check transmission fluid JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 1768 of 2199

STANDARD PROCEDURE - OIL PUMP VOLUME
CHECK
Measuring the oil pump output volume will deter-
mine if sufficient oil flow to the transmission oil
cooler exists, and whether or not an internal trans-
mission failure is present.
Verify that the transmission fluid is at the proper
level. Refer to the Fluid Level Check procedure in
this section. If necessary, fill the transmission to the
proper level with MopartATF +4, type 9602, Auto-
matic Transmission Fluid.
(1) Disconnect theTo coolerline at the cooler
inlet and place a collecting container under the dis-
connected line.CAUTION: With the fluid set at the proper level,
fluid collection should not exceed (1) quart or inter-
nal damage to the transmission may occur.
(2) Run the engineat 1800 rpm, with the shift
selector in neutral. Verify that the transmission fluid
temperature is below 104.5É C (220É F) for this test.
(3) If one quart of transmission fluid is collected in
the container in 30 seconds or less, oil pump flow vol-
ume is within acceptable limits. If fluid flow is inter-
mittent, or it takes more than 30 seconds to collect
one quart of fluid, refer to the Hydraulic Pressure
tests in this section for further diagnosis.
(4) Re-connect theTo coolerline to the transmis-
sion cooler inlet.
Fig. 90 Oil Pump Reaction Shaft
1 - PUMP HOUSING 4 - SEAL RING (5)
2 - SEAL 5 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
3 - OIL FILTER SEAL 6 - PUMP VALVE BODY
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 249
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1788 of 2199

position, the clutch will engage after the shift to
third gear, at approximately 56 km/h (35 mph) at
light throttle.
The TCM controls the torque converter by way of
internal logic software. The programming of the soft-
ware provides the TCM with control over the L/R-CC
Solenoid. There are four output logic states that can
be applied as follows:
²No EMCC
²Partial EMCC
²Full EMCC
²Gradual-to-no EMCC
NO EMCC
Under No EMCC conditions, the L/R Solenoid is
OFF. There are several conditions that can result in
NO EMCC operations. No EMCC can be initiated
due to a fault in the transmission or because the
TCM does not see the need for EMCC under current
driving conditions.
PARTIAL EMCC
Partial EMCC operation modulates the L/R Sole-
noid (duty cycle) to obtain partial torque converter
clutch application. Partial EMCC operation is main-
tained until Full EMCC is called for and actuated.
During Partial EMCC some slip does occur. Partial
EMCC will usually occur at low speeds, low load and
light throttle situations.
FULL EMCC
During Full EMCC operation, the TCM increases
the L/R Solenoid duty cycle to full ON after PartialEMCC control brings the engine speed within the
desired slip range of transmission input speed rela-
tive to engine rpm.
GRADUAL-TO-NO EMCC
This operation is to soften the change from Full or
Partial EMCC to No EMCC. This is done at mid-
throttle by decreasing the L/R Solenoid duty cycle.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission and torque converter
from vehicle.
(2) Place a suitable drain pan under the converter
housing end of the transmission.
CAUTION: Verify that transmission is secure on the
lifting device or work surface, the center of gravity
of the transmission will shift when the torque con-
verter is removed creating an unstable condition.
The torque converter is a heavy unit. Use caution
when separating the torque converter from the
transmission.
(3) Pull the torque converter forward until the cen-
ter hub clears the oil pump seal.
(4) Separate the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
INSTALLATION
Check converter hub and drive flats for sharp
edges, burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and
flats with 320/400 grit paper or crocus cloth if neces-
sary. Verify that the converter hub o-ring is properly
installed and is free from debris. The hub must be
smooth to avoid damaging the pump seal at installa-
tion.
(1) Lubricate oil pump seal lip with transmission
fluid.
(2) Place torque converter in position on transmis-
sion.
CAUTION: Do not damage oil pump seal or con-
verter hub o-ring while inserting torque converter
into the front of the transmission.
(3) Align torque converter to oil pump seal open-
ing.
(4) Insert torque converter hub into oil pump.
(5) While pushing torque converter inward, rotate
converter until converter is fully seated in the oil
pump gears.
(6) Check converter seating with a scale and
straightedge (Fig. 117). Surface of converter lugs
should be at least 13 mm (1/2 in.) to rear of straight-
edge when converter is fully seated.
(7) If necessary, temporarily secure converter with
C-clamp attached to the converter housing.
Fig. 116 Stator Operation
1 - DIRECTION STATOR WILL FREE WHEEL DUE TO OIL
PUSHING ON BACKSIDE OF VANES
2 - FRONT OF ENGINE
3 - INCREASED ANGLE AS OIL STRIKES VANES
4 - DIRECTION STATOR IS LOCKED UP DUE TO OIL PUSHING
AGAINST STATOR VANES
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 269
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1789 of 2199

(8) Install the transmission in the vehicle.
(9) Fill the transmission with the recommended
fluid.
TRANSMISSION CONTROL
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The relay is supplied fused B+ voltage, energized
by the TCM, and is used to supply power to the sole-
noid pack when the transmission is in normal oper-
ating mode.
OPERATION
When the relay is ªoffº, no power is supplied to the
solenoid pack and the transmission is in ªlimp-inº
mode. After a controller reset, the TCM energizes the
relay. Prior to this, the TCM verifies that the con-
tacts are open by checking for no voltage at the
switched battery terminals. After this is verified, the
voltage at the solenoid pack pressure switches is
checked. After the relay is energized, the TCM mon-
itors the terminals to verify that the voltage is
greater than 3 volts.
TRANSMISSION RANGE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) is part of
the solenoid module, which is mounted to the top of
the valve body inside the transmission.
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) has five
switch contact pins that:
²Determine shift lever position
²Supply ground to the Starter Relay in Park and
Neutral only.
²Supply +12 V to the backup lamps in Reverse
only.
The TRS also has an integrated temperature sen-
sor (thermistor) that communicates transmission
temperature to the TCM and PCM.
OPERATION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) communi-
cates shift lever position to the TCM as a combina-
tion of open and closed switches. Each shift lever
position has an assigned combination of switch states
(open/closed) that the TCM receives from four sense
circuits. The TCM interprets this information and
determines the appropriate transmission gear posi-
tion and shift schedule.
There are many possible combinations of open and
closed switches (codes). Seven of these possible codes
are related to gear position and five are recognized
as ªbetween gearº codes. This results in many codes
which shouldnever occur. These are called
ªinvalidº codes. An invalid code will result in a DTC,
and the TCM will then determine the shift lever
position based on pressure switch data. This allows
reasonably normal transmission operation with a
TRS failure.
GEAR C5 C4 C3 C2 C1
ParkCL OP OP CL CL
Temp 1CL OP OP CL OP
ReverseOP OP OP CL OP
Temp 2OP OP CL CL OP
Neutral 1OP OP CL CL CL
Neutral 2OP CL CL CL CL
Temp 3OP CL CL CL OP
DriveOP CL CL OP OP
Temp 4OP CL OP OP OP
Manual 2CL CL OP OP OP
Temp 5CL OP OP OP OP
Manual 1CL OP CL OP OP
Fig. 117 Checking Torque Converter Seating-Typical
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
21 - 270 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1792 of 2199
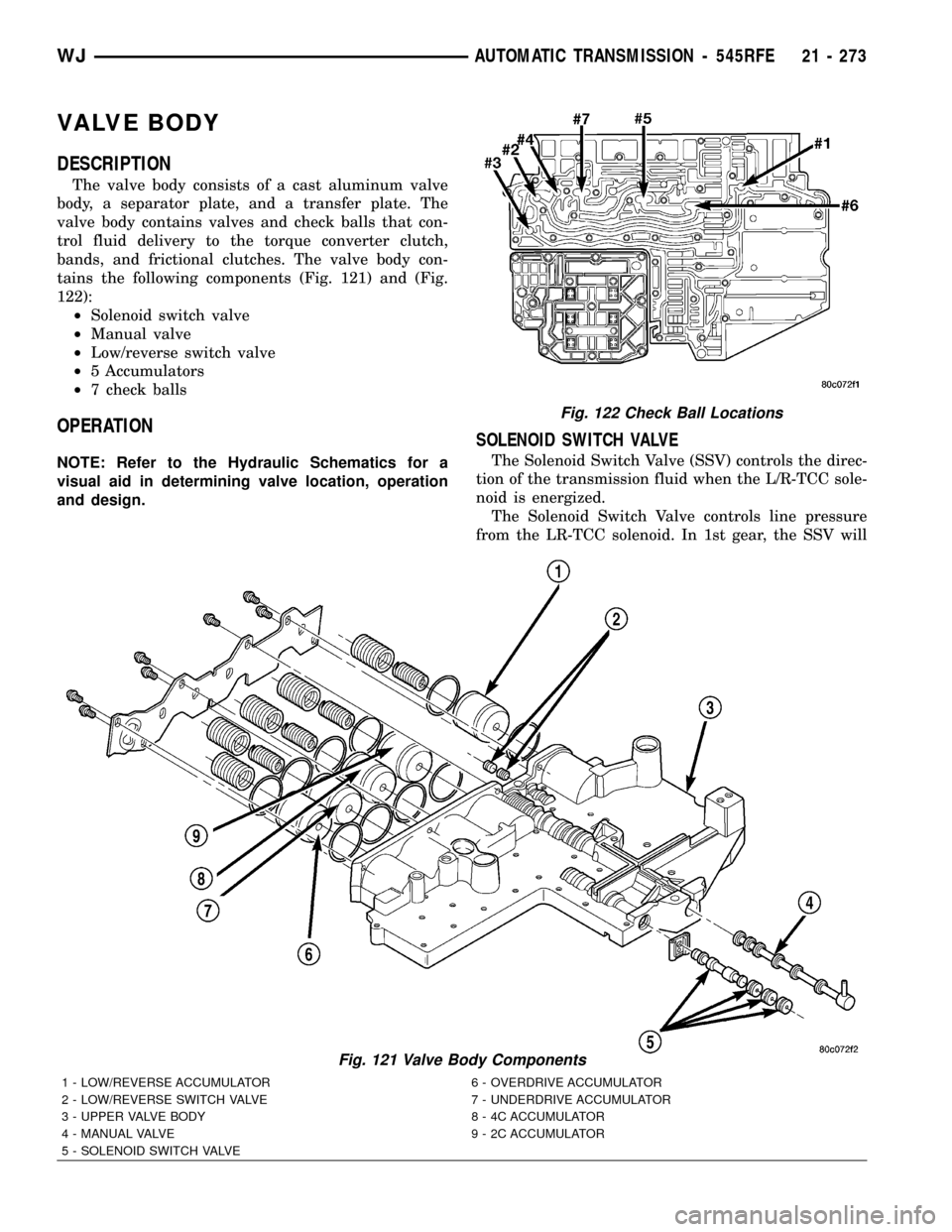
VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION
The valve body consists of a cast aluminum valve
body, a separator plate, and a transfer plate. The
valve body contains valves and check balls that con-
trol fluid delivery to the torque converter clutch,
bands, and frictional clutches. The valve body con-
tains the following components (Fig. 121) and (Fig.
122):
²Solenoid switch valve
²Manual valve
²Low/reverse switch valve
²5 Accumulators
²7 check balls
OPERATION
NOTE: Refer to the Hydraulic Schematics for a
visual aid in determining valve location, operation
and design.
SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
The Solenoid Switch Valve (SSV) controls the direc-
tion of the transmission fluid when the L/R-TCC sole-
noid is energized.
The Solenoid Switch Valve controls line pressure
from the LR-TCC solenoid. In 1st gear, the SSV will
Fig. 121 Valve Body Components
1 - LOW/REVERSE ACCUMULATOR 6 - OVERDRIVE ACCUMULATOR
2 - LOW/REVERSE SWITCH VALVE 7 - UNDERDRIVE ACCUMULATOR
3 - UPPER VALVE BODY 8 - 4C ACCUMULATOR
4 - MANUAL VALVE 9 - 2C ACCUMULATOR
5 - SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
Fig. 122 Check Ball Locations
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 273
Page 1796 of 2199

CLEANING
Clean the valve housings, valves, plugs, springs,
and separator plates with a standard parts cleaning
solution only. Do not use gasoline, kerosene, or any
type of caustic solution. (Fig. 131)
Do not immerse any of the electrical components in
cleaning solution. Clean the electrical components by
wiping them off with dry shop towels only.
Dry all except the electrical parts with compressed
air. Make sure all passages are clean and free from
obstructions.Do not use rags or shop towels to
dry or wipe off valve body components. Lint
from these materials can stick to valve body
parts, interfere with valve operation, and clog
filters and fluid passages.
INSPECTION
Inspect all of the valve body mating surfaces for
scratches, nicks, burrs, or distortion. Use a straight-edge to check surface flatness. Minor scratches may
be removed with crocus cloth using only very light
pressure.
Minor distortion of a valve body mating surface
may be corrected by smoothing the surface with a
sheet of crocus cloth. Position the crocus cloth on a
surface plate, sheet of plate glass or equally flat sur-
face. If distortion is severe or any surfaces are
heavily scored, the valve body will have to be
replaced.
Inspect the valves and plugs (Fig. 132) for
scratches, burrs, nicks, or scores. Minor surface
scratches on steel valves and plugs can be removed
with crocus cloth butdo not round off the edges
of the valve or plug lands.Maintaining sharpness
of these edges is vitally important. The edges prevent
foreign matter from lodging between the valves and
plugs and the bore.
Fig. 130 Valve Body Components
1 - SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
2 - MANUAL VALVE
3 - LOW REVERSE SWITCH VALVE
4 - LOW REVERSE ACCUMULATOR
5 - 2ND CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR
6 - UNDERDRIVE ACCUMULATOR
7 - OVERDRIVE ACCUMULATOR
8 - 4TH CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR
9 - CHECK BALLS (7)
Fig. 131 Valve Body Components
1 - SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
2 - MANUAL VALVE
3 - LOW REVERSE SWITCH VALVE
4 - LOW REVERSE ACCUMULATOR
5 - 2ND CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR
6 - UNDERDRIVE ACCUMULATOR
7 - OVERDRIVE ACCUMULATOR
8 - 4TH CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR
9 - CHECK BALLS (7)
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 277
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1797 of 2199

Inspect all the valve and plug bores in the valve
body. Use a penlight to view the bore interiors.
Replace the valve body if any bores are distorted or
scored. Inspect all of the valve body springs. The
springs must be free of distortion, warpage or broken
coils.
Trial fit each valve and plug in its bore to check
freedom of operation. When clean and dry, the valves
and plugs should drop freely into the bores.
Valve body bores do not change dimensionally with
use. If the valve body functioned correctly when new,
it will continue to operate properly after cleaning and
inspection. It should not be necessary to replace a
valve body assembly unless it is damaged in han-
dling.
Inspect all the accumulator bores in the valve body.
Use a penlight to view the bore interiors. Replace the
valve body if any bores are distorted or scored.Inspect all of the accumulator springs. The springs
must be free of distortion, warpage or broken coils.
Inspect all the fluid seals on the valve body (Fig.
133). Replace any seals that are cracked, distorted, or
damaged in any way. These seals pass fluid pressure
directly to the clutches. Any pressure leak at these
points, may cause transmission performance prob-
lems.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Lubricate valves, springs, and the housing
valve bores with clean transmission fluid.
(2) Install solenoid switch valve, manual valve,
and the low/reverse switch valve into the valve body.
(3) Install the retainers to hold each valve into the
valve body.
(4) Install the valve body check balls into their
proper locations.
(5) Position the transfer plate onto the valve body.
(6) Install the screws to hold the transfer plate to
the valve body. Tighten the screws to 5.6 N´m (50 in.
lbs.).
(7) Install the accumulator pistons and springs
into the valve body in the location from which they
were removed. Note that all accumulators except the
overdrive have two springs. The overdrive accumula-
tor piston has only one spring.
Fig. 132 Valve Body Components
1 - SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
2 - MANUAL VALVE
3 - LOW REVERSE SWITCH VALVE
4 - LOW REVERSE ACCUMULATOR
5 - 2ND CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR
6 - UNDERDRIVE ACCUMULATOR
7 - OVERDRIVE ACCUMULATOR
8 - 4TH CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR
9 - CHECK BALLS (7)
Fig. 133 Valve Body Seals
1 - UNDERDRIVE ACCUMULATOR (2 SPRINGS)
2 - 4TH CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR (2 SPRINGS)
3 - 2ND CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR (2 SPRINGS)
4 - LOW REVERSE ACCUMULATOR (2 SPRINGS)
5 - LOW/REVERSE PASSAGE SEAL
6 - 2ND CLUTCH PASSAGE SEAL
7 - 4TH CLUTCH PASSAGE SEAL
8 - OVERDRIVE ACCUMULATOR (1 SPRING)
21 - 278 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1798 of 2199

(8) Position the accumulator cover onto the valve
body.
(9) Install the screws to hold the accumulator
cover onto the valve body. Tighten the screws to 4.5
N´m (40 in. lbs.).
(10) Install the TRS selector plate onto the valve
body and the manual valve.
(11) Install the solenoid and pressure switch
assembly onto the valve body.
(12) Install the screws to hold the solenoid and
pressure switch assembly onto the valve body.
Tighten the screws to 5.7 N´m (50 in. lbs.). Tighten
the screws adjacent to the arrows cast into the bot-
tom of the transfer plate first.
(13) Position the detent spring onto the valve body.
(14) Install the screw to hold the detent spring
onto the valve body. Tighten the screw to 4.5 N´m (40
in. lbs.).
(15) Install new clutch passage seals onto the
valve body, if necessary
INSTALLATION
(1) Check condition of seals on valve body and the
solenoid and pressure switch assembly. Replace seals
if cut or worn.
(2) Place TRS selector plate in the PARK position.
(3) Place the transmission in the PARK position.
(4) Lubricate seal on the solenoid and pressure
switch assembly connector with petroleum jelly.(5) Position valve body in transmission and align
the manual lever on the valve body to the pin on the
transmission manual shift lever.
(6) Seat valve body in case and install one or two
bolts to hold valve body in place.
(7) Tighten valve body bolts alternately and evenly
to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.) torque.
(8) Install a new primary oil filter seal in the oil
pump inlet bore. Seat the seal in the bore with the
butt end of a hammer, or other suitable tool.
CAUTION: The primary oil filter seal MUST be fully
installed flush against the oil pump body. DO NOT
install the seal onto the filter neck and attempt to
install the filter and seal as an assembly. Damage to
the transmission will result.
(9) Place replacement filter in position on valve
body and into the oil pump.
(10) Install screw to hold filter to valve body.
Tighten screw to 4.5 N´m (40 in. lbs.) torque.
(11) Connect the solenoid and pressure switch
assembly connector.
(12) Install oil pan. Tighten pan bolts to 12 N´m
(105 in. lbs.) torque.
(13) Lower vehicle and fill transmission with
MopartATF +4, type 9602, fluid.
(14) Check and adjust gearshift cable, if necessary.
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 279
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1814 of 2199

REAR OUTPUT SHAFT/YOKE/DRIVE CHAIN
Check condition of the seal contact surfaces of the
yoke slinger (Fig. 49). This surface must be clean and
smooth to ensure proper seal life. Replace the yoke
nut and seal washer as neither part should be
reused.
Inspect the shaft threads, sprocket teeth, and bear-
ing surfaces. Minor nicks on the teeth can be
smoothed with an oilstone. Use 320-400 grit emery to
smooth minor scratches on the shaft bearing sur-
faces. Rough threads on the shaft can be chased if
necessary. Replace the shaft if the threads are dam-
aged, bearing surfaces are scored, or if any sprocket
teeth are cracked or broken.
Examine the drive chain and shaft bearings.
Replace the chain and both sprockets if the chain is
stretched, distorted, or if any of the links bind.
Replace the bearings if rough, or noisy.
LOW RANGE ANNULUS GEAR
Inspect annulus gear condition carefully. The gear
is only serviced as part of the front case. If the gear
is damaged, it will be necessary to replace the gear
and front case as an assembly. Do not attempt to
remove the gear (Fig. 50)
FRONT-REAR CASES AND FRONT RETAINER
Inspect the cases and retainer for wear and dam-
age. Clean the sealing surfaces with a scraper and
3M all purpose cleaner. This will ensure proper
sealer adhesion at assembly. Replace the input
retainer seal; do not reuse it.Check case condition. If leaks were a problem, look
for gouges and severe scoring of case sealing sur-
faces. Also make sure the front case mounting studs
are in good condition.
Check the front case mounting studs and vent
tube. The tube can be secured with LoctiteŸ 271 or
680 if loose. The stud threads can be cleaned up with
a die if necessary. Also check condition of the fill/
drain plug threads in the rear case. The threads can
be repaired with a thread chaser or tap if necessary.
Or the threads can be repaired with HelicoilŸ stain-
less steel inserts if required.
OIL PUMP/OIL PICKUP
Examine the oil pump pickup parts. Replace the
pump if any part appears to be worn or damaged. Do
not disassemble the pump as individual parts are not
available. The pump is only available as a complete
assembly. The pickup screen, hose, and tube are the
only serviceable parts and are available separately.
ASSEMBLY
Lubricate transfer case components with automatic
transmission fluid or petroleum jelly (where indi-
cated) during assembly.
CAUTION: The bearing bores in various transfer
case components contain oil feed holes. Make sure
replacement bearings do not block the holes.
Fig. 49 Seal Contact Surface Of Yoke Slinger
1 - FRONT SLINGER (PART OF YOKE)
2 - SEAL CONTACT SURFACE MUST BE CLEAN AND SMOOTH
Fig. 50 Low Range Annulus Gear
1 - FRONT CASE
2 - LOW RANGE ANNULUS GEAR
WJTRANSFER CASE - NV242 21 - 295
TRANSFER CASE - NV242 (Continued)
Page 1826 of 2199

NV242HD REAR RETAINER
(1) Apply bead of MopartSealer, or LoctiteŸ
Ultra Gray, to mating surface of rear retainer. Sealer
bead should be a maximum of 3/16 in.
(2) Install rear retainer on rear case. Tighten
retainer bolts to 20-27 N´m (15-20 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install new output shaft bearing snap-ring
(Fig. 91). Lift mainshaft slightly to seat snap-ring in
shaft groove, if necessary.
(4) Apply 3 mm (1/8 in.) wide bead of Mopartgas-
ket maker or silicone adhesive sealer to mounting
surface of extension housing. Allow sealer to set-up
slightly before proceeding.(5) Install extension housing on rear retainer.
(6) Install extension housing bolts and tighten to
35-46 N´m (26-34 ft. lbs.).
COMPANION FLANGE
(1) Lubricate companion flange hub with transmis-
sion fluid and install flange on front shaft.
(2) Install new seal washer on front shaft.
(3) Install flange on front shaft and tighten nut to
122-176 N´m (90-130 ft. lbs.).
INSTALLATION
(1) Mount transfer case on a transmission jack.
(2) Secure transfer case to jack with chains.
(3) Position transfer case under vehicle.
(4) Align transfer case and transmission shafts
and install transfer case on transmission.
(5) Install and tighten transfer case attaching nuts
to 35 N´m (26 ft. lbs.) torque (Fig. 4).
(6) Align and connect propeller shafts. (Refer to 3 -
DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER
SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT - INSTALLATION)
(7) Fill transfer case with correct fluid. Check
transmission fluid level. Correct as necessary.
(8) Install rear crossmember and skid plate, if
equipped. Tighten crossmember bolts to 41 N´m (30
ft. lbs.) torque.
(9) Remove transmission jack and support stand.
(10) Connect shift rod to transfer case range lever.
(11) Connect transfer case vent hose and transfer
case position sensor.
(12) Adjust transfer case shift cable.
(13) Lower vehicle and verify transfer case shift
operation.
Fig. 91 Install Output Bearing Snap-ring
1 - REAR RETAINER
2 - SNAP-RING
3 - REAR BEARING
WJTRANSFER CASE - NV242 21 - 307
TRANSFER CASE - NV242 (Continued)
Page 1855 of 2199
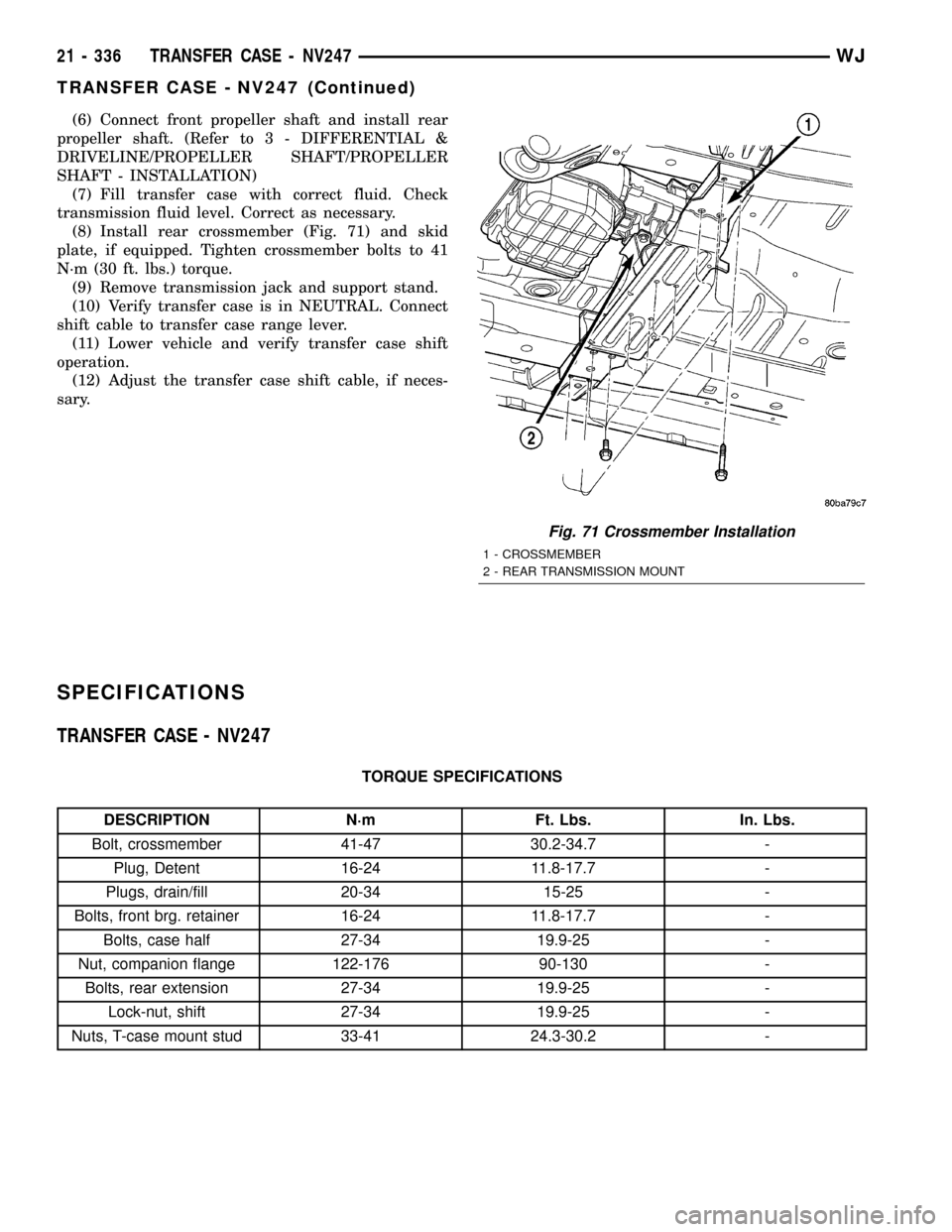
(6) Connect front propeller shaft and install rear
propeller shaft. (Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL &
DRIVELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT/PROPELLER
SHAFT - INSTALLATION)
(7) Fill transfer case with correct fluid. Check
transmission fluid level. Correct as necessary.
(8) Install rear crossmember (Fig. 71) and skid
plate, if equipped. Tighten crossmember bolts to 41
N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(9) Remove transmission jack and support stand.
(10) Verify transfer case is in NEUTRAL. Connect
shift cable to transfer case range lever.
(11) Lower vehicle and verify transfer case shift
operation.
(12) Adjust the transfer case shift cable, if neces-
sary.
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSFER CASE - NV247
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Bolt, crossmember 41-47 30.2-34.7 -
Plug, Detent 16-24 11.8-17.7 -
Plugs, drain/fill 20-34 15-25 -
Bolts, front brg. retainer 16-24 11.8-17.7 -
Bolts, case half 27-34 19.9-25 -
Nut, companion flange 122-176 90-130 -
Bolts, rear extension 27-34 19.9-25 -
Lock-nut, shift 27-34 19.9-25 -
Nuts, T-case mount stud 33-41 24.3-30.2 -
Fig. 71 Crossmember Installation
1 - CROSSMEMBER
2 - REAR TRANSMISSION MOUNT
21 - 336 TRANSFER CASE - NV247WJ
TRANSFER CASE - NV247 (Continued)