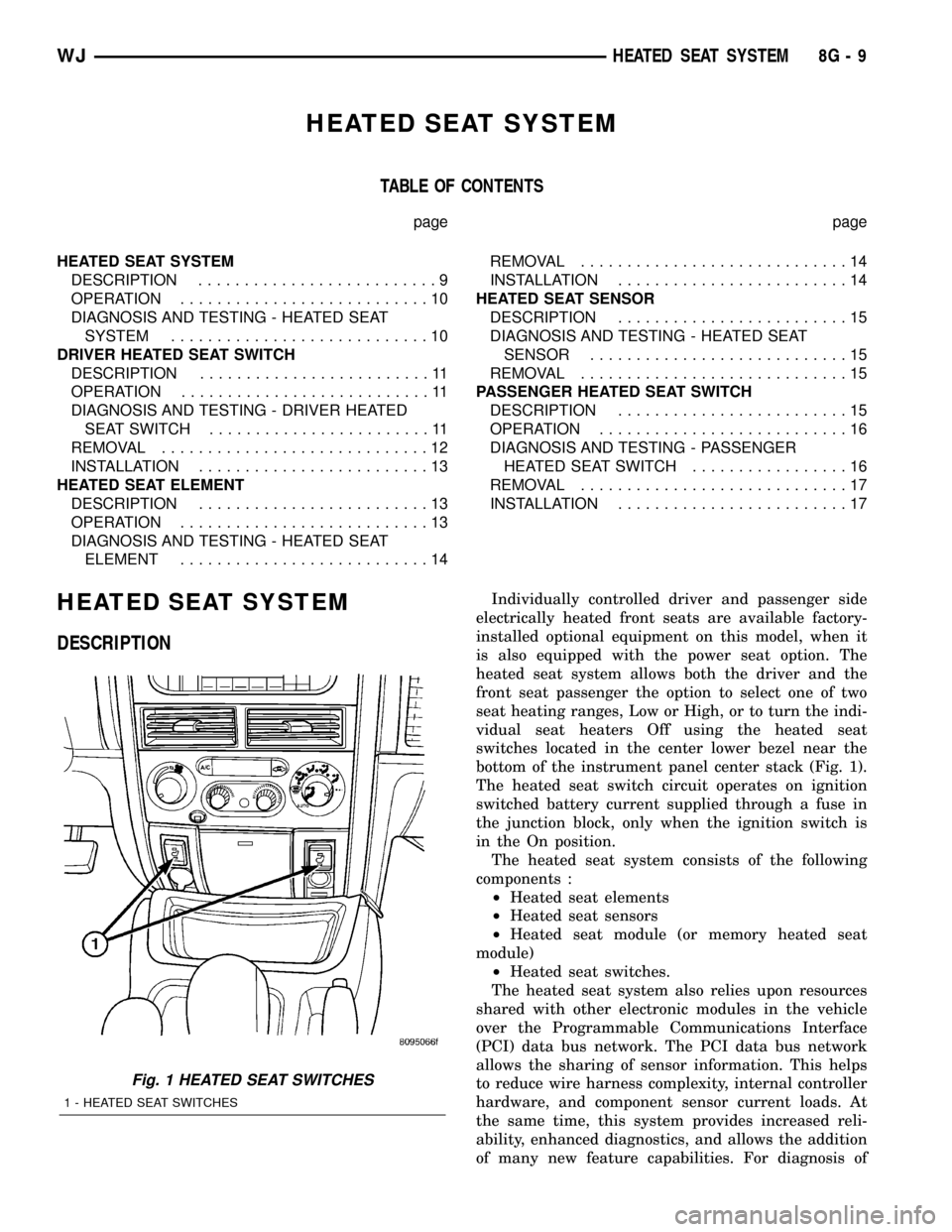
bottom of the instrument panel center stack (Fig. 1).
The heated seat switch circuit operates on ignition
switched battery current supplied through a fuse in
the junction block, only when the ignition switch is
in the On position.
The heated seat system consists of the following
components :
²Heated seat elements
²Heated seat sensors
²Heated seat module (or memory heated seat
module)
²Heated seat switches.
The heated seat system also relies upon resources
shared with other electronic modules in the vehicle
over the Programmable Communications Interface
(PCI) data bus network. The PCI data bus network
allows the sharing of sensor information. This helps
to reduce wire harness complexity, internal controller
hardware, and component sensor current loads. At
the same time, this system provides increased reli-
ability, enhanced diagnostics, and allows the addition
of many new feature capabilities. For diagnosis of
Fig. 1 HEATED SEAT SWITCHES
1 - HEATED SEAT SWITCHES
WJHEATED SEAT SYSTEM 8G - 9
Page 390 of 2199
HORN
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HORN SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HORN SYSTEM . . . 2
HORN
DESCRIPTION..........................3
OPERATION............................3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HORN..........3
REMOVAL.............................3
INSTALLATION..........................4
HORN RELAY
DESCRIPTION..........................4OPERATION............................4
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HORN RELAY....4
REMOVAL.............................5
INSTALLATION..........................5
HORN SWITCH
DESCRIPTION..........................6
OPERATION............................6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HORN SWITCH . . . 6
REMOVAL.............................7
INSTALLATION..........................7
HORN SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
A dual-note electric horn system is standard facto-
ry-installed equipment on this model. The standard
equipment horn system features one low-note horn
unit and one high-note horn unit. The horn system
allows the vehicle operator to provide an audible
warning of the presence or approach of the vehicle to
pedestrians and the drivers of other vehicles in near
proximity. The horn system uses a non-switched
source of battery current so that the system will
remain functional, regardless of the ignition switch
position.
The horn system can also be activated by the Body
Control Module (BCM). The BCM is programmed to
activate the horns in order to provide the following
features:
²Remote Keyless Entry (RKE) system lock
request audible verification (except export)
²RKE system panic mode audible alert
²Vehicle Theft Security System (VTSS) audible
alarm.
This vehicle also offers several customer program-
mable features, which allows the selection of several
optional electronic features to suit individual prefer-
ences. Refer to Overhead Console for more informa-
tion on the customer programmable feature options.
Customer programmable feature options affecting the
horn system include:
²Sound Horn on Lock- Allows the option of
having the horn sound a short chirp as an audible
verification that the RKE system received a valid
Lock request from the RKE transmitter, or having no
audible verification.The horn system includes the following compo-
nents:
²Clockspring
²Horns
²Horn relay
²Horn switch
Certain functions and features of the horn system
rely upon resources shared with other electronic
modules in the vehicle over the Programmable Com-
munications Interface (PCI) data bus network. The
PCI data bus network allows the sharing of sensor
information. This helps to reduce wire harness com-
plexity, internal controller hardware, and component
sensor current loads. At the same time, this system
provides increased reliability, enhanced diagnostics,
and allows the addition of many new feature capabil-
ities. For diagnosis of these electronic modules or of
the PCI data bus network, the use of a DRB scan
tool and the proper Diagnostic Procedures manual
are recommended.
The other electronic modules that may affect horn
system operation are as follows:
²Body Control Module (BCM)(Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-
ULES/BODY CONTROL/CENTRAL TIMER MODUL
- DESCRIPTION) for more information.
²Electronic Vehicle Information Center
(EVIC)(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/OVERHEAD
CONSOLE/ELECTRONIC VEHICLE INFO CENTER
- DESCRIPTION) for more information.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS/CLOCK-
SPRING - DESCRIPTION) for more information on
this component. Refer to the appropriate wiring
information. The wiring information includes wiring
diagrams, proper wire and connector repair proce-
dures, details of wire harness routing and retention,
WJHORN 8H - 1
Page 398 of 2199

IGNITION CONTROL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
IGNITION CONTROL
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................1
SPECIFICATIONS
ENGINE FIRING ORDER - 4.0L 6-CYLINDER
ENGINE..............................2
ENGINE FIRING ORDERÐ4.7L V-8 ENGINE . . 2
IGNITION COIL RESISTANCE - 4.0L ENGINE . 2
IGNITION COIL RESISTANCEÐ4.7L V-8
ENGINE..............................2
IGNITION TIMING......................2
SPARK PLUGS........................3
TORQUE - IGNITION SYSTEM............3
AUTO SHUT DOWN RELAY
DESCRIPTION - PCM OUTPUT.............3
OPERATION
OPERATION - PCM OUTPUT.............3
OPERATION - ASD SENSE - PCM INPUT....4
REMOVAL.............................4
INSTALLATION..........................4
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - 4.0L....................4
DESCRIPTION - 4.7L....................5
OPERATION
OPERATION - 4.0L.....................5
OPERATION - 4.7L.....................5
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L.......................6
REMOVAL - 4.7L.......................7INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4.0L...................8
INSTALLATION - 4.7L...................9
COIL RAIL
DESCRIPTION..........................9
OPERATION...........................10
REMOVAL.............................10
INSTALLATION.........................11
IGNITION COIL
DESCRIPTION.........................11
OPERATION...........................12
REMOVAL.............................12
INSTALLATION.........................12
IGNITION COIL CAPACITOR
DESCRIPTION.........................13
OPERATION...........................13
REMOVAL.............................13
INSTALLATION.........................13
KNOCK SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................13
OPERATION...........................13
REMOVAL.............................14
INSTALLATION.........................15
SPARK PLUG
DESCRIPTION.........................15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SPARK PLUG
CONDITIONS.........................15
REMOVAL.............................18
CLEANING............................18
INSTALLATION.........................18
IGNITION CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
Two different ignition systems are used. One type
of system is for the 4.0L 6±cylinder engine. The other
is for the 4.7L V-8 engine.
OPERATION
The 4.0L 6±cylinder engine uses a one-piece coil
rail containing three independent coils. Although cyl-
inder firing order is the same as 4.0L engines of pre-
vious years, spark plug firing is not. The 3 coils dual-
fire the spark plugs on cylinders 1±6, 2±5 and/or 3±4.
When one cylinder is being fired (on compressionstroke), the spark to the opposite cylinder is being
wasted (on exhaust stroke). The one-piece coil bolts
directly to the cylinder head. Rubber boots seal the
secondary terminal ends of the coils to the top of all
6 spark plugs. One electrical connector (located at
the rear end of the coil rail) is used for all three coils.
The 4.7L V-8 engine uses 8 dedicated and individ-
ually fired coil for each spark plug. Each coil is
mounted directly to the top of each spark plug. A sep-
arate electrical connector is used for each coil.
Because of coil design, spark plug cables (second-
ary cables) are not used on either engine. Adistrib-
utor is not usedwith either the 4.0L or 4.7L
engines.
WJIGNITION CONTROL 8I - 1
Page 416 of 2199
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
DESCRIPTION..........................2
OPERATION............................4
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - INSTRUMENT
CLUSTER............................7
REMOVAL.............................9
DISASSEMBLY.........................10
ASSEMBLY............................11
INSTALLATION.........................12
ABS INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................13
OPERATION...........................13
AIRBAG INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................14
OPERATION...........................14
BRAKE/PARK BRAKE INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................15
OPERATION...........................15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE
INDICATOR..........................16
CHECK GAUGES INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................16
OPERATION...........................17
COOLANT LOW INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................17
OPERATION...........................18
CRUISE INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................18
OPERATION...........................18
ENGINE TEMPERATURE GAUGE
DESCRIPTION.........................19
OPERATION...........................19
FRONT FOG LAMP INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................20
OPERATION...........................20
FUEL GAUGE
DESCRIPTION.........................21
OPERATION...........................21
HIGH BEAM INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................22
OPERATION...........................22
LOW FUEL INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................22
OPERATION...........................23
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (MIL)
DESCRIPTION.........................23OPERATION...........................23
ODOMETER
DESCRIPTION.........................24
OPERATION...........................25
OIL PRESSURE GAUGE
DESCRIPTION.........................25
OPERATION...........................26
OVERDRIVE OFF INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................26
OPERATION...........................26
REAR FOG LAMP INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................27
OPERATION...........................27
SEATBELT INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................28
OPERATION...........................28
SHIFT INDICATOR (TRANSFER CASE)
DESCRIPTION.........................29
OPERATION...........................29
SKIS INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................29
OPERATION...........................29
SPEEDOMETER
DESCRIPTION.........................30
OPERATION...........................31
TACHOMETER
DESCRIPTION.........................31
OPERATION...........................31
TRANS TEMP INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................32
OPERATION...........................32
TURN SIGNAL INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................33
OPERATION...........................33
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TURN SIGNAL
INDICATOR..........................33
VOLTAGE GAUGE
DESCRIPTION.........................34
OPERATION...........................34
WAIT-TO-START INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................35
OPERATION...........................35
WATER-IN-FUEL INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................36
OPERATION...........................36
WJINSTRUMENT CLUSTER 8J - 1
Page 452 of 2199
LAMPS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR............... 1LAMPS/LIGHTING - INTERIOR............... 28
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR
DESCRIPTION - TURN SIGNAL & HAZARD
WARNING SYSTEM.....................2
OPERATION - TURN SIGNAL & HAZARD
WARNING SYSTEM.....................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TURN SIGNAL &
HAZARD WARNING SYSTEMS............3
SPECIFICATIONS
EXTERIOR LAMPS.....................4
AUTO HEADLAMP SENSOR
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTO
HEADLAMP SENSOR (AHL)..............4
REMOVAL.............................4
INSTALLATION..........................4
BRAKE LAMP SWITCH
DESCRIPTION..........................5
OPERATION............................5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Ð BRAKE LAMP
SWITCH.............................5
REMOVAL.............................5
INSTALLATION..........................5
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT.........................6
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - BULB......................6
REMOVAL - CHMSL....................6
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - BULB..................6
INSTALLATION - CHMSL.................7
COMBINATION FLASHER
DESCRIPTION..........................7
OPERATION............................7
REMOVAL.............................9
INSTALLATION..........................9
DAYTIME RUNNING LAMP MODULE
DESCRIPTION..........................9OPERATION............................9
REMOVAL.............................9
INSTALLATION..........................9
FOG LAMP
REMOVAL.............................10
INSTALLATION.........................10
FOG LAMP UNIT
REMOVAL.............................10
INSTALLATION.........................10
ADJUSTMENTS
FOG LAMP ADJUSTMENT...............10
HEADLAMP
DESCRIPTION.........................11
OPERATION...........................11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Ð HEADLAMP
SYSTEM............................12
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Ð HEADLAMP . . 14
REMOVAL - BULB.......................14
INSTALLATION - BULB...................15
HEADLAMP SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................15
OPERATION...........................15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Ð HEADLAMP
SWITCH............................15
HEADLAMP UNIT
REMOVAL.............................16
INSTALLATION.........................16
ADJUSTMENTS........................16
LICENSE PLATE LAMP
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - BULB.....................17
REMOVAL - LAMP.....................18
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - BULB.................18
INSTALLATION - LAMP.................18
WJLAMPS 8L - 1
Page 479 of 2199
LAMPS/LIGHTING - INTERIOR
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
LAMPS/LIGHTING - INTERIOR
SPECIFICATIONS
...................................28
COURTESY LAMP
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - BULB.....................29
REMOVAL - LAMP.....................29
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - BULB.................29
INSTALLATION - LAMP.................29
DOME LAMP
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - BULB.....................29
REMOVAL - LAMP.....................29
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - BULB.................29
INSTALLATION - LAMP.................29
DOOR AJAR SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - DOOR AJAR SWITCH.....29
DESCRIPTION - FLIP UP GLASS AJAR
SWITCH............................29DESCRIPTION - LIFTGATE AJAR SWITCH . . 30
OPERATION
OPERATION - DOOR AJAR SWITCH.......30
OPERATION - FLIP UP GLASS AJAR
SWITCH............................30
OPERATION - LIFTGATE AJAR SWITCH....30
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DOOR AJAR
SWITCH............................30
GLOVE BOX LAMP/SWITCH
REMOVAL.............................31
INSTALLATION.........................31
READING LAMP
DESCRIPTION.........................32
OPERATION...........................32
REMOVAL.............................32
INSTALLATION.........................32
TRANS RANGE INDICATOR ILLUMINATION
DESCRIPTION.........................32
VANITY LAMP
REMOVAL.............................32
INSTALLATION.........................32
LAMPS/LIGHTING - INTERIOR
SPECIFICATIONS
CAUTION: Do not use bulbs other than the bulbs
listed in the Bulb Application Table. Damage to
lamp can result.
Service procedures for most of the lamps in the
instrument panel, are located in Electrical, Instru-
ment Panel. Some components have lamps that can
only be serviced by an Authorized Service Center
(ASC) after the component is removed from the vehi-
cle.
LAMP BULB TYPE
A/C HEATER NOT SERVICED
ASH RECEIVER 161
CLIMATE CONTROL 74
PASSENGER ASSIST
HANDLE214±2
FRONT READING 192
GLOVE COMPARTMENT 194
TELLTALE/HAZARD LAMP 74
HEATER NOT SERVICED
OVERHEAD CONSOLE 192
RADIO ASC
REAR CARGO 214±2
UNDER PANEL COURTESY 906
CLUSTER ILLUMINATION 103
SUNVISOR VANITY CHRYSLER P/N
6501966
8L - 28 LAMPS/LIGHTING - INTERIORWJ
Page 484 of 2199
MESSAGE SYSTEMS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
OVERHEAD CONSOLE
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................1
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MODULE LAMP
REPLACEMENT.......................1
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COURTESY
LAMP REPLACEMENT..................1
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MODULE LENS
REPLACEMENT.......................2
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ELECTRONIC
VEHICLE INFORMATION CENTER
PROGRAMMING.......................2
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COMPASS
DEMAGNETIZING......................4
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COMPASS
CALIBRATION.........................5
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COMPASS
VARIATION ADJUSTMENT................5
REMOVAL.............................5
INSTALLATION..........................6
SPECIAL TOOLS
OVERHEAD CONSOLE SYSTEMS.........6
ELECTRONIC VEHICLE INFO CENTER
DESCRIPTION..........................6OPERATION............................9
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ELECTRONIC
VEHICLE INFORMATION CENTER.........9
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE PRESSURE
SYSTEM TEST.......................10
REMOVAL.............................10
INSTALLATION.........................10
UNIVERSAL TRANSMITTER
DESCRIPTION.........................11
OPERATION...........................11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - UNIVERSAL
TRANSMITTER.......................11
AMBIENT TEMP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................12
OPERATION...........................12
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AMBIENT
TEMPERATURE SENSOR...............12
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AMBIENT
TEMPERATURE SENSOR CIRCUIT........12
REMOVAL.............................12
INSTALLATION.........................13
OVERHEAD CONSOLE
DESCRIPTION
An overhead console is standard factory-installed
equipment on this model. The overhead console
includes the Electronic Vehicle Information Center
(EVIC) and two reading and courtesy lamps (Fig. 1).
On vehicles equipped with a power sunroof option,
the overhead console also houses the power sunroof
switch between the two reading and courtesy lamps.
The overhead console is mounted with one screw and
two snap-clips to a molded plastic retainer bracket
located above the headliner. The retainer bracket is
secured with adhesive to the inside surface of the
roof panel.
Following are general descriptions of the major
components used in the overhead console. Refer to
Overhead Consolein Wiring Diagrams for complete
circuit diagrams.
OPERATION
See the owner's manual in the vehicle glove box for
more information on the use and operation of the
various overhead console features.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MODULE LAMP
REPLACEMENT
(1) Remove the overhead console (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/OVERHEAD CONSOLE - REMOV-
AL).
(2) Using a flat blade screwdriver twist out socket/
lamp (Fig. 2).
(3) Replace lamp(s) as necessary.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COURTESY LAMP
REPLACEMENT
(1) Open hood, disconnect and isolate the negative
battery cable.
WJMESSAGE SYSTEMS 8M - 1