Throttle valve JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 1646 of 2199

simultaneous movement without causing the trans-
mission throttle lever to either move ahead of, or lag
behind the lever on the throttle body.
ADJUSTMENT VERIFICATION
(1) Turn ignition key to OFF position.
(2) Remove air cleaner.
(3) Verify that lever on throttle body (Fig. 242) is
at curb idle position. Then verify that the transmis-
sion throttle lever (Fig. 243) is also at idle (fully for-
ward) position.
(4) Slide cable off attachment stud on throttle body
lever.
(5) Compare position of cable end to attachment
stud on throttle body lever:
²Cable end and attachment stud should be
aligned (or centered on one another) to within 1 mm
(0.039 in.) in either direction (Fig. 244).
²If cable end and attachment stud are misaligned
(off center), cable will have to be adjusted as
described in Throttle Valve Cable Adjustment proce-
dure.
(6) Reconnect cable end to attachment stud. Then
with aid of a helper, observe movement of transmis-
sion throttle lever and lever on throttle body.
²If both levers move simultaneously from idle to
half-throttle and back to idle position, adjustment is
correct.
²If transmission throttle lever moves ahead of, or
lags behind throttle body lever, cable adjustment will
be necessary. Or, if throttle body lever prevents
transmission lever from returning to closed position,
cable adjustment will be necessary.
ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
(1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
(2) Remove air cleaner if necessary.
(3) Disconnect cable end from attachment stud.
Carefully slide cable off stud. Do not pry or pull
cable off.
(4) Verify that transmission throttle lever is in
fully closed position. Then be sure lever on throttle
body is at curb idle position.
(5) Pry the T.V. cable lock (A) into the UP position
(Fig. 244). This will unlock the cable and allow for
readjustment.
(6) Apply just enough tension on the T.V. cable (B)
to remove any slack in the cable.Pulling too tight
will cause the T.V. lever on the transmission to
move out of its idle position, which will result
in an incorrect T.V. cable adjustment.Slide the
sheath of the T.V. cable (D) back and forth until the
centerlines of the T.V. cable end (B) and the throttle
bell crank lever (C) are aligned within one millimeter
(1mm) (Fig. 244).
(7) While holding the T.V. cable in the set position
push the T.V. cable lock (A) into the down position
(Fig. 244). This will lock the present T.V. cable
adjustment.
Fig. 242 Throttle Valve Cable
1 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
2 - THROTTLE VALVE LEVER
3 - THROTTLE BODYFig. 243 Throttle Valve Cable at Transmission
1 - TRANSMISSION SHIFTER CABLE
2 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
3 - TRANSFER CASE SHIFTER CABLE
4 - TRANSFER CASE SHIFTER CABLE BRACKET RETAINING
BOLT(S)
5 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE BRACKET RETAINING BOLT
6 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS
7 - TRANSMISSION FLUID LINES
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 127
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE (Continued)
Page 1647 of 2199

NOTE: Be sure that as the cable is pulled forward
and centered on the throttle lever stud, the cable
housing moves smoothly with the cable. Due to the
angle at which the cable housing enters the spring
housing, the cable housing may bind slightly and
create an incorrect adjustment.
(8) Reconnect the T.V. cable (B) to the throttle
bellcrank lever (C).
(9) Check cable adjustment. Verify transmission
throttle lever and lever on throttle body move simul-
taneously.
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION
The torque converter (Fig. 245) is a hydraulic
device that couples the engine crankshaft to the
transmission. The torque converter consists of an
outer shell with an internal turbine, a stator, an
overrunning clutch, an impeller and an electronically
applied converter clutch. The converter clutch pro-
vides reduced engine speed and greater fuel economy
when engaged. Clutch engagement also provides
reduced transmission fluid temperatures. The torque
converter hub drives the transmission oil (fluid)
pump.
The torque converter is a sealed, welded unit that
is not repairable and is serviced as an assembly.
CAUTION: The torque converter must be replaced if
a transmission failure resulted in large amounts of
metal or fiber contamination in the fluid. If the fluid
is contaminated, flush the all transmission fluid
cooler(s) and lines.
Fig. 244 Throttle Valve Cable at Throttle Linkage
1 - THROTTLE LINKAGE
2 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE LOCKING CLIP
3 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
Fig. 245 Torque Converter Assembly
1 - TURBINE
2 - IMPELLER
3 - HUB
4-STATOR
5 - FRONT COVER
6 - CONVERTER CLUTCH DISC
7 - DRIVE PLATE
21 - 128 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE (Continued)
Page 1652 of 2199

TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The torque converter clutch is hydraulically
applied and is released when fluid is vented from the
hydraulic circuit by the torque converter control
(TCC) solenoid on the valve body. The torque con-
verter clutch is controlled by the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM). The torque converter clutch engages
in fourth gear, and in third gear under various con-
ditions, such as when the O/D switch is OFF, when
the vehicle is cruising on a level surface after the
vehicle has warmed up. The torque converter clutch
will disengage momentarily when an increase in
engine load is sensed by the PCM, such as when the
vehicle begins to go uphill or the throttle pressure is
increased.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission and torque converter
from vehicle.
(2) Place a suitable drain pan under the converter
housing end of the transmission.
CAUTION: Verify that transmission is secure on the
lifting device or work surface, the center of gravity
of the transmission will shift when the torque con-
verter is removed creating an unstable condition.
The torque converter is a heavy unit. Use caution
when separating the torque converter from the
transmission.
(3) Pull the torque converter forward until the cen-
ter hub clears the oil pump seal.
(4) Separate the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
INSTALLATION
Check converter hub and drive notches for sharp
edges, burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and
notches with 320/400 grit paper or crocus cloth if nec-
essary. The hub must be smooth to avoid damaging
the pump seal at installation.
(1) Lubricate oil pump seal lip with transmission
fluid.
(2) Place torque converter in position on transmis-
sion.
CAUTION: Do not damage oil pump seal or bushing
while inserting torque converter into the front of the
transmission.
(3) Align torque converter to oil pump seal open-
ing.
(4) Insert torque converter hub into oil pump.
(5) While pushing torque converter inward, rotate
converter until converter is fully seated in the oil
pump gears.
(6) Check converter seating with a scale and
straightedge (Fig. 253). Surface of converter lugs
should be 1/2 in. to rear of straightedge when con-
verter is fully seated.
(7) If necessary, temporarily secure converter with
C-clamp attached to the converter housing.
(8) Install the transmission in the vehicle.
(9) Fill the transmission with the recommended
fluid.
Fig. 252 Stator Operation
1 - DIRECTION STATOR WILL FREE WHEEL DUE TO OIL
PUSHING ON BACKSIDE OF VANES
2 - FRONT OF ENGINE
3 - INCREASED ANGLE AS OIL STRIKES VANES
4 - DIRECTION STATOR IS LOCKED UP DUE TO OIL PUSHING
AGAINST STATOR VANES
Fig. 253 Checking Torque Converter Seating -
Typical
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 133
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1654 of 2199

VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION
The valve body consists of a cast aluminum valve
body, a separator plate, and transfer plate. The valve
body contains valves and check balls that control
fluid delivery to the torque converter clutch, bands,
and frictional clutches. The valve body contains the
following components (Fig. 255), (Fig. 256), (Fig.
257), and (Fig. 258):
²Regulator valve
²Regulator valve throttle pressure plug
²Line pressure plug and sleeve
²Kickdown valve
²Kickdown limit valve
²1-2 shift valve
²1-2 control valve
²2-3 shift valve²2-3 governor plug
²3-4 shift valve
²3-4 timing valve
²3-4 quick fill valve
²3-4 accumulator
²Throttle valve
²Throttle pressure plug
²Switch valve
²Manual valve
²Converter clutch lock-up valve
²Converter clutch lock-up timing Valve
²Shuttle valve
²Shuttle valve throttle plug
²Boost Valve
²10 check balls
By adjusting the spring pressure acting on the reg-
ulator valve, transmission line pressure can be
adjusted.
Fig. 255 Upper Housing Control Valve Locations
1 - UPPER HOUSING 8 - MANUAL VALVE
2 - REGULATOR VALVE 9 - 1-2 GOVERNOR PLUG
3 - SWITCH VALVE 10 - GOVERNOR PLUG COVER
4 - REGULATOR VALVE SPRING 11 - THROTTLE PLUG
5 - KICKDOWN VALVE 12 - 2-3 GOVERNOR PLUG
6 - KICKDOWN DETENT 13 - SHUTTLE VALVE PRIMARY SPRING
7 - THROTTLE VALVE AND SPRING
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 135
Page 1655 of 2199

Fig. 256 Shuttle and Boost Valve Locations
1 - SPRING 8 - SHUTTLE VALVE COVER
2 - RETAINER 9 - SHUTTLE VALVE
3 - BOOST VALVE 10 - SHUTTLE VALVE PRIMARY SPRING
4 - BOOST VALVE PLUG 11 - GOVERNOR PLUG COVER
5 - SPRING GUIDES 12 - THROTTLE PLUG
6 - E-CLIP 13 - UPPER HOUSING
7 - SHUTTLE VALVE SECONDARY SPRING 14 - BOOST VALVE COVER
21 - 136 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1656 of 2199

Fig. 257 Upper Housing Shift Valve and Pressure Plug Locations
1 - UPPER HOUSING 8 - RETAINER
2 - 1-2 SHIFT VALVE AND SPRING 9 - 1-2 SHIFT CONTROL VALVE AND SPRING
3 - 2-3 SHIFT VALVE AND SPRING 10 - PRESSURE PLUG COVER
4 - 2-3 THROTTLE PLUG 11 - LINE PRESSURE PLUG
5 - LIMIT VALVE HOUSING 12 - PLUG SLEEVE
6 - LIMIT VALVE COVER 13 - THROTTLE PRESSURE SPRING AND PLUG
7 - LIMIT VALVE AND SPRING
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 137
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1658 of 2199
OPERATION
NOTE: Refer to the Hydraulic Schematics for a
visual aid in determining valve location, operation
and design.
CHECK BALLS
CHECK BALL NUMBER DESCRIPTION
1 Allows either the manual valve to put line pressure on the 1-2 governor plug or
the KD Valve to put WOT line pressure on the 1-2 governor plug.
2 Allows either the manual valve to put line pressure on the 2-3 governor plug or
the KD Valve to put WOT line pressure on the 2-3 governor plug.
3 Allows either the Reverse circuit or the 3rd gear circuit to pressurize the front
clutch.
4 Allows either the Manual Low circuit from the Manual Valve or the Reverse
from the Manual Valve circuit to pressurize the rear servo.
5 Directs line pressure to the spring end of the 2-3 shift valve in either Manual
Low or Manual 2nd, forcing the downshift to 2nd gear regardless of governor
pressure.
6 Provides a by-pass around the front servo orifice so that the servo can release
quickly.
7 Provides a by-pass around the rear clutch orifice so that the clutch can release
quickly.
8 Directs reverse line pressure through an orifice to the throttle valve eliminating
the extra leakage and insuring that Reverse line pressure pressure will be
sufficient.
9 Provides a by-pass around the rear servo orifice so that the servo can release
quickly.
ECE (10) Allows the lockup clutch to used at WOT in 3rd gear by putting line pressure
from the 3-4 Timing Valve on the interlock area of the 2-3 shift valve, thereby
preventing a 3rd gear Lock-up to 2nd gear kickdown.
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 139
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1659 of 2199
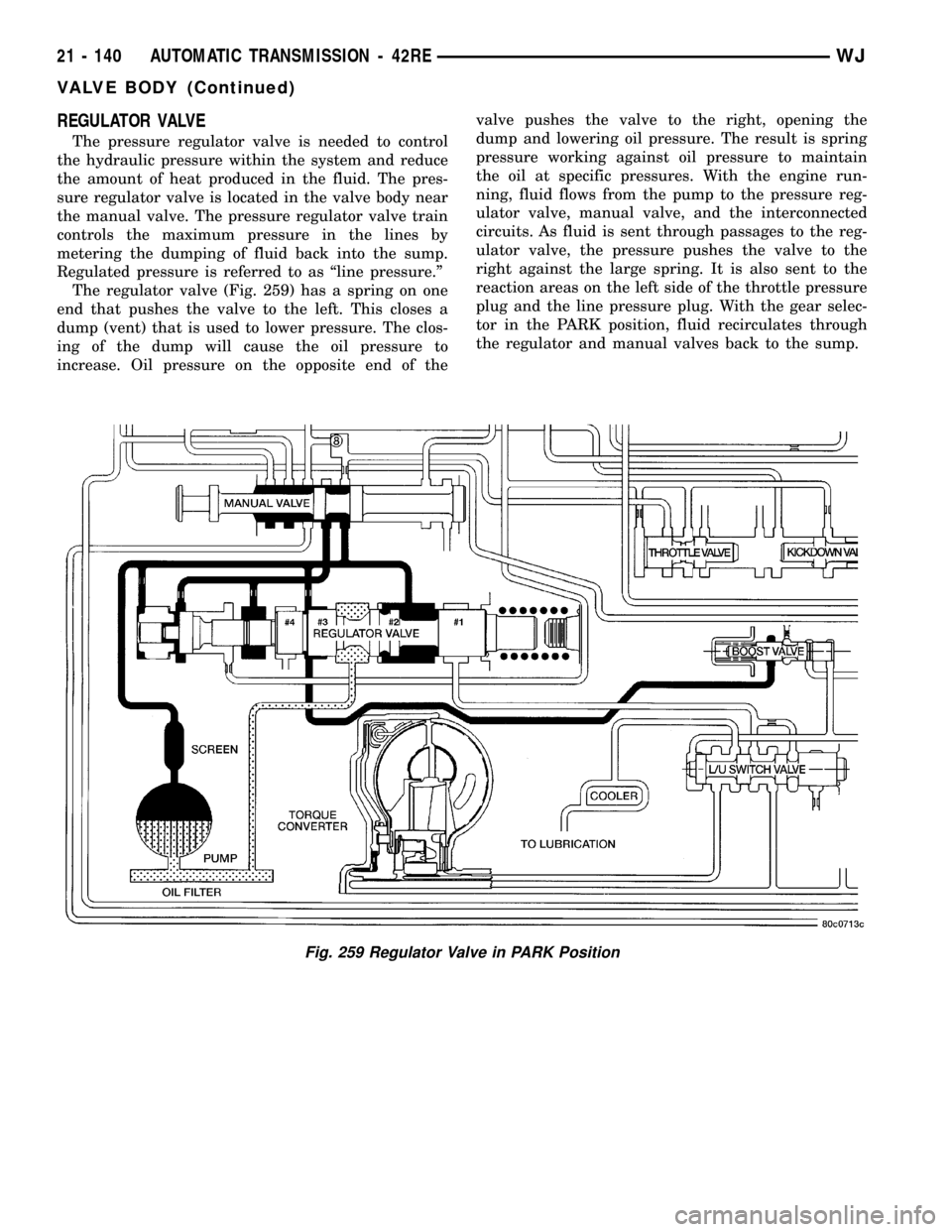
REGULATOR VALVE
The pressure regulator valve is needed to control
the hydraulic pressure within the system and reduce
the amount of heat produced in the fluid. The pres-
sure regulator valve is located in the valve body near
the manual valve. The pressure regulator valve train
controls the maximum pressure in the lines by
metering the dumping of fluid back into the sump.
Regulated pressure is referred to as ªline pressure.º
The regulator valve (Fig. 259) has a spring on one
end that pushes the valve to the left. This closes a
dump (vent) that is used to lower pressure. The clos-
ing of the dump will cause the oil pressure to
increase. Oil pressure on the opposite end of thevalve pushes the valve to the right, opening the
dump and lowering oil pressure. The result is spring
pressure working against oil pressure to maintain
the oil at specific pressures. With the engine run-
ning, fluid flows from the pump to the pressure reg-
ulator valve, manual valve, and the interconnected
circuits. As fluid is sent through passages to the reg-
ulator valve, the pressure pushes the valve to the
right against the large spring. It is also sent to the
reaction areas on the left side of the throttle pressure
plug and the line pressure plug. With the gear selec-
tor in the PARK position, fluid recirculates through
the regulator and manual valves back to the sump.
Fig. 259 Regulator Valve in PARK Position
21 - 140 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1660 of 2199
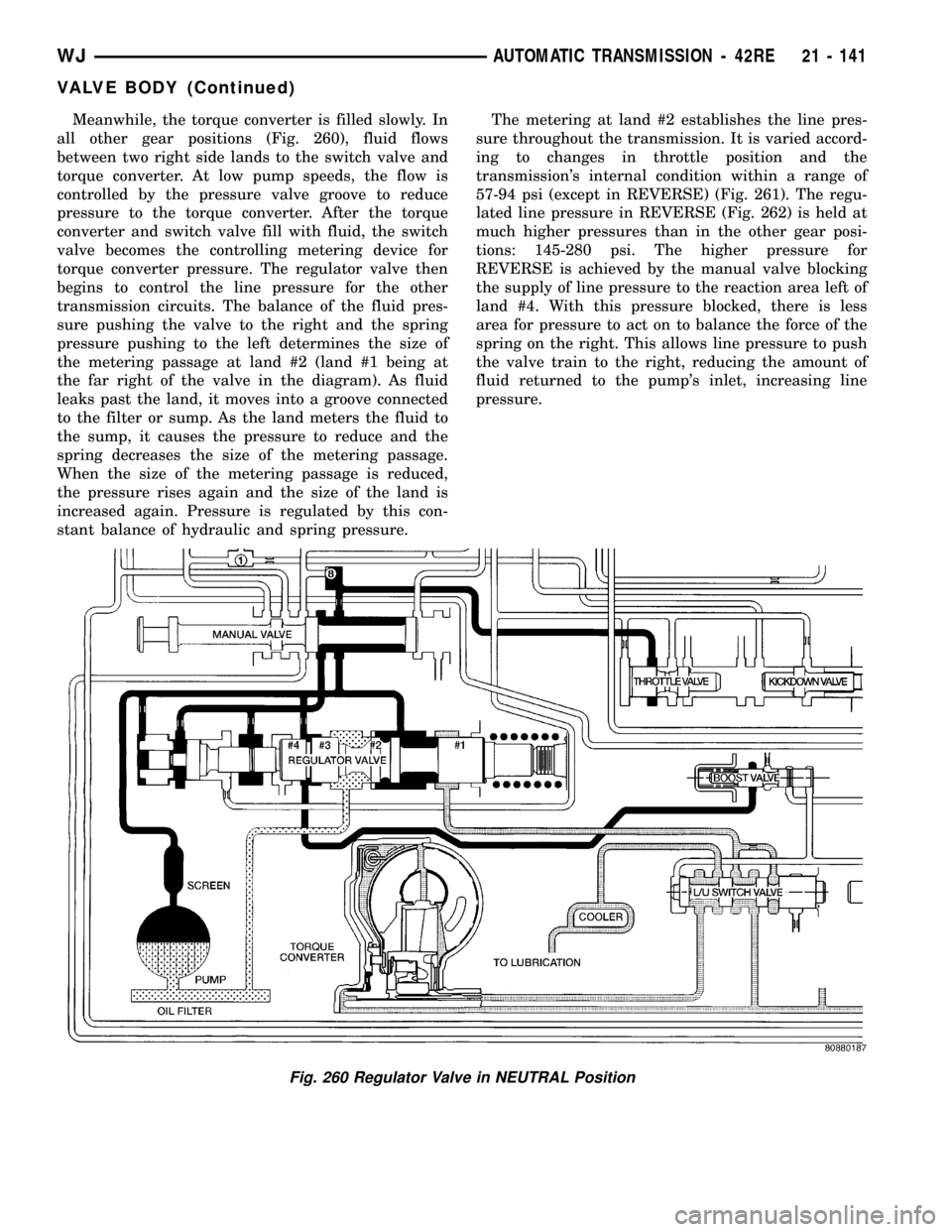
Meanwhile, the torque converter is filled slowly. In
all other gear positions (Fig. 260), fluid flows
between two right side lands to the switch valve and
torque converter. At low pump speeds, the flow is
controlled by the pressure valve groove to reduce
pressure to the torque converter. After the torque
converter and switch valve fill with fluid, the switch
valve becomes the controlling metering device for
torque converter pressure. The regulator valve then
begins to control the line pressure for the other
transmission circuits. The balance of the fluid pres-
sure pushing the valve to the right and the spring
pressure pushing to the left determines the size of
the metering passage at land #2 (land #1 being at
the far right of the valve in the diagram). As fluid
leaks past the land, it moves into a groove connected
to the filter or sump. As the land meters the fluid to
the sump, it causes the pressure to reduce and the
spring decreases the size of the metering passage.
When the size of the metering passage is reduced,
the pressure rises again and the size of the land is
increased again. Pressure is regulated by this con-
stant balance of hydraulic and spring pressure.The metering at land #2 establishes the line pres-
sure throughout the transmission. It is varied accord-
ing to changes in throttle position and the
transmission's internal condition within a range of
57-94 psi (except in REVERSE) (Fig. 261). The regu-
lated line pressure in REVERSE (Fig. 262) is held at
much higher pressures than in the other gear posi-
tions: 145-280 psi. The higher pressure for
REVERSE is achieved by the manual valve blocking
the supply of line pressure to the reaction area left of
land #4. With this pressure blocked, there is less
area for pressure to act on to balance the force of the
spring on the right. This allows line pressure to push
the valve train to the right, reducing the amount of
fluid returned to the pump's inlet, increasing line
pressure.
Fig. 260 Regulator Valve in NEUTRAL Position
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 141
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1662 of 2199
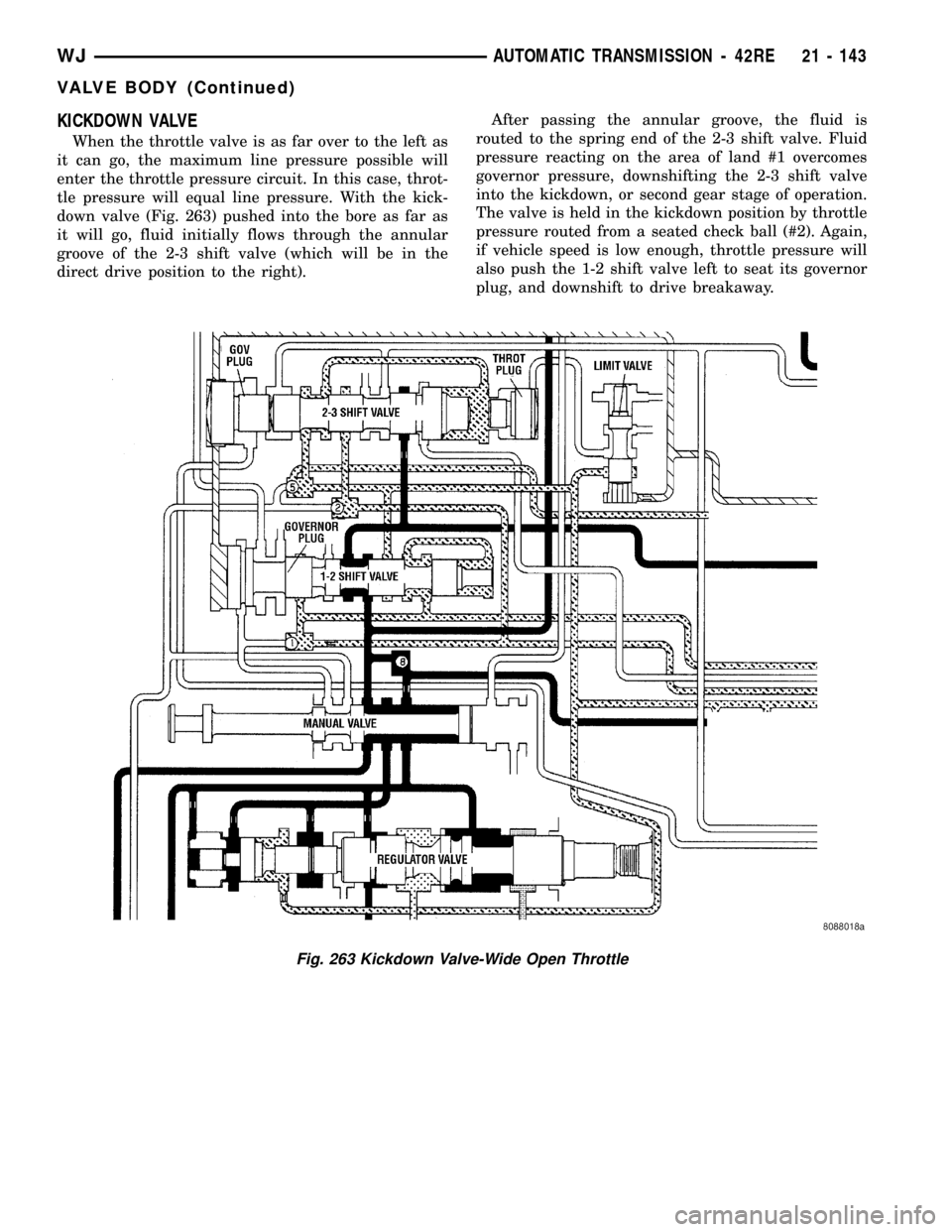
KICKDOWN VALVE
When the throttle valve is as far over to the left as
it can go, the maximum line pressure possible will
enter the throttle pressure circuit. In this case, throt-
tle pressure will equal line pressure. With the kick-
down valve (Fig. 263) pushed into the bore as far as
it will go, fluid initially flows through the annular
groove of the 2-3 shift valve (which will be in the
direct drive position to the right).After passing the annular groove, the fluid is
routed to the spring end of the 2-3 shift valve. Fluid
pressure reacting on the area of land #1 overcomes
governor pressure, downshifting the 2-3 shift valve
into the kickdown, or second gear stage of operation.
The valve is held in the kickdown position by throttle
pressure routed from a seated check ball (#2). Again,
if vehicle speed is low enough, throttle pressure will
also push the 1-2 shift valve left to seat its governor
plug, and downshift to drive breakaway.
Fig. 263 Kickdown Valve-Wide Open Throttle
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 143
VALVE BODY (Continued)