fluid spec JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Manual Online
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 1614 of 2199

GEAR CASE AND PARK LOCK
(1) Remove locating ring from gear case.
(2) Remove park pawl shaft retaining bolt and
remove shaft, pawl and spring.
(3) Remove reaction plug snap-ring and remove
reaction plug.
(4) Remove output shaft seal.
CLEANING
Clean the geartrain and case components with sol-
vent. Dry all parts except the bearings with com-
pressed air. Allow bearings to air dry.
Do not use shop towels for wiping parts dry unless
the towels are made from a lint-free material. A suf-
ficient quantity of lint (from shop towels, cloths, rags,
etc.) could plug the transmission filter and fluid pas-
sages.
Discard the old case gasket and seals. Do not
attempt to salvage these parts. They are not reus-
able. Replace any of the overdrive unit snap-rings if
distorted or damaged.
Minor nicks or scratches on components can be
smoothed with crocus cloth. However, do not attempt
to reduce severe scoring on any components with
abrasive materials. Replace severely scored compo-
nents; do not try to salvage them.
INSPECTION
Check condition of the park lock components and
the overdrive case.
Check the bushings in the overdrive case. Replace
the bushings if severely scored or worn. Also replace
the case seal if loose, distorted, or damaged.
Examine the overdrive and direct clutch discs and
plates. Replace the discs if the facing is worn,
severely scored, or burned and flaking off. Replace
the clutch plates if worn, heavily scored, or cracked.
Check the lugs on the clutch plates for wear. The
plates should slide freely in the drum. Replace the
plates or drum if binding occurs.
Check condition of the annulus gear, direct clutch
hub, clutch drum and clutch spring. Replace the gear,
hub and drum if worn or damaged. Replace the
spring if collapsed, distorted, or cracked.
Be sure the splines and lugs on the gear, drum and
hub are in good condition. The clutch plates and
discs should slide freely in these components.
Inspect the thrust bearings and spring plate.
Replace the plate if worn or scored. Replace the bear-
ings if rough, noisy, brinnelled, or worn.
Inspect the planetary gear assembly and the sun
gear and bushings. If either the sun gear or the
bushings are damaged, replace the gear and bush-
ings as an assembly. The gear and bushings are not
serviced separately.The planetary carrier and pinions must be in good
condition. Also be sure the pinion pins are secure and
in good condition. Replace the carrier if worn or dam-
aged.
Inspect the overrunning clutch and race. The race
surface should be smooth and free of scores. Replace
the overrunning clutch assembly or the race if either
assembly is worn or damaged in any way.
Replace the shaft pilot bushing and inner bushing
if damaged. Replace either shaft bearing if rough or
noisy. Replace the bearing snap-rings if distorted or
cracked.
Check the machined surfaces on the output shaft.
These surfaces should clean and smooth. Very minor
nicks or scratches can be smoothed with crocus cloth.
Replace the shaft if worn, scored or damaged in any
way.
Inspect the output shaft bushings. The small bush-
ing is the intermediate shaft pilot bushing. The large
bushing is the overrunning clutch hub bushing.
Replace either bushing if scored, pitted, cracked, or
worn.
ASSEMBLY
GEARTRAIN AND DIRECT CLUTCH
(1) Soak direct clutch and overdrive clutch discs in
MopartATF +4, type 9602, transmission fluid. Allow
discs to soak for 10-20 minutes.
(2) Install new pilot bushing and clutch hub bush-
ing in output shaft if necessary (Fig. 155). Lubricate
bushings with petroleum jelly, or transmission fluid.
(3) Install annulus gear on output shaft, if
removed. Then install annulus gear retaining snap-
ring (Fig. 156).
Fig. 155 Output Shaft Pilot Bushing
1 - OUTPUT SHAFT HUB
2 - OVERRUNNING CLUTCH HUB BUSHING
3 - INTERMEDIATE SHAFT PILOT BUSHING
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 95
OVERDRIVE UNIT (Continued)
Page 1632 of 2199

INSPECTION
Check sun gear and driving shell condition.
Replace the gear if damaged or if the bushings are
scored or worn. The bushings are not serviceable.
Replace the driving shell if worn, cracked or dam-
aged.Replace planetary gear sets if gears, pinion pins, or
carrier are damaged in any way. Replace the annulus
gears and supports if either component is worn or
damaged.
Inspect the geartrain spacers, thrust plates, snap-
rings, and thrust washers. Replace any of these parts
that are worn, distorted or damaged. Do not attempt
to reuse these parts.
The planetary gear thrust washers are different
sizes. The large diameter washers go on the front
planetary and the smaller washers go on the rear
planetary. All the washers have four locating tabs on
them. These tabs fit in the holes or slots provided in
each planetary gear.
Inspect the output shaft carefully. Pay particular
attention to the machined bushing/bearing surfaces
on the shaft and the governor valve shaft bore at the
shaft rear.
Replace the output shaft if the machined surfaces
are scored, pitted, or damaged in any way. Also
replace the shaft if the splines are damaged, or
exhibits cracks at any location (especially at the gov-
ernor valve shaft bore).
The annulus gears can be removed from their sup-
ports if necessary. Just remove the snap-rings and
separate the two parts when replacement is neces-
sary. In addition, the annulus gear bushings can be
replaced if severely worn, or scored. However it is not
necessary to replace the bushings if they only exhibit
normal wear. Check bushing fit on the output shaft
to be sure.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Lubricate output shaft and planetary compo-
nents with transmission fluid. Use petroleum jelly to
lubricate and hold thrust washers and plates in posi-
tion.
(2) Assemble rear annulus gear and support if dis-
assembled. Be sure support snap-ring is seated and
that shoulder-side of support faces rearward (Fig.
208).
(3) Install rear thrust washer on rear planetary
gear. Use enough petroleum jelly to hold washer in
place. Also be sure all four washer tabs are properly
engaged in gear slots.
(4) Install rear annulus over and onto rear plane-
tary gear (Fig. 208).
(5) Install assembled rear planetary and annulus
gear on output shaft (Fig. 209). Verify that assembly
is fully seated on shaft.
Fig. 206 Front Planetary And Annulus Gear
Disassembly
1 - FRONT ANNULUS
2 - THRUST WASHER
3 - THRUST PLATE
4 - FRONT THRUST WASHER
5 - FRONT PLANETARY
Fig. 207 Removing Driving Shell, Rear Planetary
And Rear Annulus
1 - REAR ANNULUS
2 - REAR PLANETARY
3 - DRIVING SHELL
4 - OUTPUT SHAFT
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 113
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN/OUTPUT SHAFT (Continued)
Page 1639 of 2199

INSPECTION
Replace the clutch discs if warped, worn, scored,
burned/charred, the lugs are damaged, or if the fac-
ing is flaking off. Replace the top and bottom pres-
sure plates if scored, warped, or cracked. Be sure the
driving lugs on the pressure and clutch plates are
also in good condition. The lugs must not be bent,
cracked or damaged in any way.
Replace the piston spring and wave spring if either
part is distorted, warped or broken.
Check the lug grooves in the clutch retainer. The
clutch and pressure plates should slide freely in the
slots. Replace the retainer if the grooves are worn or
damaged. Also check action of the check balls in the
retainer and piston. Each check ball must move
freely and not stick.
Replace the retainer bushing if worn, scored, or
doubt exists about bushing condition.
Inspect the piston and retainer seal surfaces for
nicks or scratches. Minor scratches can be removed
with crocus cloth. However, replace the piston and/or
retainer if the seal surfaces are seriously scored.
Check condition of the fiber thrust washer and
metal output shaft thrust washer. Replace either
washer if worn or damaged.
Check condition of the seal rings on the input shaft
and clutch retainer hub. Replace the seal rings only
if worn, distorted, or damaged. The input shaft front
seal ring is teflon with chamfered ends. The rear ring
is metal with interlocking ends.
Check the input shaft for wear, or damage. Replace
the shaft if worn, scored or damaged in any way.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Soak clutch discs in transmission fluid while
assembling other clutch parts.
(2) Install new seal rings on clutch retainer hub
and input shaft, if necessary, (Fig. 227) and (Fig.
228).
(a) Be sure clutch hub seal ring is fully seated in
groove and is not twisted.
(3) Lubricate splined end of input shaft and clutch
retainer with transmission fluid. Then press input
shaft into retainer (Fig. 229). Use a suitably sized
press tool to support retainer as close to input shaft
as possible.
(4) Install input shaft snap-ring (Fig. 226).
(5) Invert retainer and press input shaft in oppo-
site direction until snap-ring is seated.
(6) Install new seals on clutch piston. Be sure lip
of each seal faces interior of clutch retainer.
(7) Lubricate lip of piston seals with generous
quantity of MopartDoor Ease. Then lubricate
retainer hub and bore with light coat of transmission
fluid.
(8) Install clutch piston in retainer. Use twisting
motion to seat piston in bottom of retainer. A thin
strip of plastic (about 0.0209thick), can be used to
guide seals into place if necessary.
CAUTION: Never push the clutch piston straight in.
This will fold the seals over causing leakage and
clutch slip. In addition, never use any type of metal
tool to help ease the piston seals into place. Metal
tools will cut, shave, or score the seals.
(9) Install piston spring in retainer and on top of
piston (Fig. 230). Concave side of spring faces down-
ward (toward piston).
(10) Install wave spring in retainer (Fig. 230). Be
sure spring is completely seated in retainer groove.
(11) Install bottom pressure plate (Fig. 225).
Ridged side of plate faces downward (toward piston)
and flat side toward clutch pack.
(12) Install first clutch disc in retainer on top of
bottom pressure plate. Then install a clutch plate fol-
lowed by a clutch disc until entire clutch pack is
installed (4 discs and 3 plates are required) (Fig.
225).
(13) Install top pressure plate.
(14) Install selective snap-ring. Be sure snap-ring
is fully seated in retainer groove.
(15) Using a suitable gauge bar and dial indicator,
measure clutch pack clearance (Fig. 231).
(a) Position gauge bar across the clutch drum
with the dial indicator pointer on the pressure
plate (Fig. 231).
(b) Using two small screw drivers, lift the pres-
sure plate and release it.
Fig. 226 Removing Input Shaft Snap-Ring
1 - REAR CLUTCH RETAINER
2 - INPUT SHAFT SNAP-RING
3 - SNAP-RING PLIERS
21 - 120 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
REAR CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 1659 of 2199
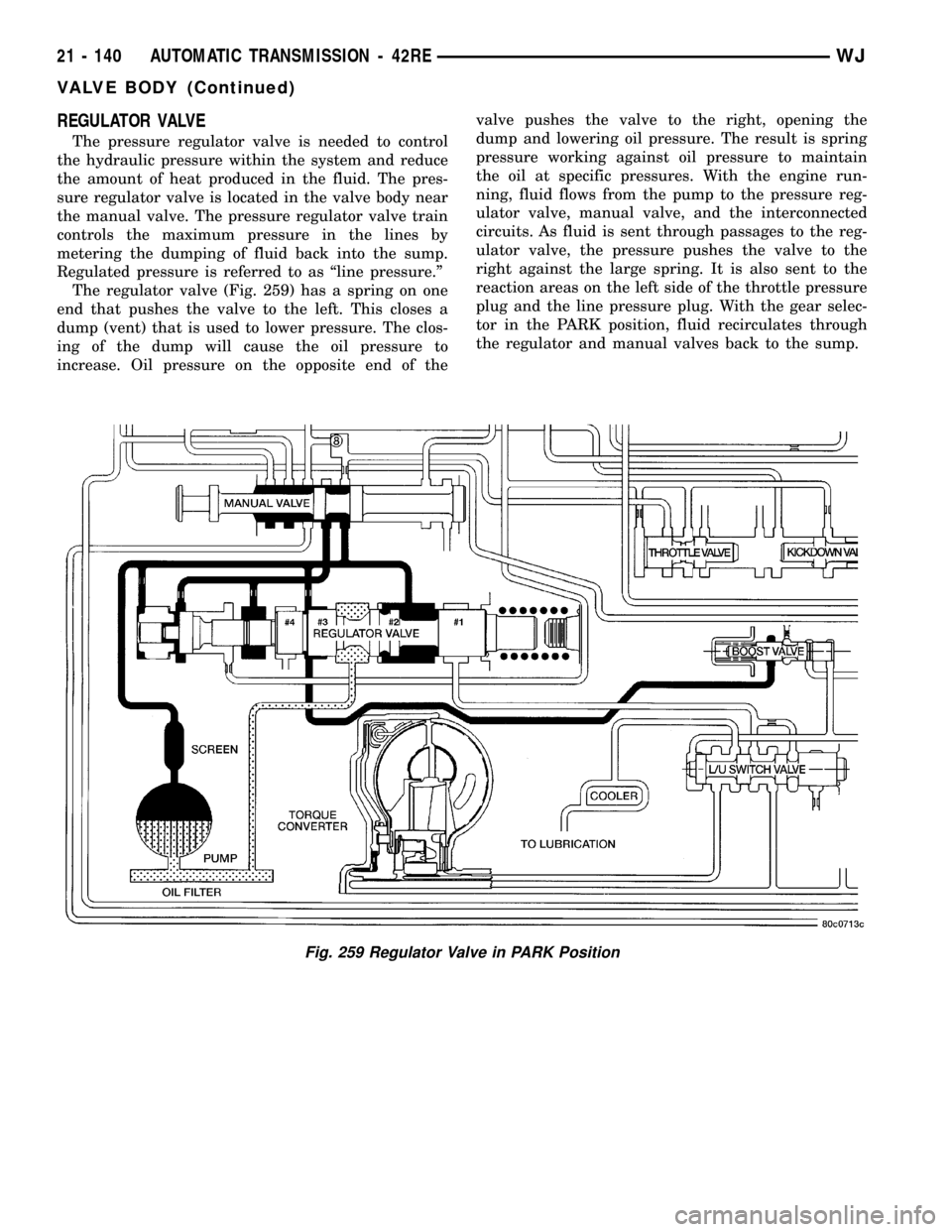
REGULATOR VALVE
The pressure regulator valve is needed to control
the hydraulic pressure within the system and reduce
the amount of heat produced in the fluid. The pres-
sure regulator valve is located in the valve body near
the manual valve. The pressure regulator valve train
controls the maximum pressure in the lines by
metering the dumping of fluid back into the sump.
Regulated pressure is referred to as ªline pressure.º
The regulator valve (Fig. 259) has a spring on one
end that pushes the valve to the left. This closes a
dump (vent) that is used to lower pressure. The clos-
ing of the dump will cause the oil pressure to
increase. Oil pressure on the opposite end of thevalve pushes the valve to the right, opening the
dump and lowering oil pressure. The result is spring
pressure working against oil pressure to maintain
the oil at specific pressures. With the engine run-
ning, fluid flows from the pump to the pressure reg-
ulator valve, manual valve, and the interconnected
circuits. As fluid is sent through passages to the reg-
ulator valve, the pressure pushes the valve to the
right against the large spring. It is also sent to the
reaction areas on the left side of the throttle pressure
plug and the line pressure plug. With the gear selec-
tor in the PARK position, fluid recirculates through
the regulator and manual valves back to the sump.
Fig. 259 Regulator Valve in PARK Position
21 - 140 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1672 of 2199
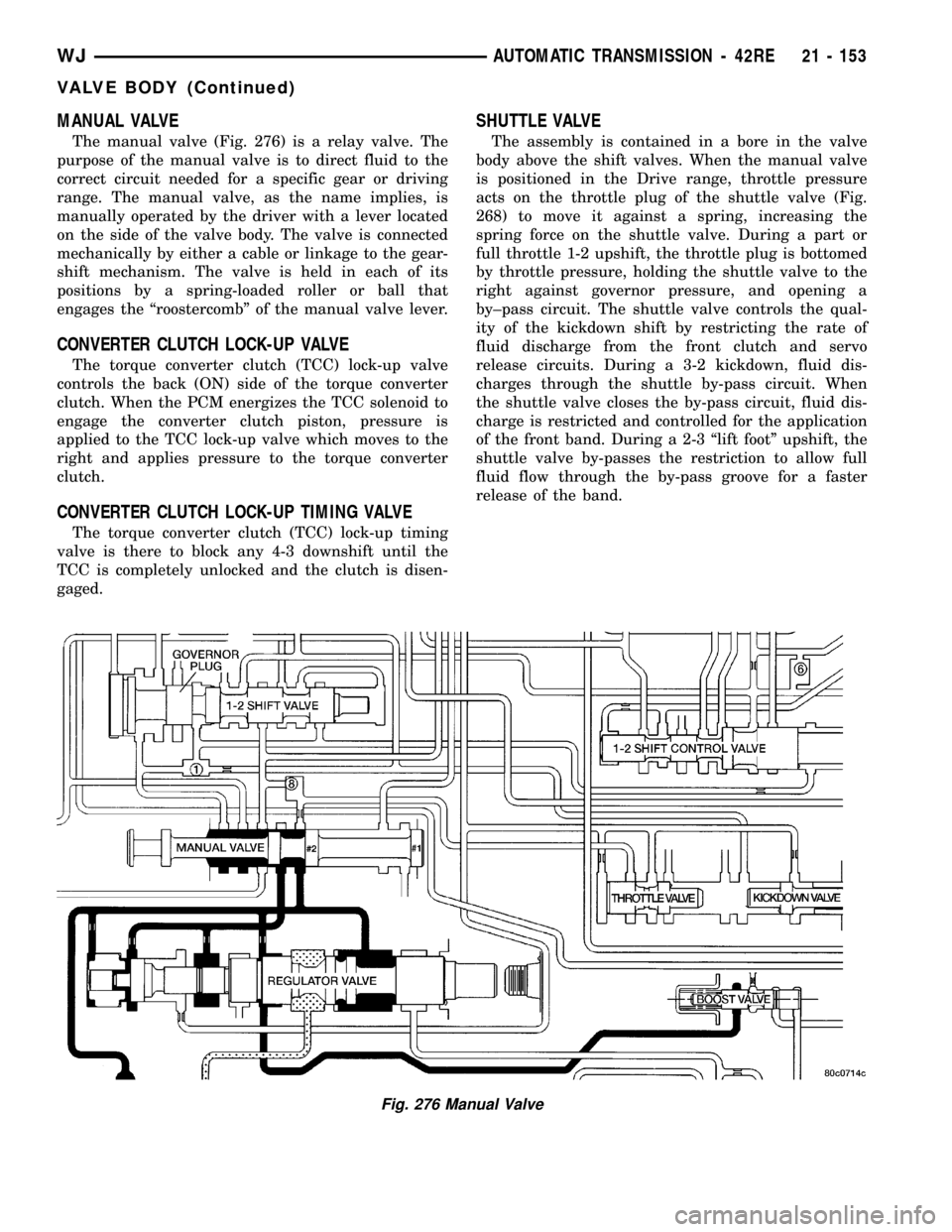
MANUAL VALVE
The manual valve (Fig. 276) is a relay valve. The
purpose of the manual valve is to direct fluid to the
correct circuit needed for a specific gear or driving
range. The manual valve, as the name implies, is
manually operated by the driver with a lever located
on the side of the valve body. The valve is connected
mechanically by either a cable or linkage to the gear-
shift mechanism. The valve is held in each of its
positions by a spring-loaded roller or ball that
engages the ªroostercombº of the manual valve lever.
CONVERTER CLUTCH LOCK-UP VALVE
The torque converter clutch (TCC) lock-up valve
controls the back (ON) side of the torque converter
clutch. When the PCM energizes the TCC solenoid to
engage the converter clutch piston, pressure is
applied to the TCC lock-up valve which moves to the
right and applies pressure to the torque converter
clutch.
CONVERTER CLUTCH LOCK-UP TIMING VALVE
The torque converter clutch (TCC) lock-up timing
valve is there to block any 4-3 downshift until the
TCC is completely unlocked and the clutch is disen-
gaged.
SHUTTLE VALVE
The assembly is contained in a bore in the valve
body above the shift valves. When the manual valve
is positioned in the Drive range, throttle pressure
acts on the throttle plug of the shuttle valve (Fig.
268) to move it against a spring, increasing the
spring force on the shuttle valve. During a part or
full throttle 1-2 upshift, the throttle plug is bottomed
by throttle pressure, holding the shuttle valve to the
right against governor pressure, and opening a
by±pass circuit. The shuttle valve controls the qual-
ity of the kickdown shift by restricting the rate of
fluid discharge from the front clutch and servo
release circuits. During a 3-2 kickdown, fluid dis-
charges through the shuttle by-pass circuit. When
the shuttle valve closes the by-pass circuit, fluid dis-
charge is restricted and controlled for the application
of the front band. During a 2-3 ªlift footº upshift, the
shuttle valve by-passes the restriction to allow full
fluid flow through the by-pass groove for a faster
release of the band.
Fig. 276 Manual Valve
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 153
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1673 of 2199
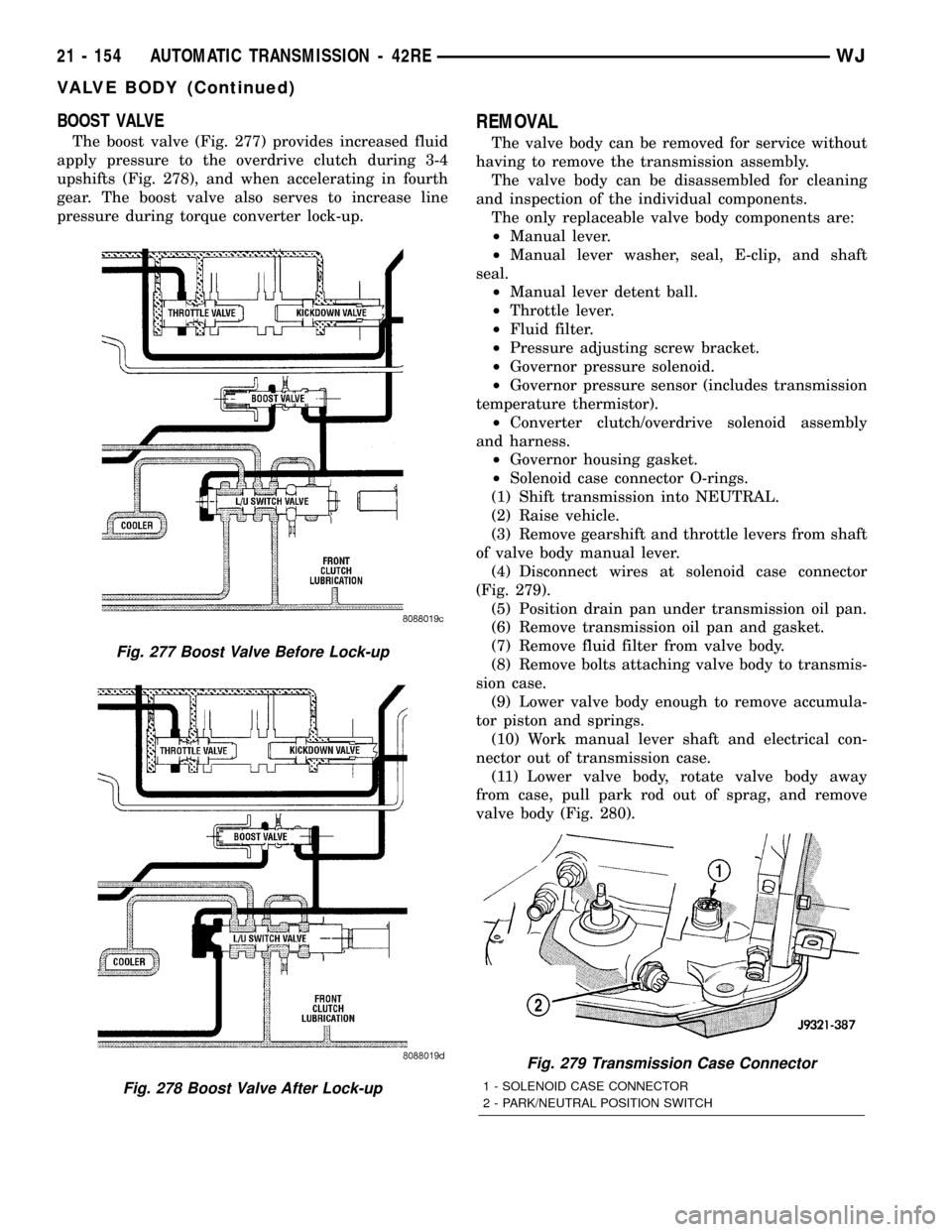
BOOST VALVE
The boost valve (Fig. 277) provides increased fluid
apply pressure to the overdrive clutch during 3-4
upshifts (Fig. 278), and when accelerating in fourth
gear. The boost valve also serves to increase line
pressure during torque converter lock-up.
REMOVAL
The valve body can be removed for service without
having to remove the transmission assembly.
The valve body can be disassembled for cleaning
and inspection of the individual components.
The only replaceable valve body components are:
²Manual lever.
²Manual lever washer, seal, E-clip, and shaft
seal.
²Manual lever detent ball.
²Throttle lever.
²Fluid filter.
²Pressure adjusting screw bracket.
²Governor pressure solenoid.
²Governor pressure sensor (includes transmission
temperature thermistor).
²Converter clutch/overdrive solenoid assembly
and harness.
²Governor housing gasket.
²Solenoid case connector O-rings.
(1) Shift transmission into NEUTRAL.
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) Remove gearshift and throttle levers from shaft
of valve body manual lever.
(4) Disconnect wires at solenoid case connector
(Fig. 279).
(5) Position drain pan under transmission oil pan.
(6) Remove transmission oil pan and gasket.
(7) Remove fluid filter from valve body.
(8) Remove bolts attaching valve body to transmis-
sion case.
(9) Lower valve body enough to remove accumula-
tor piston and springs.
(10) Work manual lever shaft and electrical con-
nector out of transmission case.
(11) Lower valve body, rotate valve body away
from case, pull park rod out of sprag, and remove
valve body (Fig. 280).
Fig. 277 Boost Valve Before Lock-up
Fig. 278 Boost Valve After Lock-up
Fig. 279 Transmission Case Connector
1 - SOLENOID CASE CONNECTOR
2 - PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH
21 - 154 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1685 of 2199

Wipe the governor pressure sensor and solenoid
valve with dry, lint free shop towels only. The O-rings
on the sensor and solenoid valve are the only service-
able components. Be sure the vent ports in the sole-
noid valve are open and not blocked by dirt or debris.
Replace the valve and/or sensor only when DRB scan
tool diagnosis indicates this is necessary. Or, if either
part has sustained physical damage (dented,
deformed, broken, etc.).
CAUTION: Do not turn the small screw at the end of
the solenoid valve for any reason. Turning the
screw in either direction will ruin solenoid calibra-
tion and result in solenoid failure. In addition, the
filter on the solenoid valve is NOT serviceable. Do
not try to remove the filter as this will damage the
valve housing.
INSPECTION
Inspect the throttle and manual valve levers and
shafts. Do not attempt to straighten a bent shaft or
correct a loose lever. Replace these components if
worn, bent, loose or damaged in any way.
Inspect all of the valve body mating surfaces for
scratches, nicks, burrs, or distortion. Use a straight-
edge to check surface flatness. Minor scratches may
be removed with crocus cloth using only very light
pressure.Minor distortion of a valve body mating surface
may be corrected by smoothing the surface with a
sheet of crocus cloth. Position the crocus cloth on a
surface plate, sheet of plate glass or equally flat sur-
face. If distortion is severe or any surfaces are
heavily scored, the valve body will have to be
replaced.
CAUTION: Many of the valves and plugs, such as
the throttle valve, shuttle valve plug, 1-2 shift valve
and 1-2 governor plug, are made of coated alumi-
num. Aluminum components are identified by the
dark color of the special coating applied to the sur-
face (or by testing with a magnet). Do not sand alu-
minum valves or plugs under any circumstances.
This practice could damage the special coating
causing the valves/plugs to stick and bind.
Inspect the valves and plugs for scratches, burrs,
nicks, or scores. Minor surface scratches on steel
valves and plugs can be removed with crocus cloth
butdo not round off the edges of the valve or
plug lands.Maintaining sharpness of these edges is
vitally important. The edges prevent foreign matter
from lodging between the valves and plugs and the
bore.
Inspect all the valve and plug bores in the valve
body. Use a penlight to view the bore interiors.
Replace the valve body if any bores are distorted or
scored. Inspect all of the valve body springs. The
springs must be free of distortion, warpage or broken
coils.
Check the two separator plates for distortion or
damage of any kind. Inspect the upper housing,
lower housing, 3-4 accumulator housing, and transfer
plate carefully. Be sure all fluid passages are clean
and clear. Check condition of the upper housing and
transfer plate check balls as well. The check balls
and ball seats must not be worn or damaged.
Trial fit each valve and plug in its bore to check
freedom of operation. When clean and dry, the valves
and plugs should drop freely into the bores.
Valve body bores do not change dimensionally with
use. If the valve body functioned correctly when new,
it will continue to operate properly after cleaning and
inspection. It should not be necessary to replace a
valve body assembly unless it is damaged in han-
dling.
The only serviceable valve body components are
listed below. The remaining valve body components
are serviced only as part of a complete valve body
assembly. Serviceable parts are:
²dual solenoid and harness assembly
²solenoid gasket
²solenoid case connector O-rings and shoulder
bolt
²switch valve and spring
Fig. 310 Accumulator Housing Components
1 - ACCUMULATOR PISTON
2 - 3-4 ACCUMULATOR HOUSING
3 - TEFLON SEALS
4 - PISTON SPRING
5 - COVER PLATE AND SCREWS
21 - 166 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1696 of 2199

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE
DESCRIPTION........................178
OPERATION..........................179
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION.....................179
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRELIMINARY . 180
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD
TESTING...........................180
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TEST....................181
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIR CHECKING
TRANSMISSION CLUTCH OPERATION....182
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CONVERTER
HOUSING FLUID LEAK................182
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ALUMINUM
THREAD REPAIR.....................183
REMOVAL............................183
DISASSEMBLY........................185
CLEANING...........................190
INSPECTION.........................190
ASSEMBLY...........................190
INSTALLATION........................197
SCHEMATICS AND DIAGRAMS
HYDRAULIC SCHEMATICS.............199
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSMISSION.....................220
SPECIAL TOOLS
RFE TRANSMISSION.................221
4C RETAINER/BULKHEAD
DISASSEMBLY........................224
ASSEMBLY...........................224
ADAPTER HOUSING SEAL
REMOVAL............................225
INSTALLATION........................225
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
MECHANISM
DESCRIPTION........................226
OPERATION..........................226
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK......226
ADJUSTMENTS - BRAKE TRANSMISSION
SHIFT INTERLOCK...................227
FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL.............228
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID.......................228DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION....................228
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK............................229
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND
FILTER REPLACEMENT...............230
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TRANSMISSION
FILL...............................230
GEARSHIFT CABLE
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - GEARSHIFT
CABLE.............................231
REMOVAL............................231
INSTALLATION........................231
ADJUSTMENTS - GEARSHIFT CABLE......232
HOLDING CLUTCHES
DESCRIPTION........................233
OPERATION..........................234
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION........................235
OPERATION..........................235
DISASSEMBLY........................237
ASSEMBLY...........................238
INPUT SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................244
OPERATION..........................244
REMOVAL............................244
INSTALLATION........................244
LINE PRESSURE (LP) SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................245
OPERATION..........................245
REMOVAL............................245
INSTALLATION........................245
LOW/REVERSE CLUTCH
DISASSEMBLY........................246
CLEANING...........................247
INSPECTION.........................247
ASSEMBLY...........................247
OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION........................248
OPERATION..........................248
STANDARD PROCEDURE - OIL PUMP
VOLUME CHECK.....................249
DISASSEMBLY........................250
CLEANING...........................252
INSPECTION.........................252
ASSEMBLY...........................253
OIL PUMP FRONT SEAL
REMOVAL............................253
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 177
Page 1697 of 2199
INSTALLATION........................253
OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................254
OPERATION..........................254
REMOVAL............................254
INSTALLATION........................254
OVERDRIVE SWITCH
DESCRIPTION........................254
OPERATION..........................254
PARK LOCK CABLE
REMOVAL............................255
INSTALLATION........................255
PISTONS
DESCRIPTION........................256
OPERATION..........................256
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN
DESCRIPTION........................258
OPERATION..........................260
DISASSEMBLY........................260
CLEANING...........................260
INSPECTION.........................260
ASSEMBLY...........................261
SHIFT MECHANISM
DESCRIPTION........................261
OPERATION..........................261
REMOVAL............................261
INSTALLATION........................263
SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
DESCRIPTION........................263
OPERATION..........................263
SOLENOIDS
DESCRIPTION........................263OPERATION..........................264
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION........................264
OPERATION..........................268
REMOVAL............................269
INSTALLATION........................269
TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY
DESCRIPTION........................270
OPERATION..........................270
TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................270
OPERATION..........................270
TRANSMISSION SOLENOID/TRS ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION........................271
OPERATION..........................271
REMOVAL............................272
INSTALLATION........................272
TRANSMISSION TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................272
OPERATION..........................272
VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION........................273
OPERATION..........................273
REMOVAL............................274
DISASSEMBLY........................275
CLEANING...........................277
INSPECTION.........................277
ASSEMBLY...........................278
INSTALLATION........................279
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION -
545RFE
DESCRIPTION
The 545RFE automatic transmission is a sophisti-
cated, multi-range, electronically controlled transmis-
sion which combines optimized gear ratios for
responsive performance, state of the art efficiency
features and low NVH. Other features include driver
adaptive shifting and three planetary gear sets to
provide wide ratio capability with precise ratio steps
for optimum driveability. The three planetary gear
sets also make available a unique alternate second
gear ratio. The primary 2nd gear ratio fits between
1st and 3rd gears for normal through-gear accelera-
tions. The alternate second gear ratio (2prime) allows
smoother 4-2 kickdowns at high speeds to provide
2nd gear passing performance over a wider highway
cruising range. An additional overdrive ratio (0.67:1)
is also provided for greater fuel economy and less
NVH at highway speeds.The hydraulic portion of the transmission consists
of the transmission fluid, fluid passages, hydraulic
valves, and various line pressure control components.
The primary mechanical components of the trans-
mission consist of the following:
²Three multiple disc input clutches
²Three multiple disc holding clutches
²Five hydraulic accumulators
²Three planetary gear sets
²Dual Stage Hydraulic oil pump
²Valve body
²Solenoid pack
The TCM is the ªheartº or ªbrainº of the electronic
control system and relies on information from vari-
ous direct and indirect inputs (sensors, switches, etc.)
to determine driver demand and vehicle operating
conditions. With this information, the TCM can cal-
culate and perform timely and quality shifts through
various output or control devices (solenoid pack,
transmission control relay, etc.).
21 - 178 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
Page 1700 of 2199

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TEST
An accurate tachometer and pressure test gauges
are required. Test Gauge C-3293-SP has a 300 psi
range and is used at all locations where pressures
exceed 100 psi.
Pressure Test Port Locations
Only two pressure ports are supplied on the trans-
mission case. The torque converter clutch apply and
release ports are located on the right side of the
transmission case (Fig. 2).
To determine the line pressure, there are two avail-
able methods. The DRBtscan tool can be used to
read line pressure from the line pressure sensor. The
second method is to install Line Pressure Adapter
8259 (Fig. 4) into the transmission case and then
install the pressure gauge and the original sensor
into the adapter. This will allow a comparison of the
DRBtreadings and the gauge reading to determe the
accuracy of the line pressure sensor. The DRBtline
pressure reading should match the gauge reading
within 10 psi.
In order to access any other pressure tap locations,
the transmission oil pan must be removed, the pres-
sure port plugs removed and Valve Body Pressure
Tap Adapter 8258-A (Fig. 5) installed. The extensions
supplied with Adapter 8258-A will allow the installa-
tion of pressure gauges to the valve body. Refer to
(Fig. 3) for correct pressure tap location identifica-
tion.
TEST PROCEDURE
All pressure readings should be taken with the
transmission fluid level full, transmission oil at the
normal operating temperature, and the engine at
1500 rpm. Check the transmission for proper opera-
tion in each gear position that is in question or if a
specific element is in question, check the pressure
readings in at least two gear positions that employ
that element. Refer to the Hydraulic Schematics at
the rear of this section to determine the correct pres-
sures for each element in a given gear position.
Fig. 2 Torque Converter Pressure Locations
1 - TCC RELEASE
2 - TO COOLER
3 - TCC APPLY
4 - FROM COOLER
5 - LINE PRESSURE SENSOR
Fig. 3 Pressure Tap Locations
Fig. 4 Line Pressure Adapter 8259
1 - LINE PRESSURE SENSOR PORT
2 - LINE PRESSURE SENSOR
3 - TOOL 8259
4 - PRESSURE TAP
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 181
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE (Continued)